Submitted:
02 January 2024
Posted:
03 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Study design
2.2. Study population
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Statistical analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Funding
References
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.D.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molloy, E.J.; Bearer, C.F. Paediatric and neonatal sepsis and inflammation. Pediatr. Res. 2022, 91, 267–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markwart, R.; Saito, H.; Harder, T.; Tomczyk, S.; Cassini, A.; Fleischmann-Struzek, C.; Reichert, F.; Eckmanns, T.; Allegranzi, B. Epidemiology and burden of sepsis acquired in hospitals and intensive care units: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 1536–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudd, K.E.; Johnson, S.C.; Agesa, K.M.; Shackelford, K.A.; Tsoi, D.; Kievlan, D.R.; Colombara, D.V.; Ikuta, K.S.; Kissoon, N.; Finfer, S.; et al. Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and mortality, 1990-2017: analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet. 2020, 395, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlapbach, L.J.; Kissoon, N.; Alhawsawi, A.; Aljuaid, M.H.; Daniels, R.; Gorordo-Delsol, L.A.; Machado, F.; Malik, I.; Nsutebu, E.F.; Finfer, S.; et al. World Sepsis Day: a global agenda to target a leading cause of morbidity and mortality. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2020, 319, L518–L522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinhart, K.; Daniels, R.; Kissoon, N.; Machado, F.R.; Schachter, R.D.; Finfer, S. Recognizing Sepsis as a Global Health Priority - A WHO Resolution. NEJM 2017, 377, 414–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, M.P.; Stenstrom, R.; Paquette, K.; Stabler, S.N.; Akhter, M.; Davidson, A.C.; Gavric, M.; Lawandi, A.; Jinah, R.; Saeed, Z.; et al. Blood Culture Results Before and After Antimicrobial Administration in Patients With Severe Manifestations of Sepsis: A Diagnostic Study. Ann. Intern. Med. 2019, 171, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Póvoa, P.; Coelho, L.; Dal-Pizzol, F.; Ferrer, R.; Huttner, A.; Conway Morris, A.; Nobre, V.; Ramirez, P.; Rouze, A.; Salluh, J.; et al. How to use biomarkers of infection or sepsis at the bedside: guide to clinicians. Intensive Care Med. 2023, 49, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierrakos, C.; Velissaris, D.; Bisdorff, M.; Marshall, J.C.; Vincent, J.L. Biomarkers of sepsis: time for a reappraisal. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, J.; Khan, S.; Zahra, R.; Razaq, A.; Zain, A.; Razaq, L.; Razaq, M. Role of Procalcitonin and C-reactive Protein as Predictors of Sepsis and in Managing Sepsis in Postoperative Patients: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2022, 14, e31067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patnaik, R.; Azim, A.; Agarwal, V. Neutrophil CD64 a Diagnostic and Prognostic Marker of Sepsis in Adult Critically Ill Patients: A Brief Review. Indian J. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 24, 1242–1250. [Google Scholar]
- Urrechaga, E.; Bóveda, O.; Aguirre, U. Role of leucocytes cell population data in the early detection of sepsis. J. Clin. Pathol. 2018, 71, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciaccio, A.M.; Agnello, L.; Sasso, B.L.; Giglio, R.V.; Iacona, A.; Gambino, C.M.; Scazzone, C.; Tuttolomondo, A.; Ciaccio, M. Monocyte Distribution Width (MDW) as a biomarker of sepsis: An evidenced-based laboratory medicine approach. Clin. Chim. Acta 2023, 540, 117214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agnello, L.; Vidali, M.; Lo Sasso, B.; Giglio, R.V.; Gambino, C.M.; Scazzone, C.; Ciaccio, A.M.; Bivona, G.; Ciaccio, M. Monocyte distribution width (MDW) as a screening tool for early detecting sepsis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. CCLM 2022, 60, 786–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crouser, E.D.; Parrillo, J.E.; Seymour, C.; Angus, D.C.; Bicking, K.; Tejidor, L.; Magari, R.; Careaga, D.; Williams, J.; Closser, D.R.; et al. Improved Early Detection of Sepsis in the ED With a Novel Monocyte Distribution Width Biomarker. Chest 2017, 152, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crouser, E.D.; Parrillo, J.E.; Seymour, C.W.; Angus, D.C.; Bicking, K.; Esguerra, V.G.; Peck-Palmer, O.M.; Magari, R.T.; Julian, M.W.; Kleven, J.M.; et al. Monocyte Distribution Width: A Novel Indicator of Sepsis-2 and Sepsis-3 in High-Risk Emergency Department Patients. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 47, 1018–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polilli, E.; Sozio, F.; Frattari, A.; Persichitti, L.; Sensi, M.; Posata, R.; Di Gregorio, M.; Sciacca, A.; Flacco, M.E.; Manzoli, L.; et al. Comparison of Monocyte Distribution Width (MDW) and Procalcitonin for early recognition of sepsis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambden, S.; Laterre, P.F.; Levy, M.M.; Francois, B. The SOFA score-development, utility and challenges of accurate assessment in clinical trials. Crit. Care 2019, 23, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teasdale, G.; Jennett, B. Assessment of coma and impaired consciousness. A practical scale. Lancet 1974, 2, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Li, N.; Zhang, S.; Liu, S.; Zhang, H.; Yue, B. Combination of NeuX and NeuZ can predict neutrophil dysplasia features of myelodysplastic neoplasms in peripheral blood. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2023, 45, 522–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Pan, S.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Qi, H.; Xie, J.; Qu, J. The clinical value of hematological neutrophil and monocyte parameters in the diagnosis and identification of sepsis, Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, X.; Wang, Y.; Xie, M.; Qiu, S.; Zhou, J. Elevated neutrophil - to - monocyte ratio as a prognostic marker for poor outcomes in neonatal sepsis. Heliyon 2022, 8, e11181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piotrowski, D.; Sączewska-Piotrowska, A.; Jaroszewicz, J.; Boroń-Kaczmarska, A. Lymphocyte-To-Monocyte Ratio as the Best Simple Predictor of Bacterial Infection in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis. IJERPH 2020, 17, 1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buoro, S.; Manenti, B.; Seghezzi, M.; Dominoni, P.; Barbui, T.; Ghirardi, A.; Carobbio, A.; Marchesi, G.; Riva, I.; Nasi, A.; et al. Innovative haematological parameters for early diagnosis of sepsis in adult patients admitted in intensive care unit. J. Clin. Pathol. 2018, 71, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelagalli, M.; Giovannelli, A.; Calabrese, C.; Sarubbi, S.; Minieri, M.; Nuccetelli, M.; et al. Leucocyte differential count and morphometric parameters by Mindray BC-6800 Plus: a possible predictive tool for screening of sepsis. Biochimica Clinica 2023, 47, 141–150. [Google Scholar]
- Arora, P.; Gupta, P.K.; Lingaiah, R.; Mukhopadhyay, A.K. Volume, conductivity, and scatter parameters of leukocytes as early markers of sepsis and treatment response. J. Lab. Physicians 2019, 11, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mammen, J.; Choudhuri, J.; Paul, J.; Sudarsan, T.I.; Josephine, T.; Mahasampath, G.; Jeyaseelan, V.; Nair, S.C.; Peter, J.V. Cytomorphometric Neutrophil and Monocyte Markers May Strengthen the Diagnosis of Sepsis. J. Intensive Care Med. 2018, 33, 656–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, C.; Pamer, E.G. Monocyte recruitment during infection and inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 762–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Li, L.; Luo, J. Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of Monocyte Distribution Width in Sepsis. J. Inflamm. Res. 2022, 15, 4107–4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, H.R.; Robb, C.T.; Perretti, M.; Rossi, A.G. The role of neutrophils in inflammation resolution. Semin. Immunol. 2016, 28, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Li, H.R.; Yu, C.M.; Li, P.; Deng, X.M.; Wang, J.F. Dysregulation of neutrophil death in sepsis. Front. immunol. 2022, 13, 963955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, H.; Qu, M.; Nan, K.; Cao, H.; Cata, J.P.; Chen, W.; Miao, C. Review: The Emerging Role of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in Sepsis and Sepsis-Associated Thrombosis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 653228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.; Zhang, L.; Tang, X.; Tang, Y. The Value of Neutrophil/Lymphocyte Ratio Combined with Red Blood Cell Distribution Width in Evaluating the Prognosis of Emergency Patients with Sepsis. Emerg. Med. Int. 2022, 1673572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.D.; Lippi, G.; Montagnana, M. Diagnostic and prognostic value of red blood cell distribution width in sepsis: A narrative review. Clin. Biochem. 2020, 77, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montagnana, M.; Cervellin, G.; Meschi, T.; Lippi, G. The role of red blood cell distribution width in cardiovascular and thrombotic disorders. CCLM 2011, 50, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, L.; Rhodes, A.; Alhazzani, W.; Antonelli, M.; Coopersmith, C.M.; French, C.; Machado, F.R.; Mcintyre, L.; Ostermann, M.; Prescott, H.C.; et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock 2021. Intensive Care Med. 2021, 47, 1181–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Demographic and clinical characteristics | All patients n = 327 |
Sepsis patients n = 223 |
Non-sepsis patients n = 104 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 70 (57 – 77) | 71 (60 – 78) | 64 (52 – 75) |
|
Male, n (%) Female, n (%) |
205 (63) 122 (37) |
134 (60) 89 (40) |
71 (68) 33 (32) |
| SOFA SCORE | 6 (4 – 8) | 6 (4 – 8) | 6 (4 – 7) |
| PaO2/FiO2, mmHg | 209 (130 – 332) | 175 (116 – 274) | 303 (174 – 403) |
| PLT, x109/L | 195 (131 – 259) | 190 (116 – 261) | 206 (163 – 255) |
| MAP, mmHg | 81 (67 – 97) | 79 (65 – 93) | 90 (71 – 107) |
| Bilirubin, μmol/L | 13.68 (10.26-23.94) | 15.39 (10.26-25.65) | 13.68 (8.55-20.52) |
| Creatinine, μmol/L | 87.54 (61.89-150.31) | 114.95 (61.89-203.37) | 61.89 (53.05-88.42) |
| GCS | 15 (9 – 15) | 15 (14 – 15) | 8 (5 – 14) |
| Lac, mmol/L | 1.6 (1 - 3) | 1.6 (1.0 – 3.1) | 1.4 (0.9 – 2.6) |
| ICU LOS, d | 3 (1 – 9) | 3 (1 – 7) | 5.5 (1.0 – 12) |
| Hospital LOS, d | 17 (8 – 32) | 19 (10 – 33) | 11 (6 – 28) |
| ICU mortality, n (%) | 98 (30) | 77 (34) | 21 (20) |
| Hospital mortality, n (%) | 122 (37) | 100 (45) | 22 (21) |
| PREDICTOR | Without Sepsis (n=104) | With Sepsis (n=223) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hb, g/L | 127 (107-142) | 108 (90-128) | <0.001 |
| RDW, % | 13.4 (12.7-14.3) | 14.8 (13.8-16.6) | <0.001 |
| WBC,x109/L | 12.7 (10.1-16.1) | 11.2 (6.8-15.8) | 0.022 |
| NE#,x109/L | 11.0 (8.1-14.1) | 9.6 (5.5-14.0) | 0.061 |
| LY#,x109/L | 0.8 (0.5-1.3) | 0.6 (0.4-1.1) | 0.002 |
| MO#,x109/L | 0.6 (0.4-0.9) | 0.4 (0.2-0.7) | <0.001 |
| NLR | 13.6 (6.6-22.5) | 13.4 (6.9-24.5) | 0.644 |
| NMR | 16.8 (12.2-24.3) | 21.5 (13.3-36.2) | <0.001 |
| LMR | 1.3 (0.8-2.1 | 1.5 (0.9-2.8) | 0.030 |
| PLT,x109/L | 206 (163-255) | 190 (116-261) | 0.099 |
| NeuX | 361 (345-389) | 408 (371-446) | <0.001 |
| NeuY | 479 (455-500) | 541 (495-607) | <0.001 |
| NeuZ | 1858 (1793-1910) | 1792 (1712-1874) | <0.001 |
| LymX | 94 (90-99) | 97 (91-104) | 0.002 |
| LymY | 765 (736-805) | 775 (728-833) | 0.203 |
| LymZ | 962 (944-978) | 954 (931-982) | 0.484 |
| MonX | 208 (202-218) | 224 (211-245) | <0.001 |
| MonY | 1046 (996-1080) | 1144 (1065-1225) | <0.001 |
| MonZ | 1312 (1292-1334) | 1348 (1303-1408) | <0.001 |
| CRP, mg/L | 20.6 (8.6-54.3) | 140.6 (64.8-207.2) | <0.001 |
| PCT, ng/mL | 0.17 (0.08-0.54) | 2.67 (0.36-19.60) | <0.001 |
| PREDICTOR | UNIVARIATE LR | MULTIVARIATE LR without CRP | MULTIVARIATE LR with CRP |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | <0.001 | 0.608 | 0.579 |
| Sex | 0.155 | ||
| Hb | <0.001 | 0.797 | 0.574 |
| RDW | <0.001 | 0.005 | 0.002 |
| WBC | 0.490 | ||
| NE# | 0.749 | ||
| LY# | 0.397 | ||
| MO# | <0.001 | 0.125 | 0.026 |
| NLR | 0.152 | ||
| NMR | 0.003 | 0.103 | 0.142 |
| LMR | 0.295 | ||
| PLT | 0.915 | ||
| NeuX | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.001 |
| NeuY | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.006 |
| NeuZ | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| LymX | 0.001 | 0.648 | 0.719 |
| LymY | 0.072 | ||
| LymZ | 0.426 | ||
| MonX | <0.001 | 0.040 | 0.229 |
| MonY | <0.001 | 0.638 | 0.584 |
| MonZ | <0.001 | 0.031 | 0.005 |
| CRP | <0.001 | <0.001 |
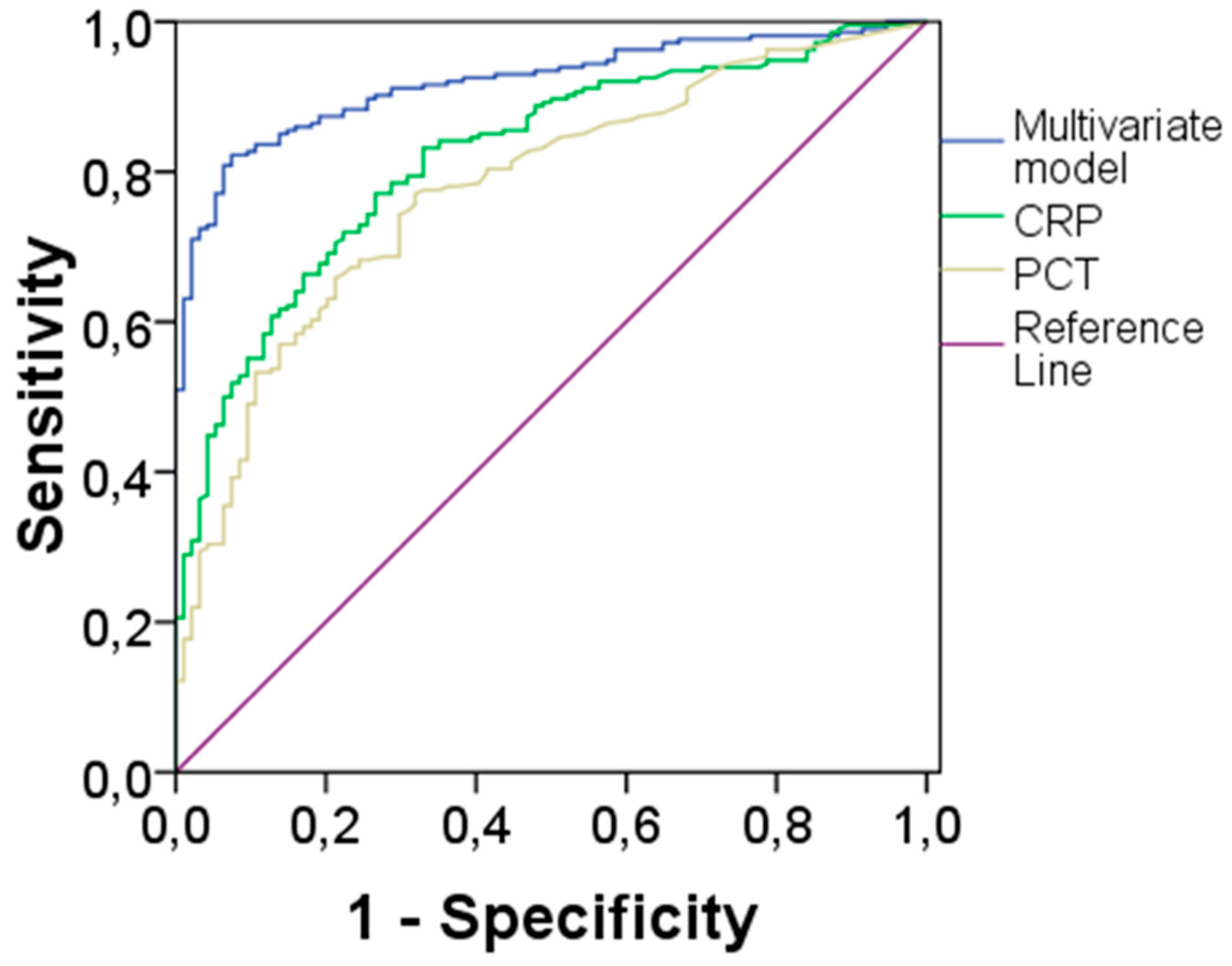
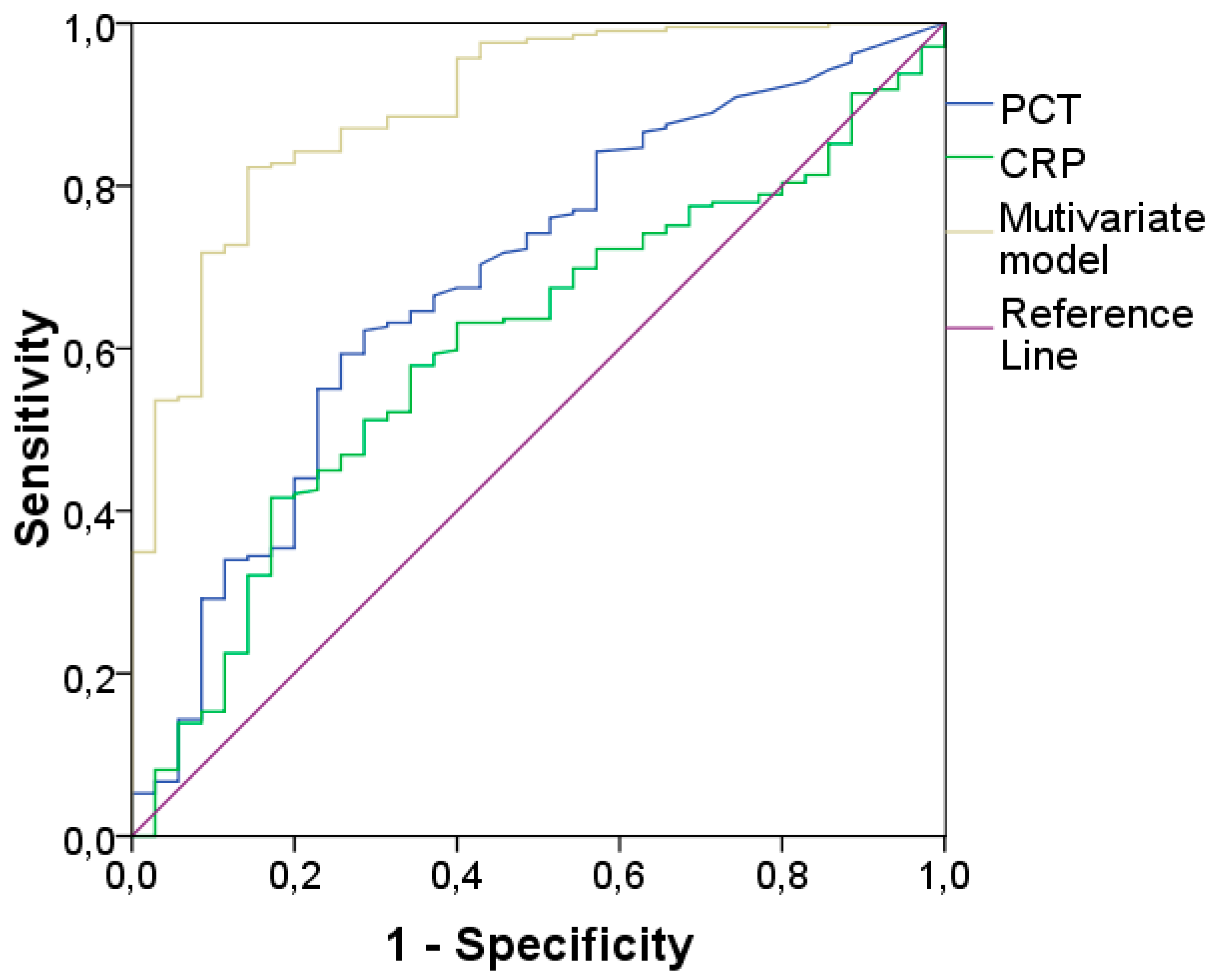
| BIOMARKER | AUC | 95% CI | CUT-OFF* | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRP | 0.83 | 0.79-0.88 | 6.07 | 77% | 77% |
| PCT | 0.78 | 0.73-0.84 | 0.33 | 77% | 70% |
| Multivariate Model | 0.92 | 0.89-0.95 | 0.655# | 82% | 89% |
| PREDICTOR | UNIVARIATE CR within ICU | MULTIVARIATE CR within ICU | UNIVARIATE CR within Hospital | MULTIVARIATE CR within Hospital |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Sex | 0.370 | 0.740 | ||
| Hb | 0.087 | 0.216 | ||
| RDW | <0.001 | 0.068 | <0.001 | 0.138 |
| WBC | 0.778 | 0.143 | ||
| NE# | 0.695 | 0.190 | ||
| LY# | 0.498 | 0.531 | ||
| MO# | 0.265 | 0.106 | ||
| NLR | 0.164 | 0.027 | 0.158 | |
| NMR | 0.536 | 0.981 | ||
| LMR | 0.210 | 0.530 | ||
| PLT | 0.522 | 0.071 | ||
| NeuX | 0.005 | 0.331 | 0.005 | 0.748 |
| NeuY | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.040 |
| NeuZ | 0.258 | 0.300 | ||
| LymX | 0.657 | 0.439 | ||
| LymY | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| LymZ | 0.026 | 0.320 | 0.013 | 0.065 |
| MonX | <0.001 | 0.041 | 0.002 | 0.373 |
| MonY | 0.055 | 0.024 | 0.021 | |
| MonZ | 0.146 | 0.216 | ||
| CRP | 0.292 | 0.407 |
| PREDICTOR | Without sepsis (n=56) | With sepsis (n=223) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hb, g/L | 125 (115-137) | 108 (90-128) | <0.001 |
| RDW, % | 14.5 (13.3-15.6) | 14.8 (13.8-16.6) | 0.074 |
| WBC,x109/L | 12.5 (8.5-17.6) | 11.2 (6.8-15.8) | 0.096 |
| NE#,x109/L | 10.4 (7.1-15.3) | 9.6 (5.5-14.0) | 0.340 |
| LY#,x109/L | 1.2 (0.8-1.7) | 0.6 (0.4-1.1) | <0.001 |
| MO#,x109/L | 0.7 (0.5-0.9) | 0.4 (0.2-0.7) | <0.001 |
| NLR | 9.1 (4.8-16.6) | 13.4 (6.9-24.5) | 0.003 |
| NMR | 15.3 (10.7-20.9) | 21.5 (13.3-36.2) | <0.001 |
| LMR | 1.6 (1.0-2.5) | 1.5 (0.9-2.8) | 0.953 |
| PLT,x109/L | 264 (200-322) | 190 (116-261) | <0.001 |
| NeuX | 387 (350-421) | 408 (371-446) | 0.008 |
| NeuY | 467 (437-512) | 541 (495-607) | <0.001 |
| NeuZ | 1770 (1684-1861) | 1792 (1712-1874) | 0.084 |
| LymX | 95 (91-101) | 97 (91-104) | 0.180 |
| LymY | 771 (738-823) | 775 (728-833) | 0.857 |
| LymZ | 966 (950-988) | 954 (931-982) | 0.008 |
| MonX | 219 (206-229) | 224 (211-245) | 0.003 |
| MonY | 1096 (1045-1161) | 1144 (1065-1225) | 0.005 |
| MonZ | 1349 (1318-1400) | 1348 (1303-1408) | 0.585 |
| CRP, mg/L | 94.5 (44.6-154.2) | 140.6 (64.8-207.2) | 0.008 |
| PCT, ng/mL | 0.37 (0.10-1.74) | 2.67 (0.36-19.60) | <0.001 |
| PREDICTOR | UNIVARIATE LR | MULTIVARIATE LR without CRP |
MULTIVARIATE LR with CRP |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Sex | 0.110 | ||
| Hb | <0.001 | 0.005 | 0.006 |
| RDW | 0.086 | ||
| WBC | 0.510 | ||
| NE# | 0.938 | ||
| LY# | 0.101 | ||
| MO# | <0.001 | 0.779 | 0.838 |
| NLR | 0.007 | 0.180 | 0.188 |
| NMR | <0.001 | 0.049 | 0.047 |
| LMR | 0.322 | ||
| PLT | <0.001 | 0.007* | 0.007 |
| NeuX | 0.005 | 0.495 | 0.473 |
| NeuY | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| NeuZ | 0.061 | ||
| LymX | 0.055 | ||
| LymY | 0.576 | ||
| LymZ | 0.117 | ||
| MonX | 0.002 | 0.916 | 0.846 |
| MonY | 0.007 | 0.013 | 0.013 |
| MonZ | 0.845 | ||
| CRP | 0.017 | 0.633 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





