1. Introduction
The determination of physicochemical properties of polymers adsorbed on oxides play an important role in various industrial applications and chemical processes, including
specific composites such as plastics, paper, and rubber [
1]. The surface modification of polymers by adsorption on metallic oxides is crucial in several industrial processes and products [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7,
8,
9,
10]. Indeed, the adsorption of polymer on solid surfaces, in a solvent, is very useful for the dispersion or aggregation of concentrated suspensions or slurries. The adsorption process can contribute to the strength of the polymer segment contacts in the areas of adhesives, coatings and polymer composites. For example, the physicochemical and mechanical properties of polymer composites are not only affected by the adhesion strength between polymer and reinforced filler but also by the variations of the temperature.
The behavior of polymer composites strongly depends on the values of the transition temperatures and more particularly on their glass transitions. Polymers have different types of behavior, around the glass temperature (
Tg) depending on the temperature in the glass and liquid states. Most physical properties, including, for example, the enthalpy, rheological, and other surface properties change with temperature and time until reaching equilibrium, if polymers are heated below
Tg [
8,
9,
10,
11,
12]. This is directly related to the physical aging or structure relaxation of polymers or devices made of glassy polymers [
13,
14].
The determination of the physicochemical properties of polymers adsorbed on oxides is required to prevent their behaviors in the contact with other solids, liquids or gas. The composites polymer/metallic oxides are very used for the coatings of paintings or industrial packing. Polymer composites or nanocomposites, such as acrylate polymers or poly methyl methacrylate (PMMA) adsorbed on oxides can be used in many applications such as, artificial muscles, urban furniture, aeronautics, and microelectronics due to their high mechanical properties and high capacitance density [
8,
15,
16,
17,
18,
19,
20,
21].
Many studies were interested in the determination of the physicochemical properties [
22,
23,
24,
25,
26,
27,
28,
29,
30,
31,
32,
33,
34,
35,
36,
37,
38,
39,
40,
41,
42,
43,
44,
45,
46] and the glass transition temperatures [
47,
48,
49,
50,
51,
52,
53,
54,
55,
56,
57,
58] by inverse gas chromatography (IGC) at infinite dilution. This technique was applied to quantify the interactions between polymers, composites or oxides and organic molecules under the of infinite dilution conditions [
22,
23,
24,
25,
26,
27,
28,
29,
30,
31,
32,
33,
34,
35,
36,
37,
38,
39,
40,
41,
42,
43,
44,
45,
46,
47,
48,
49,
50,
51,
52,
53,
54,
55,
56,
57,
58]. The Lewis acid–base properties of insulating thermoplastic and thermosetting polymer materials [
13,
14,
47,
48,
49,
50,
51,
52,
53,
54,
55,
56,
57,
58], and the solubility parameters in appropriate solvents were also determined by IGC technique. Papirer et al. [
59] have studied the effect of surface acid–base characteristics of PMMA adsorbed on alumina, whereas, Hamieh et al. [
55,
56,
57,
58] have highlighted the presence of three transition temperatures of PMMA in the bulk phase and when adsorbed on silica and alumina.
However, the effect of the temperature change on the polar interactions and the Lewis acid-base properties near the transition temperatures of PMMA adsorbed on silica has never yet studied in literature.
We proposed in this paper to use IGC technique at infinite dilution to study the impact of the variation of the temperature on the London dispersive and polar free interaction energy, and Lewis’s acid-base parameters of PMMA/silica system for different recovery fractions of PMMA adsorbed on silica by applying our new methodology. Indeed, this recent method used the London dispersion equation [
44,
45] and proposed a new thermodynamic parameter
using the deformation polarizability
of the probe and the ionization energies of the solid
and the solvent
following this relation:
By using the parameter , it was possible to obtain accurate values of the free interaction energy between the solid surfaces and the adsorbed organic molecules. The separation between the dispersive and polar interaction energies of PMMA adsorbed on silica at various recovery fractions allowed us to obtain the polar enthalpy and entropy of adsorption and the surface acid-base parameters of the composite PMMA/silica, such as the enthalpic and entropic Lewis’s acid-base constants of the solid substrates.
2. Chromatographic Methods and Materials
The net retention time
and volume
of n-alkanes and polar molecules adsorbed on PMMA/silica surfaces were experimentally obtained by using the inverse gas chromatography (IGC) at infinite dilution [
22,
23,
24,
25,
26,
27,
28,
29,
30,
31,
32,
33,
34,
35,
36,
37,
38,
39,
40,
41,
42,
43,
44,
45,
46,
47,
48,
49,
50,
51,
52,
53,
54,
55,
56,
57,
58,
59]. This led to the free energy of adsorption
of adsorbed solvents on the solid surface (Equation 1):
Where T is the absolute temperature of the chromatographic column containing the solid material, R the perfect gas constant, and a constant depending on the temperature and reference characteristics referred to the two-dimensional state of adsorbed film.
is equal to the sum of the London dispersion component
and the polar component
of the free energy adsorption (Equation 2)
The London dispersion free energy can be expressed as:
Where and
is the Avogadro’s number,
the permittivity of vacuum,
S denoting the solid particle and
X the solvent molecule separated by a distance
, and
and
are the respective ionization energies of the solid and the solvent
. The new chromatographic chosen parameter of interaction between the solid and the solvent is given by
In the case of n-alkanes
adsorbed on the solid material,
can be given by:
The straight-line of n-alkanes representing the variations of
against
allowed us to determine the polar free energy
of polar solvents adsorbed on PMMA/silica composites as a function of the temperature by using the following equation:
The polar enthalpy
and entropy
of organic molecules were then determined from the variations of
using the following thermodynamic relations:
The values of
and
of adsorbed polar solvents were obtained as a function of the temperature and allowed us to quantify the Lewis’s enthalpic acid base constants
and
, and entropic acid base parameters
and
with respect of the temperature:
Where
AN and
DN are respectively the Gutmann electron donor and acceptor numbers of the polar solvents [
60]. The used values were those corrected by Riddle and Fowkes [
61].
The model organic molecules used as probes to quantify their interactions with the composites PMMA/silica were the following:
- -
the n-alkanes such as n-pentane, n-hexane, n-heptane, n-octane, and n-nonane
- -
-
the polar molecules, divided into three groups:
- ⮚
Lewis’s acid solvents such as dichloromethane, chloroform, and carbon tetrachloride
- ⮚
Basic solvent such as ethyl acetate, diethyl ether, tetrahydrofuran
- ⮚
Amphoteric such as toluene
PMMA and silica solid particles with different recovery fractions of adsorbed polymer used in this work were the same solid materials previously characterized in other studies by using other models and chromatographic methods [
39,
55,
62]. The previous experimental data of
of the various probes adsorbed on PMMA/silica composites obtained from IGC technique at infinite dilution was used to study the effect of the temperature on the various thermodynamic and physicochemical parameters of the adsorption of PMMA on silica at different recovery fractions.
4. Conclusions
A new methodology was proposed to study the physicochemical properties of the composites constituted by the adsorption of PMMA on silica particles with various coverage rates between (case of silica) and corresponding to a monolayer. The inverse gas chromatography at infinite dilution was used by applying the London dispersion interaction energy to separate the polar and dispersive energy of adsorbed solvents on the different solid surfaces. A new intrinsic thermodynamic parameter including the deformation polarizability of solvents and the harmonic mean of the ionization energies of solid surface and organic molecules. The determination of the polar interaction energy as a function of the temperature relative to the various composites PMMA/silica let to the values of the polar enthalpy and entropy. It was showed that all polar surface variables depended on the temperature and the coverage rates of PMMA adsorbed on silica particles.
The Lewis enthalpic and entropic acid-base parameters were determined for the various solid surfaces. All acid-base parameters of PMMA and PMMA/silica were found strongly dependent on the temperature. Only those of silica particles did not depend on the temperature. Silica exhibited higher acidic surface (twice more acidic than basic), whereas, the acid-base parameters of PMMA in bulk phase showed higher basic character varying as a function of the temperature (8 times more basic than acid in general). The acidity of the composites PMMA/silica slightly varied versus the temperature relatively to the highest values of Lewis basic parameters. However, the basicity of PMMA/silica increased with the recovery fraction to reach a maximum for a monolayer of adsorption. It seemed that the acidity of PMMA/silica for a monolayer reached the highest value.
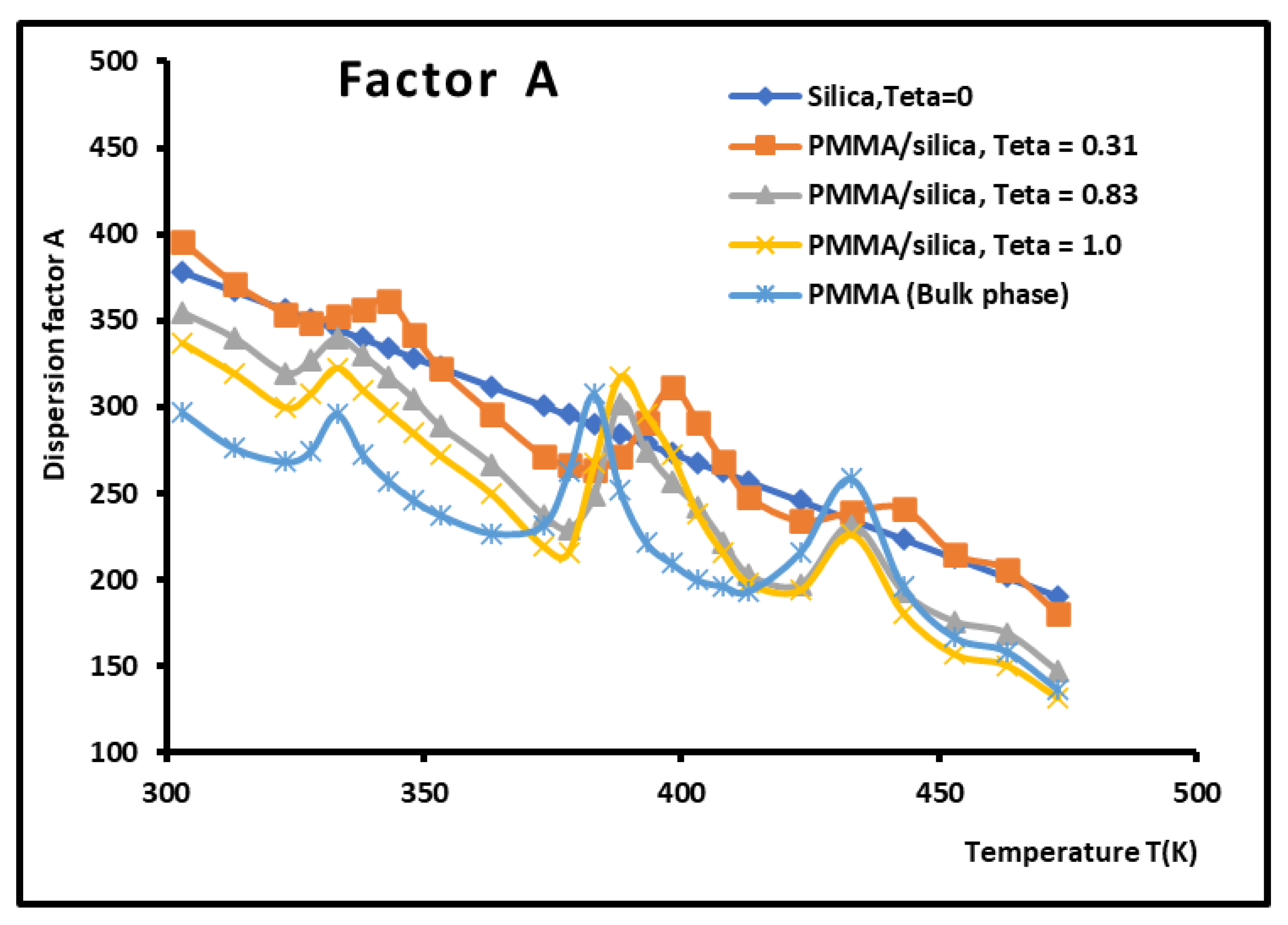
The variations of the different thermodynamic and physicochemical parameters showed secondary minima and maxima highlighting the presence of several transition temperature for PMMA in bulk phase and for the systems PMMA/silica with different recovery fractions with a shift of such temperatures in the case of a recovery fraction equal to 31%
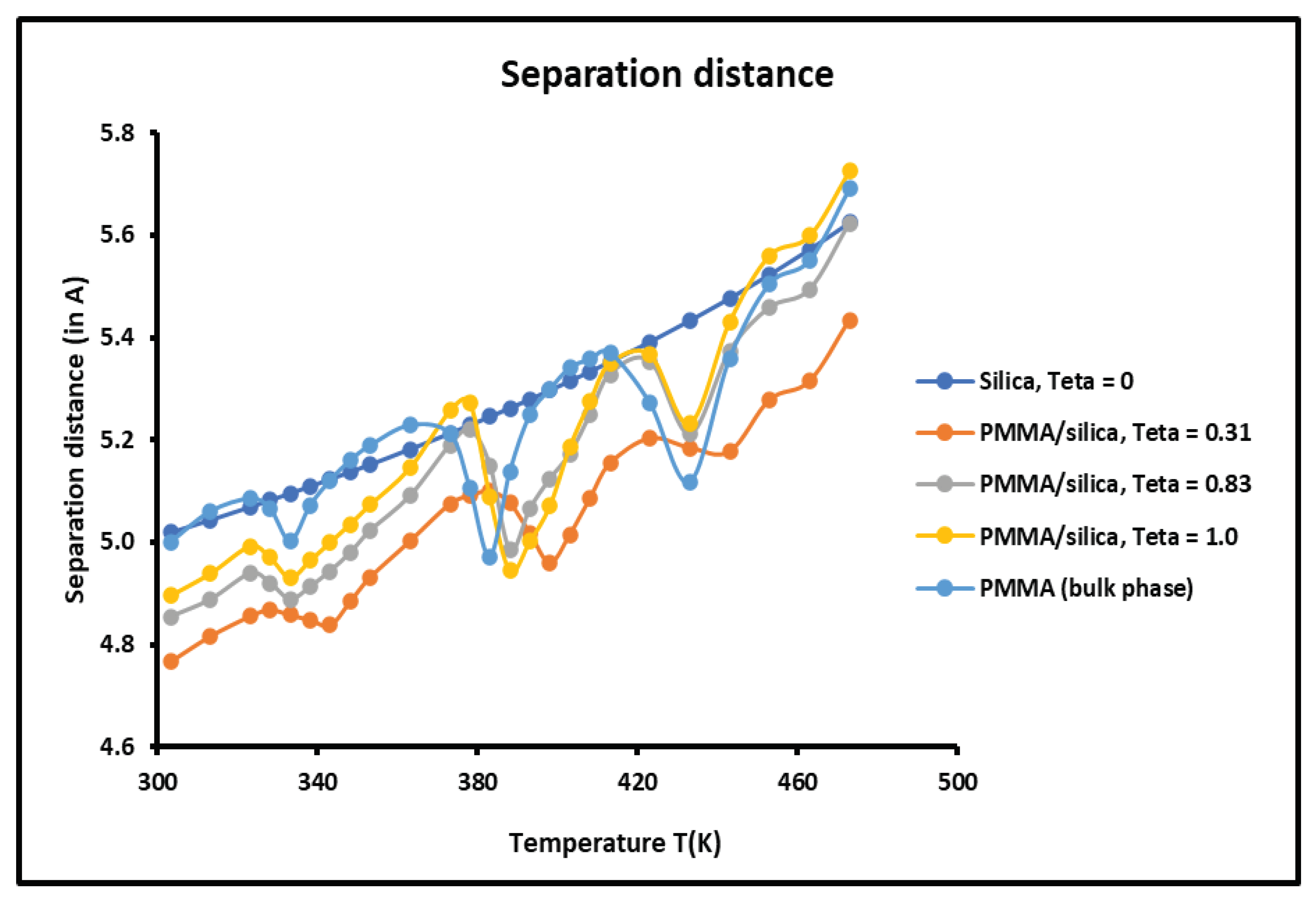
This new study also determined the average separation distance between the organic solvents and the various solid surfaces. It was showed that the separation distance is comprised between 4 and . It was observed a slight variation of the intermolecular distance as a function of the temperature and the recovery fraction of PMMA on silica particles.
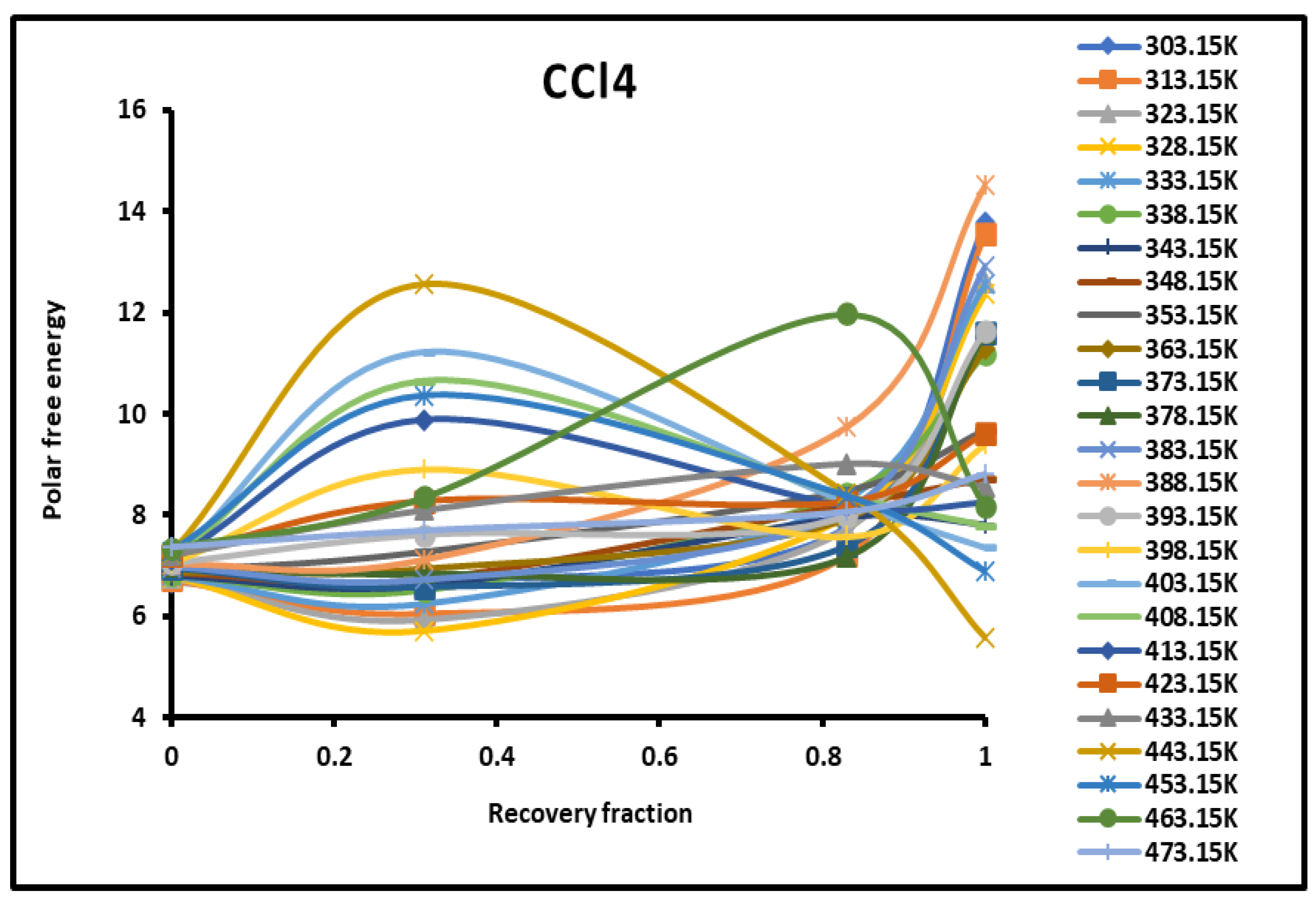
Figure 1.
Evolution of the polar free interaction energy ( (kJ/mol) of CCl4 as a function of the recovery fraction of PMMA adsorbed on silica at different temperatures.
Figure 1.
Evolution of the polar free interaction energy ( (kJ/mol) of CCl4 as a function of the recovery fraction of PMMA adsorbed on silica at different temperatures.
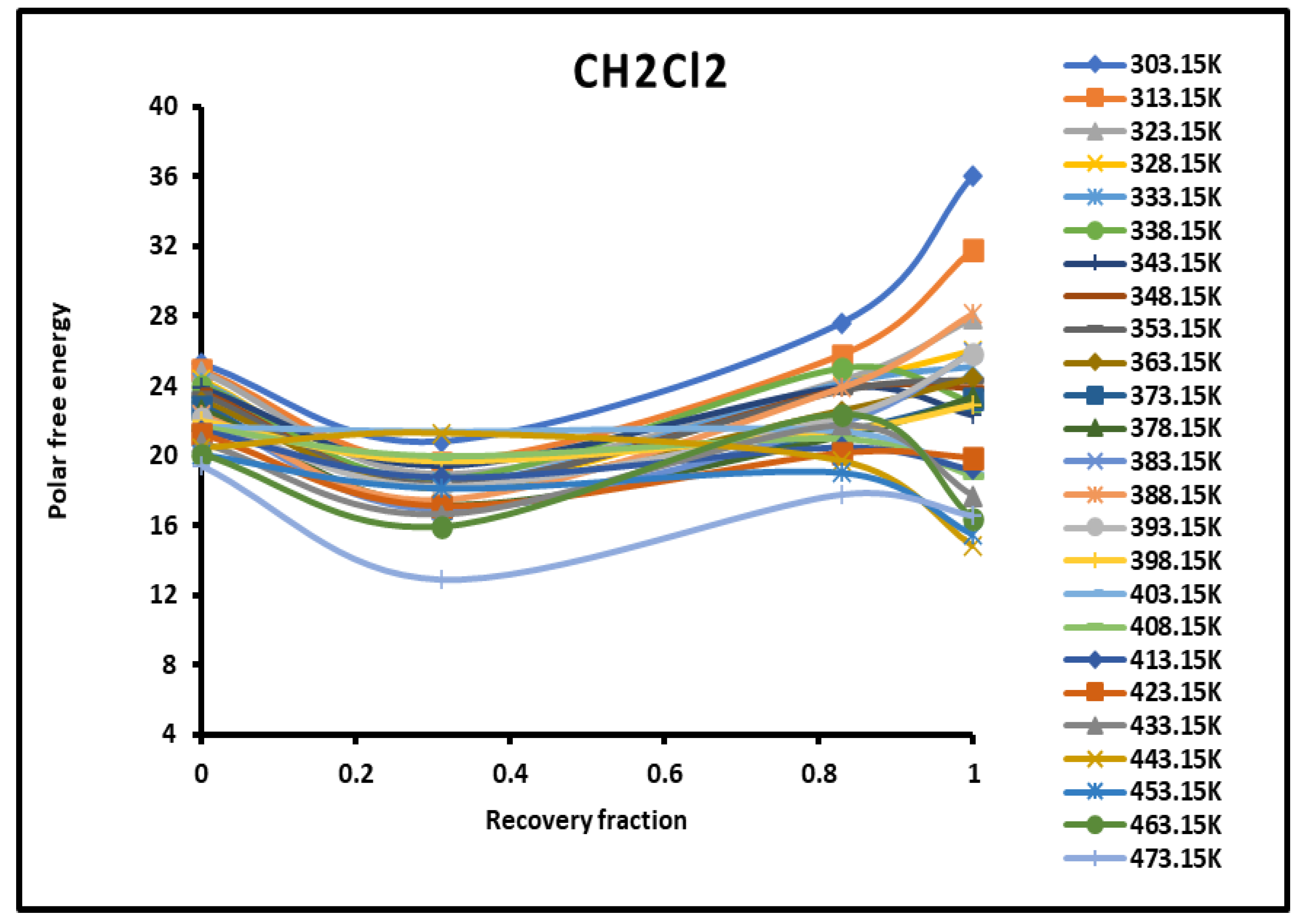
Figure 2.
Evolution of the polar free interaction energy ( (kJ/mol) of CH2Cl2 as a function of the recovery fraction of PMMA adsorbed on silica at different temperatures.
Figure 2.
Evolution of the polar free interaction energy ( (kJ/mol) of CH2Cl2 as a function of the recovery fraction of PMMA adsorbed on silica at different temperatures.
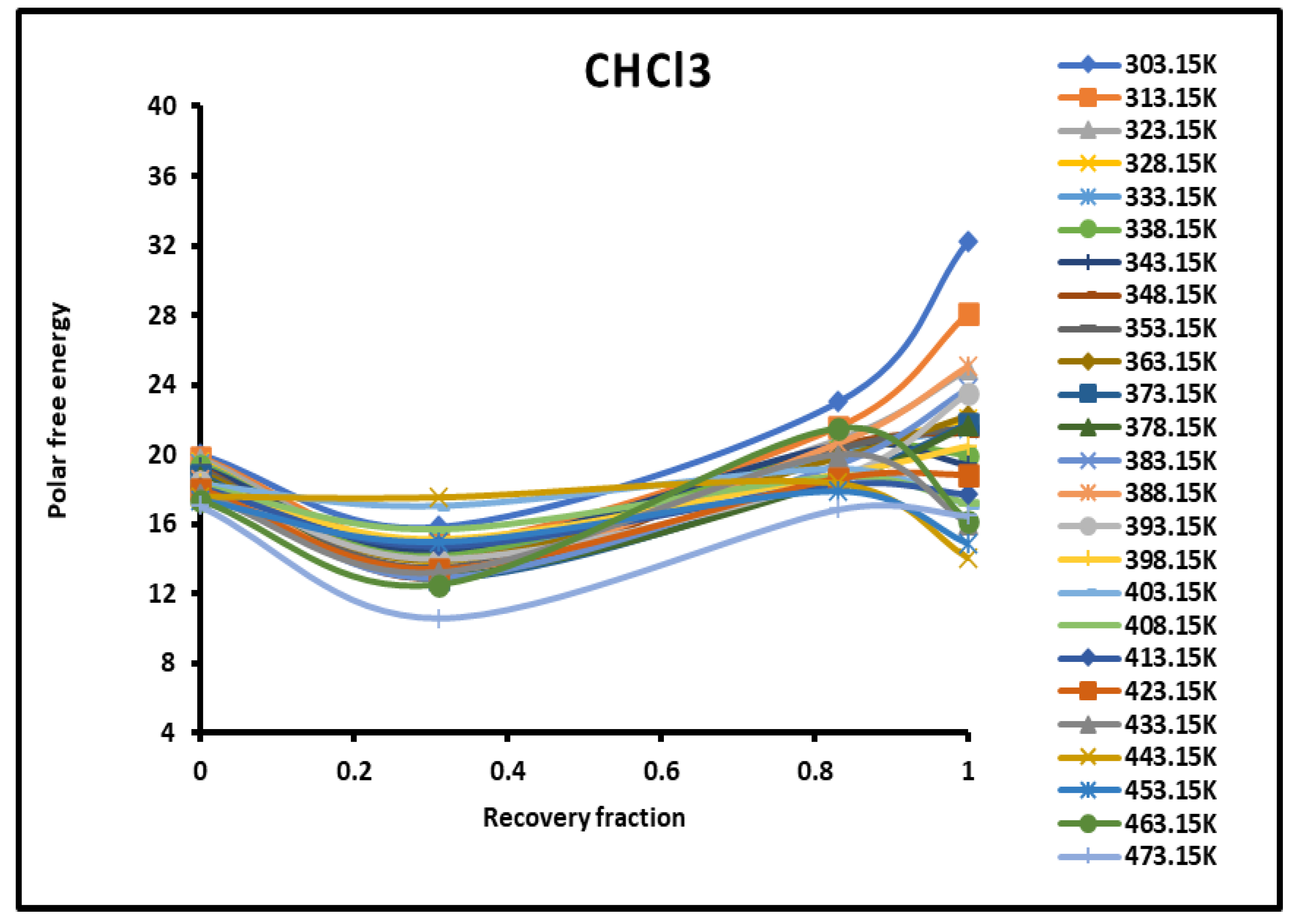
Figure 3.
Evolution of the polar free interaction energy ( (kJ/mol) of CHCl3 as a function of the recovery fraction of PMMA adsorbed on silica at different temperatures.
Figure 3.
Evolution of the polar free interaction energy ( (kJ/mol) of CHCl3 as a function of the recovery fraction of PMMA adsorbed on silica at different temperatures.
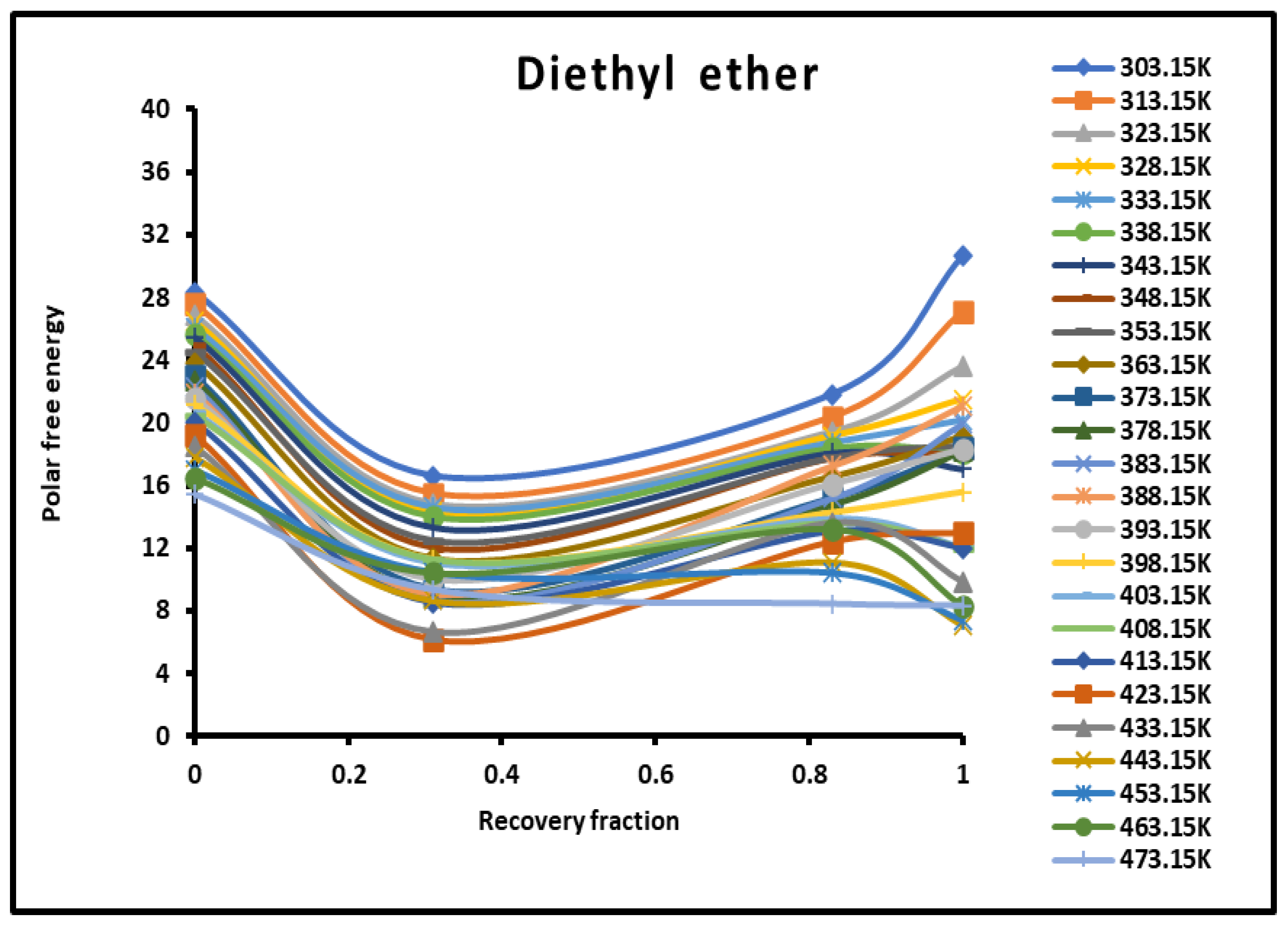
Figure 4.
Evolution of the polar free interaction energy ( (kJ/mol) of diethyl ether as a function of the recovery fraction of PMMA adsorbed on silica at different temperatures.
Figure 4.
Evolution of the polar free interaction energy ( (kJ/mol) of diethyl ether as a function of the recovery fraction of PMMA adsorbed on silica at different temperatures.
Figure 5.
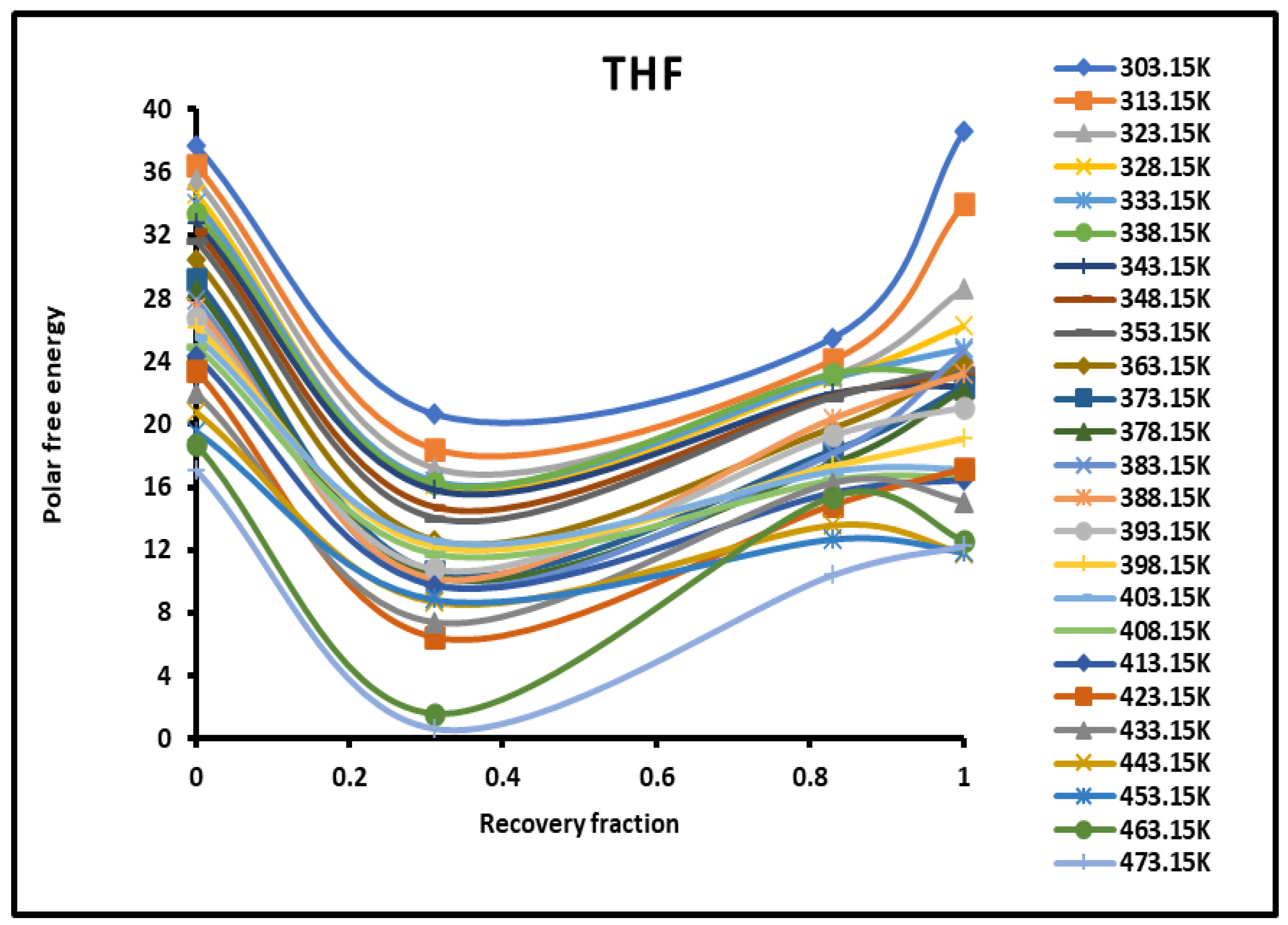
Evolution of the polar free interaction energy ( (kJ/mol) of tetrahydrofuran (THF) as a function of the recovery fraction of PMMA adsorbed on silica at different temperatures.
Figure 5.
Evolution of the polar free interaction energy ( (kJ/mol) of tetrahydrofuran (THF) as a function of the recovery fraction of PMMA adsorbed on silica at different temperatures.
Figure 6.
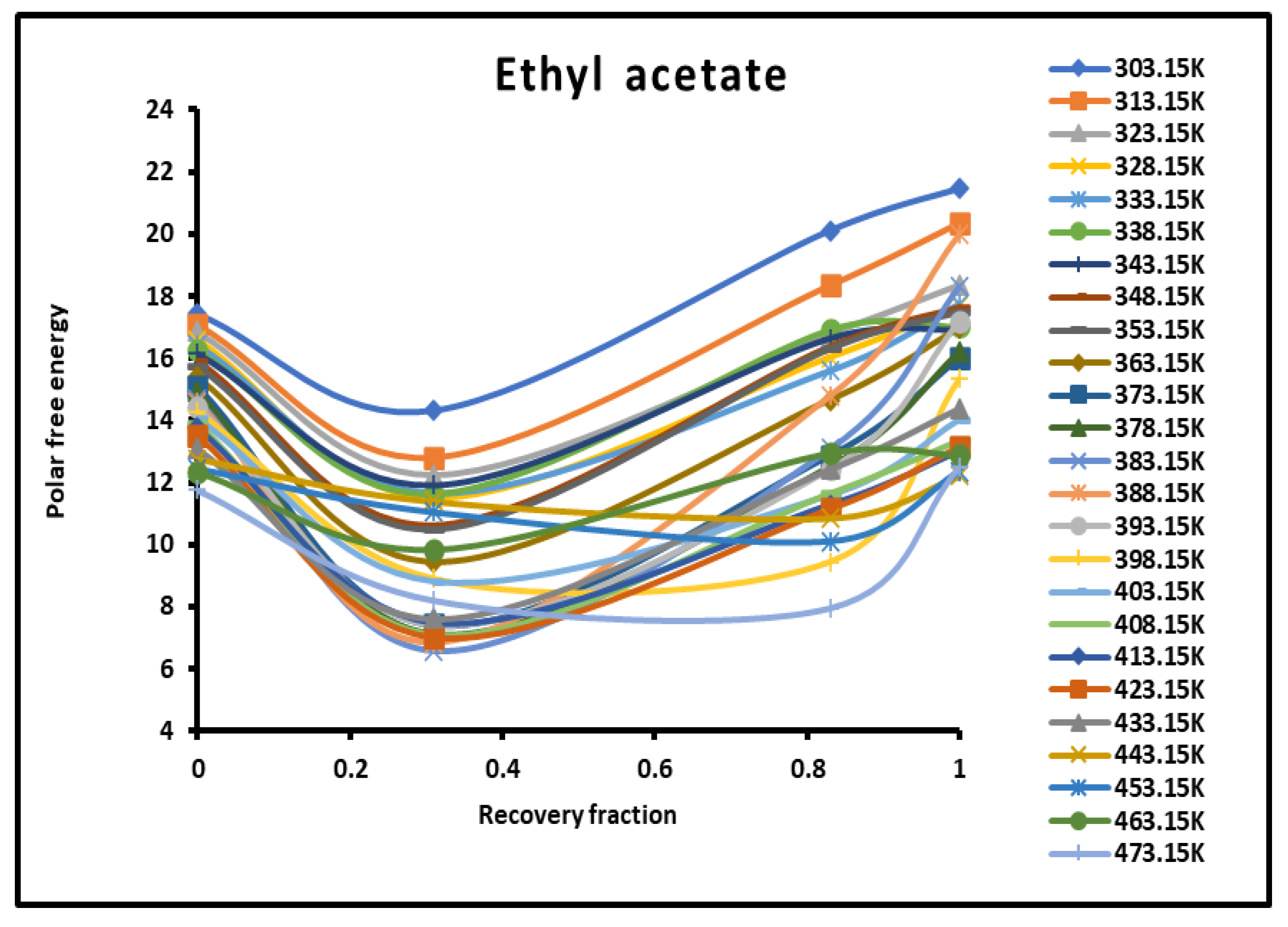
Evolution of the polar free interaction energy ( (kJ/mol) of ethyl acetate as a function of the recovery fraction of PMMA adsorbed on silica at different temperatures.
Figure 6.
Evolution of the polar free interaction energy ( (kJ/mol) of ethyl acetate as a function of the recovery fraction of PMMA adsorbed on silica at different temperatures.
Figure 7.
Evolution of the polar free interaction energy ( (kJ/mol) of ethyl acetate as a function of the recovery fraction of PMMA adsorbed on silica at different temperatures.
Figure 7.
Evolution of the polar free interaction energy ( (kJ/mol) of ethyl acetate as a function of the recovery fraction of PMMA adsorbed on silica at different temperatures.
Figure 8.
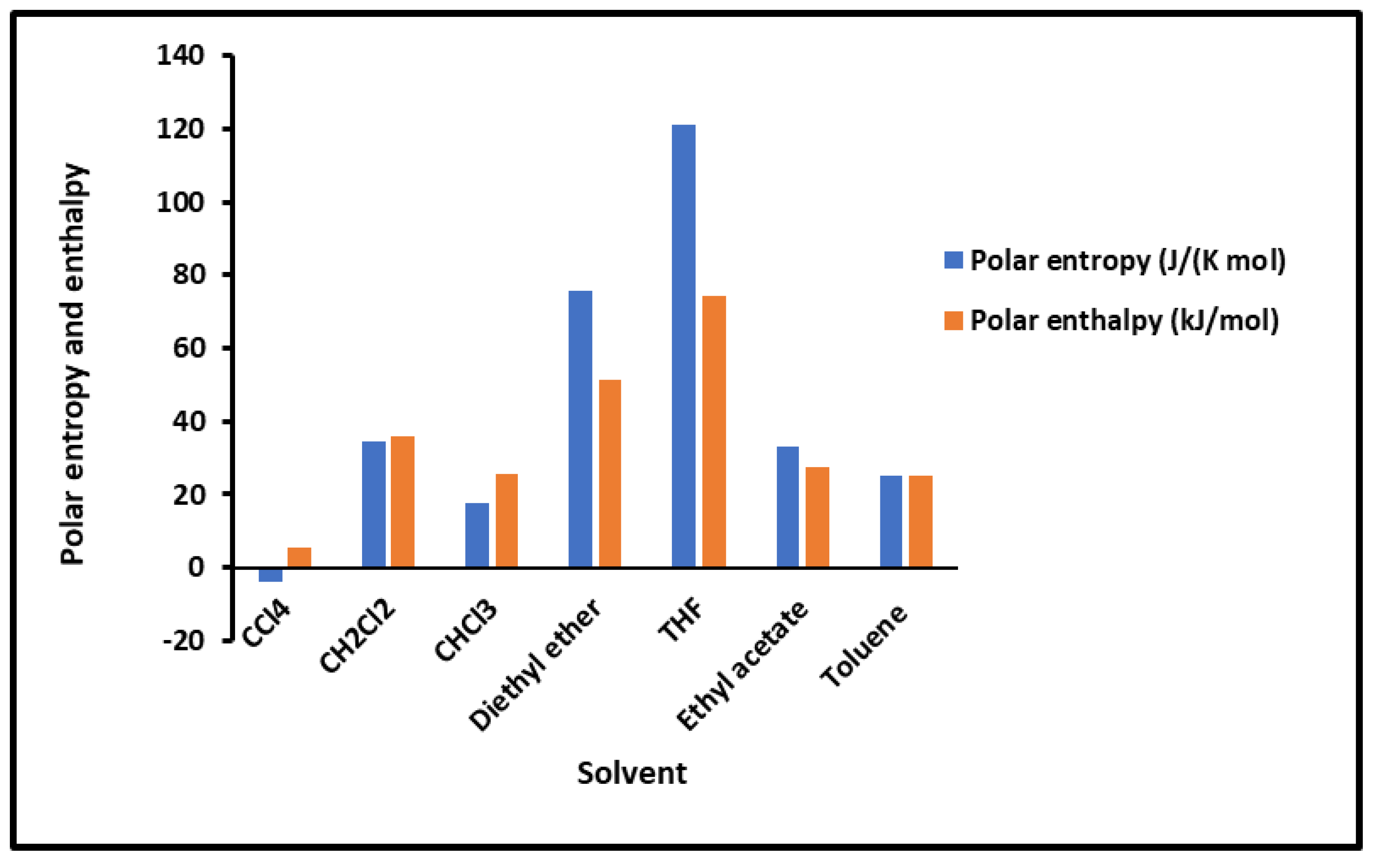
Values of the interaction enthalpy ( and entropy ( of polar solvents adsorbed on silica independent from the temperature.
Figure 8.
Values of the interaction enthalpy ( and entropy ( of polar solvents adsorbed on silica independent from the temperature.
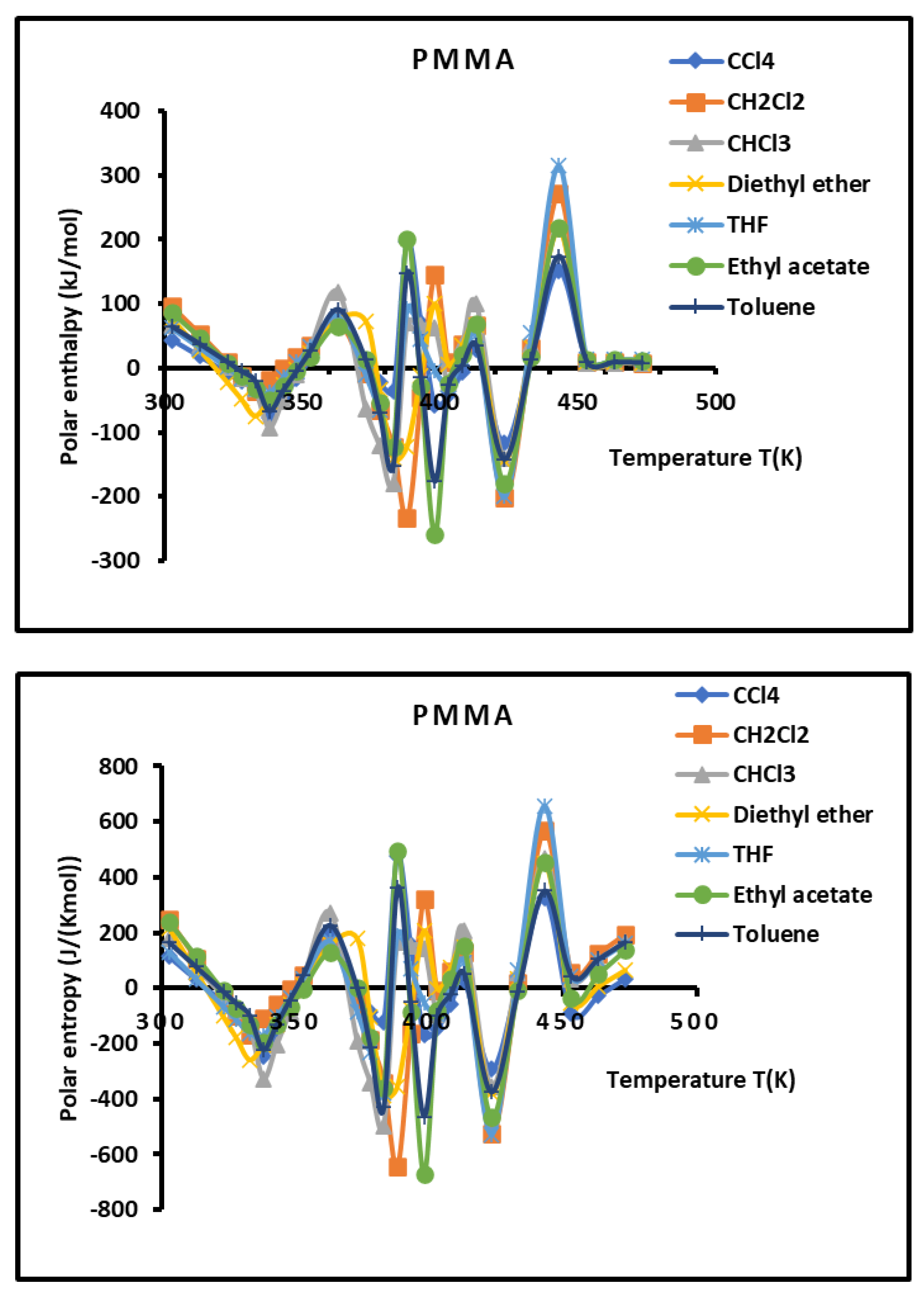
Figure 9.
Variations of the interaction enthalpy ( and entropy ( of polar solvents adsorbed on PMMA as a function of the temperature.
Figure 9.
Variations of the interaction enthalpy ( and entropy ( of polar solvents adsorbed on PMMA as a function of the temperature.
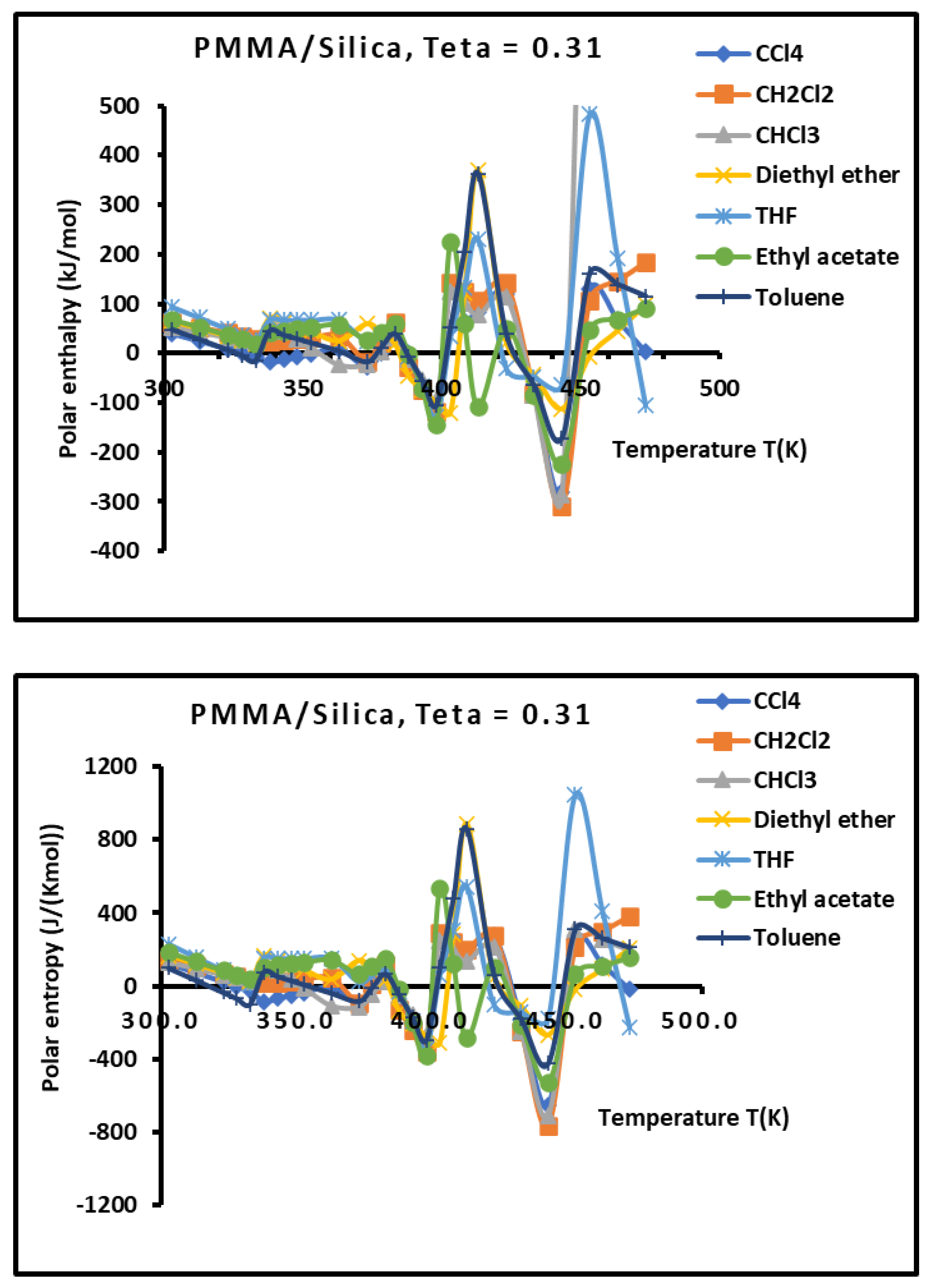
Figure 10.
Variations of the interaction enthalpy ( and entropy ( of polar solvents adsorbed on PMMA/silica for as a function of the temperature.
Figure 10.
Variations of the interaction enthalpy ( and entropy ( of polar solvents adsorbed on PMMA/silica for as a function of the temperature.
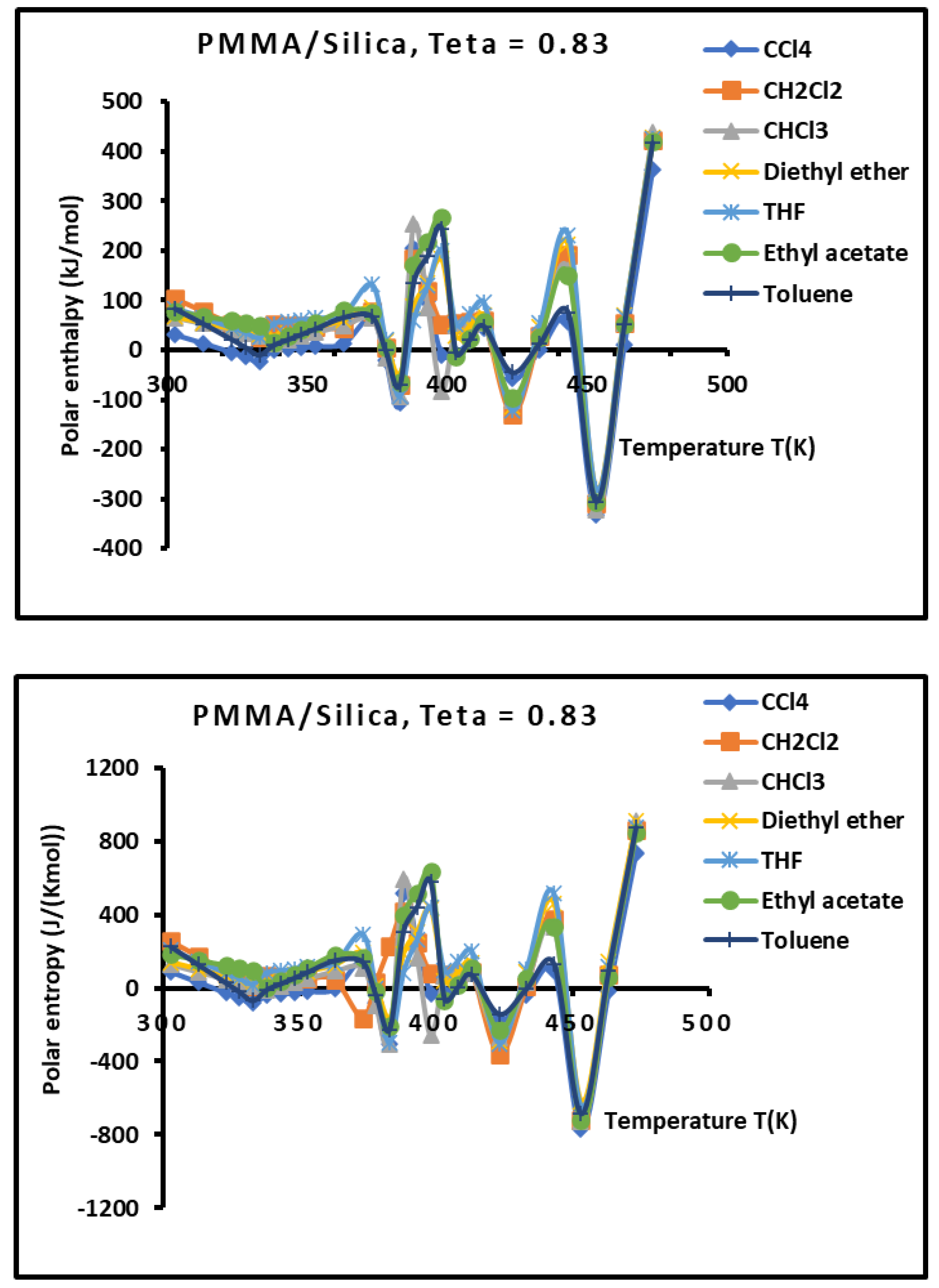
Figure 11.
Variations of the interaction enthalpy ( and entropy ( of polar solvents adsorbed on PMMA/silica for as a function of the temperature.
Figure 11.
Variations of the interaction enthalpy ( and entropy ( of polar solvents adsorbed on PMMA/silica for as a function of the temperature.
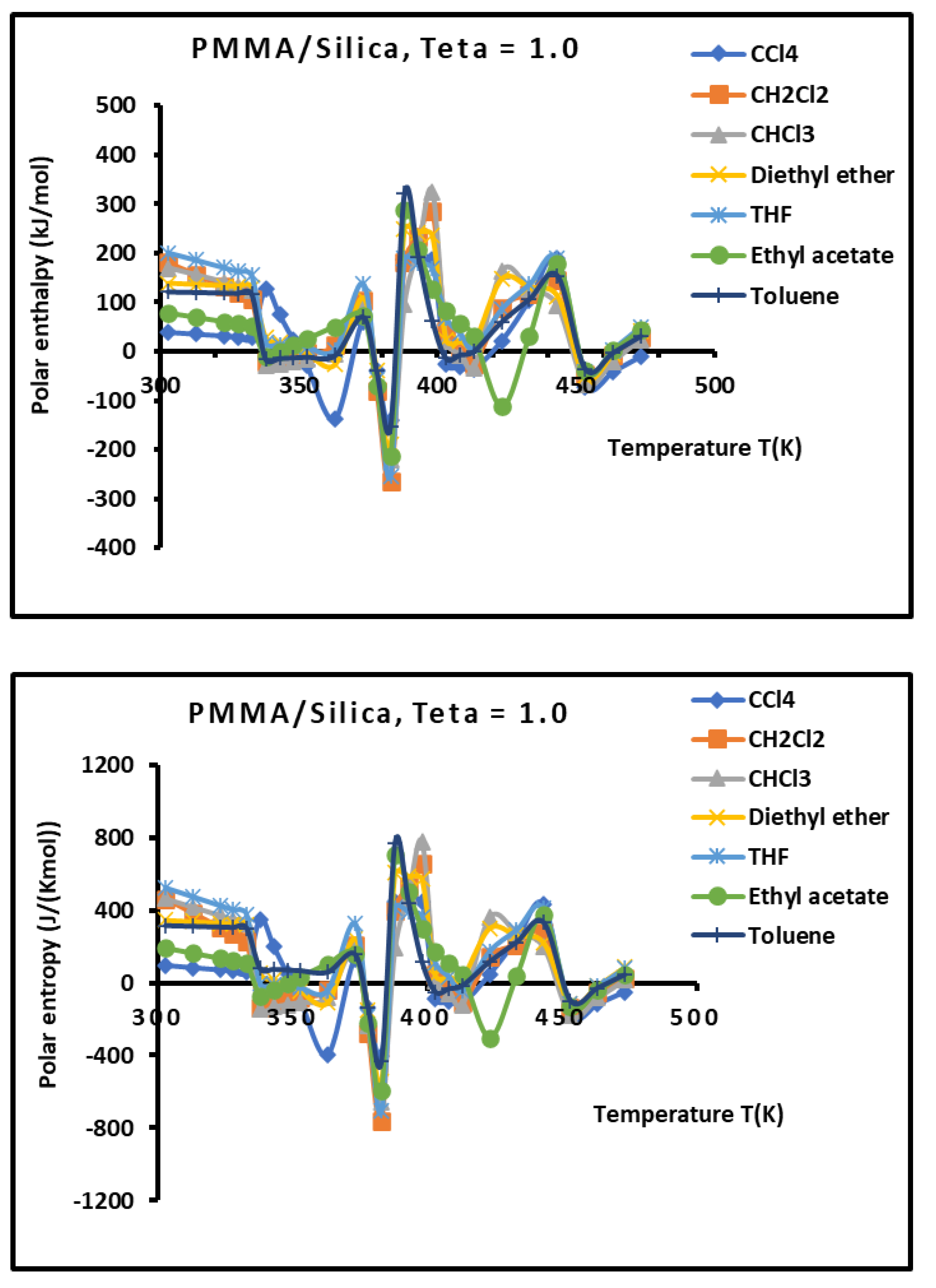
Figure 12.
Variations of the interaction enthalpy ( and entropy ( of polar solvents adsorbed on PMMA/silica for
(monolayer case) as a function of the temperature.
Figure 12.
Variations of the interaction enthalpy ( and entropy ( of polar solvents adsorbed on PMMA/silica for
(monolayer case) as a function of the temperature.
Figure 13.
Variations of the dispersion factor A (SI unit) of PMMA/silica at different recovery fractions as a function of the temperature.
Figure 13.
Variations of the dispersion factor A (SI unit) of PMMA/silica at different recovery fractions as a function of the temperature.
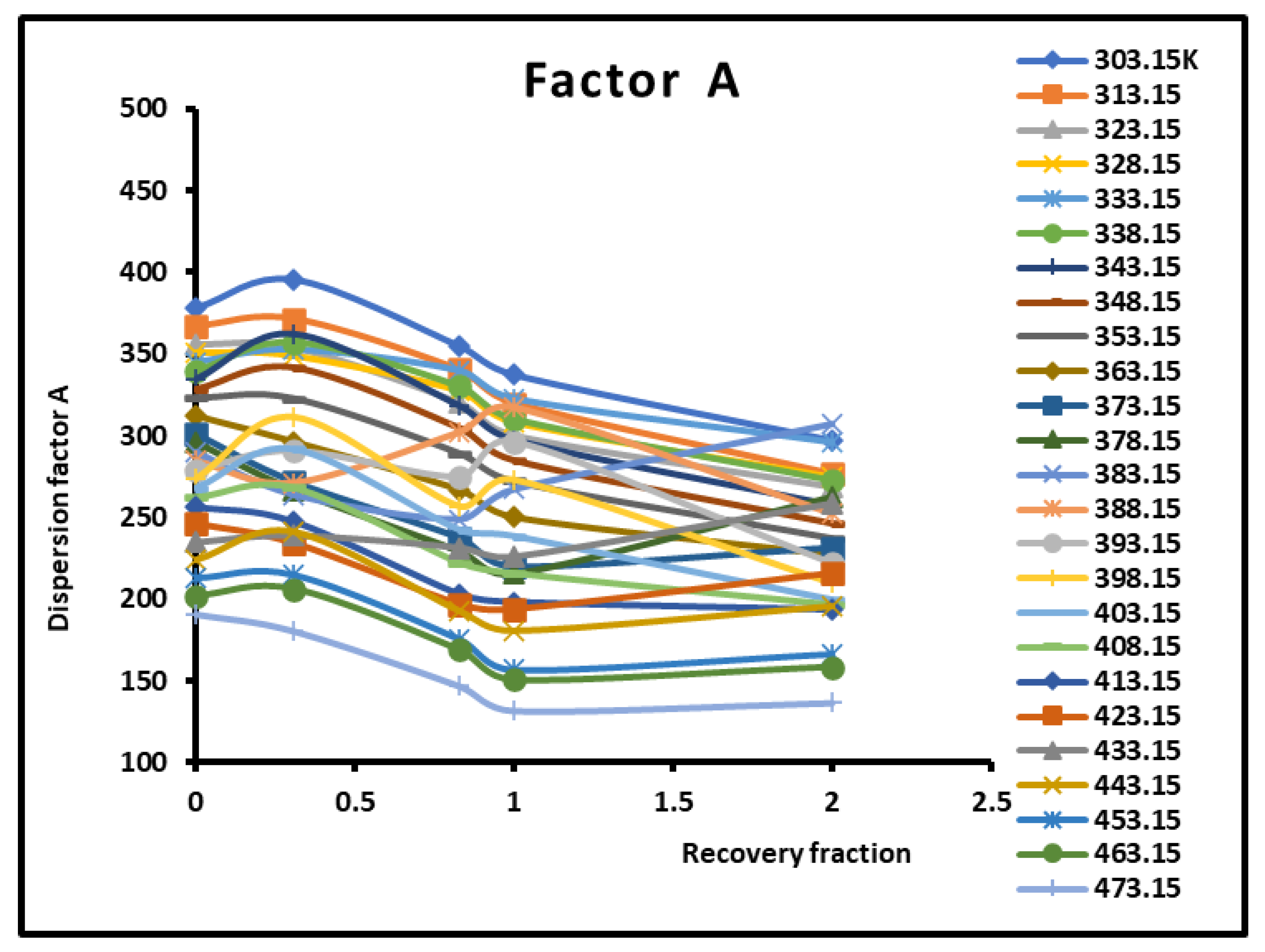
Figure 14.
Variations of the dispersion factor A (SI unit) of different solid surfaces as a function of the recovery fraction for different temperatures.
Figure 14.
Variations of the dispersion factor A (SI unit) of different solid surfaces as a function of the recovery fraction for different temperatures.
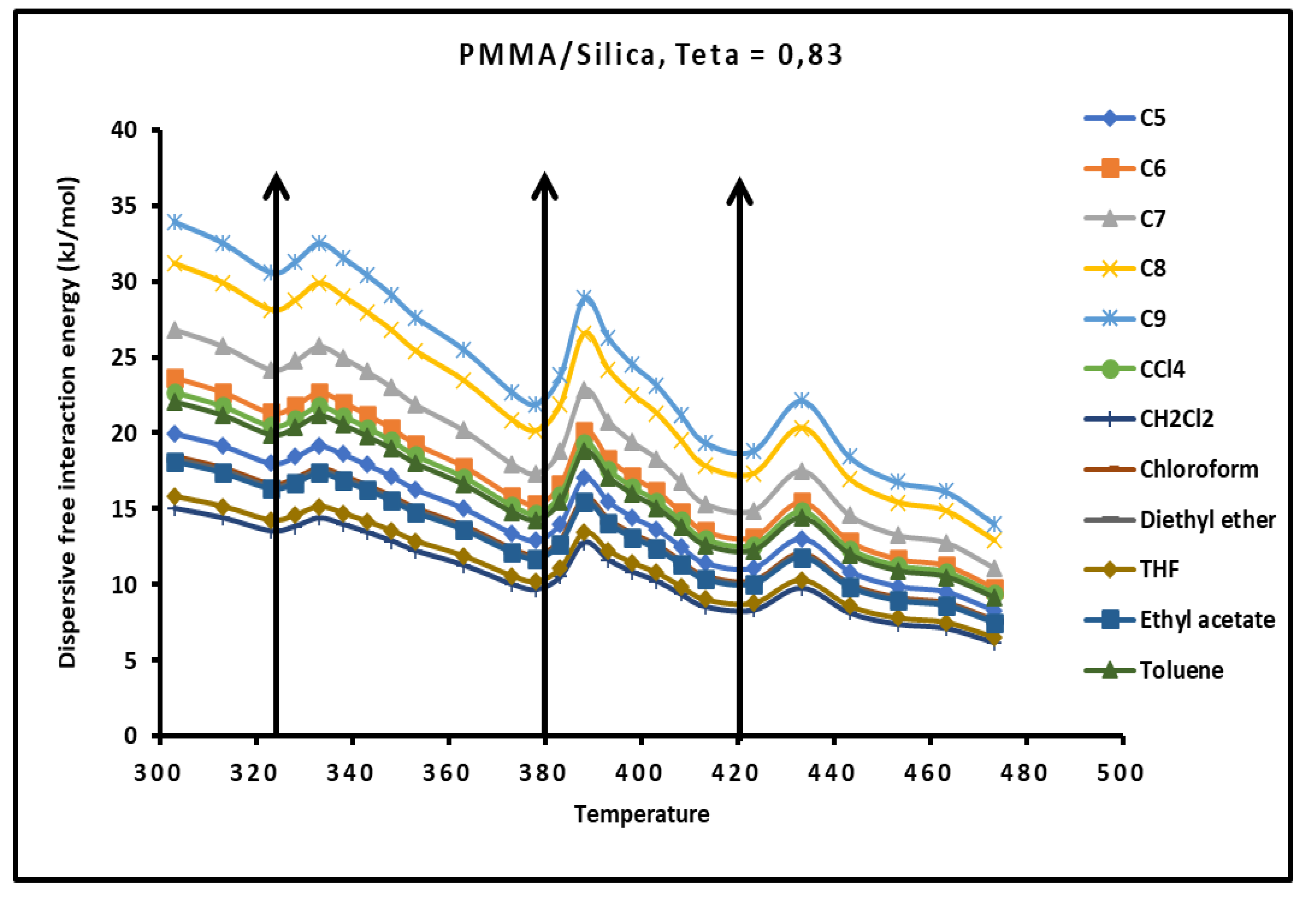
Figure 15.
Evolution of the London free dispersive interaction energy ( of organic solvents adsorbed on PMMA/silica for as a function of the temperature.
Figure 15.
Evolution of the London free dispersive interaction energy ( of organic solvents adsorbed on PMMA/silica for as a function of the temperature.
Figure 16.
Variations of the separation distance H as a function of the temperature for the different solid surfaces.
Figure 16.
Variations of the separation distance H as a function of the temperature for the different solid surfaces.
Table 1.
Values of ( kJ/mol) of polar molecules adsorbed on silica particles as a function of the temperature.
Table 1.
Values of ( kJ/mol) of polar molecules adsorbed on silica particles as a function of the temperature.
| Polar free energy of Solvents adsorbed on silica |
| Temperature T(K) |
CCl4
|
CH2Cl2
|
CHCl3
|
Diethyl ether |
THF |
Ethyl acetate |
Toluene |
| 303.15 |
6.674 |
25.241 |
20.030 |
28.337 |
37.697 |
17.422 |
17.701 |
| 313.15 |
6.715 |
24.896 |
19.854 |
27.581 |
36.486 |
17.089 |
17.452 |
| 323.15 |
6.752 |
24.807 |
19.752 |
26.838 |
35.506 |
16.852 |
17.328 |
| 328.15 |
6.777 |
24.379 |
19.590 |
26.447 |
34.669 |
16.590 |
17.078 |
| 333.15 |
6.797 |
24.206 |
19.502 |
26.069 |
34.064 |
16.423 |
16.954 |
| 338.15 |
6.818 |
24.034 |
19.414 |
25.691 |
33.458 |
16.257 |
16.829 |
| 343.15 |
6.809 |
23.876 |
19.303 |
25.462 |
32.786 |
16.149 |
16.722 |
| 348.15 |
6.859 |
23.689 |
19.238 |
24.935 |
32.247 |
15.924 |
16.580 |
| 353.15 |
6.879 |
23.516 |
19.150 |
24.557 |
31.642 |
15.757 |
16.456 |
| 363.15 |
6.884 |
23.102 |
18.927 |
23.805 |
30.437 |
15.394 |
16.170 |
| 373.15 |
6.961 |
22.826 |
18.798 |
23.045 |
29.220 |
15.091 |
15.958 |
| 378.15 |
6.982 |
22.654 |
18.710 |
22.667 |
28.614 |
14.925 |
15.833 |
| 383.15 |
6.969 |
22.285 |
18.547 |
22.315 |
27.908 |
14.704 |
15.598 |
| 388.15 |
7.023 |
22.309 |
18.534 |
21.911 |
27.403 |
14.592 |
15.584 |
| 393.15 |
7.043 |
22.136 |
18.446 |
21.533 |
26.798 |
14.425 |
15.460 |
| 398.15 |
7.064 |
21.964 |
18.358 |
21.155 |
26.192 |
14.259 |
15.335 |
| 403.15 |
7.127 |
21.689 |
18.248 |
20.674 |
25.592 |
14.080 |
15.184 |
| 408.15 |
7.105 |
21.619 |
18.182 |
20.399 |
24.981 |
13.926 |
15.086 |
| 413.15 |
7.125 |
21.446 |
18.094 |
20.021 |
24.376 |
13.759 |
14.962 |
| 423.15 |
7.205 |
21.206 |
18.006 |
19.185 |
23.401 |
13.498 |
14.834 |
| 433.15 |
7.207 |
20.756 |
17.742 |
18.509 |
21.954 |
13.093 |
14.464 |
| 443.15 |
7.248 |
20.411 |
17.566 |
17.753 |
20.743 |
12.760 |
14.215 |
| 453.15 |
7.289 |
20.066 |
17.390 |
16.997 |
19.532 |
12.427 |
13.966 |
| 463.15 |
7.348 |
20.070 |
17.346 |
16.496 |
18.659 |
12.350 |
13.973 |
| 473.15 |
7.371 |
19.376 |
17.038 |
15.485 |
17.110 |
11.761 |
13.468 |
Table 2.
Values of ( kJ/mol) of polar molecules adsorbed on PMMA particles as a function of the temperature.
Table 2.
Values of ( kJ/mol) of polar molecules adsorbed on PMMA particles as a function of the temperature.
| Polar free energy of Solvents adsorbed on PMMA |
| Temperature T(K) |
CCl4
|
CH2Cl2
|
CHCl3
|
Diethyl ether |
THF |
Ethyl acetate |
Toluene |
| 303.15 |
10.765 |
18.520 |
16.079 |
15.039 |
19.851 |
16.029 |
13.204 |
| 313.15 |
10.254 |
16.940 |
14.930 |
13.956 |
18.940 |
14.694 |
12.212 |
| 323.15 |
10.294 |
16.034 |
15.101 |
14.437 |
18.822 |
14.037 |
11.443 |
| 328.15 |
10.808 |
15.902 |
15.552 |
15.362 |
19.155 |
14.498 |
11.677 |
| 333.15 |
11.434 |
17.105 |
16.068 |
16.544 |
19.846 |
15.192 |
12.190 |
| 338.15 |
9.631 |
14.792 |
13.161 |
13.037 |
17.712 |
13.243 |
10.501 |
| 343.15 |
10.629 |
15.055 |
14.098 |
13.685 |
18.247 |
13.912 |
11.245 |
| 348.15 |
11.414 |
15.178 |
15.013 |
14.115 |
18.667 |
14.430 |
11.989 |
| 353.15 |
11.721 |
14.911 |
14.782 |
13.980 |
18.464 |
14.285 |
11.936 |
| 363.15 |
10.816 |
13.717 |
12.961 |
12.873 |
17.352 |
13.499 |
10.680 |
| 373.15 |
10.821 |
12.279 |
9.454 |
11.020 |
16.585 |
12.891 |
10.111 |
| 378.15 |
11.206 |
13.019 |
10.825 |
10.962 |
17.252 |
13.325 |
10.604 |
| 383.15 |
11.772 |
14.521 |
12.968 |
12.321 |
18.652 |
14.659 |
12.181 |
| 388.15 |
12.487 |
10.832 |
12.193 |
10.936 |
16.403 |
11.700 |
9.624 |
| 393.15 |
10.950 |
12.707 |
11.533 |
11.870 |
15.718 |
10.781 |
8.900 |
| 398.15 |
11.029 |
12.170 |
10.930 |
11.397 |
15.638 |
12.783 |
10.237 |
| 403.15 |
11.465 |
11.776 |
10.791 |
11.399 |
15.942 |
13.202 |
10.136 |
| 408.15 |
11.830 |
11.631 |
10.794 |
11.360 |
16.258 |
13.460 |
10.355 |
| 413.15 |
11.758 |
11.135 |
10.040 |
10.942 |
16.106 |
13.146 |
10.197 |
| 423.15 |
11.929 |
11.458 |
10.113 |
11.090 |
17.047 |
13.434 |
10.433 |
| 433.15 |
13.579 |
13.574 |
11.582 |
12.569 |
19.030 |
15.576 |
12.048 |
| 443.15 |
12.136 |
10.220 |
8.929 |
9.901 |
15.065 |
13.114 |
10.016 |
| 453.15 |
12.047 |
9.388 |
7.939 |
9.244 |
14.165 |
12.620 |
9.682 |
| 463.15 |
12.299 |
8.917 |
7.617 |
9.151 |
13.848 |
12.645 |
9.287 |
| 473.15 |
11.924 |
7.776 |
6.642 |
8.470 |
12.938 |
11.811 |
8.280 |
Table 3.
Values of ( kJ/mol) of polar molecules adsorbed on the system PMMA/silica as a function of the temperature for a recovery fraction θ = 0.31.
Table 3.
Values of ( kJ/mol) of polar molecules adsorbed on the system PMMA/silica as a function of the temperature for a recovery fraction θ = 0.31.
|
Polar free energy of Solvents adsorbed on PMMA/silica for
|
| Temperature T(K) |
CCl4
|
CH2Cl2
|
CHCl3
|
Diethyl ether |
THF |
Ethyl acetate |
Toluene |
| 303.15 |
6.698 |
20.777 |
15.865 |
16.603 |
20.647 |
14.300 |
14.620 |
| 313.15 |
6.055 |
19.604 |
14.885 |
15.493 |
18.449 |
12.803 |
13.694 |
| 323.15 |
5.932 |
18.973 |
14.390 |
14.799 |
17.228 |
12.216 |
13.726 |
| 328.15 |
5.704 |
18.169 |
13.853 |
14.282 |
16.141 |
11.486 |
13.530 |
| 333.15 |
6.253 |
18.442 |
14.047 |
14.603 |
16.362 |
11.672 |
14.064 |
| 338.15 |
6.519 |
18.608 |
14.218 |
13.973 |
16.216 |
11.637 |
14.235 |
| 343.15 |
6.605 |
19.382 |
14.562 |
13.340 |
15.835 |
11.926 |
14.005 |
| 348.15 |
6.730 |
18.336 |
12.890 |
12.001 |
14.743 |
10.618 |
13.470 |
| 353.15 |
7.264 |
18.364 |
13.507 |
12.453 |
14.008 |
10.503 |
13.290 |
| 363.15 |
6.952 |
18.115 |
13.879 |
11.315 |
12.626 |
9.424 |
13.254 |
| 373.15 |
6.584 |
17.019 |
12.869 |
9.437 |
10.630 |
7.416 |
12.282 |
| 378.15 |
6.844 |
17.200 |
13.082 |
8.936 |
10.315 |
7.107 |
12.492 |
| 383.15 |
6.714 |
16.865 |
12.933 |
8.706 |
9.823 |
6.584 |
12.327 |
| 388.15 |
7.111 |
17.412 |
13.320 |
9.047 |
10.139 |
6.829 |
12.940 |
| 393.15 |
7.605 |
18.243 |
13.964 |
9.984 |
10.797 |
7.413 |
13.547 |
| 398.15 |
8.913 |
19.648 |
15.146 |
11.268 |
12.232 |
8.909 |
14.775 |
| 403.15 |
11.229 |
21.423 |
17.010 |
11.072 |
12.576 |
8.802 |
16.772 |
| 408.15 |
10.654 |
19.980 |
15.734 |
11.281 |
11.759 |
7.117 |
15.461 |
| 413.15 |
9.879 |
18.756 |
14.746 |
8.496 |
9.743 |
7.482 |
12.252 |
| 423.15 |
8.281 |
17.133 |
13.433 |
6.152 |
6.444 |
7.003 |
12.634 |
| 433.15 |
8.092 |
16.598 |
13.170 |
6.621 |
7.368 |
7.619 |
13.247 |
| 443.15 |
12.550 |
21.255 |
17.518 |
8.654 |
8.665 |
11.397 |
16.279 |
| 453.15 |
10.367 |
18.117 |
14.996 |
10.447 |
8.862 |
11.040 |
14.673 |
| 463.15 |
8.354 |
15.912 |
12.490 |
10.442 |
1.559 |
9.852 |
11.573 |
| 473.15 |
7.697 |
12.895 |
10.572 |
9.325 |
0.595 |
8.197 |
8.969 |
Table 4.
Values of ( kJ/mol) of polar molecules adsorbed on the system PMMA/silica as a function of the temperature for a recovery fraction .
Table 4.
Values of ( kJ/mol) of polar molecules adsorbed on the system PMMA/silica as a function of the temperature for a recovery fraction .
|
Polar free energy of Solvents adsorbed on PMMA/silica for
|
| Temperature T(K) |
CCl4
|
CH2Cl2
|
CHCl3
|
Diethyl ether |
THF |
Ethyl acetate |
Toluene |
| 303.15 |
7.773 |
27.605 |
23.019 |
21.816 |
25.479 |
20.114 |
17.258 |
| 313.15 |
7.219 |
25.780 |
21.588 |
20.382 |
24.106 |
18.354 |
15.812 |
| 323.15 |
7.726 |
24.330 |
20.823 |
19.402 |
23.091 |
16.800 |
15.052 |
| 328.15 |
7.983 |
24.125 |
20.151 |
19.158 |
22.906 |
16.021 |
14.985 |
| 333.15 |
8.322 |
24.143 |
20.132 |
18.742 |
22.962 |
15.604 |
15.539 |
| 338.15 |
8.421 |
24.970 |
20.394 |
18.368 |
23.217 |
16.923 |
15.672 |
| 343.15 |
7.970 |
23.919 |
20.547 |
18.073 |
21.957 |
16.634 |
14.982 |
| 348.15 |
8.213 |
23.804 |
20.465 |
17.719 |
21.787 |
16.379 |
15.316 |
| 353.15 |
8.480 |
23.752 |
20.339 |
17.763 |
21.690 |
16.315 |
15.442 |
| 363.15 |
7.946 |
22.566 |
19.802 |
16.558 |
19.764 |
14.651 |
13.973 |
| 373.15 |
7.400 |
21.338 |
18.643 |
15.259 |
18.336 |
12.867 |
13.259 |
| 378.15 |
7.177 |
21.114 |
18.505 |
14.790 |
17.504 |
12.511 |
12.966 |
| 383.15 |
8.088 |
21.872 |
19.412 |
15.216 |
18.162 |
13.086 |
13.592 |
| 388.15 |
9.738 |
23.872 |
20.633 |
17.249 |
20.357 |
14.790 |
15.021 |
| 393.15 |
7.975 |
22.237 |
18.677 |
16.071 |
19.312 |
12.425 |
13.092 |
| 398.15 |
7.579 |
21.453 |
18.849 |
14.284 |
17.365 |
9.449 |
10.478 |
| 403.15 |
8.266 |
21.428 |
19.153 |
13.895 |
17.001 |
11.597 |
13.409 |
| 408.15 |
8.378 |
20.973 |
18.729 |
13.601 |
16.463 |
11.654 |
13.423 |
| 413.15 |
8.176 |
20.481 |
18.274 |
13.057 |
15.661 |
11.281 |
13.111 |
| 423.15 |
8.263 |
20.132 |
18.597 |
12.392 |
14.863 |
11.137 |
12.497 |
| 433.15 |
9.011 |
21.753 |
19.964 |
13.615 |
16.245 |
12.413 |
13.101 |
| 443.15 |
8.413 |
19.670 |
18.315 |
11.083 |
13.556 |
10.859 |
12.321 |
| 453.15 |
8.373 |
19.017 |
17.896 |
10.411 |
12.693 |
10.113 |
12.024 |
| 463.15 |
11.973 |
22.320 |
21.465 |
13.227 |
15.364 |
12.954 |
15.267 |
| 473.15 |
8.067 |
17.745 |
16.842 |
8.413 |
10.414 |
7.945 |
10.717 |
Table 5.
Values of ( kJ/mol) of polar molecules adsorbed on the system PMMA/silica as a function of the temperature for a recovery fraction .
Table 5.
Values of ( kJ/mol) of polar molecules adsorbed on the system PMMA/silica as a function of the temperature for a recovery fraction .
|
Polar free energy of Solvents adsorbed on PMMA/silica for
|
| Temperature T(K) |
CCl4
|
CH2Cl2
|
CHCl3
|
Diethyl ether |
THF |
Ethyl acetate |
Toluene |
| 303.15 |
13.797 |
36.031 |
32.260 |
30.623 |
38.590 |
21.479 |
26.098 |
| 313.15 |
13.567 |
31.827 |
28.141 |
27.132 |
33.996 |
20.360 |
23.011 |
| 323.15 |
12.594 |
27.832 |
24.874 |
23.581 |
28.575 |
18.376 |
20.293 |
| 328.15 |
12.366 |
26.052 |
22.043 |
21.509 |
26.236 |
17.682 |
17.852 |
| 333.15 |
12.572 |
25.107 |
21.512 |
20.173 |
24.834 |
17.746 |
17.145 |
| 338.15 |
11.175 |
23.004 |
19.957 |
18.075 |
22.883 |
17.019 |
15.721 |
| 343.15 |
7.827 |
22.303 |
19.418 |
17.043 |
22.426 |
16.908 |
15.316 |
| 348.15 |
8.731 |
23.918 |
21.243 |
17.929 |
23.166 |
17.644 |
16.472 |
| 353.15 |
9.682 |
24.387 |
21.614 |
18.557 |
23.527 |
17.500 |
17.214 |
| 363.15 |
11.294 |
24.438 |
22.228 |
19.161 |
23.921 |
16.971 |
17.656 |
| 373.15 |
11.607 |
23.218 |
21.724 |
18.422 |
22.395 |
15.990 |
16.949 |
| 378.15 |
11.599 |
23.350 |
21.692 |
18.202 |
22.230 |
16.213 |
17.043 |
| 383.15 |
12.922 |
25.912 |
23.757 |
19.957 |
24.657 |
18.321 |
18.608 |
| 388.15 |
14.514 |
28.129 |
25.061 |
21.098 |
23.208 |
20.016 |
17.299 |
| 393.15 |
11.630 |
25.838 |
23.488 |
18.299 |
21.089 |
17.162 |
14.154 |
| 398.15 |
9.405 |
22.887 |
20.451 |
15.594 |
19.094 |
15.325 |
12.647 |
| 403.15 |
7.366 |
18.964 |
17.081 |
12.048 |
17.162 |
14.041 |
13.030 |
| 408.15 |
7.781 |
18.878 |
17.221 |
12.010 |
16.629 |
13.365 |
13.403 |
| 413.15 |
8.249 |
19.192 |
17.691 |
12.004 |
16.478 |
13.009 |
13.687 |
| 423.15 |
9.622 |
19.875 |
18.807 |
12.975 |
17.161 |
13.139 |
14.195 |
| 433.15 |
8.548 |
17.697 |
16.005 |
9.842 |
15.043 |
14.366 |
12.628 |
| 443.15 |
5.562 |
14.849 |
14.031 |
7.101 |
11.750 |
12.211 |
9.983 |
| 453.15 |
6.883 |
15.433 |
14.892 |
7.366 |
11.880 |
12.355 |
11.138 |
| 463.15 |
8.179 |
16.389 |
16.175 |
8.339 |
12.549 |
12.883 |
11.825 |
| 473.15 |
8.812 |
16.525 |
16.477 |
8.298 |
12.238 |
12.504 |
11.793 |
Table 6.
Values of the enthalpic acid base parameters , , / and , and the entropic acid base parameters , , / and of PMMA as a function of the temperature.
Table 6.
Values of the enthalpic acid base parameters , , / and , and the entropic acid base parameters , , / and of PMMA as a function of the temperature.
| T(K) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 303.15 |
0.478 |
3.881 |
4.358 |
8.120 |
0.90 |
18.20 |
19.10 |
20.15 |
| 313.15 |
0.317 |
2.523 |
2.840 |
7.953 |
0.56 |
7.52 |
8.08 |
13.40 |
| 323.15 |
0.090 |
0.664 |
0.754 |
7.413 |
-0.62 |
-3.15 |
-3.77 |
5.12 |
| 328.15 |
-0.122 |
-0.522 |
-0.644 |
4.293 |
-1.00 |
-4.91 |
-5.90 |
4.93 |
| 333.15 |
-0.153 |
-0.636 |
-0.789 |
4.160 |
-1.38 |
-6.06 |
-7.44 |
4.41 |
| 338.15 |
-0.144 |
-0.658 |
-0.802 |
4.568 |
-0.88 |
-7.59 |
-8.47 |
8.63 |
| 343.15 |
0.152 |
-0.695 |
-0.543 |
-4.565 |
-0.59 |
-8.31 |
-8.91 |
14.04 |
| 348.15 |
0.170 |
-0.529 |
-0.358 |
-3.103 |
-0.16 |
-1.87 |
-2.03 |
11.61 |
| 353.15 |
0.278 |
1.826 |
2.105 |
6.560 |
0.20 |
2.78 |
2.98 |
14.04 |
| 363.15 |
0.536 |
3.122 |
3.658 |
5.828 |
0.92 |
15.67 |
16.59 |
17.10 |
| 373.15 |
0.433 |
3.955 |
4.388 |
9.135 |
0.90 |
7.40 |
8.30 |
8.24 |
| 378.15 |
0.398 |
3.739 |
4.138 |
9.385 |
-1.99 |
-8.98 |
-10.97 |
4.52 |
| 383.15 |
0.186 |
1.527 |
1.713 |
8.217 |
-0.66 |
-6.52 |
-7.19 |
9.84 |
| 388.15 |
0.521 |
5.841 |
6.362 |
11.213 |
0.91 |
12.80 |
13.71 |
14.05 |
| 393.15 |
0.274 |
1.750 |
2.024 |
6.389 |
0.29 |
2.47 |
2.76 |
8.42 |
| 398.15 |
0.266 |
0.560 |
0.826 |
2.106 |
0.27 |
-1.89 |
-1.62 |
-6.93 |
| 403.15 |
0.220 |
-0.630 |
-0.410 |
-2.864 |
-0.45 |
-1.32 |
-1.77 |
2.92 |
| 408.15 |
0.174 |
0.800 |
0.975 |
4.595 |
0.22 |
-0.66 |
-0.44 |
-2.95 |
| 413.15 |
0.433 |
3.358 |
3.791 |
7.755 |
0.90 |
6.21 |
7.10 |
6.91 |
| 423.15 |
0.488 |
2.131 |
2.619 |
4.366 |
-4.56 |
-14.72 |
-19.27 |
3.23 |
| 433.15 |
0.543 |
0.904 |
1.447 |
1.665 |
0.66 |
-0.40 |
0.26 |
-0.61 |
| 443.15 |
1.755 |
7.262 |
9.016 |
4.138 |
5.88 |
19.88 |
25.76 |
3.38 |
| 453.15 |
0.111 |
1.044 |
1.155 |
9.419 |
0.60 |
-1.83 |
-1.22 |
-3.04 |
| 463.15 |
0.107 |
1.047 |
1.154 |
9.766 |
1.00 |
1.60 |
2.61 |
1.60 |
| 473.15 |
0.100 |
0.980 |
1.080 |
9.832 |
1.40 |
6.23 |
7.63 |
4.44 |
Table 7.
Values of the enthalpic acid base parameters , , / and , and the entropic acid base parameters , , / and of PMMA/silica for as a function of the temperature.
Table 7.
Values of the enthalpic acid base parameters , , / and , and the entropic acid base parameters , , / and of PMMA/silica for as a function of the temperature.
| T(K) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 303.15 |
0.884 |
3.819 |
4.704 |
4.318 |
2.11 |
10.71 |
12.82 |
5.06 |
| 313.15 |
0.704 |
2.319 |
3.023 |
3.291 |
1.53 |
5.84 |
7.37 |
3.81 |
| 323.15 |
0.519 |
0.770 |
1.288 |
1.484 |
0.95 |
0.97 |
1.91 |
1.02 |
| 328.15 |
0.424 |
-0.023 |
0.400 |
-0.055 |
0.65 |
-0.52 |
0.14 |
-0.79 |
| 333.15 |
0.327 |
-0.828 |
-0.501 |
-2.532 |
0.36 |
-0.73 |
-0.37 |
-2.02 |
| 338.15 |
0.789 |
0.508 |
1.298 |
0.644 |
1.97 |
-0.94 |
1.03 |
-0.48 |
| 343.15 |
0.781 |
0.387 |
1.168 |
0.495 |
1.95 |
-1.19 |
0.76 |
-0.61 |
| 348.15 |
0.773 |
0.264 |
1.037 |
0.341 |
1.92 |
-1.20 |
0.72 |
-0.63 |
| 353.15 |
0.764 |
0.139 |
0.903 |
0.181 |
1.90 |
-1.34 |
0.56 |
-0.71 |
| 363.15 |
0.747 |
-0.117 |
0.630 |
-0.157 |
1.85 |
-1.67 |
0.19 |
-0.90 |
| 373.15 |
2.013 |
2.013 |
4.026 |
1.000 |
4.85 |
15.21 |
20.05 |
3.14 |
| 378.15 |
0.425 |
0.594 |
1.020 |
1.397 |
0.84 |
-0.56 |
0.28 |
-0.67 |
| 383.15 |
0.781 |
0.387 |
1.168 |
0.495 |
1.95 |
-0.73 |
1.21 |
-0.38 |
| 388.15 |
-0.530 |
-1.038 |
-1.568 |
1.959 |
-0.57 |
-2.05 |
-2.62 |
3.61 |
| 393.15 |
-0.717 |
-1.493 |
-2.210 |
2.083 |
-1.54 |
-3.12 |
-4.66 |
2.03 |
| 398.15 |
-0.917 |
-2.588 |
-3.505 |
2.821 |
-2.39 |
-3.21 |
-5.60 |
1.34 |
| 403.15 |
0.584 |
7.647 |
8.231 |
13.084 |
-3.52 |
12.57 |
9.05 |
-3.58 |
| 408.15 |
1.006 |
11.211 |
12.216 |
11.149 |
2.39 |
18.37 |
20.76 |
7.67 |
| 413.15 |
2.013 |
14.818 |
16.831 |
7.362 |
4.85 |
21.18 |
26.03 |
4.37 |
| 423.15 |
-2.076 |
9.053 |
6.977 |
-4.361 |
-3.51 |
13.30 |
9.79 |
-3.79 |
| 433.15 |
-0.729 |
-2.522 |
-3.250 |
3.460 |
-1.26 |
-1.61 |
-2.87 |
1.27 |
| 443.15 |
0.550 |
-1.493 |
-0.944 |
-2.718 |
0.99 |
-1.72 |
-0.73 |
-1.74 |
| 453.15 |
4.266 |
9.254 |
13.520 |
2.169 |
10.38 |
-1.11 |
9.27 |
-0.11 |
| 463.15 |
1.213 |
15.550 |
16.763 |
12.821 |
3.76 |
10.71 |
14.47 |
2.84 |
| 473.15 |
-1.907 |
14.815 |
12.908 |
-7.768 |
-2.85 |
10.46 |
7.61 |
-3.67 |
Table 8.
Values of the enthalpic acid base , , / and , and the entropic acid base parameters , , / and of PMMA/silica for as a function of the temperature.
Table 8.
Values of the enthalpic acid base , , / and , and the entropic acid base parameters , , / and of PMMA/silica for as a function of the temperature.
| T(K) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 303.15 |
0.736 |
5.459 |
6.195 |
7.421 |
1.73 |
14.24 |
15.97 |
8.23 |
| 313.15 |
0.621 |
3.385 |
4.006 |
5.448 |
1.36 |
7.51 |
8.86 |
5.52 |
| 323.15 |
0.503 |
1.243 |
1.747 |
2.471 |
0.99 |
0.77 |
1.76 |
0.78 |
| 328.15 |
0.443 |
0.147 |
0.590 |
0.333 |
0.80 |
-1.40 |
-0.60 |
-1.74 |
| 333.15 |
0.381 |
-0.966 |
-0.584 |
-2.531 |
0.62 |
-1.92 |
-1.31 |
-3.12 |
| 338.15 |
0.579 |
-0.169 |
0.410 |
-0.292 |
1.07 |
-2.54 |
-1.47 |
-2.37 |
| 343.15 |
0.605 |
0.520 |
1.125 |
0.860 |
1.15 |
-1.89 |
-0.74 |
-1.64 |
| 348.15 |
0.632 |
1.220 |
1.851 |
1.931 |
1.23 |
-0.28 |
0.94 |
-0.23 |
| 353.15 |
0.659 |
1.929 |
2.588 |
2.929 |
1.30 |
1.74 |
3.04 |
1.33 |
| 363.15 |
0.714 |
3.379 |
4.093 |
4.732 |
1.46 |
5.79 |
7.24 |
3.97 |
| 373.15 |
0.893 |
3.854 |
4.747 |
4.316 |
1.91 |
0.69 |
2.60 |
0.36 |
| 378.15 |
0.315 |
-1.651 |
-1.336 |
-5.240 |
0.30 |
-0.70 |
-0.40 |
-2.34 |
| 383.15 |
0.605 |
0.520 |
1.125 |
0.860 |
1.15 |
2.31 |
3.46 |
2.01 |
| 388.15 |
0.778 |
22.143 |
22.921 |
28.465 |
-2.56 |
13.14 |
10.57 |
-5.12 |
| 393.15 |
0.962 |
14.877 |
15.839 |
15.464 |
1.76 |
12.13 |
13.89 |
6.90 |
| 398.15 |
2.200 |
7.518 |
9.718 |
3.417 |
4.89 |
11.61 |
16.50 |
2.38 |
| 403.15 |
0.595 |
-1.252 |
-0.657 |
-2.105 |
1.18 |
-2.16 |
-0.99 |
-1.84 |
| 408.15 |
0.743 |
1.285 |
2.028 |
1.730 |
1.54 |
0.41 |
1.95 |
0.27 |
| 413.15 |
0.893 |
3.854 |
4.747 |
4.316 |
1.91 |
6.66 |
8.57 |
3.50 |
| 423.15 |
-1.125 |
-1.531 |
-2.656 |
1.361 |
-1.46 |
-2.53 |
-3.99 |
1.74 |
| 433.15 |
0.602 |
0.223 |
0.824 |
0.370 |
1.38 |
-1.26 |
0.12 |
-0.91 |
| 443.15 |
2.369 |
6.543 |
8.912 |
2.762 |
5.41 |
10.87 |
16.28 |
2.01 |
| 453.15 |
-1.704 |
-4.480 |
-6.185 |
2.629 |
-2.26 |
-4.54 |
-6.80 |
2.01 |
| 463.15 |
0.679 |
2.897 |
3.577 |
4.264 |
1.26 |
2.74 |
4.00 |
2.18 |
| 473.15 |
4.310 |
23.213 |
27.523 |
5.386 |
2.06 |
2.73 |
4.80 |
1.33 |
Table 9.
Values of the enthalpic acid base parameters , , / and , and the entropic acid base parameters , , / and of PMMA/silica for as a function of the temperature.
Table 9.
Values of the enthalpic acid base parameters , , / and , and the entropic acid base parameters , , / and of PMMA/silica for as a function of the temperature.
| T(K) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 303.15 |
2.135 |
6.006 |
8.141 |
2.813 |
5.06 |
14.99 |
20.06 |
2.96 |
| 313.15 |
1.805 |
5.719 |
7.524 |
3.169 |
4.61 |
14.06 |
18.67 |
3.05 |
| 323.15 |
1.661 |
5.423 |
7.084 |
3.266 |
4.16 |
13.13 |
17.29 |
3.16 |
| 328.15 |
1.587 |
5.272 |
6.859 |
3.322 |
3.93 |
12.67 |
16.60 |
3.22 |
| 333.15 |
1.512 |
5.118 |
6.630 |
3.385 |
3.70 |
12.20 |
15.90 |
3.30 |
| 338.15 |
2.177 |
6.179 |
8.357 |
2.838 |
-2.30 |
15.92 |
13.62 |
-6.92 |
| 343.15 |
0.385 |
3.423 |
3.808 |
8.884 |
-3.19 |
12.37 |
9.19 |
-3.88 |
| 348.15 |
0.452 |
0.627 |
1.078 |
1.388 |
-2.59 |
4.01 |
1.42 |
-1.55 |
| 353.15 |
0.510 |
-1.015 |
-0.506 |
-1.992 |
0.51 |
4.36 |
4.87 |
8.54 |
| 363.15 |
0.611 |
-1.645 |
-1.035 |
-2.695 |
0.75 |
13.22 |
13.96 |
17.68 |
| 373.15 |
0.385 |
-0.996 |
-0.611 |
-2.585 |
0.45 |
6.65 |
7.10 |
14.73 |
| 378.15 |
-0.439 |
-0.731 |
-1.169 |
1.666 |
-2.86 |
11.09 |
8.23 |
-3.88 |
| 383.15 |
-0.735 |
3.423 |
2.688 |
-4.659 |
-2.31 |
9.21 |
6.90 |
-3.99 |
| 388.15 |
1.235 |
21.076 |
22.312 |
17.060 |
2.59 |
19.86 |
22.46 |
7.66 |
| 393.15 |
1.188 |
18.884 |
20.072 |
15.892 |
2.47 |
21.30 |
23.78 |
8.61 |
| 398.15 |
1.141 |
13.057 |
14.197 |
11.448 |
2.35 |
18.65 |
21.01 |
7.93 |
| 403.15 |
0.887 |
-1.004 |
-0.117 |
-1.132 |
1.64 |
-1.93 |
-0.29 |
-1.17 |
| 408.15 |
0.558 |
-0.941 |
-0.383 |
-1.687 |
0.83 |
-1.86 |
-1.03 |
-2.25 |
| 413.15 |
0.224 |
-0.452 |
-0.228 |
-2.017 |
0.73 |
-1.81 |
-1.08 |
-2.49 |
| 423.15 |
0.786 |
2.985 |
3.771 |
3.798 |
1.57 |
4.81 |
6.38 |
3.08 |
| 433.15 |
1.060 |
9.697 |
10.756 |
9.149 |
2.21 |
13.41 |
15.62 |
6.08 |
| 443.15 |
1.340 |
13.578 |
14.918 |
10.131 |
2.85 |
15.73 |
18.58 |
5.53 |
| 453.15 |
-1.978 |
6.298 |
4.320 |
-3.184 |
-1.53 |
-1.92 |
-3.46 |
1.26 |
| 463.15 |
0.188 |
-0.611 |
-0.422 |
-3.242 |
0.23 |
-0.74 |
-0.51 |
-3.25 |
| 473.15 |
0.571 |
1.133 |
1.703 |
1.985 |
1.04 |
-0.74 |
0.31 |
-0.71 |
Table 10.
Values of the enthalpic acid base parameters , , / and , and the entropic acid base parameters , , / and of silica.
Table 10.
Values of the enthalpic acid base parameters , , / and , and the entropic acid base parameters , , / and of silica.
| Solid surface |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Silica |
0.807 |
0.412 |
1.219 |
0.510 |
1.39 |
-1.32 |
0.07 |
-0.95 |
Table 11.
Values of the dispersion factor A of the various PMMA/silica as a function of the temperature. The maxima of A are represented in bold.
Table 11.
Values of the dispersion factor A of the various PMMA/silica as a function of the temperature. The maxima of A are represented in bold.
| T(K) |
|
|
|
|
PMMA |
| 303.15 |
378.20 |
395.51 |
354.74 |
337.33 |
297.06 |
| 313.15 |
367.18 |
371.55 |
340.26 |
319.84 |
276.45 |
| 323.15 |
356.15 |
353.99 |
319.89 |
299.94 |
268.35 |
| 328.15 |
350.64 |
348.49 |
327.15 |
308.07 |
274.64 |
| 333.15 |
345.13 |
353.01 |
340 |
322.86 |
296.16 |
| 338.15 |
339.62 |
357.02 |
330.02 |
310.12 |
272.62 |
| 343.15 |
334.11 |
361.76 |
317.89 |
297.17 |
257.28 |
| 348.15 |
328.60 |
341.88 |
304.58 |
284.75 |
245.91 |
| 353.15 |
323.09 |
322.53 |
289.18 |
272.25 |
237.62 |
| 363.15 |
312.07 |
296.06 |
266.8 |
250.08 |
227 |
| 373.15 |
301.04 |
271.64 |
237.43 |
219.87 |
231.39 |
| 378.15 |
295.53 |
266.5 |
229.4 |
215.81 |
262.31 |
| 383.15 |
290.02 |
263.87 |
248.84 |
267.22 |
307.3 |
| 388.15 |
284.51 |
271.09 |
302.26 |
317.52 |
252.09 |
| 393.15 |
279.00 |
290.69 |
274.76 |
296.44 |
221.75 |
| 398.15 |
273.49 |
311.45 |
256.56 |
272.99 |
209.51 |
| 403.15 |
267.98 |
291.54 |
242.31 |
238.62 |
199.78 |
| 408.15 |
262.47 |
268.3 |
222.02 |
215.57 |
196.16 |
| 413.15 |
256.96 |
247.67 |
202.81 |
198.03 |
193.27 |
| 423.15 |
245.93 |
233.94 |
196.97 |
194.06 |
215.82 |
| 433.15 |
234.91 |
238.92 |
231.59 |
226.19 |
258.37 |
| 443.15 |
223.89 |
241.02 |
192.79 |
180.85 |
195.77 |
| 453.15 |
212.87 |
214.66 |
175.48 |
156.95 |
166.58 |
| 463.15 |
201.85 |
206.05 |
168.88 |
150.69 |
158.53 |
| 473.15 |
190.82 |
180.38 |
146.81 |
131.75 |
136.51 |