Submitted:
13 February 2024
Posted:
14 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Pig Populations Enrolled for the Investigation
2.2. Serological Analyses
2.3. Samples Collection and RNA Extraction
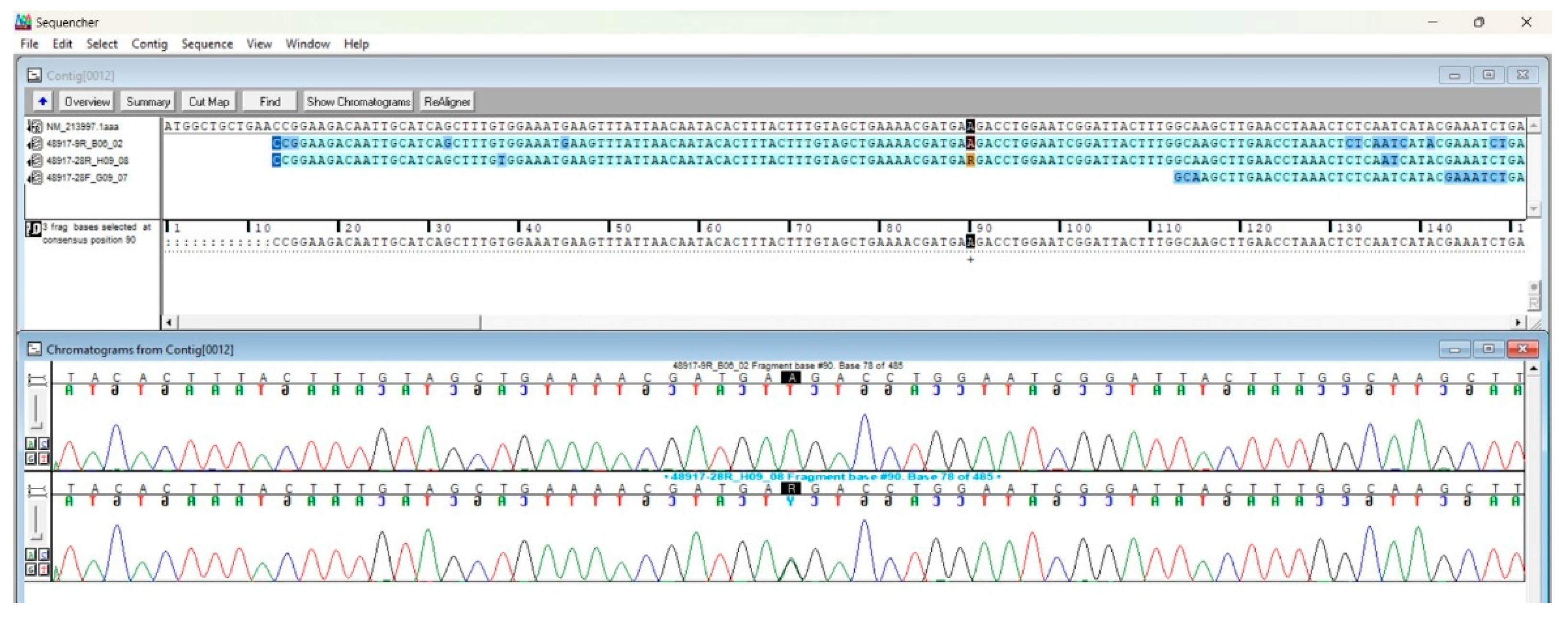
2.4. IL-18 RT-PCR and Sanger Sequencing
2.5. Genetic Data Elaboration
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- OIE Terrestrial Manual, 2018.
- Attias, M.; Teixeira, D.E.; Benchimol, M.; Vommaro, R.C.; Crepaldi, P.H.; De Souza, W. The life-cycle of Toxoplasma gondii reviewed using animations. Parasit. Vectors. 2020, 13, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, M.; Berhanu, G.; Steinmetz, C.H.D.; Durglishvili, N. Toxoplasmosis: An Emerging and Re-emerging Zoonosis of Global Public Health Concern. Am. J. Infect. Dis 2021, 9, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P.; Cerqueira-Cézar, C.K.; Murata, F.H.A.; Kwok, O.C.H.; Hill, D.; Yang, Y.; Su, C. All about Toxoplasma gondii infections in pigs: 2009-2020. Vet. Parasitol. 2020, 288, 109185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayani, M.; Riahi, S.M.; Bazrafshan, N.; Ray Gamble, H.; Rostami, A. Toxoplasma gondii infection and risk of Parkinson and Alzheimer diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis on observational studies. Acta Trop. 2019, 196, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archibald, L.K. and Quisling, R.G. Central nervous system infections. In Textbook of neurointensive care. Springer, London. 2013, pp 427-517.
- Hodge, J.M.; Coghill, A.E.; Kim, Y.; Bender, N.; Smith-Warner, S.A.; Gapstur, S.; Teras, L.R.; Grimsrud, T.K.; Waterboer, T.; Egan, K.M. Toxoplasma gondii infection and the risk of adult glioma in two prospective studies. Int. J. Cancer. 2021, 148, 2449–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.D.; Wang, S.C.; Liu, H.H.; Ma, H.Y.; Li, Z.Y.; Wei, F.; Zhu, X.Q.; Liu, Q. Prevalence and burden of Toxoplasma gondii infection in HIV-infected people: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet HIV. 2017, 4, e177–e188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunay, I.R.; Gajurel, K.; Dhakal, R., Liesenfeld, O.; Montoya, J.G. Treatment of Toxoplasmosis: Historical Perspective, Animal Models, and Current Clinical Practice. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 12, e00057-17. [CrossRef]
- Rorman, E.; Zamir, C.S.; Rilkis, I.; Ben-David, H. Congenital Toxoplasmosis--prenatal aspects of Toxoplasma gondii infection. Reprod Toxicol. 2006, 21, 458–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, L.M.; Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasmosis: A history of clinical observations. Int. J. Parasitol. 2009, 39, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasmosis in pigs-The last 20 years. Vet. Parasitol. 2009, 164, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasmosis of Animals and Humans. Second edition. CRC Press; 2010 313 pages. ISBN 978-1-4200-9236-3 (Hardback).
- Zhou, P.; Chen, Z.; Li, H.L.; Zheng, H.; He, S.; Lin, R.Q.; Zhu, XQ. Toxoplasma gondii infection in humans in China. Parasit. Vectors. 2011, 4, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condoleo, R.; Rinaldi, L.; Sette, S.; Mezher, Z. Risk Assessment of Human Toxoplasmosis Associated with the Consumption of Pork Meat in Italy. Risk Anal. 2018, 38, 1202–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, M.; Viscardi, M.; Sgroi, G.; DʼAlessio, N.; Veneziano, V.; Pellicano, R.; Brunetti, R.; Fusco, G. Real-time PCR detection of Toxoplasma gondii in tissue samples of wild boars (Sus scrofa) from southern Italy reveals high prevalence and parasite load. Parasit. Vectors. 2019, 12, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, D.F.; Fowler, F.; Silveira, C.; Nóbrega, M.J.; Nobrega, H.A.J.; Nascimento, H.; Rizzo, L.V.; Commodaro, A.G.; & Belfort, R.Jr. Prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii DNA in Processed Pork Meat. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2018, 15, 734–736. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Lu, S.; Zheng, B. Toxoplasmosis vaccines: what we have and where to go? NPJ Vaccines. 2022, 7, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emam, M.; Livernois, A.; Paibomesai, M.; Atalla, H.; Mallard, B. Genetic and Epigenetic Regulation of Immune Response and Resistance to Infectious Diseases in Domestic Ruminants. Vet. Clin. North Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2019, 35, 405–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwok, A.J.; Mentzer A, Knight, J.C. Host genetics and infectious disease: new tools, insights and translational opportunities. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2021, 22, 137-153. [CrossRef]
- Fast, C.; Groschup, M.H. Classical and atypical scrapie in sheep and goats. In Prions and Diseases. Animals, Humans and the Environment; Zou, W.-Q., Gambetti, P., Eds.; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2013; Volume 2, pp. 15–44. ISBN 978-1-4614-5338-3. [Google Scholar]
- Torricelli, M.; Sebastiani, C.; Ciullo, M.; Ceccobelli, S.; Chiappini, B.; Vaccari, G.; Capocefalo, A; Conte, M.; Giovannini, S.; Lasagna, E.; Sarti, F.M.; Biagetti, M. PRNP Polymorphisms in Eight Local Goat Populations/Breeds from Central and Southern Italy. Animals. 2021, 11, 333. [CrossRef]
- White, S.N.; Knowles, D.P. Expanding possibilities for intervention against small ruminant lentiviruses through genetic marker-assisted selective breeding. Viruses. 2013, 5, 1466–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcangeli, C.; Lucarelli, D.; Torricelli, M.; Sebastiani, C.; Ciullo, M.; Pellegrini, C; Felici, A.; Costarelli, S.; Giammarioli, M.; Feliziani, F.; Passamonti, F.; Biagetti, M. First Survey of SNPs in TMEM154, TLR9, MYD88 and CCR5 Genes in Sheep Reared in Italy and Their Association with Resistance to SRLVs Infection. Viruses. 2021, 13, 1290. [CrossRef]
- Arcangeli, C.; Torricelli, M.; Sebastiani, C.; Lucarelli, D.; Ciullo, M.; Passamonti, F.; Giammarioli, M.; Biagetti, M. Genetic Characterization of Small Ruminant Lentiviruses (SRLVs) Circulating in Naturally Infected Sheep in Central Italy. Viruses. 2022, 14, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Q.; Dunkelberger, J.; Lim, K.S.; Lunney, J.K.; Tuggle, C.K.; Rowland, R.R.R.; Dekkers, J.C.M. ; Associations of natural variation in the CD163 and other candidate genes on host response of nursery pigs to porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus infection. J. Anim. Sci. 2021, 99, skab274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torricelli, M.; Fratto, A.; Ciullo, M.; Sebastiani, C.; Arcangeli, C.; Felici, A.; Giovannini, S.; Sarti, F.M.; Sensi, M.; Biagetti, M. Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome (PRRS) and CD163 Resistance Polymorphic Markers: What Is the Scenario in Naturally Infected Pig Livestock in Central Italy? Animals. 2023, 13, 2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravitz, A.; Pelzer, K.; Sriranganathan, N. The Paratuberculosis Paradigm Examined: A Review of Host Genetic Resistance and Innate Immune Fitness in Mycobacterium avium subsp. Paratuberculosis Infection. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 721706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzone, P.; Di Paolo, A.; Petrucci, L.; Torricelli, M.; Corneli, S.; Sebastiani, C.; Ciullo, M.; Sebastianelli, M.; Costarelli, S.; Scoccia, E.; Sbarra, F.; Gabbianelli, F.; Chillemi, G.; Valentini, A.; Pezzotti, G.; Biagetti, M. Evaluation of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) Associated with Genetic Resistance to Bovine Paratuberculosis in Marchigiana Beef Cattle, an Italian Native Breed. Animals. 2023, 13, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasai, M.; Pradipta, A.; Yamamoto, M. Host immune responses to Toxoplasma gondii. Int. Immunol. 2018, 30, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, D.; Arranz-Solís, D.; Saeij, J.P.J. Influence of the Host and Parasite Strain on the Immune Response During Toxoplasma Infection. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 15, 580425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, K.; Nakanishi, K.; Tsutsui, H. Interleukin-18 in Health and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, G.; Kastelein, R.; Hunter, CA. Interleukin-18 (IL-18) enhances innate IL-12-mediated resistance to Toxoplasma gondii. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 6932–69328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, F.J.; Amode, M.R.; Aneja A.; Austine-Orimoloye, O.; Azov A.G.; Barnes I.; Becker, A.; Bennett R.; Berry A.; Bhai, J. et al., Ensembl 2023, Nucleic Acids Research, Volume 51, Issue D1, 6 January 2023, Pages D933–D941. 6 January; 51. [CrossRef]
- Hou, B.; Benson, A.; Kuzmich, L.; DeFranco, A.L.; Yarovinsky, F. Critical coordination of innate immune defense against Toxoplasma gondii by dendritic cells responding via their Toll-like receptors. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2011, 108, 278–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo’pez-Yglesias, A.H.; Camanzo, E.; Martin, A.T; Araujo, A.M.; Yarovinsky, F. TLR11- independent inflammasome activation is critical for CD4+ T cell-derived IFN-γ production and host resistance to Toxoplasma gondii. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarovinsky, F. Innate immunity to Toxoplasma gondii infection. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 109–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorfu, G.; Cirelli, K.M.; Melo, M.B.; Mayer-Barber, K.; Crown, D.; Koller, B.H.; Masters, S. , Sher, A., Leppla, S. H., Moayeri, M., Saeij, J. P., & Grigg, M. E. Dual role for inflammasome sensors NLRP1 and NLRP3 in murine resistance to Toxoplasma gondii. mBio. 2014, 5, e01117-13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Sequencher® version 5.4.6 DNA sequence analysis software, Gene Codes Corporation, Ann Arbor, MI USA. http://www.genecodes.com.
- Ahmadpour, E.; Bazmani, A.; Kohansal, M.H.; Kazemi, A.; Babaloo, Z. IL-18 gene polymorphism in patients with visceral leishmaniasis in East Azarbaijan, Iran. J Parasit Dis. 2016, 40, 981–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boothroyd, J. C., and Hakimi, M.A. Effectors produced by rhoptries and dense granules: an intense conversation between parasite and host in many languages. Toxoplasma gondii. 2020, 2000, 789–806. [CrossRef]
- Stelzer, S.; Basso, W.; Benavides Silván, J.; Ortega-Mora, L.M.; Maksimov, P.; Gethmann, J.; Conraths, F.J.; Schares, G. Toxoplasma gondii infection and toxoplasmosis in farm animals: Risk factors and economic impact. Food Waterborne Parasitol. 2019, 15, e00037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wujcicka, W.; Gaj, Z.; Wilczyński, J.; Nowakowska, D. Contribution of IL6 -174 G>C and IL1B +3954 C>T polymorphisms to congenital infection with Toxoplasma gondii. Eur. J. Clin. Microbio.l Infect. Dis. 2015, 34, 2287–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wujcicka, W.; Wilczyński. J.; Śpiewak, E.; Nowakowska D. Genetic modifications of cytokine genes and Toxoplasma gondii infections in pregnant women. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 121, 283-292. [CrossRef]
- Andrade, J.M.A.; de Oliveira, C.B.S.; Meurer, Y.D.S.R.; Santana, J.E.; de Almeida, Y.G.B.; Vilela Dos Santos, P.; de Souza, D.M.S.; Costa, G.P.; Talvani, A.; Palomino, G.M.; Freitas, J.C.O.C.; de Andrade-Neto, V.F. Genetic polymorphism in IL17RA induces susceptibility to Toxoplasma gondii infection in Brazilian pregnant women. Acta Trop. 2020, 211, 105594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wujcicka, W.; Gaj, Z.; Wilczyński, J.; Nowakowska, D. Possible role of TLR4 and TLR9 SNPs in protection against congenital Toxoplasmosis. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2015, 34, 2121–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacci, C.; Vismarra, A.; Mangia, C.; Bonardi, S.; Bruini, I.; Genchi, M.; Kramer, L.; Brindani, F. Detection of Toxoplasma gondii in free-range, organic pigs in Italy using serological and molecular methods. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 202, 54–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veronesi, F.; Ranucci, D.; Branciari, R.; Miraglia, D.; Mammoli, R.; Fioretti, DP. Seroprevalence and risk factors for Toxoplasma gondii infection on finishing swine reared in the Umbria region, central Italy. Zoonoses Public Health. 2011, 58, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, A.; Veronesi, F.; Milardi, G.L.; Ranucci, D.; Branciari, R.; Diaferia, M.; Gabrielli, S. Sequence variation in the B1 gene among Toxoplasma gondii isolates from swine and cats in Italy. Res. Vet. Sci. 2017, 115, 353–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veronesi, F.; Santoro, A.; Milardi, G.L.; Diaferia, M.; Branciari, R.; Miraglia, D.; Cioffi, A.; Gabrielli, S.; Ranucci D. Comparison of PCR assays targeting the multi-copy targets B1 gene and 529 bp repetitive element for detection of Toxoplasma gondii in swine muscle. Food Microbiol. 2017, 63:213-216. [CrossRef]
- Vergara, A.; Marangi, M.; Caradonna, T.; Pennisi, L.; Paludi, D.; Papini, R.; Ianieri, A.; Giangaspero, A.; Normanno, G. Toxoplasma gondii Lineages Circulating in Slaughtered Industrial Pigs and Potential Risk for Consumers. J Food Prot. 2018, 81, 1373–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calarco, L.; Barratt, J.; Ellis, J. Detecting sequence variants in clinically important protozoan parasites. Int. J. Parasitol. 2020, 50, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| ID Farm | Region | Area (municipality) | Breeding farm type |
| #1 | Tuscany | Cortona (AR) | fattening - finishing |
| #2 | Tuscany | Cortona (AR) | fattening |
| #3 | Umbria | Deruta (PG) | fattening |
| #4 | Umbria | Perugia (PG) | fattening |
| #5 | Umbria | San Venanzo (PG) | fattening - semiwild |
| #6 | Umbria | Fratta Todina (PG) | closed cycle reproduction |
| #7 | Umbria | Torgiano (PG) | fattening complete cycle |
| #8 | Emilia-Romagna | Poggio Torriana (RN) | fattening complete cycle |
| #9 | Umbria | Torgiano (PG) | open cycle reproduction/fattening |
| #10 | Umbria | Assisi (PG) | fattening - semiwild |
| #11 | Umbria | Perugia (PG) | fattening - finishing |
| #12 | Umbria | Corciano (PG) | fattening - weaning |
| #13 | Umbria | Perugia (PG) | closed cycle reproduction |
| #14 | Umbria | Perugia (PG) | open cycle reproduction |
| #15 | Umbria | Perugia (PG) | fattening complete cycle |
| #16 | Umbria | Perugia (PG) | open cycle reproduction |
| #17 | Marche | Frontone (PU) | fattening - leaning |
| #18 | Umbria | Gubbio (PG) | open cycle reproduction |
| #19 | Umbria | Collazzone (PG) | closed cycle reproduction - semiwild |
| #20 | Umbria | Castiglione del Lago (PG) | fattening - finishing |
| #21 | Umbria | Perugia (PG) | fattening complete cycle |
| #22 | Umbria | Bettona (PG) | fattening complete cycle |
| #23 | Umbria | Cannara (PG) | fattening complete cycle |
| #24 | Umbria | Marsciano (PG) | fattening complete cycle |
| #25 | Umbria | Castel Ritaldi (PG) | fattening complete cycle |
| #26 | Umbria | Collazzone (PG) | fattening - weaning |
| #27 | Umbria | Spello (PG) | fattening - weaning |
| #28 | Umbria | Bastia (PG) | fattening - finishing |
| #29 | Umbria | Cortona (AR) | fattening |
| #30 | Umbria | Deruta (PG) | fattening |
| #31 | Umbria | Passignano (PG) | none recovered and available information |
| #32 | Umbria | S. Enea/Perugia (PG) | fattening |
| #33 | Umbria | Perugia (PG) | fattening |
| #34 | Umbria | S. Enea/Perugia (PG) | fattening |
| #35 | Umbria | Fratta Todina (PG) | wild/outdoor |
| Primer Sequence 5’--->3’ | Amplicon Lenght | Reference | |
| IL-18 | (Forward) ATGGCTGCTGAACCGGAA | 609 bp | This study |
| (Reverse) CAGAAAGTTCAAACCATGCAGT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





