Submitted:
14 December 2023
Posted:
14 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
2.2. Molecular protocol
2.3. Data analysis
3. Results
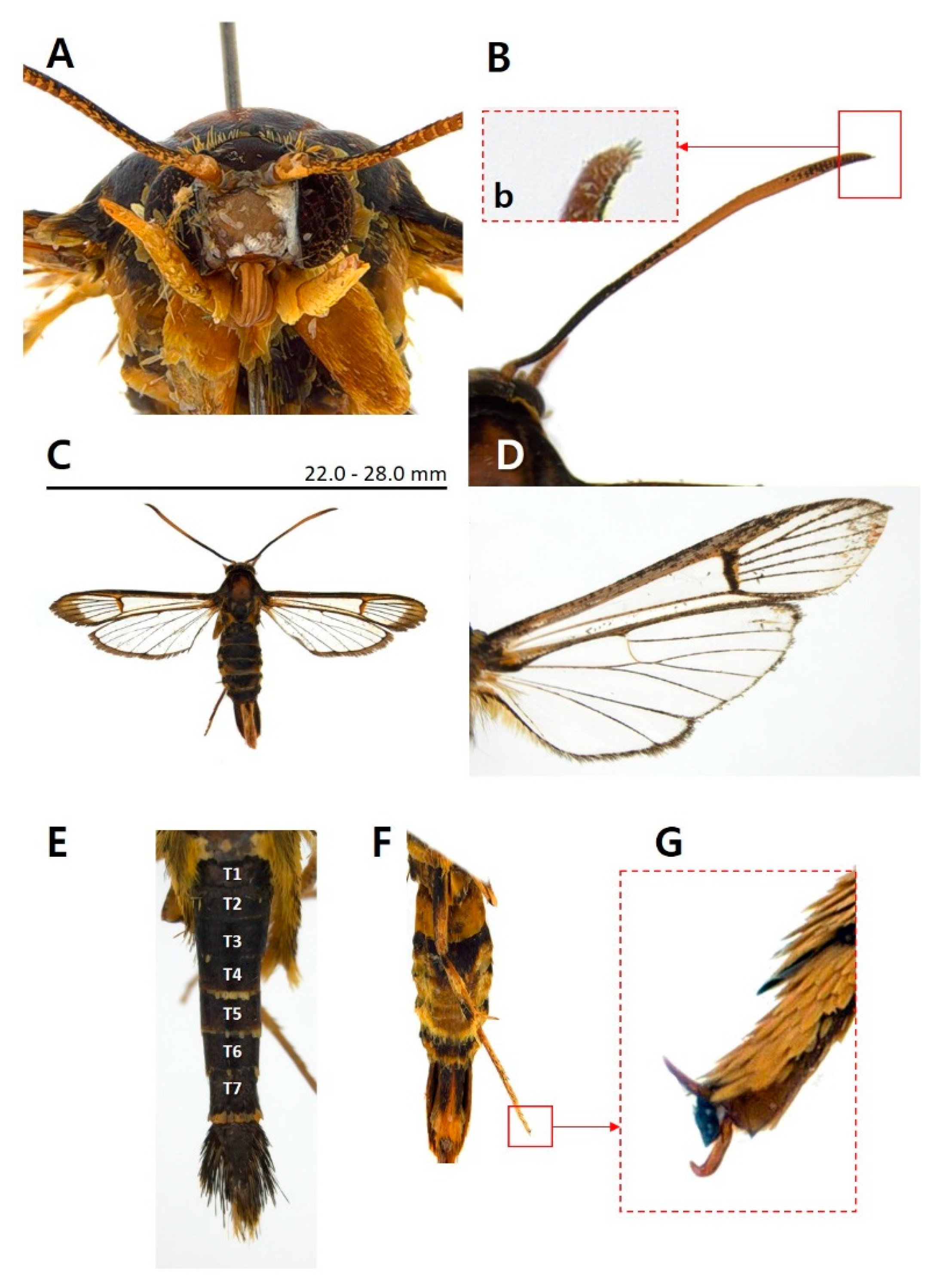
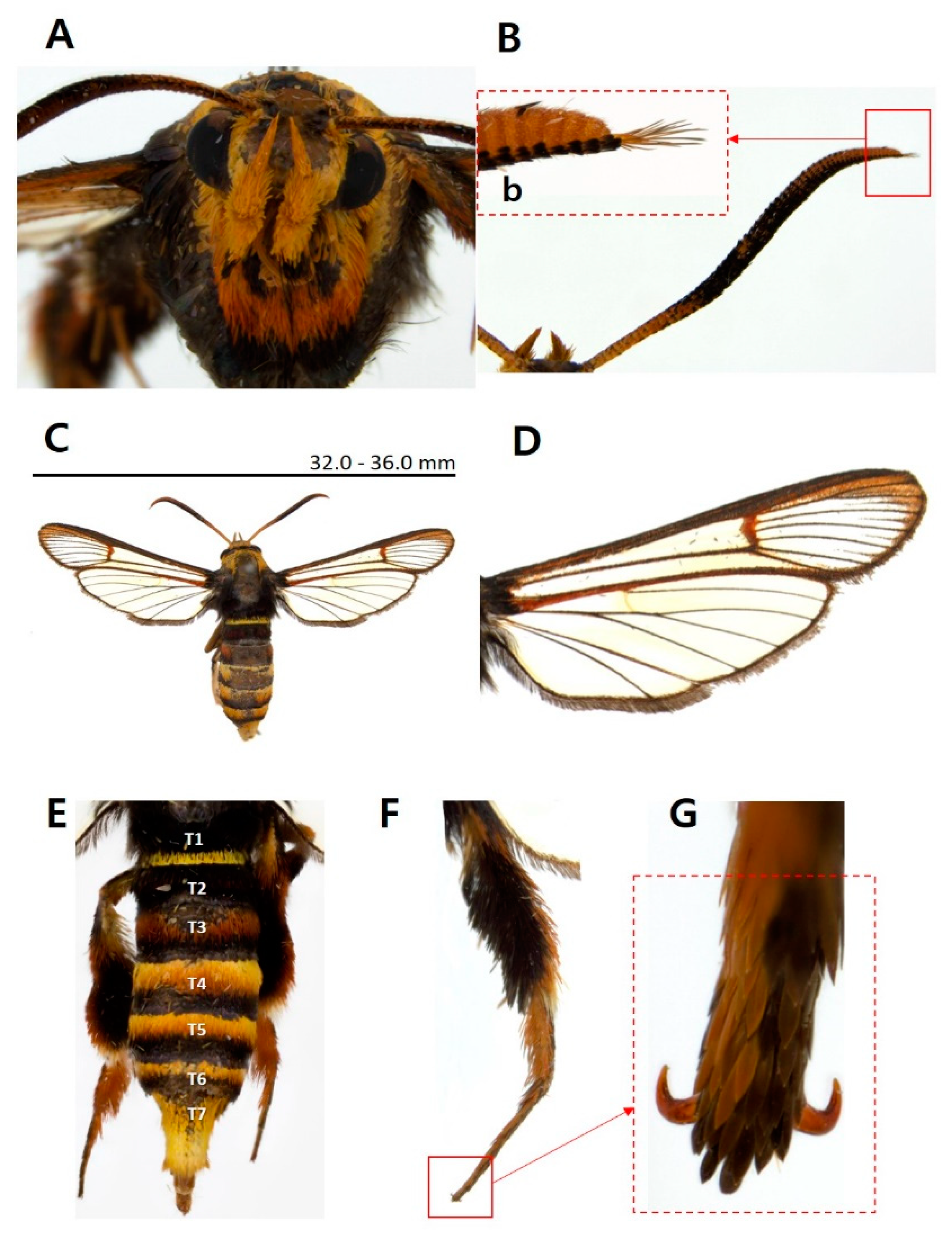
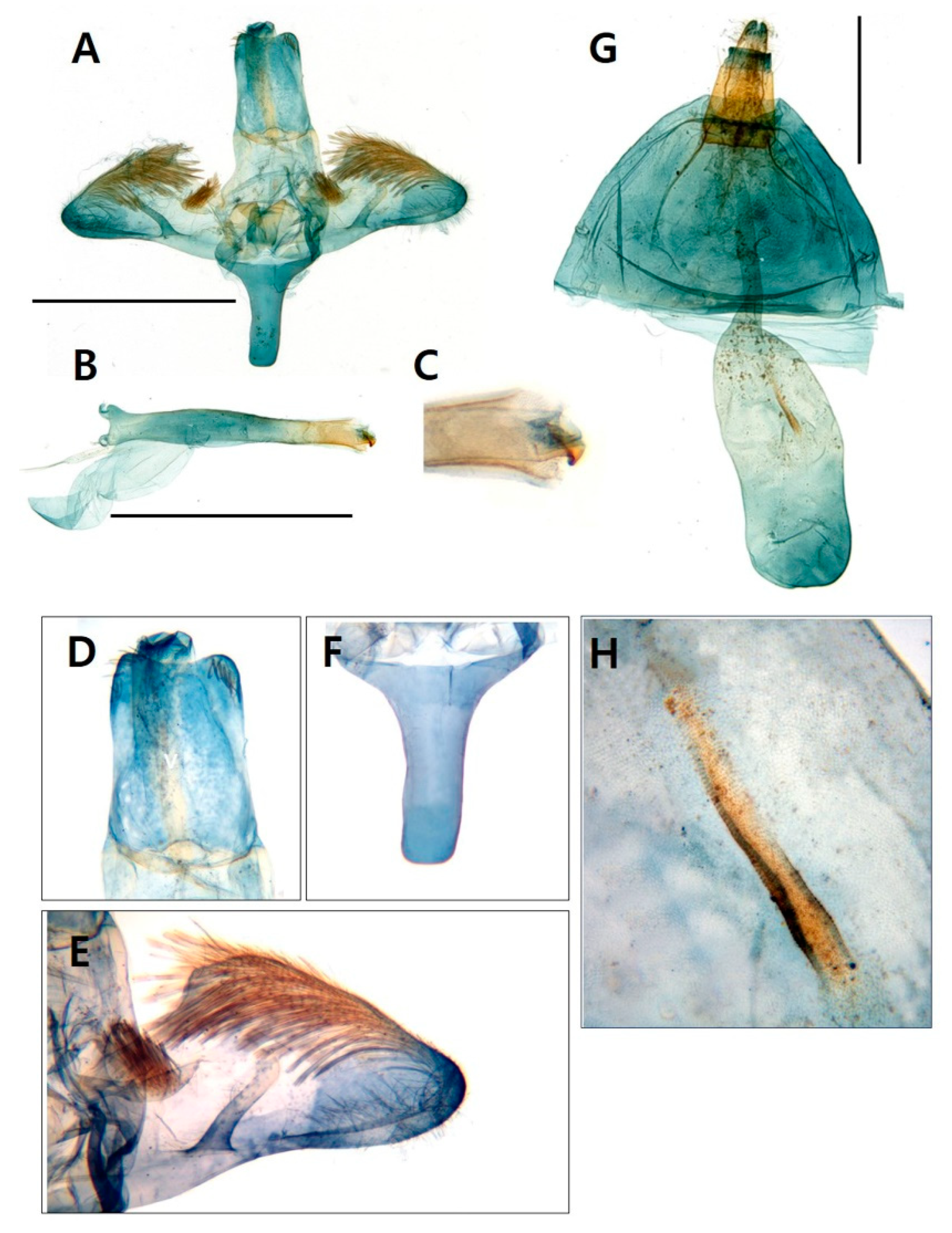
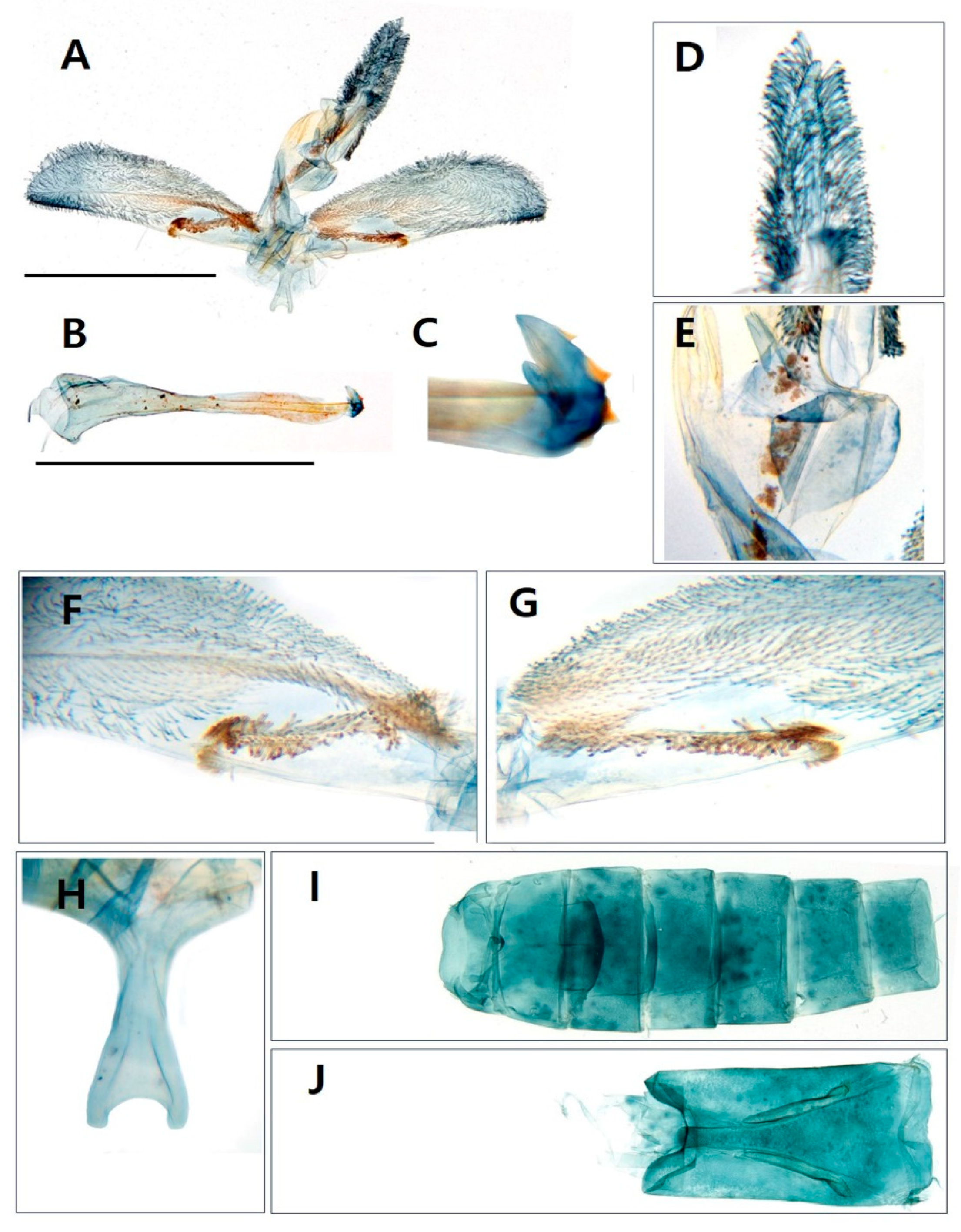
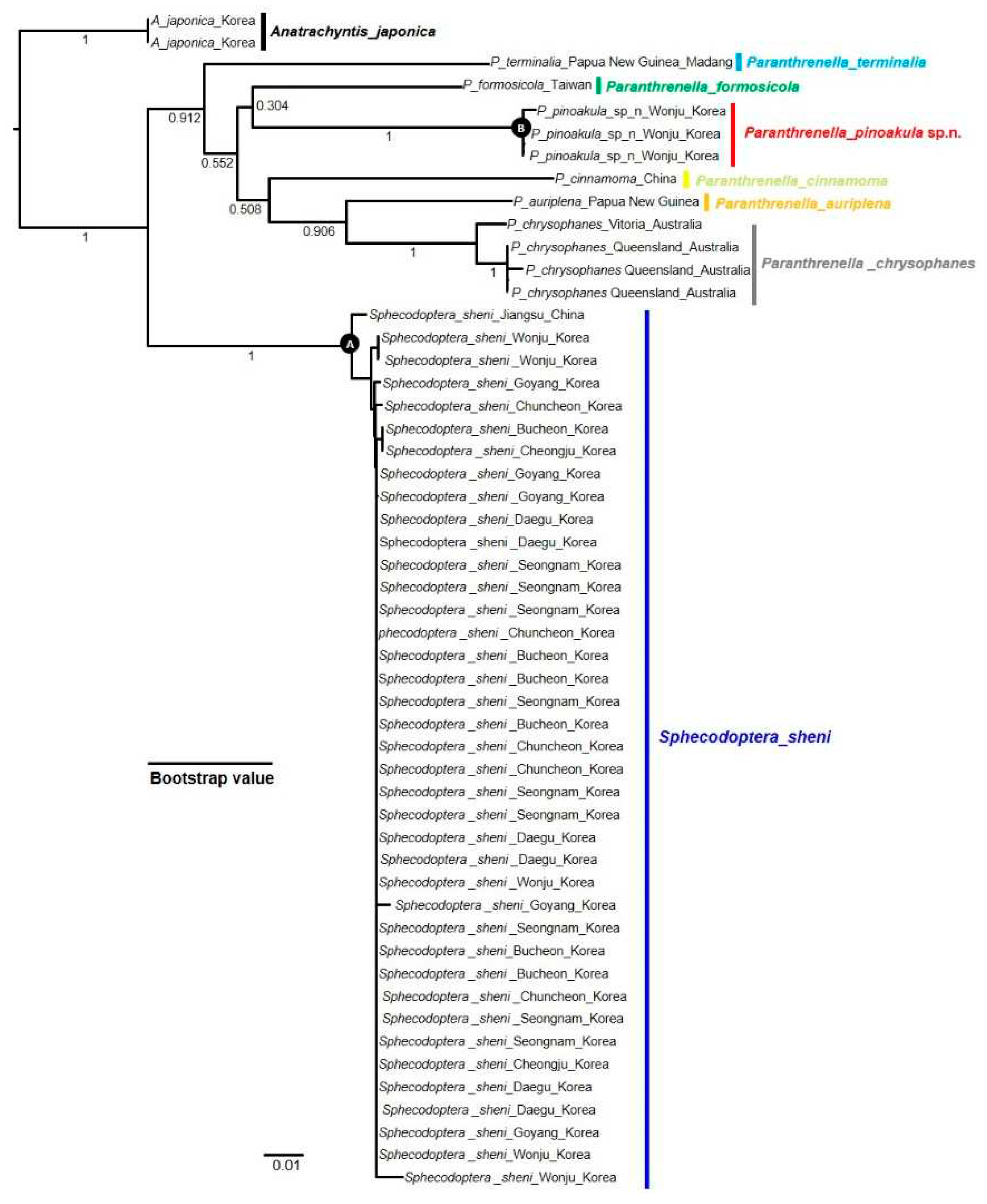
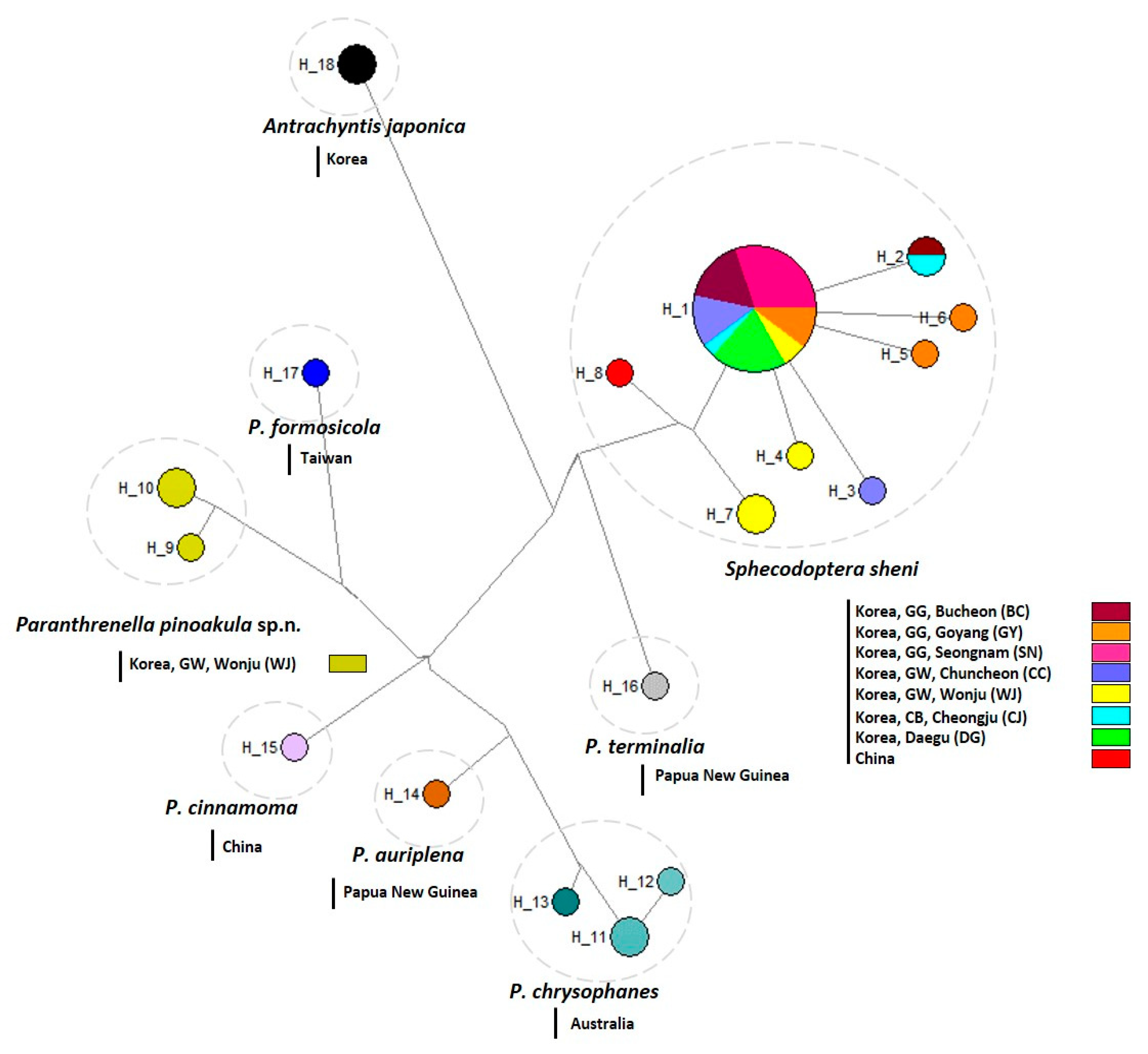
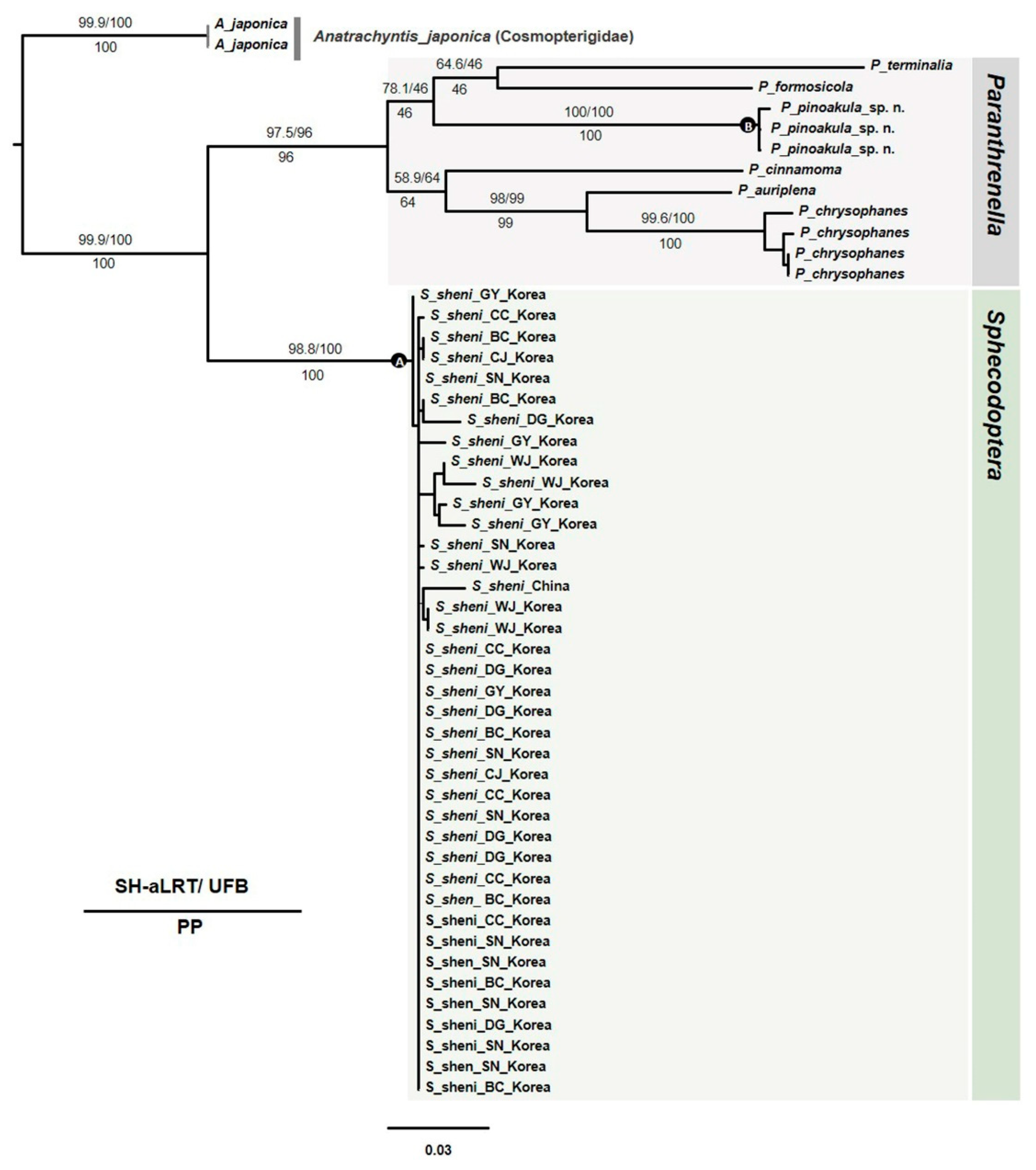
3.1. Morphological identification
3.1.1. Taxonomic accounts
- Genus Sphecodoptera Hampson, [1893]
- Sphecodoptera Hampson, [1893]: 189. Type species. Sphecia repanda Walker
- Sphecia Hampson, 1919: 80.
- Sesia Spatenka, Lastuvka, Gorbunov, Tosevski & Arita, 1993: 87
- Spherodoptera Matsumura, 1931: 1017.
- Scasiba Matsumura, 1931: 8.
- Sphecodoptera sheni (Arita & Xu, 1994)
- Sesia sheni Arita & Xu, 1994: 61. Type locality. Nanjing, Jiangsu, China
- Scasiba caryavora Xu & Arita, 1994: 2.
- Sphecodoptera sheni Kallies, Arita, Owada & Wang, 2014: 587.
- Genus Paranthrenella Strand, 1916
- Paranthrenella Strand, 1916: 47. Type Species. Paranthrenella formosicola Strand
- Paranthrenella pinoakula sp. nov. Kim
3.2. Molecular analyses
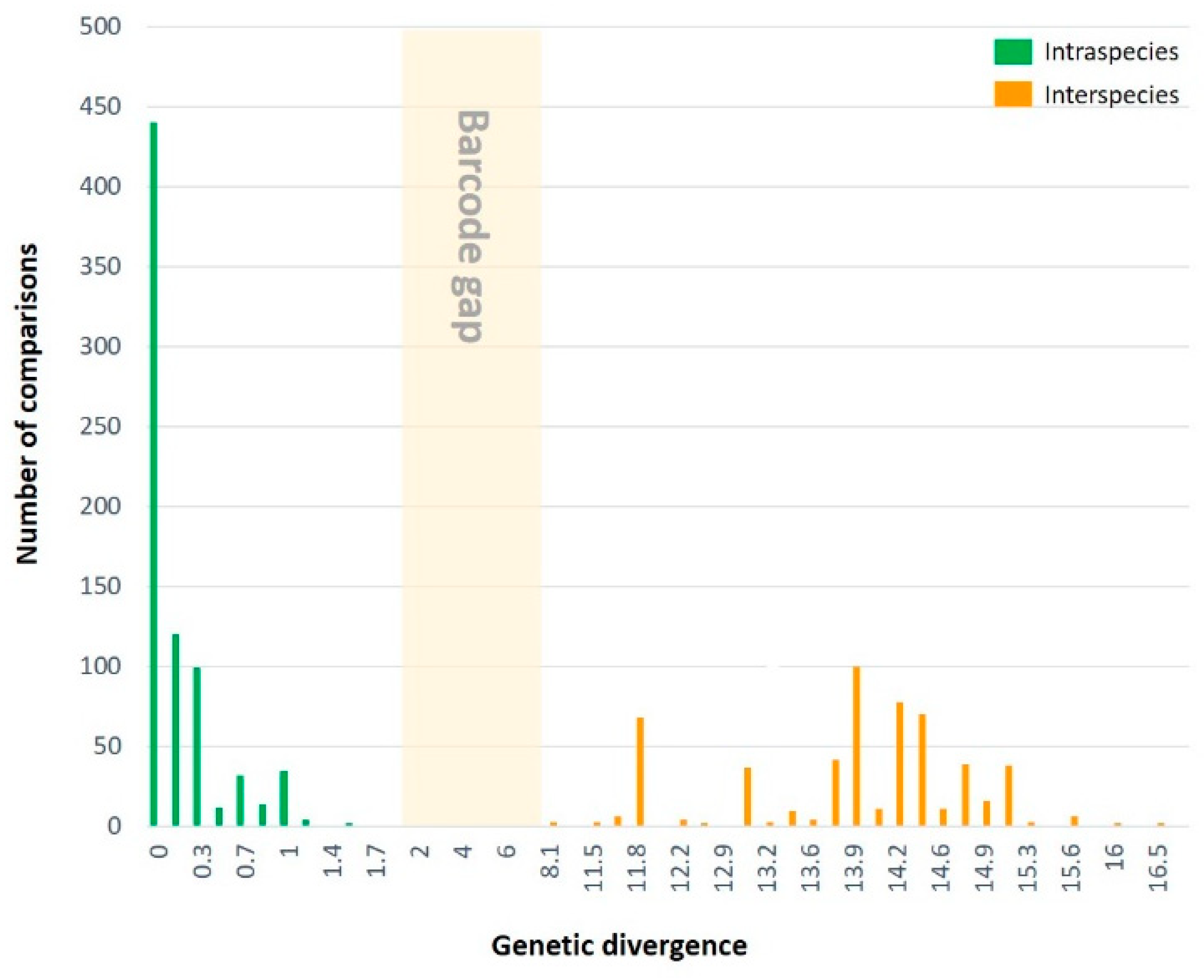
3.2.1. Genetic divergence and distribution
3.2.2. NJ Tree analysis
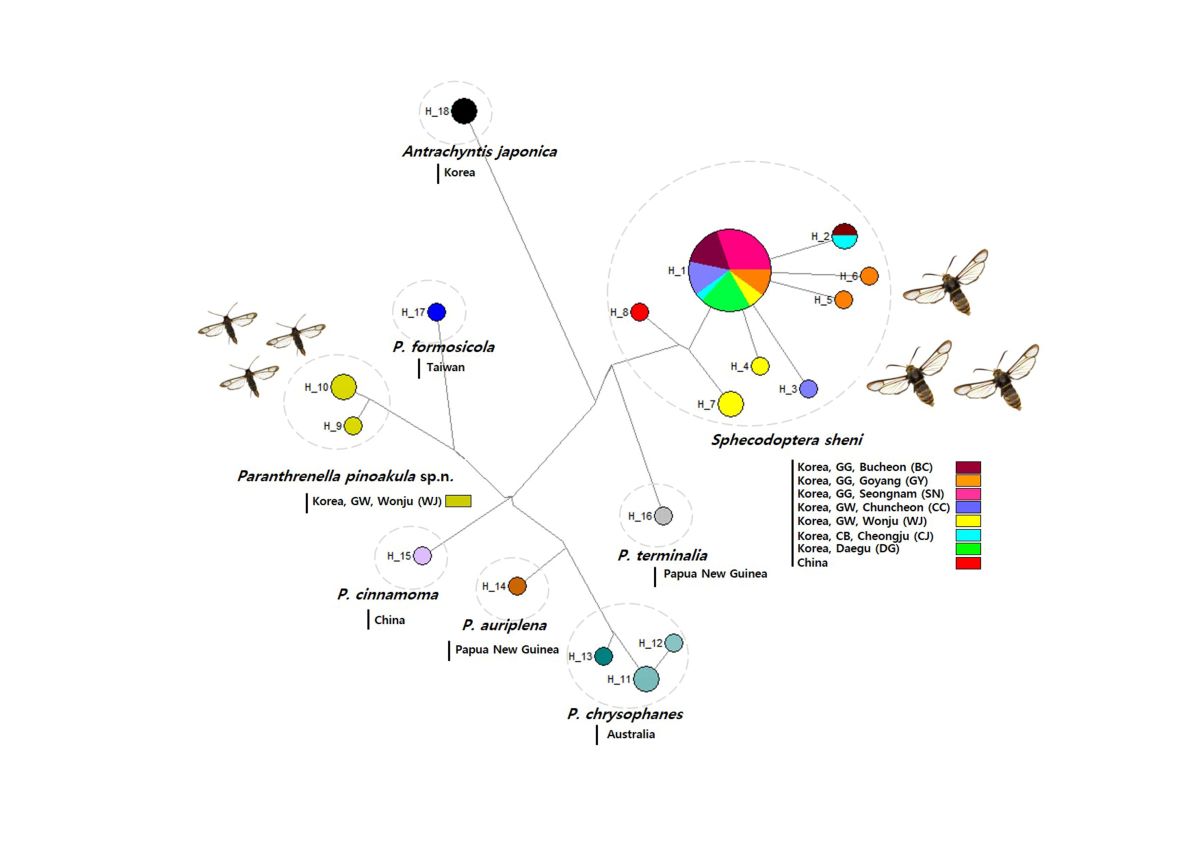
3.2.3. Haplotype analysis
3.2.4. Phylogenetic tree
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lehmann, P.; Ammunét, T.; Barton, M.; Battisti, A.; Eigenbrode, S.D.; Jepsen, J.U.; Kalinkat, G.; Neuvonen, S.; Niemelä, P.; Terblanche, J.S.; Økland, B. Complex responses of global insect pests to climate warming. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment 2020, 18, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Economic Forum. Global risks report 2023. 18th Edition. Insight report; World Economic forum: Switzerland. 2023; p. 98.
- Pühringer, F; Kallies, A. Provisional checklist of the Sesiidae of the world (Lepidoptera: Ditrysia). Mitteilungen der Entomologischen Arbeisgemeinschaft Salzkammergut 2004, 4, 1-85. [CrossRef]
- Pühringer, F; Kallies, A. Provisional checklist of the Sesiidae of the world (Lepidoptera: Ditrysia). Mitteilungen der Entomologischen Arbeisgemeinschaft Salzkammergut 2004, 4, 1-85.
- Kim, S.; Lee, W.; Lee, S. Estimation of a new molecular marker of the genus Stathmopoda (Lepidoptera: Stathmopodidae): Comparing EF1a and COI sequences. Journal of Asia-Pacific Entomology, 2017, 20, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folmer, O.; Black, M.; Hoeh, W.; Lutz, R.; Vrijenhoek, R. DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Molecular Marine Biology and Biotechnology 1994, 3, 294–299. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Molecu lar Biology and Evolution 2016, 33(7), 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, B.Q.; Schmid, H.A.; Chernomor, O.; Dominik, S.; Michael, D.W.; Arndt, V.H.; Robert, L. IQ-TREE 2: New Models and Efficient Methods for Phylogenetic Inference in the Genomic Era. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 2020, 37 (5), 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernomor, O.; Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. Terrace aware data structure for phylogenomic inference from supermatrices. Systematic Biology 2016, 65 (6), 997–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.F.; Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nature methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, D.T.; Chernomor, O.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q.; Vinh, L.S. UFBoot2: improving the ultrafast bootstrap approximation. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 2018; 35, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anisimova, M.; Gil, M.; Dufayard, J.F.; Dessimoz, C.; Gascuel, O. Survey of branch support methods demonstrates accuracy, power, and robustness of fast likelihood-based approximation schemes. Systematic Biology 2011, 60, 685–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.Y. Primary study of Aegeria molybdoceps Hampson. Plant protection, 1988, 3, 23–25. [Google Scholar]
- Arita, Y; Xu, Z-G.; Liu, Y-Q. A new Sesia (Lepidoptera, Sesiidae), clearwing borer on Pecan from Nanjing, China. Tinea 1994, 14 (1), 61-64.



| 1. Different taxonomic levels | ||||
| Taxonomic level (No. of Comparison Pairs) | K2P Pairwase distances | |||
| Maximum | Minimum | Average | ||
| Within species (647) | 1.9 | 0.0 | 0.3 | |
| Between species (564) | 16.8 | 8.1 | 13.8 | |
| 2. Intraspecific genetic divergence | ||||
| Species | Comparison pairs | Intraspecific genetic divergence | ||
| (CP) | Maximum | Minimum | Average | |
| Sphecodoptera sheni | 637 | 1.7 | 0.0 | 0.2 |
| Paranthrenella pinoakulasp.n. | 3 | 0.3 | 0.0 | 0.2 |
| Paranthrenella auriplena | - | - | - | - |
| Paranthrenella cinnamoma | - | - | - | - |
| Paranthrenella chrysophanes | 6 | 1.9 | 0.0 | 0.9 |
| Paranthrenella formosicola | - | - | - | - |
| Paranthrenella terminalis | - | - | - | - |
| Anatrachyntis japonica | 1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 3. Interspecific genetic divergence | ||||
| species | Sphecodoptera sheni | P. pinoakulasp. n. | P. auriplena | P. cinnamoma |
| Sphecodoptera sheni | CP=114, 14.6(14.2-15.3) | CP=38, 14.2(13.9-14.9) | CP=38, 15.1(14.9-15.8) | |
| Paranthrenella pinoakulasp.n. | CP=3, 13.9(13.9-13.9) | CP=3, 13.0(13.0-13.0) | ||
| Paranthrenella auriplena | CP=1, 11.5(11.5-11.5) | |||
| Paranthrenella cinnamoma | ||||
| Paranthrenella chrysophanes | ||||
| Paranthrenella formosicola | ||||
| Paranthrenella terminalis | ||||
| Anatrachyntis japonica | CP=78, 11.8(11.5-12.5) | CP=6, 14.9(14.9-14.9) | CP=2, 13.7(13.7-13.7) | CP=2, 15.6(15.6-15.6) |
| species | P. chrysophanes | P. formosicola | P. terminalis | |
| Sphecodoptera sheni | CP=152, 14.0(13.7-14.9) | CP=38, 13.1(12.9-13.7) | CP=38, 13.7(13.4-14.4) | |
| Paranthrenella pinoakulasp.n. | CP=12, 13.4(13.0-13.7) | CP=3, 11.8(11.7-12.0) | CP=3, 14.3(14.2-14.4) | |
| Paranthrenella auriplena | CP=4, 8.2(8.1-8.4) | CP=1, 13.2(13.2-13.2) | CP=1, 14.9(14.9-14.9) | |
| Paranthrenella cinnamoma | CP=4, 138(13.7-13.9) | CP=1 12.2(12.2-12.2) | CP=1, 14.4(14.4-14.4) | |
| Paranthrenella chrysophanes | CP=4, 14.4(14.2-14.6) | CP=4, 16.5(16.3-16.8) | ||
| Paranthrenella formosicola | CP=1, 12.2(12.2-12.2) | |||
| Paranthrenella terminalis | ||||
| Anatrachyntis japonica | CP=8, 15.6(15.3-16.0) | CP=2, 14.9(14.9-14.9) | CP=2, 14.1(14.1-14.1) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





