Submitted:
18 March 2024
Posted:
19 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials for Testing
2.2. Experimental Design
2.2.1. Screening Test for Optimal Concentration of Prohexadione-Calcium
2.2.2. Effect of Pro-Ca Primed on the Growth of Oilseed Rape Seedlings under Salt Stress
2.3. Measurement Items and Methods
2.3.1. Prohexadione-Calcium Concentration Screening Test
2.3.2. Effect of Pro-Ca Primed on the Growth of Oilseed Rape Seedlings under Salt Stress
Determination of Morphological Indicators
Measurement of Photosynthetic Pigments
Measurement of Photosynthetic Properties
Determination of Membrane Lipid Peroxidation Products
Determination of Antioxidant Enzymes
Determination of Ionic Content
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
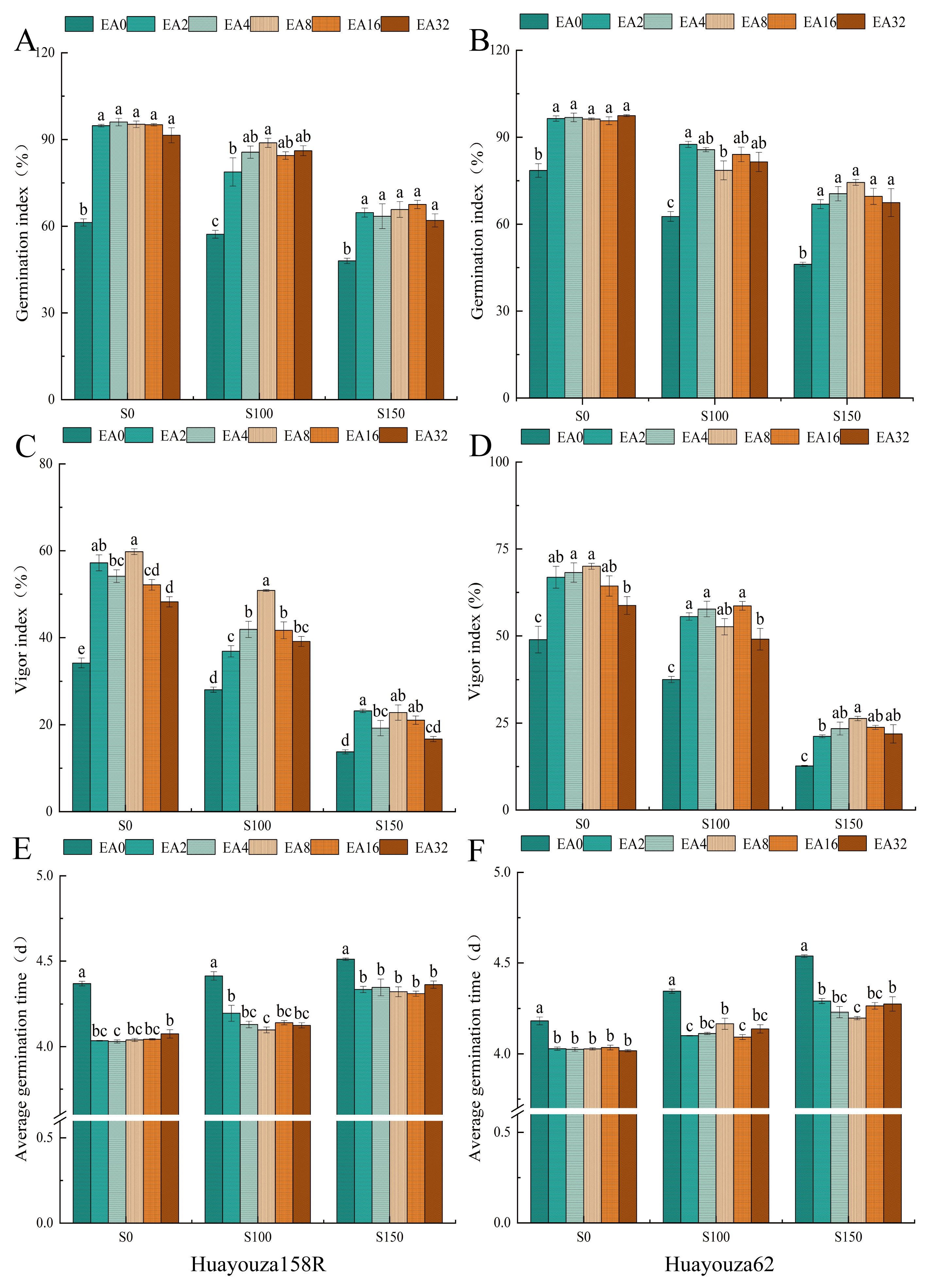
3.1. Effect of Pro-Ca Primed on Seed Germination under Salt Stress
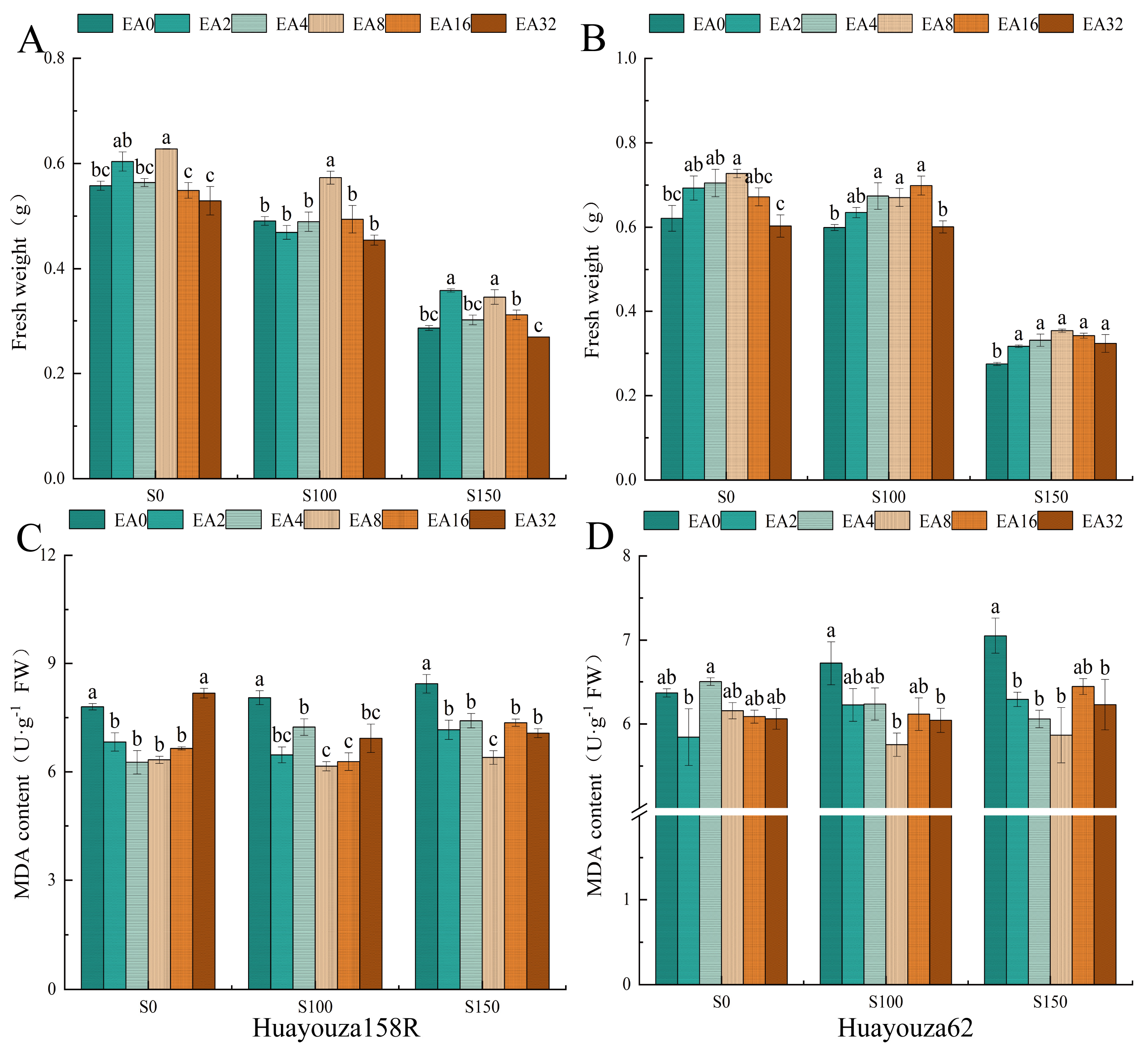
3.2. Effect of Pro-Ca Primed on Fresh Weight and Malondialdehyde of Young Shoots
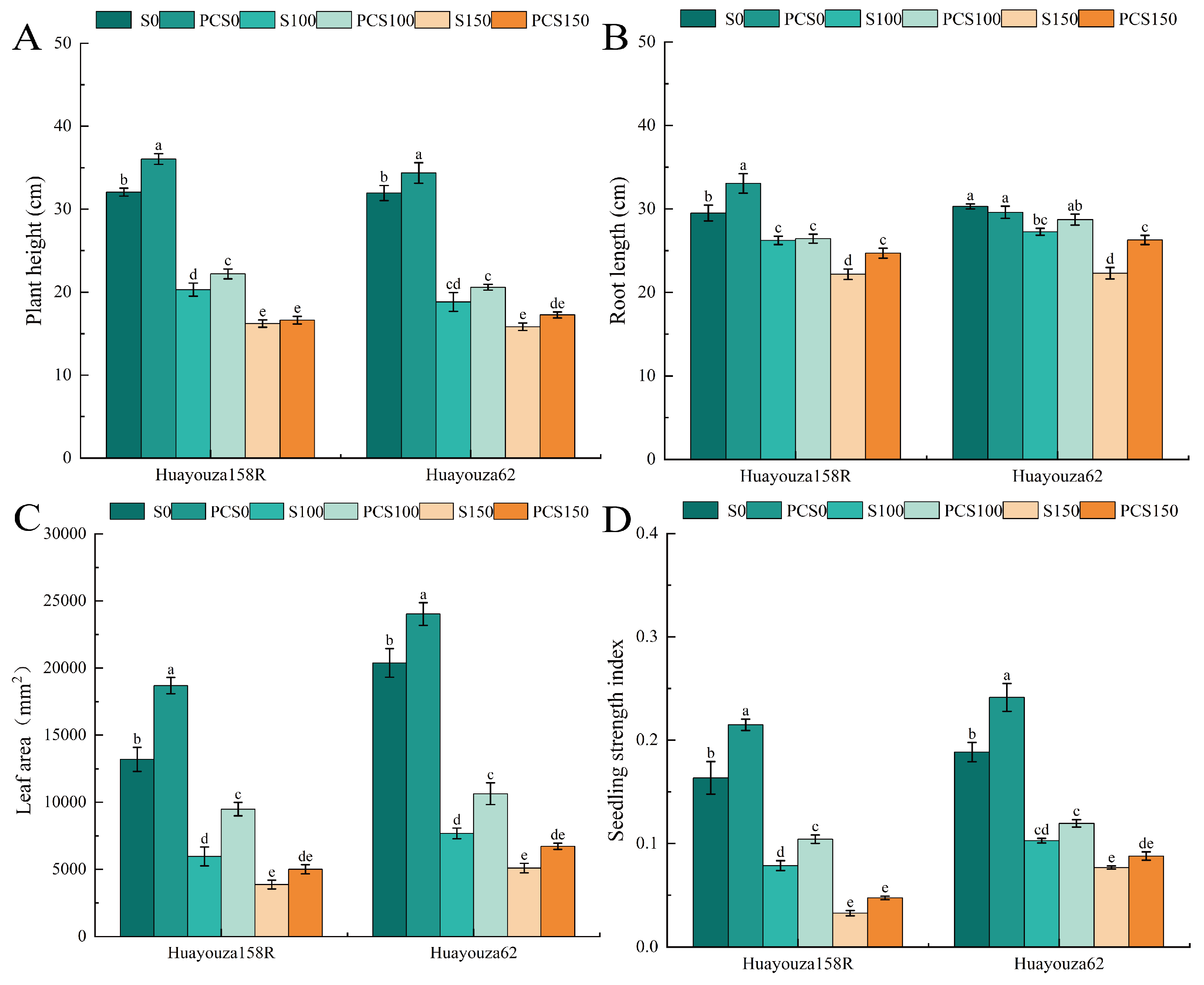
3.3. Effect of Pro-Ca Primed on the Morphology of Oilseed Rape under Salt Stress
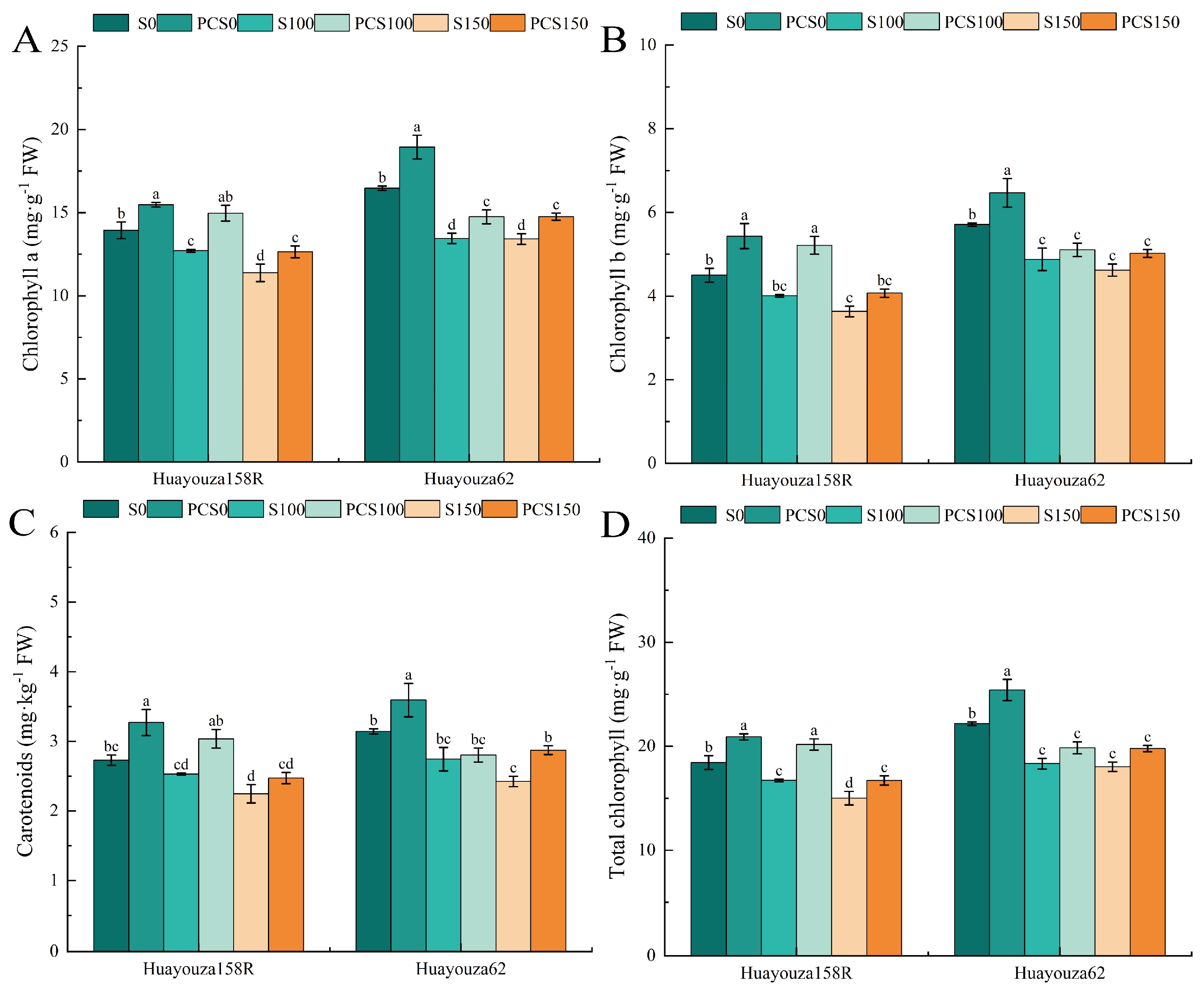
3.4. Effect of Pro-Ca Primed on Photosynthetic Pigments in Oilseed Rape under Salt Stress
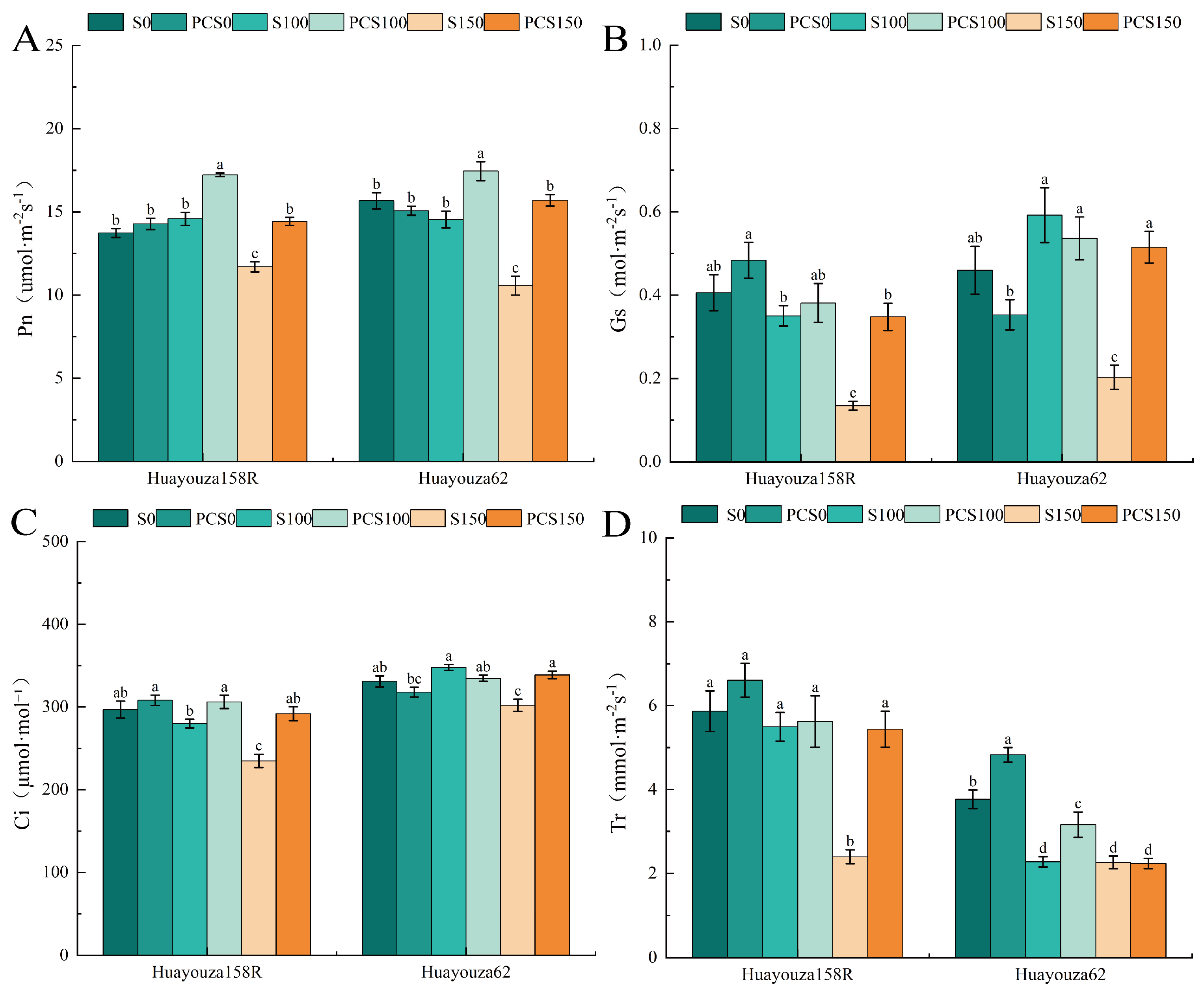
3.5. Effect of Pro-Ca Primed on Photosynthetic Properties of Oilseed Rape under Salt Stress
3.6. Effect of Pro-Ca Primed on Membrane Lipid Peroxidation in Oilseed Rape under Salt Stress
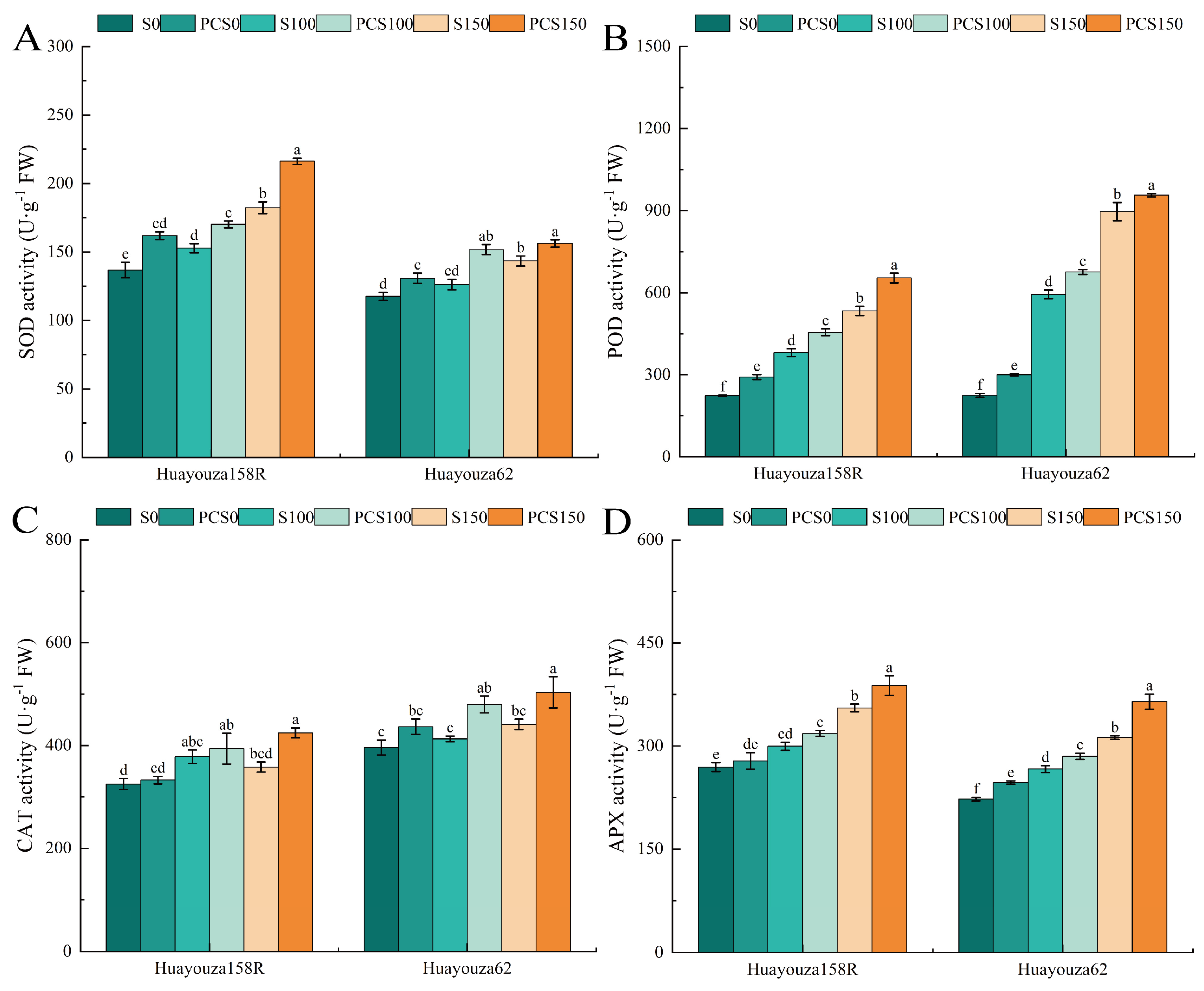
3.7. Effect of Pro-Ca Primed on Antioxidant Enzymes in Oilseed Rape under Salt Stress
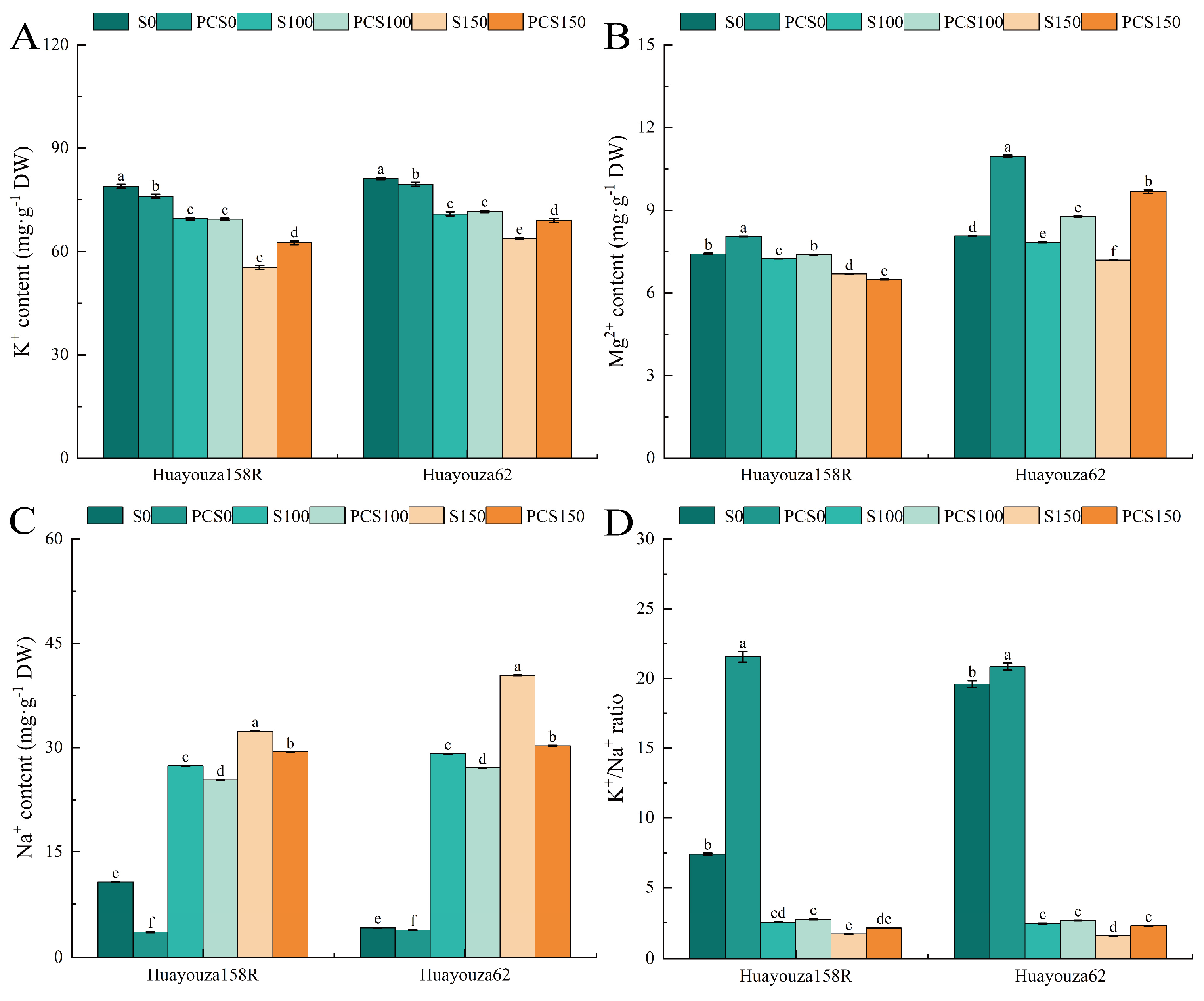
3.8. Effect of Pro-Ca Primed on Ion Content of Oilseed Rape under Salt Stress
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jat Baloch, M.Y.; Zhang, W.; Sultana, T.; Akram, M.; Shoumik, B.A.A.; Khan, M.Z.; Farooq, M.A. Utilization of sewage sludge to manage saline–alkali soil and increase crop production: Is it safe or not? Environ. Technol. Innov. 2023, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radha, B.; Sunitha, N.C.; Sah, R.P.; TP, M.A.; Krishna, G.K.; Umesh, D.K.; Thomas, S.; Anilkumar, C.; Upadhyay, S.; Kumar, A.; et al. Physiological and molecular implications of multiple abiotic stresses on yield and quality of rice. Frontiers in Plant Science 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaji; Hazem, M. Emerging technologies and management of crop stress tolerance || The use of chlorophyll fluorescence kinetics analysis to study the performance of photosynthetic machinery in plants; Elsevier Inc.: 2014; pp. 347–384.
- Kim, J.B.; So, J.M.; Bae, D.H. Global warming impacts on severe drought characteristics in Asia monsoon region. Water 2020, 12, 1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Chang, L.; Li, G.; Li, Y. Advances and future research in ecological stoichiometry under saline-alkali stress. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2022, 30, 5475–5486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etesami, H.; Fatemi, H.; Rizwan, M. Interactions of nanoparticles and salinity stress at physiological, biochemical and molecular levels in plants: A review. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety 2021, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoque, M.N.; Imran, S.; Hannan, A.; Paul, N.C.; Mahamud, M.A.; Chakrobortty, J.; Sarker, P.; Irin, I.J.; Brestic, M.; Rhaman, M.S. Organic amendments for mitigation of salinity stress in plants: A review. Life 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Xian, M.; Li, J. Current situation and development trends of rapeseed variety improvement in China. Journal of China Agricultural University 2024, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Wang, H. Security strategy for the nation’s edible vegetable oil supplies under the new circumstances. Chinese Journal of Oil Crop Sciences 2024, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Sun, W.; Fang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Cui, X.; Mu, C.; Bai, J.; An, L.; Luo, X.; Wan, H.; et al. Effects of different winter rape mulchings on soil physical and chemical properties and microorganisms. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas 2023, 41, 128–139. [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama, I.; Miyazawa, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Kamiya, Y.; Abe, H.; Sakurai, A. Effects of a new plant growth regulator Prohexadione Calcium (BX-112) on shoot elongation caused by exogenously applied gibberellins in rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings. Plant and Cell Physiology 1990, 31, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Yin, Y.; Shen, F.; Luo, B.; Tang, X.; He, H.; Chen, D. Effects of Prohexadione Calcium on physiological index of tobacco seedlings during cold stress. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences 2016, 29, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Fan, T.; Wang, C.; Wan, G.; Jiang, T.; Zhang, J.; Wang, T.; Chen, K. Effect of Prohexadione Calcium on senescence, yield and quality of summer-planting peanut. Journal of Peanut Science 2008, 37, 32–36. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, N.; Yu, M.; Li, Y.; Jin, D.; Zheng, D. Prohexadione-calcium alleviates saline-alkali stress in soybean seedlings by improving the photosynthesis and up-regulating antioxidant defense. Ecotoxicology Environmental Safety 2021, 220, 112369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, E.A. Seed priming to alleviate salinity stress in germinating seeds. Journal of Plant Physiology 2016, 192, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasiou, E.; Lorentz, K.O.; Stein, G.J.; Mitchell, P.D. Prehistoric schistosomiasis parasite found in the Middle East. The Lancet Infectious Diseases 2014, 14, 553–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, W.; Wang, L.; Sun, Y. Exogenous melatonin improves seedling health index and drought tolerance in tomato. Plant Growth Regulation 2015, 77, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnon, D.I. Copper enzyme in isolated chloroplasts. polyphenoloxidase in beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol 1949, 24, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Hu, Y.; Du, X.; Tang, H.; Shen, C.; Wu, J. Salicylic acid alleviates the adverse effects of salt stress in Torreya grandis cv. merrillii seedlings by activating photosynthesis and enhancing antioxidant systems. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 0109492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannopolitis, C.N.; Ries, S.K. Superoxide dismutases: I. occurrence in higher plants 1 2. Plant Physiol. 1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Pei, Y.; Wang, H.; Jin, Z.; Liu, Z.; Qiao, Z.; Fang, H.; Zhang, Y. Hydrogen sulfide alleviates cadmium-induced cell death through restraining ROS accumulation in roots of Brassica rapa L. ssp. pekinensis. Oxidative Medicine Cellular Longevity 2015, 2015, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.Y.; Liu, J.Y.; Li, H.; Hu, W.J.; Shen, Z.J.; Qiao, F.; Zhu, C.Q.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Zheng, H.L. Proteomic analysis reveals the protective role of exogenous hydrogen sulfide against salt stress in rice seedlings. Nitric Oxide 2021, 111–112, 14–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abass, A.M.; Nasser, A.M.; Leonard, W.; Alamri, S.A.; Pravej, A.; Muhammad, A.; Parvaiz, A.; Yuan, H. Potential of exogenously sourced kinetin in protecting Solanum lycopersicum from NaCl-induced oxidative stress through up-regulation of the antioxidant system, ascorbate-glutathione cycle and glyoxalase system. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, B.; Huang, B. Mechanism of salinity tolerance in plants: Physiological, biochemical, and molecular characterization. International Journal of Genomics 2014, 2014, 701596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.P.S.; Adhikari, R.; Paudel, P.; Shah, B.; Pokhrel, S.; Puri, S.; Adhikari, R.; Bhujel, S. Effect of different chemical priming agents on physiological and morphological characteristics of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Heliyon 2023, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, S.; Chen, X.; Zhang, R.; Xing, Y.; Jiang, B.; Li, B.; Xu, X.; Zhou, Y. The efficacy of different seed priming agents for promoting sorghum germination under salt stress. PLoS ONE 2021, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monjezi, N.; Yaghoubian, I.; Smith, D.L. Cell-free supernatant of Devosia sp. (strain SL43) mitigates the adverse effects of salt stress on soybean (Glycine max L.) seed vigor index. Frontiers in Plant Science 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A. Plant abiotic stress challenges from the changing environment. Frontiers in Plant Science 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahimova, U.; Zivcak, M.; Gasparovic, K.; Rastogi, A.; Allakhverdiev, S.I.; Yang, X.; Brestic, M. Electron and proton transport in wheat exposed to salt stress: Is the increase of the thylakoid membrane proton conductivity responsible for decreasing the photosynthetic activity in sensitive genotypes? Photosynth. Res. 2021, 150, 195–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezer, İ.; Kiremit, M.S.; Öztürk, E.; Subrata, B.A.G.; Osman, H.M.; Akay, H.; Arslan, H. Role of melatonin in improving leaf mineral content and growth of sweet corn seedlings under different soil salinity levels. Scientia Horticulturae 2021, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.N.; Li, Y.; Fu, C.; Hu, J.; Chen, L.; Yan, J.; Khan, Z.; Wu, H.; Li, Z. CeO2 nanoparticles seed priming increases salicylic acid level and ROS scavenging ability to improve rapeseed salt tolerance. Global Challenges 2022, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Min, W.; Hou, Z. Comparative effects of salt and alkali stress on antioxidant system in cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum L.) leaves. Open Chemistry 2019, 17, 1352–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Jia, J.; Lian, Z.; Hu, Y.; Guo, J.; Huo, H.; Zhu, Y.; Gong, H. Silicon enhances the salt tolerance of cucumber through increasing polyamine accumulation and decreasing oxidative damage. Ecotoxicology environmental safety 2019, 169, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, F.; Liu, W.; Cao, H.; Song, L.; Ji, S.; Tong, L.; Ding, R. Stomatal conductance of tomato leaves is regulated by both abscisic acid and leaf water potential under combined water and salt stress. Physiologia Plantarum 2021, 172, 2070–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Li, G.; Yang, J.; Huang, X.; Hou, H. Effect of salt stress on growth, physiological parameters, and ionic concentration of water dropwort (Oenanthe javanica) cultivars. Frontiers in Plant Science 2021, 12, 660409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadelha, C.G.; Cotta Coutinho, I.A.; Kennedy, D.P.P.; Sergimar; Miguel, E.D.C.; De Carvalho, H.H.; Lopes, L.D.S.; Gomes-Filho, E. Sodium uptake and transport regulation, and photosynthetic efficiency maintenance as the basis of differential salt tolerance in rice cultivars. Environmental experimental botany 2021, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Tan, L.; Liu, F.; Cai, H.; Sun, C. Identification of quantitative trait loci associated with salt tolerance at seedling stage from Oryza rufipogon. Journal of Genetics and Genomics 2011, 38, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.-H. Toxcity of heavy metal ions to plants and their toxicological mechanism. Journal of Longyan Teachers Colleg 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Cao, F.; You, Q.; Qi, W. Effects of salt stress on concentrations of Na+,K+ and Na+/K+ in the leaves of four tree species and evaluation of salt tolerance. Journal of Plant Resources and Environment 2001, 10, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moynier, F.; Fujii, T. Theoretical isotopic fractionation of magnesium between chlorophylls. Scientific Reports 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, N.; Koussevitzky, S.; Mittler, R.O.N.; Miller, G.A.D. ROS and redox signalling in the response of plants to abiotic stress. Plant Cell Environ. 2011, 35, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, J.A.; Ferrer, M.A.; Jiménez, A.; Barceló, A.R.; Sevilla, F. Antioxidant systems and O2-/H2O2 production in the apoplast of pea leaves. Its relation with salt-induced necrotic lesions in minor veins. American Society of Plant Biologists 2001, 127, 817–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuamnakthong, S.; Nampei, M.; Ueda, A. Characterization of Na+ exclusion mechanism in rice under saline-alkaline stress conditions. Plant Science 2019, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




