Submitted:
05 March 2024
Posted:
05 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
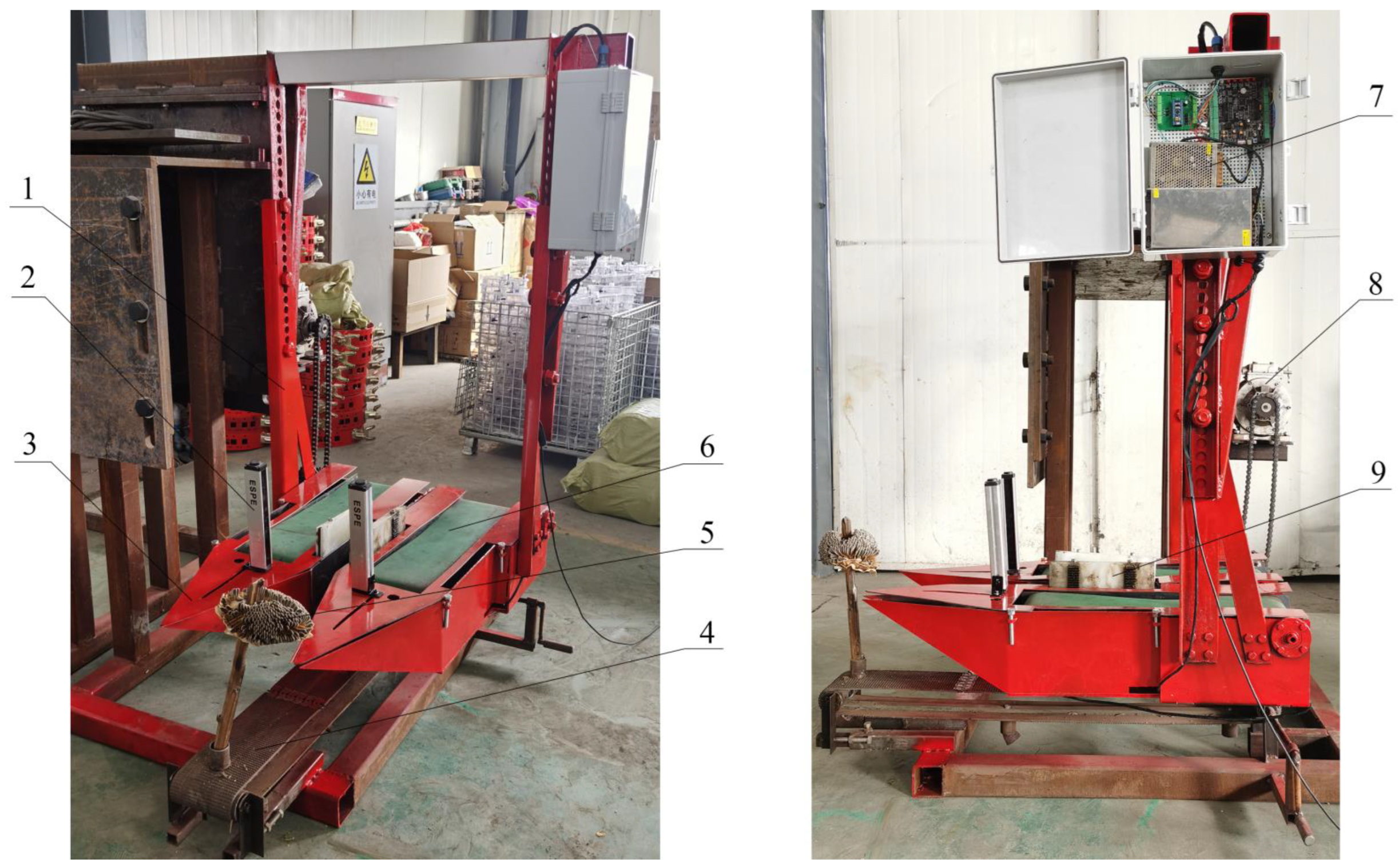
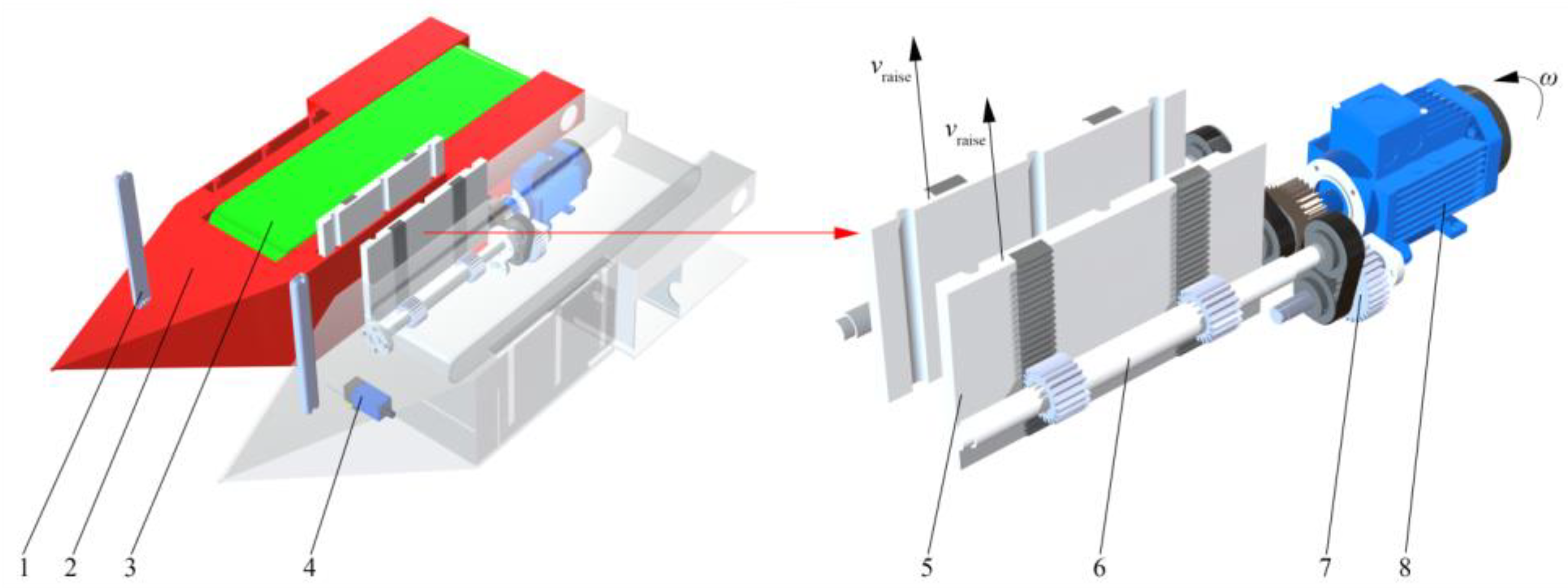
2.1. Overall Structure of Sunflower Harvesting Platform
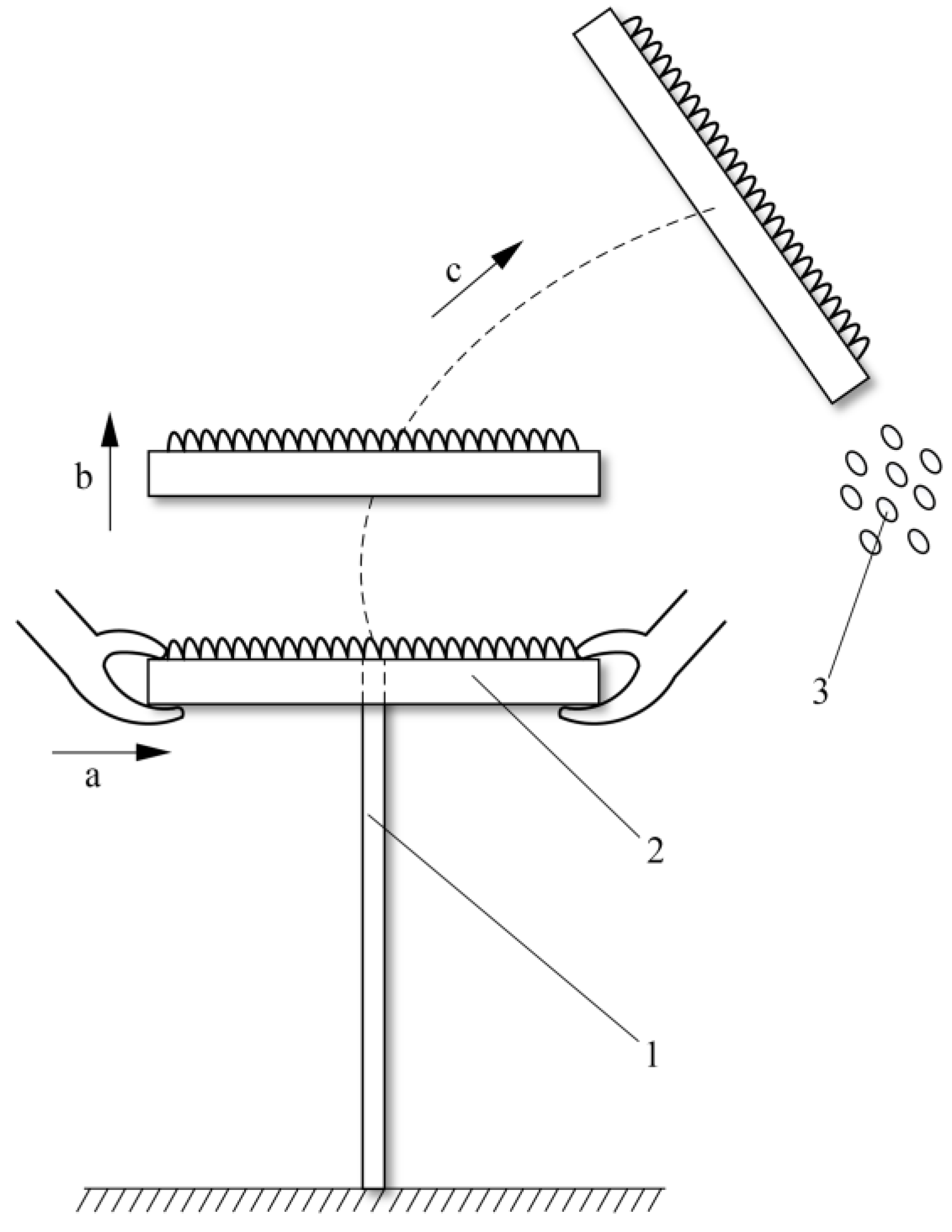
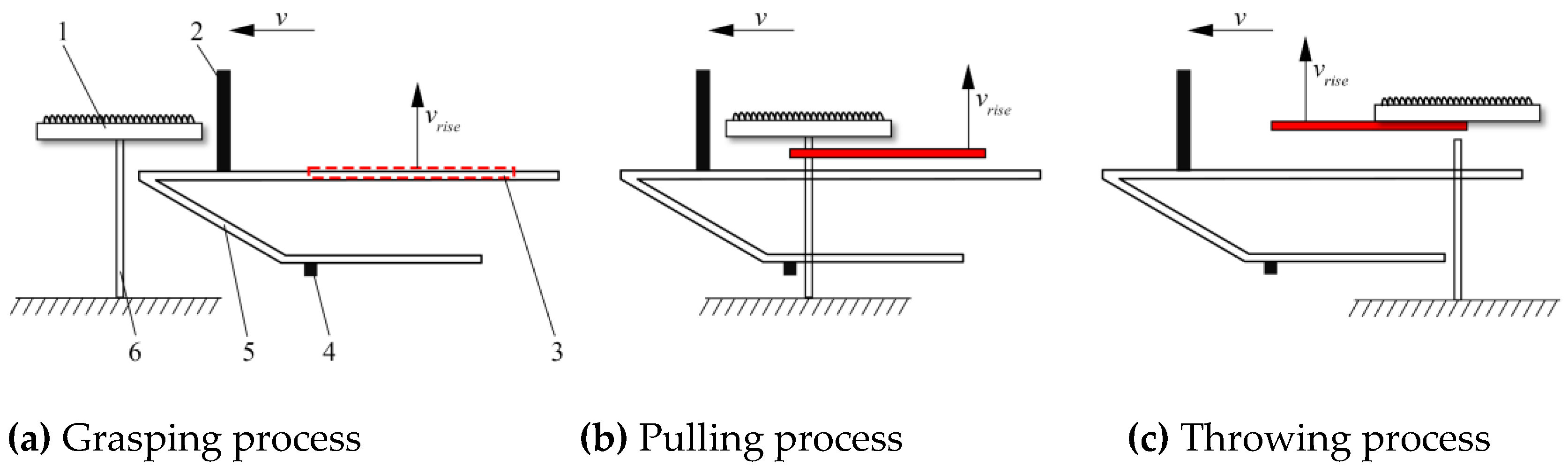
2.2. The Working Principle of Sunflower Harvesting Platform
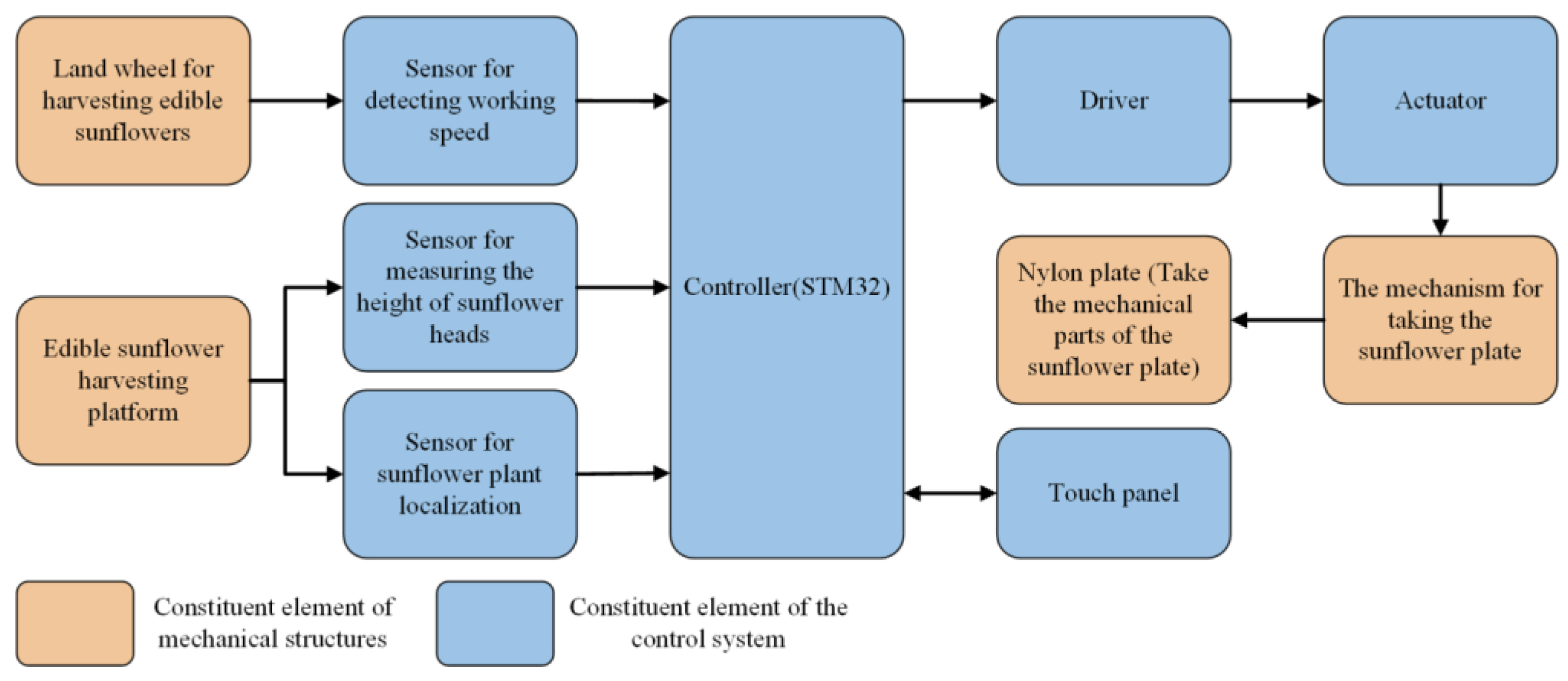
2.3. Design of Plate Taking Control System
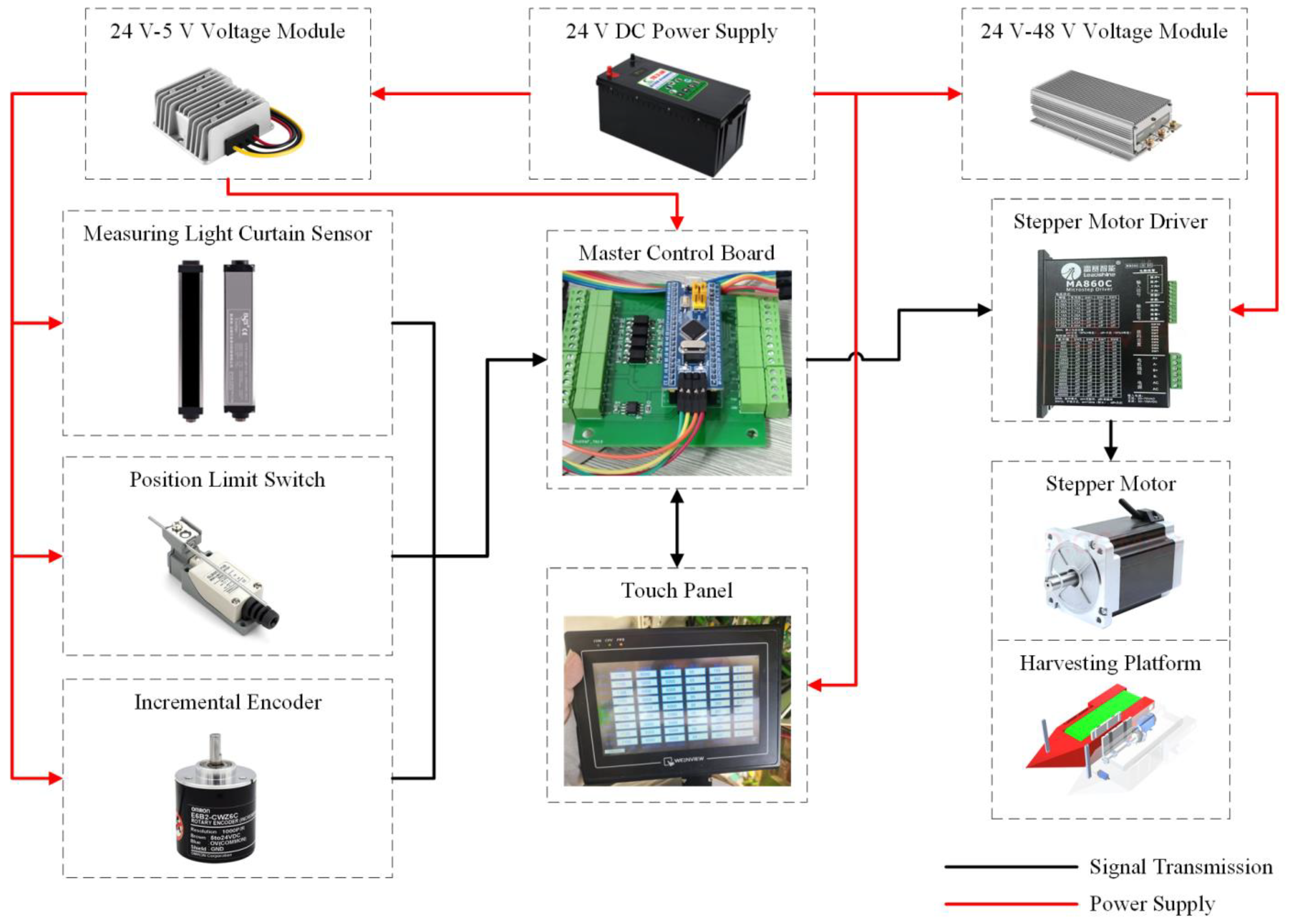
2.4. Hardware Design of Control System
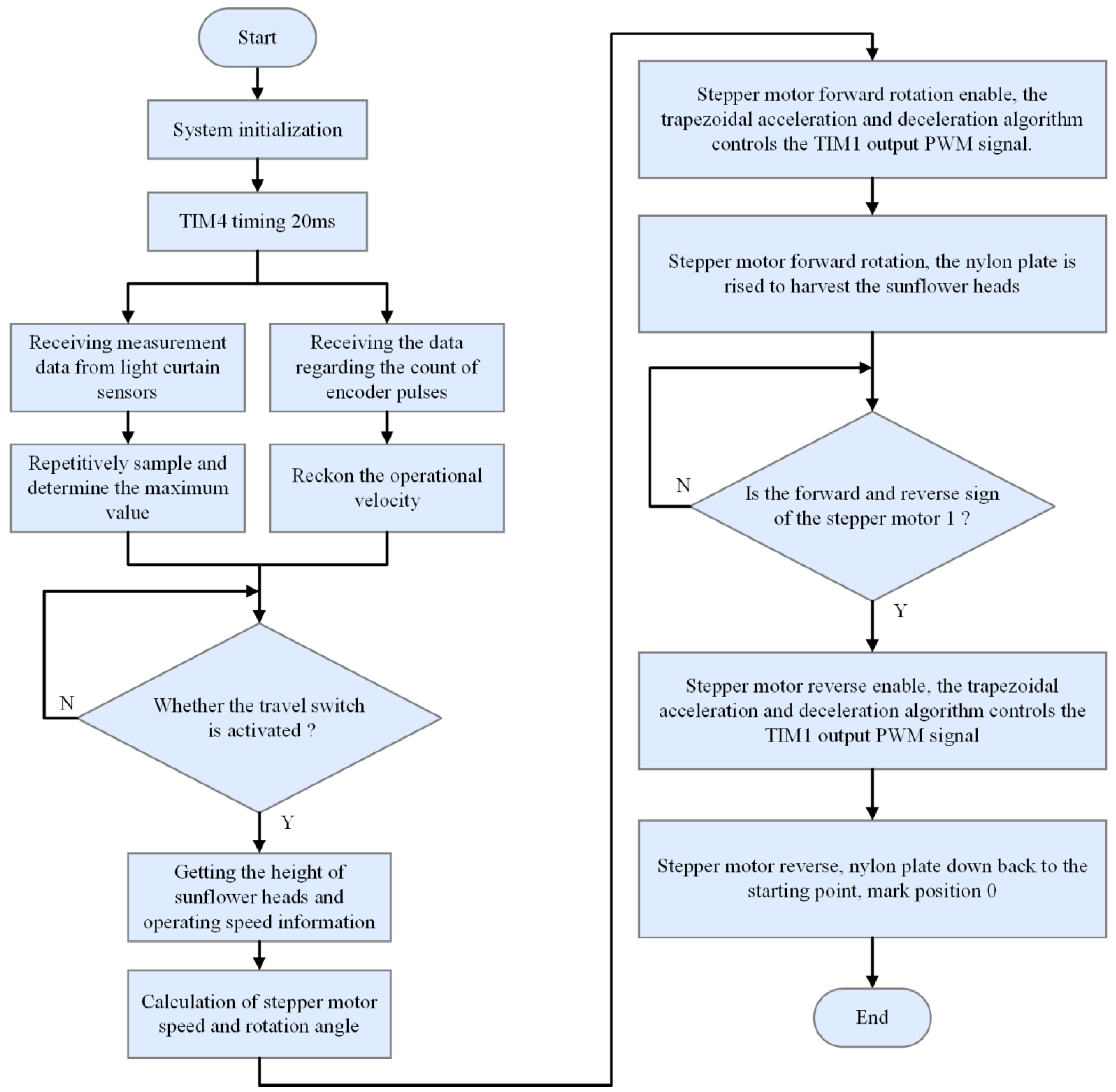
2.5. Control System Software Design
2.6. Design of Trapezoidal Acceleration and Deceleration Control Algorithm
2.7. Bench Experiment Materials and Conditions
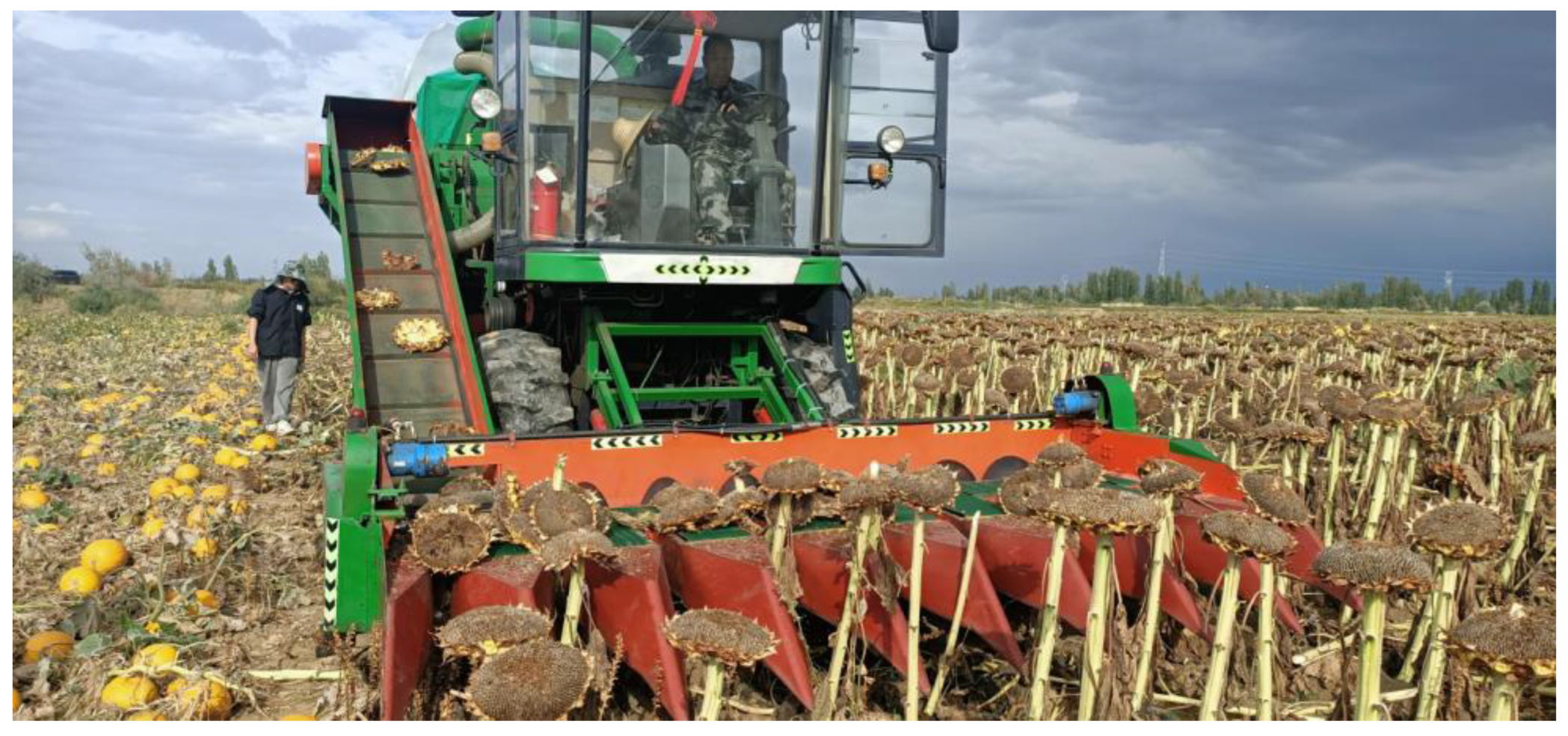
2.8. Field Experiment Materials and Conditions
3. Result and Analysis
3.1. Bench Experiment
3.1.1. Height Recognition Experiment of Sunflower Plate Inserted on Its Rod
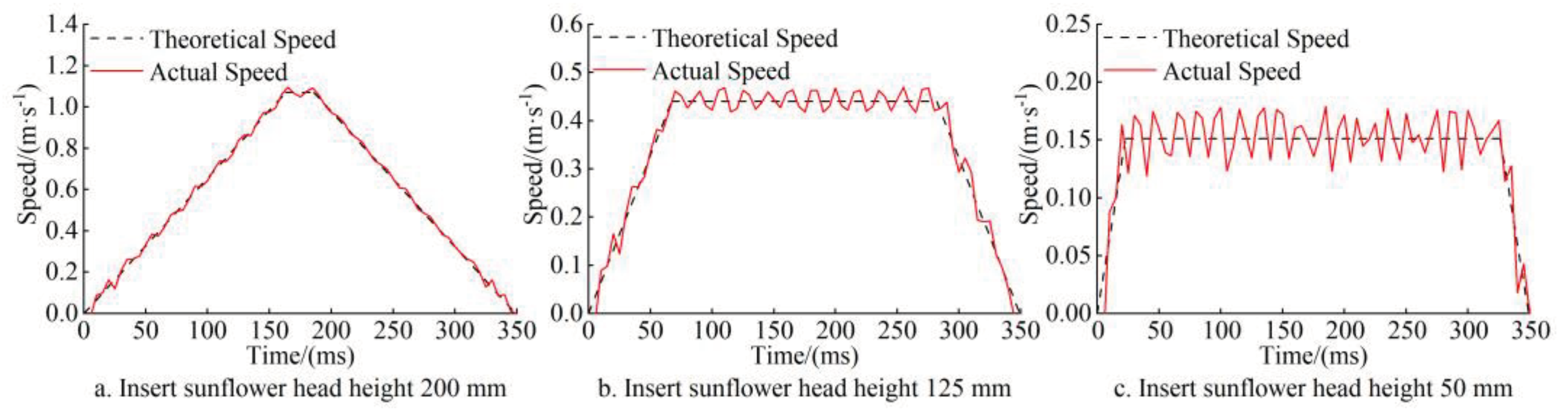
3.1.2. The Speed Control Experiment of Taking Sunflower Plate
3.1.3. Experiment of Picking Sunflower Plate
3.2. Field Experiment
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- According to the analysis of the operating parameters of the sunflower plate and the working principle of the harvesting device, the overall scheme of the plate control system was determined. The system is composed of working speed detection sensor, position detection sensor, height detection sensor, controller, driver and stepper motor. According to the relevant parameters, the relationship between the speed of the stepper motor, the rotation angle, the working speed and the height of the sunflower plate inserted on the sunflower rod is established.
- (2)
- The sunflower harvest experiment bench was built to carry out the bench experiment of the control system. The results showed that the absolute error of the height measurement of each edible sunflower was less than 4 mm. The actual speed curve of the taking plate components basically conforms to the trapezoidal acceleration and deceleration motion law, and the speed error of the taking plate components does not exceed 0.028 m/s. Under the simulated field operating conditions, the maximum positioning error was 1.25 mm, the maximum relative error was 1.2 %, the average relative error was 0.94 %, and the overall grain loss rate was less than 2.26 %. It shows that the algorithm of the system is reliable, the positioning accuracy is high, the grain loss rate is small, and the picking operation can be completed well.
- (3)
- The taking plate control system designed in this paper was installed on the sunflower harvester, and the field experiment was carried out. The results showed that the total loss rate was less than 5 % when the forward speed of the harvester was 0.4~0.8 m/s. When the forward speed is 0.6 m/s, the minimum harvest loss rate of the unit is 2.32 %. It shows that the control system meets the requirements of the harvesting operation of the edible sunflower in the segmented harvesting mode, which improves the harvesting efficiency of the edible sunflower and reduces the harvesting loss rate.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Z.Q. Technical solutions for mechanized harvest of anemone. Mechanization of Rural and Pastoral Areas 2019, 17-18. (in Chinese).
- Vargas, M.; Albors, A.; Chiralt, A. Application of chitosan-sunflower oil edible films to pork meat hamburgers. Proc Food Sci 2011, 1, 39-43. [CrossRef]
- Zorzi, C.Z.; Garske, R.P.; Flôres, S.H.; Thys, R.C.S. Sunflower protein concentrate: A possible and beneficial ingredient for gluten -free bread. Innov Food Sci Emerg 2020, 66. [CrossRef]
- Luan, S.B. Study on countermeasures of sunflower production and development in Heilongjiang Province. Agricultural Technology Service 2017, 34, 152. (in Chinese).
- Han, C.J.; Wang, C.C.; Zhu, X.L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.J. Design of imitating manual harvesting device for edible sunflower. Transactions of the CSAE 2019, 35, 14-22. (in Chinese). [CrossRef]
- Han, C.J.; Diao, H.W.; Qiu, S.L.; Zhu, X.L.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, P.P. Design and Experiment of Edible Sunflower Plate Taking Device Based on Manual Plate Taking Principle. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery 2022, 53, 123-131. (in Chinese). [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.K.; Han, C.J.; Li, G.X.; Xu, Y.; Du, X.H. Design and test of flexible belt type sunflower tray harvester. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization 2022, 43, 33-38. (in Chinese). [CrossRef]
- Lian, G.D.; Zong, W.Y.; Feng, W.; Ma, L.; F., C.Y.; Wei, X.X. Design and Experiment of Cutting Threshing Integrated Type Header for Harvesting of Edible Sunflower. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery 2023, 54, 122-131+154. (in Chinese). [CrossRef]
- Han, C.J.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, X.L.; Zhang, X.J. Design and Test of Edible Sunflower Plate Harvester Base on Reciprocating Lever. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research 2018, 40, 125-128. (in Chinese). [CrossRef]
- Csanadi, T.; Hamphoff, B. A header for efficient sunflower harvesting - Deployment of special sunflower head. Vdi Bericht 2007, 2001, 343-346.
- Dalmis, I.S.; Kayisoglu, B.; Bayhan, Y.; Toruk, F.; Durgut, F.T. Determination of the Effects of Rotation Speed and Forward Speed on Combine Harvester Driven Stalk Chopper Assembly Operating Performance. J Agr Sci-Tarim Bili 2013, 19, 54-62. [CrossRef]
- Latterini, F.; Stefanoni, W.; Sebastiano, S.; Baldi, G.M.; Pari, L. Evaluating the Suitability of a Combine Harvester Equipped with the Sunflower Header to Harvest Cardoon Seeds: A Case Study in Central Italy. Agronomy-Basel 2020, 10, 1981-1993. [CrossRef]
- Startsev, A.S.; Makarov, S.A.; Nesterov, E.S.; Kazakov, Y.F.; Terentyev, A.G. Comparative evaluation of the operation of a combine harvester with an additional sieve with adjustable holes for sunflower harvesting. Iop C Ser Earth Env 2020, 433, 1-9. [CrossRef]
- Startsev, A.S.; Demin, E.E.; Danilin, A.V.; Vasilyev, O.A.; Terentyev, A.G. Results of the production test of sunflower harvesting attachment with an auger reel. Iop C Ser Earth Env 2020, 433, 1-7. [CrossRef]
- Stefanoni, W.; Latterini, F.; Malkogiannidis, V.; Salpiggidis, V.; Alexopoulou, E.; Pari, L. Mechanical Harvesting of Castor Bean (L.) with a Combine Harvester Equipped with Two Different Headers: A Comparison of Working Performance. Energies 2022, 15. [CrossRef]
- Mavolo, L.; Rivero, D.; Botta, G. Evaluation of different construction materials in the shield sunflower harvester head (Helianthus annuus L.) for the reduction of capitulum shelling. Agriscientia 2022, 39, 1-10. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Luo, C.M.; Zong, W.Y.; Huang, X.M.; Ma, L.N.; Lian, G.D. Optimization of Clamping and Conveying Device for Sunflower Oil Combine Harvester Header. Agriculture-Basel 2021, 11, 859-878. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.X.; Zhang, Y.; He, Y.Z. Design and test of backpack harvester for sunflowers. Journal of Machine Design 2018, 35, 67-71. (in Chinese). [CrossRef]
- Jian, Z.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.P.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, X.M. The mechanical harvesting technology of edible sunflower by 4ZXRKS-4 harvester. Journal of Agricultural Engineering Technology 2018, 38, 48. (in Chinese). [CrossRef]
- Jian, Z.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.P.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, X.M. Structural performance analysis and parameter debugging of 4ZXRKS-4 type sunflower grain harvester. Journal of Agricultural Engineering Technology 2019, 39, 62. (in Chinese). [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Tang, W.; Dong, J.X.; Wang, F. Positioning-control Based on Trapezoidal Velocity Curve for High-precision Basis Weight Control Valve. Paper and Biomaterials 2017, 2, 42-50.
- Cai, N.; Qin, G.; Zhang, H.M.; Zhang, H.B. Research on speed control technology of stepper motor. Electronic Measurement Technology 2021, 44, 84-88. (in Chinese). [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.J.; Liu, Q.X.; Zhou, L.; Bu, L.; Li, X.Q.; Zhang, J.Q. Modeling of stepper motor control system and optimization of acceleration and deceleration curve. Electric Machines and Control 2018, 22, 37-42+52. (in Chinese). [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Wang, N.; Cao, W.N.; Li, J.Q.; Ye, X.C. Fuzzy PID control of manipulator positioning for taking the whole row seedlings of tomato plug seedlings. Transactions of the CSAE 2020, 36, 21-30. (in Chinese). [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Du, Y.F.; Liu, L.; Mao, E.R. Design and experiment of the automatic control system for low damage corn grain direct harvesters. Transactions of the CSAE 2023, 39, 34-42. (in Chinese). [CrossRef]
- Technical Protocols of production mechanization in Sunflower. 2013, DB 65/T 3541--2013.
- Liu, G.W.; Ni, Y.L.; Yang, T.X.; Qi, Y.D.; Jin, C.Q. Design and experiment of header height automatic control system for soybean harvester. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization 2023, 44, 155-160+152. (in Chinese). [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.M.; Wang, W.X.; Li, X.; Chen, F.X.; Shen, X.C. Design and test of cotton top height measurement system based on automatic control. Journal of GANSU Agricultural University 2018, 53, 176-184. (in Chinese). [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.J.; Jin, Z.B.; Bai, X.P.; Wang, S.J.; Huang, W.Y. Design and Experiment of Servo Control System for Sugarcane Header. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery 2023, 54, 119-128+138. (in Chinese). [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.B. Design and Experiment of Servo Control System for Sugarcane Header. master, Shenyang Agricultural University, 2023.
- Equipment for harvesting-Combine harvesters-Test procedure. 2008, GB/T 8097-2008.
- Reliability determination test methods for grain combine harvesters. 2008, JB/T 6287-2008.


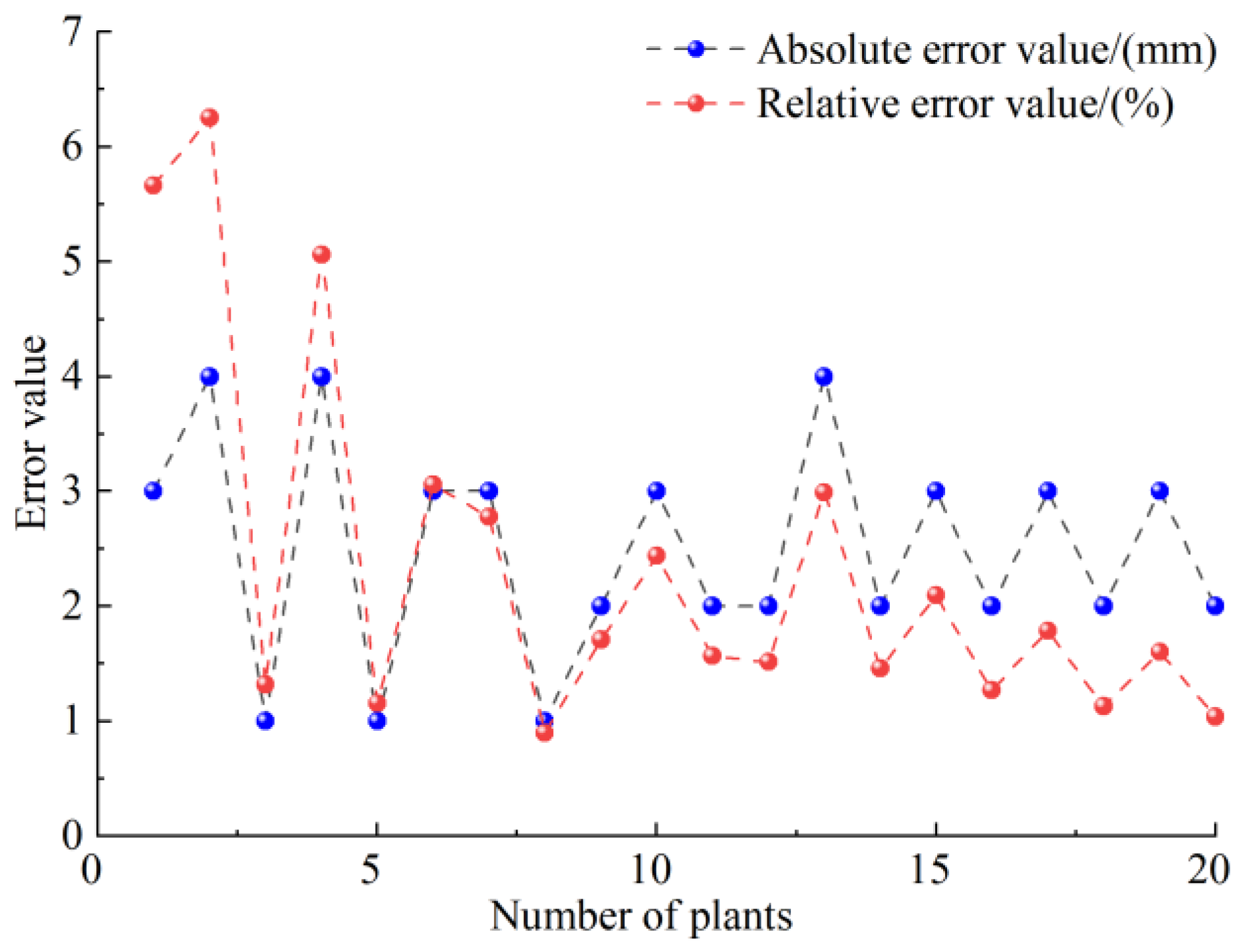
| Number | Actual height value (mm) | The measured value of the light curtain sensor (mm) | Absolute Error (mm) | Relative Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 53 | 50 | 3 | 5.66 |
| 2 | 64 | 60 | 4 | 6.25 |
| 3 | 76 | 75 | 1 | 1.32 |
| 4 | 79 | 75 | 4 | 5.06 |
| 5 | 86 | 85 | 1 | 1.16 |
| 6 | 98 | 95 | 3 | 3.06 |
| 7 | 108 | 105 | 3 | 2.78 |
| 8 | 111 | 110 | 1 | 0.90 |
| 9 | 117 | 115 | 2 | 1.71 |
| 10 | 123 | 120 | 3 | 2.44 |
| 11 | 127 | 125 | 2 | 1.57 |
| 12 | 132 | 130 | 2 | 1.52 |
| 13 | 134 | 130 | 4 | 2.99 |
| 14 | 137 | 135 | 2 | 1.46 |
| 15 | 143 | 140 | 3 | 2.10 |
| 16 | 157 | 155 | 2 | 1.27 |
| 17 | 168 | 165 | 3 | 1.79 |
| 18 | 177 | 175 | 2 | 1.13 |
| 19 | 188 | 185 | 3 | 1.60 |
| 20 | 192 | 190 | 2 | 1.04 |
| Number | Operating Speed (m/s) | Theoretical Displacement (mm) | Actual Displacement (mm) | Absolute Error (mm) | Relative Error (%) |
Total Loss Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.4 | 50 | 50.60 | 0.60 | 1.20 | 1.31 |
| 2 | 0.4 | 125 | 124.20 | 0.80 | 0.64 | 1.62 |
| 3 | 0.4 | 200 | 198.80 | 1.20 | 0.60 | 1.98 |
| 4 | 0.6 | 50 | 50.80 | 0.80 | 1.60 | 1.43 |
| 5 | 0.6 | 125 | 126.40 | 1.40 | 0.87 | 1.74 |
| 6 | 0.6 | 200 | 201.25 | 1.25 | 1.12 | 2.11 |
| 7 | 0.8 | 50 | 50.40 | 0.40 | 0.80 | 1.55 |
| 8 | 0.8 | 125 | 126.20 | 1.20 | 0.96 | 1.83 |
| 9 | 0.8 | 200 | 201.40 | 1.40 | 0.70 | 2.26 |
| Speed of Advance (m/s) | Total Loss Rate (%) |
|---|---|
| 0.4 | 2.87 |
| 0.6 | 2.32 |
| 0.8 | 3.16 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




