Submitted:
09 February 2024
Posted:
12 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. Amplification and Sequencing of SRK, SLG Alleles
2.2.1. Extraction of Genomic DNA and Amplification of SRK, SLG Alleles
2.2.2. Identification of S Haplotypes Based on BLAST Search
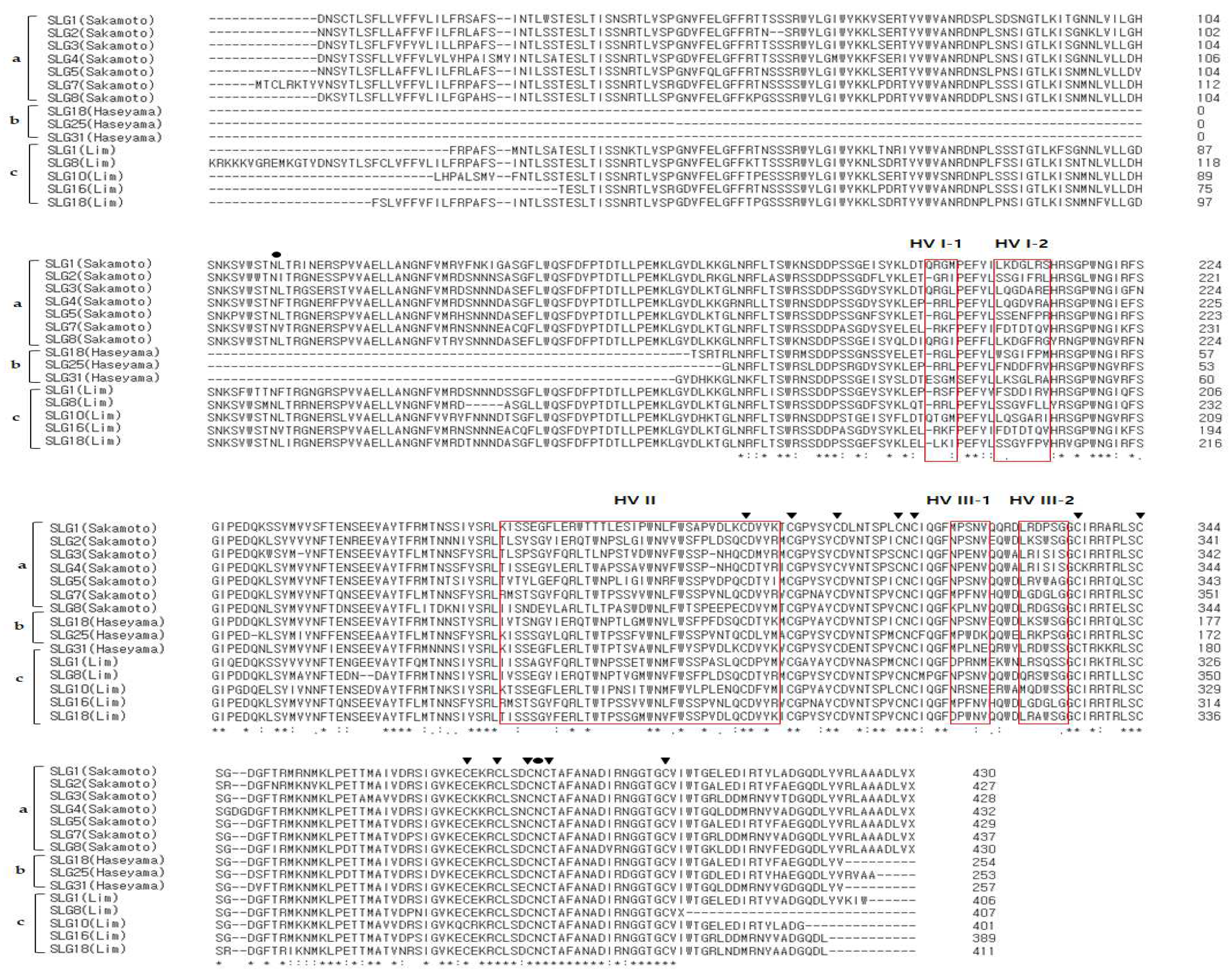
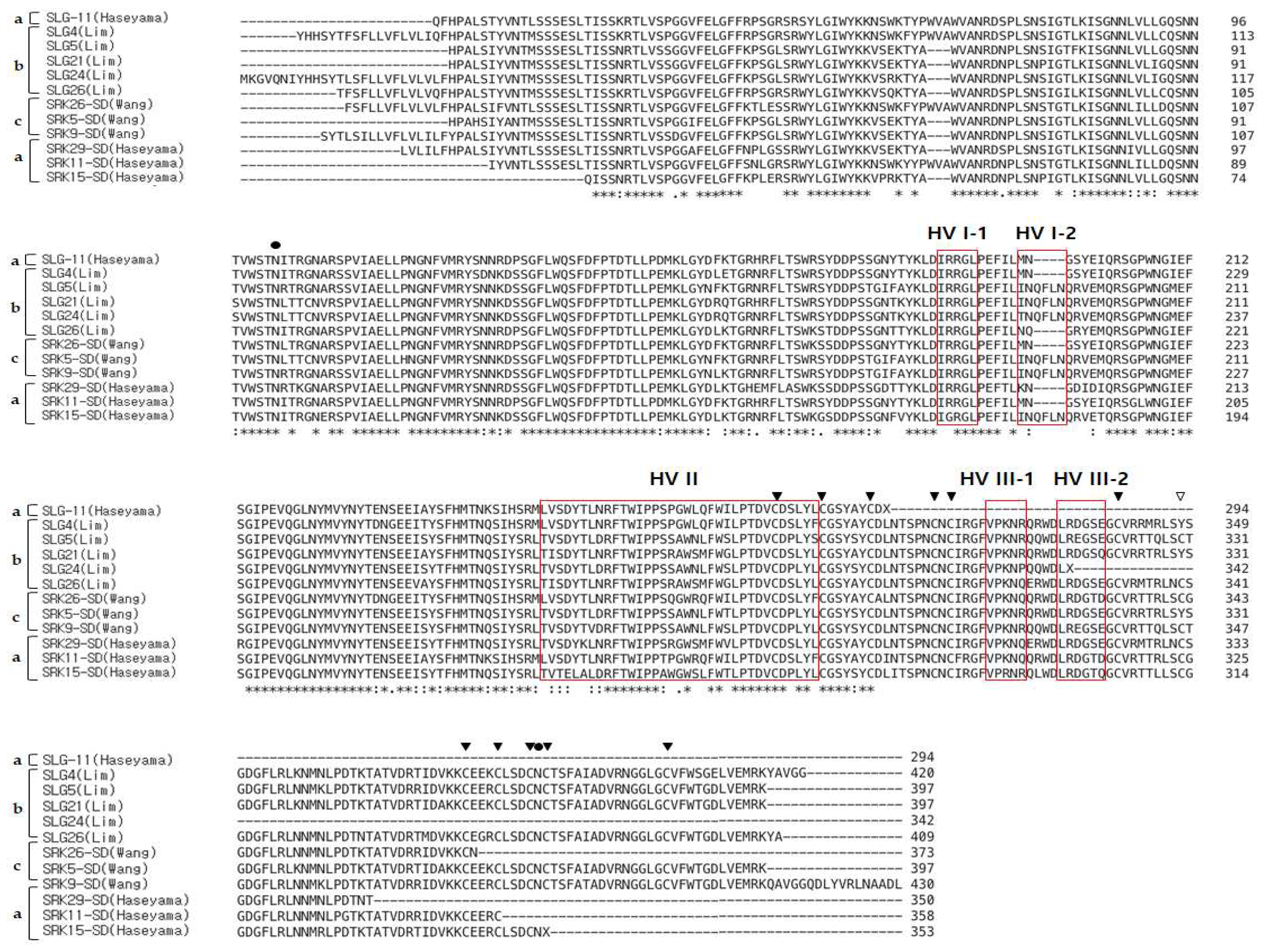
2.3. Multiple Sequence Alignment (MSA)
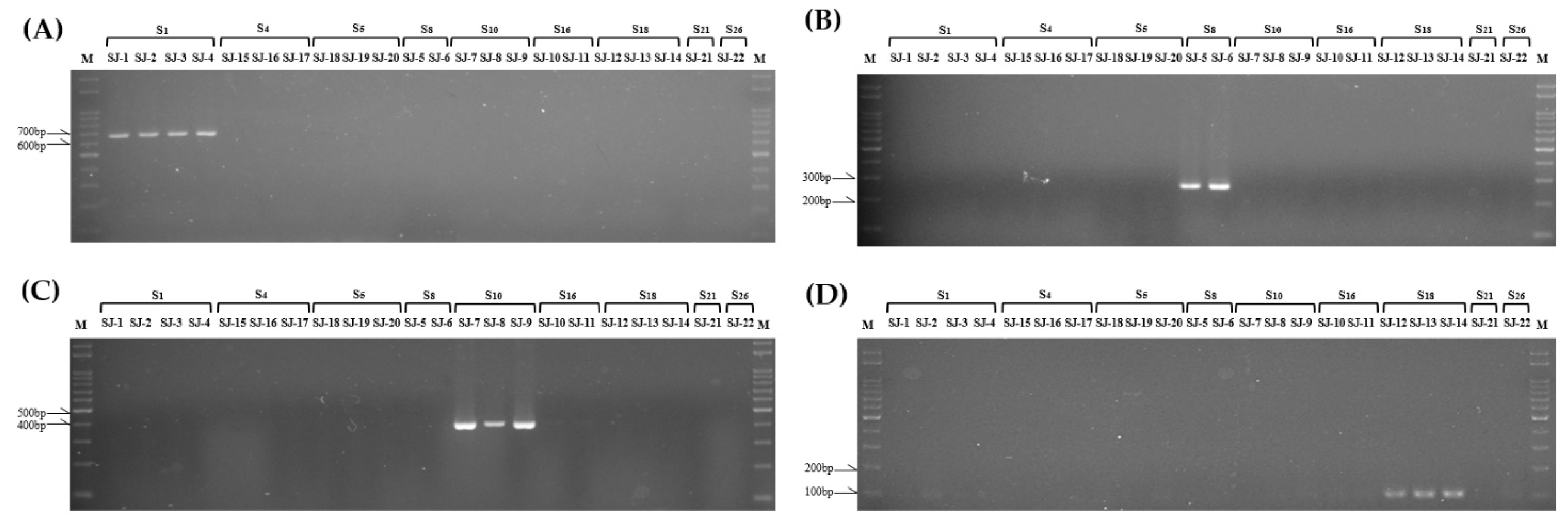
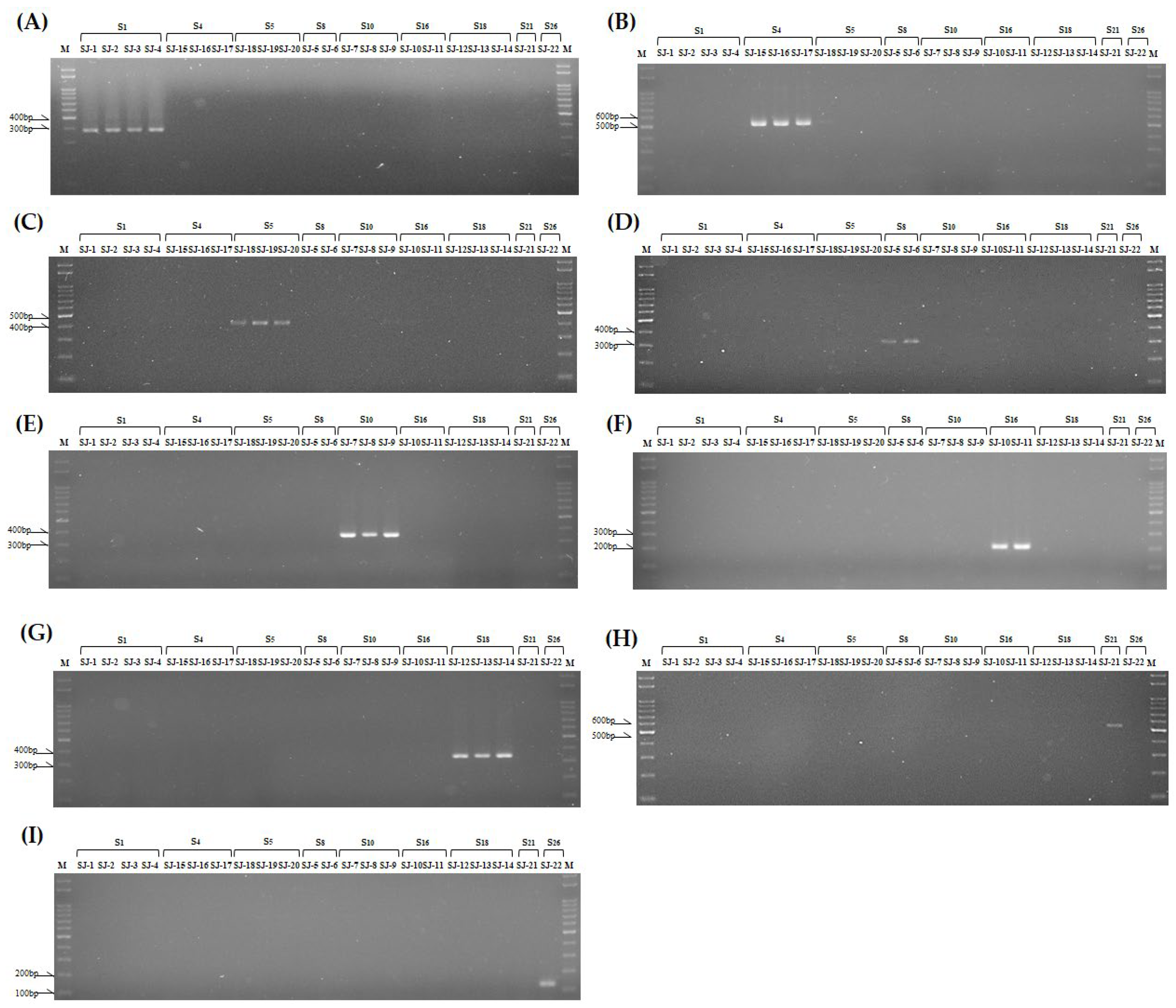
2.4. Development of S Haplotype-Specific Markers
3. Results
3.1. Amplification of SRK, SLG Alleles Using Universal Primers
3.2. Identification of S Haplotypes Based on BLAST Search
| Acc. | S Haplotype | Gene region | Tool | Gene | NCBI Acc. | Iden(%) | Query Cov |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SJ-1~4 | S1 (Lim) | SRK-KD (1,063bp) | BLASTn | SRK1 (Lim) | AY052579 | 100% | 99% |
| SLG (1,220bp) | BLASTn | SLG1 (Lim) | AY052572 | 99% | 99% | ||
| SJ-5~6 | S8 (Lim) | SRK-KD (1,133bp) | BLASTn |
SRK8 (Lim) SRK19 SRK-19 SRK-18 |
AY052583 KX961713 LC341229 LC341228 |
100% 100% 100% 97% |
100% 100% 97% 97% |
| SLG (1,201bp) | BLASTn | SLG-19 | LC341238 | 99% | 55% | ||
| SJ-7~9 | S10 (Lim) | BLASTn |
SRK10 (Lim) SRK11 (Lim) SRK16 (Lim) SRK20 (Lim) SRK29 (Lim) SRK-22 SRK-23 SRK-31 SRK7 SRK10 SRK16 SRK17 |
AY052585 AY534533 AY534535 AY534537 AY534541 LC341231 LC341232 LC341234 KX961701 KX961704 KX961710 KX961711 |
99.9% 98% 98% 98% 99% 98% 98% 99% 98% 98% 99% 98% |
100% 100% 100% 100% 100% 95% 99% 96% 78% 78% 78% 78% |
|
| SRK-KD (1,051bp) | |||||||
| SLG (1,202bp) | BLASTn | SLG10 (Lim) | AY052576 | 99.9% | 100% |
| Acc. | S Haplotype | Gene Region | Tool | Gene | NCBI Acc. | Iden(%) | Query Cov |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SJ-10~11 | S16 (Lim) | SRK-KD (1,071bp) | BLASTn |
SRK16 (Lim) SRK-22 SRK10 (Lim) SRK11 (Lim) SRK20 (Lim) SRK29 (Lim) SRK-23 SRK-31 SRK7 SRK10 SRK16 SRK17 |
AY052579 LC341231 AY052585 AY534533 AY534537 AY534541 LC341232 LC341234 KX961701 KX961704 KX961710 KX961711 |
99.9% 100% 98% 98% 97% 98% 97% 98% 99% 98% 99% 99% |
100% 94% 100% 100% 100% 100% 100% 94% 76% 76% 76% 76% |
| SLG (1,168bp) | BLASTn |
SLG-22 SLG-7 |
LC341239 AB009684 |
100% 99.9% |
64% 100% |
||
| SJ-12~14 | S18 (Lim) | SRK-KD (1,108bp) | BLASTn |
SRK18 (Lim) SRK-6 |
AY534536 LC341226 |
99.9% 99.9% |
100% 95% |
| SLG (1,235bp) | BLASTn |
SLG18 (Lim) SLG-6 |
AY527401 AB009682 |
100% 100% |
100% 100% |
||
| SJ-15~17 | S4 (Lim) | SRK-KD (Not amplified) |
- | - | - | - | - |
| SLG (1,002bp) | BLASTn |
SLG4 (Lim) SLG-26 SLG-11 |
AY052577 LC341241 LC341236 |
99% 99% 97% |
100% 99% 87% |
||
| SJ-18~20 | S5 (Lim) | SRK-KD (1,053bp) | BLASTn |
SRK-5 (Wang) SRK-9 (Wang) SRK6 |
- - KP117077 |
99% 99% 99% |
99% 99% 94% |
| SLG (1,004bp) | BLASTn |
SRK-5 (Wang) SLG5 (Lim) SLG21 (Lim) SLG24 (Lim) SRK1 SRK-9 SLG-9 Rs chr7 Rs chr8 |
- AY052578 AY529650 AY529651 KX961695 AB114851 LC341235 OY743213 LR778317 |
99% 97% 95% 96% 96% 96% 95% 95, 97% 95, 97% |
94% 100% 100% 100% 100% 98% 90% 100% 100% |
| Acc. | S Haplotype | Gene Region | Tool | Gene | NCBI Acc. | Iden(%) | Query Cov |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SJ-21 | S21 (Lim) | SRK-KD (1,015bp) | BLASTn |
SRK-9 (Wang) SRK-5 (Wang) SRK6 |
- - KP117077 |
99% 99% 99% |
99% 99% 96% |
| SLG (1,055bp) | BLASTn |
SLG21 (Lim) SLG-9 Rs chr7 Rs chr8 Rs SLG S13-like SLG24 (Lim) SLG5 (Lim) SRK-1 SRK-9 |
AY529650 LC341235 OY743213 LR778317 XM_056990347 AY529651 AY052578 KX961695 AB114851 |
100% 100% 100, 94% 100, 94% 100% 96% 94% 94% 94% |
84% 77% 100% 100% 100% 84% 84% 100% 100% |
||
| SJ-22 | S26 (Lim) | SRK-KD (Not amplified) |
- | - | - | - | - |
| SLG (802bp) | BLASTn | SLG26 (Lim) | AY529652 | 100% | 100% | ||
| SLG-29 | LC341242 | 100% | 100% |
3.3. Multiple Sequence Alignment (MSA) of SRK, SLG Alleles
3.4. Development of S Haplotype-Specific Markers
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Manivannan, A.; et al. Deciphering the nutraceutical potential of Raphanus sativus—A comprehensive overview. Nutrients 2019, 11, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamba, M.; et al. Nutritional and phytochemical characterization of radish (Raphanus sativus): A systematic review. Trends in Food Science & Technology 2021, 113, 205–218. [Google Scholar]
- De Nettancourt, D. Incompatibility in angiosperms. Sexual Plant Reproduction 1997, 10, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinata, K.; et al. A review of recent studies on homomorphic self-incompatibility. International review of cytology 1993, 143, 257–296. [Google Scholar]
- Newbigin, E.; Anderson, M.A.; Clarke, A.E. Gametophytic Self-Incompatibility Systems. The Plant Cell 1993, 5, 1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Nettancourt, D. and D. de Nettancourt, The genetics of self-incompatibility. Incompatibility and Incongruity in Wild and Cultivated Plants, 2001: P. 25-72.
- Stone, S.L. and D.R. Goring, The molecular biology of self-incompatibility systems in flowering plants. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture 2001, 67, 93–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Suwabe, K.; Suzuki, G. Molecular genetics, physiology and biology of self-incompatibility in Brassicaceae. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci 2012, 88, 519–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casselman, A.L.; et al. Determining the physical limits of the Brassica S locus by recombinational analysis. The Plant Cell 2000, 12, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitashiba, H. and J.B. Nasrallah, Self-incompatibility in Brassicaceae crops: Lessons for interspecific incompatibility. Breeding science 2014, 64, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takasaki, T.; et al. The S receptor kinase determines self-incompatibility in Brassica stigma. Nature 2000, 403, 913–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M. and K. Hinata, 5 Self-incompatibility, in Developments in Plant Genetics and Breeding, C. Gómez-Campo, Editor. 1999, Elsevier. p. 149-183.
- Takayama, S. and A. Isogai, SELF-INCOMPATIBILITY IN PLANTS. Annual Review of Plant Biology 2005, 56, 467–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Suwabe, K.; Suzuki, G. Molecular genetics, physiology and biology of self-incompatibility in Brassicaceae. Proceedings of the Japan Academy, Series B 2012, 88, 519–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, R.; Nasrallah Me Fau-Nasrallah, J.B.; Nasrallah, J.B. Post-transcriptional maturation of the S receptor kinase of Brassica correlates with co-expression of the S-locus glycoprotein in the stigmas of two Brassica strains and in transgenic tobacco plants. (0032-0889 (Print)).
- Nasrallah, J.B. and M.E. Nasrallah, Pollen[mdash]Stigma Signaling in the Sporophytic Self-Incompatibility Response. Plant Cell 1993, 5, 1325–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takayama, S. and A. Isogai, Molecular mechanism of self-recognition in Brassica self-incompatibility. Journal of Experimental Botany 2003, 54, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; et al. Development of a system for S locus haplotyping based on the polymorphic SLL2 gene tightly linked to the locus determining self-incompatibility in radish (Raphanus sativus L.). Euphytica 2016, 209, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, J.C.; et al. Molecular cloning of a putative receptor protein kinase gene encoded at the self-incompatibility locus of Brassica oleracea. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1991, 88, 8816–8820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; et al. A high degree of homology exists between the protein encoded by SLG and the S receptor domain encoded by SRK in self-incompatible Brassica campestris L. Plant Cell Physiol 1994, 35, 1221–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatakeyama, K.; et al. Dominance relationships between S-alleles in self-incompatible Brassica campestris L. Heredity 1998, 80, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; et al. Coevolution of the S-locus genes SRK, SLG and SP11/SCR in Brassica oleracea and B. rapa. Genetics 2002, 162, 931–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, S. and S. Takayama, Multilayered dominance hierarchy in plant self-incompatibility. Plant Reprod 2018, 31, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, M.; et al. Classification and Identification of S Haplotypes in Radish Based on Kinase domain of SRK Sequence Analysis. Plants 2022, 11, 2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; et al. Identification and classification of Shaplotypes in radish (Raphanus sativus). Plant Breeding, 2018.
- Fang, Z.; Sun, P.; Liu, Y. Problems on the utilization of heterosis in cabbage and the selection of self-incompatibility genotypes. Chung-kuo nung yeh k'o hsueh= Scientia agricultura sinica, 1983.
- Pastuglia, M.; et al. Rapid induction by wounding and bacterial infection of an S gene family receptor-like kinase gene in Brassica oleracea. The Plant Cell 1997, 9, 49–60. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, S.H.; et al. Identification and classification of S haplotypes in Raphanus sativus by PCR-RFLP of the S locus glycoprotein (SLG) gene and the S locus receptor kinase (SRK) gene. Theor Appl Genet 2002, 104, 1253–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.T.; et al. Application of SCAR markers to self-incompatibility genotyping in breeding lines of radish (Raphanus sativus L.). Korean Journal of Breeding Science 2009, 41, 397–402. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, L.; et al. Identification of S haplotypes in cabbage inbred lines (Brassica oleracea var. capitata L. ). Scientia Horticulturae 2013, 164, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishio, T. and K. Sakamoto, Polymorphism of Self-Incompatibility Genes. 2017. p. 177-188.
- Haseyama, Y.; et al. Nucleotide sequence analysis of S-locus genes to unify S haplotype nomenclature in radish. Molecular Breeding 2018, 38, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, O.N. and H.Y. Park, Assessment of genetic diversity in cultivated radishes (Raphanus sativus) by agronomic traits and SSR markers. Scientia Horticulturae 2017, 223, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, J.J. and J.L. Doyle, A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. 1987.
- Sakamoto, K.; Kusaba, M.; Nishio, T. Polymorphism of the S -locus glycoprotein gene (SLG ) and the S -locus related gene (SLR1 ) in Raphanus sativus L. and self-incompatible ornamental plants in the Brassicaceae. Molecular and General Genetics MGG 1998, 258, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabrillac, D.; et al. The S15 Self-Incompatibility Haplotype in Brassica oleracea Includes Three S Gene Family Members Expressed in Stigmas. The Plant Cell 1999, 11, 971–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takuno, S.; et al. Effects of recombination on hitchhiking diversity in the Brassica self-incompatibility locus complex. Genetics 2007, 177, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusaba, M. and T. Nishio, Comparative analysis of S haplotypes with very similar SLG alleles in Brassica rapa and Brassica oleracea. The Plant Journal 1999, 17, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, Y.; Sato, K.; Nishio, T. Interspecific pairs of class II S haplotypes having different recognition specificities between Brassica oleracea and Brassica rapa. Plant Cell Physiol 2006, 47, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyenoyama, M.K. Evolutionary dynamics of self-incompatibility alleles in Brassica. Genetics 2000, 156, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tantikanjana, T.; et al. An alternative transcript of the S locus glycoprotein gene in a class II pollen-recessive self-incompatibility haplotype of Brassica oleracea encodes a membrane-anchored protein. The Plant Cell 1993, 5, 657–666. [Google Scholar]
- Nasrallah, J.B.; Rundle, S.J.; Nasrallah, M.E. Genetic evidence for the requirement of the Brassica S-locus receptor kinase gene in the self-incompatibility response. The Plant Journal 1994, 5, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusaba, M.; et al. Striking sequence similarity in inter- and intra-specific comparisons of class I SLG alleles from Brassica oleracea and Brassica campestris: Implications for the evolution and recognition mechanism. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 1997, 94, 7673–7678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, R.; Sugimura, T.; Nishio, T. Gene conversion from SLG to SRK resulting in self-compatibility in Brassica rapa. FEBS Lett 2006, 580, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edh, K.; Wide, B.R.; Ceplitis, A. The Evolution and Diversification of S-Locus Haplotypes in the Brassicaceae Family. Genetics 2009, 181, 977–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-S.; Kim, S. Identification of the S locus core sequences determining self-incompatibility and S multigene family from draft genome sequences of radish (Raphanus sativus L.). Euphytica 2017, 214, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Accession Number | Type of Fleshy Root | Color of Fleshy Root | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| SJ-1 | Narrow elliptic | Green and White | South Chinese |
| SJ-2 | Acicular | Green and White | South Chinese |
| SJ-3 | Narrow elliptic | Green and White | South Chinese |
| SJ-4 | Oblong | Green and White | South Chinese |
| SJ-5 | Medium elliptic | Green and White | North Chinese |
| SJ-6 | Medium elliptic | Green and White | North Chinese |
| SJ-7 | Bell shaped | Green and White | North Chinese |
| SJ-8 | Oblong | Green and White | South Chinese |
| SJ-9 | Oblong | Green and White | South Chinese |
| SJ-10 | Oblong | Green and White | South Chinese |
| SJ-11 | Oblong | Green and White | South Chinese |
| SJ-12 | Ovate | Green and White | South Chinese |
| SJ-13 | Medium elliptic | Green and White | North Chinese |
| SJ-14 | Medium elliptic | Green and White | North Chinese |
| SJ-15 | Bell shaped | Green and White | North Chinese |
| SJ-16 | Oblong | White | South Chinese |
| SJ-17 | Oblong | White | South Chinese |
| SJ-18 | Bell shaped | Green and White | North Chinese |
| SJ-19 | Oblong | Green and White | South Chinese |
| SJ-20 | Oblong | Green and White | South Chinese |
| SJ-21 | Bell shaped | Green and White | South Chinese |
| SJ-22 | Narrow elliptic | Green and White | North Chinese |
| Gene | Forward | Reverse | Annealing Temperature / Cycle |
|---|---|---|---|
| Class I SRK-KD | UVSRK-F | UVSRK-R | 54℃ / 34X |
| Class I SLG | SLG-I-F PS22 |
SLG-I-R SLG-I-R |
50℃ / 39X 54℃ / 35X |
| Class II SRK-KD | KS2 | KA2 | 61℃ / 35X |
| Class II SLG | SLG-II-F Rs9SLG-F UVSLGII-F |
SLG-II-R Rs9SLG-R UVSLGII-R |
55.5℃ / 39X 53℃ / 35X 61℃ / 30X |
| S haplotype | Primer Set | Forward | Reverse | Expected Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 (Lim) | SRK1 SLG1 |
KD1-F SLG1-F |
KD1-R SLG1-R |
665bp 388bp |
| S4 (Lim) | SLG4 | SLG4-F | SLG4-R | 529bp |
| S5 (Lim) | SLG5 | SLG5-F | SLG5-R | 409bp |
| S8 (Lim) | SRK8 SLG8 |
KD8-F SLG8-F |
KD8-R SLG8-R |
271bp 314bp |
| S10 (Lim) | SRK10 SLG10 |
KD10-F SLG10-F |
KD10-R SLG10-R |
411bp 369bp |
| S16 (Lim) | SLG16 | SLG16-F | SLG16-R | 216bp |
| S18 (Lim) | SRK18 SLG18 |
KD18-F SLG18-F |
KD18-R SLG18-R |
105bp 353bp |
| S21 (Lim) | SLG21 | SLG21-F | SLG21-R | 529bp |
| S26 (Lim) | SLG26 | SLG26-F | SLG26-R | 131bp |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





