Submitted:
23 November 2023
Posted:
23 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
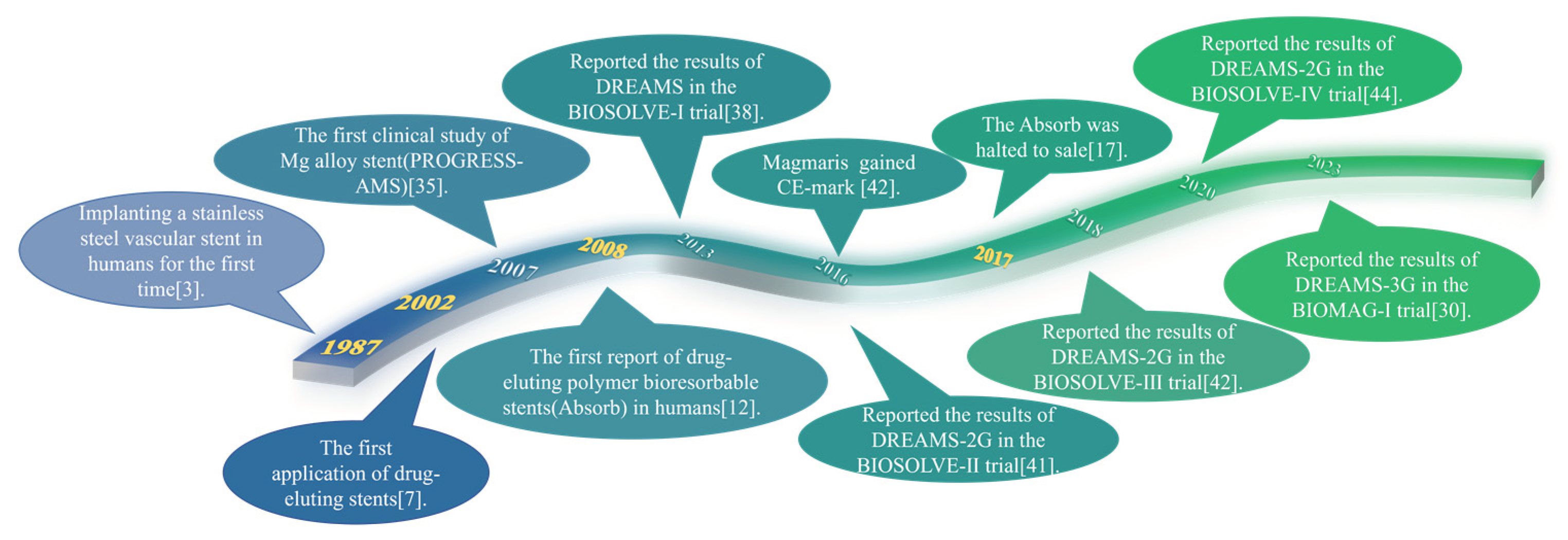
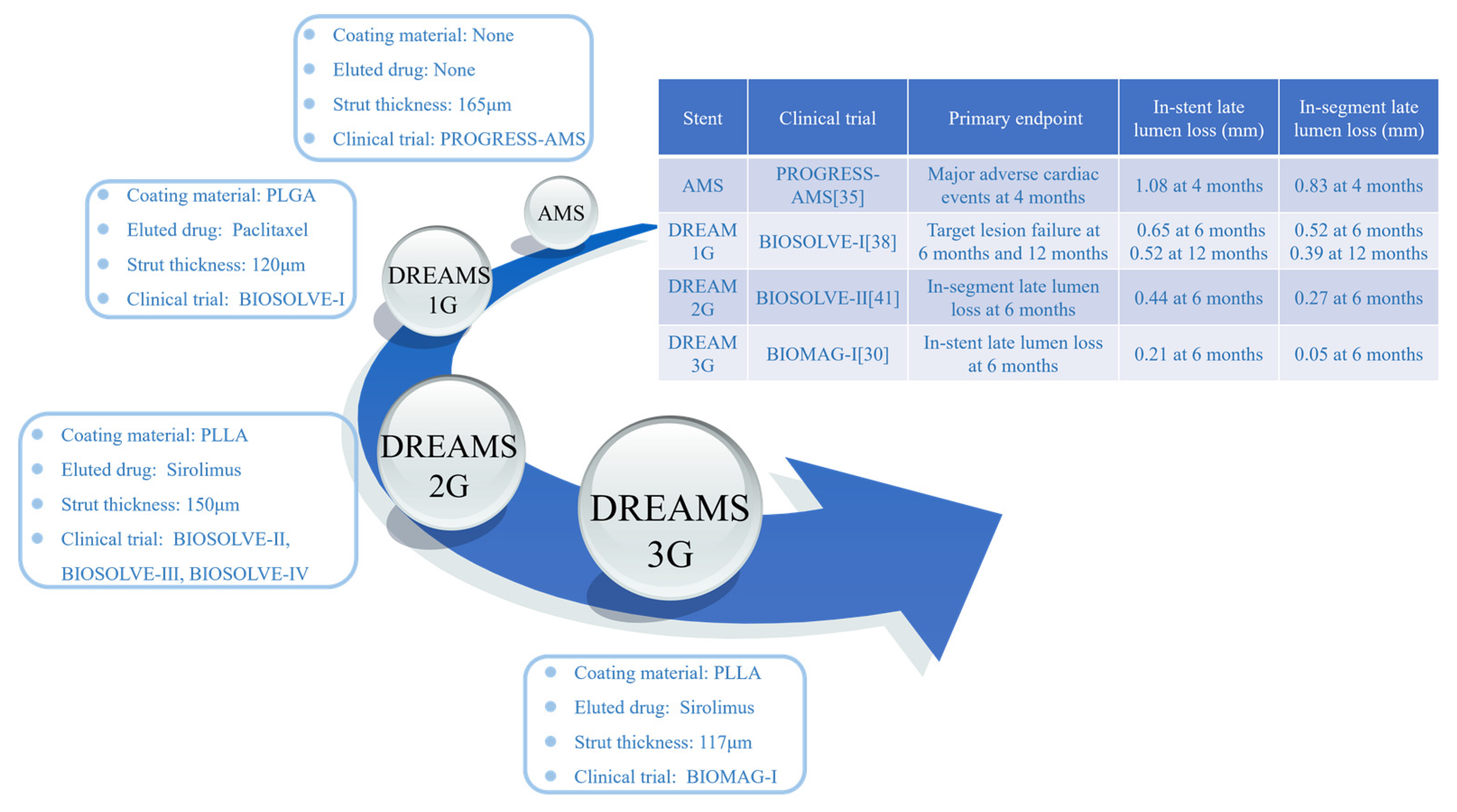
2. Development history of magnesium alloy stents
3. Corrosion mechanism of magnesium alloys and stents
3.1. Corrosion mechanism of magnesium alloys
3.2. Corrosion mechanism of magnesium alloy stents
4. Traditional strategy for protection of magnesium alloy stents
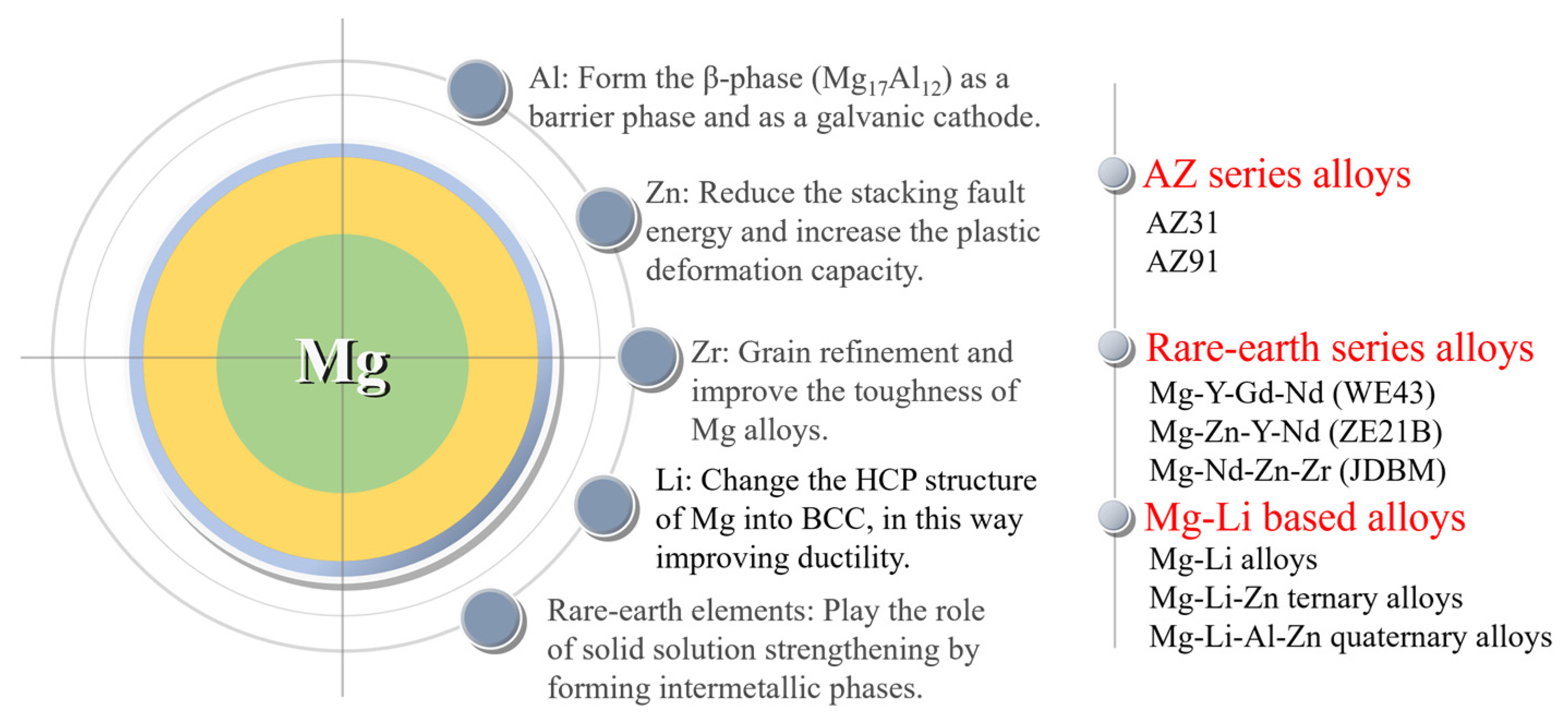
4.1. Alloying design for magnesium alloy stents
4.2. Optimization of magnesium alloy stent structure
4.3. Protective coating on magnesium alloy stents
4.3.1. Inner chemical conversion coating
4.3.2. Outer polymer coating
- Polylactic acid (PLA) coating
- Poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) coating
- Polycaprolactone (PCL) coating
- Poly (trimethylene carbonate) (PTMC) coating
- Polyurethanes (PU) coating
- Silane coating
5. Research trend and outlook of magnesium alloy stents
5.1. Research trend of magnesium alloy stents
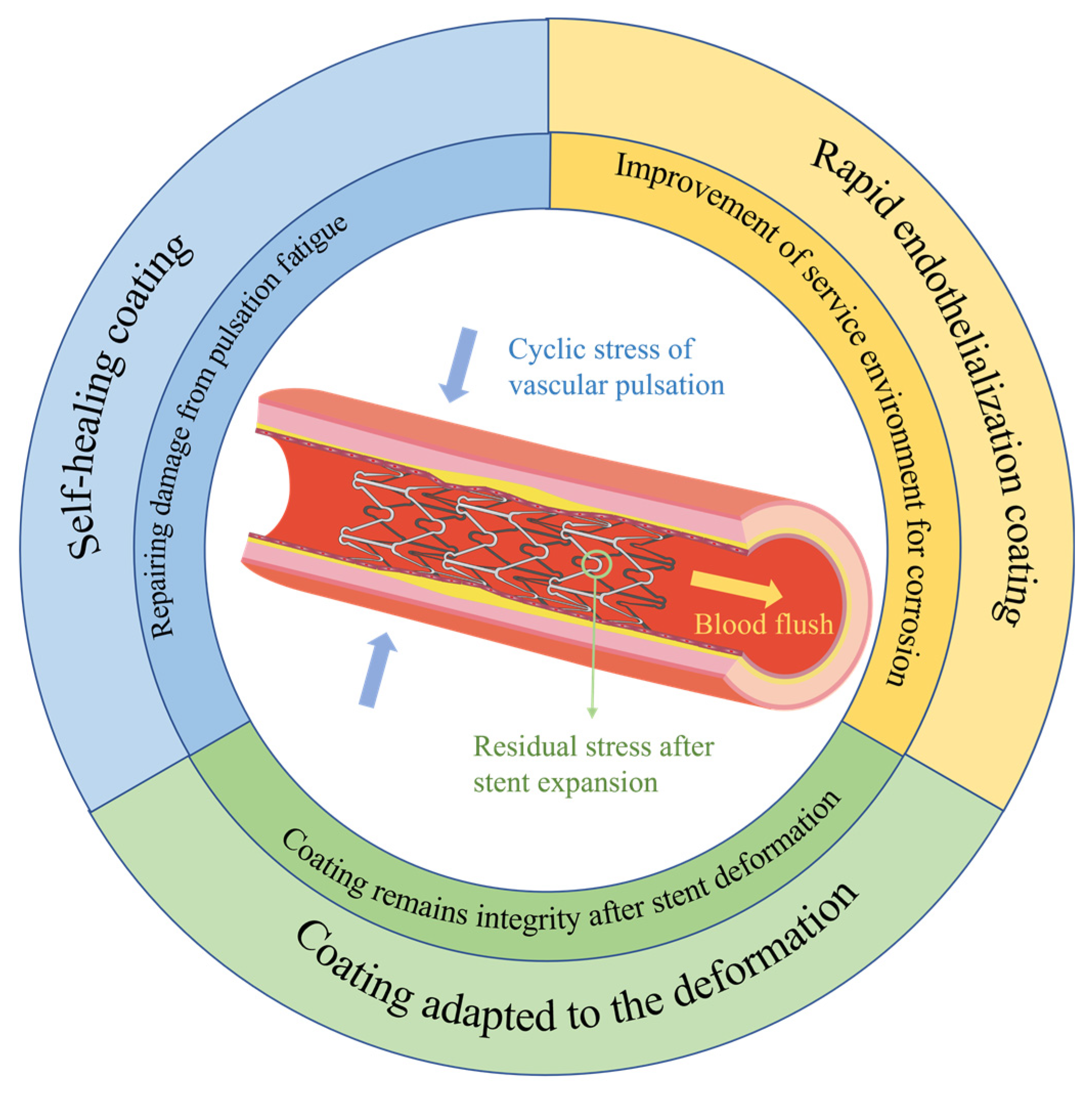
5.1.1. Study of protective coatings adapted to the deformation mechanics of stents
5.1.2. Rapid endothelialization coating on magnesium alloy stents
5.1.3. Introduction of self-healing mechanism into coating on magnesium alloy stents
5.2. Outlook
References
- Cardiovascular Diseases. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/cardiovascular-diseases (accessed on 31 July 2023).
- Qi, P.; Yang, Y.; Maitz, F.M.; Huang, N. Current Status of Research and Application in Vascular Stents. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 4362–4370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigwart, U.; Puel, J.; Mirkovitch, V.; Joffre, F.; Kappenberger, L. Intravascular Stents to Prevent Occlusion and Re-Stenosis after Transluminal Angioplasty. N Engl J Med 1987, 316, 701–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serruys, P.; Dejaegere, P.; Kiemeneij, F.; Macaya, C.; Rutsch, W.; Heyndrickx, G.; Emanuelsson, H.; Marco, J.; Legrand, V.; Materne, P.; et al. A Comparison of Balloon-Expandable-Stent Implantation with Balloon Angioplasty in Patients with Coronary-Artery Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1994, 331, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, R.; Mintz, G.; Dussaillant, G.; Popma, J.; Pichard, A.; Satler, L.; Kent, K.; Griffin, J.; Leon, M. Patterns and Mechanisms of In-Stent Restenosis - A Serial Intravascular Ultrasound Study. CIRCULATION 1996, 94, 1247–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claessen, B.E.; Henriques, J.P.S.; Jaffer, F.A.; Mehran, R.; Piek, J.J.; Dangas, G.D. Stent Thrombosis. JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions 2014, 7, 1081–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morice, M.-C.; Hayashi, E.B.; Guagliumi, G. A Randomized Comparison of a Sirolimus-Eluting Stent with a Standard Stent for Coronary Revascularization. The New England Journal of Medicine 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, G.; Ellis, S.; Cannon, L.; Mann, J.; Greenberg, J.; Spriggs, D.; O’Shaughnessy, C.; DeMaio, S.; Hall, P.; Popma, J.; et al. Comparison of a Polymer-Based Paclitaxel-Eluting Stent with a Bare Metal Stent in Patients with Complex Coronary Artery Disease - A Randomized Controlled Trial. JAMA-JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN MEDICAL ASSOCIATION 2005, 294, 1215–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joner, M.; Finn, A.V.; Farb, A.; Mont, E.K.; Kolodgie, F.D.; Ladich, E.; Kutys, R.; Skorija, K.; Gold, H.K.; Virmani, R. Pathology of Drug-Eluting Stents in Humans. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 2006, 48, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erne, P.; Schier, M.; Resink, T.J. The Road to Bioabsorbable Stents: Reaching Clinical Reality? Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 2006, 29, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotomi, Y.; Onuma, Y.; Collet, C.; Tenekecioglu, E.; Virmani, R.; Kleiman, N.S.; Serruys, P.W. Bioresorbable Scaffold: The Emerging Reality and Future Directions. Circ Res 2017, 120, 1341–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ormiston, J.A.; Serruys, P.W.; Regar, E.; Dudek, D.; Thuesen, L.; Webster, M.W.; Onuma, Y.; Garcia-Garcia, H.M.; McGreevy, R.; Veldhof, S. A Bioabsorbable Everolimus-Eluting Coronary Stent System for Patients with Single de-Novo Coronary Artery Lesions (ABSORB): A Prospective Open-Label Trial. The Lancet 2008, 371, 899–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, R.; Yang, Y.; Han, Y.; Huo, Y.; Chen, J.; Yu, B.; Su, X.; Li, L.; Kuo, H.-C.; Ying, S.-W.; et al. Bioresorbable Vascular Scaffolds Versus Metallic Stents in Patients With Coronary Artery Disease. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 2015, 66, 2298–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonan, R.; Asgar, A.W. Biodegradable Stents - Where Are We in 2009? US Cardiology 2009;6(1):81–4, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, Z.A.; Serruys, P.W.; Kimura, T.; Gao, R.; Ellis, S.G.; Kereiakes, D.J.; Onuma, Y.; Simonton, C.; Zhang, Z.; Stone, G.W. 2-Year Outcomes with the Absorb Bioresorbable Scaffold for Treatment of Coronary Artery Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Seven Randomised Trials with an Individual Patient Data Substudy. The Lancet 2017, 390, 760–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaji, K.; Ueki, Y.; Souteyrand, G.; Daemen, J.; Wiebe, J.; Nef, H.; Adriaenssens, T.; Loh, J.P.; Lattuca, B.; Wykrzykowska, J.J.; et al. Mechanisms of Very Late Bioresorbable Scaffold Thrombosis. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 2017, 70, 2330–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- No More Absorb BVS: Abbott Puts a Stop to Sales | Tctmd.Com. Available online: https://www.tctmd.com/news/no-more-absorb-bvs-abbott-puts-stop-sales (accessed on 9 October 2023).
- Liu, B.; Zheng, Y.F. Effects of Alloying Elements (Mn, Co, Al, W, Sn, B, C and S) on Biodegradability and in Vitro Biocompatibility of Pure Iron. Acta Biomaterialia 2011, 7, 1407–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moravej, M.; Mantovani, D. Biodegradable Metals for Cardiovascular Stent Application: Interests and New Opportunities. IJMS 2011, 12, 4250–4270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Chang, R.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, Y. Moving Research Direction in the Field of Metallic Bioresorbable Stents-A Mini-Review. Bioactive Materials 2023, 24, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapiero, H.; Tew, K.D. Trace Elements in Human Physiology and Pathology: Zinc and Metallothioneins. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2003, 57, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, P.K.; Drelich, J.; Goldman, J. Zinc Exhibits Ideal Physiological Corrosion Behavior for Bioabsorbable Stents. Advanced Materials 2013, 25, 2577–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, W.; Behrens, P.; Brandt-Wunderlich, C.; Siewert, S.; Grabow, N.; Schmitz, K.-P. In Vitro Performance Investigation of Bioresorbable Scaffolds – Standard Tests for Vascular Stents and Beyond. Cardiovascular Revascularization Medicine 2016, 17, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grogan, J.A.; O’Brien, B.J.; Leen, S.B.; McHugh, P.E. A Corrosion Model for Bioabsorbable Metallic Stents. Acta Biomaterialia 2011, 7, 3523–3533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Dou, J.; Wang, Z.; Hu, C.; Yu, H.; Chen, C. Research Progress of Biodegradable Magnesium-Based Biomedical Materials: A Review. Journal of Alloys and Compounds 2022, 923, 166377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Huang, H.; Pei, J.; Jin, Z.; Guan, S.; Yuan, G.; Gy; Jn; Sg; Jn; et al. Research and Development Strategy for Biodegradable Magnesium-Based Vascular Stents: A Review. Biomater Transl 2021, 2, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heublein, B. Biocorrosion of Magnesium Alloys: A New Principle in Cardiovascular Implant Technology? Heart 2003, 89, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossard, M.; Madanchi, M.; Avdijaj, D.; Attinger-Toller, A.; Cioffi, G.M.; Seiler, T.; Tersalvi, G.; Kobza, R.; Schüpfer, G.; Cuculi, F. Long-Term Outcomes After Implantation of Magnesium-Based Bioresorbable Scaffolds—Insights From an All-Comer Registry. Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine 2022, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, J.; Onuma, Y.; Ormiston, J.; Abizaid, A.; Waksman, R.; Serruys, P. Bioresorbable Scaffolds: Rationale, Current Status, Challenges, and Future. European Heart Journal 2014, 35, 765–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haude, M.; Wlodarczak, A.; Van Der Schaaf, R.J.; Torzewski, J.; Ferdinande, B.; Escaned, J.; Iglesias, J.F.; Bennett, J.; Toth, G.; Joner, M.; et al. Safety and Performance of the Third-Generation Drug-Eluting Resorbable Coronary Magnesium Scaffold System in the Treatment of Subjects with de Novo Coronary Artery Lesions: 6-Month Results of the Prospective, Multicenter BIOMAG-I First-in-Human Study. eClinicalMedicine 2023, 59, 101940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waksman, R.; Pakala, R.; Kuchulakanti, P.K.; Baffour, R.; Hellinga, D.; Seabron, R.; Tio, F.O.; Wittchow, E.; Hartwig, S.; Harder, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Bioabsorbable Magnesium Alloy Stents in Porcine Coronary Arteries. Cathet. Cardiovasc. Intervent. 2006, 68, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slottow, T.L.P.; Pakala, R.; Okabe, T.; Hellinga, D.; Lovec, R.J.; Tio, F.O.; Bui, A.B.; Waksman, R. Optical Coherence Tomography and Intravascular Ultrasound Imaging of Bioabsorbable Magnesium Stent Degradation in Porcine Coronary Arteries. Cardiovascular Revascularization Medicine 2008, 9, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Mario, C.; Griffiths, H.; Goktekin, O.; Peeters, N.; Verbist, J.; Bosiers, M.; Deloose, K.; Heublein, B.; Rohde, R.; Kasese, V.; et al. Drug-Eluting Bioabsorbable Magnesium Stent. Journal of Interventional Cardiology 2004, 17, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, P.; Bosiers, M.; Verbist, J.; Deloose, K.; Heublein, B. Preliminary Results After Application of Absorbable Metal Stents in Patients With Critical Limb Ischemia. Journal of Endovascular Therapy 2005, 12, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erbel, R.; Mario, C.D.; Bartunek, J.; Bonnier, J.; de Bruyne, B.; Eberli, F.R.; Erne, P.; Haude, M.; Heublein, B.; Horrigan, M.; et al. Temporary Scaffolding of Coronary Arteries with Bioabsorbable Magnesium Stents: A Prospective, Non-Randomised Multicentre Trial. 2007; 369. [Google Scholar]
- Waksman, R.; Erbel, R.; Di Mario, C.; Bartunek, J.; De Bruyne, B.; Eberli, F.R.; Erne, P.; Haude, M.; Horrigan, M.; Ilsley, C.; et al. Early- and Long-Term Intravascular Ultrasound and Angiographic Findings After Bioabsorbable Magnesium Stent Implantation in Human Coronary Arteries. JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions 2009, 2, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittchow, E.; Adden, N.; Riedmüller, J.; Savard, C.; Waksman, R.; Braune, M. Bioresorbable Drug-Eluting Magnesium-Alloy Scaffold: Design and Feasibility in a Porcine Coronary Model. EuroIntervention 2013, 8, 1441–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haude, M.; Erbel, R.; Erne, P.; Verheye, S.; Degen, H.; Böse, D.; Vermeersch, P.; Wijnbergen, I.; Weissman, N.; Prati, F.; et al. Safety and Performance of the Drug-Eluting Absorbable Metal Scaffold (DREAMS) in Patients with de-Novo Coronary Lesions: 12 Month Results of the Prospective, Multicentre, First-in-Man BIOSOLVE-I Trial. The Lancet 2013, 381, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waksman, R.; Zumstein, P.; Pritsch, M.; Wittchow, E.; Haude, M.; Lapointe-Corriveau, C.; Leclerc, G.; Joner, M. Second-Generation Magnesium Scaffold Magmaris: Device Design and Preclinical Evaluation in a Porcine Coronary Artery Model. EuroIntervention 2017, 13, 440–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joner, M.; Ruppelt, P.; Zumstein, P.; Lapointe-Corriveau, C.; Leclerc, G.; Bulin, A.; Castellanos, M.I.; Wittchow, E.; Haude, M.; Waksman, R. Preclinical Evaluation of Degradation Kinetics and Elemental Mapping of First- and Second-Generation Bioresorbable Magnesium Scaffolds. EuroIntervention 2018, 14, e1040–e1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haude, M.; Ince, H.; Abizaid, A.; Toelg, R.; Lemos, P.A.; von Birgelen, C.; Christiansen, E.H.; Wijns, W.; Neumann, F.-J.; Kaiser, C.; et al. Safety and Performance of the Second-Generation Drug-Eluting Absorbable Metal Scaffold in Patients with de-Novo Coronary Artery Lesions (BIOSOLVE-II): 6 Month Results of a Prospective, Multicentre, Non-Randomised, First-in-Man Trial. The Lancet 2016, 387, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haude, M.; Ince, H.; Kische, S.; Abizaid, A.; Tölg, R.; Alves Lemos, P.; Van Mieghem, N.M.; Verheye, S.; von Birgelen, C.; Christiansen, E.H.; et al. Safety and Clinical Performance of a Drug Eluting Absorbable Metal Scaffold in the Treatment of Subjects with de Novo Lesions in Native Coronary Arteries: Pooled 12-month Outcomes of BIOSOLVE-II and BIOSOLVE-III. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 2018, 92, E502–E511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rola, P.; Włodarczak, A.; Łanocha, M.; Barycki, M.; Szudrowicz, M.; Kulczycki, J.J.; Jaroszewska-Pozorska, J.; Gosiewska, A.; Woźnica, K.; Lesiak, M.; et al. Outcomes of the Two Generations of Bioresorbable Scaffolds (Magmaris vs. Absorb) in Acute Coronary Syndrome in Routine Clinical Practice. Cardiology Journal 2022, 0. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verheye, S.; Wlodarczak, A.; Montorsi, P.; Torzewski, J.; Bennett, J.; Haude, M.; Starmer, G.; Buck, T.; Wiemer, M.; Nuruddin, A.A.B.; et al. BIOSOLVE-IV-Registry: Safety and Performance of the Magmaris Scaffold: 12-Month Outcomes of the First Cohort of 1,075 Patients. Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions 2021, 98, E1–E8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubero-Gallego, H.; Vandeloo, B.; Gomez-Lara, J.; Romaguera, R.; Roura, G.; Gomez-Hospital, J.A.; Cequier, A. Early Collapse of a Magnesium Bioresorbable Scaffold. JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions 2017, 10, e171–e172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barkholt, T.Ø.; Neghabat, O.; Terkelsen, C.J.; Christiansen, E.H.; Holm, N.R. Restenosis in a Collapsed Magnesium Bioresorbable Scaffold. Circ: Cardiovascular Interventions 2017, 10, e005677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Blas, S.; Miñana, G.; Sanchis, J. Optical Coherence Tomography of Magnesium Bioresorbable Scaffold Restenosis. Revista Española de Cardiología (English Edition) 2018, 71, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, S.V.S.; Prasad, S.B.; Verma, K.; Mishra, R.K.; Kumar, V.; Singh, S. The Role and Significance of Magnesium in Modern Day Research-A Review. Journal of Magnesium and Alloys 2022, 10, 1–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zanna, S.; Ardelean, H.; Frateur, I.; Schmutz, P.; Song, G.; Atrens, A.; Marcus, P. A First Quantitative XPS Study of the Surface Films Formed, by Exposure to Water, on Mg and on the Mg–Al Intermetallics: Al3Mg2 and Mg17Al12. Corrosion Science 2009, 51, 1115–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Saijilafu; Wu, X.; Wu, K.; Chen, J.; Tan, L.; Witte, F.; Yang, H.; Mantovani, D.; Zhou, H.; et al. Biodegradable Mg-Based Alloys: Biological Implications and Restorative Opportunities. International Materials Reviews, 2022; 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapetto, C.; Leoncini, M. Magmaris: A New Generation Metallic Sirolimus-Eluting Fully Bioresorbable Scaffold: Present Status and Future Perspectives. Journal of Thoracic Disease 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Chen, S.; Gastaldi, D.; Petrini, L.; Mantovani, D.; Yang, K.; Tan, L.; Migliavacca, F. Experimental Data Confirm Numerical Modeling of the Degradation Process of Magnesium Alloys Stents. Acta Biomaterialia 2013, 9, 8730–8739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Cheng, J.; Zhao, G.; Hu, X.; Gu, X.; Su, J. Computational Modeling of the Corrosion Process and Mechanical Performance of Biodegradable Stent. J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 2021, 1888, 012019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Petrini, L.; Gastaldi, D.; Villa, T.; Vedani, M.; Lesma, E.; Previtali, B.; Migliavacca, F. Finite Element Shape Optimization for Biodegradable Magnesium Alloy Stents. Ann Biomed Eng 2010, 38, 2829–2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Sato, K.; Koga, Y.; Sasaki, M.; Niidome, T. Corrosion Resistance of HF-Treated Mg Alloy Stent Following Balloon Expansion and Its Improvement through Biodegradable Polymer Coating. J Coat Technol Res 2020, 17, 1023–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Song, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, X. Interaction between a High Purity Magnesium Surface and PCL and PLA Coatings during Dynamic Degradation. Biomed. Mater. 2011, 6, 025005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, X.N.; Zhou, W.R.; Zheng, Y.F.; Cheng, Y.; Wei, S.C.; Zhong, S.P.; Xi, T.F.; Chen, L.J. Corrosion Fatigue Behaviors of Two Biomedical Mg Alloys – AZ91D and WE43 – In Simulated Body Fluid. Acta Biomaterialia 2010, 6, 4605–4613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, B.; Lin, H.; Yang, H.; Zheng, F.; Chen, M. Assessment of Structure Integrity, Corrosion Behavior and Microstructure Change of AZ31B Stent in Porcine Coronary Arteries. Journal of Materials Science & Technology 2019, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Zhao, M.; Zhou, X.; Yang, H.; Liu, J.; Guo, H.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, J.-A. A Numerical Corrosion-Fatigue Model for Biodegradable Mg Alloy Stents. Acta Biomaterialia 2019, 97, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guangling Song. Corrosion Protection of magnesium alloys; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, CHN, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Guan, S.; Zhu, S.; Ren, C.; Hou, S. Microstructure and Corrosion Properties of as Sub-Rapid Solidification Mg–Zn–Y–Nd Alloy in Dynamic Simulated Body Fluid for Vascular Stent Application. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 2010, 21, 2001–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yuan, G.; Mao, L.; Niu, J.; Ding, W. Biocorrosion Properties of As-Extruded Mg–Nd–Zn–Zr Alloy Compared with Commercial AZ31 and WE43 Alloys. Materials Letters 2012, 66, 209–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeflang, M.A.; Dzwonczyk, J.S.; Zhou, J.; Duszczyk, J. Long-Term Biodegradation and Associated Hydrogen Evolution of Duplex-Structured Mg–Li–Al–(RE) Alloys and Their Mechanical Properties. Materials Science and Engineering: B 2011, 176, 1741–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witte, F.; Kaese, V.; Haferkamp, H.; Switzer, E.; Meyer-Lindenberg, A.; Wirth, C.J.; Windhagen, H. In Vivo Corrosion of Four Magnesium Alloys and the Associated Bone Response. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 3557–3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Zhu, S.; Wang, L.; Liu, Q.; Yue, G.; Wang, J.; Guan, S. The Microstructure and Properties of Cyclic Extrusion Compression Treated Mg–Zn–Y–Nd Alloy for Vascular Stent Application. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials 2012, 8, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhu, S.; Wang, L.; Guan, S. Processing and Properties of Magnesium Alloy Micro-Tubes for Biodegradable Vascular Stents. Materials Science and Engineering: C 2018, 90, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, P.; Mei, D.; Furushima, T.; Zhu, S.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Guan, S. In Vitro Corrosion Properties of HTHEed Mg-Zn-Y-Nd Alloy Microtubes for Stent Applications: Influence of Second Phase Particles and Crystal Orientation. Journal of Magnesium and Alloys 2022, 10, 1286–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Chen, M.; Yang, M.; Wei, J.; Liu, D. In Vitro Corrosion Resistance and Cytocompatibility of Nano-Hydroxyapatite Reinforced Mg–Zn–Zr Composites. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 2010, 21, 1321–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zong, Y.; Yuan, G.; Zhang, X.; Mao, L.; Niu, J.; Ding, W. Comparison of Biodegradable Behaviors of AZ31 and Mg–Nd–Zn–Zr Alloys in Hank’s Physiological Solution. Materials Science and Engineering: B 2012, 177, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Wang, W.; Huang, H.; Pei, J.; Qu, H.; Yuan, G.; Li, Y. The Degradation and Transport Mechanism of a Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr Stent in Rabbit Common Carotid Artery: A 20-Month Study. Acta Biomaterialia 2018, 69, 372–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, D.; Zhou, X.; Liu, J.; Li, W.; Shen, D.; Zheng, Y.; Gu, W.; Jiang, J.; Li, M.; Chu, X.; et al. Degradation Behaviors and In-Vivo Biocompatibility of a Rare Earth- and Aluminum-Free Magnesium-Based Stent. Acta Biomaterialia 2021, 124, 382–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Bian, D.; Gao, S.; Leeflang, S.; Guo, H.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, J. Study on the Mg-Li-Zn Ternary Alloy System with Improved Mechanical Properties, Good Degradation Performance and Different Responses to Cells. Acta Biomaterialia 2017, 62, 418–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Zhao, D.; Lee, B.; Roy, A.; Yao, R.; Chen, S.; Dong, Z.; Heineman, W.R.; Kumta, P.N. Effect of Lithium and Aluminum on the Mechanical Properties, In Vivo and In Vitro Degradation, and Toxicity of Multiphase Ultrahigh Ductility Mg–Li–Al–Zn Quaternary Alloys for Vascular Stent Application. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 1950–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, T.Y.; Kwok, J.S.; Nguyen, C.T.; Fox, K. Evaluating Magnesium Alloy WE43 for Bioresorbable Coronary Stent Applications. MRS Advances 2021, 6, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Gastaldi, D.; Yang, K.; Tan, L.; Petrini, L.; Migliavacca, F. Finite Element Analyses for Design Evaluation of Biodegradable Magnesium Alloy Stents in Arterial Vessels. Materials Science and Engineering: B 2011, 176, 1733–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echeverry-Rendon, M.; Duque, V.; Quintero, D.; Harmsen, M.C.; Echeverria, F. Novel Coatings Obtained by Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation to Improve the Corrosion Resistance of Magnesium-Based Biodegradable Implants. Surface and Coatings Technology 2018, 354, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Cao, L.; Liu, Y.; Xu, X.; Wu, X. Evaluation of Magnesium Ions Release, Biocorrosion, and Hemocompatibility of MAO/PLLA-Modified Magnesium Alloy WE42. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2011, 96B, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Z.; Tian, P.; Liu, X.; Zhou, B. In Vitro Degradation, Hemolysis, and Cytocompatibility of PEO/PLLA Composite Coating on Biodegradable AZ31 Alloy: PEO/PLLA Composite Coating on Biodegradable AZ31 Alloy. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2015, 103, 342–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahim, M.I.; Tavares, A.; Evertz, F.; Kieke, M.; Seitz, J.-M.; Eifler, R.; Weizbauer, A.; Willbold, E.; Jürgen Maier, H.; Glasmacher, B.; et al. Phosphate Conversion Coating Reduces the Degradation Rate and Suppresses Side Effects of Metallic Magnesium Implants in an Animal Model. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials 2017, 105, 1622–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van PHUONG, N.; Gupta, M.; Moon, S. Enhanced Corrosion Performance of Magnesium Phosphate Conversion Coating on AZ31 Magnesium Alloy. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China 2017, 27, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.Y.; Lian, J.S.; Niu, L.Y.; Jiang, Z.H.; Jiang, Q. Growth of Zinc Phosphate Coatings on AZ91D Magnesium Alloy. Surface and Coatings Technology 2006, 201, 1814–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, L.Y.; Jiang, Z.H.; Li, G.Y.; Gu, C.D.; Lian, J.S. A Study and Application of Zinc Phosphate Coating on AZ91D Magnesium Alloy. Surface and Coatings Technology 2006, 200, 3021–3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Su, Y.; Lu, Y.; Lian, J.; Li, G. Composite Microstructure and Formation Mechanism of Calcium Phosphate Conversion Coating on Magnesium Alloy. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 163, G138–G143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Guo, Y.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Li, G.; Lian, J.; Ren, L. Preparation and Corrosion Behaviors of Calcium Phosphate Conversion Coating on Magnesium Alloy. Surface and Coatings Technology 2016, 307, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zai, W.; Zhang, X.; Su, Y.; Man, H.C.; Li, G.; Lian, J. Comparison of Corrosion Resistance and Biocompatibility of Magnesium Phosphate (MgP), Zinc Phosphate (ZnP) and Calcium Phosphate (CaP) Conversion Coatings on Mg Alloy. Surface and Coatings Technology 2020, 397, 125919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; Zhu, H.; Chen, L.; Zhou, H.; Yuan, G.; Song, C. Enhancement of Corrosion Resistance and Biocompatibility of Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr Alloy Achieved with Phosphate Coating for Vascular Stent Application. Journal of Materials Research and Technology 2020, 9, 6409–6419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zai, W.; Su, Y.; Man, H.C.; Lian, J.; Li, G. Effect of pH Value and Preparation Temperature on the Formation of Magnesium Phosphate Conversion Coatings on AZ31 Magnesium Alloy. Applied Surface Science 2019, 492, 314–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wu, G.; Zhang, Y.-H.; Zhao, Q. Growth and Characterization of Mg(OH)2 Film on Magnesium Alloy AZ31. Applied Surface Science 2011, 257, 6129–6137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Li, H.; Wang, D.; Tian, P.; Tian, Y.; Yuan, G.; Xu, D.; Liu, X. Enhanced Corrosion Resistance and Biocompatibility of Magnesium Alloy by Mg–Al-Layered Double Hydroxide. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 35033–35044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamiyama, N.; Panomsuwan, G.; Yamamoto, E.; Sudare, T.; Saito, N.; Ishizaki, T. Effect of Treatment Time in the Mg(OH)2/Mg–Al LDH Composite Film Formed on Mg Alloy AZ31 by Steam Coating on the Corrosion Resistance. Surface and Coatings Technology 2016, 286, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Hsia, C.; Uan, J. Characterization of Mg,Al-Hydrotalcite Conversion Film on Mg Alloy and Cl− and CO32- Anion-Exchangeability of the Film in a Corrosive Environment. Scripta Materialia 2007, 56, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Peng, F.; Wang, D.; Qiao, Y.; Xu, D.; Liu, X. Layered Double Hydroxide/Poly-Dopamine Composite Coating with Surface Heparinization on Mg Alloys: Improved Anticorrosion, Endothelialization and Hemocompatibility. Biomater. Sci. 2018, 6, 1846–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Tan, J.; Du, H.; Qian, S.; Liu, X. Comparison Study of Mg(OH)2, Mg-Fe LDH, and FeOOH Coatings on PEO-Treated Mg Alloy in Anticorrosion and Biocompatibility. Applied Clay Science 2022, 225, 106535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; Yuan, G.; Niu, J.; Zong, Y.; Ding, W. In Vitro Degradation Behavior and Biocompatibility of Mg–Nd–Zn–Zr Alloy by Hydrofluoric Acid Treatment. Materials Science and Engineering: C 2013, 33, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, L.; Shen, L.; Chen, J.; Wu, Y.; Kwak, M.; Lu, Y.; Xue, Q.; Pei, J.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, G.; et al. Enhanced Bioactivity of Mg–Nd–Zn–Zr Alloy Achieved with Nanoscale MgF 2 Surface for Vascular Stent Application. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 5320–5330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhu, P.; Chen, S.; Zhang, B.; Yang, K. In Vitro Study on Degradation of AZ31B Magnesium Alloy with Fluoride Conversion Coating. Materials Technology 2017, 32, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrowski, N.J.; Lee, B.; Roy, A.; Ramanathan, M.; Kumta, P.N. Biodegradable Poly(Lactide-Co-Glycolide) Coatings on Magnesium Alloys for Orthopedic Applications. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 2013, 24, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.-Y.; Cui, L.-Y.; Zeng, R.-C.; Li, S.-Q.; Chen, X.-B.; Zheng, Y.; Kannan, M.B. Advances in Functionalized Polymer Coatings on Biodegradable Magnesium Alloys – A Review. Acta Biomaterialia 2018, 79, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farah, S.; Anderson, D.G.; Langer, R. Physical and Mechanical Properties of PLA, and Their Functions in Widespread Applications — A Comprehensive Review. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 2016, 107, 367–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Zhang, X.; Niu, J.; Shi, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Dai, D.; Chen, C.; Pei, J.; Yuan, G.; Zhang, R. Biosafety and Efficacy Evaluation of a Biodegradable Magnesium-Based Drug-Eluting Stent in Porcine Coronary Artery. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 7330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, W.; Chen, Y.; Fan, H.; Chen, S.; Wang, H.; Song, X. A Novel PLLA/MgF2 Coating on Mg Alloy by Ultrasonic Atomization Spraying for Controlling Degradation and Improving Biocompatibility. Materials 2023, 16, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menze, R.; Wittchow, E. In Vitro and in Vivo Evaluation of a Novel Bioresorbable Magnesium Scaffold with Different Surface Modifications. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater 2021, 109, 1292–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wan, P.; Zhang, B.; Eren Erişen, D.; Yang, H.; Yang, K. A Novel Polymer Critical Re-Melting Treatment for Improving Corrosion Resistance of Magnesium Alloy Stent. Journal of Materials Science & Technology 2019, 35, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Pei, J.; Zhang, J.; Niu, J.; Zhang, H.; Guo, S.; Li, Z.; Yuan, G. Enhanced Corrosion Resistance and Cytocompatibility of Biodegradable Mg Alloys by Introduction of Mg(OH)2 Particles into Poly (L-Lactic Acid) Coating. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 41796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
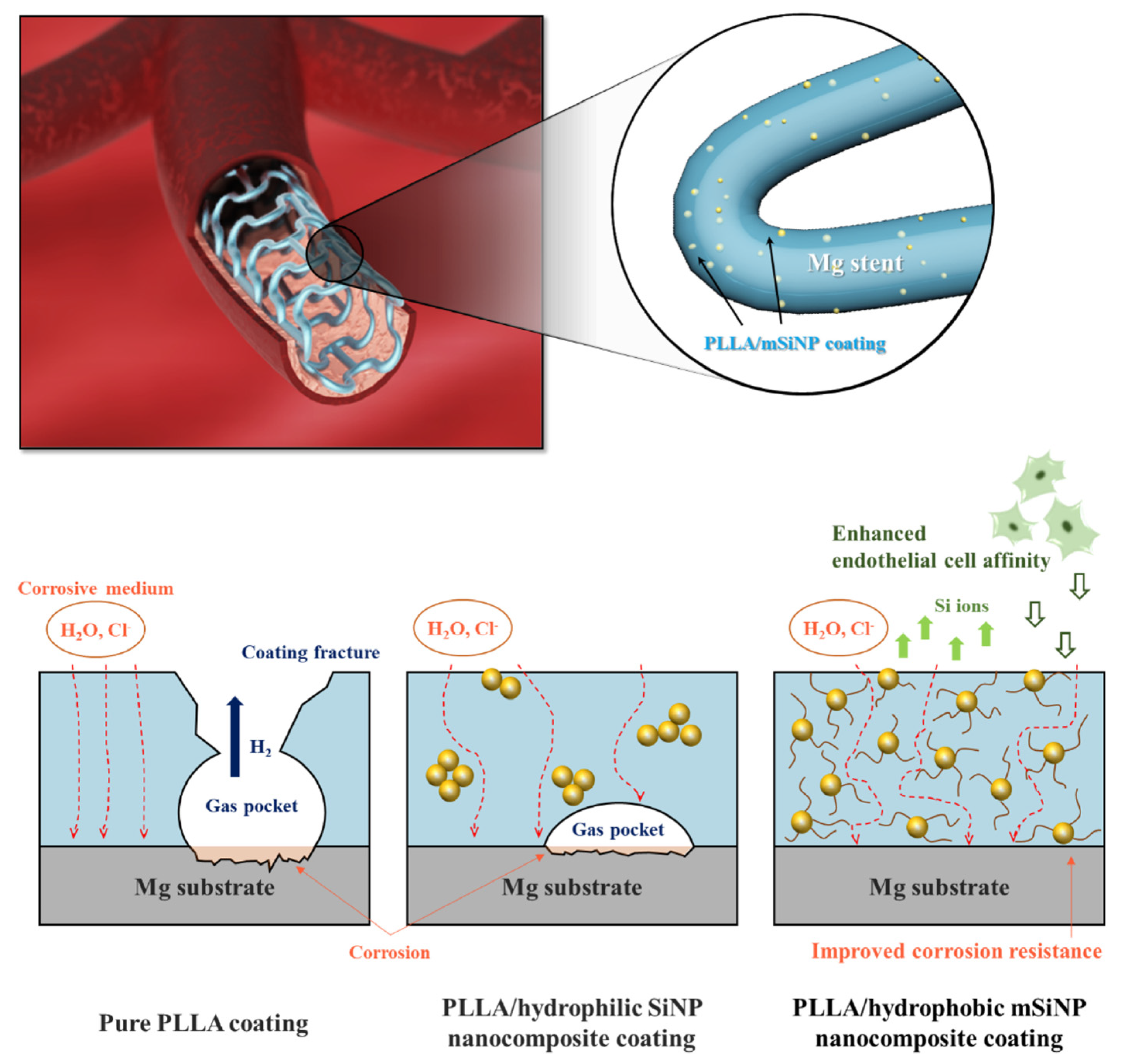
- Park, S.; Lee, H.; Kim, H.-E.; Jung, H.-D.; Jang, T.-S. Bifunctional Poly (l-Lactic Acid)/Hydrophobic Silica Nanocomposite Layer Coated on Magnesium Stents for Enhancing Corrosion Resistance and Endothelial Cell Responses. Materials Science and Engineering: C 2021, 127, 112239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Yagoshi, K.; Koga, Y.; Sasaki, M.; Niidome, T. Optimized Polymer Coating for Magnesium Alloy-Based Bioresorbable Scaffolds for Long-Lasting Drug Release and Corrosion Resistance. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces 2018, 163, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.N.; Cao, P.; Zhang, X.N.; Zhang, S.X.; He, Y.H. In Vitro Degradation and Cell Attachment of a PLGA Coated Biodegradable Mg–6Zn Based Alloy. J Mater Sci 2010, 45, 6038–6045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danhier, F.; Ansorena, E.; Silva, J.M.; Coco, R.; Le Breton, A.; Préat, V. PLGA-Based Nanoparticles: An Overview of Biomedical Applications. Journal of Controlled Release 2012, 161, 505–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
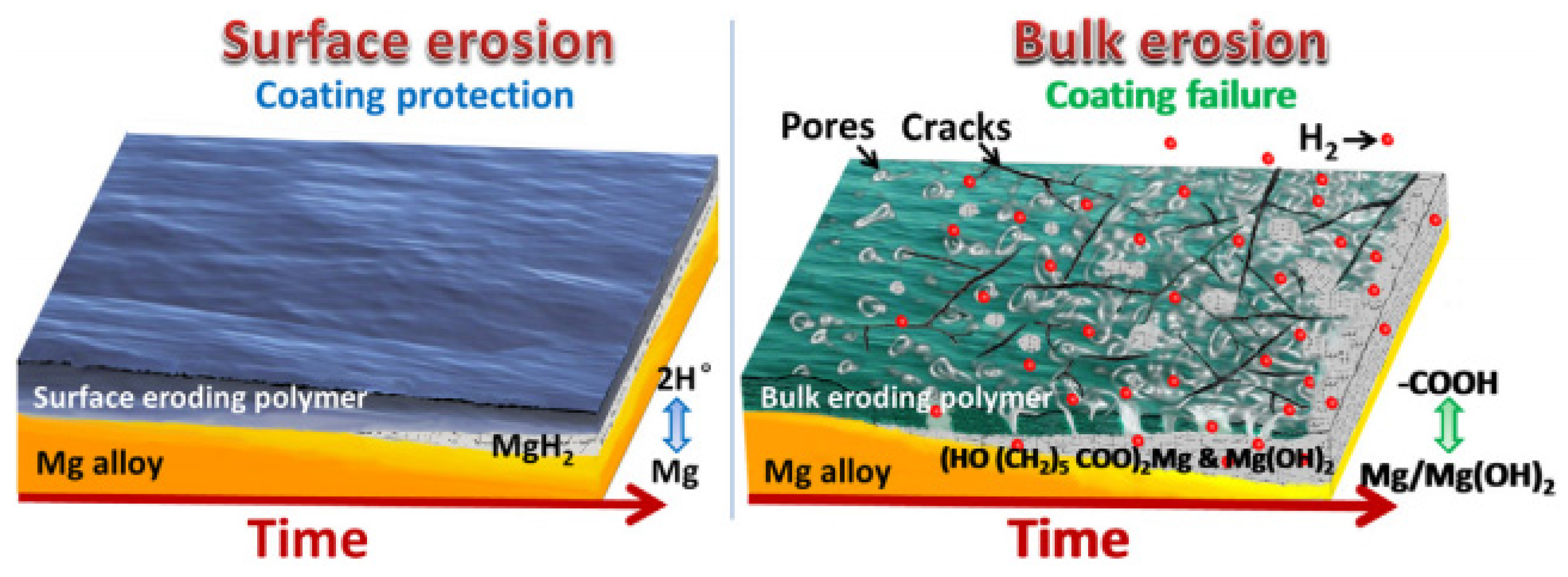
- Burkersroda, F. von; Schedl, L.; Göpferich, A. Why Degradable Polymers Undergo Surface Erosion or Bulk Erosion. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 4221–4231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.-H.; Cheon, K.-H.; Jo, K.-I.; Ahn, J.-H.; Kim, H.-E.; Jung, H.-D.; Jang, T.-S. An Asymmetric Surface Coating Strategy for Improved Corrosion Resistance and Vascular Compatibility of Magnesium Alloy Stents. Materials & Design 2020, 196, 109182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labet, M.; Thielemans, W. Synthesis of Polycaprolactone: A Review. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dash, T.K.; Konkimalla, V.B. Polymeric Modification and Its Implication in Drug Delivery: Poly-ε-Caprolactone (PCL) as a Model Polymer. Mol. Pharmaceutics 2012, 9, 2365–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazdimamaghani, M.; Razavi, M.; Vashaee, D.; Tayebi, L. Surface Modification of Biodegradable Porous Mg Bone Scaffold Using Polycaprolactone/Bioactive Glass Composite. Materials Science and Engineering: C 2015, 49, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, H.M.; Yeung, K.W.K.; Lam, K.O.; Tam, V.; Chu, P.K.; Luk, K.D.K.; Cheung, K.M.C. A Biodegradable Polymer-Based Coating to Control the Performance of Magnesium Alloy Orthopaedic Implants. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 2084–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knigge, S.; Mueller, M.; Fricke, L.; Schilling, T.; Glasmacher, B. In Vitro Investigation of Corrosion Control of Magnesium with Degradable Polycaprolactone Coatings for Cardiovascular Grafts. Coatings 2023, 13, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Yamamoto, A. Characteristics and Cytocompatibility of Biodegradable Polymer Film on Magnesium by Spin Coating. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces 2012, 93, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, K. Poly(Trimethylene Carbonate)-Based Polymers Engineered for Biodegradable Functional Biomaterials. Biomater. Sci. 2016, 4, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Kuijer, R.; Bulstra, S.K.; Grijpma, D.W.; Feijen, J. The in Vivo and in Vitro Degradation Behavior of Poly(Trimethylene Carbonate). Biomaterials 2006, 27, 1741–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; He, Y.; Maitz, M.F.; Collins, B.; Xiong, K.; Guo, L.; Yun, Y.; Wan, G.; Huang, N. A Surface-Eroding Poly(1,3-Trimethylene Carbonate) Coating for Fully Biodegradable Magnesium-Based Stent Applications: Toward Better Biofunction, Biodegradation and Biocompatibility. Acta Biomaterialia 2013, 9, 8678–8689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zong, L.; Liu, C.; Wang, C.; Qi, C.; Wang, N.; Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Jian, X. Dual Strengthened Corrosion Control of Biodegradable Coating on Magnesium Alloy for Vascular Stent Application. Progress in Organic Coatings 2023, 174, 107297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zong, L.; Liu, C.; Ding, W.; Zhu, L.; Qi, C.; Wang, C.; Shao, S.; Wang, J.; Jian, X. Strengthened Corrosion Control of Biodegradable Poly(Trimethylene Carbonate) Coating on Bioabsorbable Mg Alloy by Introducing Graphene Oxide. Surface and Coatings Technology 2022, 451, 129052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Li, S.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, C.; Gu, X.; Fan, Y. A Surface-Eroding Poly(1,3-Trimethylene Carbonate) Coating for Magnesium Based Cardiovascular Stents with Stable Drug Release and Improved Corrosion Resistance. Bioactive Materials 2022, 7, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Wang, J.; Zhao, A.; He, D.; Maitz, M.F.; Zhou, N.; Huang, N. Atorvastatin Eluting Coating for Magnesium-Based Stents: Control of Degradation and Endothelialization in a Microfluidic Assay and In Vivo. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2020, 5, 1900947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ye, S.; Zhu, Y.; Gu, X.; Higuchi, S.; Wan, G.; Wagner, W.R. Covalently-Attached, Surface-Eroding Polymer Coatings on Magnesium Alloys for Corrosion Control and Temporally Varying Support of Cell Adhesion. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 7, 2000356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Guan, J.; Fujimoto, K.L.; Hashizume, R.; Pelinescu, A.L.; Wagner, W.R. Tailoring the Degradation Kinetics of Poly(Ester Carbonate Urethane)Urea Thermoplastic Elastomers for Tissue Engineering Scaffolds. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 4249–4258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, X.; Mao, Z.; Ye, S.-H.; Koo, Y.; Yun, Y.; Tiasha, T.R.; Shanov, V.; Wagner, W.R. Biodegradable, Elastomeric Coatings with Controlled Anti-Proliferative Agent Release for Magnesium-Based Cardiovascular Stents. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces 2016, 144, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wang, P.; Chu, C.-C.; Xi, T. A Novel Biodegradable and Biologically Functional Arginine-Based Poly(Ester Urea Urethane) Coating for Mg–Zn–Y–Nd Alloy: Enhancement in Corrosion Resistance and Biocompatibility. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 1787–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wang, P.; Chu, C.-C.; Xi, T. Arginine-Leucine Based Poly (Ester Urea Urethane) Coating for Mg-Zn-Y-Nd Alloy in Cardiovascular Stent Applications. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces 2017, 159, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Chu, C.-C. A New Family of Functional Biodegradable Arginine-Based Polyester Urea Urethanes: Synthesis, Chracterization and Biodegradation. Polymer 2013, 54, 4112–4125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
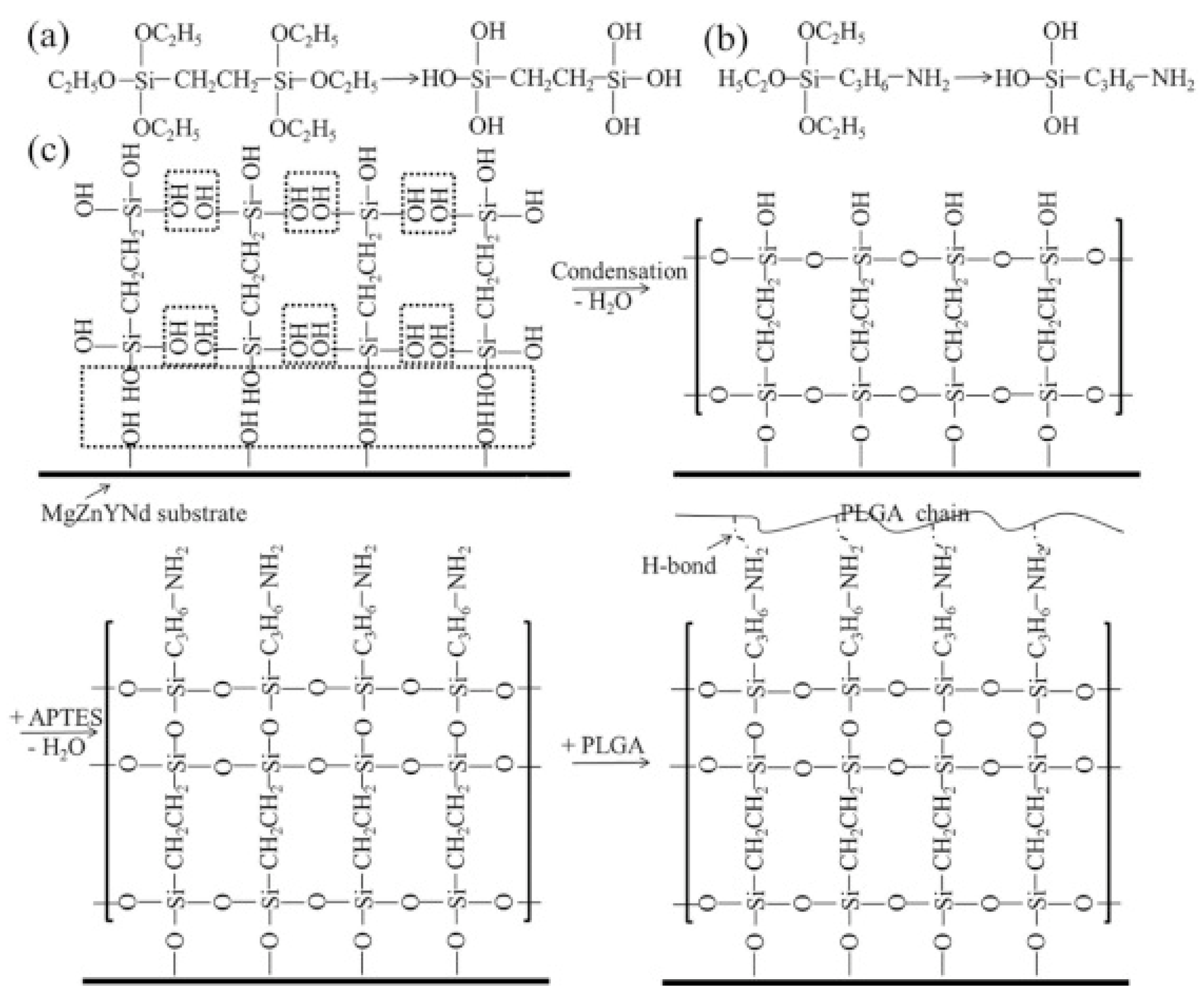
- Liu, J.; Zheng, B.; Wang, P.; Wang, X.; Zhang, B.; Shi, Q.; Xi, T.; Chen, M.; Guan, S. Enhanced in Vitro and in Vivo Performance of Mg–Zn–Y–Nd Alloy Achieved with APTES Pretreatment for Drug-Eluting Vascular Stent Application. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 17842–17858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Xi, T. Enhanced Anti-Corrosion Ability and Biocompatibility of PLGA Coatings on MgZnYNd Alloy by BTSE-APTES Pre-Treatment for Cardiovascular Stent. Journal of Materials Science & Technology 2016, 32, 845–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
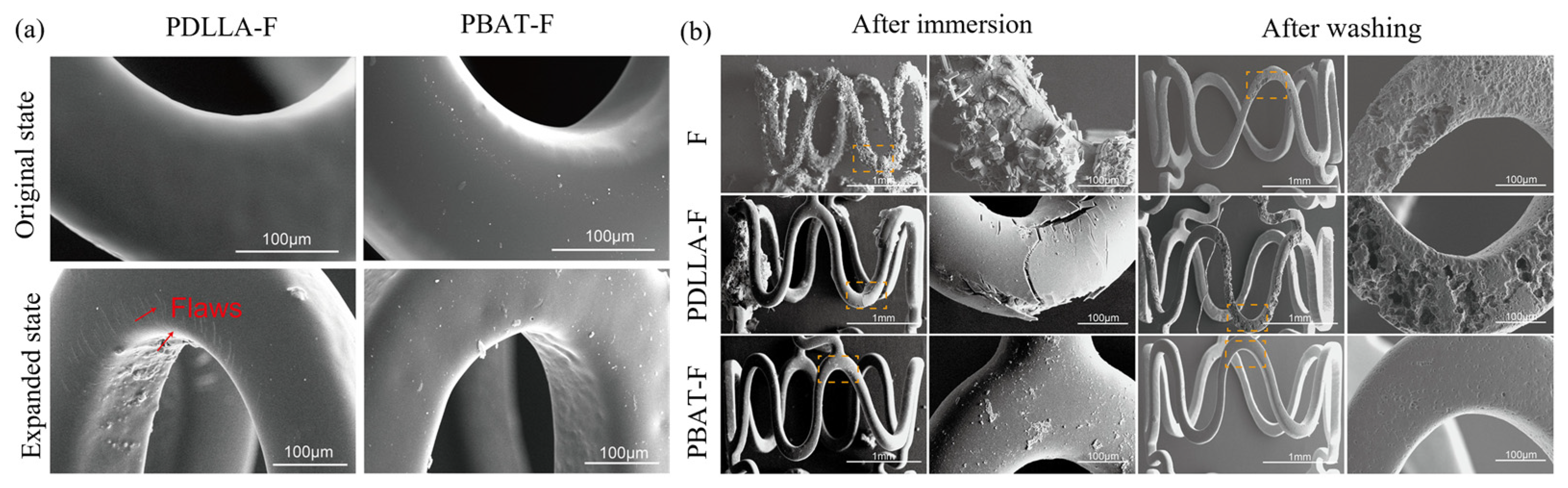
- Shi, L.; Chen, S.; Zheng, F.; Liu, M.; Yang, H.; Zhang, B. Corrosion Resistance Evaluation of Biodegradable Magnesium Alloy Vascular Stents Optimized by Mechanical Adapted Polymer Coating Strategy. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects 2023, 658, 130664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Chen, s. s; Shahzad, M.B.; Wei, Z.; Leng, B. Enhanced Corrosion Resistance and Biocompatibility of an Elastic Poly (Butyleneadipate-Co-Terephthalate) Composite Coating for AZ31 Magnesium Alloy Vascular Stents. Progress in Organic Coatings 2022, 172, 107138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, S.H.; Park, C.B. Human Endothelial Cell Growth on Mussel-Inspired Nanofiber Scaffold for Vascular Tissue Engineering. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 9431–9437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.-L.; Ren, K.-F.; Chang, H.; Jia, F.; Li, B.-C.; Ji, Y.; Ji, J. Direct Adhesion of Endothelial Cells to Bioinspired Poly(Dopamine) Coating Through Endogenous Fibronectin and Integrin A5β1. Macromolecular Bioscience 2013, 13, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Tu, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Luo, R.; Li, X.; Xie, Y.; Maitz, M.F.; Wang, J.; Huang, N. Mussel-Inspired Coating of Polydopamine Directs Endothelial and Smooth Muscle Cell Fate for Re-Endothelialization of Vascular Devices. Advanced Healthcare Materials 2012, 1, 548–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbell, J.A.; Massia, S.P.; Desai, N.P.; Drumheller, P.D. Endothelial Cell-Selective Materials for Tissue Engineering in the Vascular Graft Via a New Receptor. Nat Biotechnol 1991, 9, 568–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Li, J.; Wang, S.; Zhu, S.; Zhu, C.; Zheng, B.; Yang, G.; Guan, S. Surface Modification of the Biodegradable Cardiovascular Stent Material Mg–Zn–Y–Nd Alloy via Conjugating REDV Peptide for Better Endothelialization. J. Mater. Res. 2018, 33, 4123–4133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Zhu, S.; Wang, L.; Guan, S. Preparation of Functional Coating on Magnesium Alloy with Hydrophilic Polymers and Bioactive Peptides for Improved Corrosion Resistance and Biocompatibility. Journal of Magnesium and Alloys 2022, 10, 1957–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-Q.; Tong, P.-D.; Wang, L.; Qiu, Z.-H.; Li, J.-A.; Li, H.; Guan, S.-K.; Lin, C.-G.; Wang, H.-Y. One-Step Fabrication of Self-Healing Poly(Thioctic Acid) Coatings on ZE21B Mg Alloys for Enhancing Corrosion Resistance, Anti-Bacterial/Oxidation, Hemocompatibility and Promoting Re-Endothelialization. Chemical Engineering Journal 2023, 451, 139096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Qi, X.; Wang, T.; Ren, L.; Yang, K.; Zhong, H. In Vitro Study of Stimulation Effect on Endothelialization by a Copper Bearing Cobalt Alloy. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A 2018, 106, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Ma, J.; Kang, S.; Chen, S. Copper-Loaded Chitosan Coating for Improved in-Vitro Corrosion Resistance and Endothelialization of Magnesium Alloy Stents. Materials Chemistry and Physics 2023, 305, 127931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
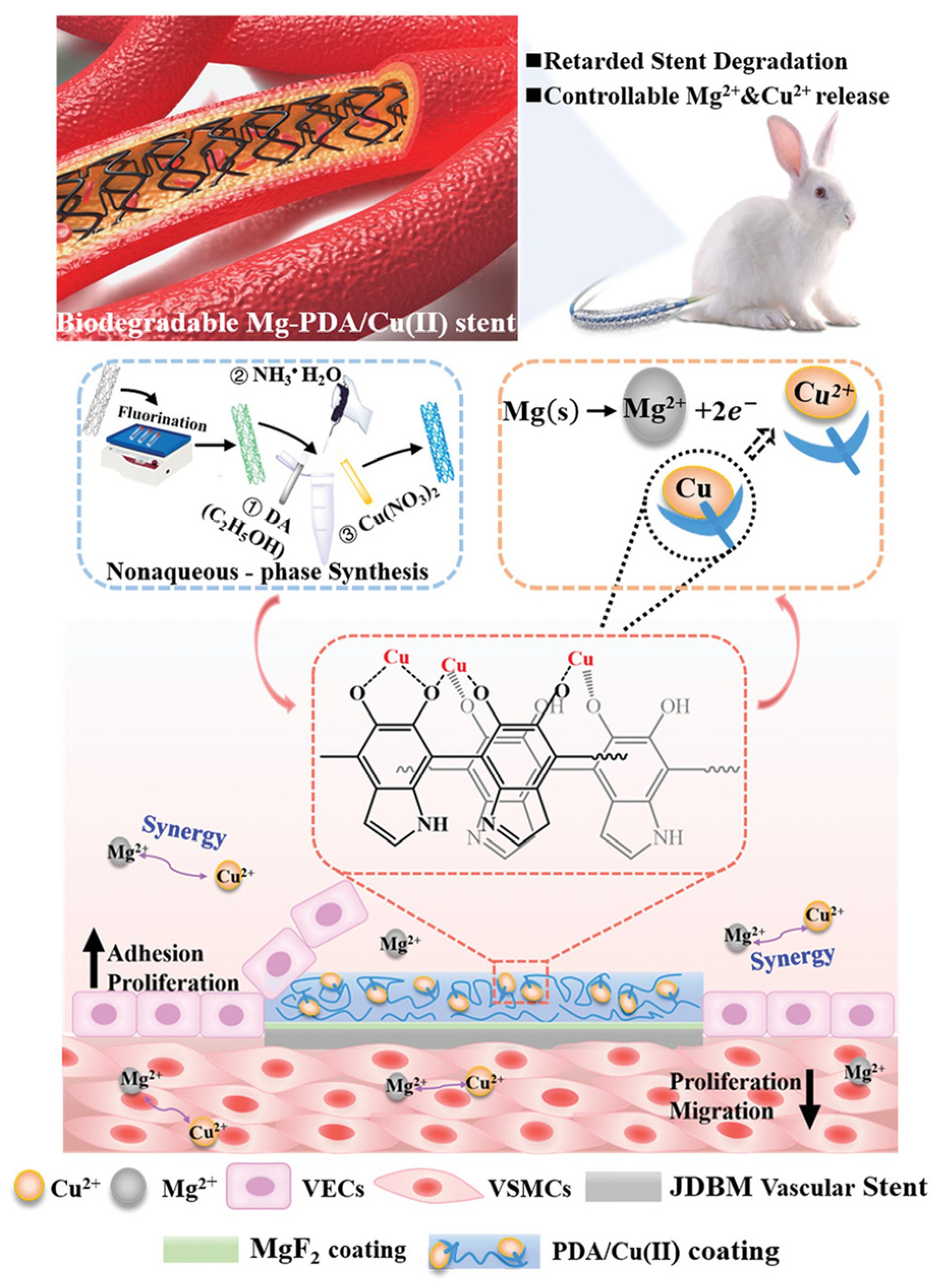
- Li, L.-Y.; Yang, Z.; Pan, X.-X.; Feng, B.-X.; Yue, R.; Yu, B.; Zheng, Y.-F.; Tan, J.-Y.; Yuan, G.-Y.; Pei, J. Incorporating Copper to Biodegradable Magnesium Alloy Vascular Stents via a Cu(II)-Eluting Coating for Synergistic Enhancement in Prolonged Durability and Rapid Re-Endothelialization. Advanced Functional Materials 2022, 32, 2205634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




