Submitted:
19 January 2024
Posted:
22 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methods
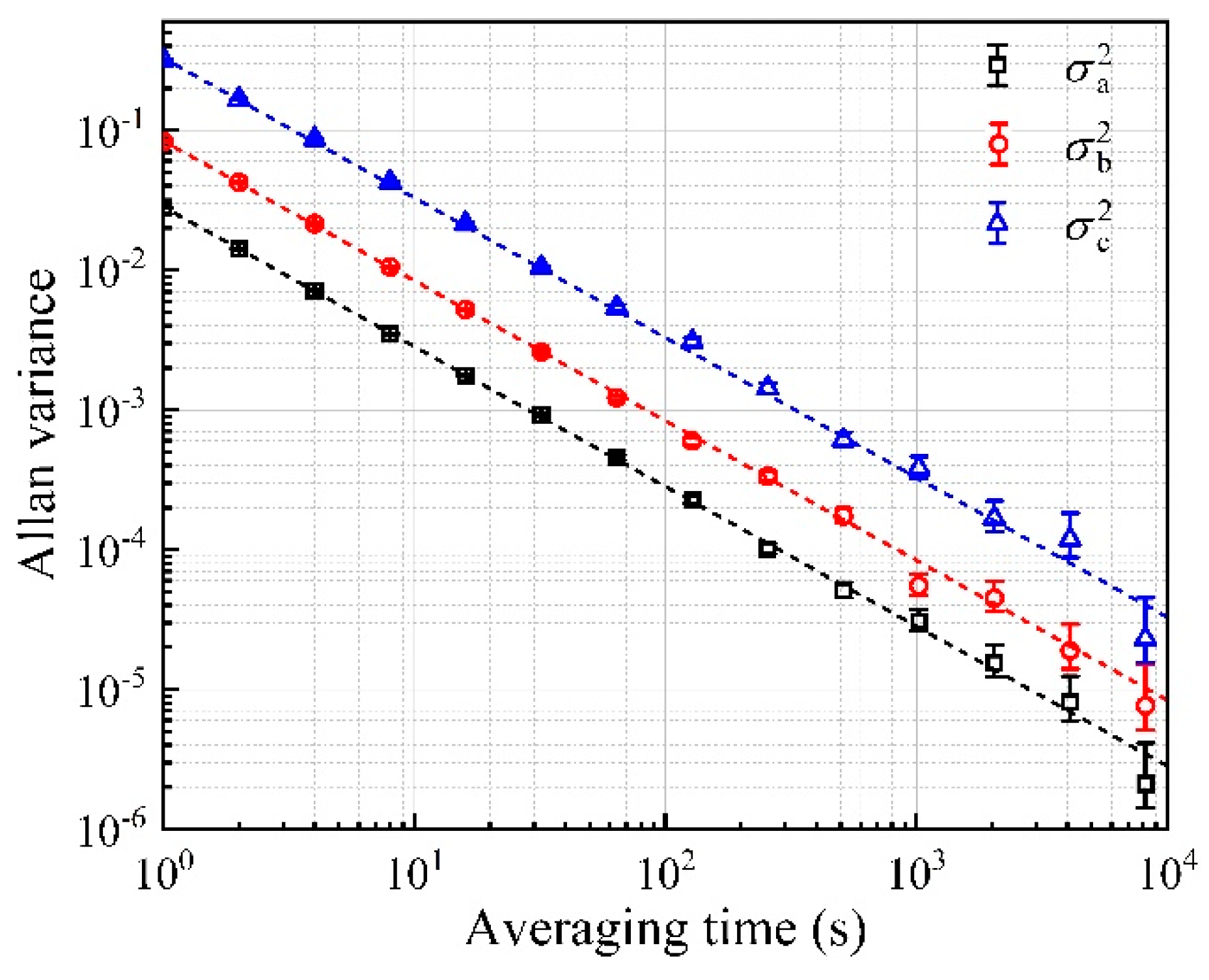
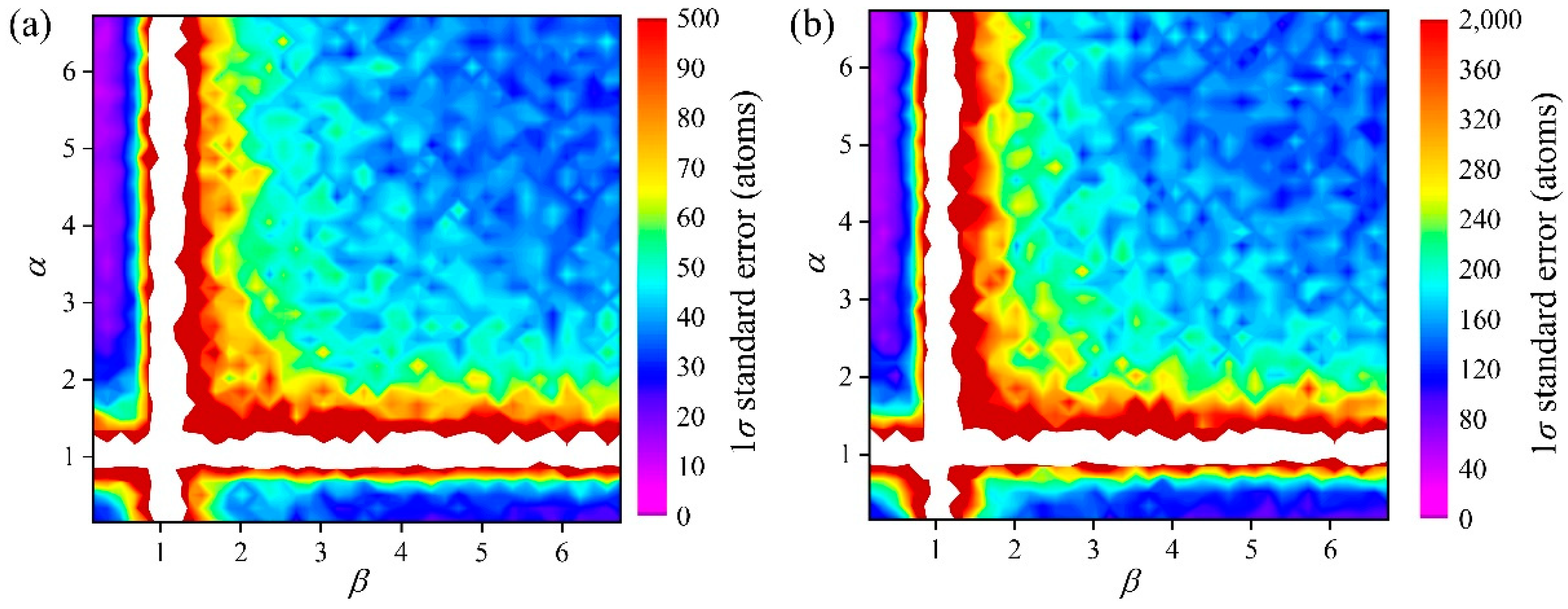
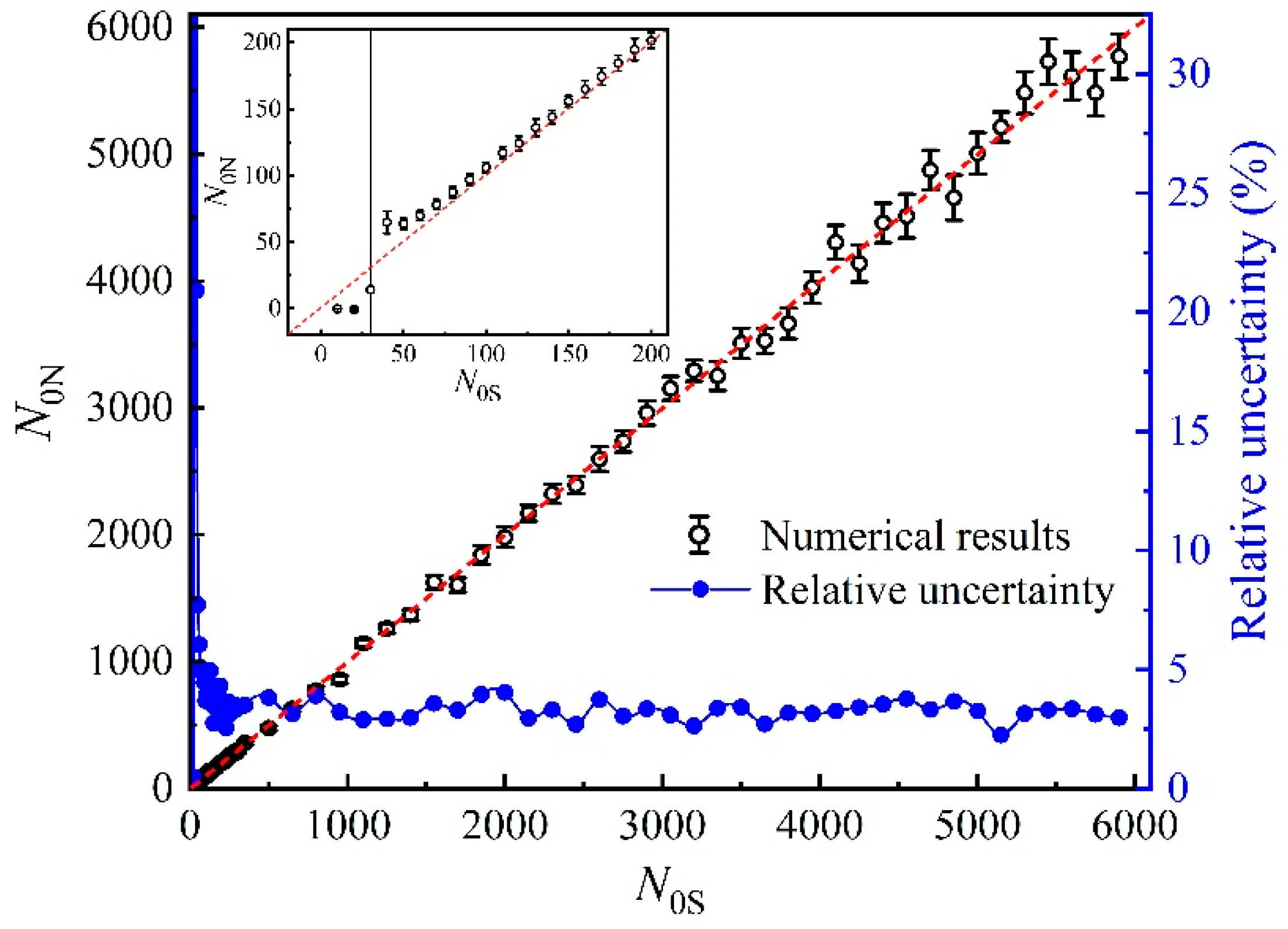
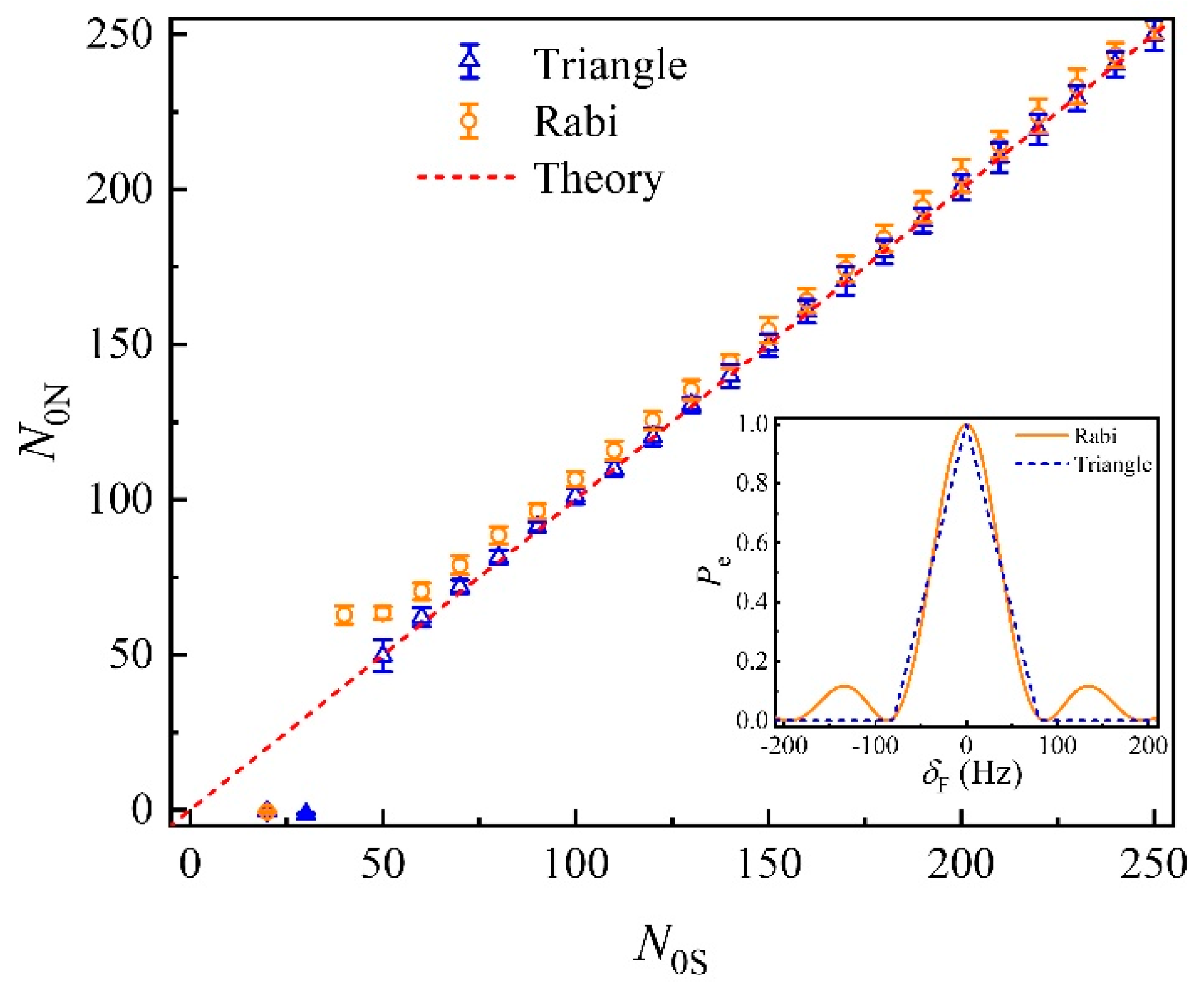
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bothwell1, T.; Kedar, D.; Oelker, E.; Robinson, J.M.; Bromley, S.L.; Tew, W.L.; Ye, J.; Kennedy, C.J. JILA SrI optical lattice clock with uncertainty of 2.0×10-18. Metrologia 2019, 56, 065004. [CrossRef]
- McGrew, W.F.; Zhang, X.R.; Fasano, J.S.; Schäffer, A.; Beloy, K.; Nicolodi, D.; Brown, R.C.; Hinkley, N.; Milani, G.; Schioppo, M.; Yoon, T.H.; Ludlow, A.D. Atomic clock performance enabling geodesy below the centimetre level. Nature 2018, 564, 87. [CrossRef]
- Brewer, S.M.; Chen, J.S.; Hankin, A.M.; Clements, E.R.; Chou, C.W.; Wineland, D.J.; Hume, D.B.; Leibrandt, D.R. 27Al+ quantum-logic clock with a systematic uncertainty below 10-18. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2019, 123, 033201.
- Lu, X.T.; Guo, F.; Wang, Y.B.; Xu, Q.F.; Zhou, C.H.; Xia, J.J.; Wu, W.J.; Chang, H. Absolute frequency measurement of the 87Sr optical lattice clock at NTSC using international atomic time. Metrologia 2023, 60, 015008. [CrossRef]
- Gross, C.; Bloch, I. Quantum simulations with ultracold atoms in optical lattices. Science 2017, 357, 995. [CrossRef]
- Nunn, J.; Dorner, U.; Michelberger, P.K.; Lee, C.; Langford, N.K.; Walmsley, I.A.; Jaksch, D. Quantum memory in an optical lattice. Phys. Rev. A 2010, 82, 022327. [CrossRef]
- Daley, A.J.; Boyd, M.M.; Ye, J.; Zoller, P. Quantum computing with Alkaline-earth-metal atoms. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 101, 170504. [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.J.; Lu, X.T.; Li, T.; Xia, J.J.; Wang, T.; Zhang, X.F.; Chang, H. Floquet engineering Hz-level Rabi spectra in shallow optical lattice clock. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2022, 128, 073603. [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.T.; Wang, T.; Li, T.; Zhou, C.H.; Yin, M.J.; Wang, Y.B.; Zhang, X.F.; Chang, H. Doubly modulated optical lattice clock: interference and topology. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2021, 127, 033601. [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, R.; Dörscher, S.; Al-Masoudi, A.; Benkler, E.; Legero, T.; Sterr, U.; Weyers, S.; Rahm, J.; Lipphardt, B.; Lisdat, C. Long term measurement of the 87Sr clock frequency at the limit of primary Cs clocks. Phys. Rev. Res. 2020, 2, 033242. [CrossRef]
- Takamoto, M.; Ushijima, I.; Ohmae, N.; Yahagi, T.; Kokado, K.; Shinkai, H.; Katori, H. Test of general relativity by a pair of transportable optical lattice clocks. Nat. Photon. 2020, 14, 411. [CrossRef]
- Miyake, H.; Pisenti, N.C.; Elgee, P.K.; Sitaram, A.; Campbell, G.K. Isotope-shift spectroscopy of the 1S0→3P1 and 1S0→3P0 transitions in strontium. Phys. Rev. Res. 2019, 1, 033113. [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, C.J.; Oelker, E.J.; Robinson, M.; Bothwell, T.; Kedar, D.; Milner, W.R.; Marti, G.E.; Derevianko, A.; Ye, J. Precision metrology meets cosmology: Improved constraints on ultralight dark matter from atom-cavity frequency comparisons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2020, 125, 201302. [CrossRef]
- Rey, A.M.; A. Gorshkov, V.C.; Kraus, V.M.; Martin, J.; Bishof, M.; Swallows, M.D.; Zhang, X.; Benko, C.; Ye, J.; Lemke, N.D.; Ludlow, A.D. Probing many-body interactions in an optical lattice clock. Ann. Phys. 2014, 340, 311. [CrossRef]
- Gregor, O.K.; Melina, P.; Gustav, W.; Mark, B.; Olivier, M.; Wolf, K. Atom number calibration in absorption imaging at very small atom numbers. Cent. Eur. J. Phys. 2012, 10, 1054. [CrossRef]
- Reinaudi, G.; Lahaye, T.; Wang, Z.; Guery-Odelin, D. Strong saturation absorption imaging of dense clouds of ultracold atoms. Opt. Lett. 2007, 32, 3143. [CrossRef]
- Hueck, K.; Luick, N.; Sobirey, L.; Siegl, J.; Lompe, T.; Moritz, H.; Clark, L.W.; Chin, C. Calibrating high intensity absorption imaging of ultracold atoms. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 8670. [CrossRef]
- Bothwell, T.; Kennedy, C.J.; Aeppli, A.; Robinson, J.M.; Oelker, E.; Staron, A. Ye, J. Resolving the gravitational redshift across a millimetre-scale atomic sample. Nature 2022, 602, 420. [CrossRef]
- Aeppli, A.; Chu, A.J.; Bothwell, T.; Kennedy, C.J.; Kedar, D.; He, P.; Rey, A.M.; Ye, J. Hamiltonian engineering of spin-orbit-coupled fermions in a Wannier-Stark optical lattice clock. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eadc9242. [CrossRef]
- Santarelli, G.; Laurent, Ph.; Lemonde, P.; Clairon, A.; Mann, A.G.; Chang, S.; Luiten, A.N.; Salomon, C. Quantum projection noise in an atomic fountain: a high stability cesium frequency standard. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1999, 82, 4619. [CrossRef]
- Al-Masoudi, A.; Dörscher, S.; Häfner, S.; Sterr, U.; Lisdat, C. Noise and instability of an optical lattice clock. Phys. Rev. A 2015, 92, 063814. [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.T.; Xia, J.J.; Lu, B.Q.; Wang, Y.B.; Wang, T.; Chang, H. Determining the atom number from detection noise in a one-dimensional optical lattice clock. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2022, 120, 151104. [CrossRef]
- Takamoto, M.; Takano, T.; Katori, H. Frequency comparison of optical lattice clocks beyond the Dick limit. Nat. Photon. 2011, 5, 288. [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.T.; Zhou, C.H.; Li, T.; Wang, Y.B.; Chang, H. Synchronous frequency comparison beyond the Dick limit based on dual-excitation spectrum in an optical lattice clock. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2020, 117, 231101. [CrossRef]
- Campbell, S.L.; Hutson, R.B.; Marti, G.E.; Goban, A.; Darkwah Oppong, N.; McNally, R.L.; Sonderhouse, L.; Robinson, J.M.; Zhang, W.; Bloom, B.J.; Ye, J. A Fermi-degenerate three-dimensional optical lattice clock. Science 2017, 358, 90. [CrossRef]
- Lemonde, P.; Laurent, P.; Santarelli, G.; Abgrall, M.; Sortais, Y.; Bize, S.; Nicolas, C.; Zhang, S.; Clairon, A.; Dimarcq, N.; Petit, P.; Mann, A.G.; Luiten, A.N.; Chang, S.; Salomon, C. 2001 Frequency Measurement and Control: Advanced Techniques and Future Trends (Vol. 79) (Berlin: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg) pp.131-153. [CrossRef]
- Dick, G.J. in Proceedings of 19th Annual Precise Time and Time Interval Meeting, Redendo Beach, 1987 (US Naval Observatory, Washington, DC, 1988), pp. 133-147.
- Nicholson, T.L.; Martin, M.J.; Williams, J.R.; Bloom, B.J.; Bishof, M.M.; Swallows, D.; Campbell, S.L.; Ye, J. Comparison of two independent Sr optical clocks with 1×10-17 stability at 103 s. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 109, 230801.
- Orenes, D.B.; Sewell, R.J.; Lodewyck, J.; Mitchell, M.W. Improving short-term stability in optical lattice clocks by quantum nondemolition measurement. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2020, 128, 153201. [CrossRef]
- Pedrozo-Peñafie, E.; Colombo, S.; Shu, C.; Adiyatullin, A.F.; Li, Z.Y.; Mendez, E.; Braverman, B.; Kawasaki, A.; Akamatsu, D.; Xiao, Y.H.; Vuletić, V. Entanglement on an optical atomic-clock transition. Nature 2020, 588, 414. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




