Submitted:
17 February 2024
Posted:
20 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant materials
2.2. Evaluation of powdery mildew resistance
2.3. Molecular marker and nulli-tetrasomic analysis
2.4. Genetic mapping and data analysis
3. Results
3.1. Genetic analysis of powdery mildew resistance gene in Changanhongmai
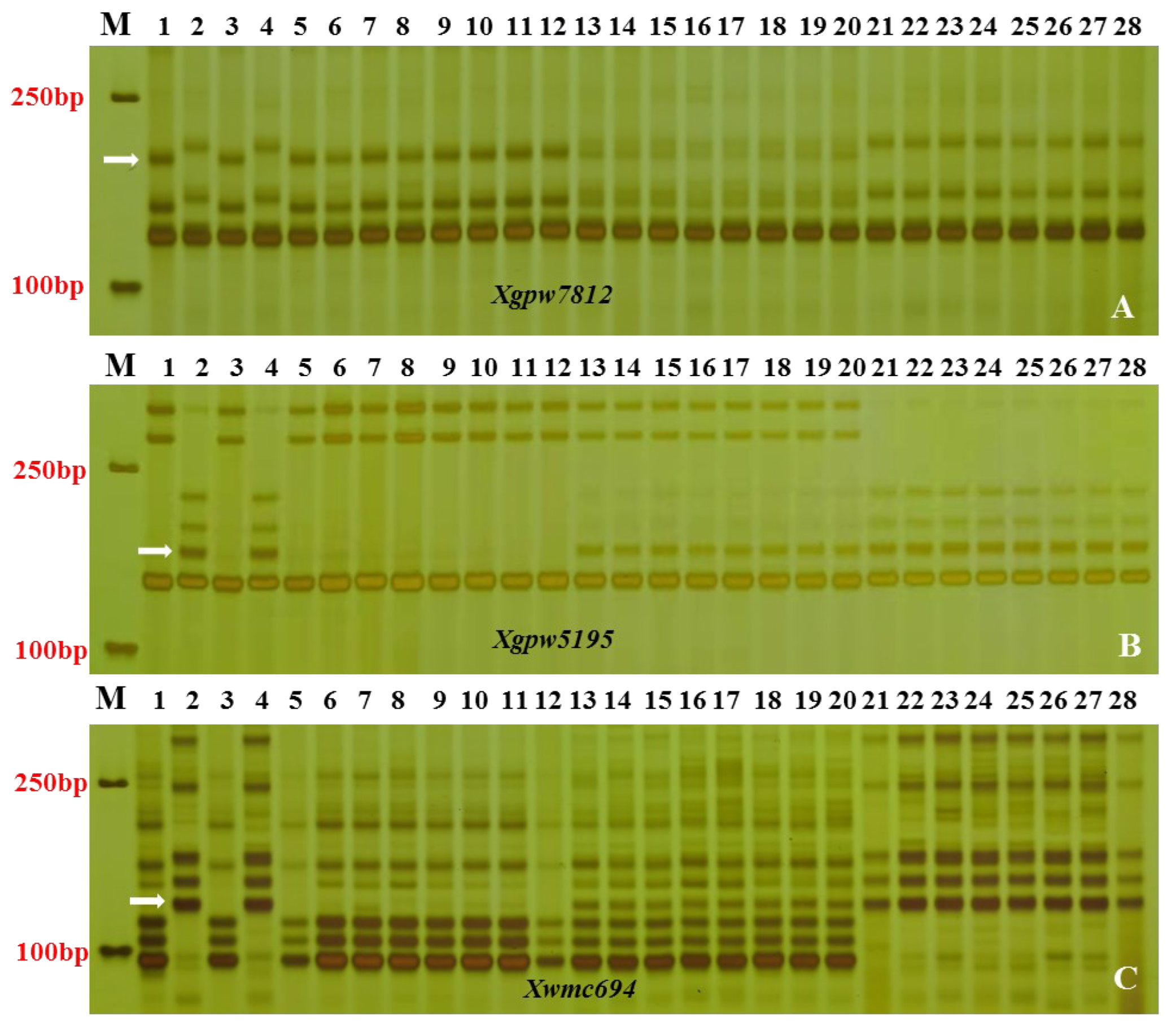
3.2. Linkage analysis of SSR polymorphic markers
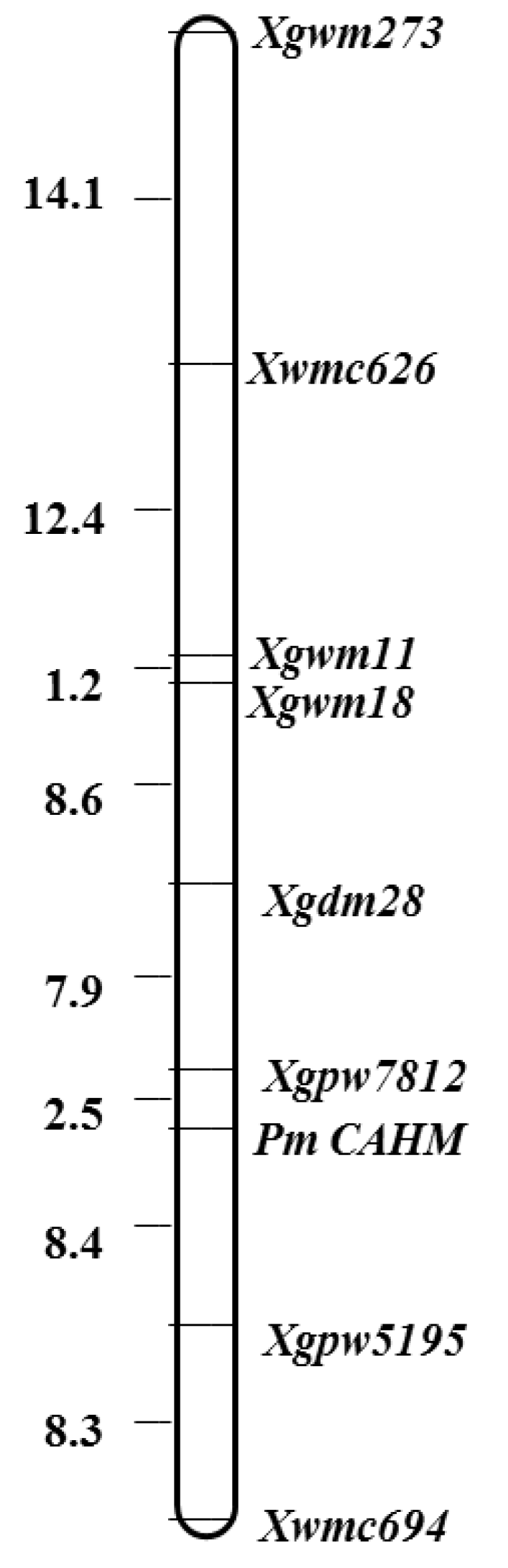
3.3. Chromosomal mapping and genetic linkage map construction
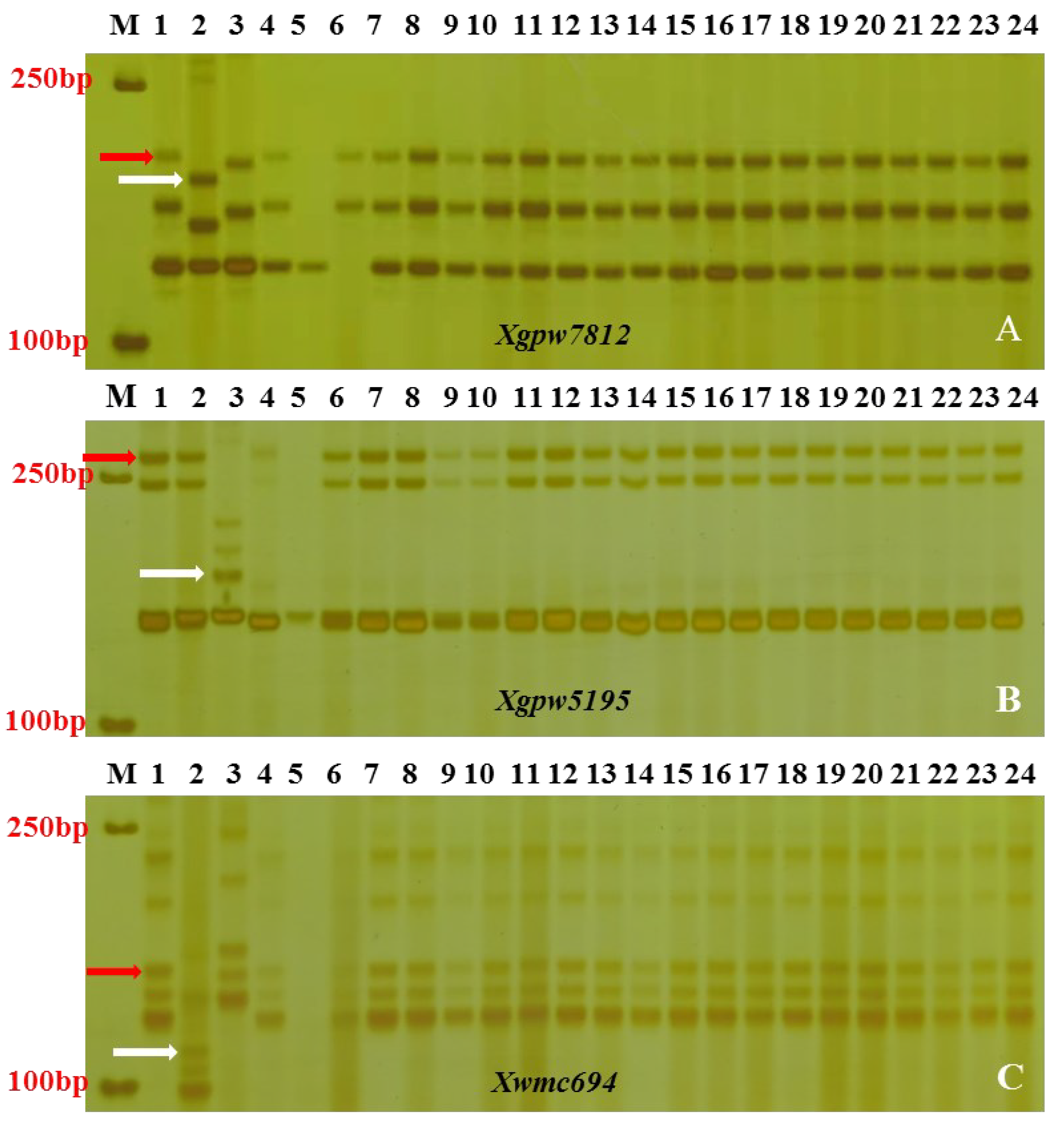
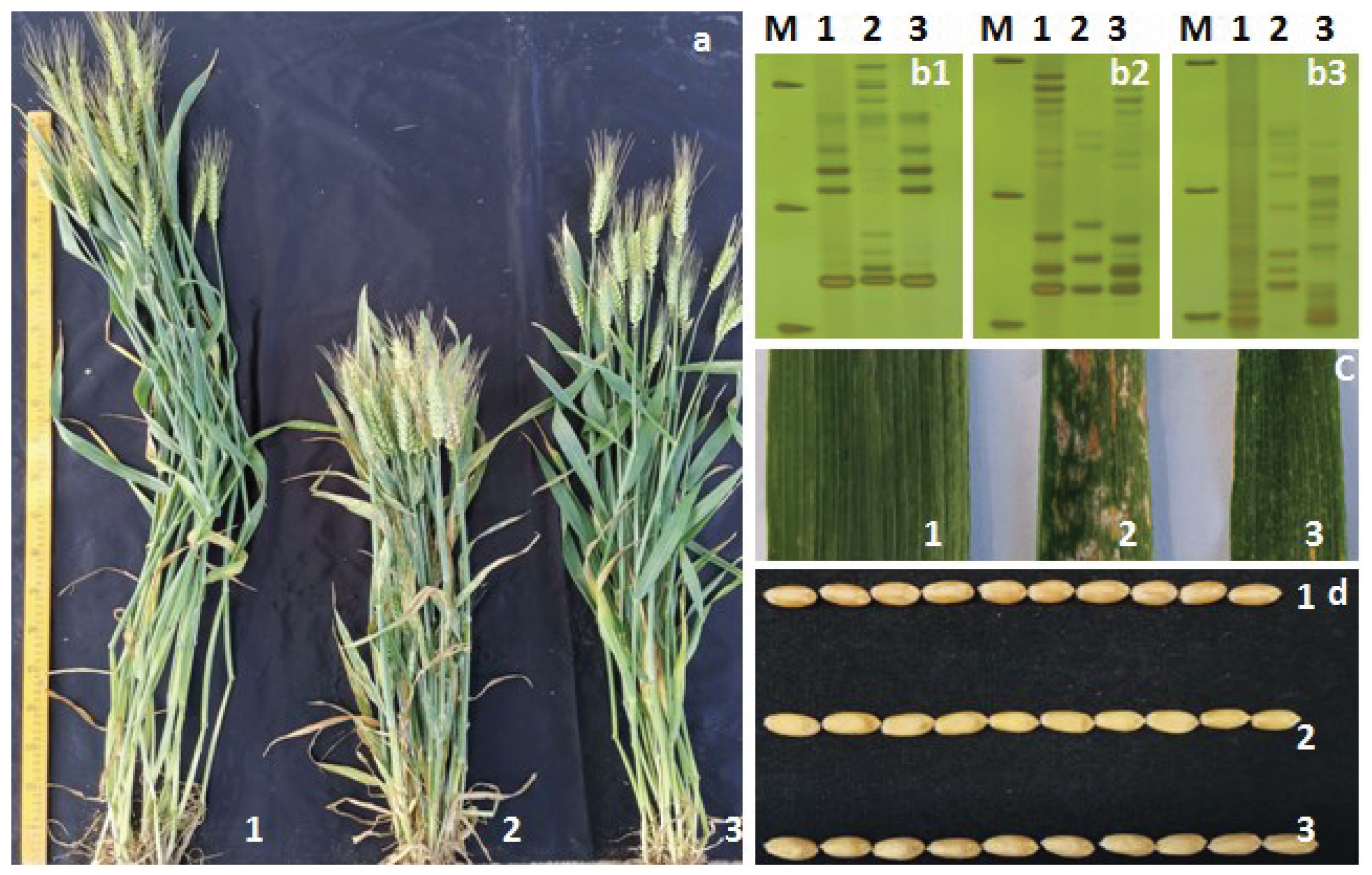
3.4. Breeding with PmCAHM
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Curtis, T.; Halford, N.G. Food security: the challenge of increasing wheat yield and the importance of not compromising food safety. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2014, 164, 354–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H. J.; Zhou, Y.; Xin, W. L.; Wei, Y. Q.; Zhang, J. L.; Guo, L. L. Wheat breeding in northern China: Achievements and technical advances. Crop. J. 2019, 7, 718–729. [CrossRef]
- Bapela, T.; Shimelis, H.; Terefe, T.; Bourras, S.; Sánchez-Martín, J.; Douchkov, D.; Desiderio, F.; Tsilo, T.J. Breeding Wheat for Powdery Mildew Resistance: Genetic Resources and Methodologies—A Review. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicker, T.; Oberhaensli, S.; Parlange, F.; Buchmann, J. P.; Shatalina, M.; Roffler, S.; Ben-David, R.; Dolezel, J.; Simkova, H.; Schulze-Lefert, P.; Spanu, P. D.; Bruggmann, R.; Amselem, J.; Quesneville, H.; Ver Loren van Themaat, E.; Paape, T.; Shimizu, K. K.; Keller, B. The wheat powdery mildew genome shows the unique evolution of an obligate biotroph. Nat Genet. 2013, 45, 1092–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordeeva, E.; Shamanin, V.; Shoeva, O.; Kukoeva, T.; Morgounov, A.; Khlestkina, E. The Strategy for Marker-Assisted Breeding of Anthocyanin-Rich Spring Bread Wheat (Triticum aestivum L. ) Cultivars in Western Siberia. Agronomy. 2020, 10, 1603. [Google Scholar]
- Vikas, V.K.; Kumar, S.; Archak, S.; Tyagi, R.K.; Kumar, J.; Jacob, S.; Sivasamy, M.; Jayaprakash, P.; Saharan, M.S.; Basandrai, A.K.; et al. Screening of 19,460 genotypes of wheat species for resistance to powdery mildew and identification of potential candidates using focused identification of germplasm strategy (FIGS). Crop. Sci. 2020, 60, 2857–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wei, Z.-Z.; Sela, H.; Govta, L.; Klymiuk, V.; Roychowdhury, R.; Chawla, H. S.; Ens, J.; Wiebe, K.; Bocharova, V.; Ben-David, R.; Pawar, P. B.; Jaiwar, S.; Molnár, I.; Doležel, J.; Pozniak, C. J.; Fahima, T. Long-read genome sequencing accelerated the cloning of Pm69 by resolving the complexity of a rapidly evolving resistance gene cluster in wheat. bioRxiv. 2022.
- Aravindh, R.; Sivasamy, M.; Ganesamurthy, K.; Jayaprakash, P.; Gopalakrishnan, C.; Geetha, M.; Nisha, R.; Shajitha, P.; Peter, J.; Sindhu, P.A. Marker assisted stacking/pyramiding of stem rust, leaf rust and powdery mildew disease resistance genes (Sr2/Lr27/Yr30, Sr24/Lr24 and Sr36/Pm6) for durable resistance in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Elect. J. Plant Breed. 2020, 11, 907–915. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, A.; Xing, L.; Wang, X.; Yang, X.; Wang, W.; Sun, Y.; Qian, C.; Ni, J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, D.; Wang, X.; Chen, P. Serine/threonine kinase gene Stpk-V, a key member of powdery mildew resistance gene Pm21, confers powdery mildew resistance in wheat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011, 108, 7727–7732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Luo, J.; Wan, L.; Luo, J.; Li, Y.; Fu, S.; Liu, D.; Hao, M.; Tang, Z. Chromosomes polymorphisms of Sichuan wheat cultivars displayed by ND-FISH landmarks. Cereal Res. Commun. 2022, 50, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X. Q.; Hsam, S. L. K.; Zeller, F. J. Identification of powdery mildew resistance genes in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L. em Thell.). IX. Cultivars, land races and breeding lines grown in China. Plant Breeding 2010, 116, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Lei, Y.; Pei, D.; Wu, H.; Liu, X.; Fang, J.; Guo, J.; Wang, C.; Guo, J.; Zhang, J.; et al. Predominant wheat-alien chromosome translocations in newly developed wheat of China. Mol. Breed. 2021, 41, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Liu, R.; Ma, P.; Du, H.; Zhang, H.; Wu, Q.; Yang, L.; Gong, S.; Liu, T.; Huo, N.; et al. Characterization of Pm68, a new powdery mildew resistance gene on chromosome 2BS of Greek durum wheat TRI 1796. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2021, 134, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Dong, Z.; Ma, C.; Xia, Q.; Tian, X.; Sehgal, S.; Koo, D.-H.; Friebe, B.; Ma, P.; Liu, W. A spontaneous wheat-Aegilops longissima translocation carrying Pm66 confers resistance to powdery mildew. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2020, 133, 1149–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Hu, J.; Song, W.; Qiu, D.; Cui, L.; Wu, P.; Zhang, H.; Liu, H.; Yang, L.; Qu, Y.; et al. Pm61: a recessive gene for resistance to powdery mildew in wheat landrace Xuxusanyuehuang identified by comparative genomics analysis. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2018, 131, 2085–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.L.; Han, D.J.; Chen, X.M.; Gou, H.L.; Guo, S.J.; Rong, L.; Wang, Q.L.; Huang, L.L.; Kang, Z.S. Characterization and molecular mapping of stripe rust resistance gene Yr61 in winter wheat cultivar Pindong 34. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2014, 127, 2349–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zheng, X.; Zhong, X.; Tan, W.; Ma, C.; Wang, Y.; Tian, R.; Yang, S.; Li, X.; Xia, C.; et al. Transfer of the high-temperature adult-plant stripe rust resistance gene Yr62 in four Chinese wheat cultivars. Mol. Breed. 2023, 43, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Zhu, F.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, J.; Yan, W.; Zhang, Q.; Jacobi, A.; Cai, S. Genetic analysis and molecular mapping of a new powdery mildew resistant gene Pm46 in common wheat. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2012, 125, 967–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X. Q.; Wang, L. X.; Xu, M. X.; Roder, M. S. Microsatellite mapping of the powdery mildew resistance gene Pm5e in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2003; 106, 858–865. [CrossRef]
- Xue, F.; Wang, C.; Li, C.; Duan, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, N.; Wang, Y.; Ji, W. Molecular mapping of a powdery mildew resistance gene in common wheat landrace Baihulu and its allelism with Pm24. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2012, 125, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P. T.; Zhang, H. X.; Xu, H. X.; Xu, Y. F.; Cao, Y. W.; Zhang, X. T.; An, D. G. The gene confers broad-spectrum powdery mildew resistance in the multi-allelic chromosome region of the Chinese wheat cultivar YingBo 700. Molecular Breeding. 2015, 35, (5). [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Sun, H.; Song, W.; Lu, M.; Huang, J.; Wu, L.; Wang, X.; Li, H. Genetic analysis and detection of the gene MlLX99 on chromosome 2BL conferring resistance to powdery mildew in the wheat cultivar Liangxing 99. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2013, 126, 3081–3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Zeller, F.; Hsam, S.; Wenzel, G.; Mohler, V. Chromosomal location of AFLP markers in common wheat utilizing nulli-tetrasomic stocks. Genome 2000, 43, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, A.; Kosugi, S.; Yoshida, K.; Natsume, S.; Takagi, H.; Kanzaki, H.; Matsumura, H.; Yoshida, K.; Mitsuoka, C.; Tamiru, M.; et al. Genome sequencing reveals agronomically important loci in rice using MutMap. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voorrips, R.; Van, d. M., J; van den Heuvel, L. P. W. J.; Ooijen, J.; Jw, V. T. V. JoinMap® 4.0: Software for the calculation of genetic linkage maps in experimental populations. 2006.
- Xiao, M.; Song, F.; Jiao, J.; Wang, X.; Xu, H.; Li, H. Identification of the gene Pm47 on chromosome 7BS conferring resistance to powdery mildew in the Chinese wheat landrace Hongyanglazi. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2013, 126, 1397–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, C.; Li, G.; Cowger, C.; Carver, B.F.; Xu, X. Characterization of Pm59, a novel powdery mildew resistance gene in Afghanistan wheat landrace PI 181356. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2018, 131, 1145–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F. K.; Li, Y. H.; Yang, B. J.; Yuan, H. B.; Jin, C.; Zhou, L. X.; Pei, H. C.; Zhao, L. F.; Li, Y. W.; Zhou, Y. L.; Xie, J. K.; Shen, Q. H. Powdery mildew disease resistance and marker-assisted screening at the locus in wild diploid wheat. Crop J. 2020, 8, (2), 252-259. [CrossRef]
- Petersen, S.; Lyerly, J.H.; Worthington, M.L.; Parks, W.R.; Cowger, C.; Marshall, D.S.; Brown-Guedira, G.; Murphy, J.P. Mapping of powdery mildew resistance gene Pm53 introgressed from Aegilops speltoides into soft red winter wheat. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2015, 128, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Koo, D.-H.; Xia, Q.; Li, C.; Bai, F.; Song, Y.; Friebe, B.; Gill, B.S. Homoeologous recombination-based transfer and molecular cytogenetic mapping of powdery mildew-resistant gene Pm57 from Aegilops searsii into wheat. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2017, 130, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.C.; Li, G.Q.; Cowger, C.; Carver, B.F.; Xu, X.Y. Characterization of Pm63, a powdery mildew resistance gene in Iranian landrace PI 628024. Theor Appl Genet. 2019, 132:1137-1144. [CrossRef]
- Xue, F.; Wang, C. Y.; Li, C.; Duan, X. Y.; Zhou, Y. L.; Zhao, N. J.; Wang, Y. J.; Ji, W. Q. Molecular mapping of a powdery mildew resistance gene in common wheat landrace Baihulu and its allelism with Pm24. Theor Appl Genet. 2012, 125, 1425-1432. [CrossRef]
- Lu, N.; Lu, M. X.; Liu, P.; Xu, H. X.; Qiu, X. L.; Hu, S. S.; Wu, Y. N.; Bai, S. L.; Wu, J. Z.; Xue, S. L. Fine mapping a broad-spectrum powdery mildew resistance gene in Chinese landrace Datoumai, PmDTM, and its relationship with Pm24. Plant Dis. 2020a,104:1709-1714. [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Guo, L.; Wang, Z. Z.; Li, B. B.; Li, J.; Li, Y. H.; Qiu, D.; Shi, W. Q.; Yang, L. J.; Wang, N. A rare gain of function mutation in a wheat tandem kinase confers resistance to powdery mildew. Nat Commun. 2020b, 11:680.35. [CrossRef]
- Tosa, Y.; Tokunaga, H.; Ogura, H. Identification of a gene for resistance to wheatgrass powdery mildew fungus in the common wheat cultivar Chinese Spring. Genome 1988, 30, 612–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsam, S.L.K.; Huang, X.Q.; Zeller, F.J. Chromosomal location of genes for resistance to powdery mildew in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L. em. Thell.). 6. Alleles at the Pm5 locus. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2002, 102, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Guo, G.; Wang, Y.; Hu, T.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Qiu, D.; Li, Y.; Wu, Q.; Lu, P.; et al. A rare single nucleotide variant in Pm5e confers powdery mildew resistance in common wheat. New Phytol. 2020, 228, 1011–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Yi, Y.; Ma, P.; Qie, Y.; Fu, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, X.; An, D. Molecular tagging of a new broad-spectrum powdery mildew resistance allele Pm2c in Chinese wheat landrace Niaomai. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2015, 128, 2077–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lillemo, M.; Asalf, B.; Singh, R. P.; Huerta-Espino, J.; Chen, X. M.; He, Z. H.; Bjornstad, A. The adult plant rust resistance loci Lr34/Yr18 and Lr46/Yr29 are important determinants of partial resistance to powdery mildew in bread wheat line Saar. Theor Appl Genet. 2008, 116, 1155–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peusha, H.; Enno, T.; Priilinn, O. Chromosomal location of powdery mildew resistance genes and cytogenetic analysis of meiosis in common wheat cultivar Meri. Hereditas 2000, 132, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visioli, G.; Giannelli, G.; Agrimonti, C.; Spina, A.; Pasini, G. Traceability of Sicilian Durum Wheat Landraces and Historical Varieties by High Molecular Weight Glutenins Footprint. Agronomy 2021, 11, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pais, I.P.; Moreira, R.; Coelho, A.R.; Semedo, J.N.; Reboredo, F.H.; Coutinho, J.; Lidon, F.C.; Maçãs, B.; Scotti-Campos, P. Unveiling the Impact of Growth Traits on the Yield of Bread Wheat Germplasm Subjected to Waterlogging. Agriculture 2024, 14, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirangelo, T.M. NLR- and mlo-Based Resistance Mechanisms against Powdery Mildew in Cannabis sativa. Plants 2024, 13, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, K.; He, D.; Guo, J.; Li, G.; Li, B.; Chen, X. Molecular Advances in Breeding for Durable Resistance against Pests and Diseases in Wheat: Opportunities and Challenges. Agronomy 2023, 13, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharib, M.A.A.H.; Qabil, N.; Salem, A.H.; Ali, M.M.A.; Awaad, H.A.; Mansour, E. Characterization of wheat landraces and commercial cultivars based on morpho-phenological and agronomic traits. Cereal Res. Commun. 2021, 49, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, N.; Lu, M.; Liu, P.; Xu, H.; Shulin, X. Fine Mapping a Broad-Spectrum Powdery Mildew Resistance Gene in Chinese Landrace Datoumai, PmDTM, and Its Relationship with Pm24. Plant Disease. 2020, 104, 1709-1714. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, P.; Guo, M.; Hao, X.; Guo, X.; Yao, Q.; Guo, Q.; Li, Q.; Wang, B. Evaluation of powdery mildew resistance and molecular detection of resistance genes in an international wheat collection. Crop Protection. 2022, 160, 106033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, S.L.; Wang, H.; Ma, Y.Y.; Sun, T.P.; Wang, Y.X.; Meng, F.; Wang, X.T.; Yang, Z.H.; Zhang,J.L.; Du, J.X.; Li, S.P.; Li, Z.F. Fine mapping of powdery mildew resistance gene PmXNM in a Chinese wheat landrace Xiaonanmai. Theor Appl Genet. 2024, 137:35. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Materials | Observed plant number | Expected ratio | χ2 value | P-value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resistant | Segregating | Susceptible | ||||
| S333 | 10 | |||||
| SY225 | 10 | |||||
| F1 | 10 | |||||
| F2 | 122 | 54 | 3:01 | 2.73 | 0.9 | |
| F2:3 | 47 | 75 | 54 | 1:02:01 | 4.4 | 0.96 |
| Marker | Type | Primer (5’-3’) | Location | Geltype/Restrictionenzyme | Tm ◦C/t (h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xgpw7812 | SSR | F: CTTTATCAGGCATGGAACTGC | 1BS | 8% non-denaturing | 60 |
| R: CTTTATCAGGCATGGAACTGC | polyacrylamide gel/- | ||||
| Xgwm273 | SSR | F: ATTGGACGGACAGATGCTTT | 1BS | 8% non-denaturing | 60 |
| R: AGCAGTGAGGAAGGGGATC | polyacrylamide gel/- | ||||
| Xwmc626 | SSR | F: AGCCCATAAACATCCAACACGG | 1BS | 8% non-denaturing | 60 |
| R: AGGTGGGCTTGGTTACGCTCTC | polyacrylamide gel/- | ||||
| Xgwm11 | SSR | F: GGATAGTCAGACAATTCTTGTG | 1BS | 8% non-denaturing | 62 |
| R: GTGAATTGTGTCTTGTATGCTTCC | polyacrylamide gel/- | ||||
| Xgwm1818 | SSR | F: TGGCGCCATGATTGCATTATCTTC | 1BS | 8% non-denaturing | 62 |
| R: GGTTGCTGAAGAACCTTATTTAGG | polyacrylamide gel/- | ||||
| Xgdm2828 | SSR | F: ATCTGACTTCATGGTTTATAT | 1BS | 8% non-denaturing | 62 |
| R: TCAAGAATGAAGACATAGTT | polyacrylamide gel/- | ||||
| Xwmc694 | SSR | F: ATTTGCCCTTGTGAGCCGTT | 1BS | 8% non-denaturing | 58 |
| R: GACCTGGGTGGGACCCATTA | polyacrylamide gel/- | ||||
| Xgpw5195 | SSR | F: CGACTCTCGCTTCAGCTTG | 1BS | 8% non-denaturing | 60 |
| R: GGTTCTTCACGCCATTGATT | polyacrylamide gel/- |
| Materials | TGW (g) | Plant height (cm) | Spike length (cm) | Spike grain number | Infection type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Changanhongmai | 45 | 120 | 8.5 | 42 | 0 |
| FY1718 | 44.5 | 80 | 9 | 46 | 4 |
| NW1748 | 45.9 | 95 | 9.2 | 46 | 0-1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





