Submitted:
15 February 2024
Posted:
16 February 2024
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Rationale for Usage
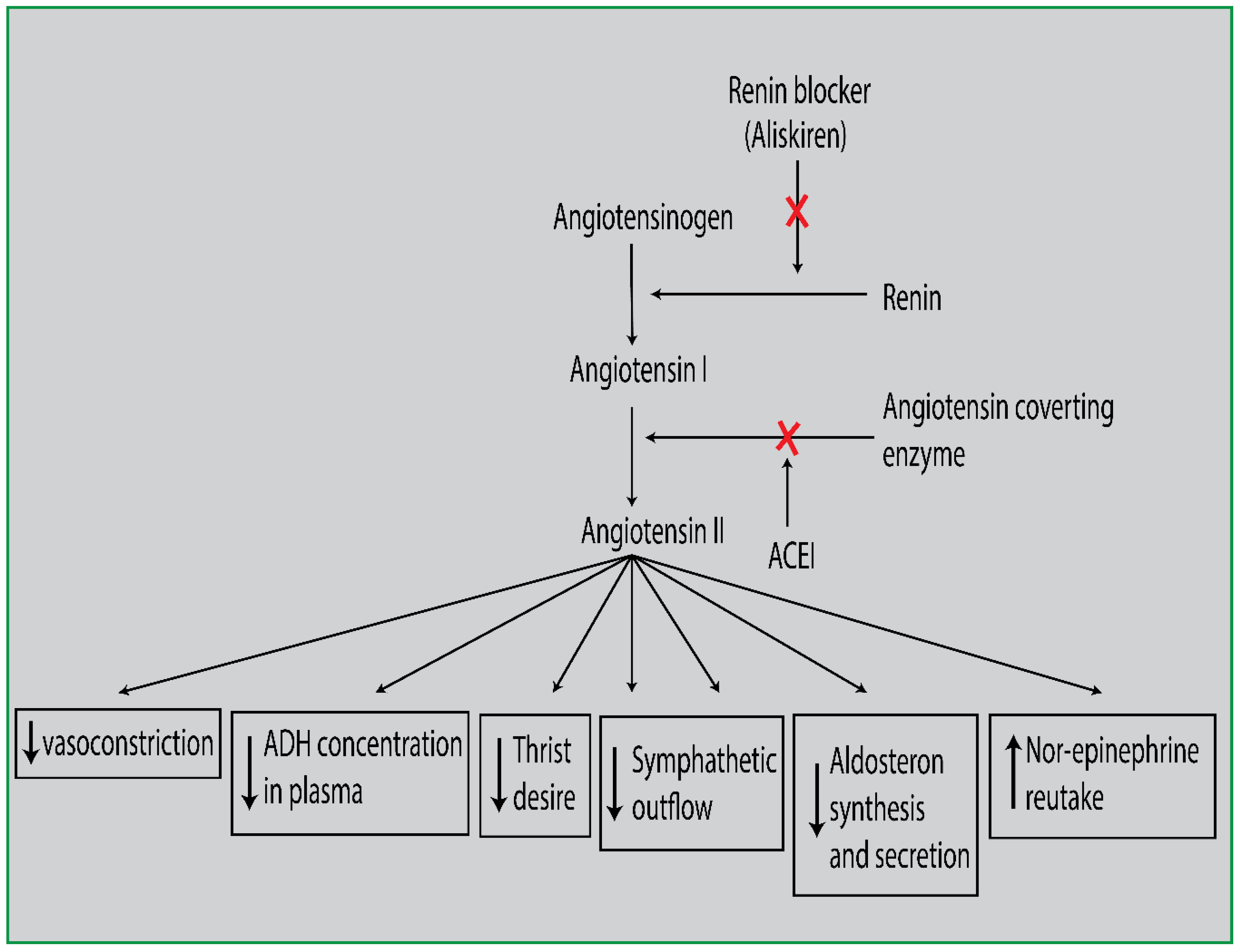
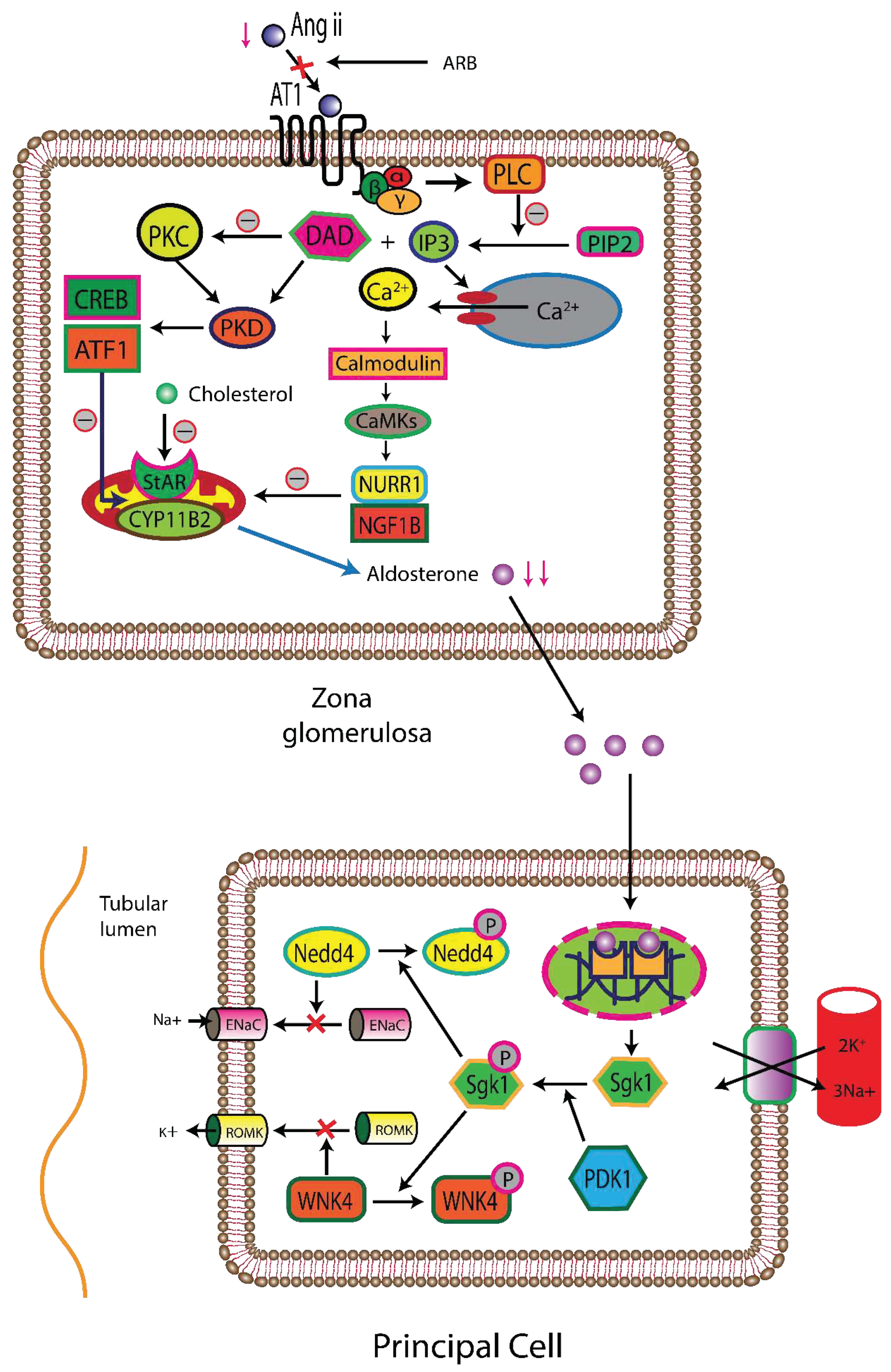
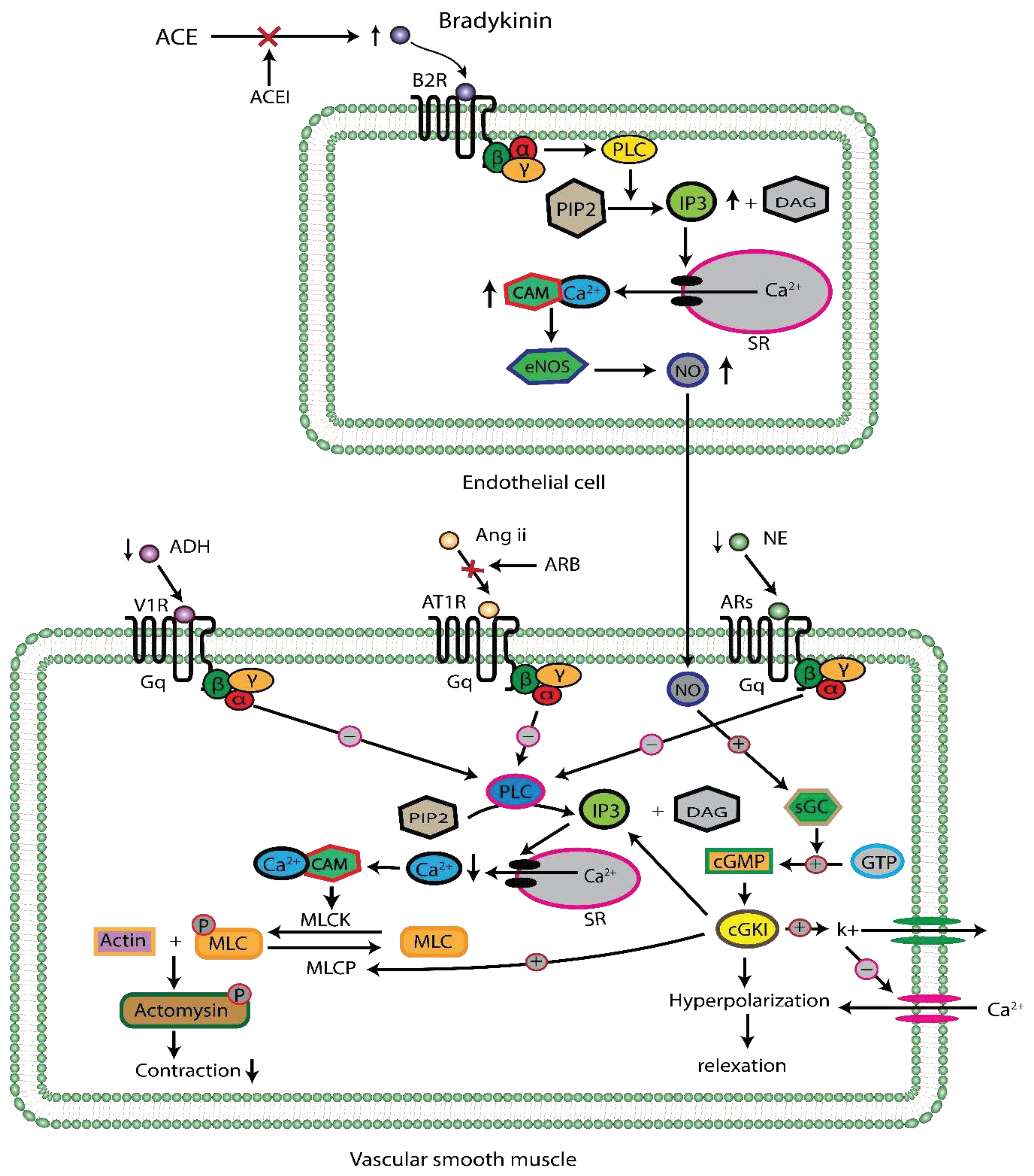
Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone System
Calcium Channel Blocker
Diuretic
Clinical Trial Evaluation
Perindopril/Indapamide vs. Placebo (PROGRESS TRAIL)
Perindopril/Indapamide vs. Placebo (ADVANCE TRAIL)
Perindopril/Indapamide vs. Placebo (HYVET TRAIL)
Losartan/Hydrochlorothiazide vs. Atenolol/Hydrochlorothiazide (LIFE TRAIL)
A Calcium Antagonist vs. Non-Calcium Antagonist (INVEST TRAIL)
Amlodipine-Based Regiment vs. Atenolol Based Regiment (ASCOT-BPLA TRAIL)
Benazepril/Amlodipine vs. Benazepril/Hydrochlorothiazide (ACCOMPLISH TRAIL)
Benazepril/Amlodipine vs. Benazepril/Hydrochlorothiazide (ACCOMPLISH TRAIL)
| class | Cmax | F | T1/2 | VD | Proteinbinding | CLr | Refer-ence |
| CCBAmlodipine | 6-8h | 64% | 40-50h | 21L/kg | 98% | 0.23-0.4L/h/kg | [159] |
| Felodipine | 0.5-5h | 15% | 25 h | 10 L/kg | >99 | 1-1.5 L/min | [160] |
| Verapamil | 2.2h | 20% | 2.7-4.8h | 310-406 L | 90% | 875 ml/min | [161] |
| ARB Olmesartan medoxomil/Olmesartan |
1.7–2.5h | 26% | 15 h | 35L | 99.7% | 1.31 L/h | [162,163] |
| valsartan | 2h | 23% | 6.1h | 17L | 85-99% | 2.2 L/h | [164] |
| Telmisartan | 1h | 43% | 24h | 500L | >99% | >800ml/min | [165] |
| Candesartan cilexetil/candesartan | 3,5-6h | 40% | 3.5-11h | 0.13L/kg | 99.5% | 0.0222 L/h/kg | [166,167] |
| Eprosartan | 1-2h | 13% | 5-9h | 13L | 98% | 130ml/min | [168] |
| Irbesartan | 1.3-3h | 60-80% | 11-18h | 53-93L | 90% | 167ml/min | [166] |
| Losartan | 1-2h | 33% | 1.7-2.1h | 34.4 ± 17.9L | 98.6–98.8% | 4.3-5.6L/h | [169] |
| ACEI Benazepril/Benazeprilat |
1.5h | 37% | 22.3h | 8.7L | 95% | 1.4-1.7L/h | [170] |
| Captopril | 0.75-1h | 65% | 2h | 0.8 L/kg | 23-31% | 0.7L/h/kg | [171] |
| Enalapril/ enalaprilat | 4h | 36-44% | 11h | 50% | 8-9.5L/h | [172,173] | |
| Fosinopril/Fosinoprilat | 2.8-3.1h | 25-29% | 11.5-12h | 9.8-10.6L | 95-99.8% | 1.55-2.35 L/h | [174] |
| Lisinopril | 8h | 20-28% | 12.6h | 24L | no | 6.36L/h | [175] |
| Quinapril/quinaprilat | 2.5h | 50-60% | 3.2h | 13.9L | 97% | 68 ml/min. | [176] |
| Diuretics hydrochlorothiazide |
1.5-4h | 60-70% | 5.6-14.8h | 275.3 L | 40-68% | [177] |
| Combination type | Dose (mg) | Trade name | Cost |
| CCB+ACEI Amlodipine-benazepril Hydrochloride |
2.5/10, 5/10, 5/20, 10/20 | Lotrel | $14 ($215)- $16 ($390) |
| Enalaprilmaleate-felodipine | 5/5 | Lexxel | |
| Trandolapril-verapamil | 2/180, 1/240, 2/240, 4/240 | Tarka | $47 ($185)- $65 ($185) |
| CCB+ARB Amlodipine/Olmesartan medoxomil |
5/20,5/40,10/20,10/40 | Azor | $23 ($280)- $28 ($350) |
| Amlodipine/Valsartan | 5/160,320/5,10/160,10/320 | Exforge | $20 ($270)- $25 ($385) |
| Amlodipine/Telmisartan | 5/40,5/80,10/40,10/80 | Twynsta | $50 (NA)- $55 ($240) |
| Diuretic+ACEI Benazepril-hydrochlorothiazide |
5/6.25, 10/12.5, 20/12.5, 20/25 | Lotensin HCT | $21 (NA)- $24 (NA) |
| Captopril-hydrochlorothiazide | 25/15, 25/25, 50/15, 50/25 | Capozide | |
| Enalapril-hydrochlorothiazide | 5/12.5, 10/25 | Vaseretic | $10 (NA)- $10 ($395) |
| Fosinopril-hydrochlorothiazide | 10/12.5, 20/12.5 | Monopril/HCT | |
| Lisinopril-hydrochlorothiazid | 10/12.5, 20/12.5, 20/25 | Prinzide, Zestoretic | $4 ($400)- $6 ($400) |
| Moexipril-hydrochlorothiazide | 7.5/12.5, 15/25 | Uniretic | |
| Quinapril-hydrochlorothiazide | 10/12.5, 20/12.5, 20/25 | Accuretic | $17 ($150) |
| Diuretic+ARB Candesartan-hydrochlorothiazide |
16/12.5, 32/12.5,32/25 | Atacand HCT | $48 ($150)- $50 ($165) |
| Eprosartan-hydrochlorothiazide | 600/12.5, 600/25 | Teveten-HCT | |
| Irbesartan-hydrochlorothiazide | 150/12.5, 300/12.5 | Avalide | $15 ($235)- $20 ($255) |
| Losartan-hydrochlorothiazide | 50/12.5, 100/12.5,100/25 | Hyzaar | $4 ($130)- $9 ($175) |
| Olmesartan medoxomil-hydrochlorothiazide | 20/12.5,40/12.5,40/25 | Benicar HCT | $14 ($225)- $16 ($310) |
| Telmisartan-hydrochlorothiazide | 40/12.5, 80/12.5 | Micardis-HCT | $47 ($220) |
| Valsartan-hydrochlorothiazide | 80/12.5, 160/12.5, 160/25,320/12.5,320/25 | Diovan-HCT | $14 ($270)- $18 ($420) |
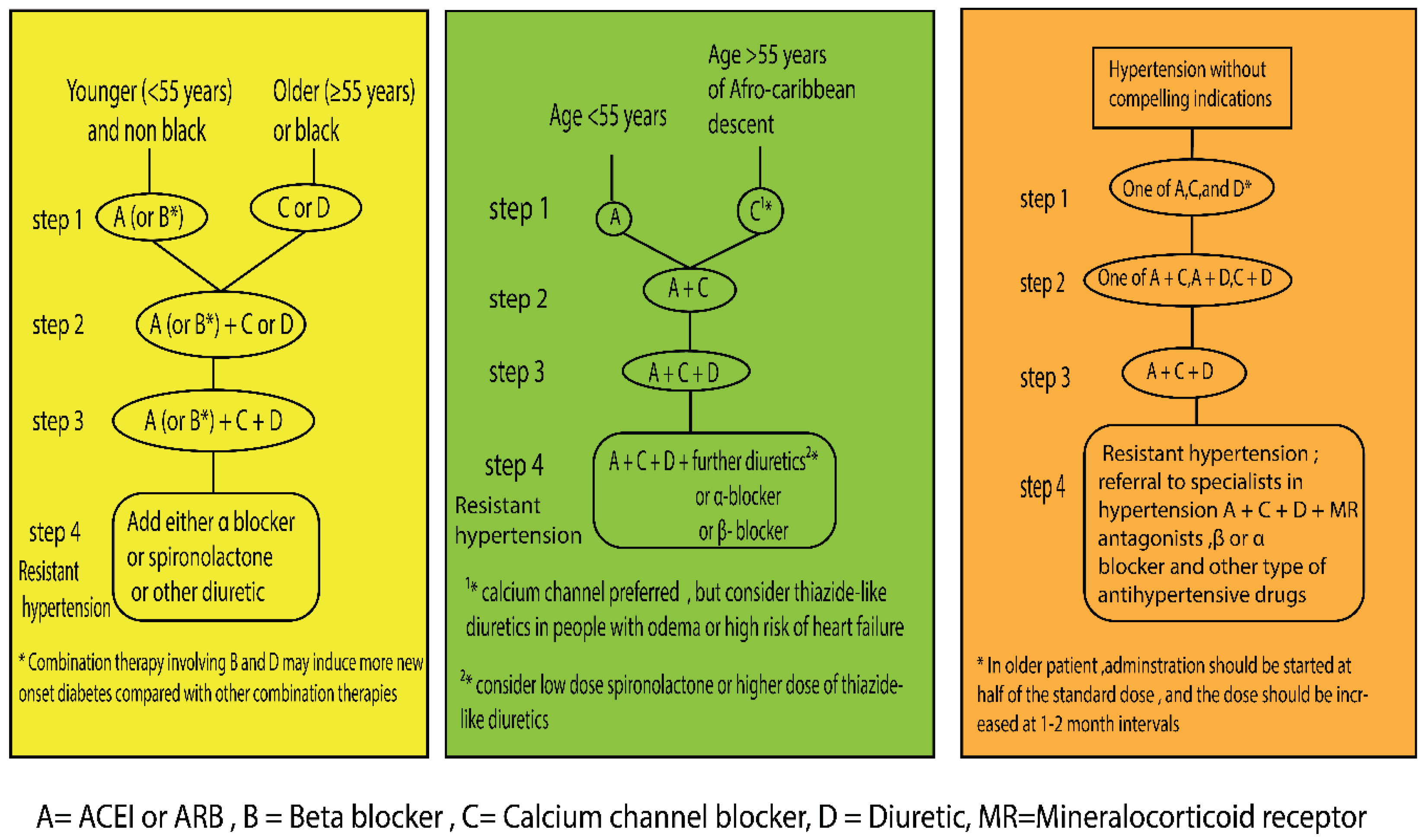
Pharmacological Treatment Strategy
Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Consent of participants
Consent of publication
Data availability
Conflict of interest
References
- Gaziano, T., Reddy, K. S., Paccaud, F., Horton, S., & Chaturvedi, V. (2006). Cardiovascular disease. Disease Control Priorities in Developing Countries. 2nd edition.
- 2. Nabel, E. G. (2003). Cardiovascular disease. New England Journal of Medicine, 349(1), 60-72.
- Kannel, W. B. (1993). Hypertension as a risk factor for cardiac events--epidemiologic results of long-term studies. Journal of cardiovascular pharmacology, 21, S27-37. [CrossRef]
- Snow, P. J. D., Jones, A. M., & Daber, K. S. (1955). Coronary disease: a pathological study. British Heart Journal, 17(4), 503. [CrossRef]
- Henderson, A. (1996). Coronary heart disease: overview. The Lancet, 348, S1-S4. [CrossRef]
- Libby, P., & Theroux, P. (2005). Pathophysiology of coronary artery disease. Circulation, 111(25), 3481-3488.
- Yildiz, M., Oktay, A. A., Stewart, M. H., Milani, R. V., Ventura, H. O., & Lavie, C. J. (2020). Left ventricular hypertrophy and hypertension. Progress in cardiovascular diseases, 63(1), 10-21. [CrossRef]
- Maganti, K., Rigolin, V. H., Sarano, M. E., & Bonow, R. O. (2010, May). Valvular heart disease: diagnosis and management. In Mayo Clinic Proceedings (Vol. 85, No. 5, pp. 483-500). Elsevier. [CrossRef]
- Wijesurendra, R. S., & Casadei, B. (2019). Mechanisms of atrial fibrillation. Heart.
- 10. Wijesurendra, R. S., & Casadei, B. (2015). Atrial fibrillation: effects beyond the atrium?. Cardiovascular research, 105(3), 238-247. [CrossRef]
- Markus, H. (2004). Cerebral perfusion and stroke. Journal of neurology, neurosurgery, and psychiatry, 75(3), 353. [CrossRef]
- Novak, V., Chowdhary, A., Farrar, B., Nagaraja, H., Braun, J., Kanard, R., ... & Slivka, A. (2003). Altered cerebral vasoregulation in hypertension and stroke. Neurology, 60(10), 1657-1663. [CrossRef]
- Albright Jr, R. C. (2001, January). Acute renal failure: a practical update. In Mayo Clinic Proceedings (Vol. 76, No. 1, pp. 67-74). Elsevier.
- 14. Bellomo, R., Kellum, J. A., & Ronco, C. (2004). Defining acute renal failure: physiological principles. Intensive care medicine, 30, 33-37. [CrossRef]
- Luke, R. G. (1998). Chronic renal failure—a vasculopathic state. New England Journal of Medicine, 339(12), 841-843. [CrossRef]
- Kjeldsen, S. E. (2018). Hypertension and cardiovascular risk: General aspects. Pharmacological research, 129, 95-99. [CrossRef]
- Mills, K. T., Bundy, J. D., Kelly, T. N., Reed, J. E., Kearney, P. M., Reynolds, K., ... & He, J. (2016). Global disparities of hypertension prevalence and control: a systematic analysis of population-based studies from 90 countries. Circulation, 134(6), 441-450. [CrossRef]
- Fryar, C. D., Ostchega, Y., Hales, C. M., Zhang, G., & Kruszon-Moran, D. (2017). Hypertension Prevalence and Control Among Adults: United States, 2015-2016. NCHS data brief, (289), 1–8.
- Mills, K. T., Stefanescu, A., & He, J. (2020). The global epidemiology of hypertension. Nature Reviews Nephrology, 16(4), 223-237. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J. (2013). Epidemiology of hypertension. Clinical Queries: Nephrology, 2(2), 56-61.
- Giles, T. D., Materson, B. J., Cohn, J. N., & Kostis, J. B. (2009). Definition and classification of hypertension: an update. The journal of clinical hypertension, 11(11), 611-614. [CrossRef]
- Izzo, J. L., Sica, D. A., & Black, H. R. (Eds.). (2008). Hypertension primer. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
- Beevers, G., Lip, G. Y., & O’Brien, E. (2001). The pathophysiology of hypertension. Bmj, 322(7291), 912-916. [CrossRef]
- Messerli, F. H., Williams, B., & Ritz, E. (2007). Essential hypertension. The Lancet, 370(9587), 591-603.
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. (2019). Hypertension in adults: diagnosis and management. London: National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (UK).
- James, P. A., Oparil, S., Carter, B. L., Cushman, W. C., Dennison-Himmelfarb, C., Handler, J., ... & Ortiz, E. (2014). 2014 evidence-based guideline for the management of high blood pressure in adults: report from the panel members appointed to the Eighth Joint National Committee (JNC 8). Jama, 311(5), 507-520. [CrossRef]
- Watkins, P. J., Drury, P. L., & Taylor, K. W. (1990). Diabetes and its management. Boston: Blackwell Scientific.
- Forbes, J. M., & Cooper, M. E. (2013). Mechanisms of diabetic complications. Physiological reviews, 93(1), 137-188. [CrossRef]
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K., Jafar, T. H., Nitsch, D., Neuen, B. L., & Perkovic, V. (2021). Chronic kidney disease. The lancet, 398(10302), 786-802.
- Webster, A. C., Nagler, E. V., Morton, R. L., & Masson, P. (2017). Chronic kidney disease. The lancet, 389(10075), 1238-1252.
- Levey, A. S., & Coresh, J. (2012). Chronic kidney disease. The lancet, 379(9811), 165-180.
- Cohn, J. N. (1973). Blood pressure and cardiac performance. The American Journal of Medicine, 55(3), 351-361. [CrossRef]
- Loushin, M. K., Quill, J. L., & Iaizzo, P. A. (2015). Mechanical aspects of cardiac performance. Handbook of cardiac anatomy, physiology, and devices, 335-360.
- Touyz, R. M., Alves-Lopes, R., Rios, F. J., Camargo, L. L., Anagnostopoulou, A., Arner, A., & Montezano, A. C. (2018). Vascular smooth muscle contraction in hypertension. Cardiovascular research, 114(4), 529-539. [CrossRef]
- Michael, S. K., Surks, H. K., Wang, Y., Zhu, Y., Blanton, R., Jamnongjit, M., ... & Mendelsohn, M. E. (2008). High blood pressure arising from a defect in vascular function. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 105(18), 6702-6707. [CrossRef]
- Beevers, G., Lip, G. Y., & O’Brien, E. (2001). The pathophysiology of hypertension. Bmj, 322(7291), 912-916. [CrossRef]
- Hingorani, A. D., Sharma, P., Jia, H., Hopper, R., & Brown, M. J. (1996). Blood pressure and the M235T polymorphism of the angiotensinogen gene. Hypertension, 28(5), 907-911. [CrossRef]
- Canbakan, B. (2013). Rational approaches to the treatment of hypertension: drug therapy—monotherapy, combination, or fixed-dose combination?. Kidney international supplements, 3(4), 349-351. [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-García, C., & Rubio-Guerra, A. F. (2018). Combination therapy in the treatment of hypertension. Drugs in context, 7. [CrossRef]
- Chalmers, J. (1993). The place of combination therapy in the treatment of hypertension in 1993. Clinical and Experimental Hypertension, 15(6), 1299-1313. [CrossRef]
- Gradman, A. H., Basile, J. N., Carter, B. L., Bakris, G. L., & American Society of Hypertension Writing Group. (2010). Combination therapy in hypertension. Journal of the American Society of Hypertension, 4(2), 90-98.
- Williams, B., Mancia, G., Spiering, W., Agabiti Rosei, E., Azizi, M., Burnier, M., ... & Desormais, I. (2018). 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: The Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Society of Hypertension (ESH). European heart journal, 39(33), 3021-3104.
- Morris, L. S., & Schulz, R. M. (1992). Patient compliance—an overview. Journal of clinical pharmacy and therapeutics, 17(5), 283-295.
- Blackwell, B. (1973). Patient compliance. New England Journal of Medicine, 289(5), 249-252.
- Salahuddin, A., Mushtaq, M., & Materson, B. J. (2013). Combination therapy for hypertension 2013: an update. Journal of the American Society of Hypertension, 7(5), 401-407. [CrossRef]
- Kalra, S., Kalra, B., & Agrawal, N. (2010). Combination therapy in hypertension: An update. Diabetology & metabolic syndrome, 2(1), 1-11. [CrossRef]
- Gorostidi, M., & de la Sierra, A. (2013). Combination therapy in hypertension. Advances in therapy, 30, 320-336.
- Chaszczewska-Markowska, M., Sagan, M., & Bogunia-Kubik, K. (2016). The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS)–physiology and molecular mechanisms of functioning. Advances in Hygiene and Experimental Medicine, 70, 917-927. [CrossRef]
- Atlas, S. A. (2007). The renin-angiotensin aldosterone system: pathophysiological role and pharmacologic inhibition. Journal of managed care pharmacy, 13(8 Supp B), 9-20. [CrossRef]
- Thatcher, S. E. (2017). A brief introduction into the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system: new and old techniques. The Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System: Methods and Protocols, 1-19.
- Schweda, F. (2015). Salt feedback on the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. Pflügers Archiv-European Journal of Physiology, 467, 565-576. [CrossRef]
- Taugner, R., & Hackenthal, E. (1988). On the character of the secretory granules in juxtaglomerular epithelioid cells. International review of cytology, 110, 93-131. [CrossRef]
- Barajas, L. (1979). Anatomy of the juxtaglomerular apparatus. American Journal of Physiology-Renal Physiology, 237(5), F333-F343. [CrossRef]
- Schweda, F., Friis, U., Wagner, C., Skott, O., & Kurtz, A. (2007). Renin release. Physiology, 22(5), 310-319.
- Trerattanavong, K., & Chen, J. (2023). Biochemistry, Renin. In StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing.
- Morgan, L., Pipkin, F. B., & Kalsheker, N. (1996). Angiotensinogen: molecular biology, biochemistry and physiology. The international journal of biochemistry & cell biology, 28(11), 1211-1222. [CrossRef]
- Lu, H., Cassis, L. A., Vander Kooi, C. W., & Daugherty, A. (2016). Structure and functions of angiotensinogen. Hypertension Research, 39(7), 492-500. [CrossRef]
- Jeunemaitre, X., Soubrier, F., Kotelevtsev, Y. V., Lifton, R. P., Williams, C. S., Charru, A., ... & Corvol, P. (1992). Molecular basis of human hypertension: role of angiotensinogen. Cell, 71(1), 169-180. [CrossRef]
- Wu, C., Lu, H., Cassis, L. A., & Daugherty, A. (2011). Molecular and pathophysiological features of angiotensinogen: a mini review. North American journal of medicine & science, 4(4), 183. [CrossRef]
- Dickson, M. E., & Sigmund, C. D. (2006). Genetic basis of hypertension: revisiting angiotensinogen. Hypertension, 48(1), 14-20. [CrossRef]
- Wu, C., Lu, H., Cassis, L. A., & Daugherty, A. (2011). Molecular and pathophysiological features of angiotensinogen: a mini review. North American journal of medicine & science, 4(4), 183. [CrossRef]
- Griendling, K. K., Murphy, T. J., & Alexander, R. W. (1993). Molecular biology of the renin-angiotensin system. Circulation, 87(6), 1816-1828. [CrossRef]
- Sparks, M. A., Crowley, S. D., Gurley, S. B., Mirotsou, M., & Coffman, T. M. (2014). Classical renin-angiotensin system in kidney physiology. Comprehensive Physiology, 4(3), 1201. [CrossRef]
- DORER, F. E., KAHN, J. R., LENTZ, K. E., LEVINE, M., & SKEGGS, L. T. (1974). Hydrolysis of bradykinin by angiotensin-converting enzyme. Circulation Research, 34(6), 824-827. [CrossRef]
- Pirahanchi, Y., & Sharma, S. (2019). Physiology, Bradykinin.
- Ng, K. K. F., & Vane, J. R. (1967). Conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II. Nature, 216(5117), 762-766. [CrossRef]
- Erdös, E. G. (1976). Conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II. The American journal of medicine, 60(6), 749-759. [CrossRef]
- Fountain, J. H., Kaur, J., & Lappin, S. L. (2023). Physiology, renin angiotensin system. In StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing.
- Peti-Peterdi, J., & Harris, R. C. (2010). Macula densa sensing and signaling mechanisms of renin release. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology: JASN, 21(7), 1093. [CrossRef]
- Unger, T., Chung, O., Csikos, T., Culman, J., Gallinat, S., Gohlke, P., ... & Zhu, Y. Z. (1996). Angiotensin receptors. Journal of hypertension. Supplement: official journal of the International Society of Hypertension, 14(5), S95-103.
- Greindling, K. K., Lassegue, B., & Alexander, R. W. (1996). Angiotensin receptors and their therapeutic implications. Annual review of pharmacology and toxicology, 36(1), 281-306. [CrossRef]
- Greindling, K. K., Lassegue, B., & Alexander, R. W. (1996). Angiotensin receptors and their therapeutic implications. Annual review of pharmacology and toxicology, 36(1), 281-306. [CrossRef]
- Henrion, D., Kubis, N., & Lévy, B. I. (2001). Physiological and pathophysiological functions of the AT2 subtype receptor of angiotensin II: from large arteries to the microcirculation. Hypertension, 38(5), 1150-1157. [CrossRef]
- Padia, S. H., & Carey, R. M. (2013). AT 2 receptors: beneficial counter-regulatory role in cardiovascular and renal function. Pflügers Archiv-European Journal of Physiology, 465, 99-110. [CrossRef]
- Volpe, M., Musumeci, B., De Paolis, P., Savoia, C., & Morganti, A. (2003). Angiotensin II AT2 receptor subtype: an uprising frontier in cardiovascular disease?. Journal of hypertension, 21(8), 1429-1443. [CrossRef]
- Kostenis, E., Milligan, G., Christopoulos, A., Sanchez-Ferrer, C. F., Heringer-Walther, S., Sexton, P. M., ... & Walther, T. (2005). G-protein–coupled receptor Mas is a physiological antagonist of the angiotensin II type 1 receptor. Circulation, 111(14), 1806-1813. [CrossRef]
- Oro, C., Qian, H., & Thomas, W. G. (2007). Type 1 angiotensin receptor pharmacology: signaling beyond G proteins. Pharmacology & therapeutics, 113(1), 210-226. [CrossRef]
- Thiriet, M., & Thiriet, M. (2012). G-Protein-Coupled Receptors. Signaling at the Cell Surface in the Circulatory and Ventilatory Systems, 425-591.
- Nguyen Dinh Cat, A., & Touyz, R. M. (2011). Cell signaling of angiotensin II on vascular tone: novel mechanisms. Current hypertension reports, 13(2), 122-128. [CrossRef]
- Abadir, P. M., Periasamy, A., Carey, R. M., & Siragy, H. M. (2006). Angiotensin II type 2 receptor–bradykinin B2 receptor functional heterodimerization. Hypertension, 48(2), 316-322. [CrossRef]
- Duka, A., Duka, I., Gao, G., Shenouda, S., Gavras, I., & Gavras, H. (2006). Role of bradykinin B1 and B2 receptors in normal blood pressure regulation. American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism, 291(2), E268-E274. [CrossRef]
- Bernier, S. G., Haldar, S., & Michel, T. (2000). Bradykinin-regulated interactions of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway with the endothelial nitric-oxide synthase. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 275(39), 30707-30715.
- Daiber, A., & Münzel, T. (2015). Organic nitrate therapy, nitrate tolerance, and nitrate-induced endothelial dysfunction: emphasis on redox biology and oxidative stress. Antioxidants & redox signaling, 23(11), 899-942. [CrossRef]
- Maron, B. A., & Michel, T. (2012). Subcellular localization of oxidants and redox modulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Circulation Journal, 76(11), 2497-2512. [CrossRef]
- Stocco, D. M., & Clark, B. J. (1996). Regulation of the acute production of steroids in steroidogenic cells. Endocrine reviews, 17(3), 221-244. [CrossRef]
- Lymperopoulos, A., Rengo, G., Zincarelli, C., Kim, J., Soltys, S., & Koch, W. J. (2009). An adrenal β-arrestin 1-mediated signaling pathway underlies angiotensin II-induced aldosterone production in vitro and in vivo. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 106(14), 5825-5830. [CrossRef]
- Bollag, W. B. (2011). Regulation of aldosterone synthesis and secretion. Comprehensive physiology, 4(3), 1017-1055. [CrossRef]
- Bollag, W. B. (2011). Regulation of aldosterone synthesis and secretion. Comprehensive physiology, 4(3), 1017-1055. [CrossRef]
- Scott, J. H., Menouar, M. A., & Dunn, R. J. (2017). Physiology, aldosterone.
- Pearce, D., Soundararajan, R., Trimpert, C., Kashlan, O. B., Deen, P. M., & Kohan, D. E. (2015). Collecting duct principal cell transport processes and their regulation. Clinical journal of the American Society of Nephrology: CJASN, 10(1), 135. [CrossRef]
- Sandgren, J. A., Linggonegoro, D. W., Zhang, S. Y., Sapouckey, S. A., Claflin, K. E., Pearson, N. A., ... & Grobe, J. L. (2018). Fluid and Electrolyte Homeostasis: Angiotensin AT1A receptors expressed in vasopressin-producing cells of the supraoptic nucleus contribute to osmotic control of vasopressin. American Journal of Physiology-Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology, 314(6), R770. [CrossRef]
- Okuya, S., Inenaga, K., Kaneko, T., & Yamashita, H. (1987). Angiotensin II sensitive neurons in the supraoptic nucleus, subfornical organ and anteroventral third ventricle of rats in vitro. Brain research, 402(1), 58-67. [CrossRef]
- Cuzzo, B., Padala, S. A., & Lappin, S. L. (2023). Physiology, vasopressin. In StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing.
- 94. Hanoune, J. (2010). Vasopressin receptors, the signalling cascade and mechanisms of action. Perspectives on Vasopressin.
- Morla, L., Edwards, A., & Crambert, G. (2016). New insights into sodium transport regulation in the distal nephron: Role of G-protein coupled receptors. World journal of biological chemistry, 7(1), 44. [CrossRef]
- Severs, W. B., & Summy-Long, J. (1975). The role of angiotensin in thirst. Life Sciences, 17(10), 1513-1526. [CrossRef]
- 97. Fitzsimons, J. T. (1998). Angiotensin, thirst, and sodium appetite. Physiological reviews, 78(3), 583-686. [CrossRef]
- Dibona, G. F. (2013). Sympathetic nervous system and hypertension. Hypertension, 61(3), 556-560. [CrossRef]
- Dibona, G. F. (2004). The sympathetic nervous system and hypertension: recent developments. Hypertension, 43(2), 147-150. [CrossRef]
- Esler, M. (2000). The sympathetic system and hypertension. American journal of hypertension, 13(S4), 99S-105S. [CrossRef]
- Wnorowski, A., & Jozwiak, K. (2014). Homo-and hetero-oligomerization of β2-adrenergic receptor in receptor trafficking, signaling pathways and receptor pharmacology. Cellular Signalling, 26(10), 2259-2265. [CrossRef]
- Ecker, P. M., Lin, C. C., Powers, J., Kobilka, B. K., Dubin, A. M., & Bernstein, D. (2006). Effect of targeted deletions of β1-and β2-adrenergic-receptor subtypes on heart rate variability. American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology, 290(1), H192-H199. [CrossRef]
- Woo, A. Y. H., & Xiao, R. P. (2012). β-Adrenergic receptor subtype signaling in heart: from bench to bedside. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica, 33(3), 335-341. [CrossRef]
- Lefkowitz, R. J., Rockman, H. A., & Koch, W. J. (2000). Catecholamines, cardiac β-adrenergic receptors, and heart failure. Circulation, 101(14), 1634-1637. [CrossRef]
- Stiles, G. L., Caron, M. G., & Lefkowitz, R. J. (1984). Beta-adrenergic receptors: biochemical mechanisms of physiological regulation. Physiological reviews, 64(2), 661-743. [CrossRef]
- Thomas, G. D. (2011). Neural control of the circulation. Advances in physiology education, 35(1), 28-32. [CrossRef]
- Grassi, G. (2001). Renin–angiotensin–sympathetic crosstalks in hypertension: reappraising the relevance of peripheral interactions. Journal of hypertension, 19(10), 1713-1716. [CrossRef]
- Aldehni, F., Tang, T., Madsen, K., Plattner, M., Schreiber, A., Friis, U. G., ... & Schweda, F. (2011). Stimulation of renin secretion by catecholamines is dependent on adenylyl cyclases 5 and 6. Hypertension, 57(3), 460-468. [CrossRef]
- Messerli, F. H., Bangalore, S., Bavishi, C., & Rimoldi, S. F. (2018). Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors in hypertension: to use or not to use?. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 71(13), 1474-1482. [CrossRef]
- Uehara, Y., Miura, S. I., Yahiro, E., & Saku, K. (2013). Non-ACE pathway-induced angiotensin II production. Current pharmaceutical design, 19(17), 3054-3059. [CrossRef]
- Hallberg, P., Nagy, J., Karawajczyk, M., Nordang, L., Islander, G., Norling, P., ... & Wadelius, M. (2017). Comparison of clinical factors between patients with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor–induced angioedema and cough. Annals of Pharmacotherapy, 51(4), 293-300. [CrossRef]
- Robles, N. R., Cerezo, I., & Hernandez-Gallego, R. (2014). Renin–angiotensin system blocking drugs. Journal of cardiovascular pharmacology and therapeutics, 19(1), 14-33. [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Hernández, R., Sosa-Canache, B., Velasco, M., Armas-Hernandez, M. J., Armas-Padilla, M. C., & Cammarata, R. (2002). Angiotensin II receptor antagonists role in arterial hypertension. Journal of human hypertension, 16(1), S93-S99. [CrossRef]
- Pantzaris, N. D., Karanikolas, E., Tsiotsios, K., & Velissaris, D. (2017). Renin inhibition with aliskiren: A decade of clinical experience. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 6(6), 61. [CrossRef]
- Trimarchi, H. (2011). Role of aliskiren in blood pressure control and renoprotection. International Journal of Nephrology and Renovascular Disease, 41-48. [CrossRef]
- Cooper, D., & Dimri, M. (2020). Biochemistry, Calcium Channels.
- Catterall, W. A., Perez-Reyes, E., Snutch, T. P., & Striessnig, J. (2005). International Union of Pharmacology. XLVIII. Nomenclature and structure-function relationships of voltage-gated calcium channels. Pharmacological reviews, 57(4), 411-425. [CrossRef]
- Wu, J., Yan, Z., Li, Z., Yan, C., Lu, S., Dong, M., & Yan, N. (2015). Structure of the voltage-gated calcium channel Cav1. 1 complex. Science, 350(6267), aad2395. [CrossRef]
- Ertel, E. A., Campbell, K. P., Harpold, M. M., Hofmann, F., Mori, Y., Perez-Reyes, E., ... & Catterall, W. A. (2000). Nomenclature of voltage-gated calcium channels. Neuron, 25(3), 533-535. [CrossRef]
- Dolphin, A. C. (2016). Voltage-gated calcium channels and their auxiliary subunits: physiology and pathophysiology and pharmacology. The Journal of physiology, 594(19), 5369-5390. [CrossRef]
- Shah, K., Seeley, S., Schulz, C., Fisher, J., & Gururaja Rao, S. (2022). Calcium channels in the heart: Disease states and drugs. Cells, 11(6), 943. [CrossRef]
- Hockerman, G. H., Peterson, B. Z., Johnson, and, B. D., & Catterall, W. A. (1997). Molecular determinants of drug binding and action on L-type calcium channels. Annual review of pharmacology and toxicology, 37(1), 361-396. [CrossRef]
- Neagoe, A. M., Rexhaj, E., Grossman, E., & Messerli, F. H. (2019). Beta blockers and calcium channel blockers. Cardiovascular Hemodynamics: An Introductory Guide, 73-88.
- Weir, M. R. (2007). Calcium channel blockers: their pharmacologic and therapeutic role in hypertension. American journal of cardiovascular drugs, 7(Suppl 1), 5-15. [CrossRef]
- Khalil, H., & Zeltser, R. (2023). Antihypertensive medications.[Updated 2022 May 15]. StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing.
- Elliott, W. J., & Ram, C. V. S. (2011). Calcium channel blockers. The Journal of Clinical Hypertension, 13(9), 687.
- 127. Padilla, M. C. A., Armas-Hernández, M. J., Hernández, R. H., Israili, Z. H., & Valasco, M. (2007). Update of diuretics in the treatment of hypertension. American journal of therapeutics, 14(2), 154-160. [CrossRef]
- 128. Tamargo, J., Segura, J., & Ruilope, L. M. (2014). Diuretics in the treatment of hypertension. Part 2: loop diuretics and potassium-sparing agents. Expert opinion on pharmacotherapy, 15(5), 605-621. [CrossRef]
- Roush, G. C., & Sica, D. A. (2016). Diuretics for hypertension: a review and update. American journal of hypertension, 29(10), 1130-1137. [CrossRef]
- McNally, R. J., Morselli, F., Farukh, B., Chowienczyk, P. J., & Faconti, L. (2019). A review of the prescribing trend of thiazide-type and thiazide-like diuretics in hypertension: A UK perspective. British journal of clinical pharmacology, 85(12), 2707-2713. [CrossRef]
- Liang, W., Ma, H., Cao, L., Yan, W., & Yang, J. (2017). Comparison of thiazide-like diuretics versus thiazide-type diuretics: a meta-analysis. Journal of cellular and molecular medicine, 21(11), 2634-2642. [CrossRef]
- Rapoport, R. M., & Soleimani, M. (2019). Mechanism of thiazide diuretic arterial pressure reduction: the search continues. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 10, 815. [CrossRef]
- Blowey, D. L. (2016). Diuretics in the treatment of hypertension. Pediatric nephrology, 31, 2223-2233. [CrossRef]
- Duarte, J. D., & Cooper-DeHoff, R. M. (2010). Mechanisms for blood pressure lowering and metabolic effects of thiazide and thiazide-like diuretics. Expert review of cardiovascular therapy, 8(6), 793-802. [CrossRef]
- Carter, B. L., Ernst, M. E., & Cohen, J. D. (2004). Hydrochlorothiazide versus chlorthalidone: evidence supporting their interchangeability. Hypertension, 43(1), 4-9. [CrossRef]
- Wiggam, M. I., Bell, P. M., Sheridan, B., Walmsley, A., & Atkinson, A. B. (1999). Low dose bendrofluazide (1.25 mg) effectively lowers blood pressure over 24 h: results of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover study. American journal of hypertension, 12(5), 528-531. [CrossRef]
- Peterzan, M. A., Hardy, R., Chaturvedi, N., & Hughes, A. D. (2012). Meta-analysis of dose-response relationships for hydrochlorothiazide, chlorthalidone, and bendroflumethiazide on blood pressure, serum potassium, and urate. Hypertension, 59(6), 1104-1109. [CrossRef]
- Grossman, E., Verdecchia, P., Shamiss, A., Angeli, F., & Reboldi, G. (2011). Diuretic treatment of hypertension. Diabetes care, 34(Suppl 2), S313.
- Rockhold, R. W. (1992). Thiazide diuretics and male sexual dysfunction. Drug development research, 25(2), 85-95. [CrossRef]
- Krane, R. J., Goldstein, I., & de Tejada, I. S. (1989). Impotence. New England Journal of Medicine, 321(24), 1648-1659.
- Ravioli, S., Bahmad, S., Funk, G. C., Schwarz, C., Exadaktylos, A., & Lindner, G. (2021). Risk of electrolyte disorders, syncope, and falls in patients taking thiazide diuretics: results of a cross-sectional study. The American Journal of Medicine, 134(9), 1148-1154. [CrossRef]
- Akbari, P., & Khorasani-Zadeh, A. (2023). Thiazide Diuretics. In StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing.
- Nochaiwong, S., Chuamanochan, M., Ruengorn, C., Noppakun, K., Awiphan, R., Phosuya, C., ... & Knoll, G. A. (2022). Use of thiazide diuretics and risk of all types of skin cancers: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancers, 14(10), 2566. [CrossRef]
- Malha, L., & Mann, S. J. (2016). Loop diuretics in the treatment of hypertension. Current hypertension reports, 18(4), 27. [CrossRef]
- Pickkers, P., Dormans, T. P., Russel, F. G., Hughes, A. D., Thien, T., Schaper, N., & Smits, P. (1997). Direct vascular effects of furosemide in humans. Circulation, 96(6), 1847-1852. [CrossRef]
- Musini, V. M., Rezapour, P., Wright, J. M., Bassett, K., & Jauca, C. D. (2015). Blood pressure-lowering efficacy of loop diuretics for primary hypertension. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, (5). [CrossRef]
- Blowey, D. L. (2016). Diuretics in the treatment of hypertension. Pediatric nephrology, 31, 2223-2233. [CrossRef]
- Sica, D. A., Carter, B., Cushman, W., & Hamm, L. (2011). Thiazide and loop diuretics. The journal of clinical hypertension, 13(9), 639-643. [CrossRef]
- Huxel, C., Raja, A., & Ollivierre-Lawrence, M. D. (2023). Loop diuretics. In StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing.
- Calhoun, D. A., & White, W. B. (2008). Effectiveness of the selective aldosterone blocker, eplerenone, in patients with resistant hypertension. Journal of the American Society of Hypertension, 2(6), 462-468. [CrossRef]
- PROGRESS Collaborative Group. (2001). Randomised trial of a perindopril-based blood-pressure-lowering regimen among 6105 individuals with previous stroke or transient ischaemic attack. The Lancet, 358(9287), 1033-1041. [CrossRef]
- Patel, A. (2007). Effects of a fixed combination of perindopril and indapamide on macrovascular and microvascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (the ADVANCE trial): a randomised controlled trial. The Lancet, 370(9590), 829-840. [CrossRef]
- Beckett, N. S., Peters, R., Fletcher, A. E., Staessen, J. A., Liu, L., Dumitrascu, D., ... & Bulpitt, C. J. (2008). Treatment of hypertension in patients 80 years of age or older. New England Journal of Medicine, 358(18), 1887-1898. [CrossRef]
- Dahlöf, B., Devereux, R. B., Kjeldsen, S. E., Julius, S., Beevers, G., de Faire, U., ... & Wedel, H. (2002). Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in the Losartan Intervention For Endpoint reduction in hypertension study (LIFE): a randomised trial against atenolol. The Lancet, 359(9311), 995-1003. [CrossRef]
- Pepine, C. J., Handberg, E. M., Cooper-DeHoff, R. M., Marks, R. G., Kowey, P., Messerli, F. H., ... & INVEST Investigators. (2003). A calcium antagonist vs a non–calcium antagonist hypertension treatment strategy for patients with coronary artery disease: the International Verapamil-Trandolapril Study (INVEST): a randomized controlled trial. Jama, 290(21), 2805-2816.
- Dahlöf, B., Sever, P. S., Poulter, N. R., Wedel, H., Beevers, D. G., Caulfield, M., ... & Östergren, J. (2005). Prevention of cardiovascular events with an antihypertensive regimen of amlodipine adding perindopril as required versus atenolol adding bendroflumethiazide as required, in the Anglo-Scandinavian Cardiac Outcomes Trial-Blood Pressure Lowering Arm (ASCOT-BPLA): a multicentre randomised controlled trial. The Lancet, 366(9489), 895-906. [CrossRef]
- Jamerson, K., Weber, M. A., Bakris, G. L., Dahlöf, B., Pitt, B., Shi, V., ... & Velazquez, E. J. (2008). Benazepril plus amlodipine or hydrochlorothiazide for hypertension in high-risk patients. New England Journal of Medicine, 359(23), 2417-2428. [CrossRef]
- Bakris, G. L., Sarafidis, P. A., Weir, M. R., Dahlöf, B., Pitt, B., Jamerson, K., ... & Weber, M. A. (2010). Renal outcomes with different fixed-dose combination therapies in patients with hypertension at high risk for cardiovascular events (ACCOMPLISH): a prespecified secondary analysis of a randomised controlled trial. The Lancet, 375(9721), 1173-1181. [CrossRef]
- Meredith, P. A., & Elliott, H. L. (1992). Clinical pharmacokinetics of amlodipine. Clinical pharmacokinetics, 22(1), 22-31. [CrossRef]
- Edgar, B., Lundborg, P., & Regårdh, C. G. (1987). Clinical pharmacokinetics of felodipine: a summary. Drugs, 34, 16-27. [CrossRef]
- Hamann, S. R., Blouin, R. A., & McAllister, R. G. (1984). Clinical pharmacokinetics of verapamil. Clinical pharmacokinetics, 9, 26-41. [CrossRef]
- Scott, L. J., & McCormack, P. L. (2008). Olmesartan medoxomil: a review of its use in the management of hypertension. Drugs, 68, 1239-1272. [CrossRef]
- Warner, G. T., & Jarvis, B. (2002). Olmesartan medoxomil. Drugs, 62, 1345-1353.
- Markham, A., & Goa, K. L. (1997). Valsartan: a review of its pharmacology and therapeutic use in essential hypertension. Drugs, 54, 299-311. [CrossRef]
- McClellan, K. J., & Markham, A. (1998). Telmisartan. Drugs, 56(6).
- Israili, Z. H. (2000). Clinical pharmacokinetics of angiotensin II (AT1) receptor blockers in hypertension. Journal of human hypertension, 14(1), S73-S86. [CrossRef]
- Gleiter, C. H., & Mörike, K. E. (2002). Clinical pharmacokinetics of candesartan. Clinical pharmacokinetics, 41, 7-17. [CrossRef]
- Bottorff, M. B., & Tenero, D. M. (1999). Pharmacokinetics of eprosartan in healthy subjects, patients with hypertension, and special populations. Pharmacotherapy: The Journal of Human Pharmacology and Drug Therapy, 19(4P2), 73S-78S. [CrossRef]
- Sica, D. A., Gehr, T. W., & Ghosh, S. (2005). Clinical pharmacokinetics of losartan. Clinical pharmacokinetics, 44, 797-814. [CrossRef]
- Balfour, J. A., & Goa, K. L. (1991). Benazepril: a review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic efficacy in hypertension and congestive heart failure. Drugs, 42, 511-539. [CrossRef]
- Duchin, K. L., McKinstry, D. N., Cohen, A. I., & Migdalof, B. H. (1988). Pharmacokinetics of captopril in healthy subjects and in patients with cardiovascular diseases. Clinical pharmacokinetics, 14, 241-259. [CrossRef]
- Gomez, H. J., Cirillo, V. J., & Irvin, J. D. (1985). Enalapril: a review of human pharmacology. Drugs, 30, 13-24. [CrossRef]
- Todd, P. A., & Goa, K. L. (1992). Enalapril: a reappraisal of its pharmacology and therapeutic use in hypertension. Drugs, 43, 346-381. [CrossRef]
- Murdoch, D., & McTavish, D. (1992). Fosinopril: a review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic potential in essential hypertension. Drugs, 43, 123-140. [CrossRef]
- Goa, K. L., Balfour, J. A., & Zuanetti, G. (1996). Lisinopril: a review of its pharmacology and clinical efficacy in the early management of acute myocardial infarction. Drugs, 52(4), 564-588. [CrossRef]
- Kieback, A. G., Felix, S. B., & Reffelmann, T. (2009). Quinaprilat: a review of its pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, toxicological data and clinical application. Expert Opinion on Drug Metabolism & Toxicology, 5(10), 1337-1347.
- Commander, S. J., Wu, H., Boakye-Agyeman, F., Melloni, C., Hornik, C. D., Zimmerman, K., ... & Best Pharmaceuticals for Children Act–Pediatric Trials Network Steering Committee. (2021). Pharmacokinetics of Hydrochlorothiazide in Children: A Potential Surrogate for Renal Secretion Maturation. The Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 61(3), 368-377. [CrossRef]
- Chobanian, A. V., Bakris, G. L., Black, H. R., Cushman, W. C., Green, L. A., Izzo Jr, J. L., ... & National High Blood Pressure Education Program Coordinating Committee. (2003). Seventh report of the joint national committee on prevention, detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure. hypertension, 42(6), 1206-1252. [CrossRef]
- Smith, D. K., Lennon, R. P., & Carlsgaard, P. B. (2020). Managing hypertension using combination therapy. American family physician, 101(6), 341-349.
- Williams, B., Poulter, N. R., Brown, M. J., Davis, M., McInnes, G. T., Potter, J. F., ... & Thom, S. M. (2004). British Hypertension Society guidelines for hypertension management 2004 (BHS-IV): summary. Bmj, 328(7440), 634-640. [CrossRef]
- Umemura, S., Arima, H., Arima, S., Asayama, K., Dohi, Y., Hirooka, Y., ... & Hirawa, N. (2019). The Japanese Society of Hypertension guidelines for the management of hypertension (JSH 2019). Hypertension Research, 42(9), 1235-1481. [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





