Submitted:
10 October 2023
Posted:
11 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Conjugation of Cell Penetrating Peptide to KR12 Antimicrobial Peptide
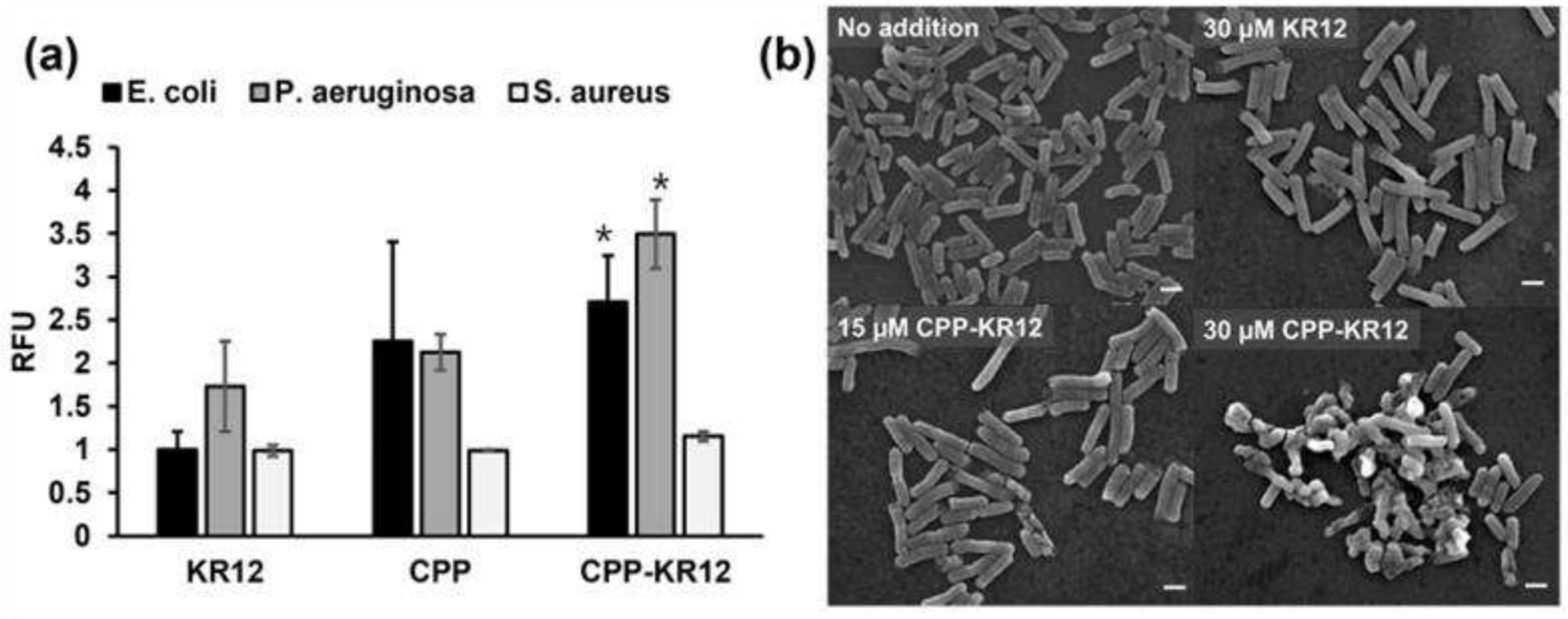
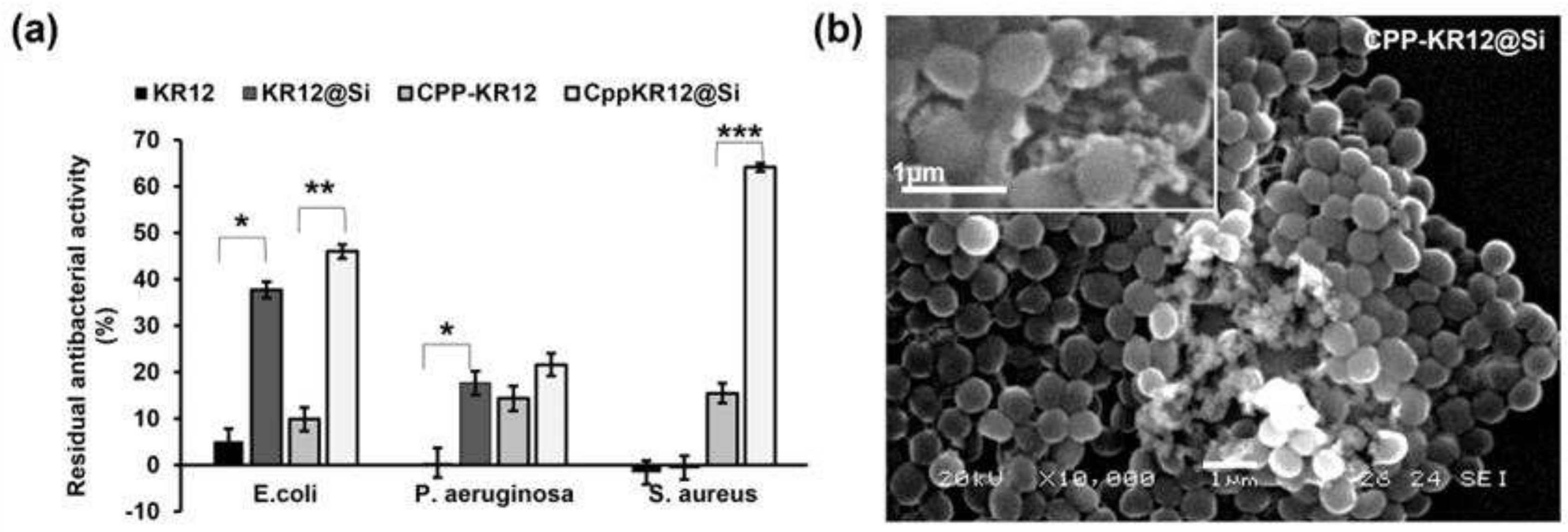
2.1.1. CPP Conjugation Enhances the Antibacterial Activity of KR12 over KR12 Alone
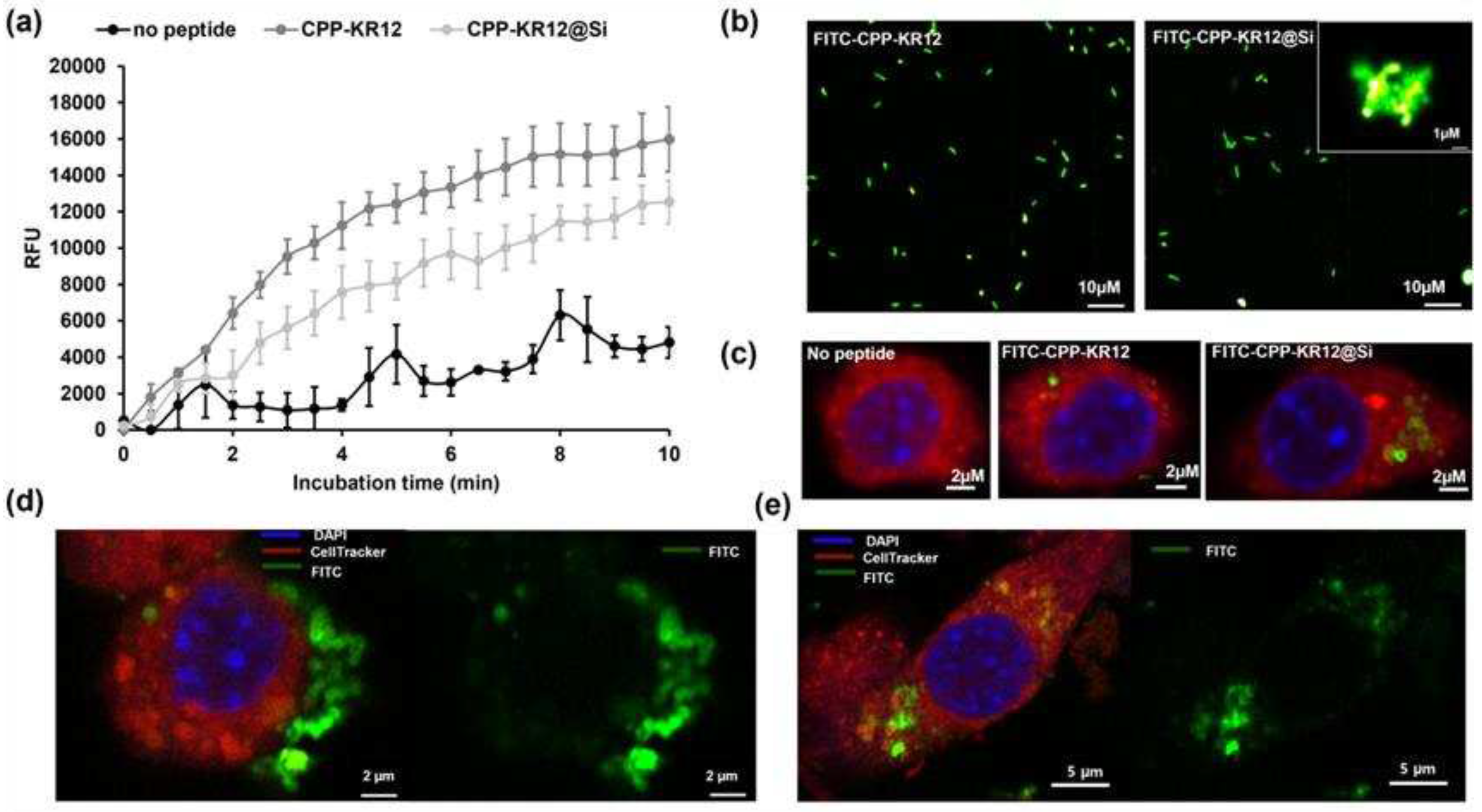
2.1.2. Comparison of AMP’s Membrane Permeability and Ability to Disrupt Cell Membranes
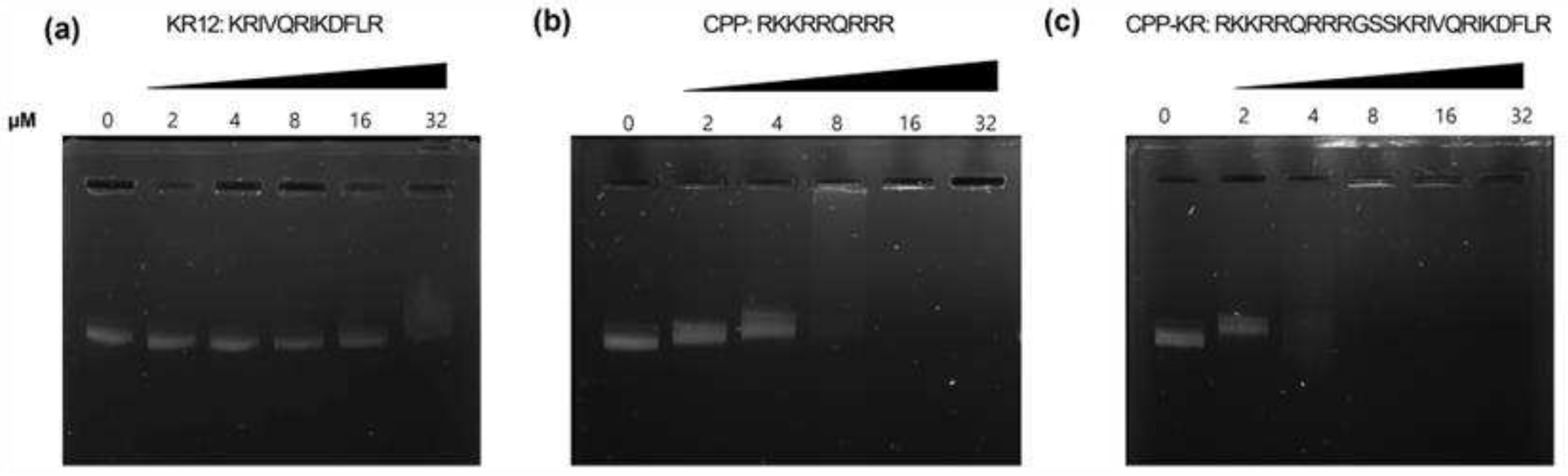
2.1.3. Comparison of AMP’s DNA Binding Ability
2.1.4. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of AMP on Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Induced Inflammation
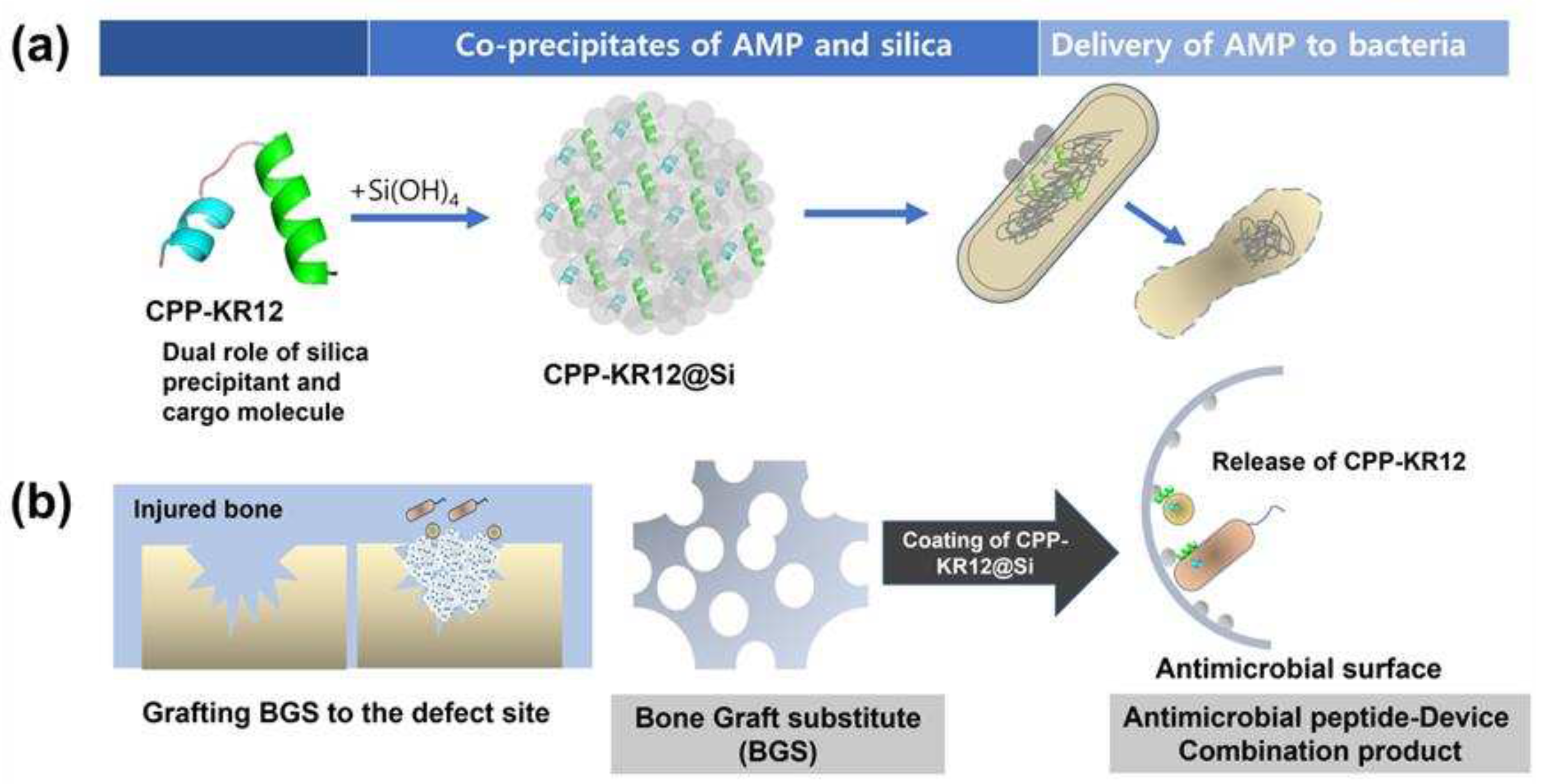
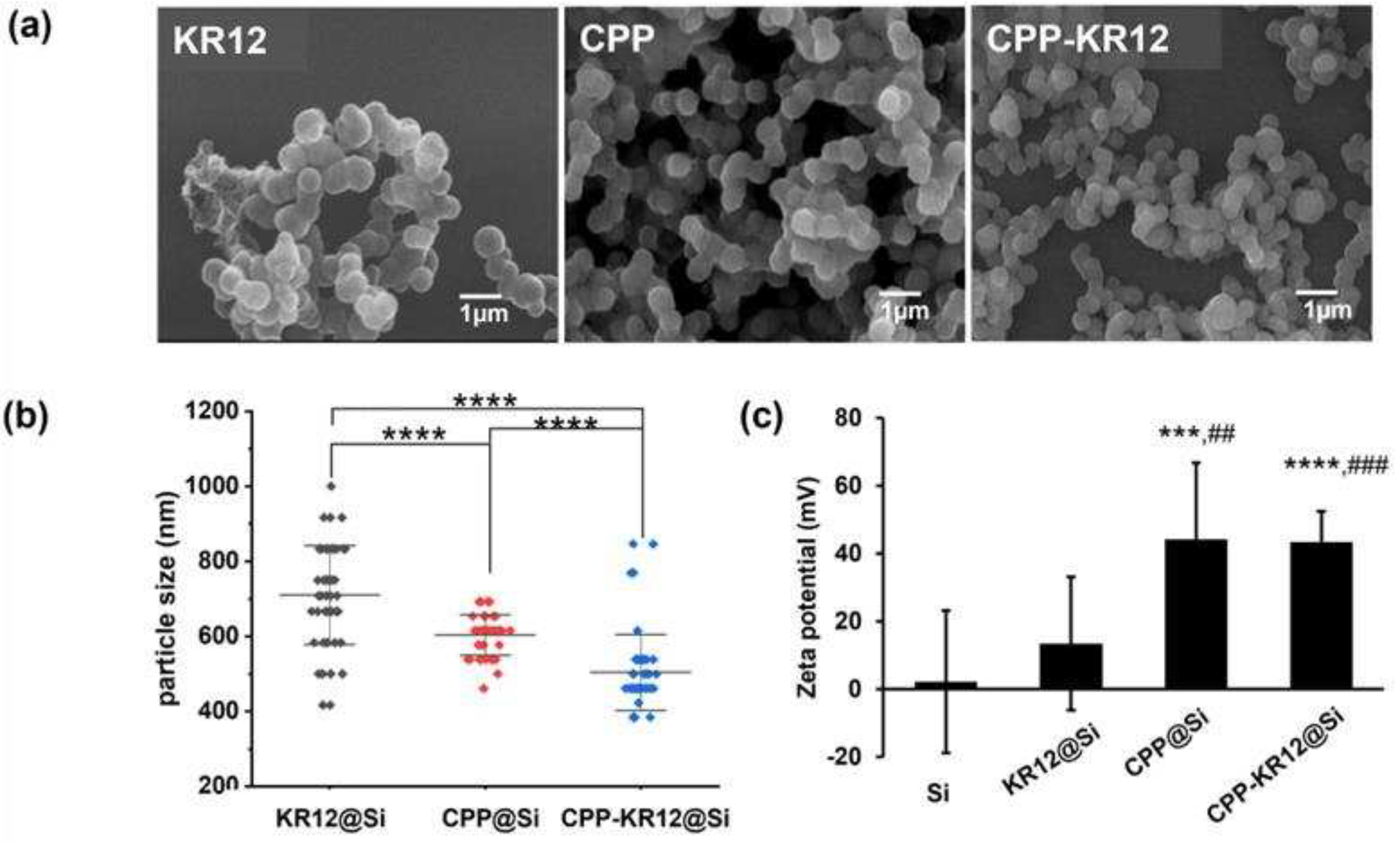
2.2. Self-Entrapment of AMPs in Silica Particles via AMP-Mediated Silica Deposition
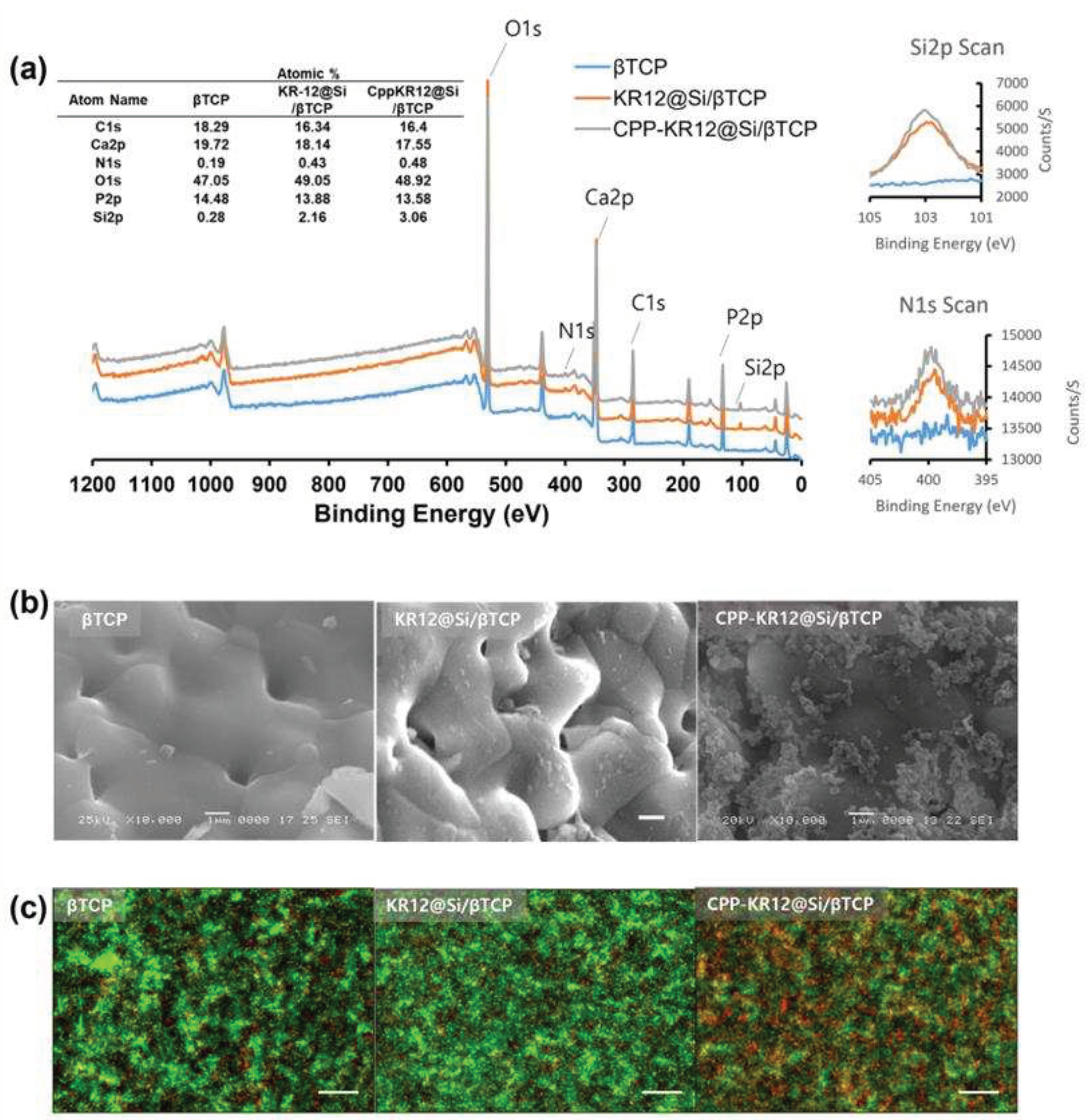
2.3. Characterization of CPP-KR12 in Silica Nanoparticle Form
2.3.1. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration of AMP@Si
2.3.2. Comparison of CPP-KR12 Delivery between Free and Immobilized Form
2.3.3. Stability of AMP@Si against Protease Treatment
2.4. Cytotoxicity and Hemolytic Activity of AMPs and AMP@Sis
2.5. AMP-Device Combination Products
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Bacterial Strains
3.3. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) of Antimicrobial Peptides (AMPs)
3.4. Silica Deposition and Quantification
3.5. Measurement of Entrapping and Loading Efficiency of AMP in Silica Particles
3.6. SYTOXTM Green Uptake Assay
3.7. Stability of AMP@Si against Protease Attack
3.8. Cytotoxicity and Hemolytic Activity Assay
3.9. Effect of AMPs on mRNA Expression of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines
3.10. Gel Retardation Assay
3.11. STED Microscopy and Confocal Images of Cells
3.12. Live/Dead Cell Assay
3.13. Zeta Potential Measurement
3.14. Sample Preparation of Bacterial Cells for Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3.15. Preparation of Bone Graft Substitute (BGS) Coated with AMP@Si (AMP@Si /β-TCP)
3.16. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3.17. High-Performance X-ray Photoelectron Spectrometer
3.18. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
5. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Uçkay, I.; Hoffmeyer, P.; Lew, D.; Pittet, D. Prevention of surgical site infections in orthopaedic surgery and bone trauma: state-of-the-art update. Journal of Hospital Infection 2013, 84, 5-12. [CrossRef]
- Bayramov, D.F.; Neff, J.A. Beyond conventional antibiotics — New directions for combination products to combat biofilm. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 2017, 112, 48-60. [CrossRef]
- Schierholz, J.M.; Beuth, J. Implant infections: a haven for opportunistic bacteria. Journal of Hospital Infection 2001, 49, 87-93. [CrossRef]
- van Barreveld, M.; Verstraelen, T.E.; Buskens, E.; van Dessel, P.F.H.M.; Boersma, L.V.A.; Delnoy, P.P.H.M.; Tuinenburg, A.E.; Theuns, D.A.M.J.; van der Voort, P.H.; Kimman, G.P.; Zwinderman, A.H.; Wilde, A.A.M.; Dijkgraaf, M.G.W.; van Barreveld, M.; Verstraelen, T.E.; Buskens, E.; van Dessel, P.F.H.M.; Boersma, L.V.A.; Delnoy, P.P.H.M.; Tuinenburg, A.E.; Theuns, D.A.M.J.; van der Voort, P.H.; Kimman, G.P.; Zwinderman, A.H.; Wilde, A.A.M.; Dijkgraaf, M.G.W. Hospital utilisation and the costs associated with complications of ICD implantation in a contemporary primary prevention cohort. Netherlands Heart Journal 2022, 31, 244-253. [CrossRef]
- Zogg, C.K.; Ottesen, T.D.; Kebaish, K.J.; Galivanche, A.; Murthy, S.; Changoor, N.R.; Zogg, D.L.; Pawlik, T.M.; Haider, A.H. The Cost of Complications Following Major Resection of Malignant Neoplasia. J Gastrointest Surg 2018, 22, 1976-1986. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Liang, H.; Clarke, E.; Jackson, C.; Xue, M. Inflammation in Chronic Wounds. Int J Mol Sci 2016, 17. [CrossRef]
- Komori, A.; Iriyama, H.; Kainoh, T.; Aoki, M.; Naito, T.; Abe, T. The impact of infection complications after trauma differs according to trauma severity. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 13803. [CrossRef]
- Dostert, M.; Trimble, M.J.; Hancock, R.E.W. Antibiofilm peptides: overcoming biofilm-related treatment failure. RSC Advances 2021, 11, 2718-2728. [CrossRef]
- Carpa, R.; Farkas, A.; Dobrota, C.; Butiuc-Keul, A. Double-Network Chitosan-Based Hydrogels with Improved Mechanical, Conductive, Antimicrobial, and Antibiofouling Properties. Gels 2023, 9. [CrossRef]
- Giangaspero, A.; Sandri, L.; Tossi, A. Amphipathic alpha helical antimicrobial peptides. Eur J Biochem 2001, 268, 5589-5600. [CrossRef]
- Huan, Y.; Kong, Q.; Mou, H.; Yi, H. Antimicrobial Peptides: Classification, Design, Application and Research Progress in Multiple Fields. Front Microbiol 2020, 11, 582779. [CrossRef]
- Huan, Y.; Kong, Q.; Mou, H.; Yi, H. Antimicrobial Peptides: Classification, Design, Application and Research Progress in Multiple Fields. Frontiers in Microbiology 2020, 11. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.-Y.; Yan, Z.-B.; Meng, Y.-M.; Hong, X.-Y.; Shao, G.; Ma, J.-J.; Cheng, X.-R.; Liu, J.; Kang, J.; Fu, C.-Y. Antimicrobial peptides: mechanism of action, activity and clinical potential. Military Medical Research 2021, 8. [CrossRef]
- Xuan, J.; Feng, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, R.; Zhang, B.; Bo, L.; Chen, Z.-S.; Yang, H.; Sun, L. Antimicrobial peptides for combating drug-resistant bacterial infections. Drug Resistance Updates 2023, 68. [CrossRef]
- Copolovici, D.M.; Langel, K.; Eriste, E.; Langel, Ü. Cell-Penetrating Peptides: Design, Synthesis, and Applications. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 1972-1994. [CrossRef]
- Ghorai, S.M.; Deep, A.; Magoo, D.; Gupta, C.; Gupta, N. Cell-Penetrating and Targeted Peptides Delivery Systems as Potential Pharmaceutical Carriers for Enhanced Delivery across the Blood–Brain Barrier (BBB). Pharmaceutics 2023, 15. [CrossRef]
- Huo, S.; Chen, C.; Lyu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Nie, B.e.; Yue, B. Overcoming Planktonic and Intracellular Staphylococcus aureus-Associated Infection with a Cell-Penetrating Peptide-Conjugated Antimicrobial Peptide. ACS Infectious Diseases 2020, 6, 3147-3162. [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Tan, P.; Dai, Z.; Wang, T.; Xu, S.; Ding, Y.; Jin, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, C.; Yue, Z.; Fu, H.; Yan, J.; Ma, X. Hydrophobic modification improves the delivery of cell-penetrating peptides to eliminate intracellular pathogens in animals. Acta Biomaterialia 2023, 157, 210-224. [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Lim, S.I.; Shin, S.-H.; Lim, Y.; Koh, J.W.; Yang, S. Conjugation of Cell-Penetrating Peptides to Antimicrobial Peptides Enhances Antibacterial Activity. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 15694-15701. [CrossRef]
- Ngambenjawong, C.; Chan, L.W.; Fleming, H.E.; Bhatia, S.N. Conditional Antimicrobial Peptide Therapeutics. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 15779-15791. [CrossRef]
- Hupcey, M.A.Z.; Ekins, S. Improving the drug selection and development process for combination devices. Drug Discovery Today 2007, 12, 844-852. [CrossRef]
- Nordström, R.; Malmsten, M. Delivery systems for antimicrobial peptides. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science 2017, 242, 17-34. [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, N.; Sumper, M.; Kröger, N. Biosilica formation in diatoms: Characterization of native silaffin-2 and its role in silica morphogenesis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2003, 100, 12075-12080. [CrossRef]
- Luckarift, H.R.; Spain, J.C.; Naik, R.R.; Stone, M.O. Enzyme immobilization in a biomimetic silica support. Nature Biotechnology 2004, 22, 211-213. [CrossRef]
- Pamirsky, I.; Golokhvast, K. Silaffins of Diatoms: From Applied Biotechnology to Biomedicine. Marine Drugs 2013, 11, 3155-3167. [CrossRef]
- Abdelhamid, M.A.A.; Pack, S.P. Biomimetic and bioinspired silicifications: Recent advances for biomaterial design and applications. Acta Biomaterialia 2021, 120, 38-56. [CrossRef]
- Ryu, Y.H.; Yeo, K.B.; Ki, M.-R.; Kim, Y.J.; Pack, S.P. Improved stability and reusability of endoglucanase from Clostridium thermocellum by a biosilica-based auto-encapsulation method. Biochemical Engineering Journal 2016, 105, 144-149. [CrossRef]
- Ki, M.-R.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, S.H.; Nguyen, T.K.M.; Kim, K.H.; Pack, S.P. Compartment-restricted and rate-controlled dual drug delivery system using a biosilica-enveloped ferritin cage. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry 2020, 81, 367-374. [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.K.; Ki, M.-R.; Kim, E.H.; Park, C.-J.; Ryu, J.J.; Jang, H.S.; Pack, S.P.; Jo, Y.K.; Jun, S.H. Biosilicated collagen/β-tricalcium phosphate composites as a BMP-2-delivering bone-graft substitute for accelerated craniofacial bone regeneration. Biomaterials Research 2021, 25. [CrossRef]
- Splith, K.; Neundorf, I. Antimicrobial peptides with cell-penetrating peptide properties and vice versa. European Biophysics Journal 2011, 40, 387-397. [CrossRef]
- Dürr, U.H.N.; Sudheendra, U.S.; Ramamoorthy, A. LL-37, the only human member of the cathelicidin family of antimicrobial peptides. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes 2006, 1758, 1408-1425. [CrossRef]
- Jacob, B.; Park, I.-S.; Bang, J.-K.; Shin, S.Y. Short KR-12 analogs designed from human cathelicidin LL-37 possessing both antimicrobial and antiendotoxic activities without mammalian cell toxicity. Journal of Peptide Science 2013, 19, 700-707. [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, S.; Nie, B.e.; Du, Z.; Long, T.; Yue, B. The antimicrobial peptide KR-12 promotes the osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow stem cells by stimulating BMP/SMAD signaling. RSC Advances 2018, 8, 15547-15557. [CrossRef]
- Derakhshankhah, H.; Jafari, S. Cell penetrating peptides: A concise review with emphasis on biomedical applications. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2018, 108, 1090-1096. [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.; Han, K.; Park, J.; Choi, S.Y. Enhanced uptake of a heterologous protein with an HIV-1 Tat protein transduction domains (PTD) at both termini. Mol Cells 2003, 16, 385-391.
- Zou, L.; Peng, Q.; Wang, P.; Zhou, B. Progress in Research and Application of HIV-1 TAT-Derived Cell-Penetrating Peptide. The Journal of Membrane Biology 2016, 250, 115-122. [CrossRef]
- Malanovic, N.; Lohner, K. Gram-positive bacterial cell envelopes: The impact on the activity of antimicrobial peptides. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes 2016, 1858, 936-946. [CrossRef]
- Melo, M.N.; Ferre, R.; Castanho, M.A.R.B. Antimicrobial peptides: linking partition, activity and high membrane-bound concentrations. Nature Reviews Microbiology 2009, 7, 245-250. [CrossRef]
- Le, C.-F.; Fang, C.-M.; Sekaran, S.D. Intracellular Targeting Mechanisms by Antimicrobial Peptides. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 2017, 61. [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Dong, S.L.; Xu, F.; Wang, X.Q.; Withers, T.R.; Yu, H.D.; Wang, X. Effect of Intracellular Expression of Antimicrobial Peptide LL-37 on Growth of Escherichia coli Strain TOP10 under Aerobic and Anaerobic Conditions. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 2013, 57, 4707-4716. [CrossRef]
- Rowe-Magnus, D.A.; Kao, A.Y.; Prieto, A.C.; Pu, M.; Kao, C.; Davies, J.E. Cathelicidin Peptides Restrict Bacterial Growth via Membrane Perturbation and Induction of Reactive Oxygen Species. mBio 2019, 10. [CrossRef]
- Pulido, D.; Nogués, M.V.; Boix, E.; Torrent, M. Lipopolysaccharide Neutralization by Antimicrobial Peptides: A Gambit in the Innate Host Defense Strategy. Journal of Innate Immunity 2012, 4, 327-336. [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Shang, D. Inhibitory Effects of Antimicrobial Peptides on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation. Mediators of Inflammation 2015, 2015, 1-8. [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Wang, W.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, S.; Li, M.; Li, N.; Pan, G.; Zhang, X.; Bai, J.; Zhu, C. Immunomodulatory biomaterials for implant-associated infections: from conventional to advanced therapeutic strategies. Biomaterials Research 2022, 26. [CrossRef]
- Noori, M.S.; Courreges, M.C.; Bergmeier, S.C.; McCall, K.D.; Goetz, D.J. Modulation of LPS-induced inflammatory cytokine production by a novel glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibitor. European Journal of Pharmacology 2020, 883. [CrossRef]
- Lechner, C.C.; Becker, C.F.W. A sequence-function analysis of the silica precipitating silaffin R5 peptide. Journal of Peptide Science 2014, 20, 152-158. [CrossRef]
- Lechner, C.; Becker, C. Silaffins in Silica Biomineralization and Biomimetic Silica Precipitation. Marine Drugs 2015, 13, 5297-5333. [CrossRef]
- Ki, M.R.; Kim, S.H.; Nguyen, T.K.M.; Son, R.G.; Jun, S.H.; Pack, S.P. BMP2-Mediated Silica Deposition: An Effective Strategy for Bone Mineralization. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 2022. [CrossRef]
- Ki, M.-R.; Nguyen, T.K.M.; Park, T.-I.; Park, H.-M.; Pack, S.P. Biomimetic Silica Particles with Self-Loading BMP-2 Knuckle Epitope Peptide and Its Delivery for Bone Regeneration. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15. [CrossRef]
- Nanomaterials for Drug Delivery and Therapy; 2019; p.^pp.
- Németh, Z.; Csóka, I.; Semnani Jazani, R.; Sipos, B.; Haspel, H.; Kozma, G.; Kónya, Z.; Dobó, D.G. Quality by Design-Driven Zeta Potential Optimisation Study of Liposomes with Charge Imparting Membrane Additives. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14. [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Xu, H.; Xia, J.; Ma, J.; Xu, J.; Li, Y.; Feng, J. D- and Unnatural Amino Acid Substituted Antimicrobial Peptides With Improved Proteolytic Resistance and Their Proteolytic Degradation Characteristics. Frontiers in Microbiology 2020, 11. [CrossRef]
- Ong, Z.Y.; Wiradharma, N.; Yang, Y.Y. Strategies employed in the design and optimization of synthetic antimicrobial peptide amphiphiles with enhanced therapeutic potentials. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 2014, 78, 28-45. [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Zhu, R.; Zhao, Y.; An, X.; Jia, F.; Peng, J.; Ma, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, J.; Su, J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, K.; Yan, W.; Wang, R. Antimicrobial activity and stability of protonectin withD-amino acid substitutions. Journal of Peptide Science 2017, 23, 392-402. [CrossRef]
- Oliva, R.; Chino, M.; Pane, K.; Pistorio, V.; De Santis, A.; Pizzo, E.; D’Errico, G.; Pavone, V.; Lombardi, A.; Del Vecchio, P.; Notomista, E.; Nastri, F.; Petraccone, L. Exploring the role of unnatural amino acids in antimicrobial peptides. Scientific Reports 2018, 8. [CrossRef]
- Khara, J.S.; Priestman, M.; Uhía, I.; Hamilton, M.S.; Krishnan, N.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.Y.; Langford, P.R.; Newton, S.M.; Robertson, B.D.; Ee, P.L.R. Unnatural amino acid analogues of membrane-active helical peptides with anti-mycobacterial activity and improved stability. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 2016, 71, 2181-2191. [CrossRef]
- Häffner, S.M.; Parra-Ortiz, E.; Browning, K.L.; Jørgensen, E.; Skoda, M.W.A.; Montis, C.; Li, X.; Berti, D.; Zhao, D.; Malmsten, M. Membrane Interactions of Virus-like Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 6787-6800. [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Papareddy, P.; Mörgelin, M.; Schmidtchen, A.; Malmsten, M. Effects of PEGylation on Membrane and Lipopolysaccharide Interactions of Host Defense Peptides. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 1337-1345. [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Malugin, A.; Ghandehari, H. Impact of Silica Nanoparticle Design on Cellular Toxicity and Hemolytic Activity. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 5717-5728. [CrossRef]
- Slowing, I.I.; Wu, C.W.; Vivero-Escoto, J.L.; Lin, V.S.Y. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Reducing Hemolytic Activity Towards Mammalian Red Blood Cells. Small 2009, 5, 57-62. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Sun, X.; Zhang, G.; Trewyn, B.G.; Slowing, I.I.; Lin, V.S.Y. Interaction of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles with Human Red Blood Cell Membranes: Size and Surface Effects. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 1366-1375. [CrossRef]
- Bellezza, I.; Giambanco, I.; Minelli, A.; Donato, R. Nrf2-Keap1 signaling in oxidative and reductive stress. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research 2018, 1865, 721-733. [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Lu, H.; Bai, Y. Nrf2 in cancers: A double-edged sword. Cancer Med 2019, 8, 2252-2267. [CrossRef]
- Greczynski, G.; Hultman, L. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy: Towards reliable binding energy referencing. Progress in Materials Science 2020, 107. [CrossRef]
- Stiefel, P.; Schmidt-Emrich, S.; Maniura-Weber, K.; Ren, Q. Critical aspects of using bacterial cell viability assays with the fluorophores SYTO9 and propidium iodide. BMC Microbiology 2015, 15. [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, M.; Azevedo, N.F.; Ivask, A. Propidium iodide staining underestimates viability of adherent bacterial cells. Scientific Reports 2019, 9. [CrossRef]
- Stocks, S.M. Mechanism and use of the commercially available viability stain,BacLight. Cytometry 2004, 61A, 189-195. [CrossRef]
- Abdelhamid, M.A.A.; Yeo, K.B.; Ki, M.-R.; Pack, S.P. Self-encapsulation and controlled release of recombinant proteins using novel silica-forming peptides as fusion linkers. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2019, 125, 1175-1183. [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Tian, H.; Chen, R.; Liu, Q.; Jia, K.; Hu, D.-L.; Chen, H.; Ye, C.; Peng, L.; Fang, R. Synergistic Antimicrobial Effect of Antimicrobial Peptides CATH-1, CATH-3, and PMAP-36 With Erythromycin Against Bacterial Pathogens. Frontiers in Microbiology 2022, 13. [CrossRef]
- Roth, B.L.; Poot, M.; Yue, S.T.; Millard, P.J. Bacterial viability and antibiotic susceptibility testing with SYTOX green nucleic acid stain. Appl Environ Microbiol 1997, 63, 2421-2431. [CrossRef]
- Ki, M.-R.; Kim, S.H.; Nguyen, T.K.M.; Son, R.G.; Jun, S.H.; Pack, S.P. BMP2-Mediated Silica Deposition: An Effective Strategy for Bone Mineralization. ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering 2022, 9, 1823-1833. [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lee, T.A.; Song, S.J.; Park, T.; Park, B. Hyperproduction of IL-6 caused by aberrant TDP-43 overexpression in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. FEBS Letters 2015, 589, 1825-1831. [CrossRef]


| Name | Sequence (N-C) | AA # | Calculated Mass (Da)1 |
Observed Mass (Da)2 |
pI1 | Net Charge1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR12 | KRIVQRIKDFLR | 12 | 1612.00 | 1612.80 | 12.79 | +4 |
| CPP | RKKRRQRRR | 9 | 1379.89 | 1380.00 | 14.00 | +8 |
| CPP-KR12 | RKKRRQRRRGSSKRIVQRIKDFLR | 24 | 3163.94 | 3165.00 | 13.39 | +12 |
| FITC-CPP-KR12 | FITC-Ahx- RKKRRQRRRGSSKRIVQRIKDFLR | 24 | 3624.05 | 3625.92 | 13.39 | +12 |
| Peptide | E. coli | P. aeruginosa | S. aureus |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR12 | 103.36±25.82 | 181.98±68.20 | > 320a |
| CPP-KR12 | 12.09±4.97 | 6.12±3.72 | 22.80±8.48 |
| Initial AMP (μg) | Entrapped AMP (μg) | Silica deposition (μg) |
LEa (%) | EEb (%) | |
| KR12@Si | 100 | 56.70±4.71 | 25.14±2.08 | 69.16 | 56.70 |
| CPP@Si | 100 | 95.45±2.06 | 30.29±2.44 | 76.31 | 95.45 |
| CPP-KR12@Si | 100 | 94.45±1.93 | 33.70±2.86 | 73.83 | 94.45 |
| Peptide | E. coli | P. aeruginosa | S. aureus |
| KR12@Si | 105.27±28.62 | N.da | 58.16±19.39 |
| CPP-KR12@Si | 14.54±4.89 | 8.40±2.81 | 28.75±16.87 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





