Submitted:
18 March 2024
Posted:
21 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
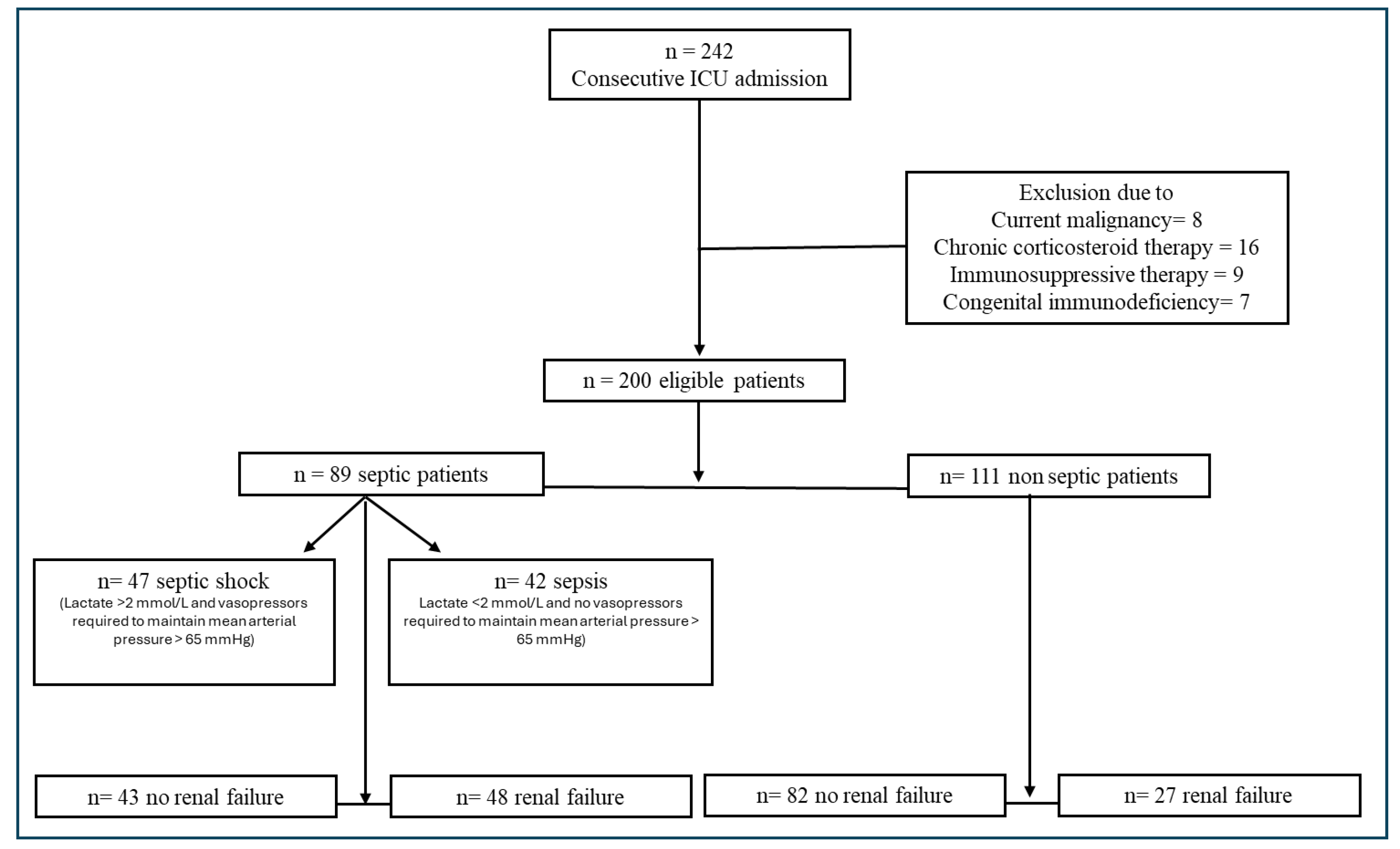
3. Results
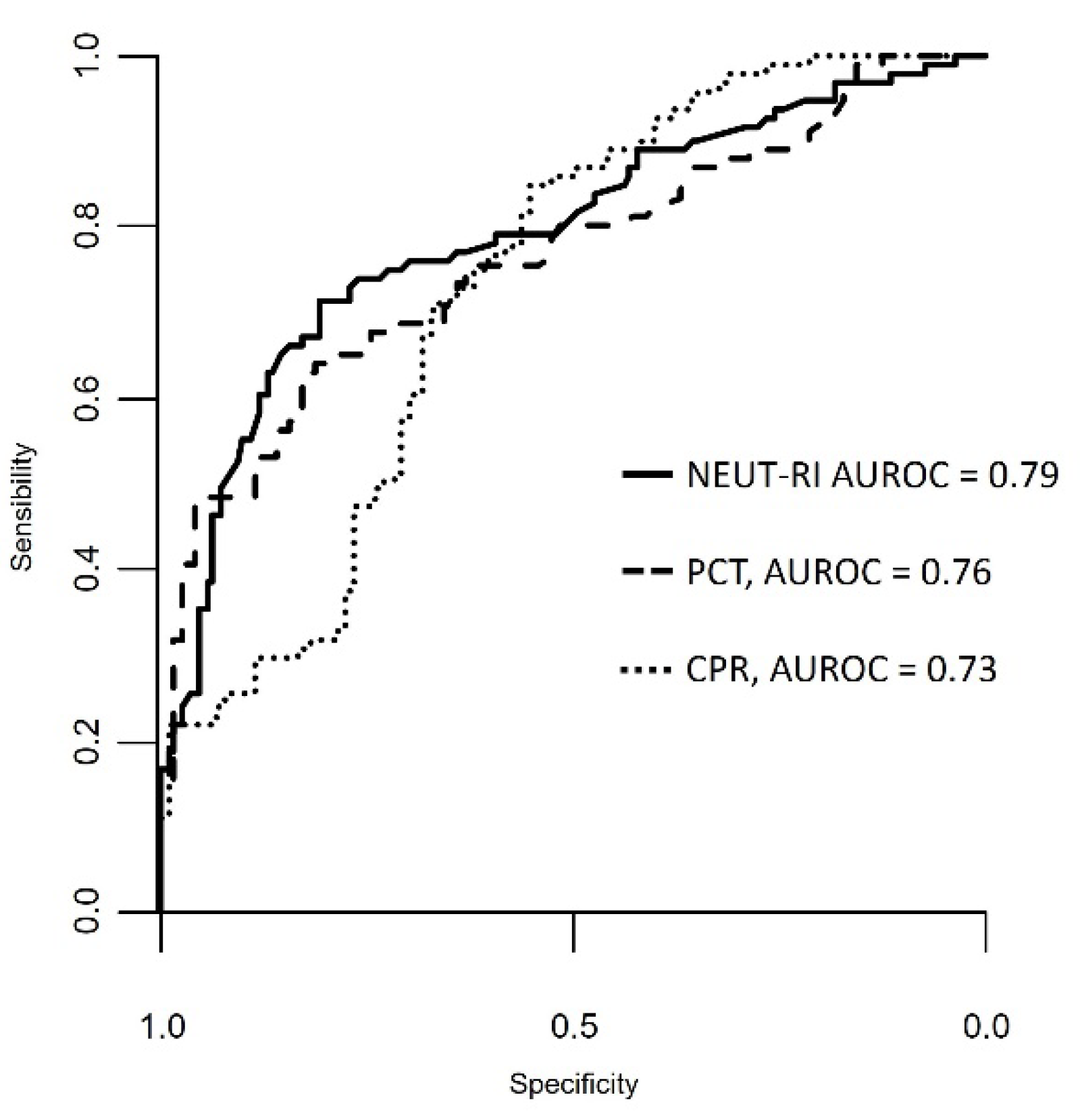
3.1.1. Iinflammatory Parameters
3.1.2. Renal Failure and Inflammatory Parameters
3.1.3. 28-Day Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.-D.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Ji, W.; Bo, L.; Bian, J. How to Improve the Care of Septic Patients Following “Surviving Sepsis Campaign: International Guidelines for Management of Sepsis and Septic Shock 2021”? J Intensive Med 2023, 3, 144–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambden, S.; Laterre, P.F.; Levy, M.M.; Francois, B. The SOFA Score-Development, Utility and Challenges of Accurate Assessment in Clinical Trials. Crit Care 2019, 23, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, L.; Rhodes, A.; Alhazzani, W.; Antonelli, M.; Coopersmith, C.M.; French, C.; Machado, F.R.; Mcintyre, L.; Ostermann, M.; Prescott, H.C.; et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: International Guidelines for Management of Sepsis and Septic Shock 2021. Intensive Care Med 2021, 47, 1181–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muteeb, G.; Rehman, M.T.; Shahwan, M.; Aatif, M. Origin of Antibiotics and Antibiotic Resistance, and Their Impacts on Drug Development: A Narrative Review. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 2023, 16, 1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamy, B.; Dargère, S.; Arendrup, M.C.; Parienti, J.-J.; Tattevin, P. How to Optimize the Use of Blood Cultures for the Diagnosis of Bloodstream Infections? A State-of-the Art. Front Microbiol 2016, 7, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelli, G.P.; Pognani, C.; Meisner, M.; Stuani, A.; Bellomi, D.; Sgarbi, L. Procalcitonin and C-Reactive Protein during Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome, Sepsis and Organ Dysfunction. Crit Care 2004, 8, R234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, R.; Hu, L.; Ling, Y.; Hou, Y.; Fang, H.; Zhang, H.; Liang, S.; He, Z.; Fang, M.; Li, J.; et al. C-Reactive Protein Concentration as a Risk Predictor of Mortality in Intensive Care Unit: A Multicenter, Prospective, Observational Study. BMC Anesthesiol 2020, 20, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Werra, I.; Jaccard, C.; Corradin, S.B.; Chioléro, R.; Yersin, B.; Gallati, H.; Assicot, M.; Bohuon, C.; Baumgartner, J.D.; Glauser, M.P.; et al. Cytokines, Nitrite/Nitrate, Soluble Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptors, and Procalcitonin Concentrations: Comparisons in Patients with Septic Shock, Cardiogenic Shock, and Bacterial Pneumonia. Crit Care Med 1997, 25, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picod, A.; Morisson, L.; de Roquetaillade, C.; Sadoune, M.; Mebazaa, A.; Gayat, E.; Davison, B.A.; Cotter, G.; Chousterman, B.G. Systemic Inflammation Evaluated by Interleukin-6 or C-Reactive Protein in Critically Ill Patients: Results From the FROG-ICU Study. Front Immunol 2022, 13, 868348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedermann, F.J.; Kaneider, N.; Egger, P.; Tiefenthaler, W.; Wiedermann, C.J.; Lindner, K.H.; Schobersberger, W. Migration of Human Monocytes in Response to Procalcitonin. Crit Care Med 2002, 30, 1112–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wacker, C.; Prkno, A.; Brunkhorst, F.M.; Schlattmann, P. Procalcitonin as a Diagnostic Marker for Sepsis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Lancet Infect Dis 2013, 13, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunkhorst, F.M.; Wegscheider, K.; Forycki, Z.F.; Brunkhorst, R. Procalcitonin for Early Diagnosis and Differentiation of SIRS, Sepsis, Severe Sepsis, and Septic Shock. Intensive Care Med 2000, 26 Suppl 2, S148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E, U.; O, B.; U, A. Role of Leucocytes Cell Population Data in the Early Detection of Sepsis. Journal of clinical pathology 2018, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Pan, S.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Qi, H.; Xie, J.; Qu, J. The Clinical Value of Hematological Neutrophil and Monocyte Parameters in the Diagnosis and Identification of Sepsis. Ann Transl Med 2021, 9, 1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornet, E.; Boubaya, M.; Troussard, X. Contribution of the New XN-1000 Parameters NEUT-RI and NEUT-WY for Managing Patients with Immature Granulocytes. Int J Lab Hematol 2015, 37, e123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.; Chang, J.; Kahng, J.; Park, H.; Jo, I.; Kim, Y.; Han, K. Development of a Novel Flow Cytometry-Based System for White Blood Cell Differential Counts: 10-Color LeukoDiff. Ann Lab Med 2019, 39, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Gu, J.; Seo, J.E.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, H.K. Diagnostic and Prognostic Values of Neutrophil Reactivity Intensity (NEUT-RI) in Pediatric Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome and Sepsis. Ann Clin Lab Sci 2023, 53, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mantovani, E.M.A.; Formenti, P.; Pastori, S.; Roccaforte, V.; Gotti, M.; Panella, R.; Galimberti, A.; Costagliola, R.; Vetrone, F.; Umbrello, M.; et al. The Potential Role of Neutrophil-Reactive Intensity (NEUT-RI) in the Diagnosis of Sepsis in Critically Ill Patients: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Diagnostics (Basel) 2023, 13, 1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finazzi, S.; Paci, G.; Antiga, L.; Brissy, O.; Carrara, G.; Crespi, D.; Csato, G.; Csomos, A.; Duek, O.; Facchinetti, S.; et al. PROSAFE: A European Endeavor to Improve Quality of Critical Care Medicine in Seven Countries. Minerva Anestesiol 2020, 86, 1305–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levey, A.S. Defining AKD: The Spectrum of AKI, AKD, and CKD. Nephron 2022, 146, 302–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3) - PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26903338/ (accessed on 22 January 2024).
- Delano, M.J.; Ward, P.A. The Immune System’s Role in Sepsis Progression, Resolution and Long-Term Outcome. Immunol Rev 2016, 274, 330–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clyne, B.; Olshaker, J.S. The C-Reactive Protein. J Emerg Med 1999, 17, 1019–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelubre, C.; Anselin, S.; Zouaoui Boudjeltia, K.; Biston, P.; Piagnerelli, M. Interpretation of C-Reactive Protein Concentrations in Critically Ill Patients. Biomed Res Int 2013, 2013, 124021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinsdale, R.J.; Devi, A.; Hampson, P.; Wearn, C.M.; Bamford, A.L.; Hazeldine, J.; Bishop, J.; Ahmed, S.; Watson, C.; Lord, J.M.; et al. Changes in Novel Haematological Parameters Following Thermal Injury: A Prospective Observational Cohort Study. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, K. Role of Kidney Injury in Sepsis. J Intensive Care 2016, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Kim, M.-J.; Ko, H.-J.; Lee, E.-J.; Kim, H.-R.; Jeon, J.-W.; Ham, Y.-R.; Na, K.-R.; Lee, K.-W.; Lee, S.-I.; et al. Diagnostic and Prognostic Roles of C-Reactive Protein, Procalcitonin, and Presepsin in Acute Kidney Injury Patients Initiating Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy. Diagnostics (Basel) 2023, 13, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuveling, E.M.; Hillege, H.L.; Bakker, S.J.L.; Gans, R.O.B.; De Jong, P.E.; De Zeeuw, D. C-Reactive Protein Is Associated with Renal Function Abnormalities in a Non-Diabetic Population. Kidney Int 2003, 63, 654–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.-L.; Xiao, Z.-H.; Yang, M.-Y.; Zhu, Y.-M. Diagnostic Value of Serum Procalcitonin in Patients with Chronic Renal Insufficiency: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2013, 28, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinbach, G.; Bölke, E.; Grünert, A.; Störck, M.; Orth, K. Procalcitonin in Patients with Acute and Chronic Renal Insufficiency. Wien Klin Wochenschr 2004, 116, 849–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivas, M.C.; Villamarin Guerrero, H.F.; Tascon, A.J.; Valderrama-Aguirre, A. Plasma Interleukin-6 Levels Correlate with Survival in Patients with Bacterial Sepsis and Septic Shock. Interv Med Appl Sci 2021, 11, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| A | B | |||||
|
Septic (n=89) |
Non septic (n=111) |
P |
Not complicated sepsis (n=47) |
Septic shock (n=42) |
P | |
| Age | 73.00 [63.00 - 79.00] | 73.00 [56.00 - 79.00] | 0.454 | 74.00 [64.00 - 78.00] | 73.00 [62.75 - 79.75] | 0.808 |
| Male% | 48.4 | 52.3 | 0.679 | 59.6 | 35.7 | 0.042 |
| Creatinine | 1.57 [0.85 - 2.85] | 1.00 [0.77 - 1.39] | < 0.001 | 1.16 [0.77 - 1.64] | 2.18 [1.67 - 3.67] | < 0.001 |
| CPR | 20.79 [12.54 - 118.91] | 6.68 [1.54 - 21.70] | < 0.001 | 18.79 [7.78 - 149.16] | 23.03 [17.97 - 87.09] | 0.7244 |
| PCT | 8.83 [0.82 - 45.88] | 0.48 [0.29 - 1.64] | < 0.001 | 1.63 [0.40 - 12.09] | 32.59 [8.83 - 100.00] | < 0.001 |
| NEUT-RI | 53.80 [49.65 - 59.05] | 48.00 [46.00 - 49.90] | < 0.001 | 51.5 [47.80 - 56.30] | 56.20 [52.30 - 61.92] | 0.0054 |
| Septic | Non Septic | |||||
|
Renal Failure (n = 43) |
Normal renal function (n = 48) |
P |
Renal Failure (n = 27) |
Normal renal function (n = 82) |
P | |
| Age | 73.00 [63.00 - 79.00] | 72.50 [63.50 - 77.50] | 0.443 | 78.00 [73.00 - 81.00] | 68.00 [53.25 - 77.00] | 0.004 |
| Male% | 37.2 | 58.3 | 0.071 | 51.9 | 52.4 | 1 |
| Creatinine | 2.81 [1.83 – 4.26] | 0.86 [0.74 – 1.28] | < 0.001 | 1.60 [1.33 – 2.59] | 0.89 [0.68 – 1.19] | < 0.001 |
| CPR | 25.53 [17.82 - 148.22] | 18.80 [7.35 - 103.27] | 0.164 | 13.45 [6.03 - 130.85] | 3.78 [1.05 - 18.59] | 0.003 |
| PCT | 32.23 [5.86 - 83.72] | 1.79 [0.39 - 13.04] | < 0.001 | 1.15 [0.31 - 3.63] | 0.47 [0.28 - 1.21] | 0.193 |
| NEUT-RI | 55.10 [52.15 - 59.05] | 51.70 [47.82 - 58.65] | 0.101 | 47.90 [46.40 - 50.05] | 48.00 [45.85 - 49.88] | 0.886 |
| Septic | Non-septic | |||||
|
Alive (n=78) |
dead (n=11) |
P |
Alive (n=95) |
dead (n=16) |
P | |
| PCR | 21.52 [11.48-137.89] | 19.06 [14.10-36.49] | 0.772 | 7.28 [1.88 - 21.70] | 1.06 [0.41 - 80.00] | 0.477 |
| PCT | 3.22 [0.59 -32.32 | 39.56 [17.39-83.72] | 0.002 | 0.46 [0.28 - 1.21] | 0.72 [0.57 - 1.10] | 0.453 |
| NEUT-RI | 53.05 [48.90-57.22] | 58.80 [54.45-73.35] | 0.005 | 47.90 [45.80 - 49.82] | 45.60 [44.00 - 47.60] | 0.184 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





