Submitted:
26 February 2024
Posted:
27 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Plant Material and Growth Conditions
2.2. Laboratory Analysis of the Presence of the Fungus
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of Plant Growth and Flowering
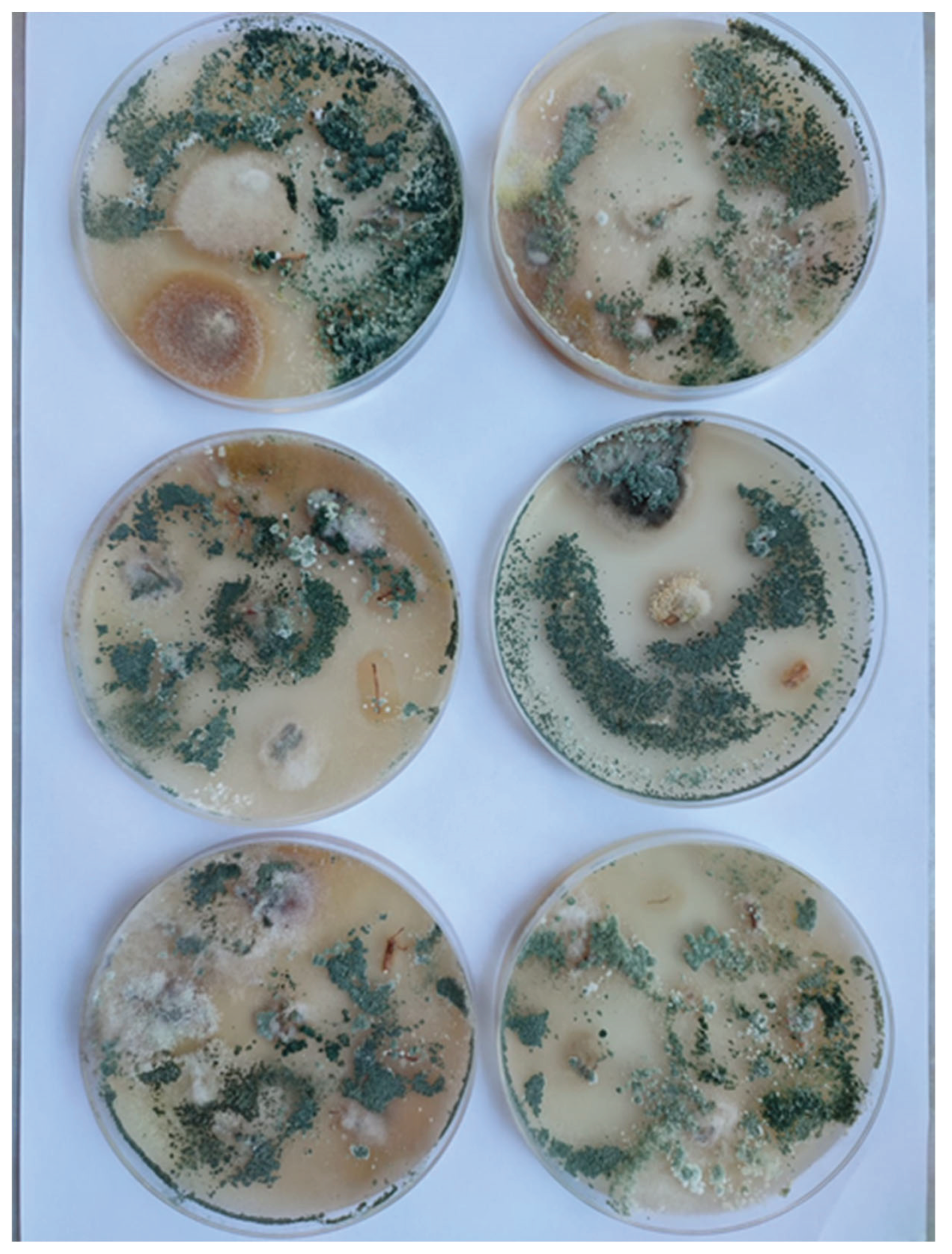
3.2. Analysis of the Presence of the Trichoderma Fungus
4. Discussion
4.1. Plant Growth and Flowering after Applying the Pruning
4.2. Growth and flowering of plants after application of Trichoderma atroviride
4.3. Growth and flowering of plants after foliar spraying with fertilizer
4.4. Growth and flowering of plants after root application of BlackJak preparation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Orozco-Obando, W., G.N. Hirsch, and H.Y. Wetzstein. Genotypic variation in flower induction and development in Hydrangea macrophylla. HortScience 2005, 40, 1695–1698. [CrossRef]
- van Gelderen, C.J., van Gelderen D.M. Encyclopedia of hydrangeas. Timber Press, Portland 2004.
- McClintock, E. A monograph of the genus Hydrangea. Proc. Calif. Acad. Sci. 1957, 24, 147–256. [Google Scholar]
- Halcomb M. Sandra R. Hydrangea production. United States: University of Tennessee, 2010.
- Durlak, W., Marcinek, B., Szmagara, M., Dudkiewicz, M., Konopińska-Mamej, A. Effect of selected preparations on some biometric features of ‘Tardiva’ panicled hydrangea (Hydrangea paniculata Siebold) depending on the irrigation frequency. Acta Sci. Pol. Hortorum Cultus 2019, 18(2), 39–51. [CrossRef]
- Pineda M., Yu B., Tian Y., Morante N., Salazar S., Hyde P.T., Setter T.L., Ceballos H. Effect of pruning young branches on fruit and seed set in Cassava. Frontiers in Plant Science 2020, 11, 1107. [CrossRef]
- Salih ZK, Ahmed MA, Masouleh SSS, Sanam MA. Pruning intensity and amino acids tryptophan and glycine on growth and flowering of Jasminum sambac. Ornamental Horticulture 2021, 27, 20–25. [CrossRef]
- Weraduwage A.M., Chen J., Weise S.E., Sharkey T.D., Anozie F.C., Morales A. The relationship between leaf area growth and biomass accumulation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Frontiers in Plant Science 2015, 6, 167. [CrossRef]
- Persello S, Grechi I, Boudon F, Normand F. Nature abhors a vacuum: deciphering the vegetative reaction of the mango tree to pruning. European J. Agronomy 2019, 104, 85–96. [CrossRef]
- Amarnath K.S., Mishra S., Singh R.K. Effect of pruning in pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) for shoot growth, flowering and fruit yield. Current J. App. Sci. Tech., 2020, 39, 114–123.
- Liu J.D., Ye X.S., Yu G.Y., Kang X.R., Wang X. Effect of pruning on endo-genetic hormone content associated with differentiation of blueberry flower buds. J. Physics 2021, 2009, 012034.
- Ponchia G., Simeoni S., Zanin G. Influence of Winter Pruning on Ornamental Plants Grown in Two Kinds of Container. Acta Horticulturae 2010, 881, 581–84.
- Zhang D,, Cai W,, Zhang X,, Li W,, Zhou Y,, Chen Y,, Mi Q,, Jin L,, Xu L,, Yu X,, Li Y. Different pruning level effects on flowering period and chlorophyll fluorescence parameters of Loropetalum chinense var. rubrum. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13406. [CrossRef]
- Chopde N., Lokhande S., Bhande M.H., Warkade V. P. Impact of time and level of pruning on growth and flowering of Jasminum sambac (L.). Research on Crops 2017, 18(1), 123–128. [CrossRef]
- Zhang C., Jia M..L, Song Z.Q., Wu J., Duan J.J. Effects of different pruning methods on the yield and quality of cut corolla rose. Journal of Shanxi Agricultural Sciences 2018, 46, 1314–1316.
- Hassanein, A.M.A. Improved quality and quantity of winter flowering in rose (Rosa spp.) by controlling the timing and type of pruning applied in autumn. World J. Agric. Sci http://www.idosi.org/wjas/wjas6(3)/5.pdf. 2010, 6(3), 260–67.
- Shoresh, M., Harman, G.E., Mastouri F. Induced systemic resistance and plant responses to fungal biocontrol agents. Annual Review of Phytopathology 2010, 48, 21–43. [CrossRef]
- Rubio M. B., Domínguez S., Monte E., Hermosa R. Comparative study of Trichoderma gene expression in interactions with tomato plants using high density oligonucleotide microarrays. Microbiology 2012, 158(1), 119–128. [CrossRef]
- Vinale, F., Nigro, M., Sivasithamparam, K., Flematti, G., Ghisalberti, E. L., Ruocco, M., Lorito, M. Harzianic acid: a novel siderophore from Trichoderma harzianum. FEMS Microbiology Letters 2013, 347(2), 123–129. [CrossRef]
- Stewart A., Hill R. Applications of Trichoderma in Plant Growth Promotion. In Biotechnology and Biology of Trichoderma, Editors: Gupta V.K., Schmoll M., Herrera-Estrella A., Upadhyay R.S., Druzhinina I., Tuohy M.G. 2014, 415–428. Amsterdam. Elsevier. [CrossRef]
- Poveda, J. Baptista, P. Filamentous fungi as biocontrol agents in olive (Olea europaea L.) diseases: mycorrhizal and endophytic fungi. Crop Protection 2021, 146, 105672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S. L., Ruocco, M., Vinale, F., Nigro, M., Marra, R., Lombardi, N., Lorito, M.Trichoderma-based products and their widespread use in agriculture. Open Mycology J 2014, 8(1). [CrossRef]
- Contreras-Cornejo H.A., Macías-Rodríguez L., Cortés-Penagos C., López Bucio J. Trichoderma virens, a plant beneficial fungus, enhances biomass production and promotes lateral root growth through an auxin dependent mechanism in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2009, 149, 1579–1592. [CrossRef]
- Lorito M., Woo S.L., Harman G.E., Monte E. Translational Research on Trichoderma: From ’Omics to the Field. Annual Review of Phytopathology 2010, 48(1), 395–417. [CrossRef]
- Samolski I., Rincón A.M., Pinzón L.M., Viterbo A., Monte E. The quid.74 gene from Trichoderma harzianum has a role in root architecture and plant biofertilization. Microbiology 2012, 158, 129–138. [CrossRef]
- López-Bucio, J., Pelagio-Floresa, R. Herrera-Estrella, A. Trichoderma as biostimulant: exploiting the multilevel properties of a plant beneficial fungus. Scientia Horticulturae 2015, 196, 109–123. [CrossRef]
- Di Vaio C., Testa A., Cirillo A., Conti S. Slow-Release Fertilization and Trichoderma Harzianum-Based Biostimulant for the Nursery Production of Young Olive Trees (Olea Europaea L.). Agronomy Research 2021, 19(3), 1396–1405. [CrossRef]
- Bi, G., Scagel. C.F. Nitrogen uptake and mobilization by hydrangea leaves from foliar sprayed urea in fall depend on plant nitrogen status. HortScience 2008, 43, 2151–2154. [CrossRef]
- Bi, G., Scagel, C.F., Harkess, R.L. Rate of nitrogen fertigation during vegetative growth and spray application of urea in the fall alters growth and flowering of florists’ hydrangeas. HortScience 2008, 43, 472–477. [CrossRef]
- De Clercq, P.; Pauwels, E.; Top, S.; Steppe, K.; Van Labeke, M.C. Effect of Seaweed-Based Biostimulants on Growth and Development of Hydrangea paniculata under Continuous or eriodic Drought tress. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szydło W., Pacholczak A. Effect of Biopreparation Asahi SL and Fertilizer Osmocote 5-6M on Growth of Hydrangea Arborescens ‘Anabelle’. Annals of Warsaw University of Life Sciences - SGGW, Horticulture and Landscape Architecture 2010, 31, 3–9.
- Fascella, G., Montoneri, E., Ginepro, M., Francavilla, M. Effect of urban biowaste derived soluble substances on growth, photosynthesis and ornamental value of Euphorbia x lomi. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 197, 90–98. [CrossRef]
- Demirer, T. Effect of leonardite application on leaf nutrient content and fruit chemical parameters of cherry (Prunus avium L.). J. Plant Nutr. 2019, 42, 2532–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olego, M.Á.; Cuesta Lasso, M.; Quiroga, M.J.; Visconti, F.; López, R.; Garzón-Jimeno, E. Effects of Leonardite Amendments on Vineyard Calcareous Soil Fertility, Vine Nutrition and Grape Quality. Plants 2022, 11, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jităreanu, C. D., Slabu, C., Marta, A. E., Bologa Covașă, M. The effect of biostimulants on the process of photosynthesis at the lettuce. Lucrări Ştiinţifice 2020, 63(2), 119–124, https:/doi:repository.uaiasi.ro/xmlui/handle/20.500.12811/1116.
- Jasim, A.H. Effect of soil sulfur fertılızer and some foliar fertilizers on growth and yield of broccoli in salıne soil. Annals of West University of Timişoara. Biology 2015, 18(2), 123–130. [Google Scholar]
- Yahya, A. B., Al-Sawaf, M. D., Almura, N. Y. Effect of biofertilizer trichoderma harzianum t-22 application, growing medium and training methods on some chararctrestics for Lantana camara plants. Mesopotamia J. Agric 2021, 49(1), 95–103.
- Cruz, L. Rutz D., Fernanda L. F., Gerusa, P., Kist, S., Maldaner, J. Development and Quality of Gladiolus Stems with the Use of Vermicompost and Trichoderma Sp. in Substrate. Ornamental Hortic. 2018, 24, 70–77. [CrossRef]
- Andrzejak, R., Janowska, B. Trichoderma spp. Improves flowering, quality, and nutritional status of ornamental plants. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2022, 23(24), 15662. [CrossRef]
- Prisa, D. Trichoderma Harzianum: Biocontrol to Rhizoctonia Solani and Biostimulation in Pachyphytum Oviferum and Crassula Falcata. World J. Advan. Res. Rev. 2018, 3(3), 011–018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisodia A., Pal A. i Singh A.K. Varietal Response and Effect of Trichoderma on Flowering in Gladiolus. J. Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry 2018, 7(3), 3658–3660.
- Sofo, A., Tataranni, G., Xiloyannis, C., Dichio, B., Scopa, A. Direct effects of Trichoderma harzianum strain T-22 on micropropagated shoots of GiSeLa6 (Prunus cerasus) rootstock. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2012, 76, 33–38. [CrossRef]
- Harman, G., Howell, C., Viterbo, A. Chet I., Lorito M. Trichoderma species — opportunistic, avirulent plant symbionts. Nat Rev Microbiol, 2004, 2, 43–56. [CrossRef]
- Ousley M.A., Lynch J.M. Whipps J. M. Effect of Trichoderma on Plant Growth: A Balance between Inhibition and Growth Promotion. Microbial Ecology 1993, 26(3), 277–85.
- Lorito, M., Woo, S. L., Harman, G. E., Monte, E. Translational research on Trichoderma: from'omics to the field. Annual Review of Phytopathology 2010, 48, 395–417. [CrossRef]
- Fiorentino, N., Ventorino, V., Woo, S. L., Pepe, O., De Rosa, A., Gioia, L., Rouphael, Y. Trichoderma-based biostimulants modulate rhizosphere microbial populations and improve N uptake efficiency, yield, and nutritional quality of leafy vegetables. Frontiers in Plant Science 2018, 9, 743. [CrossRef]
- Tucci, M., Ruocco, M., De Masi, L., De Palma, M., Lorito, M. The beneficial effect of Trichoderma spp. on tomato is modulated by the plant genotype. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2011, 12, 341–354. [CrossRef]
- Avis T.J., Gravel V., Antoun H., Tweddell R. J. (2008) Multifaceted beneficial effects of rhizosphere microorganisms on plant health and productivity. Soil Biol. Bioch. 2008, 40, 1733–1740. [CrossRef]
- Di Marco S., Osti F. Effects of Trichoderma applications on vines grown in organic nursery. 2nd Conference of the International Society of Organic Agriculture Research ISOFAR, Modena, Italy, June 18-20, 2008.
- Zhu G., Yang X., Lv M., Wang H., Liu Z., Zhang R. Effects of Trichoderma asperellum on Growth and Leaf Photosynthetic characters of Populus davidiana ×P. alba var. pyramidalis Seedlings. Bulletin of Botanical Research 2018, 38(1), 64–74.
- Rakibuzzaman, M., Akand, M. H., Siddika, M., Uddin, A. J. Impact of Trichoderma application as bio-stimulator on disease suppression, growth and yield of potato. J. Biosc. Agric. Research 2021, 27, 2252–2257. [CrossRef]
- Świerczyński S., Antonowicz A. i Bykowska J. The Effect of the Foliar Application of Biostimulants and Fertilisers on the Growth and Physiological Parameters of Maiden Apple Trees Cultivated with Limited Mineral Fertilization. Agronomy 2021, 11(6), 1216. [CrossRef]
- Świerczyński S., Bosiacki M. The Effect of Foliar Spray Treatments with Various Biostimulants and Fertilisers on the Growth of M.9 Rootstock Stoolings. Agronomy 2021, 12(3), 689. [CrossRef]
- Świerczyński S., Borowiak K., Bosiacki M., Urbaniak M., Malinowska A. Estimation of the growth of 'Vanda' maiden sweet cherry on three rootstocks and after application of foliar fertilization in a nursery. Acta Scientiarum Polonorum Hortorum Cultus 2019, 18(1), 109–18.
- Canellas, L. P., Olivares, F. L., Aguiar, N. O., Jones, D. L., Nebbioso, A., Mazzei, P. (2015). Humic and fulvic acids as biostimulants in horticulture. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 196, 15–27. [CrossRef]
- Nardi, S., Pizzeghello, D., Schiavon, M., and Ertani, A. Plant biostimulants: physiological responses induced by protein hydrolyzed-based products and humic substances in plant metabolism. Sci. Agric. 2016, 73, 18–23. [CrossRef]
- Barone, V., Bertoldo, G., Magro, F., Broccanello, C., Puglisi, I., Baglieri, A., Stevanato, P. Molecular and morphological changes induced by leonardite-based biostimulant in Beta vulgaris L. Plants 2019, 8(6), 181. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajizadeh, H. S., Heidari, B., Bertoldo, G., Della Lucia, M. C., Magro, F., Broccanello, C., et al. Expression profiling of candidate genes in sugar beet leaves treated with leonardite-bsed biostimulant. High Throughput 2019, 8, 18. [CrossRef]

| Treatment | Concentration Dose per Plant |
Application Form | Composition |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trichoderma atroviride | 10 ml | root application | spore-forming mycelium of the genus of Trichoderma atroviride |
| BlackJak | 0.5 ml·l-1 300 ml per plant |
root application | leonardite: min. 28%; organic substances: min. 20 %; humins; ulmic acids; humic acids; fulvic acids |
| Universol Green | 2 g·l-1 40 ml per plant |
foliar application | N 23%, K 8.3%, P 2.6%, Fe 0.1%, Cu 0.1%, Zn 0.1%, Mn 0.4%, B 0.01%, Mo 0.01% |
| Treatments | Unpruned | Pruned | Average for treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trichoderma atroviride | 765.0 a | 1103.7 e | 934.3 c |
| BlackJak | 739.7 a | 1036.3 d | 888.0 b |
| Universol Green | 762.3 a | 950.0 c | 856.2 b |
| Control | 741.3 a | 901.0 b | 821.2 a |
| Average for treatment | 752.1 a | 997.8 b |
| Treatments | Unpruned | Pruned | Average for treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trichoderma atroviride | 340.0 a | 1325.0 d | 832.5 c |
| BlackJak | 367.3 a | 1103.7 b | 735.5 ab |
| Universol Green | 347.0 a | 1188.0 c | 767.5 b |
| Control | 304.3 a | 1084.3 b | 694.3 a |
| Average for treatment | 339.7 a | 1175.3 b |
| Treatments | Unpruned | Pruned | Average for treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trichoderma atroviride | 17.2 e | 9.0 b | 13.1 b |
| BlackJak | 13.5 c | 4.9 a | 9.2 a |
| Universol Green | 15.4 d | 5.2 a | 10.3 a |
| Control | 13.9 cd | 4.8 a | 9.4 a |
| Average for treatment | 13.0 b | 6.0 a |
| Treatments | Unpruned | Pruned | Average for treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trichoderma atroviride | 12.0 e | 6.8 b | 9.4 c |
| BlackJak | 11.7 d | 5.9 a | 8.5 b |
| Universol Green | 10.9 d | 6.8 b | 8.8 b |
| Control | 10.1 c | 5.7 a | 7.9 a |
| Average for treatment | 11.0 b | 6.3 a |
| Treatments | Unpruned | Pruned | Average for treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trichoderma atroviride | 11.9 e | 6.8 b | 9.4 c |
| BlackJak | 11.1 d | 5.9 a | 8.5 b |
| Universol Green | 10.9 d | 6.8 b | 8.8 b |
| Control | 10.2 c | 5.7 a | 7.9 a |
| Average for treatment | 11.0 b | 6.3 a |
| Treatment | Unpruned | Pruned | Average for treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trichoderma atroviride | 11.7 c | 7.6 a | 9.6 a |
| BlackJak | 11.9 c | 8.1 a | 10.0 a |
| Universol Green | 13.1 d | 9.0 b | 11.0 b |
| Control | 12.4 cd | 7.5 a | 10.0 a |
| Average for treatment | 12.3 b | 8.0 a |
| Treatments | Unpruned | Pruned | Average for Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trichoderma atroviride | 396.0 b | 563.0 d | 479.5 bc |
| BlackJak | 351.0 b | 553.7 d | 452.3 b |
| Universol Green | 455.3 c | 548.7 d | 502.0 c |
| Control | 290.0 a | 509.0 d | 399.5 a |
| Average for treatment | 373.1 a | 543.6 b |
| Treatments | Unpruned | Pruned | Average for treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trichoderma atroviride | 376.3 | 550.0 f | 463.2 c |
| BlackJak | 365.0 b | 468.7 de | 416.8 b |
| Universol Green | 431.0 cd | 492.3 e | 461.7 c |
| Control | 307.3 a | 398.0 bc | 352.7 a |
| Average for treatment | 369.9 a | 477.3 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





