Submitted:
07 April 2024
Posted:
08 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Methods
Participants
Study Design
Monitoring External Training Load
Monitoring Internal Training Load
Statistical Analysis
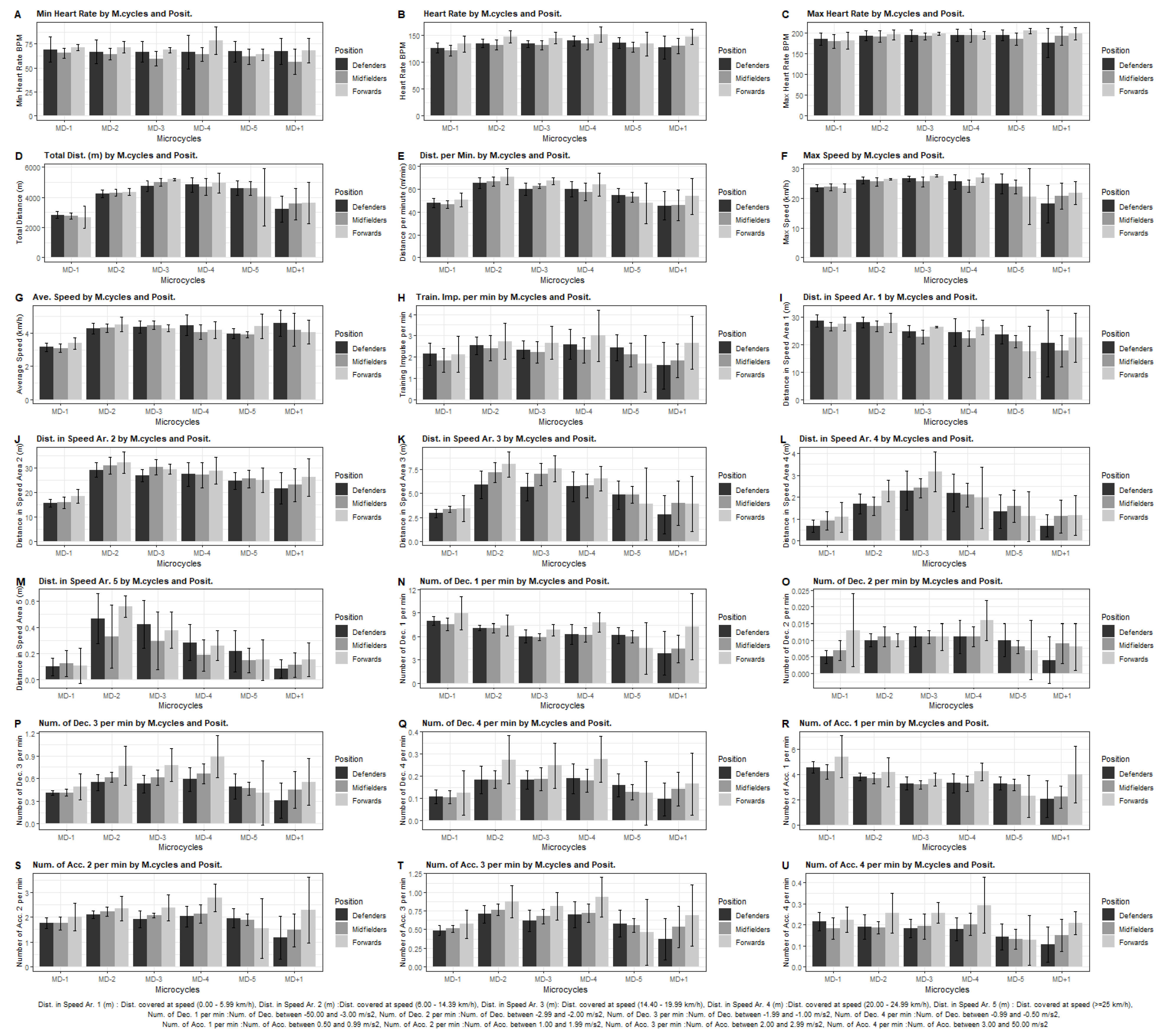
Results
| Training Performance Metrics | Description |
|---|---|
| Min HR (BPM) | Min Heart Rate during training |
| Mean Heart Rate BPM | Mean Heart Rate during training |
| Max Heart Rate BPM | Max Heart Rate during training |
| Total Distance (m) | Total in the training |
| Distance per minute (m/min) | Total Distance during training / Duration of training |
| Max Speed (km/h) | Max Speed in the training |
| Average Speed (km/h) | Average Speed in the training |
| Training Impulse per min | Multiplying the time spent in five HR zones |
| Distance in Speed Area 1 (m) | Distance covered at speed (0.00 - 5.99 km/h) |
| Distance in Speed Area 2 (m) | Distance covered at speed (6.00 - 14.39 km/h) |
| Distance in Speed Area 3 (m) | Distance covered at speed (14.40 - 19.99 km/h) |
| Distance in Speed Area 4 (m) | Distance covered at speed (20.00 - 24.99 km/h) |
| Distance in Speed Area 5 (m) | Distance covered at speed (>=25 km/h) |
| Number of Dec. 1 per min | Number of Dec between -50.00 and -3.00 m/s2 |
| Number of Dec. 2 per min | Number of Dec between -2.99 and -2.00 m/s2 |
| Number of Dec. 3 per min | Number of Dec between -1.99 and -1.00 m/s2 |
| Number of Dec. 4 per min | Number of Dec between -0.99 and -0.50 m/s2 |
| Number of Acc. 1 per min | Number of Acc between 0.50 and 0.99 m/s2 |
| Number of Acc. 2 per min | Number of Acc between 1.00 and 1.99 m/s2 |
| Number of Acc. 3 per min | Number of Acc between 2.00 and 2.99 m/s2 |
| Number of Acc. 4 per min | Number of Acc between 3.00 and 50.00 m/s2 |
| Cycle For All Players | F | p | Source of Difference | Effect Size |
||||||||||||
| MD-5 | MD-4 | MD-3 | MD-2 | MD-1 | MD+1 | |||||||||||
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |||||
| Min HR (BPM) | 64.224 | 8.980 | 67.426 | 13.683 | 64.003 | 9.071 | 66.607 | 9.083 | 67.946 | 9.263 | 62.737 | 13.749 | 2.469 | 0.068 | ----- | 0.032 (Small) |
| Mean Heart Rate (BPM) | 131.739 | 11.998 | 138.770 | 11.935 | 134.054 | 8.999 | 135.314 | 9.584 | 125.009 | 10.852 | 131.317 | 18.119 | 10.841 | <0.001 | MD-1 - MD-2, MD-3, MD-4, MD-5; MD-3 - MD-4 | 0.111 (Medium) |
| Max Heart Rate (BPM) | 192.811 | 14.319 | 194.843 | 13.836 | 194.172 | 10.818 | 193.388 | 12.163 | 182.687 | 15.199 | 187.004 | 28.116 | 3.895 | 0.032 | MD-1 - MD-2, MD-3, MD-4 | 0.069 (Medium) |
| Total Distance (m) | 4514.591 | 786.696 | 4803.911 | 524.278 | 4930.951 | 319.517 | 4287.314 | 236.855 | 2783.812 | 314.599 | 3430.211 | 978.156 | 59.865 | <0.001 | MD-1 - MD-2, MD-3, MD-4, MD-5, MD+1; MD-2 - MD-3, MD-4; MD+1 - MD-2, MD-3, MD-4, MD-5 |
0.641 (Large) |
| Distance per minute (m/min) | 52.982 | 8.011 | 59.586 | 7.666 | 62.380 | 4.436 | 66.824 | 4.892 | 47.806 | 4.109 | 47.024 | 12.980 | 31.365 | <0.001 | MD-1 - MD-2, MD-3, MD-4; MD-3 - MD-5, MD+1; MD-2 - MD-3, MD-4, MD-5, MD+1; MD-4 - MD+1 |
0.496 (Large) |
| Max Speed (km/h) | 23.804 | 4.316 | 25.203 | 2.324 | 26.350 | 1.398 | 25.968 | 1.178 | 23.607 | 1.113 | 19.803 | 5.249 | 14.585 | <0.001 | MD-1 - MD-2, MD-3; MD+1 - MD-2, MD-3, MD-4 | 0.349 (Large) |
| Average Speed (km/h) | 4.005 | 0.376 | 4.252 | 0.551 | 4.387 | 0.298 | 4.325 | 0.309 | 3.158 | 0.273 | 4.337 | 0.863 | 22.094 | <0.001 | MD-1 - MD-2, MD-3, MD-4, MD-5, MD+1; MD-5 - MD-2,MD-3 |
0.446 (Large) |
| Training Impulse per min | 2.169 | 0.729 | 2.541 | 0.736 | 2.338 | 0.516 | 2.513 | 0.542 | 2.003 | 0.573 | 1.860 | 1.008 | 8.158 | <0.001 | MD-1 - MD-2, MD-3, MD-4; MD+1 - MD-2, MD-4 | 0.119 (Medium) |
| Distance in Speed Area 1 (m) | 21.537 | 4.580 | 23.768 | 3.939 | 24.204 | 2.460 | 27.431 | 2.118 | 27.565 | 2.103 | 19.547 | 9.019 | 10.258 | <0.001 | MD-1, MD-2 - MD-3, MD-4, MD-5, MD+1 | 0.286 (Large) |
| Distance in Speed Area 2 (m) | 25.120 | 3.532 | 27.556 | 4.834 | 28.753 | 3.037 | 30.436 | 3.388 | 16.082 | 2.210 | 22.980 | 6.556 | 62.602 | <0.001 | MD-1, MD-2 - MD-3, MD-4, MD-5, MD+1; MD-1 - MD-2; MD-3, MD-4 - MD+1; MD-3 - MD-5 |
0.575 (Large) |
| Distance in Speed Area 3 (m) | 4.705 | 1.693 | 5.888 | 1.337 | 6.548 | 1.452 | 6.807 | 1.466 | 3.196 | 0.616 | 3.451 | 2.233 | 32.278 | <0.001 | MD-1 - MD-2, MD-3, MD-4, MD-5; MD-2, MD-3; MD-5, MD+1; MD-4 - MD+1 |
0.473 (Large) |
| Distance in Speed Area 4 (m) | 1.409 | 0.773 | 2.119 | 0.792 | 2.482 | 0.754 | 1.743 | 0.486 | 0.843 | 0.418 | 0.944 | 0.676 | 26.598 | <0.001 | MD-1 - MD-2, MD-3, MD-4, MD-5; MD-3, MD-4; MD-5, MD+1; MD-2 - MD-3, MD+1 |
0.455 (Large) |
| Distance in Speed Area 5 (m) | 0.176 | 0.131 | 0.237 | 0.129 | 0.361 | 0.196 | 0.422 | 0.213 | 0.109 | 0.088 | 0.103 | 0.090 | 32.697 | <0.001 | MD-1- MD-2, MD-3, MD-4; MD-2 - MD-3; MD-4, MD-5, MD+1; MD-4 - MD+1 |
0.409 (Large) |
| Number of Dec. 1 per min | 0.142 | 0.064 | 0.199 | 0.073 | 0.195 | 0.059 | 0.198 | 0.068 | 0.110 | 0.044 | 0.126 | 0.086 | 12.944 | <0.001 | MD-1 - MD-2, MD-3, MD-4; MD+1 - MD-2, MD-3, MD-4 | 0.245 (Large) |
| Number of Dec. 2 per min | 0.470 | 0.187 | 0.666 | 0.190 | 0.605 | 0.150 | 0.612 | 0.140 | 0.423 | 0.073 | 0.407 | 0.252 | 12.675 | <0.001 | MD-1 - MD-2, MD-3, MD-4; MD+1 - MD-2, MD-3, MD-4;MD-4 - MD-5 |
0.261 (Large) |
| Number of Dec. 3 per min | 0.009 | 0.005 | 0.012 | 0.005 | 0.011 | 0.003 | 0.011 | 0.003 | 0.007 | 0.005 | 0.006 | 0.007 | 4.785 | <0.01 | MD-1 - MD-4 | 0.158 (Large) |
| Number of Dec. 4 per min | 5.816 | 1.482 | 6.468 | 1.222 | 6.112 | 0.728 | 7.121 | 0.632 | 7.968 | 1.042 | 4.618 | 2.767 | 14.434 | <0.001 | MD-1 - MD-2, MD-3, MD-4, MD-5, MD+1; MD-2 - MD-3, MD+1; MD-4 - MD+1 |
0.342 (Large) |
| Number of Acc. 1 per min | 3.089 | 0.791 | 3.443 | 0.733 | 3.307 | 0.455 | 3.841 | 0.530 | 4.560 | 0.831 | 2.443 | 1.469 | 18.600 | <0.001 | MD-1 - MD-2, MD-3, MD-4, MD-5, MD+1; MD-2 - MD-3, MD+1; MD-4 - MD+1 |
0.374 (Large) |
| Number of Acc. 2 per min | 1.866 | 0.512 | 2.188 | 0.479 | 2.047 | 0.320 | 2.191 | 0.240 | 1.801 | 0.298 | 1.472 | 0.899 | 7.994 | <0.001 | MD-1 - MD-2, MD-4; MD+1 - MD-2, MD-4 | 0.205 (Large) |
| Number of Acc. 3 per min | 0.551 | 0.196 | 0.744 | 0.181 | 0.672 | 0.140 | 0.755 | 0.128 | 0.510 | 0.086 | 0.490 | 0.304 | 11.875 | <0.001 | MD-1 - MD-2, MD-3, MD-4; MD-2 - MD-3, MD-5, MD+1; MD-4 - MD-5, MD+1 |
0.263 (Large) |
| Number of Acc. 4 per min | 0.135 | 0.063 | 0.207 | 0.076 | 0.198 | 0.056 | 0.199 | 0.057 | 0.203 | 0.051 | 0.140 | 0.082 | 7.252 | <0.001 | MD-5 - MD-1, MD-3; MD-4 - MD+1 | 0.186 (Large) |
| Cycle for Defenders | F | p | Source of Difference | Effect Size |
||||||||||||
| MD-5 | MD-4 | MD-3 | MD-2 | MD-1 | MD+1 | |||||||||||
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |||||
| Min HR (BPM) | 67.110 | 10.700 | 66.523 | 17.287 | 66.699 | 10.590 | 66.865 | 12.105 | 69.048 | 13.251 | 67.158 | 13.719 | 17.621 | <0.001 | MD-1 - MD-2, MD-3, MD-4, MD-5, MD+1; MD-5 - MD-2, MD-3 |
0.524 (Large) |
| Mean Heart Rate (BPM) | 135.115 | 10.020 | 139.017 | 9.650 | 133.502 | 6.288 | 134.670 | 7.257 | 125.832 | 9.052 | 126.835 | 21.267 | 2.766 | 0.126 | ---- | 0.211 (Large) |
| Max Heart Rate (BPM) | 195.133 | 13.208 | 195.047 | 15.015 | 194.124 | 14.197 | 193.762 | 12.106 | 185.628 | 14.234 | 176.404 | 35.129 | 24.459 | <0.001 | MD-1, MD-2 - MD-3, MD-4, MD-5, MD+1; MD-1 - MD-2; MD-3 - MD-5, MD+1; MD-4 - MD+1 |
0.599 (Large) |
| Total Distance (m) | 4618.339 | 470.466 | 4839.406 | 486.795 | 4757.572 | 365.924 | 4233.559 | 252.431 | 2839.141 | 242.073 | 3228.715 | 852.330 | 15.277 | <0.001 | MD-1 - MD-2, MD-3, MD-4, MD-5; MD-2, MD-3 - MD-5, MD+1; MD-4 - MD+1 |
0.476 (Large) |
| Distance per minute (m/min) | 54.703 | 6.193 | 60.140 | 6.927 | 60.113 | 5.241 | 65.308 | 4.573 | 47.885 | 3.915 | 45.590 | 12.485 | 11.836 | 0.002 | MD-1 - MD-2, MD-3, MD-4, MD-5; MD-2 - MD-3, MD+1; MD-3, MD-4 - MD-5, MD+1 |
0.522 (Large) |
| Max Speed (km/h) | 24.852 | 3.363 | 25.603 | 2.464 | 26.638 | 0.873 | 26.165 | 1.159 | 23.511 | 1.095 | 18.097 | 6.347 | 22.568 | <0.001 | MD-1 - MD-2, MD-3, MD-4; MD-4 - MD+1; MD-2, MD-3 - MD-4, MD-5, MD+1 |
0.545 (Large) |
| Average Speed (km/h) | 3.961 | 0.301 | 4.474 | 0.638 | 4.344 | 0.368 | 4.283 | 0.323 | 3.147 | 0.268 | 4.584 | 0.794 | 13.981 | 0.002 | MD-1 - MD-2, MD-3 MD-4; MD-4 - MD+1; MD-2 - MD-3, MD-4, MD-5, MD+1; MD-3 - MD-5, MD+1 |
0.525 (Large) |
| Training Impulse per min | 2.425 | 0.605 | 2.591 | 0.692 | 2.339 | 0.428 | 2.527 | 0.405 | 2.135 | 0.516 | 1.594 | 1.091 | 3.092 | 0.105 | ---- | 0.131 (Medium) |
| Distance in Speed Area 1 (m) | 23.583 | 3.379 | 24.384 | 4.943 | 24.746 | 2.094 | 28.050 | 1.871 | 28.625 | 2.174 | 20.440 | 12.103 | 0.194 | 0.849 | ---- | 0.005 (Insig.) |
| Distance in Speed Area 2 (m) | 24.721 | 3.443 | 27.490 | 4.895 | 26.950 | 2.481 | 29.181 | 2.970 | 15.507 | 1.629 | 21.656 | 6.514 | 4.664 | 0.047 | MD-1 - MD-2, MD-3, MD-4, MD-5; MD-3 - MD-4 | 0.155 (Large) |
| Distance in Speed Area 3 (m) | 4.836 | 1.465 | 5.722 | 1.534 | 5.688 | 1.422 | 5.923 | 1.466 | 2.930 | 0.457 | 2.777 | 2.031 | 10.789 | 0.006 | MD-1 - MD-2, MD-3; MD+1 - MD-2, MD-3, MD-4 | 0.483 (Large) |
| Distance in Speed Area 4 (m) | 1.338 | 0.757 | 2.198 | 0.861 | 2.291 | 0.891 | 1.699 | 0.458 | 0.672 | 0.268 | 0.682 | 0.507 | 13.969 | 0.003 | MD-1 - MD-2, MD-3, MD-4, MD-5, MD+1; MD+1 - MD-2, MD-4; MD-2 - MD-3 |
0.522 (Large) |
| Distance in Speed Area 5 (m) | 0.217 | 0.158 | 0.281 | 0.138 | 0.422 | 0.185 | 0.465 | 0.191 | 0.096 | 0.067 | 0.078 | 0.071 | 6.499 | 0.018 | MD-1, MD+1 - MD-2, MD-4 | 0.346 (Large) |
| Number of Dec. 1 per min | 0.161 | 0.052 | 0.189 | 0.069 | 0.183 | 0.041 | 0.183 | 0.063 | 0.109 | 0.031 | 0.096 | 0.075 | 7.724 | <0.001 | MD-1 - MD-2, MD-3, MD-4; MD-2 - MD-3, MD-4, MD+1; MD-4 - MD-5, MD+1 |
0.346 (Large) |
| Number of Dec. 2 per min | 0.496 | 0.168 | 0.588 | 0.160 | 0.528 | 0.120 | 0.548 | 0.104 | 0.408 | 0.030 | 0.308 | 0.231 | 4.725 | 0.002 | MD-5 - MD-1, MD-3; MD-4 - MD+1 | 0.287 (Large) |
| Number of Dec. 3 per min | 0.010 | 0.005 | 0.011 | 0.005 | 0.011 | 0.003 | 0.010 | 0.002 | 0.005 | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.007 | 11.003 | 0.006 | MD-1 - MD-2, MD-3, MD-4, MD-5, MD+1; MD-2 - MD-3, MD+1; MD-4 - MD+1 |
0.486 (Large) |
| Number of Dec. 4 per min | 6.138 | 1.017 | 6.245 | 1.285 | 6.030 | 0.851 | 7.113 | 0.335 | 7.988 | 0.519 | 3.853 | 2.790 | 5.534 | <0.001 | MD-1 - MD-4 | 0.326 (Large) |
| Number of Acc. 1 per min | 3.289 | 0.519 | 3.313 | 0.748 | 3.305 | 0.520 | 3.838 | 0.301 | 4.578 | 0.475 | 2.079 | 1.446 | 5.925 | <0.001 | MD-1, MD+1 - MD-2, MD-3, MD-4; MD-4 - MD-5 | 0.315 (Large) |
| Number of Acc. 2 per min | 1.959 | 0.395 | 2.022 | 0.407 | 1.912 | 0.327 | 2.105 | 0.156 | 1.772 | 0.217 | 1.165 | 0.870 | 7.913 | <0.001 | MD-1, MD+1 - MD-2, MD-3, MD-4; | 0.326 (Large) |
| Number of Acc. 3 per min | 0.579 | 0.178 | 0.697 | 0.172 | 0.617 | 0.142 | 0.704 | 0.116 | 0.487 | 0.063 | 0.373 | 0.279 | 40.483 | <0.001 | MD-1 - MD-2, MD-3, MD-4, MD-5, MD+1; MD-2 - MD-3, MD-4; MD+1 - MD-2, MD-3, MD-4, MD-5 |
0.741 (Large) |
| Number of Acc. 4 per min | 0.143 | 0.062 | 0.179 | 0.056 | 0.181 | 0.044 | 0.191 | 0.058 | 0.217 | 0.044 | 0.107 | 0.085 | 7.734 | 0.012 | MD-1 - MD-2, MD-3, MD-4; MD+1 - MD-2, MD-4 |
0.225 (Large) |
| Cycle for Midfielders | F | p | Source of Difference | Effect Size |
||||||||||||
| MD-5 | MD-4 | MD-3 | MD-2 | MD-1 | MD+1 | |||||||||||
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |||||
| Min HR (BPM) | 61.515 | 7.976 | 64.165 | 7.491 | 59.610 | 7.637 | 64.466 | 6.263 | 65.518 | 5.352 | 56.379 | 13.118 | 3.195 | 0.068 | ---- | 0.142 (Large) |
| Mean Heart Rate (BPM) | 127.592 | 9.797 | 133.787 | 10.848 | 130.729 | 8.672 | 131.710 | 8.889 | 120.874 | 10.188 | 129.967 | 14.239 | 10.148 | <0.001 | MD-1 - MD-2, MD-3, MD-4, MD-5; MD-3 - MD-4 | 0.148 (Large) |
| Max Heart Rate (BPM) | 185.821 | 14.548 | 194.653 | 15.491 | 192.228 | 8.905 | 192.013 | 13.706 | 180.195 | 15.849 | 193.444 | 22.481 | 4.128 | 0.005 | MD-1 - MD-2, MD-3, MD-4 | 0.108 (Medium) |
| Total Distance (m) | 4598.732 | 442.170 | 4707.888 | 571.107 | 5010.200 | 243.073 | 4314.452 | 243.155 | 2768.898 | 184.279 | 3557.923 | 1057.164 | 30.965 | <0.001 | MD-1 - MD-2, MD-3, MD-4, MD-5, MD+1; MD-2 - MD-3, MD-4; MD+1 - MD-2, MD-3, MD-4, MD-5 |
0.693 (Large) |
| Distance per minute (m/min) | 53.262 | 4.341 | 57.404 | 7.697 | 62.854 | 2.119 | 66.762 | 3.916 | 46.658 | 3.591 | 45.942 | 13.485 | 19.698 | <0.001 | MD-1 - MD-2, MD-3, MD-4; MD-3 - MD-5, MD+1; MD-2 - MD-3, MD-4, MD-5, MD+1; MD-4 - MD+1 |
0.584 (Large) |
| Max Speed (km/h) | 23.951 | 2.292 | 24.161 | 2.140 | 25.607 | 1.689 | 25.603 | 1.389 | 23.754 | 1.177 | 20.773 | 4.485 | 6.160 | 0.017 | MD-1 - MD-2, MD-3; MD+1 - MD-2, MD-3, MD-4 | 0.331 (Large) |
| Average Speed (km/h) | 3.901 | 0.180 | 4.058 | 0.453 | 4.468 | 0.257 | 4.299 | 0.260 | 3.086 | 0.239 | 4.197 | 1.008 | 8.189 | 0.015 | MD-1 - MD-2, MD-3, MD-4, MD-5, MD+1; MD-5 - MD-2, MD-3 |
0.486 (Large) |
| Training Impulse per min | 2.097 | 0.553 | 2.323 | 0.593 | 2.215 | 0.514 | 2.414 | 0.597 | 1.828 | 0.562 | 1.823 | 0.792 | 6.823 | 0.008 | MD-1 - MD-2, MD-3, MD-4; MD+1 - MD-2, MD-4 | 0.138 (Medium) |
| Distance in Speed Area 1 (m) | 21.071 | 2.306 | 22.209 | 2.749 | 22.821 | 2.543 | 26.648 | 1.850 | 26.481 | 1.492 | 17.596 | 5.596 | 11.742 | 0.005 | MD-1, MD-2 - MD-3, MD-4, MD-5, MD+1 | 0.544 (Large) |
| Distance in Speed Area 2 (m) | 25.564 | 3.541 | 27.114 | 5.129 | 30.278 | 3.130 | 30.994 | 3.418 | 15.765 | 2.209 | 23.122 | 6.741 | 34.706 | <0.001 | MD-1 , MD-2 - MD-3, MD-4, MD-5, MD+1; MD-1 - MD-2; MD-3 - MD-5; MD+1 - MD-3, MD-5 |
0.617 (Large) |
| Distance in Speed Area 3 (m) | 4.870 | 0.902 | 5.803 | 1.251 | 7.011 | 1.143 | 7.221 | 1.062 | 3.382 | 0.324 | 3.965 | 2.322 | 21.607 | <0.001 | MD-1 - MD-2, MD-3, MD-4, MD-5; MD-2, MD-3 - MD-5, MD+1; MD-4 - MD+1 |
0.581 (Large) |
| Distance in Speed Area 4 (m) | 1.586 | 0.721 | 2.097 | 0.546 | 2.416 | 0.434 | 1.582 | 0.417 | 0.922 | 0.419 | 1.122 | 0.743 | 11.229 | <0.001 | MD-1 - MD-2, MD-3, MD-4, MD-5; MD-2 - MD-3, MD+1; MD-3, MD-4 - MD-5, MD+1 |
0.489 (Large) |
| Distance in Speed Area 5 (m) | 0.145 | 0.094 | 0.184 | 0.120 | 0.293 | 0.221 | 0.328 | 0.242 | 0.123 | 0.100 | 0.111 | 0.096 | 7.625 | <0.001 | MD-1 - MD-2, MD-3, MD-4; MD-2, MD-3 - MD-4, MD-5, MD+1; MD-4 - MD+1 |
0.244 (Large) |
| Number of Dec. 1 per min | 0.129 | 0.035 | 0.180 | 0.052 | 0.187 | 0.052 | 0.185 | 0.039 | 0.105 | 0.030 | 0.141 | 0.076 | 8.054 | <0.001 | MD-1, MD+1 - MD-2, MD-3, MD-4; | 0.313 (Large) |
| Number of Dec. 2 per min | 0.466 | 0.088 | 0.661 | 0.131 | 0.616 | 0.100 | 0.616 | 0.068 | 0.414 | 0.044 | 0.450 | 0.243 | 9.372 | 0.007 | MD-1, MD+1 - MD-2, MD-3, MD-4; MD-4 - MD-5 | 0.387 (Large) |
| Number of Dec. 3 per min | 0.008 | 0.002 | 0.011 | 0.003 | 0.011 | 0.002 | 0.011 | 0.003 | 0.007 | 0.003 | 0.009 | 0.006 | 2.277 | 0.068 | ---- | 0.197 (Large) |
| Number of Dec. 4 per min | 5.999 | 0.787 | 6.196 | 0.940 | 5.922 | 0.445 | 7.025 | 0.588 | 7.569 | 0.763 | 4.396 | 1.761 | 18.595 | <0.001 | MD-1 - MD-2, MD-3, MD-4, MD-5, MD+1; MD-2 - MD-3; MD+1 - MD-2, MD-4 |
0.542 (Large) |
| Number of Acc. 1 per min | 3.191 | 0.450 | 3.280 | 0.615 | 3.188 | 0.356 | 3.716 | 0.425 | 4.224 | 0.555 | 2.225 | 0.874 | 26.705 | <0.001 | MD-1 - MD-2, MD-3, MD-4, MD-5, MD+1; MD-2 - MD-3, MD+1; MD-4 - MD+1 |
0.563 (Large) |
| Number of Acc. 2 per min | 1.896 | 0.221 | 2.131 | 0.383 | 2.059 | 0.099 | 2.217 | 0.191 | 1.755 | 0.264 | 1.480 | 0.663 | 8.649 | 0.005 | MD-1, MD+1 - MD-2, MD-4 | 0.362 (Large) |
| Number of Acc. 3 per min | 0.556 | 0.090 | 0.719 | 0.127 | 0.674 | 0.094 | 0.763 | 0.079 | 0.510 | 0.048 | 0.532 | 0.278 | 6.393 | 0.017 | MD-1 - MD-2, MD-3, MD-4; MD-2 - MD-3; MD-2, MD-4 - MD-5, MD+1 |
0.354 (Large) |
| Number of Acc. 4 per min | 0.131 | 0.047 | 0.202 | 0.052 | 0.193 | 0.060 | 0.187 | 0.030 | 0.182 | 0.052 | 0.150 | 0.076 | 4.161 | 0.034 | MD-5 - MD-1, MD-3; MD-4 - MD+1 | 0.196 (Large) |
| Cycle for Forwards | F | p | Source of Difference | Effect Size |
||||||||||||
| MD-5 | MD-4 | MD-3 | MD-2 | MD-1 | MD+1 | |||||||||||
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |||||
| Min HR (BPM) | 63.751 | 6.278 | 78.528 | 14.559 | 68.527 | 2.624 | 71.628 | 5.988 | 71.485 | 3.197 | 67.900 | 12.662 | 2.051 | 0.156 | ----- | 0.284 (Large) |
| Mean Heart Rate (BPM) | 133.799 | 22.078 | 151.403 | 14.324 | 144.394 | 11.018 | 146.640 | 10.946 | 133.838 | 14.892 | 146.867 | 14.555 | 2.629 | 0.091 | ----- | 0.228 (Large) |
| Max Heart Rate (BPM) | 205.264 | 6.664 | 194.806 | 9.678 | 199.481 | 3.581 | 196.058 | 11.922 | 181.489 | 20.715 | 198.100 | 15.044 | 2.136 | 0.144 | ----- | 0.332 (Large) |
| Total Distance (m) | 4013.556 | 1913.923 | 4965.319 | 649.495 | 5181.962 | 59.168 | 4358.289 | 229.962 | 2676.041 | 732.284 | 3626.967 | 1367.909 | 3.674 | 0.038 | MD-1 - MD-2, MD-3, MD-4, MD-5, MD+1; MD-2 - MD-3, MD-4; MD+1 - MD-2, MD-3, MD-4, MD-5 |
0.493 (Large) |
| Distance per minute (m/min) | 47.645 | 17.960 | 63.931 | 10.248 | 67.159 | 3.095 | 71.028 | 7.268 | 50.657 | 5.972 | 53.733 | 15.932 | 2.877 | 0.073 | ----- | 0.471 (Large) |
| Max Speed (km/h) | 20.620 | 9.486 | 26.912 | 1.406 | 27.564 | 0.439 | 26.412 | 0.230 | 23.473 | 1.397 | 21.768 | 3.921 | 1.599 | 0.246 | ----- | 0.367 (Large) |
| Average Speed (km/h) | 4.397 | 0.748 | 4.175 | 0.487 | 4.286 | 0.209 | 4.509 | 0.444 | 3.377 | 0.359 | 4.051 | 0.707 | 2.001 | 0.164 | ----- | 0.423 (Large) |
| Training Impulse per min | 1.681 | 1.337 | 2.994 | 1.207 | 2.663 | 0.779 | 2.739 | 0.839 | 2.120 | 0.840 | 2.665 | 1.238 | 1.590 | 0.249 | ----- | 0.205 (Large) |
| Distance in Speed Area 1 (m) | 17.320 | 9.269 | 26.283 | 2.631 | 26.448 | 0.304 | 27.867 | 3.448 | 27.631 | 2.507 | 22.366 | 8.917 | 1.446 | 0.289 | ----- | 0.398 (Large) |
| Distance in Speed Area 2 (m) | 24.997 | 5.044 | 28.910 | 5.547 | 29.492 | 2.016 | 32.292 | 4.337 | 18.458 | 2.721 | 26.135 | 7.567 | 5.202 | 0.013 | MD-1, MD-2 - MD-3, MD-4, MD-5, MD+1; MD-1 - MD-2; MD-3 - MD-5, MD+1; MD-4 - MD+1 |
0.546 (Large) |
| Distance in Speed Area 3 (m) | 3.915 | 3.783 | 6.557 | 1.254 | 7.606 | 1.349 | 8.059 | 1.308 | 3.408 | 1.350 | 3.880 | 2.898 | 3.134 | 0.059 | ----- | 0.522 (Large) |
| Distance in Speed Area 4 (m) | 1.126 | 1.137 | 1.964 | 1.397 | 3.167 | 0.901 | 2.289 | 0.475 | 1.091 | 0.688 | 1.164 | 0.898 | 5.768 | 0.009 | MD-1 - MD-2, MD-3, MD-4, MD-5; MD-2 - MD-3, MD+1; MD-3, MD-4 - MD-5, MD+1 |
0.485 (Large) |
| Distance in Speed Area 5 (m) | 0.150 | 0.155 | 0.260 | 0.117 | 0.377 | 0.139 | 0.556 | 0.082 | 0.105 | 0.135 | 0.149 | 0.129 | 8.002 | 0.003 | MD-1 - MD-2, MD-3, MD-4; MD-2, MD-3 - MD-4, MD-5, MD+1; MD-4 - MD+1 |
0.694 (Large) |
| Number of Dec. 1 per min | 0.124 | 0.144 | 0.277 | 0.103 | 0.249 | 0.102 | 0.275 | 0.108 | 0.124 | 0.101 | 0.165 | 0.140 | 2.009 | 0.163 | ----- | 0.324 (Large) |
| Number of Dec. 2 per min | 0.410 | 0.425 | 0.891 | 0.276 | 0.780 | 0.218 | 0.770 | 0.262 | 0.488 | 0.174 | 0.557 | 0.314 | 1.981 | 0.167 | ----- | 0.352 (Large) |
| Number of Dec. 3 per min | 0.007 | 0.009 | 0.016 | 0.006 | 0.011 | 0.004 | 0.010 | 0.002 | 0.013 | 0.011 | 0.008 | 0.007 | 0.789 | 0.581 | ----- | 0.228 (Large) |
| Number of Dec. 4 per min | 4.471 | 3.276 | 7.789 | 1.206 | 6.839 | 0.755 | 7.398 | 1.356 | 8.980 | 2.149 | 7.249 | 4.228 | 1.175 | 0.386 | ----- | 0.31 (Large) |
| Number of Acc. 1 per min | 2.288 | 1.679 | 4.225 | 0.683 | 3.630 | 0.515 | 4.183 | 1.159 | 5.411 | 1.676 | 3.995 | 2.257 | 1.769 | 0.207 | ----- | 0.376 (Large) |
| Number of Acc. 2 per min | 1.540 | 1.203 | 2.783 | 0.562 | 2.372 | 0.533 | 2.349 | 0.489 | 2.002 | 0.566 | 2.269 | 1.325 | 0.912 | 0.511 | ----- | 0.23 (Large) |
| Number of Acc. 3 per min | 0.464 | 0.439 | 0.934 | 0.263 | 0.813 | 0.183 | 0.871 | 0.218 | 0.571 | 0.193 | 0.690 | 0.412 | 1.529 | 0.265 | ----- | 0.311 (Large) |
| Number of Acc. 4 per min | 0.126 | 0.118 | 0.293 | 0.132 | 0.257 | 0.050 | 0.254 | 0.095 | 0.224 | 0.061 | 0.207 | 0.055 | 1.210 | 0.371 | ----- | 0.333 (Large) |
| ALL | F | p | SOD | Effect Size |
MD-5 | F | p | SOD | Effect Size |
|||||||||||||||||
| DF | MF | FW | DF | MF | FW | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |||||||||||||||
| Min Heart Rate BPM | 67.234 | 12.450 | 61.942 | 8.520 | 70.303 | 8.736 | 5.401 | 0.006 | MF - DF, FW | 0.089 | 67.110 | 10.700 | 61.515 | 7.976 | 63.751 | 6.278 | 0.761 | 0.484 | --- | 0.087 | ||||||
| Mean Heart Rate BPM | 132.495 | 12.021 | 129.110 | 10.855 | 142.823 | 14.435 | 8.621 | <0.001 | FW - DF, MF | 0.134 | 135.115 | 10.020 | 127.592 | 9.797 | 133.799 | 22.078 | 0.822 | 0.457 | --- | 0.093 | ||||||
| Max Heart Rate BPM | 190.016 | 19.345 | 189.726 | 15.692 | 195.866 | 12.924 | 0.948 | 0.390 | --- | 0.017 | 195.133 | 13.208 | 185.821 | 14.548 | 205.264 | 6.664 | 2.577 | 0.107 | --- | 0.244 | ||||||
| Total Distance (m) | 4086.122 | 910.857 | 4159.682 | 932.125 | 4137.022 | 1232.117 | 0.070 | 0.933 | --- | 0.001 | 4618.339 | 470.466 | 4598.732 | 442.170 | 4013.556 | 1913.923 | 0.700 | 0.511 | --- | 0.080 | ||||||
| Distance per minute (m/min) | 55.623 | 9.793 | 55.480 | 10.233 | 59.026 | 13.161 | 0.823 | 0.442 | --- | 0.015 | 54.703 | 6.193 | 53.262 | 4.341 | 47.645 | 17.960 | 0.840 | 0.450 | --- | 0.095 | ||||||
| Max Speed (km/h) | 24.144 | 4.192 | 23.975 | 2.836 | 24.458 | 4.514 | 0.111 | 0.895 | --- | 0.002 | 24.852 | 3.363 | 23.951 | 2.292 | 20.620 | 9.486 | 1.064 | 0.368 | --- | 0.117 | ||||||
| Average Speed (km/h) | 4.132 | 0.671 | 4.001 | 0.647 | 4.132 | 0.583 | 0.566 | 0.569 | --- | 0.010 | 3.961 | 0.301 | 3.901 | 0.180 | 4.397 | 0.748 | 2.271 | 0.136 | --- | 0.221 | ||||||
| Training Impulse per min | 2.268 | 0.713 | 2.116 | 0.619 | 2.477 | 1.002 | 1.675 | 0.192 | --- | 0.029 | 2.425 | 0.605 | 2.097 | 0.553 | 1.681 | 1.337 | 1.236 | 0.317 | --- | 0.134 | ||||||
| Distance in Speed Area 1 (m) | 24.971 | 6.067 | 22.804 | 4.288 | 24.653 | 6.104 | 2.090 | 0.129 | --- | 0.036 | 23.583 | 3.379 | 21.071 | 2.306 | 17.320 | 9.269 | 2.452 | 0.118 | --- | 0.235 | ||||||
| Distance in Speed Area 2 (m) | 24.251 | 5.970 | 25.473 | 6.561 | 26.714 | 6.101 | 1.126 | 0.328 | --- | 0.020 | 24.721 | 3.443 | 25.564 | 3.541 | 24.997 | 5.044 | 0.104 | 0.901 | --- | 0.013 | ||||||
| Distance in Speed Area 3 (m) | 4.646 | 1.923 | 5.375 | 1.913 | 5.571 | 2.701 | 2.070 | 0.131 | --- | 0.036 | 4.836 | 1.465 | 4.870 | 0.902 | 3.915 | 3.783 | 0.361 | 0.702 | --- | 0.043 | ||||||
| Distance in Speed Area 4 (m) | 1.480 | 0.908 | 1.621 | 0.746 | 1.800 | 1.127 | 0.911 | 0.405 | --- | 0.016 | 1.338 | 0.757 | 1.586 | 0.721 | 1.126 | 1.137 | 0.415 | 0.667 | --- | 0.049 | ||||||
| Distance in Speed Area 5 (m) | 0.260 | 0.202 | 0.197 | 0.172 | 0.266 | 0.195 | 1.617 | 0.203 | --- | 0.028 | 0.217 | 0.158 | 0.145 | 0.094 | 0.150 | 0.155 | 0.653 | 0.534 | --- | 0.075 | ||||||
| Number of Dec. 1 per min | 0.153 | 0.066 | 0.155 | 0.057 | 0.202 | 0.120 | 3.284 | 0.041 | FW - DF, MF | 0.056 | 0.161 | 0.052 | 0.129 | 0.035 | 0.124 | 0.144 | 0.625 | 0.548 | --- | 0.073 | ||||||
| Number of Dec. 2 per min | 0.479 | 0.170 | 0.537 | 0.156 | 0.649 | 0.302 | 5.224 | 0.007 | DF - FW | 0.086 | 0.496 | 0.168 | 0.466 | 0.088 | 0.410 | 0.425 | 0.213 | 0.810 | --- | 0.026 | ||||||
| Number of Dec. 3 per min | 0.008 | 0.005 | 0.009 | 0.004 | 0.011 | 0.007 | 1.545 | 0.218 | --- | 0.027 | 0.010 | 0.005 | 0.008 | 0.002 | 0.007 | 0.009 | 0.431 | 0.657 | --- | 0.051 | ||||||
| Number of Dec. 4 per min | 6.228 | 1.831 | 6.184 | 1.365 | 7.121 | 2.514 | 2.005 | 0.140 | --- | 0.035 | 6.138 | 1.017 | 5.999 | 0.787 | 4.471 | 3.276 | 1.579 | 0.237 | --- | 0.165 | ||||||
| Number of Acc. 1 per min | 3.400 | 1.045 | 3.304 | 0.817 | 3.955 | 1.553 | 2.573 | 0.081 | --- | 0.044 | 3.289 | 0.519 | 3.191 | 0.450 | 2.288 | 1.679 | 2.081 | 0.157 | --- | 0.206 | ||||||
| Number of Acc. 2 per min | 1.823 | 0.535 | 1.923 | 0.419 | 2.219 | 0.816 | 3.462 | 0.035 | DF - FW | 0.059 | 1.959 | 0.395 | 1.896 | 0.221 | 1.540 | 1.203 | 0.732 | 0.497 | --- | 0.084 | ||||||
| Number of Acc. 3 per min | 0.576 | 0.201 | 0.626 | 0.166 | 0.724 | 0.307 | 3.343 | 0.039 | DF - FW | 0.057 | 0.579 | 0.178 | 0.556 | 0.090 | 0.464 | 0.439 | 0.350 | 0.710 | --- | 0.042 | ||||||
| Number of Acc. 4 per min | 0.169 | 0.067 | 0.174 | 0.058 | 0.227 | 0.094 | 4.974 | 0.009 | FW - DF, MF | 0.082 | 0.143 | 0.062 | 0.131 | 0.047 | 0.126 | 0.118 | 0.095 | 0.910 | --- | 0.012 | ||||||
| MD-4 | MD-4 | F | p | SOD | Effect Size |
MD-3 | F | p | SOD | Effect Size |
||||||||||||||||
| DF | MF | FW | DF | MF | FW | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |||||||||||||||
| Min Heart Rate BPM | 66.523 | 17.287 | 64.165 | 7.491 | 78.528 | 14.559 | 1.269 | 0.308 | --- | 0.137 | 66.699 | 10.590 | 59.610 | 7.637 | 68.527 | 2.624 | 1.815 | 0.195 | --- | 0.185 | ||||||
| Mean Heart Rate BPM | 139.017 | 9.650 | 133.787 | 10.848 | 151.403 | 14.324 | 2.876 | 0.086 | --- | 0.264 | 133.502 | 6.288 | 130.729 | 8.672 | 144.394 | 11.018 | 3.148 | 0.070 | --- | 0.282 | ||||||
| Max Heart Rate BPM | 195.047 | 15.015 | 194.653 | 15.491 | 194.806 | 9.678 | 0.001 | 0.999 | --- | 0.000 | 194.124 | 14.197 | 192.228 | 8.905 | 199.481 | 3.581 | 0.461 | 0.639 | --- | 0.054 | ||||||
| Total Distance (m) | 4839.406 | 486.795 | 4707.888 | 571.107 | 4965.319 | 649.495 | 0.271 | 0.766 | --- | 0.033 | 4757.572 | 365.924 | 5010.200 | 243.073 | 5181.962 | 59.168 | 2.826 | 0.089 | --- | 0.261 | ||||||
| Distance per minute (m/min) | 60.140 | 6.927 | 57.404 | 7.697 | 63.931 | 10.248 | 0.809 | 0.463 | --- | 0.092 | 60.113 | 5.241 | 62.854 | 2.119 | 67.159 | 3.095 | 3.671 | 0.049 | DF - FW | 0.315 | ||||||
| Max Speed (km/h) | 25.603 | 2.464 | 24.161 | 2.140 | 26.912 | 1.406 | 1.907 | 0.181 | --- | 0.192 | 26.638 | 0.873 | 25.607 | 1.689 | 27.564 | 0.439 | 2.959 | 0.081 | --- | 0.270 | ||||||
| Average Speed (km/h) | 4.474 | 0.638 | 4.058 | 0.453 | 4.175 | 0.487 | 1.199 | 0.327 | --- | 0.130 | 4.344 | 0.368 | 4.468 | 0.257 | 4.286 | 0.209 | 0.521 | 0.604 | --- | 0.061 | ||||||
| Training Impulse per min | 2.591 | 0.692 | 2.323 | 0.593 | 2.994 | 1.207 | 0.932 | 0.414 | --- | 0.104 | 2.339 | 0.428 | 2.215 | 0.514 | 2.663 | 0.779 | 0.809 | 0.463 | --- | 0.092 | ||||||
| Distance in Speed Area 1 (m) | 24.384 | 4.943 | 22.209 | 2.749 | 26.283 | 2.631 | 1.395 | 0.276 | --- | 0.149 | 24.746 | 2.094 | 22.821 | 2.543 | 26.448 | 0.304 | 3.442 | 0.057 | --- | 0.301 | ||||||
| Distance in Speed Area 2 (m) | 27.490 | 4.895 | 27.114 | 5.129 | 28.910 | 5.547 | 0.137 | 0.873 | --- | 0.017 | 26.950 | 2.481 | 30.278 | 3.130 | 29.492 | 2.016 | 3.088 | 0.073 | --- | 0.278 | ||||||
| Distance in Speed Area 3 (m) | 5.722 | 1.534 | 5.803 | 1.251 | 6.557 | 1.254 | 0.425 | 0.661 | --- | 0.050 | 5.688 | 1.422 | 7.011 | 1.143 | 7.606 | 1.349 | 3.261 | 0.065 | --- | 0.290 | ||||||
| Distance in Speed Area 4 (m) | 2.198 | 0.861 | 2.097 | 0.546 | 1.964 | 1.397 | 0.090 | 0.914 | --- | 0.011 | 2.291 | 0.891 | 2.416 | 0.434 | 3.167 | 0.901 | 1.629 | 0.227 | --- | 0.169 | ||||||
| Distance in Speed Area 5 (m) | 0.281 | 0.138 | 0.184 | 0.120 | 0.260 | 0.117 | 1.213 | 0.323 | --- | 0.132 | 0.422 | 0.185 | 0.293 | 0.221 | 0.377 | 0.139 | 0.863 | 0.441 | --- | 0.097 | ||||||
| Number of Dec. 1 per min | 0.189 | 0.069 | 0.180 | 0.052 | 0.277 | 0.103 | 2.368 | 0.126 | --- | 0.228 | 0.183 | 0.041 | 0.187 | 0.052 | 0.249 | 0.102 | 1.624 | 0.228 | --- | 0.169 | ||||||
| Number of Dec. 2 per min | 0.588 | 0.160 | 0.661 | 0.131 | 0.891 | 0.276 | 3.561 | 0.053 | --- | 0.308 | 0.528 | 0.120 | 0.616 | 0.100 | 0.780 | 0.218 | 4.257 | 0.033 | DF - FW | 0.347 | ||||||
| Number of Dec. 3 per min | 0.011 | 0.005 | 0.011 | 0.003 | 0.016 | 0.006 | 2.048 | 0.161 | --- | 0.204 | 0.011 | 0.003 | 0.011 | 0.002 | 0.011 | 0.004 | 0.101 | 0.904 | --- | 0.013 | ||||||
| Number of Dec. 4 per min | 6.245 | 1.285 | 6.196 | 0.940 | 7.789 | 1.206 | 2.410 | 0.122 | --- | 0.232 | 6.030 | 0.851 | 5.922 | 0.445 | 6.839 | 0.755 | 2.032 | 0.164 | --- | 0.203 | ||||||
| Number of Acc. 1 per min | 3.313 | 0.748 | 3.280 | 0.615 | 4.225 | 0.683 | 2.329 | 0.129 | --- | 0.226 | 3.305 | 0.520 | 3.188 | 0.356 | 3.630 | 0.515 | 1.028 | 0.380 | --- | 0.114 | ||||||
| Number of Acc. 2 per min | 2.022 | 0.407 | 2.131 | 0.383 | 2.783 | 0.562 | 3.712 | 0.047 | DF-FW | 0.317 | 1.912 | 0.327 | 2.059 | 0.099 | 2.372 | 0.533 | 2.687 | 0.099 | --- | 0.251 | ||||||
| Number of Acc. 3 per min | 0.697 | 0.172 | 0.719 | 0.127 | 0.934 | 0.263 | 2.283 | 0.134 | --- | 0.222 | 0.617 | 0.142 | 0.674 | 0.094 | 0.813 | 0.183 | 2.457 | 0.117 | --- | 0.235 | ||||||
| Number of Acc. 4 per min | 0.179 | 0.056 | 0.202 | 0.052 | 0.293 | 0.132 | 3.005 | 0.078 | --- | 0.273 | 0.181 | 0.044 | 0.193 | 0.060 | 0.257 | 0.050 | 2.369 | 0.126 | --- | 0.228 | ||||||
| MD-2 | F | p | SOD | Effect Size |
MD-1 | F | p | SOD | Effect Size |
|||||||||||||||||
| DF | MF | FW | DF | MF | FW | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |||||||||||||||
| Min Heart Rate BPM | 66.865 | 12.105 | 64.466 | 6.263 | 71.628 | 5.988 | 0.658 | 0.531 | --- | 0.076 | 69.048 | 13.251 | 65.518 | 5.352 | 71.485 | 3.197 | 0.521 | 0.604 | ---- | 0.061 | ||||||
| Mean Heart Rate BPM | 134.670 | 7.257 | 131.710 | 8.889 | 146.640 | 10.946 | 3.390 | 0.059 | --- | 0.298 | 125.832 | 9.052 | 120.874 | 10.188 | 133.838 | 14.892 | 1.725 | 0.210 | ---- | 0.177 | ||||||
| Max Heart Rate BPM | 193.762 | 12.106 | 192.013 | 13.706 | 196.058 | 11.922 | 0.115 | 0.892 | --- | 0.014 | 185.628 | 14.234 | 180.195 | 15.849 | 181.489 | 20.715 | 0.244 | 0.786 | ---- | 0.030 | ||||||
| Total Distance (m) | 4233.559 | 252.431 | 4314.452 | 243.155 | 4358.289 | 229.962 | 0.366 | 0.699 | --- | 0.044 | 2839.141 | 242.073 | 2768.898 | 184.279 | 2676.041 | 732.284 | 0.284 | 0.756 | ---- | 0.034 | ||||||
| Distance per minute (m/min) | 65.308 | 4.573 | 66.762 | 3.916 | 71.028 | 7.268 | 1.590 | 0.234 | --- | 0.166 | 47.885 | 3.915 | 46.658 | 3.591 | 50.657 | 5.972 | 1.041 | 0.376 | ---- | 0.115 | ||||||
| Max Speed (km/h) | 26.165 | 1.159 | 25.603 | 1.389 | 26.412 | 0.230 | 0.683 | 0.519 | --- | 0.079 | 23.511 | 1.095 | 23.754 | 1.177 | 23.473 | 1.397 | 0.109 | 0.897 | ---- | 0.013 | ||||||
| Average Speed (km/h) | 4.283 | 0.323 | 4.299 | 0.260 | 4.509 | 0.444 | 0.606 | 0.558 | --- | 0.070 | 3.147 | 0.268 | 3.086 | 0.239 | 3.377 | 0.359 | 1.283 | 0.304 | ---- | 0.138 | ||||||
| Training Impulse per min | 2.527 | 0.405 | 2.414 | 0.597 | 2.739 | 0.839 | 0.370 | 0.697 | --- | 0.044 | 2.135 | 0.516 | 1.828 | 0.562 | 2.120 | 0.840 | 0.621 | 0.550 | ---- | 0.072 | ||||||
| Distance in Speed Area 1 (m) | 28.050 | 1.871 | 26.648 | 1.850 | 27.867 | 3.448 | 0.945 | 0.409 | --- | 0.106 | 28.625 | 2.174 | 26.481 | 1.492 | 27.631 | 2.507 | 2.403 | 0.122 | ---- | 0.231 | ||||||
| Distance in Speed Area 2 (m) | 29.181 | 2.970 | 30.994 | 3.418 | 32.292 | 4.337 | 1.123 | 0.350 | --- | 0.123 | 15.507 | 1.629 | 15.765 | 2.209 | 18.458 | 2.721 | 2.413 | 0.121 | ---- | 0.232 | ||||||
| Distance in Speed Area 3 (m) | 5.923 | 1.466 | 7.221 | 1.062 | 8.059 | 1.308 | 3.740 | 0.046 | DF - FW | 0.319 | 2.930 | 0.457 | 3.382 | 0.324 | 3.408 | 1.350 | 1.339 | 0.290 | ---- | 0.143 | ||||||
| Distance in Speed Area 4 (m) | 1.699 | 0.458 | 1.582 | 0.417 | 2.289 | 0.475 | 2.845 | 0.088 | --- | 0.262 | 0.672 | 0.268 | 0.922 | 0.419 | 1.091 | 0.688 | 1.402 | 0.275 | ---- | 0.149 | ||||||
| Distance in Speed Area 5 (m) | 0.465 | 0.191 | 0.328 | 0.242 | 0.556 | 0.082 | 1.637 | 0.226 | --- | 0.170 | 0.096 | 0.067 | 0.123 | 0.100 | 0.105 | 0.135 | 0.174 | 0.842 | ---- | 0.021 | ||||||
| Number of Dec. 1 per min | 0.183 | 0.063 | 0.185 | 0.039 | 0.275 | 0.108 | 2.691 | 0.098 | --- | 0.252 | 0.109 | 0.031 | 0.105 | 0.030 | 0.124 | 0.101 | 0.193 | 0.826 | ---- | 0.024 | ||||||
| Number of Dec. 2 per min | 0.548 | 0.104 | 0.616 | 0.068 | 0.770 | 0.262 | 3.485 | 0.055 | --- | 0.303 | 0.408 | 0.030 | 0.414 | 0.044 | 0.488 | 0.174 | 1.501 | 0.253 | ---- | 0.158 | ||||||
| Number of Dec. 3 per min | 0.010 | 0.002 | 0.011 | 0.003 | 0.010 | 0.002 | 0.609 | 0.556 | --- | 0.071 | 0.005 | 0.002 | 0.007 | 0.003 | 0.013 | 0.011 | 3.815 | 0.044 | DF - FW | 0.323 | ||||||
| Number of Dec. 4 per min | 7.113 | 0.335 | 7.025 | 0.588 | 7.398 | 1.356 | 0.354 | 0.707 | --- | 0.042 | 7.988 | 0.519 | 7.569 | 0.763 | 8.980 | 2.149 | 2.291 | 0.133 | ---- | 0.223 | ||||||
| Number of Acc. 1 per min | 3.838 | 0.301 | 3.716 | 0.425 | 4.183 | 1.159 | 0.830 | 0.454 | --- | 0.094 | 4.578 | 0.475 | 4.224 | 0.555 | 5.411 | 1.676 | 2.634 | 0.103 | ---- | 0.248 | ||||||
| Number of Acc. 2 per min | 2.105 | 0.156 | 2.217 | 0.191 | 2.349 | 0.489 | 1.233 | 0.318 | --- | 0.134 | 1.772 | 0.217 | 1.755 | 0.264 | 2.002 | 0.566 | 0.796 | 0.468 | ---- | 0.091 | ||||||
| Number of Acc. 3 per min | 0.704 | 0.116 | 0.763 | 0.079 | 0.871 | 0.218 | 2.115 | 0.153 | --- | 0.209 | 0.487 | 0.063 | 0.510 | 0.048 | 0.571 | 0.193 | 1.037 | 0.377 | ---- | 0.115 | ||||||
| Number of Acc. 4 per min | 0.191 | 0.058 | 0.187 | 0.030 | 0.254 | 0.095 | 1.763 | 0.203 | --- | 0.181 | 0.217 | 0.044 | 0.182 | 0.052 | 0.224 | 0.061 | 1.297 | 0.301 | ---- | 0.139 | ||||||
| MD+1 | MD+1 | F | p | SOD | Effect Size |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| DF | MF | FW | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Min Heart Rate BPM | 67.158 | 13.719 | 56.379 | 13.118 | 67.900 | 12.662 | 1.575 | 0.237 | ---- | 0.165 | ||||||||||||||||
| Mean Heart Rate BPM | 126.835 | 21.267 | 129.967 | 14.239 | 146.867 | 14.555 | 1.438 | 0.266 | ---- | 0.152 | ||||||||||||||||
| Max Heart Rate BPM | 176.404 | 35.129 | 193.444 | 22.481 | 198.100 | 15.044 | 1.014 | 0.385 | ---- | 0.112 | ||||||||||||||||
| Total Distance (m) | 3228.715 | 852.330 | 3557.923 | 1057.164 | 3626.967 | 1367.909 | 0.275 | 0.763 | ---- | 0.033 | ||||||||||||||||
| Distance per minute (m/min) | 45.590 | 12.485 | 45.942 | 13.485 | 53.733 | 15.932 | 0.448 | 0.647 | ---- | 0.053 | ||||||||||||||||
| Max Speed (km/h) | 18.097 | 6.347 | 20.773 | 4.485 | 21.768 | 3.921 | 0.748 | 0.489 | ---- | 0.085 | ||||||||||||||||
| Average Speed (km/h) | 4.584 | 0.794 | 4.197 | 1.008 | 4.051 | 0.707 | 0.569 | 0.577 | ---- | 0.066 | ||||||||||||||||
| Training Impulse per min | 1.594 | 1.091 | 1.823 | 0.792 | 2.665 | 1.238 | 1.278 | 0.306 | ---- | 0.138 | ||||||||||||||||
| Distance in Speed Area 1 (m) | 20.440 | 12.103 | 17.596 | 5.596 | 22.366 | 8.917 | 0.346 | 0.713 | ---- | 0.041 | ||||||||||||||||
| Distance in Speed Area 2 (m) | 21.656 | 6.514 | 23.122 | 6.741 | 26.135 | 7.567 | 0.483 | 0.626 | ---- | 0.057 | ||||||||||||||||
| Distance in Speed Area 3 (m) | 2.777 | 2.031 | 3.965 | 2.322 | 3.880 | 2.898 | 0.605 | 0.558 | ---- | 0.070 | ||||||||||||||||
| Distance in Speed Area 4 (m) | 0.682 | 0.507 | 1.122 | 0.743 | 1.164 | 0.898 | 1.043 | 0.375 | ---- | 0.115 | ||||||||||||||||
| Distance in Speed Area 5 (m) | 0.078 | 0.071 | 0.111 | 0.096 | 0.149 | 0.129 | 0.706 | 0.508 | ---- | 0.081 | ||||||||||||||||
| Number of Dec. 1 per min | 0.096 | 0.075 | 0.141 | 0.076 | 0.165 | 0.140 | 0.935 | 0.413 | ---- | 0.105 | ||||||||||||||||
| Number of Dec. 2 per min | 0.308 | 0.231 | 0.450 | 0.243 | 0.557 | 0.314 | 1.302 | 0.299 | ---- | 0.140 | ||||||||||||||||
| Number of Dec. 3 per min | 0.004 | 0.007 | 0.009 | 0.006 | 0.008 | 0.007 | 0.997 | 0.391 | ---- | 0.111 | ||||||||||||||||
| Number of Dec. 4 per min | 3.853 | 2.790 | 4.396 | 1.761 | 7.249 | 4.228 | 1.847 | 0.190 | ---- | 0.188 | ||||||||||||||||
| Number of Acc. 1 per min | 2.079 | 1.446 | 2.225 | 0.874 | 3.995 | 2.257 | 2.296 | 0.133 | ---- | 0.223 | ||||||||||||||||
| Number of Acc. 2 per min | 1.165 | 0.870 | 1.480 | 0.663 | 2.269 | 1.325 | 1.791 | 0.199 | ---- | 0.183 | ||||||||||||||||
| Number of Acc. 3 per min | 0.373 | 0.279 | 0.532 | 0.278 | 0.690 | 0.412 | 1.368 | 0.283 | ---- | 0.146 | ||||||||||||||||
| Number of Acc. 4 per min | 0.107 | 0.085 | 0.150 | 0.076 | 0.207 | 0.055 | 1.898 | 0.182 | ---- | 0.192 | ||||||||||||||||
Discussion
Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Availability of Data and Materials
Conflicts of interest/Competing interests
Ethics approval and consent to participate
References
- Akenhead, R., Harley, J. A., & Tweddle, S. P. (2016). Examining the External Training Load of an English Premier League Football Team With Special Reference to Acceleration. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 30(9), 2424–2432. [CrossRef]
- Akyildiz, Z., Yildiz, M., & Clemente, F. M. (2020). The reliability and accuracy of Polar Team Pro GPS units. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part P: Journal of Sports Engineering and Technology, 175433712097666. [CrossRef]
- Alexandre, D., da Silva, C. D., Hill-Haas, S., Wong, D. P., Natali, A. J., De Lima, J. R. P., Filho, M. G. B. B., Marins, J. J. C. B., Garcia, E. S., & Karim, C. (2012). Heart Rate Monitoring in Soccer. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 26(10), 2890–2906. [CrossRef]
- Anderson, L., Orme, P., Michele, R. Di, Close, G. L., Drust, B., Morton, J. P., Anderson, L., Orme, P., Michele, R. Di, Close, G. L., Drust, B., Morton, J. P., Di Michele, R., Close, G. L., Morgans, R., Drust, B., & Morton, J. P. (2016a). Quantification of training load during one-, two- and three-game week schedules in professional soccer players from the English Premier League: implications for carbohydrate periodisation. Journal of Sports Sciences, 34(13), 1250–1259. [CrossRef]
- Anderson, L., Orme, P., Michele, R. Di, Close, G. L., Drust, B., Morton, J. P., Anderson, L., Orme, P., Michele, R. Di, Close, G. L., Drust, B., Morton, J. P., Di Michele, R., Close, G. L., Morgans, R., Drust, B., & Morton, J. P. (2016b). Quantification of training load during one-, two- and three-game week schedules in professional soccer players from the English Premier League: implications for carbohydrate periodisation. Journal of Sports Sciences, 34(13), 1250–1259. [CrossRef]
- Calbet, J. A. L., Losa-Reyna, J., Torres-Peralta, R., Rasmussen, P., Ponce-González, J. G., Sheel, A. W., de la Calle-Herrero, J., Guadalupe-Grau, A., Morales-Alamo, D., Fuentes, T., Rodríguez-García, L., Siebenmann, C., Boushel, R., & Lundby, C. (2015). Limitations to oxygen transport and utilization during sprint exercise in humans: evidence for a functional reserve in muscle O2 diffusing capacity. The Journal of Physiology, 593(20), 4649–4664. [CrossRef]
- Clemente, F. M., Nikolaidis, P. T., Bezerra, J. P., & Chen, Y.-S. (2018). Heart rate variations between training days and types of exercise in men and women futsal and soccer players. Human Movement, 2018(5), 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Coyne, J. O. C., Gregory Haff, G., Coutts, A. J., Newton, R. U., & Nimphius, S. (2018). The Current State of Subjective Training Load Monitoring—a Practical Perspective and Call to Action. Sports Medicine - Open, 4(1), 58. [CrossRef]
- Edwards, S. (1993). High performance training and racing. In Feet Fleet Press (Ed.), The Heart Rate Monitor Book.
- Fullagar, H. H. K., McCall, A., Impellizzeri, F. M., Favero, T., & Coutts, A. J. (2019). The Translation of Sport Science Research to the Field: A Current Opinion and Overview on the Perceptions of Practitioners, Researchers and Coaches. Sports Medicine, 49(12), 1817–1824. [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, L., Camões, M., Lima, R., Bezerra, P., Nikolaidis, P. T., Rosemann, T., Knechtle, B., & Clemente, F. (2021). Characterization of external load in different types of exercise in professional soccer. Human Movement. [CrossRef]
- Halson, S. L. (2014). Monitoring Training Load to Understand Fatigue in Athletes. Sports Medicine, 44(S2), 139–147. [CrossRef]
- Huggins, R. A., Giersch, G. E. W., Belval, L. N., Benjamin, C. L., Curtis, R. M., Sekiguchi, Y., Peltonen, J., & Casa, D. J. (2020). The Validity and Reliability of Global Positioning System Units for Measuring Distance and Velocity During Linear and Team Sport Simulated Movements. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 34(11), 3070–3077. [CrossRef]
- Kairiukstiene, Z., Poderiene, K., Velicka, D., Trinkunas, E., & Poderys, J. (2021). Cardiovascular functional limitations for sprint-type tasks in health promotion sessions. Science & Sports, 36(6), 470–476. [CrossRef]
- Laursen, P., & Buchheit, M. (2019). Science and application of high-intensity interval training: solutions to the programming puzzle. Human Kinetics.
- Martín-García, A., Gómez Díaz, A., Bradley, P. S., Morera, F., & Casamichana, D. (2018). Quantification of a Professional Football Team’s External Load Using a Microcycle Structure. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 32(12), 3511–3518. [CrossRef]
- McGuigan, H., Hassmén, P., Rosic, N., & Stevens, C. J. (2020). Training monitoring methods used in the field by coaches and practitioners: A systematic review. International Journal of Sports Science & Coaching, 15(3), 439–451. [CrossRef]
- Nobari, H., Gonçalves, L. G., Aquino, R., Clemente, F. M., Rezaei, M., Carlos-Vivas, J., Pérez-Gómez, J., Pueo, B., & Ardigò, L. P. (2022). Wearable Inertial Measurement Unit to Measure External Load: A Full-Season Study in Professional Soccer Players. Applied Sciences, 12(3), 1140. [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, R., Brito, J. P., Moreno-Villanueva, A., Nalha, M., Rico-González, M., & Clemente, F. M. (2021). Reference values for external and internal training intensity monitoring in young male soccer players: A systematic review. Healthcare (Switzerland), 9(11), 1–16. [CrossRef]
- Owen, A. L., Djaoui, L., Newton, M., Malone, S., & Mendes, B. (2017). A contemporary multi-modal mechanical approach to training monitoring in elite professional soccer. Science and Medicine in Football, 1(3), 216–221. [CrossRef]
- Owen, A. L., Lago-Peñas, C., Gómez, M.-Á., Mendes, B., & Dellal, A. (2017). Analysis of a training mesocycle and positional quantification in elite European soccer players. International Journal of Sports Science & Coaching, 12(5), 665–676. [CrossRef]
- Praça, G., Diniz, L., Clemente, F., Glória Teles Bredt, S., Couto, B., Andrade, A., & Owen, A. (2021). The influence of playing position on the physical, technical, and network variables of sub-elite professional soccer athletes. Human Movement, 22(2), 22–31. [CrossRef]
- Swallow, W. E., Skidmore, N., Page, R. M., & Malone, J. J. (2021a). An examination of in-season external training load in semi-professional soccer players: considerations of one and two match weekly microcycles. International Journal of Sports Science & Coaching, 16(1), 192–199. [CrossRef]
- Swallow, W. E., Skidmore, N., Page, R. M., & Malone, J. J. (2021b). An examination of in-season external training load in semi-professional soccer players: considerations of one and two match weekly microcycles. International Journal of Sports Science & Coaching, 16(1), 192–199. [CrossRef]
- Tomczak, M., & Tomczak, E. (2014). The need to report effect size estimates revisited. An overview of some recommended measures of effect size. Trends in Sport Sciences, 1(21), 19–25. [CrossRef]
- Weston, M. (2018). Training load monitoring in elite English soccer: a comparison of practices and perceptions between coaches and practitioners. Science and Medicine in Football, 2(3), 216–224. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





