Submitted:
27 October 2023
Posted:
30 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
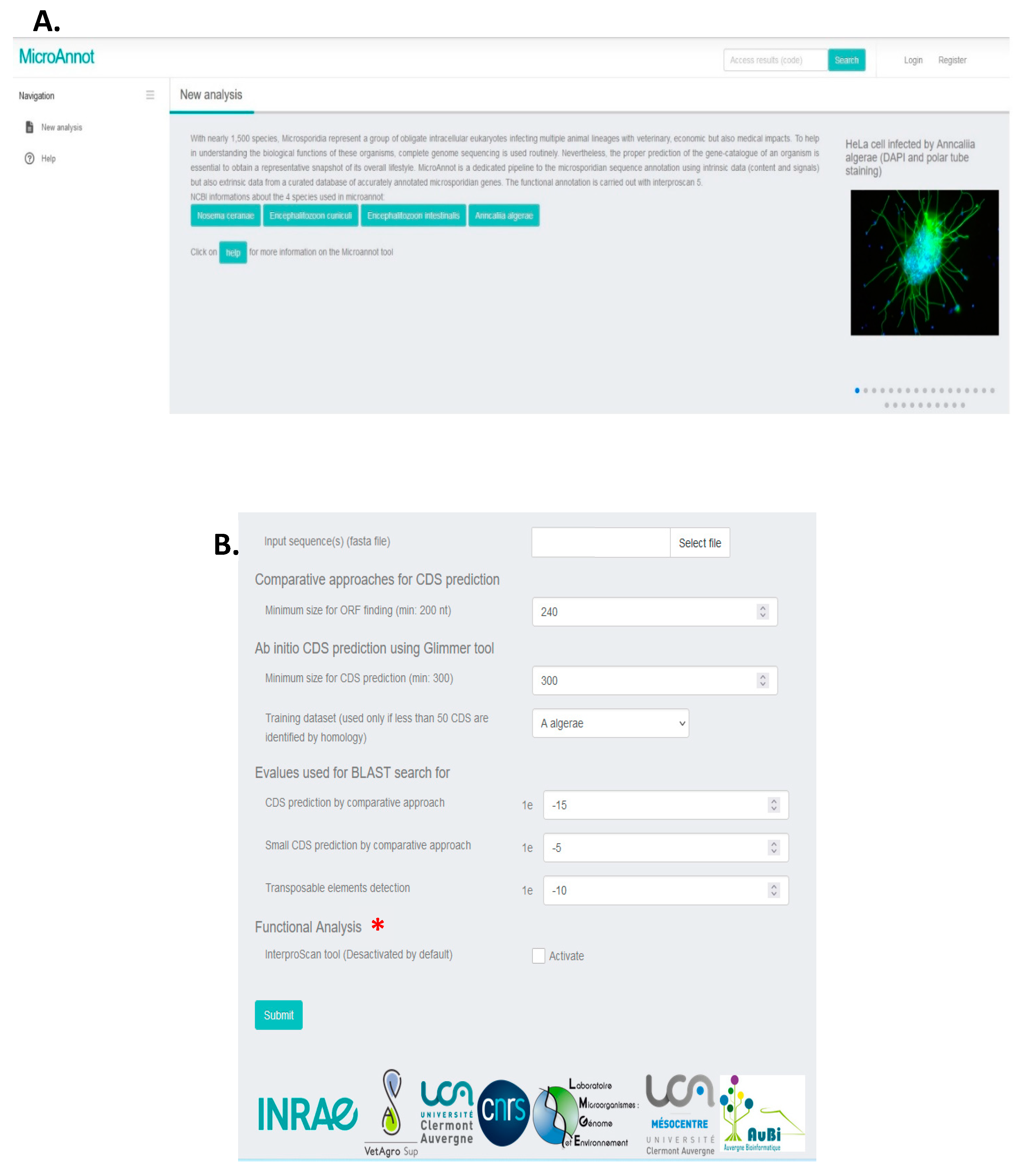
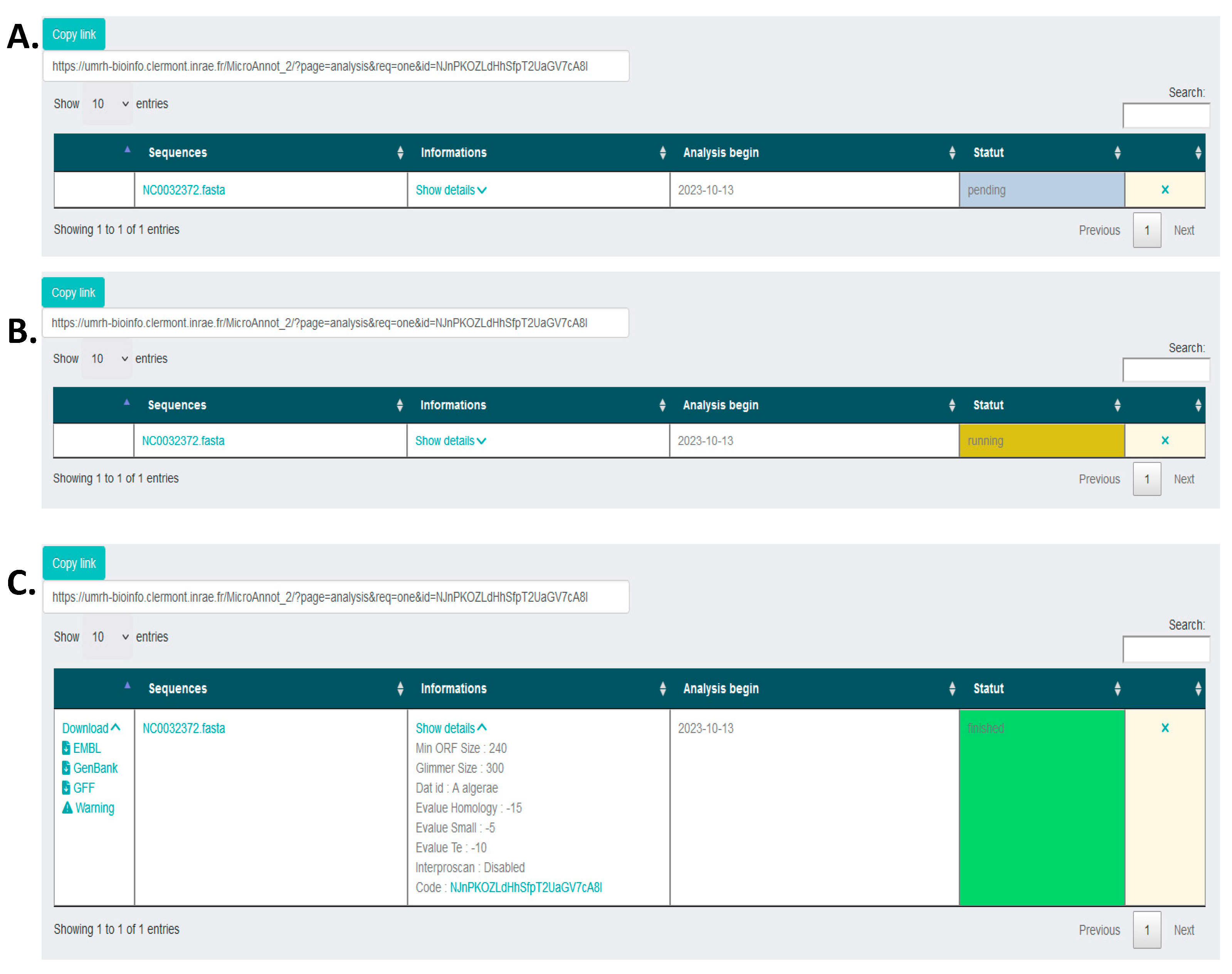
2.1. MicroAnnot Usage
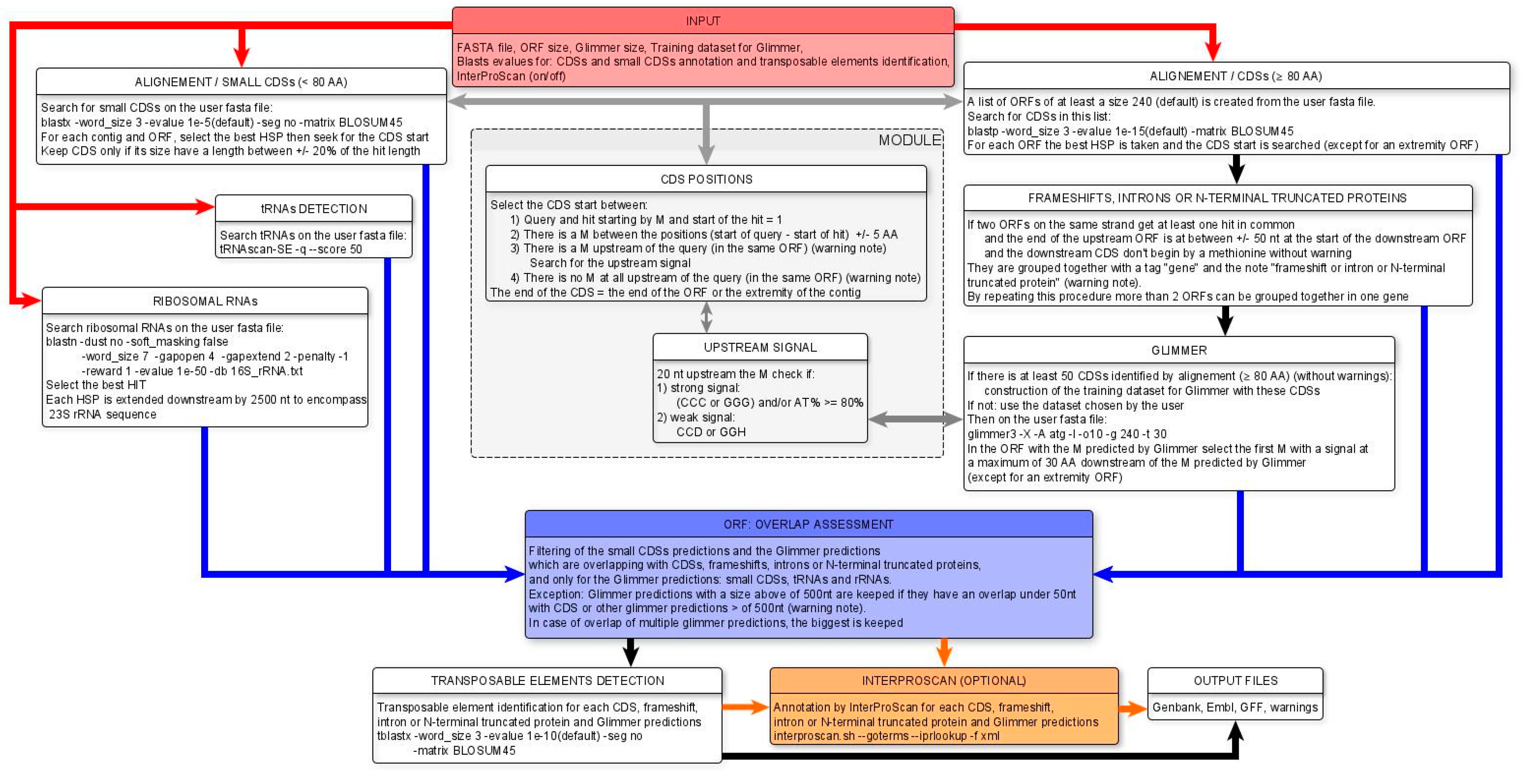
2.2. MicroAnnot Algorithm
2.3. MicroAnnot Validation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Software Implementation
4.2. Web Interface
4.3. Databases
4.4. MicroAnnot Analysis of the Four Microsporidian Genomes
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Corsaro, D. Insights into Microsporidia Evolution from Early Diverging Microsporidia. Exp Suppl 2022, 114, 71–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Weiss, L.M. Microsporidia: Obligate Intracellular Pathogens Within the Fungal Kingdom. Microbiol Spectr 2017, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stentiford, G.D.; Becnel, -J. J.; Weiss, L.M.; Keeling, P.J.; Didier, E.S.; Williams, B. -a. P.; Bjornson, S.; Kent, M.-L.; Freeman, M.A.; Brown, M.J.F.; et al. Microsporidia - Emergent Pathogens in the Global Food Chain. Trends Parasitol 2016, 32, 336–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Pan, G.; Weiss, L.M. Microsporidiosis in Humans. Clin Microbiol Rev 2021, 34, e00010-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziad, F.; Robertson, T.; Watts, M.R.; Copeland, J.; Chiu, G.; Wang, D.; Stark, D.; Graham, L.; Turner, C.; Newbury, R. Fatal Disseminated Anncaliia Algerae Myositis Mimicking Polymyositis in an Immunocompromised Patient. Neuromuscular Disorders 2021, 31, 877–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyle, C.M.; Weiss, L.M.; Rhodes, L.V.; Cali, A.; Takvorian, P.M.; Brown, D.F.; Visvesvara, G.S.; Xiao, L.; Naktin, J.; Young, E.; et al. Fatal Myositis Due to the Microsporidian Brachiola Algerae, a Mosquito Pathogen. New England Journal of Medicine 2004, 351, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, N.W.; Muehlenbachs, A.; Arif, S.; Bruminhent, J.; Deziel, P.J.; Razonable, R.R.; Wilhelm, M.P.; Metcalfe, M.G.; Qvarnstrom, Y.; Pritt, B.S. A Fatal Case of Disseminated Microsporidiosis Due to Anncaliia Algerae in a Renal and Pancreas Allograft Recipient. Open Forum Infect Dis 2019, 6, ofz285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B.A.P.; Williams, T.A.; Trew, J. Comparative Genomics of Microsporidia. Exp Suppl 2022, 114, 43–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jespersen, N.; Monrroy, L.; Barandun, J. Impact of Genome Reduction in Microsporidia. Exp Suppl 2022, 114, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradi, N.; Pombert, J.-F.; Farinelli, L.; Didier, E.S.; Keeling, P.J. The Complete Sequence of the Smallest Known Nuclear Genome from the Microsporidian Encephalitozoon Intestinalis. Nat Commun 2010, 1, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katinka, M.D.; Duprat, S.; Cornillot, E.; Méténier, G.; Thomarat, F.; Prensier, G.; Barbe, V.; Peyretaillade, E.; Brottier, P.; Wincker, P.; et al. Genome Sequence and Gene Compaction of the Eukaryote Parasite Encephalitozoon Cuniculi. Nature 2001, 414, 450–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkorchia, A.; Gasc, C.; Polonais, V.; Parisot, N.; Gallois, N.; Ribière, C.; Lerat, E.; Gaspin, C.; Pombert, J.-F.; Peyret, P.; et al. The Prediction and Validation of Small CDSs Expand the Gene Repertoire of the Smallest Known Eukaryotic Genomes. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyretaillade, E.; Parisot, N.; Polonais, V.; Terrat, S.; Denonfoux, J.; Dugat-Bony, E.; Wawrzyniak, I.; Biderre-Petit, C.; Mahul, A.; Rimour, S.; et al. Annotation of Microsporidian Genomes Using Transcriptional Signals. Nat Commun 2012, 3, 1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biderre, C.; Méténier, G.; Vivarès, C.P. A Small Spliceosomal-Type Intron Occurs in a Ribosomal Protein Gene of the Microsporidian Encephalitozoon Cuniculi. Mol Biochem Parasitol 1998, 94, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradi, N.; Gangaeva, A.; Keeling, P.J. Comparative Profiling of Overlapping Transcription in the Compacted Genomes of Microsporidia Antonospora Locustae and Encephalitozoon Cuniculi. Genomics 2008, 91, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, E.E.; Lee, R.C.H.; Corradi, N.; Grisdale, C.J.; Limpright, V.O.; Keeling, P.J.; Fast, N.M. Splicing and Transcription Differ between Spore and Intracellular Life Stages in the Parasitic Microsporidia. Mol Biol Evol 2010, 27, 1579–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinz, E.; Williams, T.A.; Nakjang, S.; Noël, C.J.; Swan, D.C.; Goldberg, A.V.; Harris, S.R.; Weinmaier, T.; Markert, S.; Becher, D.; et al. The Genome of the Obligate Intracellular Parasite Trachipleistophora Hominis: New Insights into Microsporidian Genome Dynamics and Reductive Evolution. PLoS Pathog 2012, 8, e1002979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyretaillade, E.; Gonçalves, O.; Terrat, S.; Dugat-Bony, E.; Wincker, P.; Cornman, R.S.; Evans, J.D.; Delbac, F.; Peyret, P. Identification of Transcriptional Signals in Encephalitozoon Cuniculi Widespread among Microsporidia Phylum: Support for Accurate Structural Genome Annotation. BMC Genomics 2009, 10, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B.A.P.; Slamovits, C.H.; Patron, N.J.; Fast, N.M.; Keeling, P.J. A High Frequency of Overlapping Gene Expression in Compacted Eukaryotic Genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2005, 102, 10936–10941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polonais, V.; Prensier, G.; Méténier, G.; Vivarès, C.P.; Delbac, F. Microsporidian Polar Tube Proteins: Highly Divergent but Closely Linked Genes Encode PTP1 and PTP2 in Members of the Evolutionarily Distant Antonospora and Encephalitozoon Groups. Fungal Genetics and Biology 2005, 42, 791–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascarenhas dos Santos, A.C.; Julian, A.T.; Pombert, J.-F. The Rad9–Rad1–Hus1 DNA Repair Clamp Is Found in Microsporidia. Genome Biol Evol 2022, 14, evac053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisot, N.; Pelin, A.; Gasc, C.; Polonais, V.; Belkorchia, A.; Panek, J.; El Alaoui, H.; Biron, D.G.; Brasset, E.; Vaury, C.; et al. Microsporidian Genomes Harbor a Diverse Array of Transposable Elements That Demonstrate an Ancestry of Horizontal Exchange with Metazoans. Genome Biol Evol 2014, 6, 2289–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyretaillade, E.; Boucher, D.; Parisot, N.; Gasc, C.; Butler, R.; Pombert, J.-F.; Lerat, E.; Peyret, P. Exploiting the Architecture and the Features of the Microsporidian Genomes to Investigate Diversity and Impact of These Parasites on Ecosystems. Heredity (Edinb) 2015, 114, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejigu, G.F.; Jung, J. Review on the Computational Genome Annotation of Sequences Obtained by Next-Generation Sequencing. Biology (Basel) 2020, 9, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Wu, Z.H.; Li, W.F.; Guo, R.; Xu, J.S.; Dang, X.Q.; Ma, Z.G.; Chen, Y.P.; Evans, J.D. Genome and Evolutionary Analysis of Nosema Ceranae: A Microsporidian Parasite of Honey Bees. Front Microbiol 2021, 12, 645353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailov, K.V.; Simdyanov, T.G.; Aleoshin, V.V. Genomic Survey of a Hyperparasitic Microsporidian Amphiamblys Sp. (Metchnikovellidae). Genome Biol Evol 2016, 9, 454–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndikumana, S.; Pelin, A.; Williot, A.; Sanders, J.L.; Kent, M.; Corradi, N. Genome Analysis of Pseudoloma Neurophilia: A Microsporidian Parasite of Zebrafish (Danio Rerio). J Eukaryot Microbiol 2017, 64, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelin, A.; Selman, M.; Aris-Brosou, S.; Farinelli, L.; Corradi, N. Genome Analyses Suggest the Presence of Polyploidy and Recent Human-Driven Expansions in Eight Global Populations of the Honeybee Pathogen Nosema Ceranae. Environmental Microbiology 2015, 17, 4443–4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang’ang’o, L.M.; Herren, J.K.; Tastan Bishop, Ö. Structural and Functional Annotation of Hypothetical Proteins from the Microsporidia Species Vittaforma Corneae ATCC 50505 Using in Silico Approaches. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2023, 24, 3507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, S.J.; Rothnagel, J.A. Emerging Evidence for Functional Peptides Encoded by Short Open Reading Frames. Nat Rev Genet 2014, 15, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST+: Architecture and Applications. BMC Bioinformatics 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delcher, A.L.; Bratke, K.A.; Powers, E.C.; Salzberg, S.L. Identifying Bacterial Genes and Endosymbiont DNA with Glimmer. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, P.P.; Lin, B.Y.; Mak, A.J.; Lowe, T.M. tRNAscan-SE 2.0: Improved Detection and Functional Classification of Transfer RNA Genes. Nucleic Acids Res 2021, 49, 9077–9096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.; Binns, D.; Chang, H.-Y.; Fraser, M.; Li, W.; McAnulla, C.; McWilliam, H.; Maslen, J.; Mitchell, A.; Nuka, G.; et al. InterProScan 5: Genome-Scale Protein Function Classification. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1236–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubuffet, A.; Chauvet, M.; Moné, A.; Debroas, D.; Lepère, C. A Phylogenetic Framework to Investigate the Microsporidian Communities through Metabarcoding and Its Application to Lake Ecosystems. Environ Microbiol 2021, 23, 4344–4359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scalzitti, N.; Jeannin-Girardon, A.; Collet, P.; Poch, O.; Thompson, J.D. A Benchmark Study of Ab Initio Gene Prediction Methods in Diverse Eukaryotic Organisms. BMC Genomics 2020, 21, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimonaco, N.J.; Aubrey, W.; Kenobi, K.; Clare, A.; Creevey, C.J. No One Tool to Rule Them All: Prokaryotic Gene Prediction Tool Annotations Are Highly Dependent on the Organism of Study. Bioinformatics 2022, 38, 1198–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornman, R.S.; Chen, Y.P.; Schatz, M.C.; Street, C.; Zhao, Y.; Desany, B.; Egholm, M.; Hutchison, S.; Pettis, J.S.; Lipkin, W.I.; et al. Genomic Analyses of the Microsporidian Nosema Ceranae, an Emergent Pathogen of Honey Bees. PLoS Pathog 2009, 5, e1000466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akiyoshi, D.E.; Morrison, H.G.; Lei, S.; Feng, X.; Zhang, Q.; Corradi, N.; Mayanja, H.; Tumwine, J.K.; Keeling, P.J.; Weiss, L.M.; et al. Genomic Survey of the Non-Cultivatable Opportunistic Human Pathogen, Enterocytozoon Bieneusi. PLoS Pathog 2009, 5, e1000261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, L.; David, C.; Jacobs, D.J. Ab Initio Gene Prediction for Protein-Coding Regions. Bioinformatics Advances 2023, 3, vbad105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- König, S.; Romoth, L.; Stanke, M. Comparative Genome Annotation. Methods Mol Biol 2018, 1704, 189–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capella-Gutiérrez, S.; Marcet-Houben, M.; Gabaldón, T. Phylogenomics Supports Microsporidia as the Earliest Diverging Clade of Sequenced Fungi. BMC Biology 2012, 10, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearson, W.R. Selecting the Right Similarity-Scoring Matrix. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics 2013, 43, 3.5.1–3.5.9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goel, N.; Singh, S.; Aseri, T.C. Global Sequence Features Based Translation Initiation Site Prediction in Human Genomic Sequences. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Hu, H.; Jiang, T.; Zhang, L.; Zeng, J. TITER: Predicting Translation Initiation Sites by Deep Learning. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, i234–i242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keeling, P.J.; Fast, N.M.; Corradi, N. Microsporidian Genome Structure and Function. In Microsporidia; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 2014; pp. 221–229 ISBN 978-1-118-39526-4.
- Pombert, J.-F.; Haag, K.L.; Beidas, S.; Ebert, D.; Keeling, P.J. The Ordospora Colligata Genome: Evolution of Extreme Reduction in Microsporidia and Host-To-Parasite Horizontal Gene Transfer. mBio 2015, 6, 10.1128/mbio.02400-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whelan, T.A.; Lee, N.T.; Lee, R.C.H.; Fast, N.M. Microsporidian Introns Retained against a Background of Genome Reduction: Characterization of an Unusual Set of Introns. Genome Biol Evol 2018, 11, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Zhang, K.; Xun, C.; Chu, T.; Liang, S.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, Z. Small Open Reading Frame-Encoded Micro-Peptides: An Emerging Protein World. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2023, 24, 10562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Albuquerque, N.R.M.; Ebert, D.; Haag, K.L. Transposable Element Abundance Correlates with Mode of Transmission in Microsporidian Parasites. Mobile DNA 2020, 11, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, S.; Su, W.; Liao, Y.; Chougule, K.; Agda, J.R.A.; Hellinga, A.J.; Lugo, C.S.B.; Elliott, T.A.; Ware, D.; Peterson, T.; et al. Benchmarking Transposable Element Annotation Methods for Creation of a Streamlined, Comprehensive Pipeline. Genome Biol 2019, 20, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cormier, A.; Chebbi, M.A.; Giraud, I.; Wattier, R.; Teixeira, M.; Gilbert, C.; Rigaud, T.; Cordaux, R. Comparative Genomics of Strictly Vertically Transmitted, Feminizing Microsporidia Endosymbionts of Amphipod Crustaceans. Genome Biol Evol 2020, 13, evaa245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aurrecoechea, C.; Barreto, A.; Brestelli, J.; Brunk, B.P.; Caler, E.V.; Fischer, S.; Gajria, B.; Gao, X.; Gingle, A.; Grant, G.; et al. AmoebaDB and MicrosporidiaDB: Functional Genomic Resources for Amoebozoa and Microsporidia Species. Nucleic Acids Res 2011, 39, D612–D619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vernikos, G.S. A Review of Pangenome Tools and Recent Studies. In The Pangenome: Diversity, Dynamics and Evolution of Genomes; Tettelin, H., Medini, D., Eds.; Springer: Cham (CH), 2020 ISBN 978-3-030-38280-3.
- Seatamanoch, N.; Kongdachalert, S.; Sunantaraporn, S.; Siriyasatien, P.; Brownell, N. Microsporidia, a Highly Adaptive Organism and Its Host Expansion to Humans. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2022, 12, 924007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Gao, X.; Li, R.; Zhang, L.; Huang, R.; Wang, L.; Song, Y.; Xing, Z.; Liu, T.; Nie, X.; et al. Complete Genome of a Unicellular Parasite (Antonospora Locustae) and Transcriptional Interactions with Its Host Locust. Microb Genom 2020, 6, mgen000421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polonais, V.; Niehus, S.; Wawrzyniak, I.; Franchet, A.; Gaspin, C.; Belkorchia, A.; Reichstadt, M.; Belser, C.; Labadie, K.; Couloux, A.; et al. Draft Genome Sequence of Tubulinosema Ratisbonensis, a Microsporidian Species Infecting the Model Organism Drosophila Melanogaster. Microbiology Resource Announcements 2019, 8, 10.1128/mra.00077-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacho, A.; Smirnova, E.; Huzurbazar, S.; Cui, X. A Comparison of Base-Calling Algorithms for Illumina Sequencing Technology. Brief Bioinform 2016, 17, 786–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hon, T.; Mars, K.; Young, G.; Tsai, Y.-C.; Karalius, J.W.; Landolin, J.M.; Maurer, N.; Kudrna, D.; Hardigan, M.A.; Steiner, C.C.; et al. Highly Accurate Long-Read HiFi Sequencing Data for Five Complex Genomes. Sci Data 2020, 7, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagès-Gallego, M.; De Ridder, J. Comprehensive Benchmark and Architectural Analysis of Deep Learning Models for Nanopore Sequencing Basecalling. Genome Biol 2023, 24, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pombert, J.-F.; Selman, M.; Burki, F.; Bardell, F.T.; Farinelli, L.; Solter, L.F.; Whitman, D.W.; Weiss, L.M.; Corradi, N.; Keeling, P.J. Gain and Loss of Multiple Functionally Related, Horizontally Transferred Genes in the Reduced Genomes of Two Microsporidian Parasites. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 12638–12643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouzounis, C.A.; Karp, P.D. The Past, Present and Future of Genome-Wide Re-Annotation. Genome Biol 2002, 3, comment2001.1–comment2001.6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudey, B.; Geard, N.; Verspoor, K.; Zobel, J. Propagation, Detection and Correction of Errors Using the Sequence Database Network. Brief. Bioinform. 2022, 23, bbac416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.K.; Bencurova, E.; Srivastava, M.; Pahlavan, P.; Balkenhol, J.; Dandekar, T. Improving Re-Annotation of Annotated Eukaryotic Genomes. In Big Data Analytics in Genomics; Wong, K.-C., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2016; pp. 171–195. ISBN 978-3-319-41279-5. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, X.-D. Non-Coding RNA: A New Frontier in Regulatory Biology. Natl Sci Rev 2014, 1, 190–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Zheng, N.; Hu, C.; Deng, B.; Fang, W.; Wu, Q.; Chen, P.; Huang, X.; Gao, N.; Lu, C.; et al. Nosema Bombycis microRNA-like RNA 8 (Nb-milR8) Increases Fungal Pathogenicity by Modulating BmPEX16 Gene Expression in Its Host, Bombyx Mori. Microbiol Spectr 2021, 9, e0104821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Chen, D.; Chen, H.; Xiong, C.; Zheng, Y.; Hou, C.; Du, Y.; Geng, S.; Wang, H.; Dingding, Z.; et al. Genome-Wide Identification of Circular RNAs in Fungal Parasite Nosema Ceranae. Curr Microbiol 2018, 75, 1655–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.S.; Yan, W.Y.; Huang, Q. Identification of Novel miRNAs from the Microsporidian Parasite Nosema Ceranae. Infect Genet Evol 2021, 93, 104930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Yang, Q.; Luo, L.; Li, T.; Ke, Z.; Li, T.; Chen, J.; Meng, X.; Xiang, H.; Li, C.; et al. Non-Coding RNAs Identification and Regulatory Networks in Pathogen-Host Interaction in the Microsporidia Congenital Infection. BMC Genomics 2023, 24, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkorchia, A.; Pombert, J.-F.; Polonais, V.; Parisot, N.; Delbac, F.; Brugère, J.-F.; Peyret, P.; Gaspin, C.; Peyretaillade, E. Comparative Genomics of Microsporidian Genomes Reveals a Minimal Non-Coding RNA Set and New Insights for Transcription in Minimal Eukaryotic Genomes. DNA Res 2017, 24, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.; Tang, X.; Lan, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X. The Genomic Survey of Tc1-like Elements in the Silkworm Microsporidia Nosema Bombycis. Acta Parasitol 2020, 65, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| E. cuniculi | E. intestinalis | N. ceranae | E. bieneusi | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation corrections | Falsely predicted TIS | 445 (299: 67.2%) | 199 (185: 93%) | 308 (232: 75.3) | 240 (172: 71.7%) |
| Falsely predicted gene | 11 (0: 100%) | 8 (0: 100%) | 76 (18: 76.3%) | 168 (4: 97.6%) | |
| Newly predicted introns | 3 (3:100%) | 19 (12: 63.2%) | 4 (3:75%) | - | |
| Unpredicted genes | 142 (128: 90.1%) | 115 (108: 93.9%) | 292 (250: 86.5%) | 70 (66: 94.3%) | |
| Unpredicted frameshift or sequencing error or pseudogene | - | 11(10: 90.9%) | 121 (74: 61.1%) | 43 (17: 39.5%) | |
| Additional annotation corrections | Corrected TIS | 77 | 18 | 15 | 26 |
| Falsely Predicted gene | 12 | _ | 3 | 8 | |
| Predicted introns | - | _ | 1 | _ | |
| Unpredicted genes | 23 | - | 296 | 15 | |
| Unpredicted frameshift or sequencing error or pseudogene | - | 1 | - | - | |
| TEs predicted as CDS | - | - | 42 | - | |
| Predicted TEs | - | - | 643 | - | |
| Additional annotation errors | Mispredicted TIS (warning) | 94 | 32 | 62 (49) | 68 (29) |
| Falsely Predicted gene (warning) | 1 | 1 | 11 (27) | 25 | |
| Mispredicted intron | 5 | 0 | _ | - | |
| Unpredicted genes | 47 | 4 | 22 | 33 | |
| Bad predicted TEs | 0 | 1 | - | - |
| E. cuniculi | E. intestinalis | N. ceranae | E. bieneusi | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| True gene numbers* | 2151 | 1940 | 2352 | 1770 | |
| Specificity (Sp) | 1st annotation** | 98.9% | 99.6% | 96.8% | 91% |
| MicroAnnot | 99.9% | 99.9% | 98.9% | 98.4% | |
| Sensibility (Sn) | 1st annotation** | 92.9% | 94.4% | 80% | 95.4% |
| MicroAnnot | 95.2% | 99.4% | 97.4% | 98% | |
| TIS Correctly predicted (TCP) | 1st annotation** | 80.5% | 90.0% | 88.0% | 87% |
| MicroAnnot | 90.0% | 97.8% | 94.5% | 93% | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





