Submitted:
28 November 2023
Posted:
29 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Bioceramics
2.1. Commonly Used Bioceramics
2.2. Other Ceramic Materials
2.3. Polymer-Ceramic Composite Materials
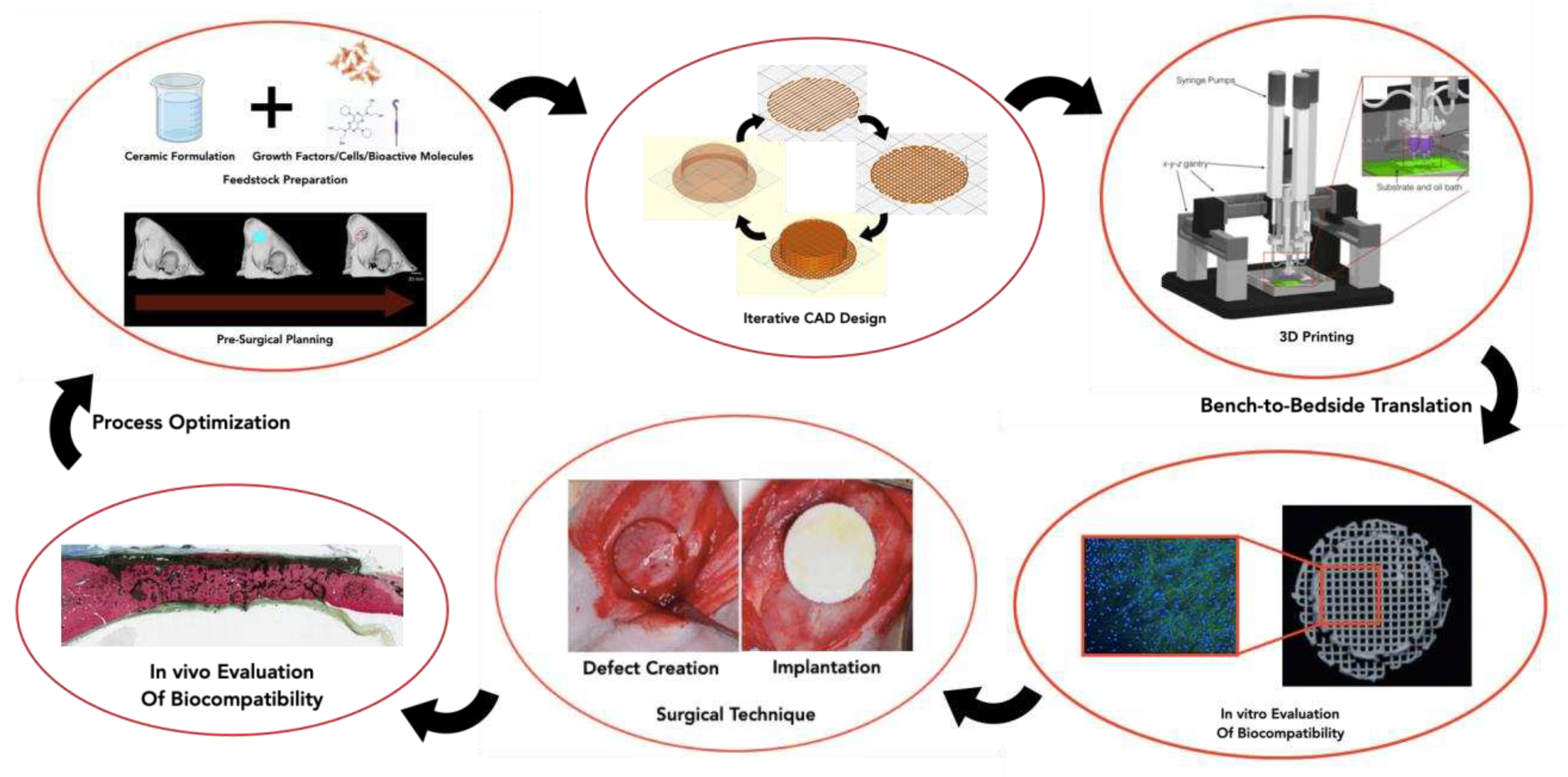
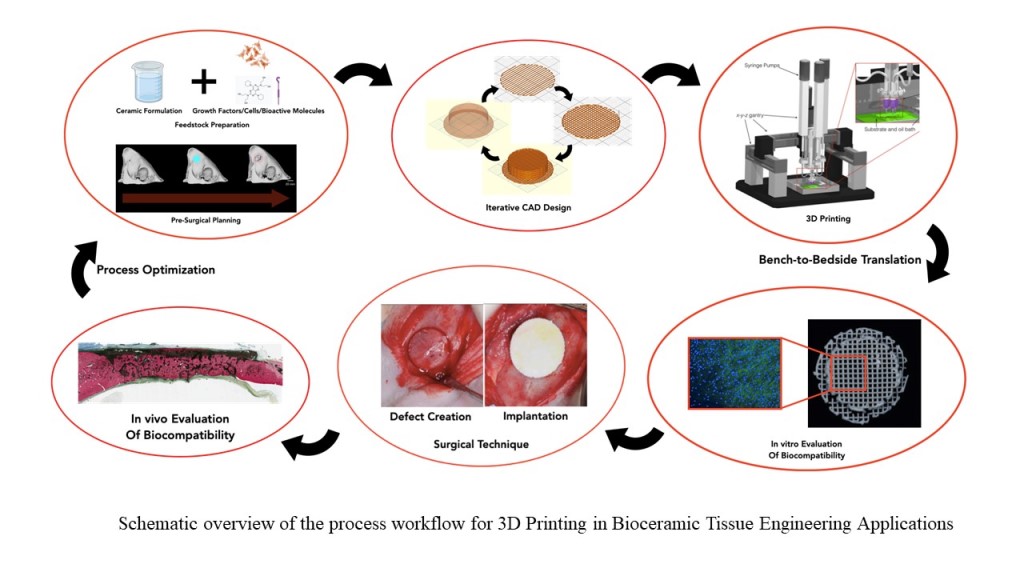
3. 3DP Methods for Fabrication of BTE Scaffolds
3.1. Laser/Light Assisted 3DP Techniques
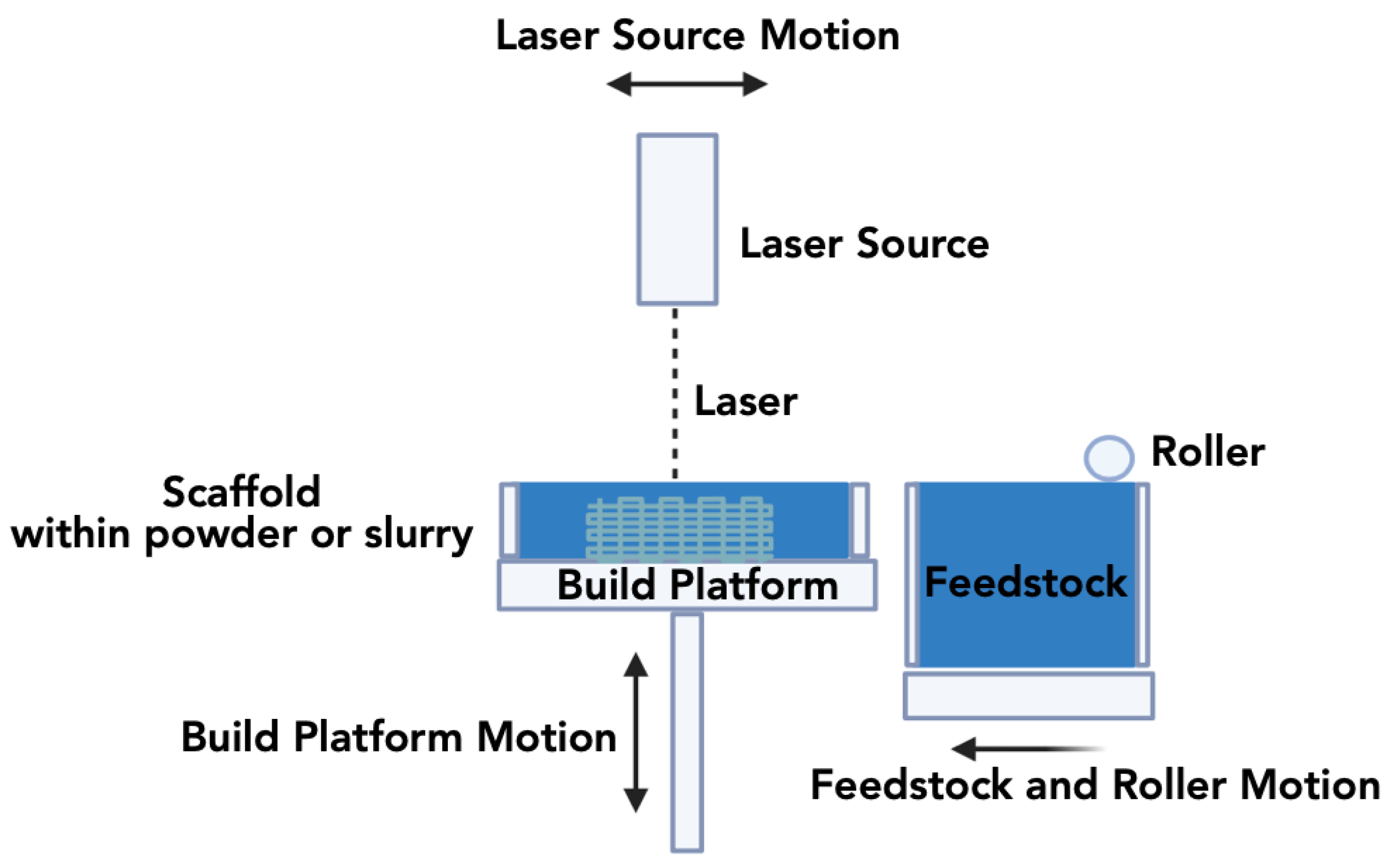
3.1.1. Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
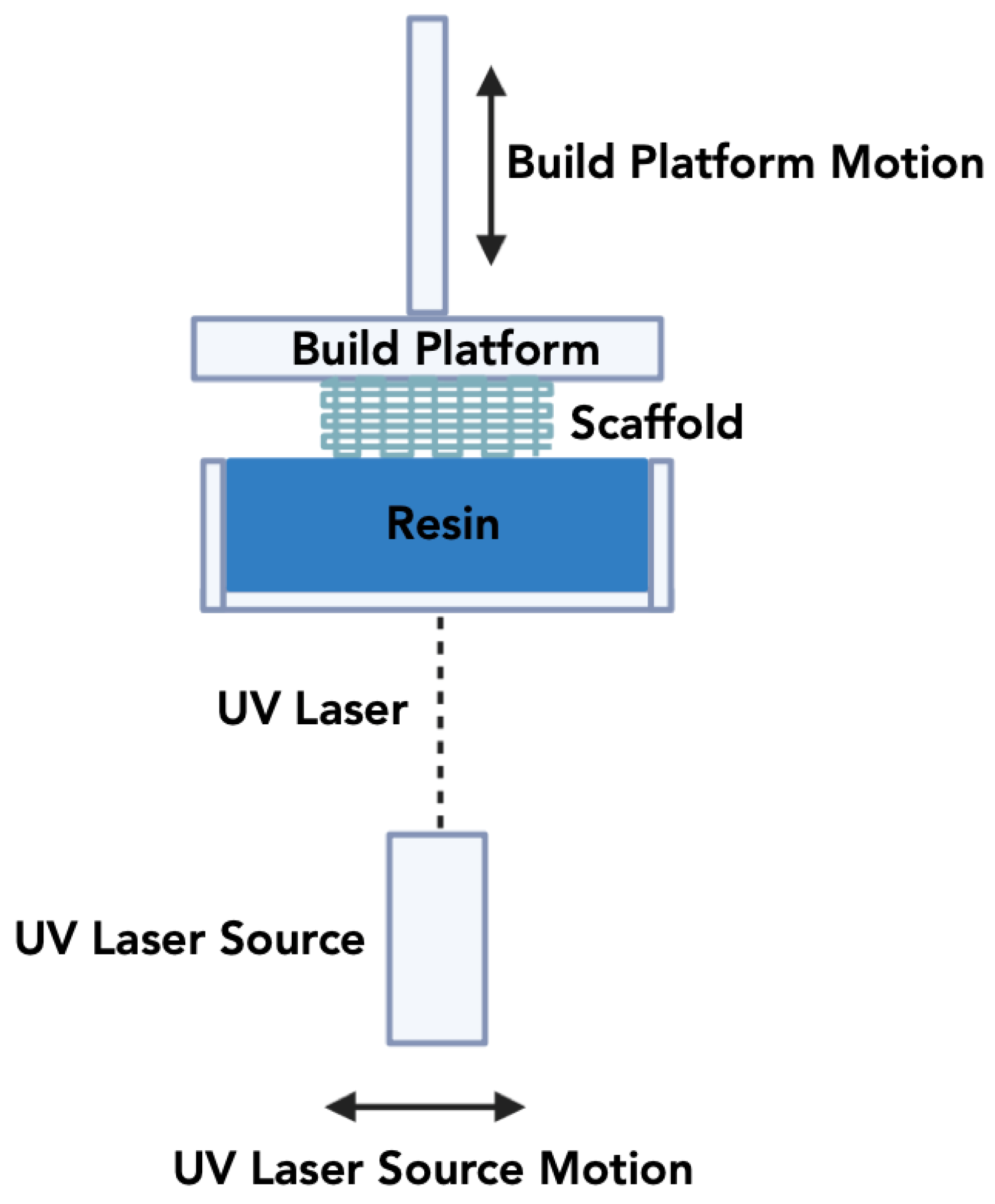
3.1.2. Stereolithography Apparatus (SLA)
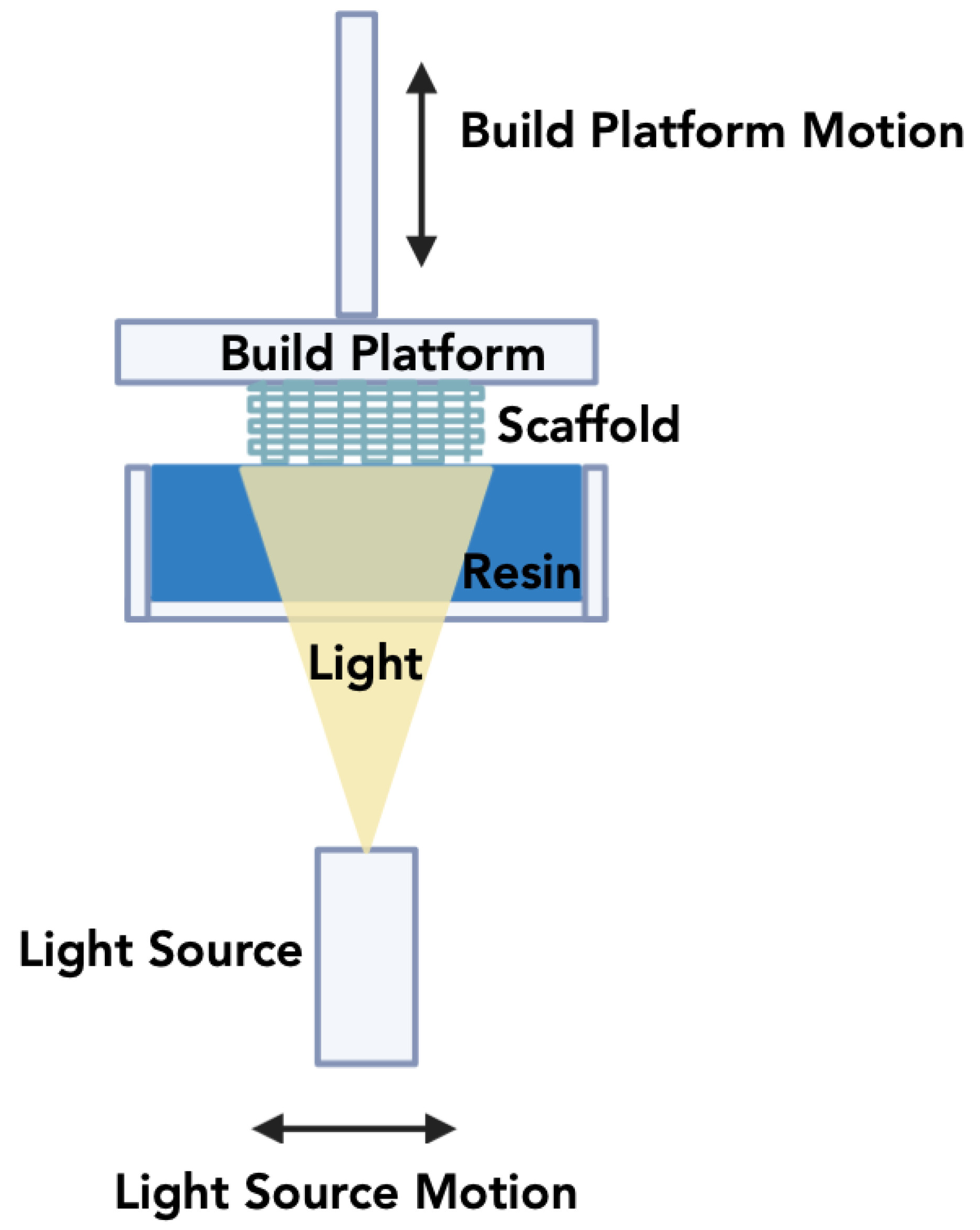
3.1.3. Digital Light Processing
3.2. Micro Extrusion Based Techniques
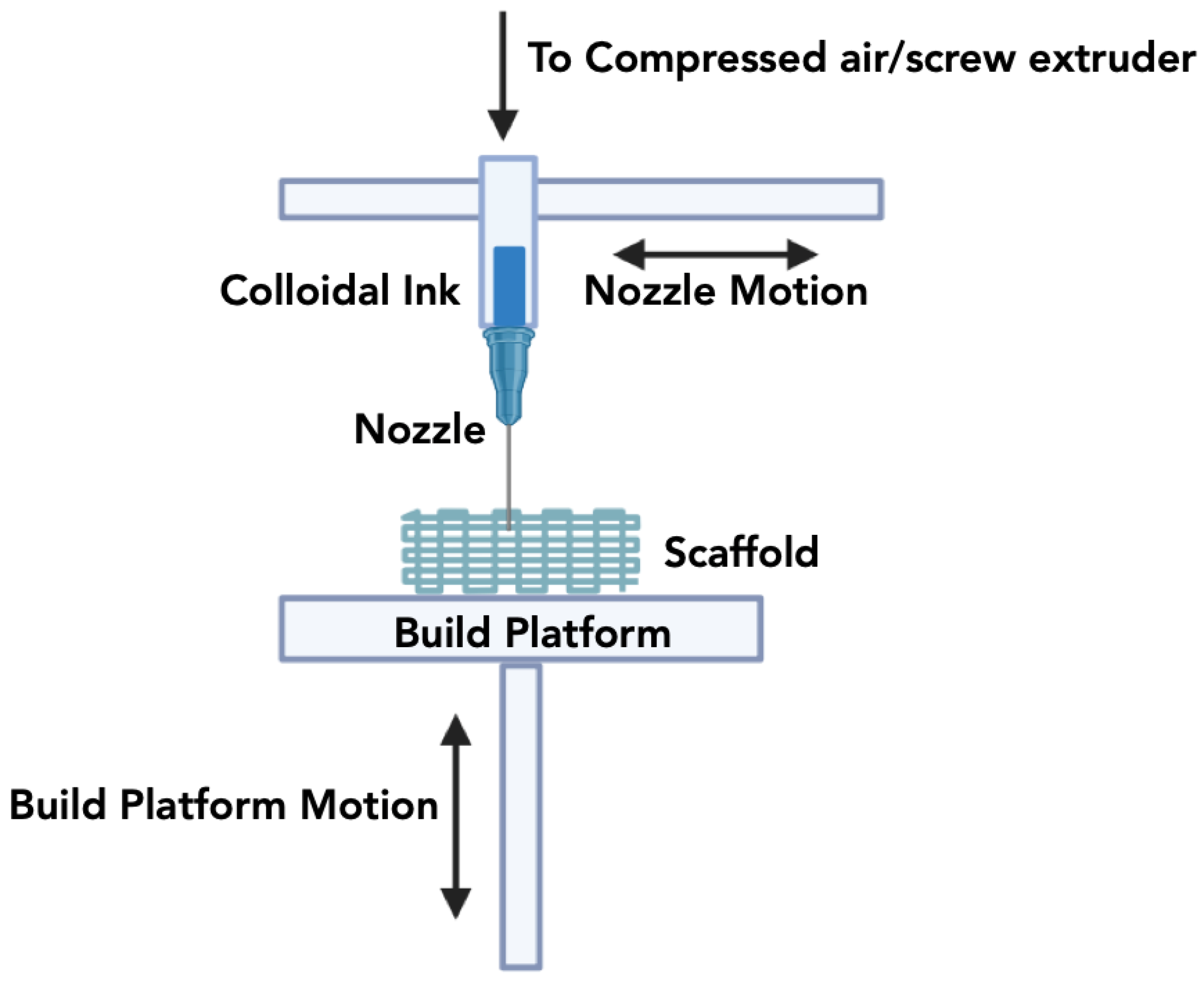
3.2.1. Direct Inkjet Writing (DIW)
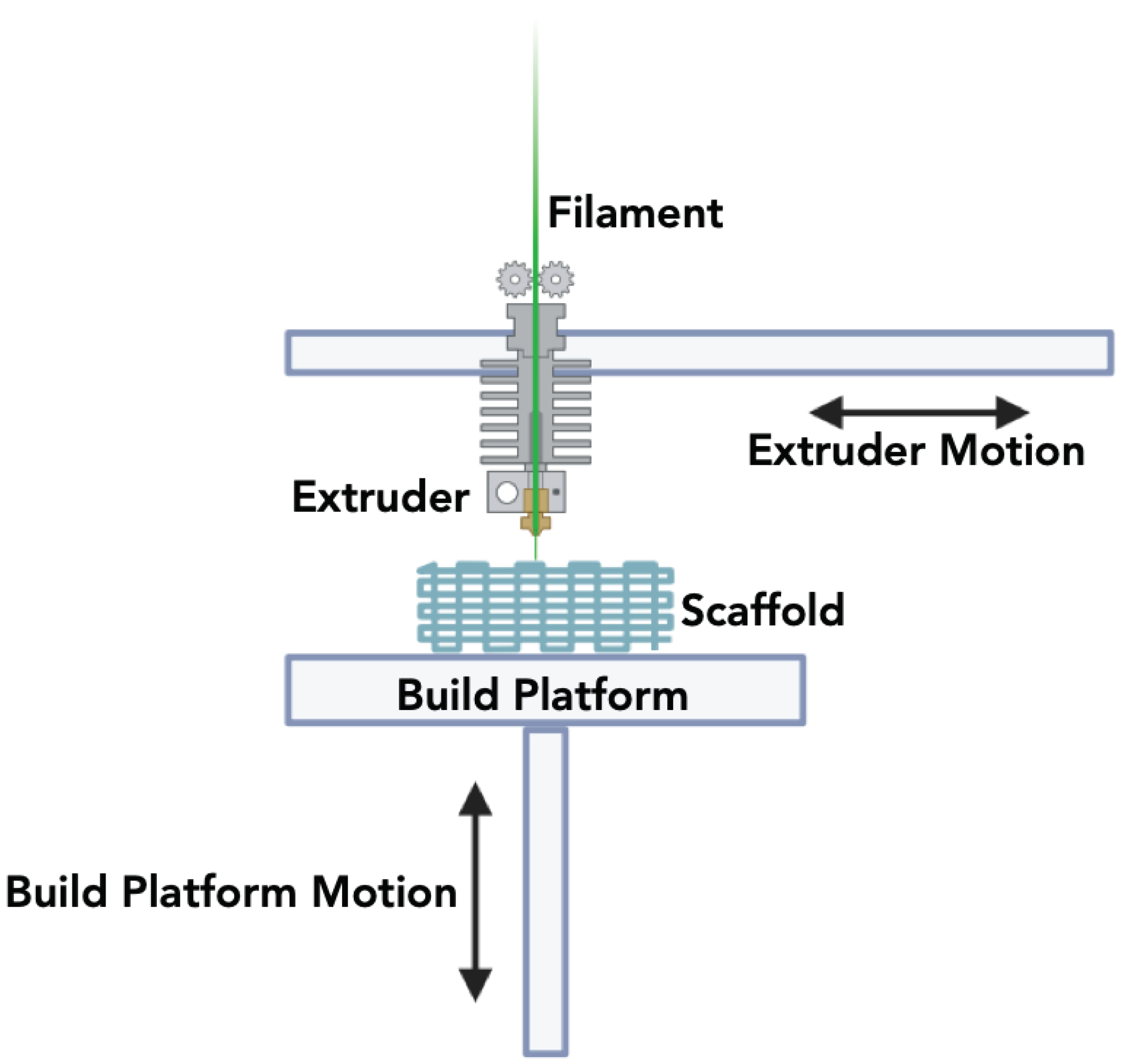
3.2.2. Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
3.3. Process Optimization and Post Processing
4. Biological Factors and Bioactive Molecules
5. Future Considerations and Requirements for 3DP of Bioceramics
References
- Wang, W.; Yeung, K. W. J. B. m., Bone grafts and biomaterials substitutes for bone defect repair: A review. Bioact Mater. 2017, 2, (4), 224-247. [CrossRef]
- Damien, C. J.; Parsons, J. R. J. J. o. A. B., Bone graft and bone graft substitutes: a review of current technology and applications. J Appl Biomater. 1991, 2, (3), 187-208. [CrossRef]
- Haugen, H. J.; Lyngstadaas, S. P.; Rossi, F.; Perale, G. J. J. o. c. p., Bone grafts: which is the ideal biomaterial? J Clin Periodontol. 2019, 46, 92-102.
- Sheikh, Z.; Hamdan, N.; Ikeda, Y.; Grynpas, M.; Ganss, B.; Glogauer, M. J. B. r., Natural graft tissues and synthetic biomaterials for periodontal and alveolar bone reconstructive applications: a review. Biomater Res. 2017, 21, (1), 9. [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, Z.; Sima, C.; Glogauer, M., Bone Replacement Materials and Techniques Used for Achieving Vertical Alveolar Bone Augmentation. Materials 2015, 8, (6), 2953-2993. [CrossRef]
- Ribas, R. G.; Schatkoski, V. M.; do Amaral Montanheiro, T. L.; de Menezes, B. R. C.; Stegemann, C.; Leite, D. M. G.; Thim, G. P. J. C. I., Current advances in bone tissue engineering concerning ceramic and bioglass scaffolds: A review. Ceramics International 2019, 45, (17), 21051-21061. [CrossRef]
- Gokyer, S.; Yilgor, E.; Yilgor, I.; Berber, E.; Vrana, E.; Orhan, K.; Monsef, Y. A.; Guvener, O.; Zinnuroglu, M.; Oto, C. J. A. B. S.; Engineering, 3D printed biodegradable polyurethaneurea elastomer recapitulates skeletal muscle structure and function. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2021, 7, (11), 5189-5205. [CrossRef]
- Zadpoor, A. A. J. B. s., Bone tissue regeneration: the role of scaffold geometry. Biomater Sci. 2015, 3, (2), 231-245. [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, Z.; Zhang, Y. L.; Tamimi, F.; Barralet, J., Effect of processing conditions of dicalcium phosphate cements on graft resorption and bone formation. Acta Biomaterialia 2017. [CrossRef]
- Tamimi, F.; Sheikh, Z.; Barralet, J., Dicalcium phosphate cements: brushite and monetite. Acta Biomater 2012, 8, (2), 474-87. [CrossRef]
- Tamimi, F.; Le Nihouannen, D.; Eimar, H.; Sheikh, Z.; Komarova, S.; Barralet, J., The effect of autoclaving on the physical and biological properties of dicalcium phosphate dihydrate bioceramics: brushite vs. monetite. Acta Biomater 2012, 8, (8), 3161-9. [CrossRef]
- Peltola, S. M.; Melchels, F. P.; Grijpma, D. W.; Kellomäki, M. J. A. o. m., A review of rapid prototyping techniques for tissue engineering purposes. Annals of Medicine 2008, 40, (4), 268-280. [CrossRef]
- Fahmy, M. D.; Jazayeri, H. E.; Razavi, M.; Masri, R.; Tayebi, L., Three-dimensional bioprinting materials with potential application in preprosthetic surgery. Journal of Prosthodontics 2016, 25, (4), 310-318. [CrossRef]
- Nyberg, E. L.; Farris, A. L.; Hung, B. P.; Dias, M.; Garcia, J. R.; Dorafshar, A. H.; Grayson, W. L., 3D-printing technologies for craniofacial rehabilitation, reconstruction, and regeneration. Annals of biomedical engineering 2017, 45, 45-57. [CrossRef]
- Hull, C. W., Apparatus for production of three-dimensional objects by stereolithography. United States Patent, Appl., No. 638905, Filed 1984.
- Kruth, J.-P., Material incress manufacturing by rapid prototyping techniques. CIRP annals 1991, 40, (2), 603-614. [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Dong, H.; Su, J.; Han, J.; Song, B.; Wei, Q.; Shi, Y., A review of 3D printing technology for medical applications. Engineering 2018, 4, (5), 729-742. [CrossRef]
- Obregon, F.; Vaquette, C.; Ivanovski, S.; Hutmacher, D.; Bertassoni, L., Three-dimensional bioprinting for regenerative dentistry and craniofacial tissue engineering. Journal of dental research 2015, 94, (9_suppl), 143S-152S. [CrossRef]
- Witek, L.; Alifarag, A. M.; Tovar, N.; Lopez, C. D.; Cronstein, B. N.; Rodriguez, E. D.; Coelho, P. G., Repair of critical-sized long bone defects using dipyridamole-augmented 3D-printed bioactive ceramic scaffolds. Journal of Orthopaedic Research® 2019, 37, (12), 2499-2507.
- DeMitchell-Rodriguez, E. M.; Shen, C.; Nayak, V. V.; Tovar, N.; Witek, L.; Torroni, A.; Yarholar, L. M.; Cronstein, B. N.; Flores, R. L.; Coelho, P. G., Bone Tissue Engineering in the Growing Calvaria: A 3D Printed Bioceramic Scaffold to Reconstruct Critical-Sized Defects in a Skeletally Immature Pig Model. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 2023, 10.1097.
- Nayak, V. V.; Slavin, B.; Bergamo, E. T.; Boczar, D.; Slavin, B. R.; Runyan, C. M.; Tovar, N.; Witek, L.; Coelho, P. G., Bone Tissue Engineering (BTE) of the Craniofacial Skeleton, Part I: Evolution and Optimization of 3D-Printed Scaffolds for Repair of Defects. The Journal of craniofacial surgery. [CrossRef]
- Trombetta, R.; Inzana, J. A.; Schwarz, E. M.; Kates, S. L.; Awad, H. A. J. A. o. b. e., 3D printing of calcium phosphate ceramics for bone tissue engineering and drug delivery. Ann Biomed Eng. 2017, 45, 23-44. [CrossRef]
- Budharaju, H.; Zennifer, A.; Sethuraman, S.; Paul, A.; Sundaramurthi, D. J. M. H., Designer DNA biomolecules as a defined biomaterial for 3D bioprinting applications. Mater Horiz. 2022, 9, (4), 1141-1166. [CrossRef]
- Budharaju, H.; Suresh, S.; Sekar, M. P.; De Vega, B.; Sethuraman, S.; Sundaramurthi, D.; Kalaskar, D. M. J. M.; Design, Ceramic Materials for 3D Printing of Biomimetic Bone Scaffolds–Current state–of–the–art & Future Perspectives. Materials & Design 2023, 112064.
- Lin, K.; Sheikh, R.; Romanazzo, S.; Roohani, I., 3D Printing of Bioceramic Scaffolds—Barriers to the Clinical Translation: From Promise to Reality, and Future Perspectives. Materials 2019, 12, (17), 2660. [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, R.; Banerjee, G., Ceramic based bio-medical implants. Interceram 2010, 59, (2), 98-102.
- Woodard, J. R.; Hilldore, A. J.; Lan, S. K.; Park, C.; Morgan, A. W.; Eurell, J. A. C.; Clark, S. G.; Wheeler, M. B.; Jamison, R. D.; Johnson, A. J. W., The mechanical properties and osteoconductivity of hydroxyapatite bone scaffolds with multi-scale porosity. Biomaterials 2007, 28, (1), 45-54. [CrossRef]
- Roberts, T. T.; Rosenbaum, A. J. J. O., Bone grafts, bone substitutes and orthobiologics: the bridge between basic science and clinical advancements in fracture healing. Organogenesis 2012, 8, (4), 114-124.
- Eliaz, N.; Metoki, N. J. M., Calcium phosphate bioceramics: a review of their history, structure, properties, coating technologies and biomedical applications. Materials (Basel). 2017, 10, (4), 334. [CrossRef]
- Kim, H. W.; Lee, E. J.; Jun, I. K.; Kim, H. E.; Knowles, J. C., Degradation and drug release of phosphate glass/polycaprolactone biological composites for hard-tissue regeneration. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2005, 75, (1), 34-41. [CrossRef]
- Hench, L. L., Bioceramics: from concept to clinic. Journal of the american ceramic society 1991, 74, (7), 1487-1510.
- Tevlin, R.; McArdle, A.; Atashroo, D.; Walmsley, G.; Senarath-Yapa, K.; Zielins, E.; Paik, K.; Longaker, M.; Wan, D., Biomaterials for craniofacial bone engineering. Journal of dental research 2014, 93, (12), 1187-1195. [CrossRef]
- Polley, C.; Distler, T.; Detsch, R.; Lund, H.; Springer, A.; Boccaccini, A. R.; Seitz, H., 3D printing of piezoelectric barium titanate-hydroxyapatite scaffolds with interconnected porosity for bone tissue engineering. Materials 2020, 13, (7), 1773. [CrossRef]
- Aboushelib, M. N.; Shawky, R., Osteogenesis ability of CAD/CAM porous zirconia scaffolds enriched with nano-hydroxyapatite particles. International Journal of Implant Dentistry 2017, 3, (1), 1-6. [CrossRef]
- Muralithran, G.; Ramesh, S., The effects of sintering temperature on the properties of hydroxyapatite. Ceramics International 2000, 26, (2), 221-230. [CrossRef]
- Lee, D. K.; Ki, M.-R.; Kim, E. H.; Park, C.-J.; Ryu, J. J.; Jang, H. S.; Pack, S. P.; Jo, Y. K.; Jun, S. H., Biosilicated collagen/β-tricalcium phosphate composites as a BMP-2-delivering bone-graft substitute for accelerated craniofacial bone regeneration. Biomaterials Research 2021, 25, 1-11. [CrossRef]
- Khiri, M. Z. A.; Matori, K. A.; Zaid, M. H. M.; Abdullah, C. A. C.; Zainuddin, N.; Alibe, I. M.; Rahman, N. A. A.; Wahab, S. A. A.; Azman, A. Z. K.; Effendy, N., Crystallization behavior of low-cost biphasic hydroxyapatite/β-tricalcium phosphate ceramic at high sintering temperatures derived from high potential calcium waste sources. Results in Physics 2019, 12, 638-644. [CrossRef]
- Bohner, M.; Santoni, B. L. G.; Döbelin, N., β-tricalcium phosphate for bone substitution: Synthesis and properties. Acta biomaterialia 2020, 113, 23-41. [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xue, K.; Kong, N.; Liu, K.; Chang, J., Silicate bioceramics enhanced vascularization and osteogenesis through stimulating interactions between endothelia cells and bone marrow stromal cells. Biomaterials 2014, 35, (12), 3803-3818. [CrossRef]
- Mei, H.; Yin, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, W., Compressive properties of 3D printed polylactic acid matrix composites reinforced by short fibers and SiC nanowires. Advanced Engineering Materials 2019, 21, (5), 1800539. [CrossRef]
- Petousis, M.; Vidakis, N.; Mountakis, N.; Grammatikos, S.; Papadakis, V.; David, C. N.; Moutsopoulou, A.; Das, S. C., Silicon carbide nanoparticles as a mechanical boosting agent in material extrusion 3D-printed polycarbonate. Polymers 2022, 14, (17), 3492. [CrossRef]
- Sailer, I.; Balmer, M.; Hüsler, J.; Hämmerle, C. H. F.; Känel, S.; Thoma, D. S., 10-year randomized trial (RCT) of zirconia-ceramic and metal-ceramic fixed dental prostheses. Journal of Dentistry 2018, 76, 32-39. [CrossRef]
- Guess, P. C.; Bonfante, E. A.; Silva, N. R.; Coelho, P. G.; Thompson, V. P., Effect of core design and veneering technique on damage and reliability of Y-TZP-supported crowns. Dental materials : official publication of the Academy of Dental Materials 2013, 29, (3), 307-16. [CrossRef]
- Naghib-zadeh, H.; Glitzky, C.; Dörfel, I.; Rabe, T., Low temperature sintering of barium titanate ceramics assisted by addition of lithium fluoride-containing sintering additives. Journal of the European Ceramic Society 2010, 30, (1), 81-86. [CrossRef]
- Ulfa, U.; Kusumandari, K.; Iriani, Y. In The effect of temperature and holding time sintering process on microstructure and dielectric properties of barium titanate by co-precipitation method, AIP Conference Proceedings, 2019; AIP Publishing.
- Klein, C. P.; Driessen, A. A.; de Groot, K.; van den Hooff, A., Biodegradation behavior of various calcium phosphate materials in bone tissue. J Biomed Mater Res 1983, 17, (5), 769-84. [CrossRef]
- Lowe, B.; Hardy, J. G.; Walsh, L. J. J. A. o., Optimizing nanohydroxyapatite nanocomposites for bone tissue engineering. ACS Omega 2019, 5, (1), 1-9. [CrossRef]
- Roopavath, U. K.; Malferrari, S.; Van Haver, A.; Verstreken, F.; Rath, S. N.; Kalaskar, D. M. J. M.; Design, Optimization of extrusion based ceramic 3D printing process for complex bony designs. Materials & Design 2019, 162, 263-270. [CrossRef]
- Moore, W. R.; Graves, S. E.; Bain, G. I., Synthetic bone graft substitutes. ANZ journal of surgery 2001, 71, (6), 354-61.
- Janus, A. M.; Faryna, M.; Haberko, K.; Rakowska, A.; Panz, T. J. M. A., Chemical and microstructural characterization of natural hydroxyapatite derived from pig bones. Microchimica Acta 2008, 161, 349-353. [CrossRef]
- Ooi, C.; Hamdi, M.; Ramesh, S. J. C. i., Properties of hydroxyapatite produced by annealing of bovine bone. Ceramics International 2007, 33, (7), 1171-1177. [CrossRef]
- Pon-On, W.; Suntornsaratoon, P.; Charoenphandhu, N.; Thongbunchoo, J.; Krishnamra, N.; Tang, I. M. J. M. S.; C, E., Hydroxyapatite from fish scale for potential use as bone scaffold or regenerative material. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016, 62, 183-189. [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Pal, U.; Dey, A. J. C. I., Natural origin hydroxyapatite scaffold as potential bone tissue engineering substitute. Ceramics International 2016, 42, (16), 18338-18346. [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Nichols, L.; Brinkley, F.; Bohna, K.; Tian, W.; Priddy, M. W.; Priddy, L. B. J. M. S.; C, E., Alkali treatment facilitates functional nano-hydroxyapatite coating of 3D printed polylactic acid scaffolds. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021, 120, 111686. [CrossRef]
- Bohner, M.; Santoni, B. L. G.; Döbelin, N. J. A. b., β-tricalcium phosphate for bone substitution: Synthesis and properties. Acta Biomater. 2020, 113, 23-41. [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, S. B.; Keong, T. K.; Cheng, C. H.; Saim, A. B.; Idrus, R. B. H. J. T. I. j. o. m. r., Tricalcium phosphate/hydroxyapatite (TCP-HA) bone scaffold as potential candidate for the formation of tissue engineered bone. Indian J Med Res. 2013, 137, (6), 1093.
- Metsger, D. S.; Driskell, T.; Paulsrud, J. J. J. o. t. A. D. A., Tricalcium phosphate ceramic--a resorbable bone implant: review and current status. J Am Dent Assoc. 1982, 105, (6), 1035-1038. [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Witek, L.; Flores, R. L.; Tovar, N.; Torroni, A.; Coelho, P. G.; Kasper, F. K.; Wong, M.; Young, S., Three-Dimensional Printing for Craniofacial Bone Tissue Engineering. Tissue engineering. Part A 2020, 26, (23-24), 1303-1311. [CrossRef]
- Lopez, C. D.; Diaz-Siso, J. R.; Witek, L.; Bekisz, J. M.; Cronstein, B. N.; Torroni, A.; Flores, R. L.; Rodriguez, E. D.; Coelho, P. G., Three dimensionally printed bioactive ceramic scaffold osseoconduction across critical-sized mandibular defects. J Surg Res 2018, 223, 115-122. [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Feng, C.; Chang, J.; Wu, C., 3D-printed bioceramic scaffolds: From bone tissue engineering to tumor therapy. Acta biomaterialia 2018, 79, 37-59. [CrossRef]
- González, P.; Borrajo, J. P.; Serra, J.; Liste, S.; Chiussi, S.; León, B.; Semmelmann, K.; de Carlos, A.; Varela-Feria, F. M.; Martínez-Fernández, J. J. K. E. M., Extensive studies on biomorphic SiC ceramics properties for medical applications. Bioceramics 2004, 254, 1029-1032. [CrossRef]
- Visbal, S.; Lira-Olivares, J.; Sekino, T.; Niihara, K.; Moon, B. K.; Lee, S. W. In Mechanical properties of Al2O3-TiO2-SiC nanocomposites for the femoral head of hip joint replacement, Materials Science Forum, 2005; Trans Tech Publ: pp 197-200. [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xue, K.; Kong, N.; Liu, K.; Chang, J. J. B., Silicate bioceramics enhanced vascularization and osteogenesis through stimulating interactions between endothelia cells and bone marrow stromal cells. Biomaterials 2014, 35, (12), 3803-3818. [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Li, Q.; Yang, X.; Chen, X.; Xu, X. J. C., Synthesis and characterization of N-doped SiC powder with enhanced photocatalytic and photoelectrochemical performance. Catalysts 2020, 10, (7), 769. [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Li, J.; Cao, F.; Yang, J.; Liu, R.; Zhao, D. J. R. B., Porous silicon carbide coated with tantalum as potential material for bone implants. Regen Biomater. 2020, 7, (5), 453-459. [CrossRef]
- Abderrazak, H.; Hmida, E. J. P.; Carbide, a. o. S., Silicon carbide: synthesis and properties. 2011, 361-388.
- Garvie, R. C.; Hannink, R. H.; Pascoe, R. T., Ceramic steel? Nature 1975, 258, (5537), 703-704.
- Zhang, Y.; Lawn, B. R., Novel Zirconia Materials in Dentistry. Journal of dental research 2018, 97, (2), 140-147. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, T. K.; Lange, F. F.; Bechtold, J. H., Effect of stress-induced phase transformation on the properties of polycrystalline zirconia containing metastable tetragonal phase. Journal of Materials Science 1978, 13, (7), 1464-1470. [CrossRef]
- Chevalier, J.; Calès, B.; Drouin, J. M. J. J. o. t. A. C. S., Low-Temperature Aging of Y-TZP Ceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society 2004, 82, 2150-2154.
- Wang, Q.; Ma, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, L.; Xie, W., Fabrication and characterization of 3D printed biocomposite scaffolds based on PCL and zirconia nanoparticles. Bio-Design and Manufacturing 2021, 4, (1), 60-71. [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Liu, W.; Liu, S.; Zhao, S.; Zhu, Y., 3D printed porous β-Ca(2)SiO(4) scaffolds derived from preceramic resin and their physicochemical and biological properties. Science and technology of advanced materials 2018, 19, (1), 495-506.
- Sakthiabirami, K.; Kang, J.-H.; Jang, J.-G.; Soundharrajan, V.; Lim, H.-P.; Yun, K.-D.; Park, C.; Lee, B.-N.; Yang, Y. P.; Park, S.-W., Hybrid porous zirconia scaffolds fabricated using additive manufacturing for bone tissue engineering applications. Materials Science and Engineering: C 2021, 123, 111950. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, X.; Shi, J., Additive manufacturing of zirconia ceramics: a state-of-the-art review. Journal of Materials Research and Technology 2020, 9, (4), 9029-9048. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-y.; Li, L.-t.; Li, B., Direct write printing of three-dimensional ZrO2 biological scaffolds. Materials & Design 2015, 72, 16-20. [CrossRef]
- Al-Radha, A. S. D.; Dymock, D.; Younes, C.; O’Sullivan, D., Surface properties of titanium and zirconia dental implant materials and their effect on bacterial adhesion. Journal of dentistry 2012, 40, (2), 146-153. [CrossRef]
- Cerrolaza, M.; Duarte, V.; Garzón-Alvarado, D. J. J. o. B. E., Analysis of bone remodeling under piezoelectricity effects using boundary elements. Journal of Bionic Engineering 2017, 14, (4), 659-671. [CrossRef]
- Jacob, J.; More, N.; Kalia, K.; Kapusetti, G. J. I.; regeneration, Piezoelectric smart biomaterials for bone and cartilage tissue engineering. Inflamm Regen 2018, 38, (1), 2. [CrossRef]
- Ismail, F. A.; Osman, R. A. M.; Idris, M. S.; Taking, S.; Jamal, Z. A. Z. In Dielectric and microstructural properties of BaTiO3 and Ba0. 9925Er0. 0075TiO3 ceramics, EPJ Web of Conferences, 2017; EDP Sciences: p 01051.
- Rocca, A.; Marino, A.; Rocca, V.; Moscato, S.; de Vito, G.; Piazza, V.; Mazzolai, B.; Mattoli, V.; Ngo-Anh, T. J.; Ciofani, G. J. I. J. o. N., Barium titanate nanoparticles and hypergravity stimulation improve differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells into osteoblasts. Int J Nanomedicine. 2015, 433-445. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.-j.; Yang, Z.-f.; Yuan, Q.-m. J. T. o. N. M. S. o. C., Barium titanate ceramic inks for continuous ink-jet printing synthesized by mechanical mixing and sol-gel methods. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2008, 18, (1), 150-154. [CrossRef]
- Zarkoob, H.; Ziaei-Rad, S.; Fathi, M.; Dadkhah, H. J. A. e. m., Synthesis, characterization and bioactivity evaluation of porous barium titanate with nanostructured hydroxyapatite coating for biomedical application. Advanced Engineering Materials 2012, 14, (6), B322-B329. [CrossRef]
- Vella, J. B., Trombetta, R. P., Hoffman, M. D., Inzana, J., Awad, H., & Benoit, D. S. W. (2018). Three dimensional printed calcium phosphate and poly(caprolactone) composites with improved mechanical properties and preserved microstructure. Journal of biomedical materials research. Part A, 106(3), 663–672. [CrossRef]
- Baker, R. M.; Tseng, L. F.; Iannolo, M. T.; Oest, M. E.; Henderson, J. H., Self-deploying shape memory polymer scaffolds for grafting and stabilizing complex bone defects: A mouse femoral segmental defect study. Biomaterials 2016, 76, 388-98. [CrossRef]
- Shah, S. R.; Kasper, F. K.; Mikos, A. G., Perspectives on the prevention and treatment of infection for orthopedic tissue engineering applications. Chinese Science Bulletin 2013, 58, (35), 4342-4348. [CrossRef]
- Shim, J.-H.; Won, J.-Y.; Sung, S.-J.; Lim, D.-H.; Yun, W.-S.; Jeon, Y.-C.; Huh, J.-B., Comparative efficacies of a 3D-printed PCL/PLGA/β-TCP membrane and a titanium membrane for guided bone regeneration in beagle dogs. Polymers 2015, 7, (10), 2061-2077. [CrossRef]
- Won, J. Y.; Park, C. Y.; Bae, J. H.; Ahn, G.; Kim, C.; Lim, D. H.; Cho, D. W.; Yun, W. S.; Shim, J. H.; Huh, J. B., Evaluation of 3D printed PCL/PLGA/beta-TCP versus collagen membranes for guided bone regeneration in a beagle implant model. Biomed Mater 2016, 11, (5), 055013.
- Senatov, F. S.; Niaza, K. V.; Zadorozhnyy, M. Y.; Maksimkin, A. V.; Kaloshkin, S. D.; Estrin, Y. Z., Mechanical properties and shape memory effect of 3D-printed PLA-based porous scaffolds. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 2016, 57, 139-48. [CrossRef]
- Senatov, F. S.; Zadorozhnyy, M. Y.; Niaza, K. V.; Medvedev, V. V.; Kaloshkin, S. D.; Anisimova, N. Y.; Kiselevskiy, M. V.; Yang, K.-C., Shape memory effect in 3D-printed scaffolds for self-fitting implants. European Polymer Journal 2017, 93, 222-231. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; George, O. J.; Petersen, K. M.; Jimenez-Vergara, A. C.; Hahn, M. S.; Grunlan, M. A., A bioactive “self-fitting” shape memory polymer scaffold with potential to treat cranio-maxillo facial bone defects. Acta Biomater 2014, 10, (11), 4597-4605. [CrossRef]
- Shuai, C.; Yu, L.; Feng, P.; Gao, C.; Peng, S., Interfacial reinforcement in bioceramic/biopolymer composite bone scaffold: The role of coupling agent. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 2020, 193, 111083. [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.; Bao, C.; Zhang, Z.; Bai, Y., Microstructure and Wear Behavior of High-Cr WCI Matrix Surface Composite Reinforced with Cemented Carbide Rods. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance 2013, 22, (7), 2064-2072. [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A. C.; Hayes, S. A.; Jones, F. R., An improved model including plasticity for the prediction of the stress in fibres with an interface/interphase region. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing 2005, 36, (2), 263-271.
- Zhang, P.; Hong, Z.; Yu, T.; Chen, X.; Jing, X., In vivo mineralization and osteogenesis of nanocomposite scaffold of poly(lactide-co-glycolide) and hydroxyapatite surface-grafted with poly(l-lactide). Biomaterials 2009, 30, (1), 58-70. [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cui, Y.; Jing, X.; Zhang, P.; Chen, X., The nanocomposite scaffold of poly(lactide-co-glycolide) and hydroxyapatite surface-grafted with l-lactic acid oligomer for bone repair. Acta Biomaterialia 2009, 5, (7), 2680-2692. [CrossRef]
- Kharaziha, M.; Fathi, M. H.; Edris, H., Effects of surface modification on the mechanical and structural properties of nanofibrous poly(ε-caprolactone)/forsterite scaffold for tissue engineering applications. Materials Science and Engineering: C 2013, 33, (8), 4512-4519.
- Tham, W. L.; Chow, W. S.; Mohd Ishak, Z. A., Effects of titanate coupling agent on the mechanical, thermal, and morphological properties of poly(methyl methacrylate)/hydroxyapatite denture base composites. Journal of Composite Materials 2011, 45, (22), 2335-2345.
- Lopez, C. D.; Witek, L.; Torroni, A.; Flores, R. L.; Demissie, D. B.; Young, S.; Cronstein, B. N.; Coelho, P. G., The role of 3D printing in treating craniomaxillofacial congenital anomalies. Birth Defects Research 2018, 110, (13), 1055-1064. [CrossRef]
- Kamboj, N.; Ressler, A.; Hussainova, I. J. M., Bioactive ceramic scaffolds for bone tissue engineering by powder bed selective laser processing: A review. Materials (Basel) 2021, 14, (18), 5338. [CrossRef]
- Bose, S.; Vahabzadeh, S.; Bandyopadhyay, A. J. M. t., Bone tissue engineering using 3D printing. Materials Today 2013, 16, (12), 496-504. [CrossRef]
- Gmeiner, R.; Deisinger, U.; Schönherr, J.; Lechner, B.; Detsch, R.; Boccaccini, A.; Stampfl, J. J. J. C. S. T., Additive manufacturing of bioactive glasses and silicate bioceramics. Journal of Ceramic Science and Technology 2015, 6, (2), 75-86.
- Seunarine, K.; Gadegaard, N.; Tormen, M.; Meredith, D.; Riehle, M.; Wilkinson, C., 3D polymer scaffolds for tissue engineering. Nanomedicine 2006. [CrossRef]
- de Hazan, Y.; Penner, D. J. J. o. t. E. C. S., SiC and SiOC ceramic articles produced by stereolithography of acrylate modified polycarbosilane systems. Journal of the European Ceramic Society 2017, 37, (16), 5205-5212. [CrossRef]
- Gentry, S. P.; Halloran, J. W. J. J. o. t. E. C. S., Depth and width of cured lines in photopolymerizable ceramic suspensions. Journal of the European Ceramic Society 2013, 33, (10), 1981-1988. [CrossRef]
- Mitteramskogler, G.; Gmeiner, R.; Felzmann, R.; Gruber, S.; Hofstetter, C.; Stampfl, J.; Ebert, J.; Wachter, W.; Laubersheimer, J. J. A. M., Light curing strategies for lithography-based additive manufacturing of customized ceramics. Additive Manufacturing 2014, 1, 110-118. [CrossRef]
- Pfaffinger, M.; Mitteramskogler, G.; Gmeiner, R.; Stampfl, J. In Thermal debinding of ceramic-filled photopolymers, Materials Science Forum 2015; Trans Tech Publ: pp 75-81.
- Chaudhary, R.; Fabbri, P.; Leoni, E.; Mazzanti, F.; Akbari, R.; Antonini, C. J. P. i. A. M., Additive manufacturing by digital light processing: a review. Progress in Additive Manufacturing 2023, 8, (2), 331-351. [CrossRef]
- Maroulakos, M.; Kamperos, G.; Tayebi, L.; Halazonetis, D.; Ren, Y., Applications of 3D printing on craniofacial bone repair: A systematic review. Journal of Dentistry 2019, 80, 1-14. [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, Y.; Maeda, H. J. T. S. W. J., Recent developments of functional scaffolds for craniomaxillofacial bone tissue engineering applications. Scientific World Journal 2013, 2013. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z., Bone regeneration by stem cell and tissue engineering in oral and maxillofacial region. Frontiers of medicine 2011, 5, (4), 401-413. [CrossRef]
- Silva, N. R.; Witek, L.; Coelho, P. G.; Thompson, V. P.; Rekow, E. D.; Smay, J., Additive CAD/CAM process for dental prostheses. J Prosthodont 2011, 20, (2), 93-6. [CrossRef]
- Witek, L.; Colon, R. R.; Wang, M. M.; Torroni, A.; Young, S.; Melville, J.; Lopez, C. D.; Flores, R. L.; Cronstein, B. N.; Coelho, P. G., Tissue-engineered alloplastic scaffolds for reconstruction of alveolar defects. In Handbook of Tissue Engineering Scaffolds: Volume One, Elsevier: 2019; pp 505-520.
- Bauermeister, A. J.; Zuriarrain, A.; Newman, M. I., Three-Dimensional Printing inPlastic and Reconstructive Surgery: A Systematic Review. Ann Plast Surg 2016, 77, (5), 569-576.
- Zhang, B.; Wang, L.; Song, P.; Pei, X.; Sun, H.; Wu, L.; Zhou, C.; Wang, K.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, X., 3D printed bone tissue regenerative PLA/HA scaffolds with comprehensive performance optimizations. Materials & Design 2021, 201, 109490. [CrossRef]
- Rahim, T. N. A. T.; Abdullah, A. M.; Md Akil, H., Recent developments in fused deposition modeling-based 3D printing of polymers and their composites. Polymer Reviews 2019, 59, (4), 589-624. [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Qin, W.; Xing, B.; Sha, N.; Jiao, T.; Zhao, Z., High performance hydroxyapatite ceramics and a triply periodic minimum surface structure fabricated by digital light processing 3D printing. Journal of Advanced Ceramics 2021, 10, 39-48. [CrossRef]
- Ding, G.; He, R.; Zhang, K.; Zhou, N.; Xu, H., Stereolithography 3D printing of SiC ceramic with potential for lightweight optical mirror. Ceramics International 2020, 46, (11), 18785-18790. [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, W.; He, R.; Zhou, M.; Wu, S.; Song, X.; Chen, Y., Effect of the particle size and the debinding process on the density of alumina ceramics fabricated by 3D printing based on stereolithography. Ceramics International 2016, 42, (15), 17290-17294. [CrossRef]
- Chioibasu, D.; Achim, A.; Popescu, C.; Stan, G. E.; Pasuk, I.; Enculescu, M.; Iosub, S.; Duta, L.; Popescu, A., Prototype orthopedic bone plates 3D printed by laser melting deposition. Materials 2019, 12, (6), 906. [CrossRef]
- Lupone, F.; Padovano, E.; Pietroluongo, M.; Giudice, S.; Ostrovskaya, O.; Badini, C., Optimization of selective laser sintering process conditions using stable sintering region approach. Express Polymer Letters 2021, 15, (2). [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Yoo, J. M.; Nam, S. Y., Additive fabrication and characterization of biomimetic composite bone scaffolds with high hydroxyapatite content. Gels 2021, 7, (3), 100. [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Shao, H.; Lin, T., Effect of magnesium silicate on 3D gel-printing of hydroxyapatite ceramic composite scaffold. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology 2019, 16, (2), 494-502. [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Shao, H.; Lin, T.; Zheng, H., 3D gel-printing—An additive manufacturing method for producing complex shape parts. Materials & Design 2016, 101, 80-87. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Huang, J.; Liu, J.; Wei, Y.; Yang, X.; Lei, L.; Chen, L.; Wu, Y.; Gou, Z., Tuning filament composition and microstructure of 3D-printed bioceramic scaffolds facilitate bone defect regeneration and repair. Regenerative Biomaterials 2021, 8, (2), rbab007. [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Ji, X.; Wu, Z.; Qi, C.; Xian, Q.; Sun, B., Digital light processing 3D printing of ceramic shell for precision casting. Materials Letters 2020, 276, 128037. [CrossRef]
- Reid, A.; Jackson, J. C.; Windmill, J., Voxel based method for predictive modelling of solidification and stress in digital light processing based additive manufacture. Soft Matter 2021, 17, (7), 1881-1887. [CrossRef]
- Wubneh, A.; Tsekoura, E. K.; Ayranci, C.; Uludağ, H. J. A. B., Current state of fabrication technologies and materials for bone tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2018, 80, 1-30. [CrossRef]
- Shivalkar, S.; Singh, S. J. T. e.; medicine, r., Solid freeform techniques application in bone tissue engineering for scaffold fabrication. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2017, 14, 187-200. [CrossRef]
- Shirazi, S. F. S.; Gharehkhani, S.; Mehrali, M.; Yarmand, H.; Metselaar, H. S. C.; Kadri, N. A.; Osman, N. A. A. J. S.; materials, t. o. a., A review on powder-based additive manufacturing for tissue engineering: selective laser sintering and inkjet 3D printing. Sci Technol Adv Mater. 2015. [CrossRef]
- Drummer, D.; Rietzel, D.; Kühnlein, F. J. P. P., Development of a characterization approach for the sintering behavior of new thermoplastics for selective laser sintering. Physics Procedia 2010, 5, 533-542. [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, K.; Deckers, J.; Zhang, Z.; Kruth, J.-P.; Vleugels, J. J. J. o. t. E. C. S., Additive manufacturing of zirconia parts by indirect selective laser sintering. ournal of The European Ceramic Society 2014, 34, (1), 81-89. [CrossRef]
- Bakshi, K.; Mulay, A. J. I. J. M. C. E., A review on selective laser sintering: A rapid prototyping technology. IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering 2016, 4, (4), 53-57.
- Kolan, K. C.; Leu, M. C.; Hilmas, G. E.; Velez, M. J. J. o. t. m. b. o. b. m., Effect of material, process parameters, and simulated body fluids on mechanical properties of 13-93 bioactive glass porous constructs made by selective laser sintering. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2012, 13, 14-24. [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.; Sheikh, R.; Romanazzo, S.; Roohani, I. J. M., 3D printing of bioceramic scaffolds—Barriers to the clinical translation: From promise to reality, and future perspectives. Materials (Basel). 2019, 12, (17), 2660. [CrossRef]
- Yves-Christian, H.; Jan, W.; Wilhelm, M.; Konrad, W.; Reinhart, P. J. P. P., Net shaped high performance oxide ceramic parts by selective laser melting. Physics Procedia 2010, 5, 587-594. [CrossRef]
- López-Álvarez, M.; Rodríguez-Valencia, C.; Serra, J.; González, P. J. P. E., Bio-inspired ceramics: promising scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Procedia Engineering 2013, 59, 51-58. [CrossRef]
- Sarment, D. P.; Sukovic, P.; Clinthorne, N. J. I. J. o. O.; Implants, M., Accuracy of implant placement with a stereolithographic surgical guide. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2003, 18, (4).
- Hull, C. W. J. U. S. P., Appl., No. 638905, Filed, Apparatus for production of three-dimensional objects by stereolithography. 1984.
- Schmidleithner, C.; Kalaskar, D. M., Stereolithography. IntechOpen: 2018.
- Bártolo, P. J., Stereolithography: materials, processes and applications. Springer Science & Business Media: 2011.
- Allen Brady, G.; Halloran, J. W. J. R. P. J., Stereolithography of ceramic suspensions. Rapid Prototyping Journal 1997, 3, (2), 61-65. [CrossRef]
- Hinczewski, C.; Corbel, S.; Chartier, T. J. J. o. t. E. C. S., Ceramic suspensions suitable for stereolithography. Journal of the European Ceramic Society 1998, 18, (6), 583-590. [CrossRef]
- Skoog, S. A.; Goering, P. L.; Narayan, R. J. J. J. o. M. S. M. i. M., Stereolithography in tissue engineering. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2014, 25, 845-856. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, D.; Zhou, W. J. P. o. t. I. o. M. E., Part B: Journal of Engineering Manufacture, Process parameters appraisal of fabricating ceramic parts based on stereolithography using the Taguchi method. Journal of Advanced Ceramics 2012, 226, (7), 1249-1258. [CrossRef]
- Schmidleithner, C.; Malferrari, S.; Palgrave, R.; Bomze, D.; Schwentenwein, M.; Kalaskar, D. M. J. B. M., Application of high resolution DLP stereolithography for fabrication of tricalcium phosphate scaffolds for bone regeneration. Biomed Mater. 2019, 14, (4), 045018. [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Ji, X.; Wu, Z.; Qi, C.; Xian, Q.; Sun, B. J. M. L., Digital light processing 3D printing of ceramic shell for precision casting. Materials Letters 2020, 276, 128037. [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.; Wang, L.; Dunn, C. K.; Kuang, X.; Duan, F.; Zhang, Z.; Qi, H. J.; Wang, T., Digital light processing 3D printing of conductive complex structures. Additive Manufacturing 2017, 18, 74-83. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, S.; Liang, H.; Liu, Y.; Bai, J.; Wang, M. J. C. I., Digital light processing (DLP) of nano biphasic calcium phosphate bioceramic for making bone tissue engineering scaffolds. Ceramics International 2022, 48, (19), 27681-27692. [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Zhang, K.; He, R.; Ding, G.; Xia, M.; Jin, X.; Xie, C. J. J. o. A. C., Additive manufacturing of hydroxyapatite bioceramic scaffolds: Dispersion, digital light processing, sintering, mechanical properties, and biocompatibility. Journal of Advanced Ceramics 2020, 9, 360-373. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liang, H.; Shi, T.; Xie, D.; Chen, R.; Han, X.; Shen, L.; Wang, C.; Tian, Z. J. C. I., Additive manufacturing of hydroxyapatite bone scaffolds via digital light processing and in vitro compatibility. Ceramics International 2019, 45, (8), 11079-11086. [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Yan, Y.; Yan, H.; Liu, C.; Li, P.; Dong, P.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, J. J. J. o. m. s., 3D printing of hydroxyapatite scaffolds with good mechanical and biocompatible properties by digital light processing. Journal of Materials Science 2018, 53, (9), 6291-6301. [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-W.; Lee, J.-B.; Koh, Y.-H.; Kim, H.-E., Digital Light Processing of Freeze-cast Ceramic Layers for Macroporous Calcium Phosphate Scaffolds with Tailored Microporous Frameworks. Materials 2019, 12, (18), 2893. [CrossRef]
- Schmidleithner, C.; Malferrari, S.; Palgrave, R.; Bomze, D.; Schwentenwein, M.; Kalaskar, D. M., Application of high resolution DLP stereolithography for fabrication of tricalcium phosphate scaffolds for bone regeneration. Biomedical Materials 2019, 14, (4), 045018. [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, H.; Colombo, P.; Bernardo, E., Direct ink writing of wollastonite-diopside glass-ceramic scaffolds from a silicone resin and engineered fillers. Journal of the European Ceramic Society 2017, 37, (13), 4187-4195. [CrossRef]
- Cesarano, J.; Segalman, R.; Calvert, P., Robocasting provides MOULDLESS fabrication from slurry deposition. Ceramic industry 1998, 148, (4), 94-96.
- Lewis, J. A., Direct ink writing of 3D functional materials. Advanced Functional Materials 2006, 16, (17), 2193-2204.
- Feilden, E.; Blanca, E. G.-T.; Giuliani, F.; Saiz, E.; Vandeperre, L., Robocasting of structural ceramic parts with hydrogel inks. Journal of the European Ceramic Society 2016, 36, (10), 2525-2533. [CrossRef]
- Three-Dimensional Printing Bioceramic Scaffolds Using Direct-Ink-Writing for Craniomaxillofacial Bone Regeneration. Tissue Eng Part C Methods .2023, 29, (7), 332-345.
- Lewis, J. A.; Smay, J. E.; Stuecker, J.; Cesarano, J., Direct Ink Writing of Three-Dimensional Ceramic Structures. Journal of the American Ceramic Society 2006, 89, (12), 3599-3609. [CrossRef]
- Miranda, P.; Saiz, E.; Gryn, K.; Tomsia, A. P., Sintering and robocasting of β-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds for orthopaedic applications. Acta biomaterialia 2006, 2, (4), 457-466. [CrossRef]
- Michna, S.; Wu, W.; Lewis, J. A., Concentrated hydroxyapatite inks for direct-write assembly of 3-D periodic scaffolds. Biomaterials 2005, 26, (28), 5632-5639. [CrossRef]
- Lewis, J. A., Colloidal processing of ceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society 2000, 83, (10), 2341-2359.
- Ashammakhi, N.; Hasan, A.; Kaarela, O.; Byambaa, B.; Sheikhi, A.; Gaharwar, A. K.; Khademhosseini, A. J. A. h. m., Advancing frontiers in bone bioprinting. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2019, 8, (7), 1801048.
- Vikram Singh, A.; Gharat, T.; Batuwangala, M.; Park, B. W.; Endlein, T.; Sitti, M. J. J. o. B. M. R. P. B. A. B., Three-dimensional patterning in biomedicine: Importance and applications in neuropharmacology. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials 2018, 106, (3), 1369-1382. [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Lewis, J. A. J. A. M., Nanoparticle inks for directed assembly of three-dimensional periodic structures. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, (19), 1639-1643. [CrossRef]
- Corcione, C. E.; Gervaso, F.; Scalera, F.; Padmanabhan, S. K.; Madaghiele, M.; Montagna, F.; Sannino, A.; Licciulli, A.; Maffezzoli, A. J. C. I., Highly loaded hydroxyapatite microsphere/PLA porous scaffolds obtained by fused deposition modelling. Ceramics International 2019, 45, (2), 2803-2810. [CrossRef]
- Kalita, S. J.; Bose, S.; Hosick, H. L.; Bandyopadhyay, A. J. M. S.; C, E., Development of controlled porosity polymer-ceramic composite scaffolds via fused deposition modeling. Materials Science and Engineering: C 2003, 23, (5), 611-620. [CrossRef]
- Janek, M.; Žilinská, V.; Kovár, V.; Hajdúchová, Z.; Tomanová, K.; Peciar, P.; Veteška, P.; Gabošová, T.; Fialka, R.; Feranc, J.; Omaníková, L.; Plavec, R.; Bača, Ľ., Mechanical testing of hydroxyapatite filaments for tissue scaffolds preparation by fused deposition of ceramics. Journal of the European Ceramic Society 2020, 40, (14), 4932-4938. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, C.; Lao, C.; Fu, Y.; Liu, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, P.; He, Y., 3D printing of ceramics: A review. Journal of the European Ceramic Society 2019, 39, (4), 661-687.
- Butscher, A.; Bohner, M.; Roth, C.; Ernstberger, A.; Heuberger, R.; Doebelin, N.; Von Rohr, P. R.; Müller, R. J. A. b., Printability of calcium phosphate powders for three-dimensional printing of tissue engineering scaffolds. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, (1), 373-385. [CrossRef]
- Griffith, M. L.; Halloran, J. W. J. J. o. t. A. C. S., Freeform fabrication of ceramics via stereolithography. Journal of the American Ceramic Society 1996, 79, (10), 2601-2608. [CrossRef]
- Uhland, S. A.; Holman, R. K.; Morissette, S.; Cima, M. J.; Sachs, E. M. J. J. o. t. A. C. S., Strength of green ceramics with low binder content. Journal of the American Ceramic Society 2001, 84, (12), 2809-2818. [CrossRef]
- Leukers, B.; Gülkan, H.; Irsen, S.; Milz, S.; Tille, C.; Seitz, H.; Schieker, M. J. M. u. W. E., Fertigung, Prüfung, Eigenschaften und Anwendungen technischer Werkstoffe, Biocompatibility of ceramic scaffolds for bone replacement made by 3D printing. Mat.-wiss. u. Werkstofftech. 2005, 36, (12), 781-787. [CrossRef]
- Vaezi, M.; Seitz, H.; Yang, S. J. T. I. J. o. A. M. T., A review on 3D micro-additive manufacturing technologies. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. 2013, 67, 1721-1754. [CrossRef]
- Hwa, L. C.; Rajoo, S.; Noor, A. M.; Ahmad, N.; Uday, M. J. C. O. i. S. S.; Science, M., Recent advances in 3D printing of porous ceramics: A review. Current Opinion in Solid State & Materials Science 2017, 21, (6), 323-347. [CrossRef]
- Gbureck, U.; Hölzel, T.; Klammert, U.; Wuerzler, K.; Mueller, F. A.; Barralet, J. E. J. A. F. M., Resorbable dicalcium phosphate bone substitutes prepared by 3D powder printing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2007, 17, (18), 3940-3945. [CrossRef]
- Agalloco, J. P.; Akers, J. E.; Madsen, R. E. J. P. J. o. P. S.; Technology, Moist heat sterilization—myths and realities. PDA J Pharm Sci Technol. 1998, 52, (6), 346-350.
- Rutala, W. A.; Weber, D. J., Infection control: the role of disinfection and sterilization. The Journal of hospital infection 1999, 43 Suppl, S43-55. [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez Colon, R.; Nayak, V. V.; Parente, P. E. L.; Leucht, P.; Tovar, N.; Lin, C. C.; Rezzadeh, K.; Hacquebord, J. H.; Coelho, P. G.; Witek, L., The presence of 3D printing in orthopedics: A clinical and material review. J Orthop Res. 2023, 41, (3), 601-613. [CrossRef]
- Melville, J. C.; Nassari, N. N.; Hanna, I. A.; Shum, J. W.; Wong, M. E.; Young, S., Immediate transoral allogeneic bone grafting for large mandibular defects. Less morbidity, more bone. A paradigm in benign tumor mandibular reconstruction? Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 2017, 75, (4), 828-838.
- Melville, J. C.; Shum, J. W.; Young, S.; Wong, M. E., Regenerative strategies for maxillary and mandibular reconstruction: a practical guide. Springer: 2019.
- Jäger, M.; Herten, M.; Fochtmann, U.; Fischer, J.; Hernigou, P.; Zilkens, C.; Hendrich, C.; Krauspe, R., Bridging the gap: bone marrow aspiration concentrate reduces autologous bone grafting in osseous defects. Journal of Orthopaedic Research 2011, 29, (2), 173-180. [CrossRef]
- Aghaloo, T. L.; Hadaya, D., Basic principles of bioengineering and regeneration. Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Clinics 2017, 29, (1), 1-7. [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Yan, J.; Yao, Z.; Zhang, C.; Li, X.; Mao, H. Q., Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Paracrine Signals and Their Delivery Strategies. Advanced Healthcare Materials 2021, 10, (7), 2001689. [CrossRef]
- Wu, V.; Helder, M. N.; Bravenboer, N.; Ten Bruggenkate, C. M.; Jin, J.; Klein-Nulend, J.; Schulten, E. A., Bone tissue regeneration in the oral and maxillofacial region: a review on the application of stem cells and new strategies to improve vascularization. Stem Cells International 2019, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Jakobsen, C.; Sørensen, J.; Kassem, M.; Thygesen, T. J. J. o. O. R., Mesenchymal stem cells in oral reconstructive surgery: a systematic review of the literature. Journal of Oral Rehabilitation 2013, 40, (9), 693-706. [CrossRef]
- Pittenger, M. F.; Mackay, A. M.; Beck, S. C.; Jaiswal, R. K.; Douglas, R.; Mosca, J. D.; Moorman, M. A.; Simonetti, D. W.; Craig, S.; Marshak, D. R., Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science (New York, N.Y.) 1999, 284, (5411), 143-7. [CrossRef]
- Wu, V.; Helder, M. N.; Bravenboer, N.; Ten Bruggenkate, C. M.; Jin, J.; Klein-Nulend, J.; Schulten, E. A. J. S. C. I., Bone tissue regeneration in the oral and maxillofacial region: a review on the application of stem cells and new strategies to improve vascularization. Stem Cells Int. 2019 Dec 30;2019:6279721. [CrossRef]
- Melville, J. C.; Nassari, N. N.; Hanna, I. A.; Shum, J. W.; Wong, M. E.; Young, S., Immediate Transoral Allogeneic Bone Grafting for Large Mandibular Defects. Less Morbidity, More Bone. A Paradigm in Benign Tumor Mandibular Reconstruction? J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2017, 75, (4), 828-838.
- Talaat, W. M.; Ghoneim, M. M.; Salah, O.; Adly, O. A., Autologous bone marrow concentrates and concentrated growth factors accelerate bone regeneration after enucleation of mandibular pathologic lesions. Journal of Craniofacial Surgery 2018, 29, (4), 992-997. [CrossRef]
- Schliephake, H., Clinical efficacy of growth factors to enhance tissue repair in oral and maxillofacial reconstruction: a systematic review. Clinical implant dentistry and related research 2015, 17, (2), 247-273. [CrossRef]
- Khojasteh, A.; Behnia, H.; Naghdi, N.; Esmaeelinejad, M.; Alikhassy, Z.; Stevens, M., Effects of different growth factors and carriers on bone regeneration: a systematic review. Oral surgery, oral medicine, oral pathology and oral radiology 2013, 116, (6), e405-e423. [CrossRef]
- Gomes-Ferreira, P. H. S.; Okamoto, R.; Ferreira, S.; De Oliveira, D.; Momesso, G. A. C.; Faverani, L. P., Scientific evidence on the use of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 (rhBMP-2) in oral and maxillofacial surgery. Oral and maxillofacial surgery 2016, 20, (3), 223-232. [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo, D. A.; Rekow, A., A review of 60 consecutive fibula free flap mandible reconstructions. Plastic and reconstructive surgery 1995, 96, (3), 585-596. [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo, D. A., Condyle transplantation in free flap mandible reconstruction. Plastic and reconstructive surgery 1994, 93, (4), 770-781.
- Teven, C. M.; Fisher, S.; Ameer, G. A.; He, T. C.; Reid, R. R., Biomimetic approaches to complex craniofacial defects. Ann Maxillofac Surg 2015, 5, (1), 4-13. [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, Y.; Maeda, H., Recent developments of functional scaffolds for craniomaxillofacial bone tissue engineering applications. The Scientific World Journal 2013, 2013. [CrossRef]
- Ramly, E. P.; Alfonso, A. R.; Kantar, R. S.; Wang, M. M.; Siso, J. R. D.; Ibrahim, A.; Coelho, P. G.; Flores, R. L. J. P.; Open, R. S. G., Safety and efficacy of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 (rhBMP-2) in craniofacial surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2019, 7, (8). [CrossRef]
- Costa, A. M.; Barbosa, A.; Neto, E.; Sousa, S. A.; Freitas, R.; Neves, J. M.; Cardoso, M. T.; Ferreirinha, F.; Sá, C. P., On the role of subtype selective adenosine receptor agonists during proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human primary bone marrow stromal cells. Journal of cellular physiology 2011, 226, (5), 1353-1366.
- Mediero, A.; Wilder, T.; Perez-Aso, M.; Cronstein, B. N., Direct or indirect stimulation of adenosine A2A receptors enhances bone regeneration as well as bone morphogenetic protein-2. The FASEB Journal 2015, 29, (4), 1577-1590. [CrossRef]
- Mediero, A.; Frenkel, S. R.; Wilder, T.; He, W.; Mazumder, A.; Cronstein, B. N., Adenosine A2A receptor activation prevents wear particle-induced osteolysis. Sci Transl Med 2012, 4, (135), 135ra65.
- Mediero, A.; Cronstein, B. N., Adenosine and bone metabolism. Trends in Endocrinology & Metabolism 2013, 24, (6), 290-300.
- Lopez, C. D.; Witek, L.; Flores, R. L.; Torroni, A.; Rodriguez, E. D.; Cronstein, B. N.; Coelho, P. G. J. R. S. f. M.; Guide, M. R. A. P., 3D Printing and Adenosine Receptor Activation for Craniomaxillofacial Regeneration. 2019, 255-267.
- FitzGerald, G. A., Dipyridamole. The New England journal of medicine 1987, 316, (20), 1247-1257.
- Patrono, C.; Coller, B.; Dalen, J. E.; Fuster, V.; Gent, M.; Harker, L. A.; Hirsh, J.; Roth, G., Platelet-active drugs: the relationships among dose, effectiveness, and side effects. Chest 1998, 114, (5 Suppl).
- Monagle, P.; Chan, A. K. C. K. C.; Goldenberg, N. A.; Ichord, R. N.; Journeycake, J. M.; Nowak-Göttl, U.; Vesely, S. K., Antithrombotic therapy in neonates and children: Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest 2012, 141, (2 Suppl). [CrossRef]
- Lopez, C. D.; Diaz-Siso, J. R.; Witek, L.; Bekisz, J. M.; Gil, L. F.; Cronstein, B. N.; Flores, R. L.; Torroni, A.; Rodriguez, E. D.; Coelho, P. G. J. P.; surgery, r., Dipyridamole augments 3D printed bioactive ceramic scaffolds to regenerate craniofacial bone. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2019, 143, (5), 1408.
- Budharaju, H.; Suresh, S.; Sekar, M. P.; De Vega, B.; Sethuraman, S.; Sundaramurthi, D.; Kalaskar, D. M., Ceramic materials for 3D printing of biomimetic bone scaffolds – Current state-of-the-art & future perspectives. Materials & Design 2023, 231, 112064.
- Sakthiabirami, K.; Soundharrajan, V.; Jin-Ho, K.; Nileshkumar, D.; Geetha, M.; Kwi-Dug, Y.; Sang-Won, P., Perspective Chapter: Additive Manufactured Zirconia-Based Bio-Ceramics for Biomedical Applications. In Advanced Additive Manufacturing, Igor, V. S., Ed. IntechOpen: Rijeka 2022; p Ch. 1.
- Yanamandra, K.; Chen, G. L.; Xu, X.; Mac, G.; Gupta, N., Reverse engineering of additive manufactured composite part by toolpath reconstruction using imaging and machine learning. Composites Science and Technology 2020, 198, 108318. [CrossRef]
- Delli, U.; Chang, S., Automated Process Monitoring in 3D Printing Using Supervised Machine Learning. Procedia Manufacturing 2018, 26, 865-870. [CrossRef]
- Guo, J. L.; Januszyk, M.; Longaker, M. T., Machine Learning in Tissue Engineering. Tissue engineering. Part A 2023, 29, (1-2), 2-19. [CrossRef]
- Conev, A.; Litsa, E. E.; Perez, M. R.; Diba, M.; Mikos, A. G.; Kavraki, L. E., Machine Learning-Guided Three-Dimensional Printing of Tissue Engineering Scaffolds. Tissue engineering. Part A 2020, 26, (23-24), 1359-1368. [CrossRef]
| Ceramic | Sintering Temperature | Characteristic | Applications | Ref. | |
| Hydroxyapatite Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2 |
1000–1250°C | Capable of fostering cell growth, possessing excellent biocompatibility and good compression strength | Repair of bone defects | [33,34,35] | |
| β-Tricalcium phosphate β-Ca3(PO4)2 |
200–1400°C | Minimal shrinkage, biodegradability, appropriate porosity reduced cracking and deformation | Hard tissue repair of defects | [36,37,38] | |
| Silicon carbide SiC |
1860–1950°C | High strength and good compressive strength | Light weight structural ceramics | [39,40,41] | |
| Zirconium oxide ZrO2 |
1000–1450°C | Biocompatibility, chemical stability, and excellent mechanical properties | Bone repair and tissue engineering | [42] | |
| Barium titanate BaTiO3 |
900–1200°C | Biocompatible and good tensile strength | Repair of extensive bone defects | [43,44] | |
| AM Method | Ceramic slurry/filament/ink/ preparation |
Printing Resolution | Advantages | Disadvantages | Reference |
| Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM) |
Filaments are produced through a blend of ceramic powders and thermoplastic polymers for 3D printing of structures. | 100µm– 1mm |
Compatible with other materials, reproducibility, low-cost and ease of operation. | Limited resolution and uneven adhesion between layers. | [113,114] |
| Stereolithography (SLA) | The printing process involves combining ceramics with a photopolymerizable resin. | 20 µm –100µm | Low wastage of ceramic materials, high resolution, and printing speed. |
Requirement for photopolymers, and the need for subsequent post-processing steps. | [115,116,117] |
| Selective laser sintering (SLS) |
The powder bed is prepared with ceramic particles of equal size to withstand laser power and temperature, ensuring a defect-free construct. | 20 µm –100µm | High resolution, fabrication of complex structures using powder as support, and high mechanical strength of printed constructs. | Demand of materials capable of enduring laser heat, managing scaffold shrinkage, and pre- and post-heating treatments. | [118,119] |
| Direct Inkjet Writing (DIW) | A homogeneous ceramic slurry is created by blending ceramic materials with polymer binders and viscosifiers into the solutions. | 100µm– 1mm |
Low cost, scalability, capability for fabrication of complex and larger structures. | High pressure, low resolution, needle clogging. | [120,121,122,123] |
| Digital light processing (DLP) |
Ceramic powder with liquid photopolymer is exposed to digital light arrays. | 25 µm –100µm | High resolution, cost-effectiveness, and accuracy of print. | Limited availability of materials, requirement for photo reactivity, and restricted build volume. | [115,124,125] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).