Submitted:
20 November 2023
Posted:
21 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Search Strategy
3. Autoimmune Diseases
4. Infectious Diseases
5. Cancer
6. Other Diseases
7. New Advances in Therapeutic Strategies
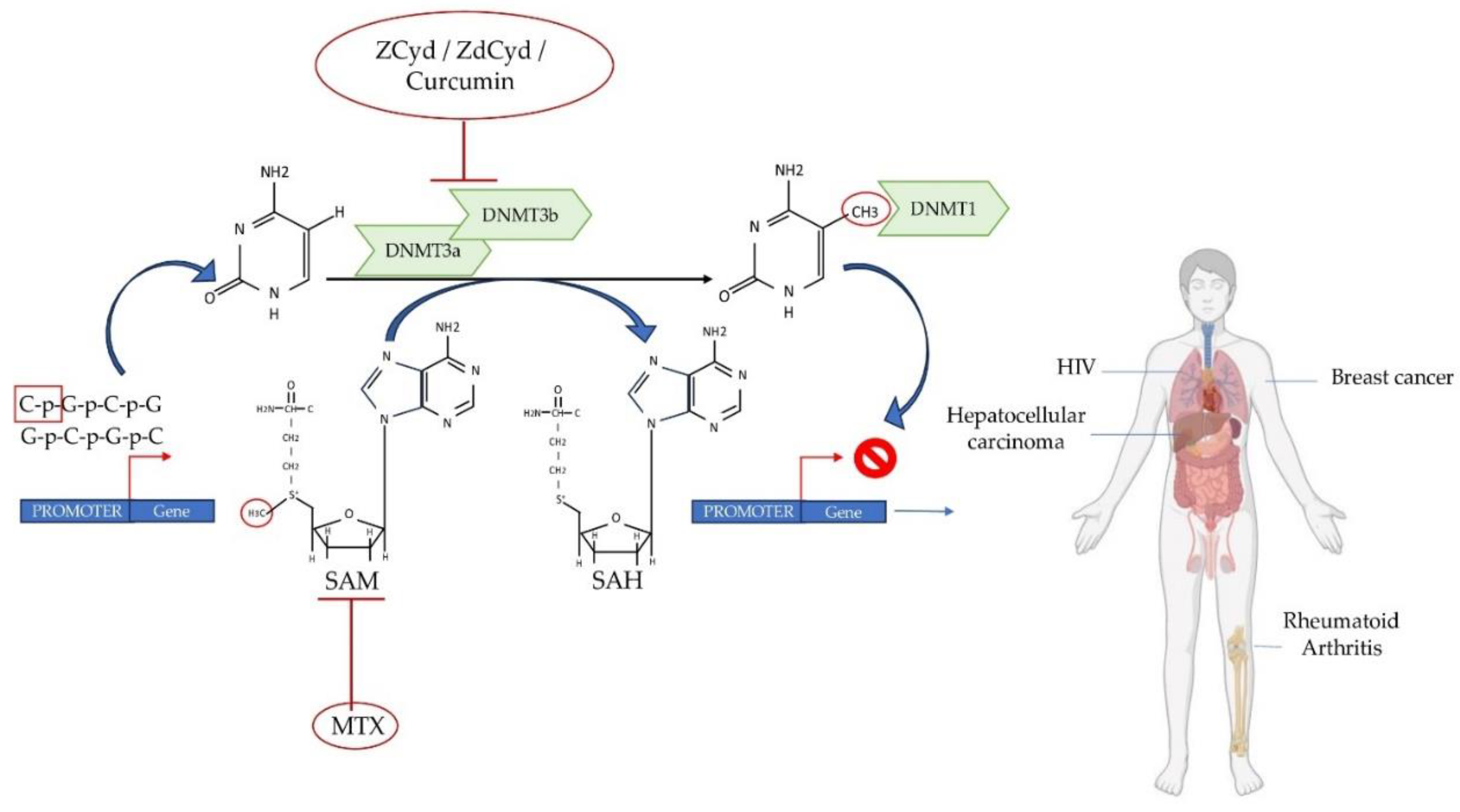
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Christakos, S.; Dhawan, P.; Verstuyf, A.; Verlinden, L.; Carmeliet, G. Vitamin D: Metabolism, Molecular Mechanism of Action, and Pleiotropic Effects. Physiol Rev 2016, 96, 365–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portales-Castillo, I.; Simic, P. PTH, FGF-23, Klotho and Vitamin D as Regulators of Calcium and Phosphorus: Genetics, Epigenetics and Beyond. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2022, 13, 992666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saccone, D.; Asani, F.; Bornman, L. Regulation of the Vitamin D Receptor Gene by Environment, Genetics and Epigenetics. Gene 2015, 561, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haussler, M.R.; Whitfield, G.K.; Kaneko, I.; Haussler, C.A.; Hsieh, D.; Hsieh, J.-C.; Jurutka, P.W. Molecular Mechanisms of Vitamin D Action. Calcif Tissue Int 2013, 92, 77–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pike, J.W.; Meyer, M.B. The Vitamin D Receptor: New Paradigms for the Regulation of Gene Expression by 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D(3). Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 2010, 39, 255–269, table of contents. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, K.; Kesterson, R.A.; Yamamoto, H.; Taketani, Y.; Nishiwaki, E.; Tatsumi, S.; Inoue, Y.; Morita, K.; Takeda, E.; Pike, J.W. Structural Organization of the Human Vitamin D Receptor Chromosomal Gene and Its Promoter. Mol Endocrinol 1997, 11, 1165–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jehan, F.; d’Alésio, A.; Garabédian, M. Exons and Functional Regions of the Human Vitamin D Receptor Gene around and within the Main 1a Promoter Are Well Conserved among Mammals. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 2007, 103, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.H. Vitamin D Signaling, Infectious Diseases, and Regulation of Innate Immunity. Infect Immun 2008, 76, 3837–3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, L.D.; Le, T.; Fan, G. DNA Methylation and Its Basic Function. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013, 38, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bock, C.; Walter, J.; Paulsen, M.; Lengauer, T. CpG Island Mapping by Epigenome Prediction. PLoS Comput Biol 2007, 3, e110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, V.; Saccone, D.S.; Tugizimana, F.; Asani, F.F.; Jeffery, T.J.; Bornman, L. Methylation of the Vitamin D Receptor (VDR) Gene, Together with Genetic Variation, Race, and Environment Influence the Signaling Efficacy of the Toll-Like Receptor 2/1-VDR Pathway. Front Immunol 2017, 8, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruthai, K.; Sankar, S.; Subramanian, M. Methylation Status of VDR Gene and Its Association with Vitamin D Status and VDR Gene Expression in Pediatric Tuberculosis Disease. Immunol Invest 2022, 51, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murdaca, G.; Tonacci, A.; Negrini, S.; Greco, M.; Borro, M.; Puppo, F.; Gangemi, S. Emerging Role of Vitamin D in Autoimmune Diseases: An Update on Evidence and Therapeutic Implications. Autoimmun Rev 2019, 18, 102350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dardalhon, V.; Korn, T.; Kuchroo, V.K.; Anderson, A.C. Role of Th1 and Th17 Cells in Organ-Specific Autoimmunity. J Autoimmun 2008, 31, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szodoray, P.; Nakken, B.; Gaal, J.; Jonsson, R.; Szegedi, A.; Zold, E.; Szegedi, G.; Brun, J.G.; Gesztelyi, R.; Zeher, M.; et al. The Complex Role of Vitamin D in Autoimmune Diseases. Scand J Immunol 2008, 68, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Illescas-Montes, R.; Melguizo-Rodríguez, L.; Ruiz, C.; Costela-Ruiz, V.J. Vitamin D and Autoimmune Diseases. Life Sci 2019, 233, 116744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ao, T.; Kikuta, J.; Ishii, M. The Effects of Vitamin D on Immune System and Inflammatory Diseases. Biomolecules 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, J.; Bishop, E.L.; Harrison, S.R.; Swift, A.; Cooper, S.C.; Dimeloe, S.K.; Raza, K.; Hewison, M. Autoimmune Disease and Interconnections with Vitamin D. Endocr Connect 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puncevičienė, E.; Gaiževska, J.; Sabaliauskaitė, R.; Šnipaitienė, K.; Vencevičienė, L.; Vitkus, D.; Jarmalaitė, S.; Butrimienė, I. Analysis of Epigenetic Changes in Vitamin D Pathway Genes in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients. Acta Med Litu 2022, 29, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayuso, T.; Aznar, P.; Soriano, L.; Olaskoaga, A.; Roldán, M.; Otano, M.; Ajuria, I.; Soriano, G.; Lacruz, F.; Mendioroz, M. Vitamin D Receptor Gene Is Epigenetically Altered and Transcriptionally Up-Regulated in Multiple Sclerosis. PLoS One 2017, 12, e0174726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulur, I.; Onder, M. Behçet Disease: New Aspects. Clin Dermatol 2017, 35, 421–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firestein, G.S. PATHOGENESIS OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS: THE INTERSECTION OF GENETICS AND EPIGENETICS. Trans Am Clin Climatol Assoc 2018, 129, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.-P.; Li, H.-M.; Huang, Q.; Wang, L.; Li, X.-M. Vitamin D Metabolic Pathway Genes Polymorphisms and Their Methylation Levels in Association With Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front Immunol 2021, 12, 731565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scazzone, C.; Agnello, L.; Bivona, G.; Lo Sasso, B.; Ciaccio, M. Vitamin D and Genetic Susceptibility to Multiple Sclerosis. Biochem Genet 2021, 59, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamout, B.I.; Alroughani, R. Multiple Sclerosis. Semin Neurol 2018, 38, 212–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, R.; Giovannoni, G. Multiple Sclerosis - a Review. Eur J Neurol 2019, 26, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirvani, S.S.; Nouri, M.; Sakhinia, E.; Babaloo, Z.; Jadideslam, G.; Shahriar, A.; Farhadi, J.; Khabbazi, A. The Expression and Methylation Status of Vitamin D Receptor Gene in Behcet’s Disease. Immun Inflamm Dis 2019, 7, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Zhu, J.; Liu, Y.; Luan, X.; Jiang, Y.; Jiang, G.; Fan, J. The Methylation State of VDR Gene in Pulmonary Tuberculosis Patients. J Thorac Dis 2017, 9, 4353–4357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Kong, W.; He, B.; Li, Z.; Song, H.; Shi, P.; Wang, J. Vitamin D and the Promoter Methylation of Its Metabolic Pathway Genes in Association with the Risk and Prognosis of Tuberculosis. Clin Epigenetics 2018, 10, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-P.; Deng, H.-L.; Wang, W.-J.; Wang, M.-Q.; Li, M.; Zhang, Y.-F.; Wang, J.; Dang, S.-S. Vitamin D Receptor Gene Methylation in Patients with Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease Caused by Enterovirus 71. Arch Virol 2020, 165, 1979–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandel, N.; Husain, M.; Goel, H.; Salhan, D.; Lan, X.; Malhotra, A.; McGowan, J.; Singhal, P.C. VDR Hypermethylation and HIV-Induced T Cell Loss. J Leukoc Biol 2013, 93, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marik, R.; Fackler, M.; Gabrielson, E.; Zeiger, M.A.; Sukumar, S.; Stearns, V.; Umbricht, C.B. DNA Methylation-Related Vitamin D Receptor Insensitivity in Breast Cancer. Cancer Biol Ther 2010, 10, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilon, C.; Rebellato, A.; Urbanet, R.; Guzzardo, V.; Cappellesso, R.; Sasano, H.; Fassina, A.; Fallo, F. Methylation Status of Vitamin D Receptor Gene Promoter in Benign and Malignant Adrenal Tumors. Int J Endocrinol 2015, 2015, 375349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, M.; Khairy, E.; Louka, M.L.; Ali-Labib, R.; Ibrahim, E.A.-S. Vitamin D Receptor Gene Methylation in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gene 2018, 653, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varshney, S.; Bhadada, S.K.; Sachdeva, N.; Arya, A.K.; Saikia, U.N.; Behera, A.; Rao, S.D. Methylation Status of the CpG Islands in Vitamin D and Calcium-Sensing Receptor Gene Promoters Does Not Explain the Reduced Gene Expressions in Parathyroid Adenomas. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2013, 98, E1631–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afshan, F.U.; Masood, A.; Nissar, B.; Chowdri, N.A.; Naykoo, N.A.; Majid, M.; Ganai, B.A. Promoter Hypermethylation Regulates Vitamin D Receptor (VDR) Expression in Colorectal Cancer-A Study from Kashmir Valley. Cancer Genet 2021, 252–253, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasperini, B.; Visconti, V.V.; Ciccacci, C.; Falvino, A.; Gasbarra, E.; Iundusi, R.; Brandi, M.L.; Botta, A.; Tarantino, U. Role of the Vitamin D Receptor (VDR) in the Pathogenesis of Osteoporosis: A Genetic, Epigenetic and Molecular Pilot Study. Genes (Basel) 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vladoiu, S.; Botezatu, A.; Anton, G.; Manda, D.; Paun, D.L.; Oros, S.; Rosca, R.; Dinu Draganescu, D. THE INVOLVEMENT OF VDR PROMOTER METHYLATION, CDX-2 VDR POLYMORPHISM AND VITAMIN D LEVELS IN MALE INFERTILITY. Acta Endocrinol (Buchar) 2017, 13, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, T.M.; Eldabah, N.; Zayed, H.A.; Genedy, R.M. Assessment of Serum Vitamin D Level and Seminal Vitamin D Receptor Gene Methylation in a Sample of Egyptian Men with Idiopathic Infertility. Andrologia 2021, 53, e14172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatami, F.; Gorji, A.; Khoshchehreh, M.; Mashhadi, R.; Pishkuhi, M.A.; Khajavi, A.; Shabestari, A.N.; Aghamir, S.M.K. The Correlation between Promoter Hypermethylation of VDR, CLDN, and CasR Genes and Recurrent Stone Formation. BMC Med Genomics 2022, 15, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Feng, Y.; Qu, C.; Yu, F.; Mao, Z.; Wang, C.; Li, W.; Li, X. Vitamin D Receptor Methylation Attenuates the Association between Physical Activity and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Case-Control Study. J Diabetes 2022, 14, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, G.; Singh, P.; Varma-Basil, M.; Bose, M. Role of Vitamins B, C, and D in the Fight against Tuberculosis. Int J Mycobacteriol 2017, 6, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.-P.; Deng, H.-L.; Xu, L.-H.; Wang, M.-Q.; Li, M.; Zhang, X.; Dang, S.-S. Association of Polymorphisms in the Vitamin D Receptor Gene with Severity of Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease Caused by Enterovirus 71. J Med Virol 2019, 91, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youssef, D.A.; Miller, C.W.; El-Abbassi, A.M.; Cutchins, D.C.; Cutchins, C.; Grant, W.B.; Peiris, A.N. Antimicrobial Implications of Vitamin D. Dermatoendocrinol 2011, 3, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, J.H. Emerging Roles of Vitamin D-Induced Antimicrobial Peptides in Antiviral Innate Immunity. Nutrients 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peric, M.; Koglin, S.; Kim, S.-M.; Morizane, S.; Besch, R.; Prinz, J.C.; Ruzicka, T.; Gallo, R.L.; Schauber, J. IL-17A Enhances Vitamin D3-Induced Expression of Cathelicidin Antimicrobial Peptide in Human Keratinocytes. J Immunol 2008, 181, 8504–8512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, C.A.; Fernandes, D.C.R.O.; Braga, A.C.O.; Cavalcante, G.C.; Sortica, V.A.; Hutz, M.H.; Leal, D.F.V.B.; Fernades, M.R.; Santana-da-Silva, M.N.; Lopes Valente, S.E.; et al. Investigation of Genetic Susceptibility to Mycobacterium Tuberculosis (VDR and IL10 Genes) in a Population with a High Level of Substructure in the Brazilian Amazon Region. Int J Infect Dis 2020, 98, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Möller, M.; de Wit, E.; Hoal, E.G. Past, Present and Future Directions in Human Genetic Susceptibility to Tuberculosis. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 2010, 58, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Yin, W.; Xie, D.; He, W.; Jiang, G.; Fan, J. 5-Aza-2′-Deoxycytidine Enhances the Antimicrobial Response of Vitamin D Receptor against Mycobacterium Tuberculosis. RSC Adv 2016, 6, 61740–61746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patton, L.L. HIV Disease. Dent Clin North Am 2003, 47, 467–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, M.R.I.; Xiong, Y. Influence of Vitamin D on Cancer Risk and Treatment: Why the Variability? Trends Cancer Res 2018, 13, 43–53. [Google Scholar]
- Chiang, K.-C.; Yeh, C.-N.; Chen, M.-F.; Chen, T.C. Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Vitamin D: A Review. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2011, 26, 1597–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, M.un N.; Khan, T.A.; Maqbool, S.A. Vitamin D Receptor Cdx-2 Polymorphism and Premenopausal Breast Cancer Risk in Southern Pakistani Patients. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0122657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larriba, M.J.; González-Sancho, J.M.; Barbáchano, A.; Niell, N.; Ferrer-Mayorga, G.; Muñoz, A. Vitamin D Is a Multilevel Repressor of Wnt/b-Catenin Signaling in Cancer Cells. Cancers (Basel) 2013, 5, 1242–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toropainen, S.; Väisänen, S.; Heikkinen, S.; Carlberg, C. The Down-Regulation of the Human MYC Gene by the Nuclear Hormone 1alpha,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 Is Associated with Cycling of Corepressors and Histone Deacetylases. J Mol Biol 2010, 400, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larriba, M.J.; Valle, N.; Pálmer, H.G.; Ordóñez-Morán, P.; Alvarez-Díaz, S.; Becker, K.-F.; Gamallo, C.; de Herreros, A.G.; González-Sancho, J.M.; Muñoz, A. The Inhibition of Wnt/Beta-Catenin Signalling by 1alpha,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 Is Abrogated by Snail1 in Human Colon Cancer Cells. Endocr Relat Cancer 2007, 14, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fetahu, I.S.; Höbaus, J.; Kállay, E. Vitamin D and the Epigenome. Front Physiol 2014, 5, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilon, C.; Urbanet, R.; Williams, T.A.; Maekawa, T.; Vettore, S.; Sirianni, R.; Pezzi, V.; Mulatero, P.; Fassina, A.; Sasano, H.; et al. 1α,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D₃ Inhibits the Human H295R Cell Proliferation by Cell Cycle Arrest: A Model for a Protective Role of Vitamin D Receptor against Adrenocortical Cancer. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 2014, 140, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łukasiewicz, S.; Czeczelewski, M.; Forma, A.; Baj, J.; Sitarz, R.; Stanisławek, A. Breast Cancer-Epidemiology, Risk Factors, Classification, Prognostic Markers, and Current Treatment Strategies-An Updated Review. Cancers (Basel) 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzaman, K.; Karami, J.; Zarei, Z.; Hosseinzadeh, A.; Kazemi, M.H.; Moradi-Kalbolandi, S.; Safari, E.; Farahmand, L. Breast Cancer: Biology, Biomarkers, and Treatments. Int Immunopharmacol 2020, 84, 106535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segovia-Mendoza, M.; García-Quiroz, J.; Díaz, L.; García-Becerra, R. Combinations of Calcitriol with Anticancer Treatments for Breast Cancer: An Update. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerario, A.M.; Moraitis, A.; Hammer, G.D. Genetics and Epigenetics of Adrenocortical Tumors. Mol Cell Endocrinol 2014, 386, 67–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, B.; Wang, Y.; Xekouki, P.; Faucz, F.R.; Jain, M.; Zhang, L.; Meltzer, P.G.; Stratakis, C.A.; Kebebew, E. Integrated Analysis of Genome-Wide Methylation and Gene Expression Shows Epigenetic Regulation of CYP11B2 in Aldosteronomas. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2014, 99, E536–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayers, D.; Boughanem, H.; Macías-González, M. Epigenetic Influences in the Obesity/Colorectal Cancer Axis: A Novel Theragnostic Avenue. J Oncol 2019, 2019, 7406078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verlinden, L.; Carmeliet, G. Integrated View on the Role of Vitamin D Actions on Bone and Growth Plate Homeostasis. JBMR Plus 2021, 5, e10577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamczewska, D.; Słowikowska-Hilczer, J.; Walczak-Jędrzejowska, R. The Association between Vitamin D and the Components of Male Fertility: A Systematic Review. Biomedicines 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymczak-Pajor, I.; Śliwińska, A. Analysis of Association between Vitamin D Deficiency and Insulin Resistance. Nutrients 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letavernier, E.; Daudon, M. Vitamin D, Hypercalciuria and Kidney Stones. Nutrients 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Li, W.; Yang, X.; Na, L.; Chen, L.; Liu, G. The Roles of Epigenetics Regulation in Bone Metabolism and Osteoporosis. Front Cell Dev Biol 2020, 8, 619301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visconti, V.V.; Cariati, I.; Fittipaldi, S.; Iundusi, R.; Gasbarra, E.; Tarantino, U.; Botta, A. DNA Methylation Signatures of Bone Metabolism in Osteoporosis and Osteoarthritis Aging-Related Diseases: An Updated Review. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomberg Jensen, M.; Bjerrum, P.J.; Jessen, T.E.; Nielsen, J.E.; Joensen, U.N.; Olesen, I.A.; Petersen, J.H.; Juul, A.; Dissing, S.; Jørgensen, N. Vitamin D Is Positively Associated with Sperm Motility and Increases Intracellular Calcium in Human Spermatozoa. Hum Reprod 2011, 26, 1307–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, A.; Shabestari, A.N.; Baghdadabad, L.Z.; Khatami, F.; Reis, L.O.; Pishkuhi, M.A.; Kazem Aghamir, S.M. Genetic Polymorphisms and Kidney Stones Around the Globe: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front Genet 2022, 13, 913908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, L.S.; Nielsen, H.M.; Hansen, L.L. Epigenetics and Cancer Treatment. Eur J Pharmacol 2009, 625, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.C.; Yoo, C.B.; Weisenberger, D.J.; Chuang, J.; Wozniak, C.; Liang, G.; Marquez, V.E.; Greer, S.; Orntoft, T.F.; Thykjaer, T.; et al. Preferential Response of Cancer Cells to Zebularine. Cancer Cell 2004, 6, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanoodi, M.; Mittal, M. Methotrexate; 2023.
- Wang, Y.-C.; Chiang, E.-P.I. Low-Dose Methotrexate Inhibits Methionine S-Adenosyltransferase in Vitro and in Vivo. Mol Med 2012, 18, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christman, J.K. 5-Azacytidine and 5-Aza-2’-Deoxycytidine as Inhibitors of DNA Methylation: Mechanistic Studies and Their Implications for Cancer Therapy. Oncogene 2002, 21, 5483–5495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Kurzrock, R. Development of Curcumin as an Epigenetic Agent. Cancer 2010, 116, 4670–4676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, P.M.; Liu, Z.; Khong, H.T. Demethylating Agents in the Treatment of Cancer. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 2010, 3, 2022–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Disease | Sample Size | Method of Analysis | Genomic Context (VDR gene) |
Analysis Outcome | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Autoimmune diseases | Rheumatoid Arthritis | 122 RA vs 123 CTRs |
MethylTarget | CpG sites in the promoter region |
VDR methylation levels in RA patients were significantly reduced compared to CTRs |
[23] |
| 35 RA vs 41 CTRs |
Pyrosequencing | 10 CpG sites in the promoter region | Methylation analysis revealed no significant differences between RA patients compared to CTRs | [19] | ||
| Multiple Sclerosis |
23 RRMS
vs 12 CTRs |
Bisulfite cloning
sequencing |
23 CpG sites in main promoter 10 CpG sites in alternative promoter located at non-coding exon 1c | Methylation levels in VDR alternative promoter were significantly higher in RRMS patients compared to CTRs | [20] | |
| Behcet's disease | 48 BD vs 60 CTRs |
MeDIP-qPCR | All CpG sites in the promoter region from −800 bp to +200 bp relative to the TSS | Methylation analysis revealed no significant differences between BD patients compared to CTRs | [27] | |
| Infectious diseases | Tuberculosis disease | 27 TB vs 30 CTRs |
Bisulfite cloning
sequencing |
16 CpG sites in VDR | TB patients were in the hypermethylation state compared to CTRs | [28] |
| 43 TB vs 33 CTRs |
MS-PCR | The location of CpG sites and CGIs present in the VDR sequence were identified by DBCAT | Methylation analysis revealed an hypermethylation in TB patients and hypomethylation in CTRs | [12] | ||
| 122 TB vs 118 CTRs |
Illumina MiSeq | 60 CpG sites in the promoter region (48299590 - 48298885) |
Methylation levels were significantly lower in TB patients compared to CTRs | [29] | ||
| Hand, foot, and mouth disease | 116 HFMD vs 60 CTRs | MethylTarget | 12 CpG in promoter region from -638 bp to -545 bp relative to the TSS | Methylation levels of VDR promoter in HFMD were lower compared to CTRs | [30] | |
| HIV | TCs obtained from healthy volunteers | Pyrosequencing | CpG in VDR promoter region from -512 bp to -28 bp relative to the TSS | HIV-infected TCs showed increased methylation in CpG sites | [31] | |
|
Cancer |
Breast cancer | 15 BCT vs 7 NBT |
MS-PCR | 3 CGIs in VDR promoter region from -789 bp to +380 bp relative to the TSS | Methylation levels of VDR promoter in BCT were significantly higher compared to NBT | [32] |
| Adrenocortical carcinoma |
23 AT vs 3 NAT |
BSP | 42 CpG sites in VDR promoter region from -693 bp to -65 bp relative to the TSS | 27/42 CpG sites were methylated in 3 ACCs | [33] | |
| Hepatocellular carcinoma |
15 HC vs 15 CLD vs 15 NT | MS-PCR | VDR promoter | Methylation levels of VDR promoter in HCC were significantly higher compared to other studies groups | [34] | |
| Parathyroid adenomas |
15 PAT vs 4 NPT |
BSP | 31 CpG sites in VDR promoter region from -538 bp to -79 bp relative to the TSS | There was no significant methylation in the promoter region of VDR in parathyroid adenomatous tissues. | [35] | |
| Colorectal cancer |
75 CCT
vs 75 NE |
MS-PCR | VDR promoter | Hypermethylation of VDR was detected in 28 (37,33%) of 75 cases | [36] | |
| Others | Osteoporosis | 25 OP vs 25 CTRs |
Pyrosequencing | 6 CpG sites in VDR promoter | No statistically significant difference was found in the methylation pattern between OP and CTRs | [37] |
| Male infertility | 69 ID vs 37 CTRs |
MS-PCR | 3 CGIs in VDR promoter | VDR methylation percentage was increased with the severity of the diagnosis, correlating with lower sperm motility and concentration, and altered sperm morphology | [38] | |
| 60 IID vs 60 CTRs |
MS-PCR | 1 CGI in VDR promoter | Methylation levels of VDR promoter in IID were significantly higher compared to CTRs | [39] | ||
| Recurrent kidney stone formation |
30 consecutive recurrent kidney stone formers vs 30 CTRs | MS-HRM | 16 CpG sites in VDR promoter | Two VDR promoter regions was hypermethylated in patients with consecutive recurrent kidney stone formers compared to CTRs | [40] | |
|
Type 2 diabetes
mellitus |
272 T2DM vs 272 CTRs | MS-HRM | 27 CpG sites in VDR promoter | Increased methylation levels of VDR were associated with decreased levels of serum insulin |
[41] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





