1. Introduction
Cutaneous inflammation is one of the most significant global issues, and the subsequent development of necrotic ulcers pose a significant global challenge, affecting millions of individuals each year [
1,
2]. The inflammation is a natural protective reaction of the organism against endogenous and exogenous damage (e.g. tissue damage, traumas, infections, immunological reactions, and tissue necrosis), composed of "five pillars": swelling, heat, redness, pain, and loss of function[
3]. Many cells from the immunological system actively participate in inflammatory processes, with macrophages being one of these cells[
4,
5,
6]. Known as phagocytes, this type of cell is deeply related to innate immunity which, in association with other leucocytes, produces chemical mediators that promote the inflammatory cascade[
7].
Epidemiological studies reveal that a substantial number of patients with inflammatory skin conditions such as dermatitis, psoriasis, and chronic wounds are at risk of developing necrotic ulcers, particularly when inflammation is inadequately controlled[
8,
9]. Furthermore, the resistance to traditional anti-inflammatories, such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), has been observed in a considerable number of cases, making the treatment of these conditions even more challenging[
10]. This underscores the urgent need for research and the development of effective anti-inflammatory therapies, as well as strategies to enhance the body's response to available treatments, in order to mitigate the devastating impact of cutaneous inflammation and reduce the incidence of necrotic ulcers[
11,
12].
Pharmacological studies that make use of medicinal plants are a prime example of research related to finding alternative drugs that present not only effective anti-inflammatory activity, but an absence of adverse effects shown by AINEs. The therapeutical effects of plants can be attributed to many secondary metabolites, present in plant species. Among these metabolites, saponins stand out with hemolytic, molluscicides, anti-helminthic, spermicide, hypocholesterolemic, and anti-inflammatory activities. Furthermore, steroidal saponins are used by the industry as a base for corticosteroid anti-inflammatory drugs, while saponin-rich plants are used in traditional medicine for inflammation treatment[
13,
14,
15].
Agave sisalana (also known as sisal) and
Punica granatum (also known as romã) are two examples of many saponin-rich species that can be found in Brazil. Brazil is the largest producer of sisal and its hardened fiber. The fiber, present in sisal leaves, corresponds to approximately 4% of its weight, with all the vegetal saponin-rich residue being discarded. Pomegranate peel is, also, a residue abundant in Brazil.
In vitro and in vivo studies with different parts of the plant demonstrated its anti-microbial and anti-inflammatory proprieties, given its secondary metabolites, in special, saponins[
13,
16].
Aiming to develop a new, topical, anti-inflammatory drug, from vegetal residues of two saponin-rich species, this paper evaluated extracts developed from sisal and pomegranate residues through in vitro phytochemical, pharmacological, and toxicological studies; the extracts were analyzed isolated and in an association. A mucoadhesive gel and gel containing the extracts in association, was also analyzed.
3. Discussion
Identifying the health benefits of phytochemicals is an essential step in the development of pharmaceuticals and functional foods. In this context, screening for saponins, a secondary metabolite used in the synthesis of corticosteroids, is of paramount importance for the proposed residual reuse in this study. The goal was the formulation of a topical gel for potential use on the oral mucosa in patients suffering from inflammation in this region [
17,
18].
In this study, the concentration of saponins found in sisal residue extract (RS) was 29.91 g of saponins per 100 g of dry extract. As for the presence of saponins in pomegranate peel extract, this study revealed an average value of 15.83 g/100 g. In the literature, there are no comparative data, which underscores the uniqueness of this research.The combination of sisal and pomegranate residue extracts (A) resulted in a saponin concentration of 22.99 g per 100 g of dry extract. This value is close to the sum of the saponin concentrations present in 50 grams of each extract, which would be 22.86 grams.
The gel containing the combination of extracts (G2), both at 0.6%, exhibited a saponin concentration of 0.52 g per 100 g of gel, meaning a higher saponin concentration when compared to the simple summation of values of this metabolite in the isolated extracts at a concentration of 0.6%, which would be 0.27 g per 100 g of gel. This suggests that the saponin concentration was not compromised by the formulation; on the contrary, it facilitated saponin detection.The association of extracts (G2) showed a concentration of 0.52 g/100g, lower than the associated extracts, but still higher than those observed in the isolated extracts.
The absence of phytochemical studies on sisal and pomegranate peel, both individually and in combination, limits a more in-depth discussion of the saponin data obtained. However, these findings already indicate that high saponin concentrations are likely responsible for the pharmacological activities analyzed in this study. This is because saponins exhibit anti-inflammatory activities and are used in medicinal chemistry for the production of steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs[
17,
18,
19].
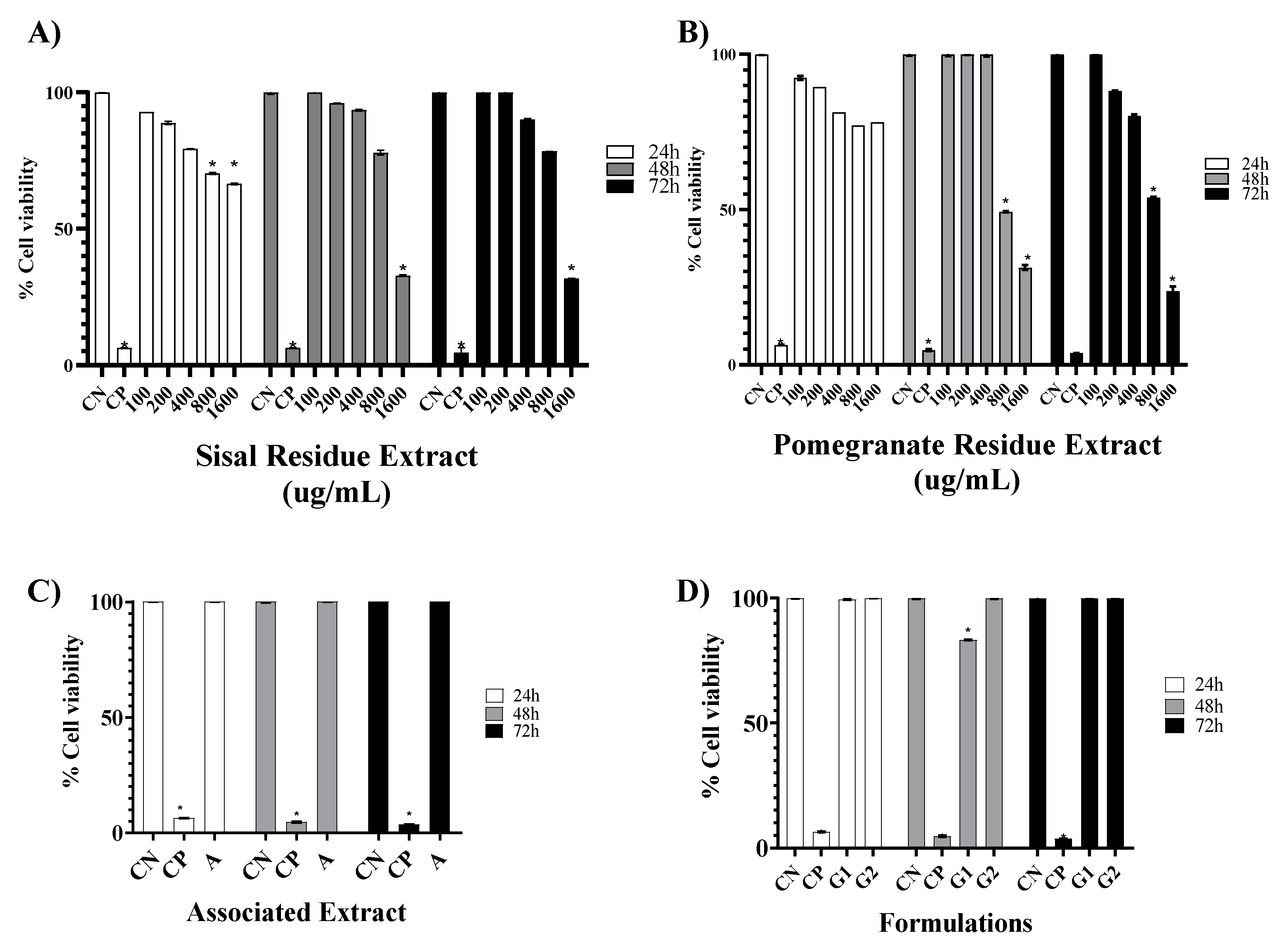
To evaluate the cytotoxic effect caused by the extracts of sisal and pomegranate waste (SR and PR) as well as the associated extracts, the base gel, and the gel with the association, the MTT assay was chosen. According to the parameters used by Amaral (2014) to classify the degree of toxicity, in the time of 24 h, the SR and PR presented cytotoxicity considered little important, because the CC50% values obtained confirmed that the concentrations analyzed were not able to reduce cell viability by 50%, the association of extracts showed high cell viability, as well as, the formulation of the base gel proved to be free of cytotoxicity, as well as, the formulation of the gel with the association increased cell viability according to the times, respectively.
The results obtained in the MTT assay showed that all SR concentrations increased cell viability as a function of treatment time. In complement, Dunder et al., 2013 in the same test at concentrations of 50-500 µM of hexanic fraction of sisal did not induce mortality in the same cell lineage of this study. In contrast, Favato [
20] with the concentration of 50 µg/mL of sisal acid hydrolysis extract demonstrated satisfactory results of cytotoxicity to melanoma cells and low systemic genotoxicity, decreasing the risk of the emergence of neoplasms secondary to treatment[
20]. Teixeira [
21] reported that at the concentration of 400 μg/mL, the extract of sisal acid hydrolysis exerted cytotoxicity, having promoted the death of 42.73% of small lung cancer cells[
21]. Thus, in this study, SR was shown to be free of toxicity to 3T3 fibroblasts and from the literature reports, future analysis of SR antitumor activity should be directed to tumor cell lines.
For PR, the concentration of 200 ug/mL in the three analyzed times did not show cytotoxicity, unlike the other concentrations, in which the concentration of 1600 ug/mL showed less than 50% viability in 72 h. However, Vieira [
22] analyzed the hydroalcoholic extract of pomegranate and found that the concentration of 1000 ug/mL exerted a 100% proliferative effect in the time of 24 h. Lorenzoni [
22] also reports increased cell viability in a 3T3 fibroblast cell line, as non-toxic. The cytotoxicity exerted at the highest concentrations of the PR may be related to the fact that it is in glycol solution with the solvent of choice, by the making partner company.
The association of plant secondary metabolites is of interest for the potentiation of pharmacological effects, but the cytotoxicity generated must be analyzed. The association of SR and PR did not impair cell viability; on the contrary, viability was increasing as a function of time. In the literature, there are no reports on the cytotoxicity generated by the association of SR and PR, but after analyzing other associations it was found through the study of Botan [
23] that the association of
Morus nigra,
Ziziphus joazeiro, and
Vitis vinifera increased cell viability in the time of 24 h in RAW 264 macrophage lineage[
23]. In summary, the associations of bioactive plant compounds show promise.
In vitro studies to analyze the cytotoxicity of formulations have been shown to be an alternative to toxicological tests on animals. Thus, the analysis of G1 and G2 was also performed using the MTT test. The results showed that G1 and G2 showed no cytotoxicity in the three treatment times. Additionally, in vitro studies on formulations of natural extracts were not found, further contributing to the originality of this research.
The absence of cytotoxicity made it possible to proceed with anti-inflammatory studies. Macrophages act as the first line of defense, mainly over the inflammatory cascade. Macrophages are cells derived from monocytes. These are released into the bloodstream after their formation in the bone marrow and subsequently, exit the blood to differentiate into macrophages in the tissues. Macrophages are found in all connective tissue sites, and in addition, they are concentrated in various organs such as the liver, spleen, and lymph nodes, where they are related to the body's defense. Thus, they play a key role in innate immunity, effectively participating in inflammatory mechanisms and modulation of the immune system [
24,
25].
Phagocytosis begins with the spreading of the macrophage and the morphological change of the cell corroborates with the increase of its plasma membrane, giving greater proximity to the substrate, as well as the activation of lysosomes and production of reactive oxygen species. Thus, the phagocyte uses surface receptors to bind to and surround a microorganism, forming a vesicle called a phagosome. The surface receptors also release signals that stimulate the fusion of phagosomes with lysosomes originating from the phagolysosomes and inflammation-activating signals that trigger the respiratory burst and the production of nitric oxide, to destroy and eliminate the phagocyted elements as well as the invaders[
24].
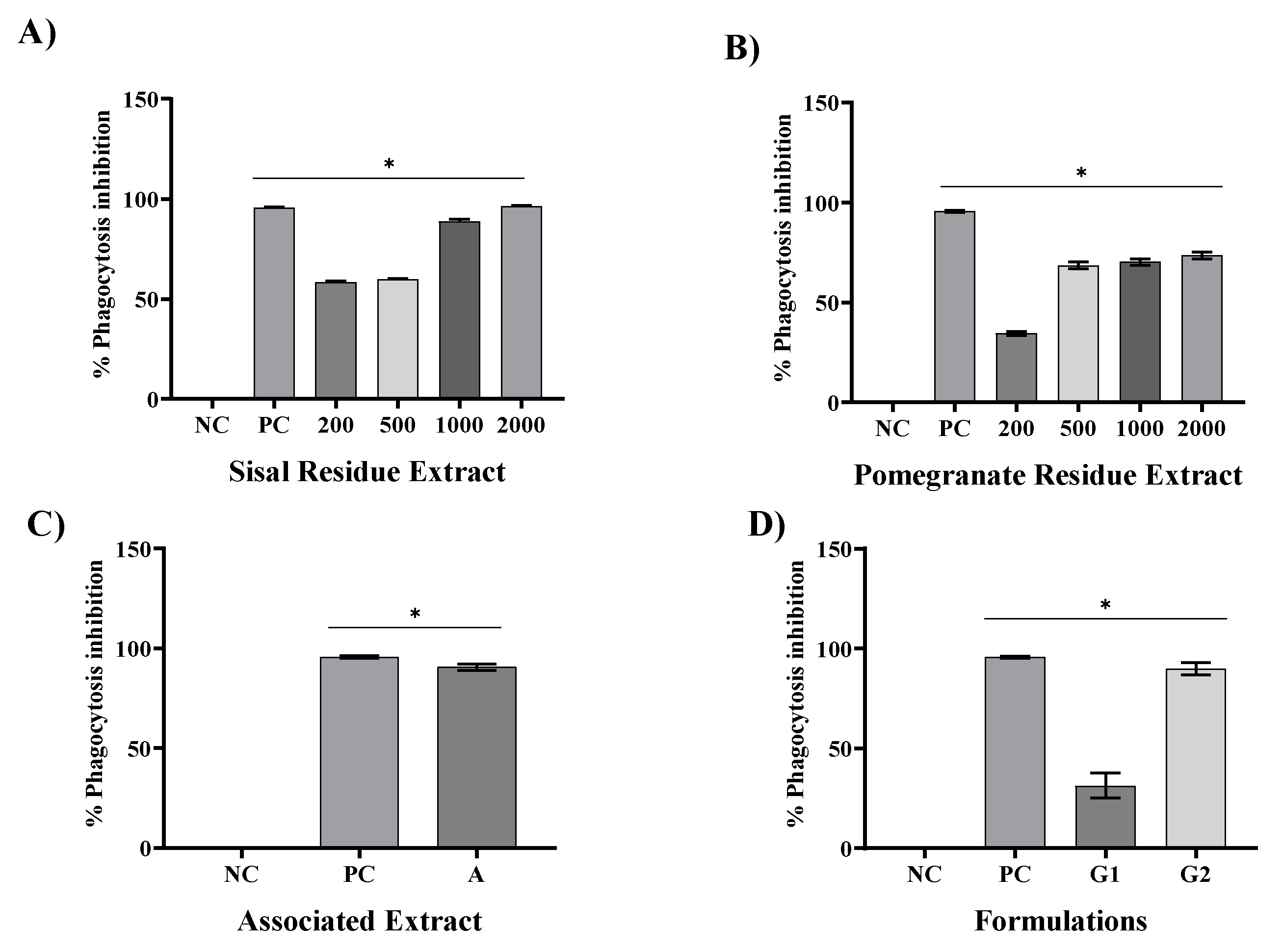
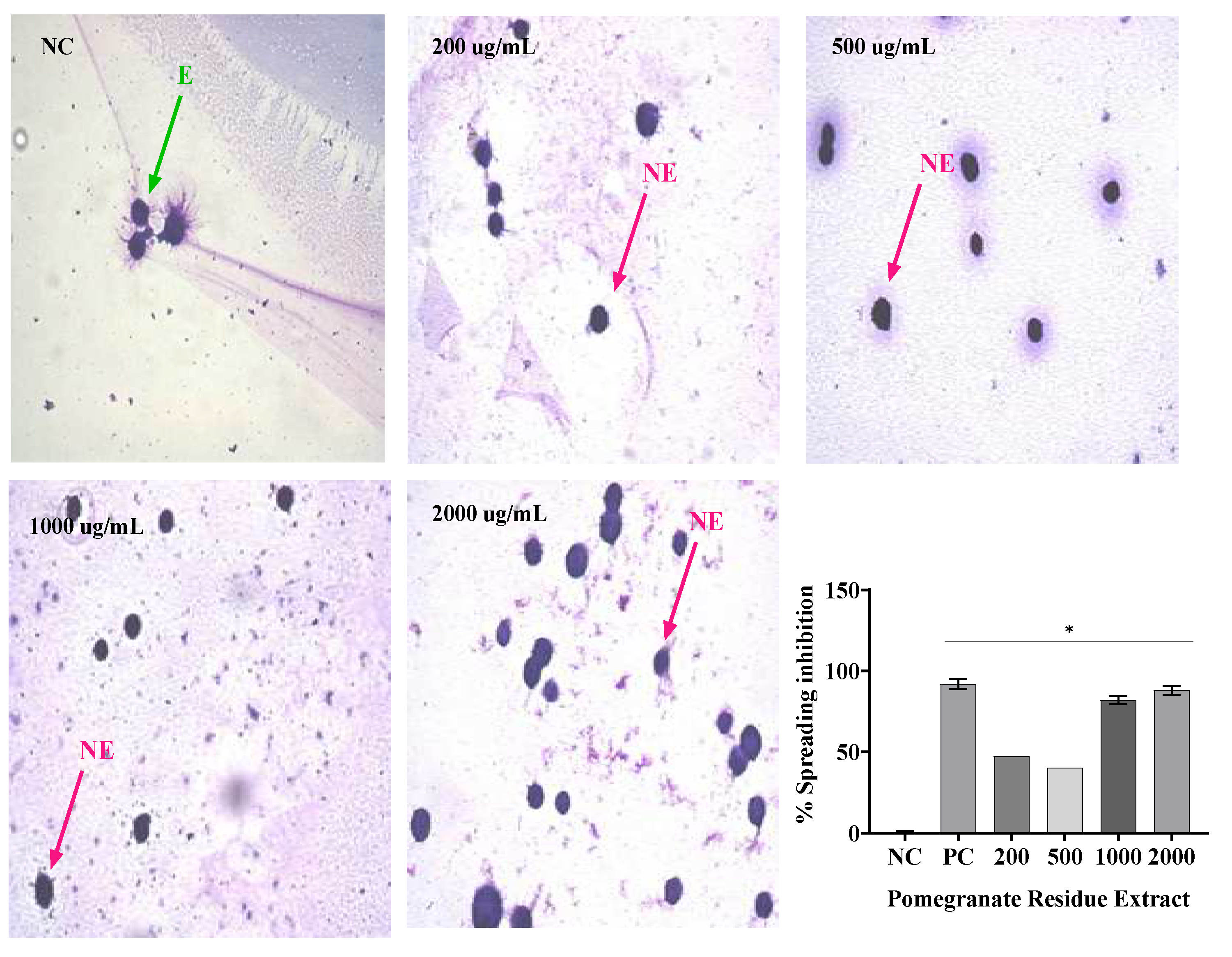
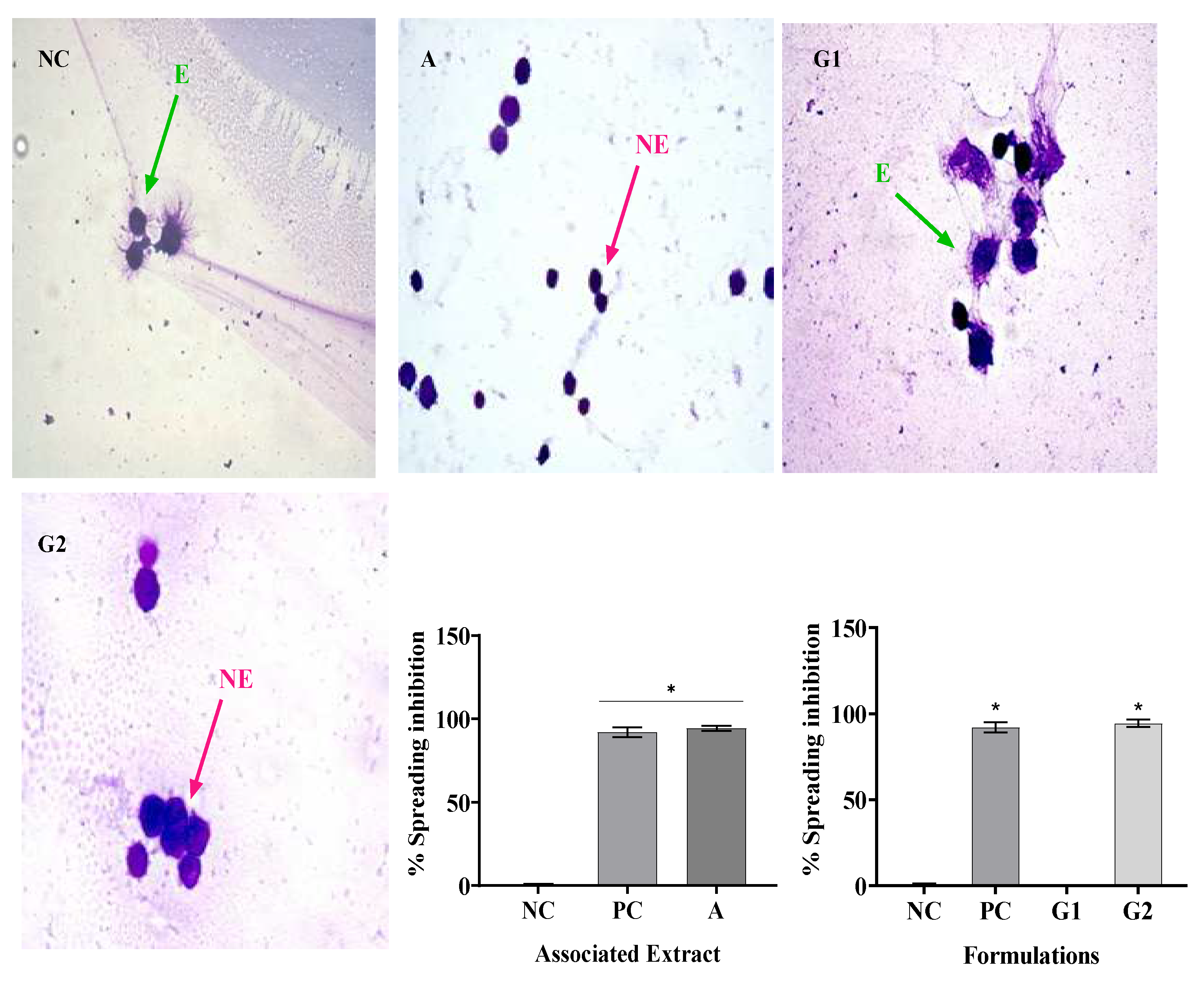
In this study, SR and PR promoted significant inhibition of phagocytosis in all their analyzed concentrations. However, the SR presented a greater ability to inhibit phagocytosis at concentrations of 1000 and 2000 ug/mL. With the association of SR and PR, it was possible to verify the occurrence of a pharmacological synergism that potentiated the anti-inflammatory effect, since the associated extracts, each one at a concentration of 600 ug/mL, promoted phagocytosis inhibition close to that presented by the SR at concentration 2000 ug/mL. The inclusion of the associated extracts in a gel formulation (G2) promoted phagocytosis inhibition similar to that of the gel containing dexamethasone, a product widely used in medical practice. Respectively, Silveira [
25] found that
Chorisia speciosa and
Hymenaea courbaril A. decreased the phagocytic capacity of RAW264 macrophages by 49.80%. Sansone [
26] on the other hand, found that the phagocytic inhibition capacity of soluble non-starch polysaccharides from bananas at the concentration of 200 ug/mL was 49.3%.
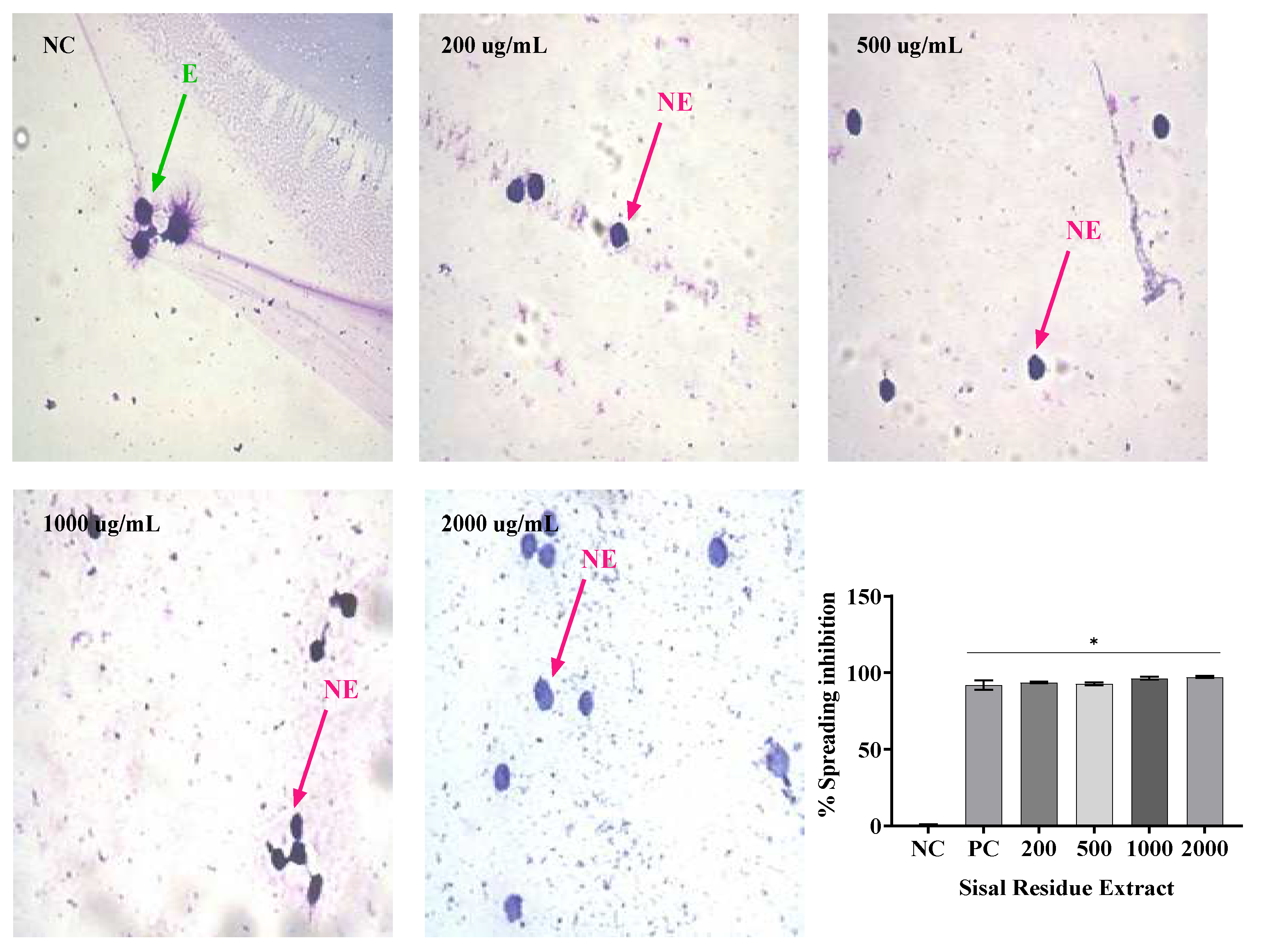
Not only can phagocytosis be evaluated
in vitro directly by the ability to visualize phagocytes engulfing particles or microorganisms, but it can also be evaluated indirectly by the frustrated attempt at phagocytosis, manifested by macrophage adherence and spreading on glass coverslip [
27].Thus, the
in vitro evaluation of the anti-inflammatory activity by the spreading technique of Raw 264 macrophages has been performed because macrophages adhere to the glass when stimulated, becoming spiked. In addition, in the presence of anti-inflammatory compounds, macrophage spreading on slides is reduced [
28].
In this study, treatment with SR in the four concentrations analyzed resulted in macrophage spreading inhibition values similar to, dexamethasone, while PR only in its highest concentration (2000 µg/mL) promoted inhibition similar to dexamethasone. The association of SR and PR as well as the gel containing the extracts promoted similar inhibition to the gel containing dexamethasone. PR did not impair the ability of SR to inhibit macrophage spreading and the association showed effective anti-inflammatory activity. In this regard, Ota et al., 2010 analyzed macrophage spreading with four doses of garlic hydroalcoholic extract, doses II to IV showed 100% macrophage spreading, unlike our study[
29].
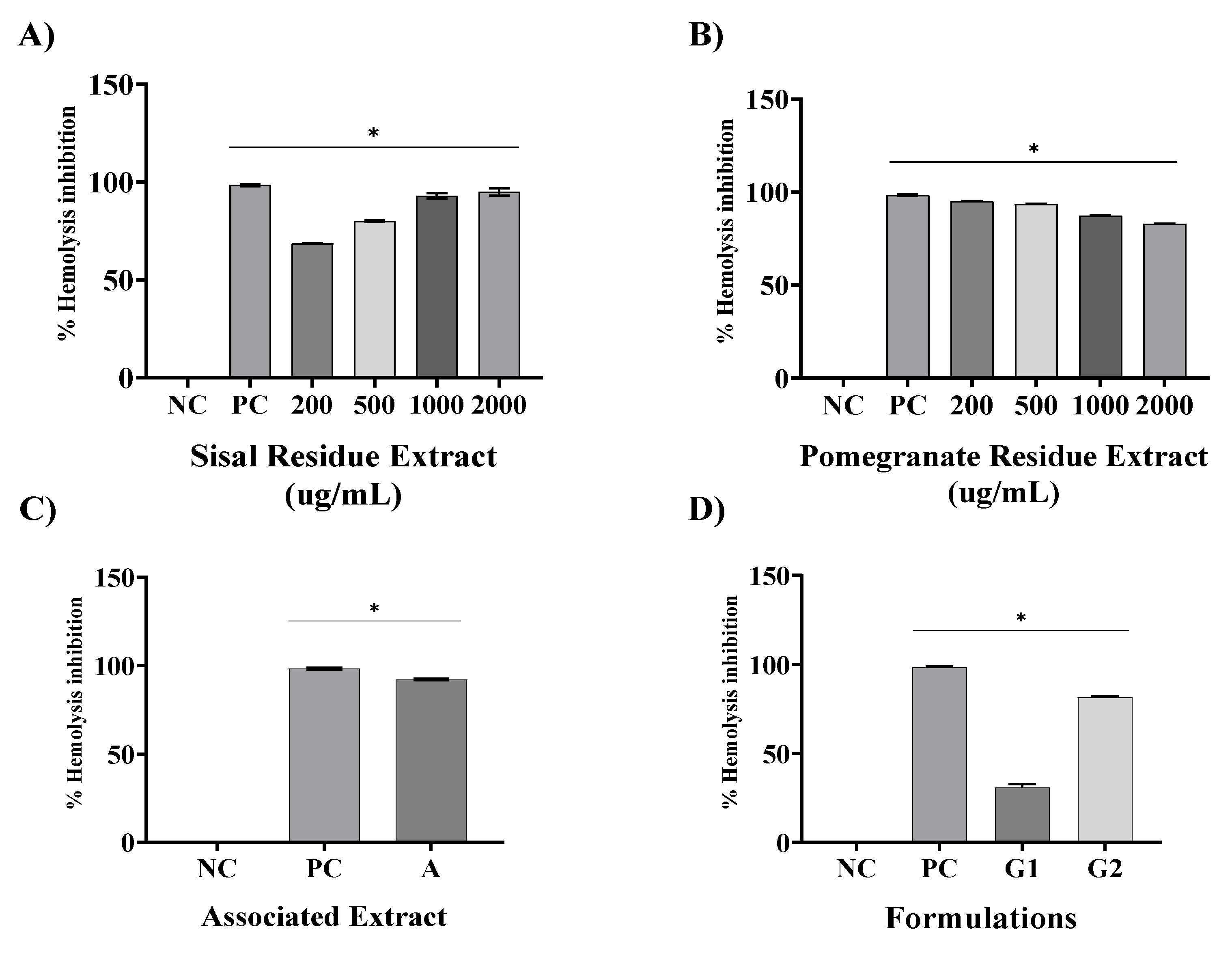
Another anti-inflammatory evaluation chosen was erythrocyte membrane stabilization method. They are widely used for the analysis of the anti-inflammatory activity of plant extracts. The erythrocyte membrane stabilization method is widely used for the analysis of the anti-inflammatory activity of plant extracts [
29], this is because during the inflammatory process, lysosome membranes are lysed and anti-inflammatory drugs inhibit this process. The membrane of human red blood cells was analyzed in this test because it is similar to the membrane of lysosomes, which in hypotonic medium undergo lysis, similar to what occurs in the inflammatory process. Thus, the inhibition of hypotonicity and lysis of the red blood cell membrane induced by hypotonic solution was verified as a mechanism of anti-inflammatory activity [
30].
Using the same method, found that the extract of
Solanum paniculatum L. at all extract concentrations of (15, 30, and 60 μg/ml), significantly protected RBCs against erythrocyte membrane rupture[
31]. In addition, Nagaharika et al. [
31] observed that at the concentration of 100 ug/mL the alcoholic plant extract of
Jatropha gossypifolia L. inhibited hemolysis by 56.8%.
C. cujete leaves and stem also showed great potential for membrane stabilization, the concentration of 100 ug/mL showed 78.81% [
32].
Of particular importance is the examination of combined extracts in our study, as exemplified in all assays. The observed synergy resulting from the combination of these extracts yielded a remarkable effect, surpassing the individual effects of SR and PR extracts. This observation underscores the potential utility of merging these botanical extracts in therapeutic interventions aimed at addressing inflammation-associated conditions. In contrast, our formulations revealed that G1, a specific formulation, exhibited limited pharmacological effects, comparable to the negative control (NC). However, G2, a distinct formulation incorporating the combined extracts, demonstrated a significant anti-inflammatory effect and potential.
6. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant material
The use of sisal and pomegranate waste has already been regulated by SisGen, through the protocol of the CAPES Print Unesp Project: Exploring Multidisciplinary Approaches for the Development of Phytotherapeutic Products. Registration number: A1266B4.
Sisal residue (mucilage) originated from Valente city, Bahia state. The species under study is Agave sisalana; the specimen belongs to the Herbarium Assisense (HASSI) of the São Paulo State University - UNESP (Assis, state of São Paulo), where a voucher specimen is deposited under the number 2597.
Pomegranate peel was acquired from Companhia Santos Flora, Mairiporã-SP. The peel comprise d a single batch already shredded, dehydrated, and sterilized.
2.3. Association of sisal and pomegranate residue extracts
To potentiate the isolated effects of sisal and pomegranate residue extracts, they were associated (A). The concentrations of each extract used in the association correspond to the Effective Concentration 50 (CC50%) values obtained in the Phagocytosis assay (Item 2.7.4) and corresponded to the values of 600 µg/mL of the SR and 600 µg/mL of the PR.
2.4. Preparation of the mucoadhesive gel
To prepare the formulation, was used the carboxymethyl sodium (Exodus, SP, Brazil) at 1.6% (w/w), glycerin (Synth, SP, Brazil) 1.2% (w/w), methylparaben (Synth, SP, Brazil) at 0.1% (w/w) and triethanolamine (Sigma, SP, Brazil) 1.4% (w/w) as a pH corrector. During the preparation, all reagents were dissolved in water and the solution was stirred until a gel-form formulation was obtained. The formulation remained at rest for 24 h. After this time, the formulation was stirred again, and the association of pomegranate and sisal extracts was added at concentrations of 600 µg/g of the SR and 600 µg/g of the PR.
2.5. Determination of total saponin
Saponin content was measured into a test tube was pipetted 0.25 mL of isolated extract (SR or PR) 200, 500, 1000 e 200 ug/mL combined extract (A) 600 ug/mL SR and PR, base gel (G1) PA and association gel (G2) 600 ug/g SR and PR), 0.25 mL of vanillin 10% (w/v) fresh and 2.5 mL H2SO4 72% (in cold temperature). The mixture was heated in a water bath for 10 min at 60 °C and cooled. The absorbance of the mixture was measured at a wavelength of 544 nm. Saponin Equijala (Sigma Aldrich cas 8047152) was used as the reference standard. The results of the isolated extracts were expressed considering the concentration of saponins per 100 grams of dry extract, and for the associated extracts the result considered the concentration of saponins for 50 of each dry extract, that is, 100 grams in total.
2.6. Determination of in vitro toxicity by the MTT assay [3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide]
The MTT cytotoxicity assay was carried out as described previously by Fracasso [
33] with some modifications. For this essay, mouse fibroblasts of dermal origin (NIH/3T3, ATCC® CRL-1658™) were inoculated in 96 well microtiter plates and incubated in a culture medium for a period of 24 h at 37 °C, 5% CO
2. After a confluence of approximately 75% (24 h), these cells were exposed to five different concentrations of SR and PR (100 µg/mL, 200 µg/mL, 400 µg/mL, 600 µg/mL, µg/mL and 1600 µg/mL), A (600 µg/mL SR and 600 µg/mL PR), G1 and G2 (600 µg/mL SR and 600 µg/mL PR), to the negative control (physiological solution) and the positive control (2% (v/v) Tween 80). The treatment time was 24 h, 48 h, and 72 h. The five concentrations were chosen to calculate the cytotoxicity concentration of the isolated extracts (CC50%) in 24 h.
2.7. Evaluation of anti-inflammatory activity in vitro
2.7.1. Experimental design
To evaluate the anti-inflammatory activity of sisal (SR) and pomegranate (PR) extracts, four concentrations were used (200 µg/mL, 500 µg/mL, 1000 µg/mL and 2000 µg/mL).
To evaluate the anti-inflammatory activity of the association of sisal and pomegranate residue extracts (A) were used 600 µg/mL of SR and 600 µg/mL of PR. The concentrations used in the formulation of the gel (G2), containing the association of sisal and pomegranate extracts, were 600 µg/g SR and 600 µg/g PR. Dexamethasone (100 μg/gr) was used as a positive control. Saline solution (0.9% saline) and base gel (G) as a negative control.
2.7.2. Cell culture
Murine macrophages of the Raw 264.7 (ATCC TIB-71) strain were thawed and cultivated in a cell culture flask with Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM) Ham's F-12 culture medium at 37 °C, 5% CO2. Anti-inflammatory efficacy and cytotoxicity assay will be performed when the culture reaches about 70-80% confluence.
2.7.3. Selection of macrophages
Cells were harvested using a cell scraper, counted in the Neubauer chamber, and centrifuged at 1500 rpm for 5 min. Then, the supernatant was discarded, and the cells were resuspended in a culture medium to reach the desired concentration for each experiment.
2.7.4. Phagocytosis
The assay was performed following the method described by Fracasso [
33] with few modifications. Once the slides were ready, they were read in triplicate using an optical microscope at 400 x magnification, performing a total count of 100 cells.
The inhibition of phagocytosis (IP) was calculated using the following formula:
Where E0 represents the mean value of the number of cells in the negative control group that phagocytosed the Zymosan particles; ET represents the mean value of the number of cells of the treated groups that phagocytosed the Zymosan particles.
2.7.5. Macrophage spreading
For the Macrophage spreading assay, the method described by Fracasso [
33]. Once the slides were ready, there were read triplicates under an optical microscope at 400x magnification, performing a total count of 100 cells.
The inhibition of spreading (IS) was calculated using the following formula:
Where E0 represents the mean value of the number of spread cells in the negative control group; ET represents the mean value of the number of cells spread in the treated groups.
2.7.6. Membrane stabilization
For the evaluation of the human red blood cell membrane stabilization (HRBC) was employed the method proposed by Ananthi and Chitra [
21], with some modifications. The test reaction was performed with the addition of 2 mL of hyposaline solution (0.18%) to induce hemolysis, 1 mL of sodium phosphate buffer (0.1 M, pH 7.4), 1 mL of the analyzed samples, and 0.5 mL of HRBC solution. The hemoglobin content in the suspension was estimated using a spectrophotometer at 560 nm.
The percentage of protection can be hence calculated from the equation as given below:
Where E0 represents the mean absorbance value of the negative control group; ET represents the mean absorbance value in the treated groups.
2.8. Statistical analysis
Data has been expressed in terms of mean ± standard deviation. Statistical analysis was performed using GraphPad Prism 7. To verify the statistical differences between the groups a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) is performed according to the experimental protocol, followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test. For all analyzes, a p-value of <0.05 was considered significant.