Submitted:
24 April 2024
Posted:
25 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Flies
2.2. Drosophila Shallow Chamber
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Data Analysis
2.4.1. Fly Tracking
2.4.2. Construction of Social Interaction Networks (SINs) and Social Network Analysis (SNA)
2.4.3. Localization of Social Interactions
2.4.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
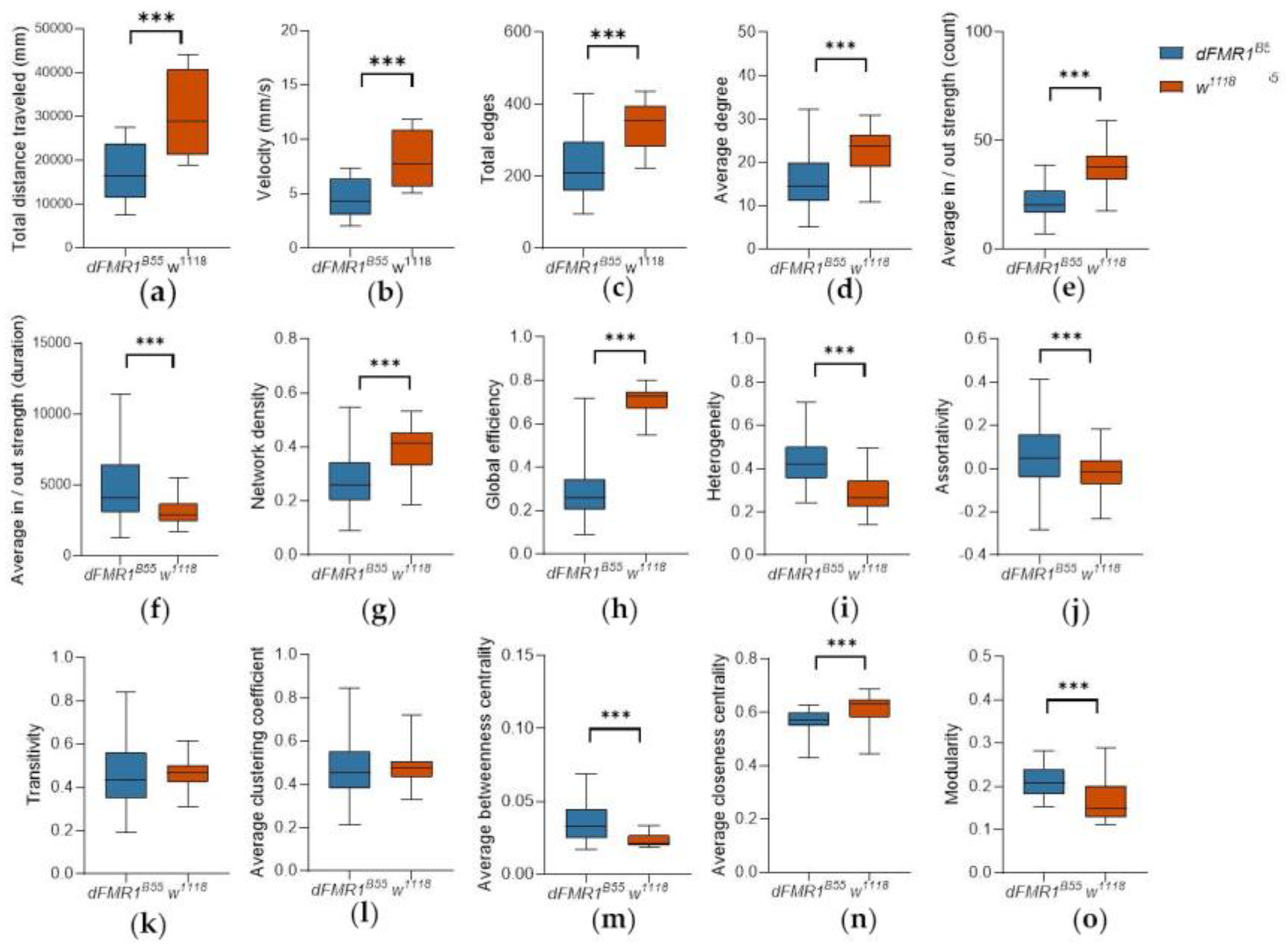
3.1. Activity Analysis
3.2. Social Network Analysis (SNA)
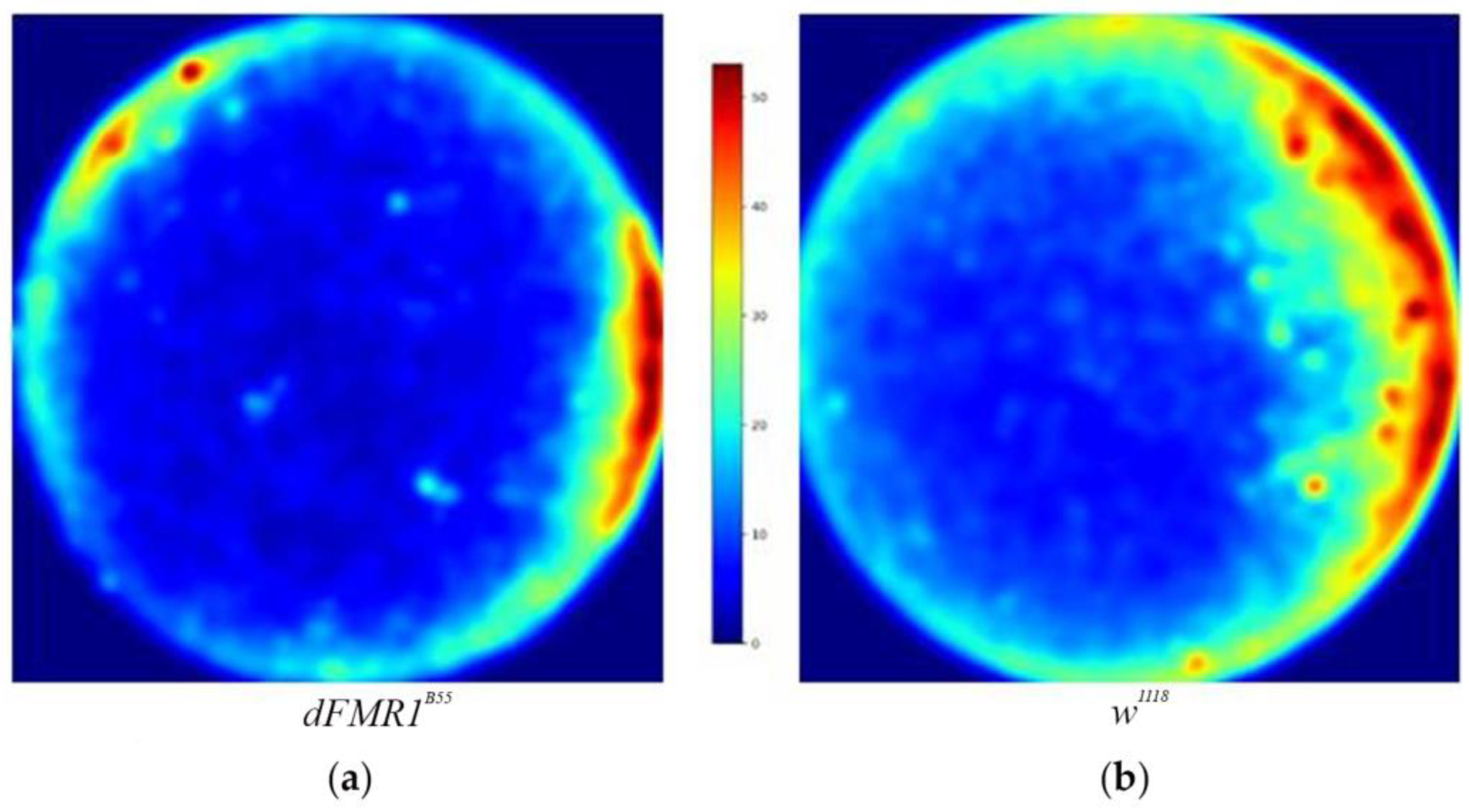
3.3. Localization of Social Interactions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Young, S.N. The neurobiology of human social behaviour: an important but neglected topic. J Psychiatry Neurosci 2008, 33, 391–2. [Google Scholar]
- Porcelli, S.; Van Der Wee, N.; van der Werff, S.; Aghajani, M.; Glennon, J.C.; van Heukelum, S.; et al. Social brain, social dysfunction and social withdrawal. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews 2019, 97, 10–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, M.R.; Bray, S.M.; Warren, S.T. Molecular mechanisms of fragile X syndrome: a twenty-year perspective. Annu Rev Pathol 2012, 7, 219–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufmann, W.E.; Cortell, R.; Kau, A.S.; Bukelis, I.; Tierney, E.; Gray, R.M. , et al. Autism spectrum disorder in fragile X syndrome: communication, social interaction, and specific behaviors. Am J Med Genet A 2004, 129a, 225–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cregenzán-Royo, O.; Brun-Gasca, C.; Fornieles-Deu, A. Behavior Problems and Social Competence in Fragile X Syndrome: A Systematic Review. Genes (Basel) 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, A.; Kang, S.; Shaffer, R.C.; Erickson, C.A.; Schmitt, L.M. Behavioral inflexibility in fragile X syndrome: Accounts from caregivers and self-advocates. Front Psychol 2023, 14, 1118652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahlhaus, R. Of Men and Mice: Modeling the Fragile X Syndrome. Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience 2018, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willemsen, R.; Kooy, R.F. Mouse models of fragile X-related disorders. Dis Model Mech 2023, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drozd, M.; Bardoni, B.; Capovilla, M. Modeling Fragile X Syndrome in Drosophila. Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience 2018, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trajković, J.; Makevic, V.; Pesic, M.; Pavković-Lučić, S.; Milojevic, S.; Cvjetkovic, S. , et al. Drosophila melanogaster as a Model to Study Fragile X-Associated Disorders. Genes (Basel) 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- den Broeder, M.J.; van der Linde, H.; Brouwer, J.R.; Oostra, B.A.; Willemsen, R.; Ketting, R.F. Generation and characterization of FMR1 knockout zebrafish. PLoS One 2009, 4, e7910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dockendorff, T.C.; Su, H.S.; McBride, S.M.; Yang, Z.; Choi, C.H.; Siwicki, K.K. , et al. Drosophila lacking dfmr1 activity show defects in circadian output and fail to maintain courtship interest. Neuron 2002, 34, 973–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, P.; Schoenfeld, B.P.; Bell, A.J.; Choi, C.H.; Bradley, M.P.; Hinchey, P. , et al. Short- and long-term memory are modulated by multiple isoforms of the fragile X mental retardation protein. J Neurosci 2010, 30, 6782–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashima, R.; Redmond, P.L.; Ghatpande, P.; Roy, S.; Kornberg, T.B.; Hanke, T. , et al. Hyperactive locomotion in a Drosophila model is a functional readout for the synaptic abnormalities underlying fragile X syndrome. Sci Signal 2017, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, J.; Dickinson, M.H.; Levine, J.D. Social structures depend on innate determinants and chemosensory processing in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2012, 109 Suppl 2, 17174–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Cheng, Y.; Gao, S.; Zhong, Y.; Ma, C.; Wang, T. , et al. Emergence of social cluster by collective pairwise encounters in Drosophila. Elife 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentzur, A.; Ben-Shaanan, S.; Benichou, J.I.C.; Costi, E.; Levi, M.; Ilany, A. , et al. Early Life Experience Shapes Male Behavior and Social Networks in Drosophila. Current Biology 2021, 31, 486–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, S.; Shimoda, M.; Nishinokubi, I.; Siomi, M.C.; Okamura, M.; Nakamura, A. , et al. A role for the Drosophila fragile X-related gene in circadian output. Curr Biol 2002, 12, 1331–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, A.F.; Chou, M.T.; Salazar, E.D.; Nicholson, T.; Saini, N.; Metchev, S. , et al. A simple assay to study social behavior in Drosophila: measurement of social space within a group. Genes Brain Behav 2012, 11, 243–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soibam, B.; Shah, S.; Gunaratne, G.H.; Roman, G.W. Modeling novelty habituation during exploratory activity in Drosophila. Behav Processes 2013, 97, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Nath, T.; Linneweber, G.A.; Claeys, A.; Guo, Z.; Li, J. , et al. A simple computer vision pipeline reveals the effects of isolation on social interaction dynamics in Drosophila. PLoS computational biology 2018, 14, e1006410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eyjolfsdottir, E.; Branson, S.; Burgos-Artizzu, X.; Hoopfer, E.; Schor, J.; Anderson, D. , et al. Detecting Social Actions of Fruit Flies. 2014, 8690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Nath, T.; Linneweber, G.A.; Claeys, A.; Guo, Z.; Li, J. , et al. A simple computer vision pipeline reveals the effects of isolation on social interaction dynamics in Drosophila. PLoS Comput Biol 2018, 14, e1006410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wice, E.W.; Saltz, J.B. Selection on heritable social network positions is context-dependent in Drosophila melanogaster. Nature Communications 2021, 12, 3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrović, M.; Meštrović, A.; Andretić Waldowski, R.; Filošević Vujnović, A. A network-based analysis detects cocaine-induced changes in social interactions in Drosophila melanogaster. PLOS ONE 2023, 18, e0275795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquaretta, C.; Battesti, M.; Klenschi, E.; Bousquet, C.A.; Sueur, C.; Mery, F. How social network structure affects decision-making in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Biol Sci 2016, 283, 20152954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen-Perkins, A.; Pastor, J.M.; Estrada, E. Two-walks degree assortativity in graphs and networks. Applied Mathematics and Computation 2017, 311, 262–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snijders, T.A. Transitivity and Triads. University of Oxford. 2012. Available online: https://www.stats.ox.ac.uk/~snijders/Trans_Triads_ha.pdf (accessed on 22 April 2024).
- Soibam, B.; Mann, M.; Liu, L.; Tran, J.; Lobaina, M.; Kang, Y.Y. , et al. Open-field arena boundary is a primary object of exploration for Drosophila. Brain and Behavior 2012, 2, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jezovit, J.A.; Alwash, N.; Levine, J.D. Using Flies to Understand Social Networks. Front Neural Circuits 2021, 15, 755093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwash, N.; Allen, A.M.; Sokolowski, M.B.; Levine, J.D. The Drosophila melanogaster foraging gene affects social networks. J Neurogenet 2021, 35, 249–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wice, E.W.; Saltz, J.B. Indirect genetic effects for social network structure in Drosophila melanogaster. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 2023, 378, 20220075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bentzur, A.; Ben-Shaanan, S.; Benichou, J.I.C.; Costi, E.; Levi, M.; Ilany, A. , et al. Early Life Experience Shapes Male Behavior and Social Networks in Drosophila. Curr Biol 2021, 31, 486–501.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rooke, R.; Rasool, A.; Schneider, J.; Levine, J.D. Drosophila melanogaster behaviour changes in different social environments based on group size and density. Commun Biol 2020, 3, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, C.H.; McBride, S.M.; Schoenfeld, B.P.; Liebelt, D.A.; Ferreiro, D.; Ferrick, N.J. , et al. Age-dependent cognitive impairment in a Drosophila fragile X model and its pharmacological rescue. Biogerontology 2010, 11, 347–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, A.R.; Kanellopoulos, A.K.; Bagni, C. Learning and behavioral deficits associated with the absence of the fragile X mental retardation protein: what a fly and mouse model can teach us. Learn Mem 2014, 21, 543–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolduc, F.V.; Valente, D.; Nguyen, A.T.; Mitra, P.P.; Tully, T. An assay for social interaction in Drosophila fragile X mutants. Fly 2010, 4, 216–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besson, M.; Martin, J.R. Centrophobism/thigmotaxis, a new role for the mushroom bodies in Drosophila. J Neurobiol 2005, 62, 386–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.; Bogert, B.A.; Li, W.; Su, K.; Lee, A.; Gao, F.B. The fragile X-related gene affects the crawling behavior of Drosophila larvae by regulating the mRNA level of the DEG/ENaC protein pickpocket1. Curr Biol 2004, 14, 1025–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayhew, A.J.; Meyre, D. Assessing the Heritability of Complex Traits in Humans: Methodological Challenges and Opportunities. Curr Genomics 2017, 18, 332–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




