Submitted:
26 April 2024
Posted:
28 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Background
1.2. Previous Research
1.3. Problem Formulation and Main Contributions
- The intermittency and variability of renewable energy sources (RES), necessitating the need for innovative hybrid energy systems (HES) that guarantee energy security while mitigating environmental impacts.
- The integration of multiple technologies within grid-connected systems, which complicates the optimization process due to the stochastic nature of RES.
- The requirement for advanced computational tools that balance exploration and exploitation within multi-objective optimization frameworks to ensure robust and consistent optimal results.
- The need for a scalable and adaptable framework that can be applied to other regions with similar energy challenges and constraints.
- Limited Evaluation of Optimization Algorithms: HRES design involves complex multi-objective decision-making processes. Current evaluation methods for optimization algorithms often rely on basic metrics, providing an incomplete assessment of their suitability for identifying the truly optimal HRES configuration within the feasible solution space.
- Lack of Comprehensive Decision Framework: A holistic framework to guide policymakers and energy specialists in selecting and integrating renewable energy solutions is needed, particularly for regions like Sub-Saharan Africa where energy access and sustainability are critical concerns.
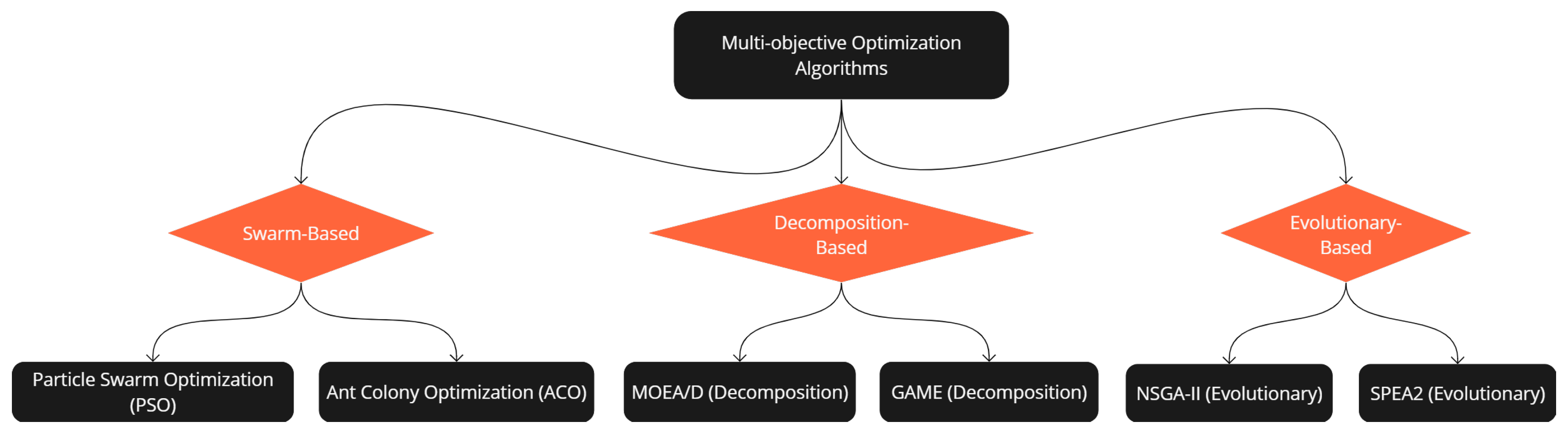
- A comprehensive algorithm selection: Utilization of variants of algorithms from three different domains (Swarm, Decomposition and Evolutionary-Based) slightly modified for robustness and consistency within the specified constraints of the case study.
- A Comprehensive Algorithm Evaluation: A clear presentation of the chosen algorithms’ variants scrutinized through seven performance metrics, the authors described as the AL-PEM approach, and directly applied to a real-world grid-connected scenario that utilizes five technologies and five objective functions to determine the efficacy of the algorithms over a 20-year planning horizon. The AL-PEM approach incorporates the Average Spacing, Rate of Convergence, Generational Distance, Computational Time, Maximum Spread, the Optimal Euclidean Distance of the solutions to the origin, and the amount of Storage used up by each algorithm. From Table 1, a summary of the most recent works on HRES using at least two soft computing tools and highlights of the performance metrics and statistical methods used have been done in comparison with the methods adopted for this journal.
- A clear presentation of the Agile Multi-Criteria Decision Tool: This tool highlights four key developmental phases from Resource Assessment to Construction and O&M phase that forms a practical framework that can be adapted for policy-making and optimization of renewable energy systems.
2. Methodology
- System Optimization: To use the MOPSO technique to determine the optimal configuration of PV panels, OWTs, biomass combustion plants, BESS, and DG systems that aligns power generation with demand and minimizes life cycle costs over a 20-year project horizon.
- Comparative Analysis: To conduct a comparative analysis of the MOPSO technique against modified MOEA/D and SPEA 2 algorithms, using the highlighted AL-PEM approach to establish the most effective optimization method specific to the chosen HRES.
- Sustainability Evaluation: To evaluate the environmental impact by aiming to minimize CO2 emissions and the Diesel Energy Fraction (DEF) in the energy mix, thereby contributing to sustainable energy development goals.
- Policy Framework Development: To provide policymakers with a decision-making framework based on the study’s findings that integrates economic viability, environmental sustainability, and social equity considerations.
- Scalability Assessment: To investigate the scalability of the proposed optimization framework in a real-life case-study-based approach.
2.1. Study Area and Resource Assessment
2.2. Configuration and Scheme
2.3. Decision Criteria and Performance Metrics
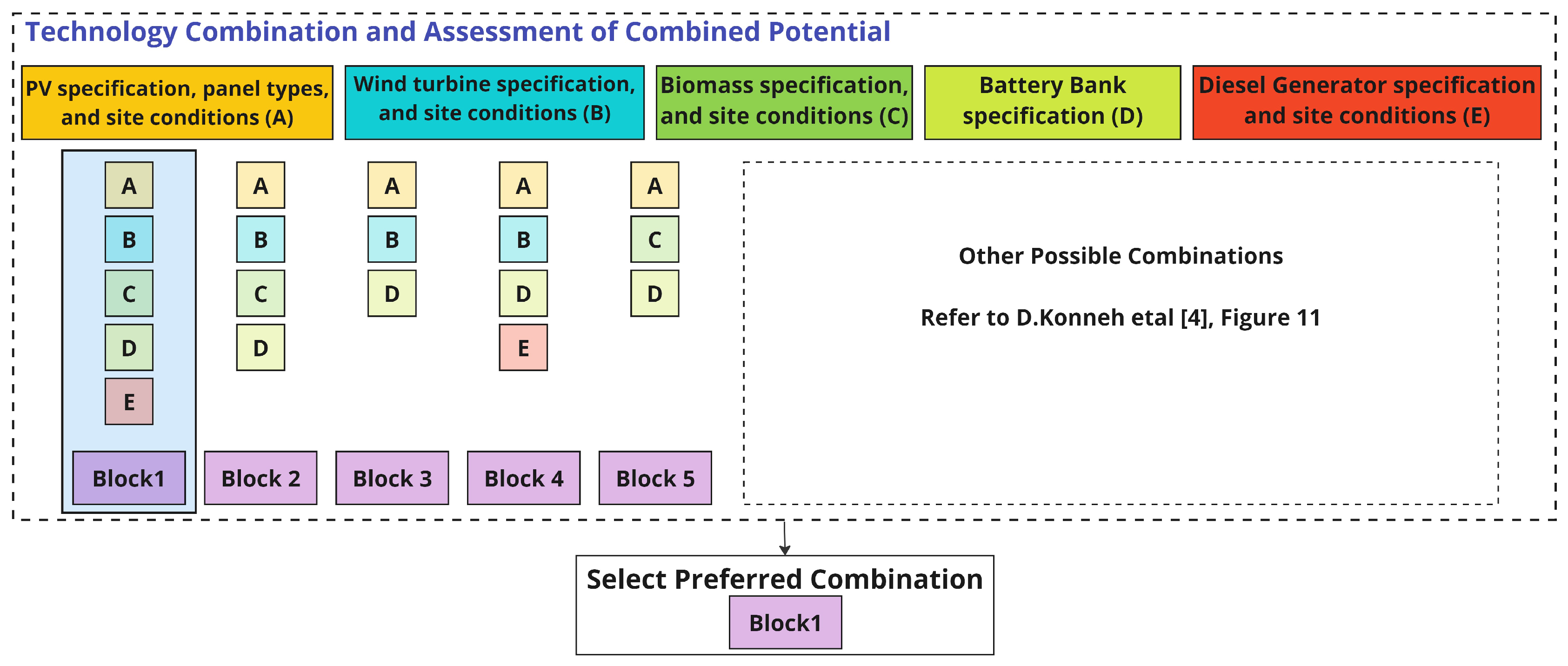
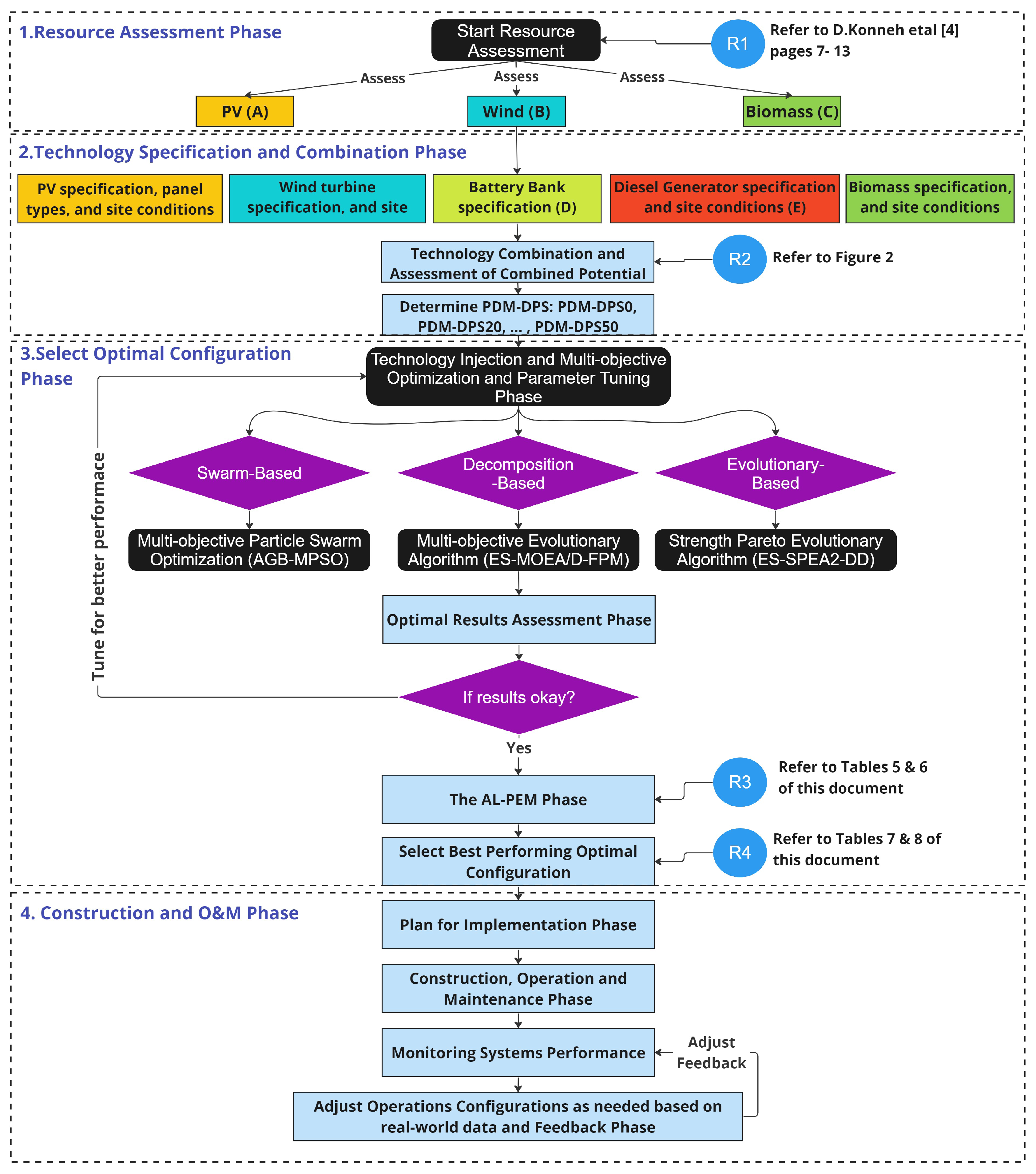
- Resource Assessment Phase: This initial phase involves the assessment of natural resources and the evaluation of Wind, PV (Photovoltaic), and Biomass potential.
- Technology Specification Phase: Subsequent to the resource evaluation, this phase specifies the technical details and capacities of the technologies under consideration.
- Combination Consideration: Here, various combinations of the assessed technologies are considered to determine feasible pairings.
- Technology Injection Condition Phase: This phase takes into account the different conditions under which power supply might be deficient and considers the budget constraints set by policymakers.
- Multi-Objective Optimization: The considered technology combinations and injection conditions are input into three multi-objective optimization algorithms. These algorithms aid in selecting the optimal configuration that aligns with the project’s budget.
- Plan for Implementation Phase: A detailed plan for the implementation of the selected technology configuration is developed.
- Construction Phase: This phase covers the actual construction and installation of energy technologies.
- Operation and Maintenance Phase: It involves the daily operation and upkeep of the implemented technologies.
- Monitoring Systems Performance Phase: Continuous monitoring of the system’s performance is conducted to ensure efficiency and reliability.
- Adjusting Configurations and Feedback Phase: The final phase allows for adjustments to the configurations based on feedback and operational data to optimize performance.
2.4. Optimization Methods
2.4.1. M-O Particle Swarm Optimization (MOPSO)
Mathematical Description
- w is the inertia weight.
- and are the cognitive and social acceleration coefficients, respectively.
- and are random numbers uniformly distributed in [0, 1].
- is the personal best position of particle i.
- is the global best position found by the entire swarm.
| Algorithm 1: Multi-objective Particle Swarm Optimization (MOPSO) |
|
- Leader Selection Mechanism: A stochastic leader selection approach, such as the Roulette Wheel, is implemented to guide particles diversely through the search space.
- Adaptive Mutation: The algorithm adopts an adaptive mutation step, with the mutation probability adjusting according to the iteration number, promoting exploration initially and exploitation subsequently.
- Repository Update: The repository’s maintenance is explicitly detailed, ensuring the preservation and continual update of a diverse solution set.
- Grid Update and Dominance: An explicit step is included for revising the grid structure based on the repository, which is crucial for sustaining diversity. Moreover, the process for culling dominated and surplus particles is specifically mentioned.
- Normalization of the Pareto Front: Prior to the final iteration, the Pareto front is normalized, which aids in delineating the true Pareto optimal solutions.
- Resulting Set: The algorithm yields a repository-derived set of non-dominated solutions as its final output, indicating a refined solution set.
| Algorithm 2: Algorithm Framework of DAM-MOPSO |
|
2.4.2. M-O Evolutionary Algorithm Based on Decomposition (MOEA/D-M2))
Mathematical Description
| Algorithm 3: General Framework of MOEA/D-M2 |
|
- Population Initialization: The population and weight vectors are initialized along with the neighborhood structure.
- Reference Point Initialization: A reference point is established to assist in scalarizing function computations.
-
Evolutionary Loop: The loop continues until a termination criterion is met, iterating over the following steps:
- Neighboring individuals are selected for mating using a crossover operator, followed by a polynomial mutation to generate offspring.
- Any constraint violation by the offspring invokes a repair mechanism.
- The offspring’s objective function is evaluated and compared against the current solutions using a weighted sum scalarizing function.
- The reference point is updated if the new solution provides a better scalarized value.
- Individual Update: Each individual in the population is compared against the new offspring, and updates are made if the offspring’s scalarized value is superior.
- External Population Maintenance: The external population is pruned of dominated solutions, and non-dominated offspring are included.
- Result Compilation: The algorithm concludes by returning the external population as the result, which comprises the non-dominated solutions.
| Algorithm 4: Algorithm Framework of ES-MOEA/D-FPM |
|
2.4.3. Strength Pareto Evolutionary Algorithm 2 (SPEA2)
Mathematical Description
| Algorithm 5: Strength Pareto Evolutionary Algorithm 2 (SPEA2) |
|
| Algorithm 6: Algorithm Framework of ES-SPEA2-DD |
|
2.4.4. Performance Metrics and Their Relation to HRES Optimization
- Computational Time: The duration the algorithm requires to converge to a solution or complete a defined set of iterations. For HRES, minimizing computational time is crucial for enabling rapid analysis and adaptive decision-making in response to fluctuating energy supplies and demands.
- Storage Used: This represents the algorithm’s memory requirement. A consistent memory usage, regardless of the operational conditions, suggests the stability and scalability of the algorithm when applied to HRES.
- Spacing: A measure of the diversity and distribution of the solutions along the Pareto front. In HRES optimization, a lower spacing value is preferred as it indicates a more evenly distributed set of solutions which can lead to more balanced decision-making.
- Average Rate of Convergence: This metric indicates the swiftness with which an algorithm approaches an optimal solution. A faster rate of convergence is beneficial for HRES optimization, as it contributes to quicker system adaptability and efficiency.
- Maximum Spread: This metric assesses the extent of the distribution of solutions across the Pareto front, with a larger spread denoting a broader range of potential system configurations. This diversity is advantageous for policy-makers in choosing HRES designs that can meet a wide array of performance objectives.
- Generational Distance: It gauges the closeness of the algorithm-generated solutions to the true Pareto front. A smaller generational distance is indicative of the algorithm’s accuracy in identifying optimal HRES configurations, which is pivotal for the system’s performance and sustainability.
2.4.5. Robustness Comparison
2.5. Summary of Objectives
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Performance Metrics Insights
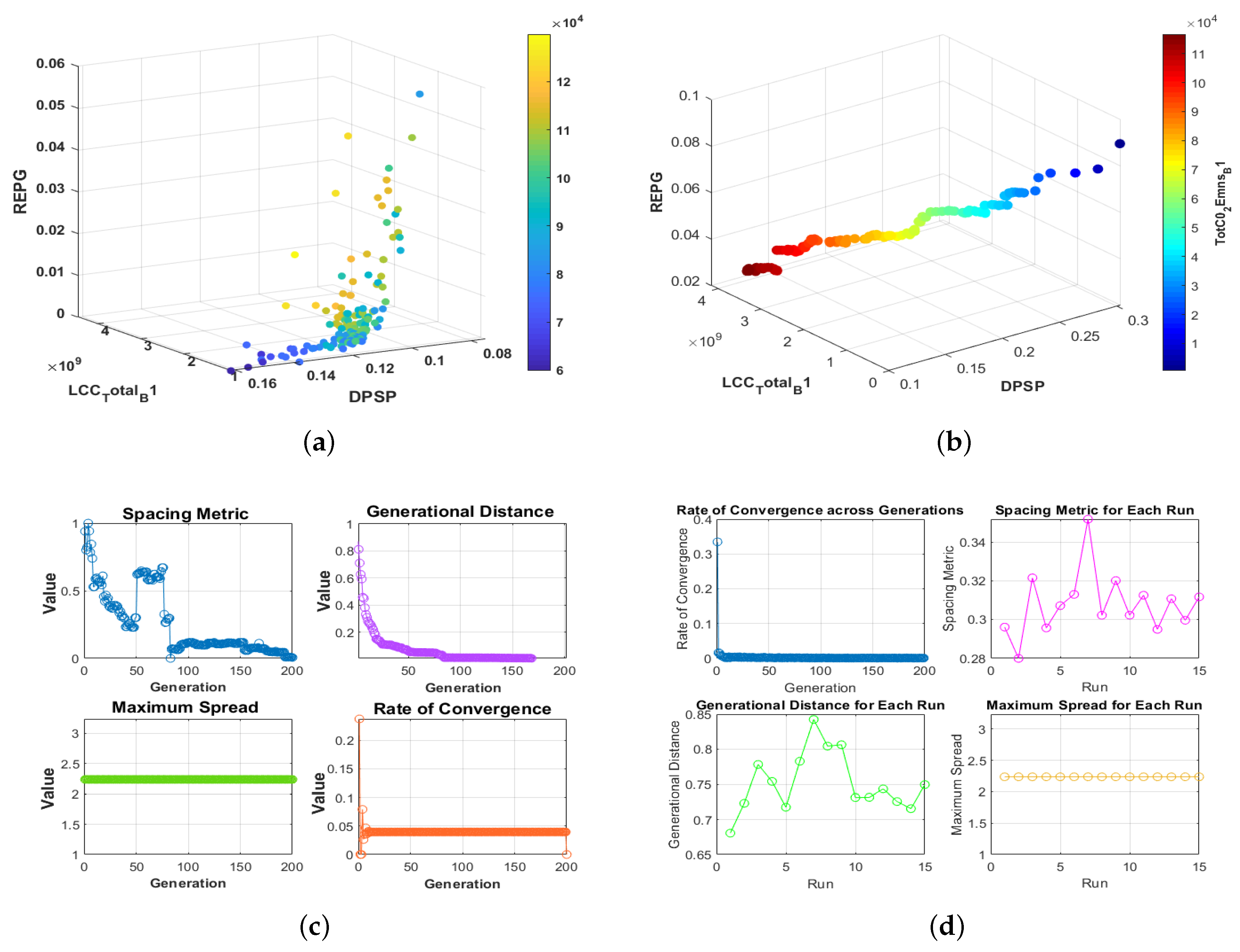
3.2. Policy Decision-Making Implications
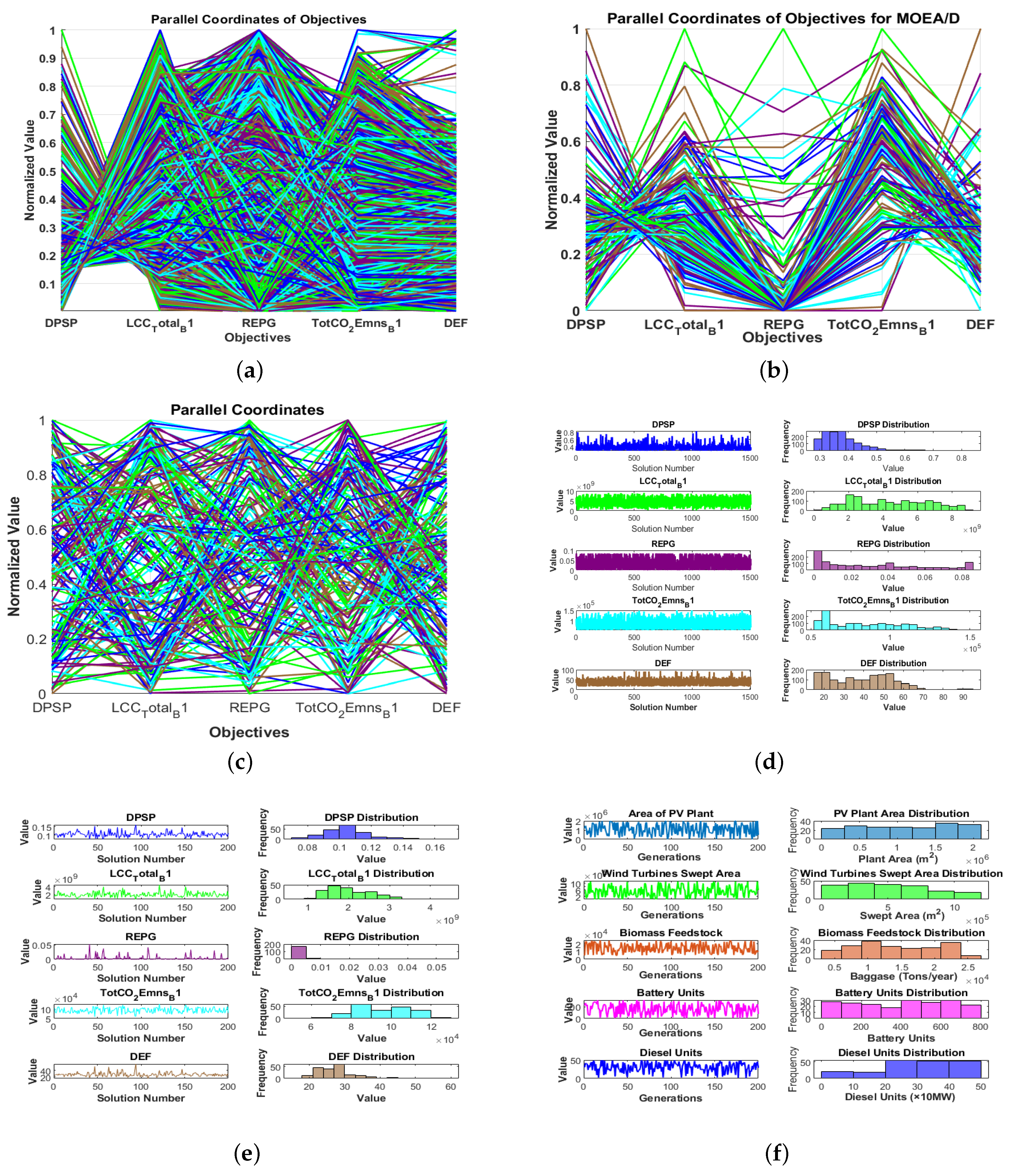
3.3. Algorithmic Adaptability, Sustainability
4. Conclusion
4.1. Synthesis with Previous Studies
4.2. Comprehensive Algorithm Assessment
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Algorithm Performance Evaluation Metrics. | |
| Biomass. | |
| Diesel Generator. | |
| Enhanced Strength Pareto Evolutionary Algorithm 2 with Dynamic Diversity. | |
| Hybrid Energy Systems. | |
| Multi-objective Particle Swarm Optimization. | |
| Multi-objective Evolutionary Algorithm based on Decomposition. | |
| Net Present Value. | |
| Operation and Maintenance. | |
| Policy Decision Metric Based on Deficiency of Power Supply. | |
| Renewable Energy Sources. | |
| Strength Pareto Evolutionary Algorithm 2. | |
| Sub-Saharan Africa. | |
| NPV of the total operation and maintenance cost of the biomass plant. | |
| Annual growth rate of the BM cost. | |
| Annual operation and maintenance cost of BM. | |
| NPV of the resale price of the biomass plant. | |
| Total cost recovered from resale. | |
| Initial cost of the biomass plant. | |
| Life cycle cost of the biomass power plant. | |
| NPV of the replacement cost of the biomass plant. | |
| Capital cost of the DG power plant. | |
| Initial cost of DG. | |
| NPV of the total operation and maintenance cost of DG. | |
| Operation and maintenance cost of DG. | |
| Annual growth rate of the DG cost. | |
| NPV of the resale price of DG. | |
| Total resale price of DG at the end of the project life. | |
| Initial cost of DG plant. |
Appendix A
| Fuel Consumption for Existing DG units Considered | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| DG unit | Fuel Operation | Number of Units | Consumption (l/h) |
| A | Diesel Oil | 20 | 240 |
| B1 | Diesel Oil | 3 | 350 |
| B2 | Diesel Oil | 5 | 240 |
| K | Heavy Fuel oil | 2 | 700 |
| Diesel Oil | 620 | ||
| L | Heavy Fuel oil | 3 | 470 |
| Diesel Oil | 430 | ||
| N1 and N2 | Heavy Fuel oil | 2 | 1024 |
| Diesel Oil | 981 | ||
| W1 and W2 | Heavy Fuel oil | 2 | 1300 |
| Diesel Oil | 1230 | ||
| M | Diesel Oil | 2 | 300 |
| LO | Diesel Oil | 1 | 300 |
| MA | Diesel Oil | 1 | 240 |
| Physical and Environmental Parameters | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Technology Type | Variable | Notation | Value |
| Wind Turbine GAMESA G128-5.0 MW/G132-5.0 MW |
Rated Power | (kW) | 5000 |
| Cut-in speed | (m/s) | 1.5 | |
| Rated Speed | (m/s) | 13 | |
| Cut-off speed | 27 | ||
| H (m) | 100 | ||
| Wind Turbine lifetime | 20 | ||
| PV Panel Sun Power X Series |
Maximum Power | (W) | 360 |
| Efficiency of Panel | 22.2 | ||
| Area of PV panel | (m) | 1.63 | |
| PV lifetime | 20 | ||
| Biomass CFB Combustion Plant |
Net calorific value of Baggase | (MJ/Kg) | 16 |
| Baggase Emissions Factor | (mmBtu/kg) | 0.0161 | |
| Efficiency of Plant | 0.42 | ||
| Lifetime of Biomass plant | 20 | ||
| Diesel Generator (DG) Nigatta Dual Fuel Diesel Plant |
Unit Plant Capacity | 10,000 | |
| Lifetime of DG plant | 20 | ||
| Net calorific value of Heavy Fuel Oil (HFO) | (mmBtu/gal) | 0.15 | |
| Net calorific value of Diesel Oil (DO) | (mmBtu/gal) | 0.148 | |
| HFO Emissions Factor | (kgCO/mmBtu) | 75.1 | |
| DO Emissions Factor | (kgCO/mmBtu) | 74.92 | |
| Battery Bank Lithium Ion |
Hourly Self Discharge | 0 | |
| Battery charging efficiency | 0.9 | ||
| Battery Discharging efficiency | 0.9 | ||
| Nominal Capacity of Battery (kWh) | 1200 | ||
| Lifetime of Battery Bank | 10 | ||
| Economic Parameters | |||
| Project lifetime | N | 20 | |
| Interest rate | i (%) | 10 | |
| Inflation rate | (%) | 4 | |
| Escalation rate | (%) | 5 | |
| Inverter efficiency | (%) | 90 | |
| Wind Turbine | Capital cost of Wind Turbine | ($/m | 544 |
| Yearly Operations and Maintenance Cost | 1.5 | ||
| Reselling Price | 30 | ||
| PV Panel | Capital cost of PV Panel | ($/kW) | 519.7 |
| Yearly Operations and Maintenance Cost | 1 | ||
| Reselling Price | 25 | ||
| Biomass Plant | Capital cost of Biomass Plant | ($/kW) | 1440 |
| Cost of Bagasse | ($/ton) | 25 | |
| Cost of Storage | ($/ton) | 12 | |
| Cost of loading | ($/ton) | 5 | |
| Cost of Transportation | ($/ton/km) | 0.057 | |
| Yearly Operations and Maintenance Cost | 0.017 | ||
| Reselling Price | 30 | ||
| Diesel Generator | Capital cost of DG plant | ($/kW) | 1000 |
| Cost of HFO | ($/litre) | 0.45 | |
| Cost of DO | ($/litre) | 0.607 | |
| HFO Consumption | (litre/hour) | 1024 | |
| DO Consumption | (litre/hour) | 981 | |
| Yearly Operations and Maintenance Cost | ($/kWh) | 0.032 | |
| Reselling Price | 30 | ||
| Battery Bank | Capital Cost of Battery | ($/kW) | 283 |
| Replacement Cost | - | ||
References
- Coello Coello, C. A.; Lechuga, M. S. MOPSO: A Proposal for Multiple Objective Particle Swarm Optimization. Proceedings of the Congress on Evolutionary Computation 2002, 1051–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Qingfu; Li, Hui. MOEA/D: A Multi-objective Evolutionary Algorithm Based on Decomposition. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation 2007, 11, 712–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitzler, Eckart; Laumanns, Marco; Thiele, Lothar. SPEA2: Improving the Strength Pareto Evolutionary Algorithm. TIK-report, 2001, 103.
- Konneh, David Abdul; Howlader, Harun Or Rashid; Shigenobu, Ryuto; Senjyu, Tomonobu; Chakraborty, Shantanu; Krishna, Narayanan. A Multi-Criteria Decision Maker for Grid-Connected Hybrid Renewable Energy Systems Selection Using Multi-Objective Particle Swarm Optimization. Sustainability 2019, 11, https://www.mdpi.com/2071–1050/11/4/1188. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/11/4/1188 (accessed on [access date]). [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, James; Eberhart, Russell. Particle Swarm Optimization. In Proceedings of ICNN’95 - International Conference on Neural Networks, 1995; Vol. 4, pp. 1942–1948. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Ping; Li, Hongpeng; Chai, Tianyou. SPEA2 based on grid density search and elite guidance for multi-objective operation optimization of wastewater treatment process. Applied Soft Computing 2023, 144, 110529. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1568494623005471 (accessed on [access date]). [CrossRef]
- Divya, S.; Paramathma, M. Krishna; Sheela, A.; Kumar, S. Dilip. Hybrid renewable energy source optimization using black widow optimization techniques with uncertainty constraints. Measurement: Sensors 2024, 31, 100968. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2665917423003045 (accessed on [access date]). [CrossRef]
- Yazdani, Hamed; Baneshi, Mehdi; Yaghoubi, Mahmood. Techno-economic and environmental design of hybrid energy systems using multi-objective optimization and multi-criteria decision making methods. Energy Conversion and Management 2023, 282, 116873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, Natasha E. ; Carvalho, Paulo C.M.; Fernández-Ramírez, Luis M.; Braga, Arthur P.S. Optimizing methodologies of hybrid renewable energy systems powered reverse osmosis plants. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2023, 182, 113377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirunavukkarasu, M.; Sawle, Yashwant; Lala, Himadri. A comprehensive review on optimization of hybrid renewable energy systems using various optimization techniques. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2023, 176, 113192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basnet, Sarad; Deschinkel, Karine; Le Moyne, Luis; Péra, Marie Cécile. A review on recent standalone and grid integrated hybrid renewable energy systems: System optimization and energy management strategies. Renewable Energy Focus 2023, 46, 103–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Akhlaque Ahmad; Minai, A.; Pachauri, Rupendra Kumar; Malik, Hasmat. Optimal Sizing, Control, and Management Strategies for Hybrid Renewable Energy Systems: A Comprehensive Review. Energies, 2022. Available online: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:251949873 (accessed on [access date]).
- Nabipour-Afrouzi, Hadi; Yii, Samuel Hii Wen; Ahmad, Jubaer; Tabassum, Mujahid. Comprehensive Review on Appropriate Sizing and Optimization Technique of Hybrid PV-Wind System. 2018 IEEE PES Asia-Pacific Power and Energy Engineering Conference (APPEEC), 2018; 364–369. Available online: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:54461845 (accessed on [access date]).
- de Farias, Lucas R. C.; Araújo, Aluizio F.R. A decomposition-based many-objective evolutionary algorithm updating weights when required. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation 2022, 68, 100980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Jing; Zheng, Yuxin; Huang, Pengcheng; Peng, Hu; Wu, Zhijian. A stable-state multi-objective evolutionary algorithm based on decomposition. Expert Systems with Applications 2024, 239, 122452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Ping; Li, Hongpeng; Chai, Tianyou. Improved Strength Pareto Evolutionary Algorithm 2 based on grid density search and elite guidance for multi-objective operation optimization of WWTP. Applied Soft Computing 2023, 144, 110529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.T.; Callaway, D.S. The cost of reliability in decentralized solar power systems in sub-Saharan Africa. Nat. Energy 2018, 3, 960–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Special Report: Energy Access Outlook. International energy Agency, 2017, France. Available online: http://www.iea.org (accessed on 10 August 2018).
- Sierra Leone Unemployment Rate. The Statistics Portal. Available online: https://www.statista.com (accessed on 30 August 2018).
- Sierra Leone Electricity Prices. GlobalPetrolPrices.com. Available online: https://www.globalpetrolprices.com/ (accessed on 24th December 2023).
- Sierra Leone Sustainable Energy For All (SE4ALL) Country Action Agenda : Sustainable Energy For All. 30 July 2015. Available online: https://www.se4all-africa.org (accessed on 30 August 2018 ).
- Tolba, M.; Rezk, H.; Tulsky, V.; Diab, A.; Abdelaziz, A.; Vanin, A. Impact of Optimum Allocation of Renewable Distributed Generations on Distribution Networks Based on Different Optimization Algorithms. Energies 2018, 11, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, A.; Riba, J.R.; Rius, A. Optimal Sizing of a Hybrid Grid-Connected Photovoltaic–Wind–Biomass Power System. Sustainability 2015, 7, 12787–12806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nižetić, S.; Papadopoulos, A.; Tina, G.; Rosa-Clot, M. Hybrid energy scenarios for residential applications based on the heat pump split air-conditioning units for operation in the Mediterranean climate conditions. Energy Build. 2017, 140, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnupriyan, J.; Manoharan, P. Multi-criteria decision analysis for renewable energy integration: A southern India focus. Renew. Energy 2018, 121, 474–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodorou, S.; Florides, G.; Tassou, S. The use of multiple criteria decision making methodologies for the promotion of RES through funding schemes in Cyprus, A review. Energy Policy 2010, 38, 7783–7792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.; Khan, M.T.; Rana, A.S.; Ali, S. Techno-economic analysis of hybrid solar-diesel-grid connected power generation system. J. Electr. Syst. Inf. Technol. 2018, 5, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiprasad, N.; Kalam, A.; Zayegh, A. Techno-economic and environmental analysis of hybrid energy systems for a university in Australia. Aust. J. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2018, 15, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharthi, Y.Z.; Siddiki, M.K.; Chaudhry, G.M. Resource Assessment and echno-Economic Analysis of a Grid-Connected Solar PV-Wind Hybrid System for Different Locations in Saudi Arabia. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adaramola, M.; Oyewola, O.; Paul, S. Technical and Economic Assessment of Hybrid Energy Systems in South-West Nigeria. Energy Explor. Exploit. 2012, 30, 533–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, S.; Samy, M.; Eteiba, M.; Wahba, W. Feasibility Study of Grid Connected PV-Biomass Integrated Energy System in Egypt. Int. J. Emerg. Electr. Power Syst. 2016, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichman, J.; Mueller, F.; Tarroja, B.; Smith Schell, L.; Samuelsen, S. Exploration of the integration of renewable resources into California’s electric system using the Holistic Grid Resource Integration and Deployment (HiGRID) tool. Energy 2013, 50, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yimen, N.; Hamandjoda, O.; Meva’a, L.; Ndzana, B.; Nganhou, J. Analyzing of a Photovoltaic/Wind/Biogas/Pumped-Hydro Off-Grid Hybrid System for Rural Electrification in Sub-Saharan Africa—Case Study of Djoundé in Northern Cameroon. Energies 2018, 11, 2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, T.C.; Hong, C.M. Dynamic operation and control of microgrid hybrid power systems. Energy 2014, 66, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.; Moghavvemi, M.; Mahlia, T. Genetic algorithm based optimization on modeling and design of hybrid renewable energy systems. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 85, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles Rodriguez, C.; Bideaux, C.; Guillouet, S.; Gorret, N.; Roux, G.; Molina-Jouve, C.; Aceves-Lara, C. Multi-objective particle swarm optimization (MOPSO) of lipid accumulation in Fed-batch cultures. In Proceedings of the 2016 24th Mediterranean Conference on Control and Automation (MED), Athens, Greece, 21–24 June 2016; pp. 979–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comparison of Three Evolutionary Algorithms: GA, PSO, adn DE. Ind. Eng. Manag. Syst. 2012, 11, 215–223. [CrossRef]
- Ting Li, B.Y. A Review of Multi-objective Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithms in Power System Economic Dispatch. Int. J. Simul. Syst. Sci. Technol. 2016, 17, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theo, W.L.; Lim, J.S.; Ho, W.S.; Hashim, H.; Lee, C.T. Review of distributed generation (DG) system planning and optimisation techniques: Comparison of numerical and mathematical modelling methods. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 67, 531–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adewuyi, O.B.; Shigenobu, R.; Senjyu, T.; Lotfy, M.E.; Howlader, A.M. Multiobjective mix generation planning considering utility-scale solar PV system and voltage stability: Nigerian case study. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2019, 168, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konneh, D.A.; Lotfy, M.E.; Shigenobu, R.; Senjyu, T. Optimal Sizing of Grid-connected Renewable Energy System in Freetown Sierra Leone. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2018, 51, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, O. Assessing and Mapping Renewable Energy Resources; World Bank, 2016, 1818 H Street, NW Washington, DC 20433 USA. Available online: http://www.esmap.org (accessed on 15 September 2018).
- Sebastian Hermann, Asami Miketa, N. F. Estimating the Renewable Energy Potential in Africa; International Renewable Energy Agency: Abu Dhabi, UAE, 2014; Available online: http://www.irena.org (accessed on 20 September 2018).
- Løken, E. Use of multicriteria decision analysis methods for energy planning problems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2007, 11, 1584–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Jing, Y.Y.; Zhang, C.F.; Zhao, J.H. Review on multi-criteria decision analysis aid in sustainable energy decision-making. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2009, 13, 2263–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remco Fischer, Jenny Lopez, S. S. Barriers and Drivers to Renewable Energy Investment in Sub-Saharan Africa. J. Environ. Investig. 2011, 2, 54–80. [Google Scholar]
- A Framework for Transforming Africa towards a Renewable Energy Powered Future With Access for All. Africa Renewable Energy Initiative (AREI). 2015. Available online: https://www.arei.org (accessed on 10 October 2018).
- Arslan, T.; Bulut, Y.M.; Altın Yavuz, A. Comparative study of numerical methods for determining Weibull parameters for wind energy potential. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 40, 820–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.; Roberts, B. Technical Potential Assessment for the Renewable Energy Zone (REZ) Process: A GIS-Based Approach; National Renewable Energy Laboratory, 2018, United State Department of Energy, USA. Available online: https://www.nrel.gov/docs/fy18osti/71004.pdf (accessed on 15 October 2018).
- Dorji, G. Environmental Aspect of Electric Energy Generation; Seminar Report, Department of Electrical Engineering, College of Science and Technology, 2015. [CrossRef]
- Glenting, Carsten; Jakobsen, N. Converting Biomass to Energy: A Guide for Developers and Investors (English); World Bank Group: Washington, DC, USA, 2017; Available online: http://documents.worldbank.org (accessed on 20 October 2018).
- Adam Brown, Simone Landolina, E.M.; Sung, J. The Clean Energy Technology Assessment Methodology: International Energy Agency Laboratory; OECD/IEA, Paris: 2016. Available online: https://www.iea.org (accessed on 25 October 2018).
- Economic and Financial Analysis Tools: National Renewable Energy Laboratory. Available online: https://www.nrel.gov/analysis/economic-financial-tools.html (accessed on 25 October 2018).
- BCS, I. Mining Industry Energy Bandwidth Study. 2007. Available online: https://www.energy.gov/eere/amo/ downloads/ us-mining-industry-energy-bandwidth-study (accessed on 27 October 2018).
- Sierra Rutile Limited. Ruidow Conference 2016. 2016. Available online: https://sierrarutile.iluka.com/reports (accessed on 27 October 2018).
- Project Appraisal Document. World Bank Group. Report No: 103305-SL. 2016. Available online: https://www.worldbank.org (accessed on 25 October 2018).
- Ministry of Energy Progress Report. Government of Sierra Leone. 2017. Available online: https://www.energy.gov.sl/wp-content/uploads/.../ProgressReportMoE.pdf (accessed on 25 October 2018).
- Asami Miketa (IRENA), Bruno Merven (Energy Research Center). West African Power Pool: Planning and Prospects for Renewable Energy. 2013. Available online: https://www.irena.org (accessed on 25 October 2018).
- Estimating the Renewable Energy Potential in Africa: A GIS-Based Approach. 2014. Available online: https://www.irena.org (accessed on 31 October 2018).
- Akdağ, S.A.; Dinler, A. A new method to estimate Weibull parameters for wind energy applications. Energy Convers. Manag. 2009, 50, 1761–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajayi, O.O.; Fagbenle, R.O.; Katende, J.; Ndambuki, J.M.; Omole, D.O.; Badejo, A.A. Wind Energy Study and Energy Cost of Wind Electricity Generation in Nigeria: Past and Recent Results and a Case Study for South West Nigeria. Energies, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obando Montaño, A. An Approach to Determine the Weibull Parameters for Wind Energy Analysis: The Case of Galicia (Spain). Energies 2014, 7, 2676–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyhani, A.; Ghasemi-Varnamkhasti, M.; Khanali, M.; Abbaszadeh, R. An assessment of wind energy potential as a power generation source in the capital of Iran, Tehran. Energy 2010, 35, 188–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, F.; Sauma, E.; Yanine, F. Business optimal design of a grid-connected hybrid PV (photovoltaic)-wind energy system without energy storage for an Easter Island’s block. Energy 2013, 61, 248–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Renewable Energy Laboratory New Transparent Cost Data Base. Available online: https://openei.org/apps/TCDB/#blank (accessed on 3 November 2018).
- Abreu, E.F.; Canhoto, P.; Prior, V.; Melicio, R. Solar resource assessment through long-term statistical analysis and typical data generation with different time resolutions using GHI measurements. Renew. Energy 2018, 127, 398–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawilska, E.; Brooks, M. An assessment of the solar resource for Durban, South Africa. Renew. Energy 2011, 36, 3433–3438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Energy Information Administration: Today in Energy. 2015. Available online: https://www.eia.gov/todayinenergy/detail.php?id=22832 (accessed on 5 November 2018).
- Global Solar Atlas. Available online: https://www.globalsolaratlas.info/ (accessed on 10 November 2018).
- Fischer, G.; Prieler, S.; Velthuizen, H; Lensink, S.M; Londo, M; Marc de Wit. Biofuel production potentials in Europe: Sustainable use of cultivated land and pastures. Part I: Land productivity potentials; 2010; p. 159 - 172. Biomass and Bioenergy. [CrossRef]
- Renewable Energy Cost Analysis - Biomass for Power Generation (2012). Available online: https://www.irena.org (accessed on 12 November 2018).
- Silva, D.A.L.; Delai, I.; Montes, M.L.D.; Ometto, A.R. Life cycle assessment of the sugarcane bagasse electricity generation in Brazil. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 32, 532–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magbity, I. Prospect of Bio-fuels in Sierra Leone. URL:https://www.grin.com/. (accessed on 10 November 2018).
- Sierra Leone: Sugar Cane, Production Quantity. Available online: http://www.factfish.com (accessed on 12 November 2018).
- Mohamad Izdin Hlal, A.; Ramachandaramurthya, K.V.; Sanjeevikumar, P.; Pouryekta, A.; Hamid Reza Kaboli, C.; Tuan Ab Rashid Bin Tuan Abdullah, D. NSGA-II and MOPSO based optimization for sizing of hybrid PV/wind/ battery energy storage system. Int. J. Power Electron. Drive Syst. 2019, 10, 463–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, A.; Riba, J.R.; Rius, A.; Puig, R. Optimal sizing of a hybrid grid-connected photovoltaic and wind power system. Appl. Energy 2015, 154, 752–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Chauhan, A. Assessment of biomass resources for decentralized power generation in Punjab. Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res. 2014, 9, 869–876. [Google Scholar]
- Kawashima, A.; Morais, M.; Martins, L.; Guerrero, V.; Abou Rafee, S.; Capucim, M.; Martins, J. Estimates and Spatial Distribution of Emissions from Sugar Cane Bagasse Fired Thermal Power Plants in Brazil. J. Geosci. Environ. Prot. 2015, 03, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Electricity Storage and Renewables (2017): Costs and Markets to 2030. Available online: https://www.irena.org (accessed on 10 November 2018).
- Cost estimates for Thermal Peaking Plants (2008): Parsons Brinckerhoff New Zealand Ltd. Available online: https://www.electricitycommission.govt.nz (accessed on 12 November 2018).
- Emission Factors for Greenhouse Gas Inventories (2018): Parsons Brinckerhoff New Zealand Ltd. Available online: https://www.epa.gov (accessed on 15 November 2018).
- CO2 Emission Factors for Fossil Fuels. Available online: https://www.umweltbundesamt.de/en/publikationen/co2-emission-factors-for-fossil-fuels (accessed on 15 November 2018).
- Khiareddine, A.; Ben Salah, C.; Rekioua, D.; Mimouni, M. Sizing methodology for hybrid photovoltaic /wind/hydrogen/battery integrated to energy management strategy for pumping system. Energy 2018, 153, 743–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, M. Kammen, K.K.; Fripp, M. Putting Renewables to Work: How Many Jobs Can the Clean Energy Industry Generate? Energy Policy 2010, 38, 919–931. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, V.; Fehrs, J. The Work That Goes Into Renewable Energy (2001). Available online: http://www.globalurban.org (accessed on 5 August 2018).

| Paper Title | Year | Soft Computing Tools | Performance Metrics / Statistical Methods |
| An Agile Approach for Adopting Sustainable Energy Solutions with Advanced Computational Techniques | This journal | Variants of MOPSO, MOEA/D, SPEA2 | Employed advanced algorithmic variants assessed through AL-PEM, including Average Spacing, Rate of Convergence, Generational Distance, Computational Time, Maximum Spread, and Optimal Euclidean Distance. SPEA2 highlighted for robustness and consistency. |
| Techno-economic and environmental impact assessment of a hybrid renewable energy system employing an enhanced combined dispatch strategy | 2023 | Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) | Employed PSO for optimizing HRES components. Emphasized the ECD strategy over LF and CC for enhanced performance in terms of reduced LCOE, NPC, and emissions. |
| Techno-economic-environmental analysis of off-grid hybrid energy systems using honey badger optimizer | 2023 | Honey Badger Optimization (HBO), Golden Jackal Optimization (GJO), Arithmetic Optimization Algorithms (AOA) | Evaluated recently developed metaheuristic techniques to minimize the total annual cost (TAC) while maintaining acceptable LPSP and renewable fraction. HBO showed the most economical results with the lowest standard deviation, indicating superior exploration-exploitation balance and suitability for optimization problems. |
| Techno-economic and environmental design of hybrid energy systems using multi-objective optimization and multi-criteria decision making methods | 2023 | HOMER for simulation, MATLAB for optimization | Utilized HOMER and MATLAB for simulation and optimization, respectively, with final design chosen through MCDM, specifically TOPSIS combined with AHP and EWM. Detailed sensitivity analysis conducted. |
| Multi-objective optimization framework of a photovoltaic-diesel generator hybrid energy system considering operating reserve | 2022 | NSGA-II, MOPSO, MODE, and MDE | Comparison based on convergence, diversity, and computational time. Robustness assessed through standard deviation of results from multiple runs. Distance-based distribution index () used to quantify solution quality. |
| Multi-objective optimization of hybrid renewable energy system by using novel autonomic soft computing techniques | 2021 | Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO), including Hierarchical Particle Swarm Optimization (HPSO) | Comparative analysis of various PSO algorithms focusing on cost and emission minimization. |
| Multi-objective optimization of grid-connected PV-wind hybrid system | 2020 | Multi-Objective Particle Swarm Optimization (MOPSO) | Evaluation using minimum, maximum, range, standard deviation, and mean values for COE, LPSP, and REF. Detailed performance metrics for each scenario. |
| Optimal sizing of hybrid renewable energy systems in presence of electric vehicles using multi-objective particle swarm optimization | 2020 | Multi-Objective Particle Swarm Optimization (MOPSO), Monte Carlo Simulation (MCS) | Focused on LPSP through sensitivity analysis and simulation of scenarios. Compared deterministic and stochastic behaviors of EVs on system performance. |
| No. | Source | Capacity (MW) | Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| Existing Sources | |||
| 1 | Bumbuna Hydro | 50 | North |
| 2 | Goma Hydro | 6 | East |
| 3 | Charlotte Hydro | 2 | West |
| 4 | Bankasoka Hydro | 2 | North |
| 4 | Makali Hydro | 0.32 | North |
| 5 | Diesel (Government) | 27.6 | Western Area |
| 6 | Diesel (Government) | 24 | Provincial |
| 7 | Diesel (IPP-Karpower) | 65 | Western Area |
| 8 | TRANSCO CLSG (WAPP) | 27 | West and Provincial |
| 9 | Addax Bio-energy | 15 | North(Low availability) |
| 10 | Newton Solar | 6 | West |
| 11 | Total Generation | 197.92 | |
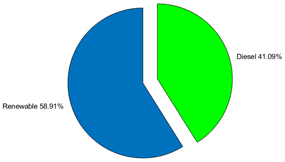
| Electricity Generated by Source | |||
 | |||
| Research Scope [MW] | |||
| 1 | Approximated Industrial Demand | 400 | |
| 2 | Approximated Commercial Demand | 180 | |
| 3 | Approximated Domestic Demand | 130 | |
| Feature | Original MOPSO | DAM-MOPSO |
|---|---|---|
| Adaptability | Fixed population size and inertia weight | Dynamic population adjustment with adaptive inertia weight |
| Diversity | Standard PSO diversity mechanisms | Enhanced by grid and mutation strategies for high diversity |
| Convergence | Convergence towards personal and global bests | Enhanced by adaptive learning factors and leader selection strategies |
| Mutation Type | Standard velocity and position updates | Adaptive mutation rate with probability tuning |
| Crossover Type | Not applicable to standard PSO | Integrates PSO velocity updating mechanisms |
| Constraint Handling | Standard PSO handling mechanisms | Repair mechanisms or constraint-aware selection |
| Performance Monitoring | Based on personal and global best updates | Based on dynamic archive update with grid-based density estimation |
| Neighborhood Size | Defined by swarm topology | Adaptive to particle distribution and grid density |
| Parent Selection | Based on the swarm’s global best | Based on local best and global best positions |
| Reference Point Update | Global and personal bests | Continuous update of personal and global bests |
| Scalarization Method | Not used in standard PSO | Not typically used in MOPSO |
| Replacement Strategy | Based on personal and global best improvements | Repository update based on non-domination and grid density |
| Consideration for Numerical Stability | Not explicitly mentioned | Ensured by velocity clamping |
| Reference Pareto Front Generation | Not specified in standard PSO | Generated dynamically as the repository is updated |
| Overall Robustness | Robust due to swarm intelligence | More robust in dynamic environments with adaptive mechanisms |
| Feature | Original MOEA/D | ES-MOEA/D-FPM | MOEA/D-SS |
| Adaptability | Fixed Population and Neighborhood, GA operators | Moderate (Consistent operators) | High (Dynamic neighborhood & operators) |
| Diversity | GA operators encourage diversity | Moderate (Fixed neighborhood selection) | High (Alternating selection strategy) |
| Convergence | GA operators and reference point update | Strong (Weighted sum scalarization) | Enhanced by replacement & adjustment |
| Mutation Type | GA operators (unspecified type) | Polynomial Mutation | GA or DE operators based on generation |
| Crossover Type | GA operators (unspecified type) | SBX Crossover | GA or DE operators based on generation |
| Constraint Handling | Repair mechanism (y → y’) | Repair mechanism included | Not explicitly mentioned |
| Performance Monitoring | Based on reference point Z* | External population for non-dominated solutions | Dynamic adjustment based on performance |
| Neighborhood Size | Fixed (B(i)) | Fixed | Adaptive (Changes with generation) |
| Parent Selection | From Neighborhood B(i) | Neighborhood-based | Neighborhood or population-based |
| Reference Point Update | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Scalarization Method | Scalarizing function-based (gch) | Weighted Sum Approach | Not explicitly mentioned |
| Replacement Strategy | Replacement based on scalarized value comparison | Direct replacement based on scalarization | Stable-state replacement strategy |
| Consideration for Numerical Stability | Not explicitly addressed | Specific mechanisms (like handling ’inf’) | Not explicitly mentioned |
| Reference Pareto Front Generation | Not specified | Reference Pareto front generated for performance evaluation | Reference Pareto front generated for performance evaluation |
| Overall Robustness | Robust due to adaptive methods and scalarization | More robust for consistent approach & constraints | More robust in dynamic environments |
| Feature | Original SPEA2 | ES-SPEA2-DD | GDSEG-SPEA2 |
| Adaptability | Fixed population and strategies | Moderate (Adaptive Archive size management and pruning) | High (Adaptive grid method and elite guidance) |
| Diversity | Fitness sharing encourages diversity | High (Pruning based on crowding) | High (Neighborhood circle strategy and mixed perturbation) |
| Convergence | Density estimation and archive update for convergence | Enhanced by fitness evaluation and archive update | Enhanced by elite guidance and conditional genetic operations |
| Mutation Type | Standard SPEA2 mutation (not specified) | Mutation with random normal perturbation within bounds | Mutation prioritized for poor-performing individuals |
| Crossover Type | Standard SPEA2 crossover (not specified) | Two-point crossover | Crossover conditional on similarity threshold |
| Constraint Handling | Repair mechanism (y → y’) | Repair mechanism for constraint violations (y → y’) | Likely repair mechanism (not explicitly mentioned) |
| Performance Monitoring | Based on archive and fitness values | Archive size management by removing crowded solutions | Improved adaptive grid method for uniform distribution of Pareto front |
| Archive Maintenance | Update archive with non-dominated solutions | Pruning based on crowding | Pruning based on crowding and grid density |
| Parent Selection | Tournament selection | Binary tournament selection | Based on similarity threshold |
| Reference Point Update | Density estimation involves reference points | Yes (for density estimation) | Not explicitly mentioned |
| Replacement Strategy | Replacement based on non-domination | Update archive with non-dominated solutions, remove dominated ones | Update archive with non-dominated solutions, remove dominated ones, apply elite guidance |
| Consideration for Numerical Stability | Not explicitly addressed | Specific mechanisms included like handling infinity | Not explicitly addressed |
| Overall Robustness | Robust due to fitness sharing and density estimation | More robust due to adaptive archive management | Highly robust with grid density search and elite guidance |
| Algorithm | Algorithm Performance Evaluation Metrics (AL-PEM) | Policy Decision Metric (PDM) Based on Deficiency of Power Supply (DPS) |
| PDM-DPS0 | ||
| DAM-MOPSO | Storage Used | 208198 |
| Spacing | 17.34 | |
| Average Rate of Convergence | 59.00 | |
| Generational Distance | 5.45 | |
| Maximum Spread | 7871.30 | |
| Total Computational Time (secs) | 8051.86 | |
| Optimal Solution based on Euclidean distance to the origin | ||
| LCC-Total | 1.90e+8 | |
| DEF | 51.39 | |
| CO2 Emissions | 54919.77 | |
| Optimal Distance | 13173.14 | |
| ES-MOEA/D-FPM | Storage Used | 286778 |
| Spacing | 0.39 | |
| Rate of Convergence | 0.03 | |
| Generational Distance | 0.05 | |
| Maximum Spread | 2.24 | |
| Computational Time | 0.05 | |
| Optimal Solution based on Euclidean distance to the origin | ||
| LCC-Total | 1.39e+9 | |
| DEF | 47.47 | |
| CO2 Emissions | 66717.46 | |
| Optimal Distance | 599633.94 | |
| ES-SPEA2-DD | Storage Used | 1520 |
| Spacing | 0.25 | |
| Rate of Convergence | 0.01 | |
| Generational Distance | 0.60 | |
| Maximum Spread | 2.24 | |
| Computational Time | 5976.50 | |
| Optimal Solution based on Euclidean distance to the origin | ||
| LCC-Total | 6.31e+8 | |
| DEF | 6.72 | |
| CO2 Emissions | 11332.09 | |
| Optimal Distance | 13173 | |
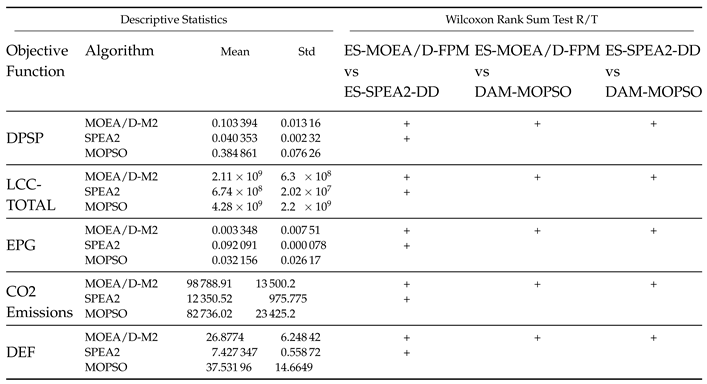
| Objective Functions | ES-SPEA2-DD | ES-MOEA/D-FPM | DAM-MOPSO |
| DPSP | + | - | + |
| LCC | + | - | - |
| EPG | + | - | + |
| CO2_Emissions | + | - | + |
| DEF | + | - | + |
| Overall Rank | 1 | 3 | 2 |
| AL-PEM For ES-SPEA2-DD | Policy Decision Metric (PDM) Based on Deficiency of Power Supply | ||||
| PDM-DPS0 | PDM-DPS20 | PDM-DPS30 | PDM-DPS40 | PDM-DPS50 | |
| Storage Used | 1520 | 1520 | 1520 | 1520 | 1520 |
| Spacing | 0.251 | 0.294 | 0.294 | 0.248 | 0.257 |
| Average Rate of Convergence | 0.01 | 0.002 | 0.009 | 0.008 | 0.009 |
| Generational Distance | 0.60 | 0.714 | 0.621 | 0.6052 | 0.586 |
| Maximum Spread | 2.236 | 2.236 | 2.236 | 2.236 | 2.236 |
| Total Computational Time | 5976.50 | 5817.70 | 5426.00 | 10092.00 | 6094.30 |
| Optimal Solution based on Euclidean distance to origin | |||||
| Total Life Cycle Cost | 6.31E+08 | 3.95E+09 | 1.97E+09 | 8.86E+08 | 1.02E+09 |
| Diesel Energy Fraction | 7 | 42 | 24 | 10 | 11 |
| CO2 Emissions | 11332.09 | 11580.13 | 44279.52 | 18406 | 19325.41 |
| Optimal Distance | 13173 | 30269 | 21286 | 15691 | 34378 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





