Submitted:
26 September 2023
Posted:
28 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
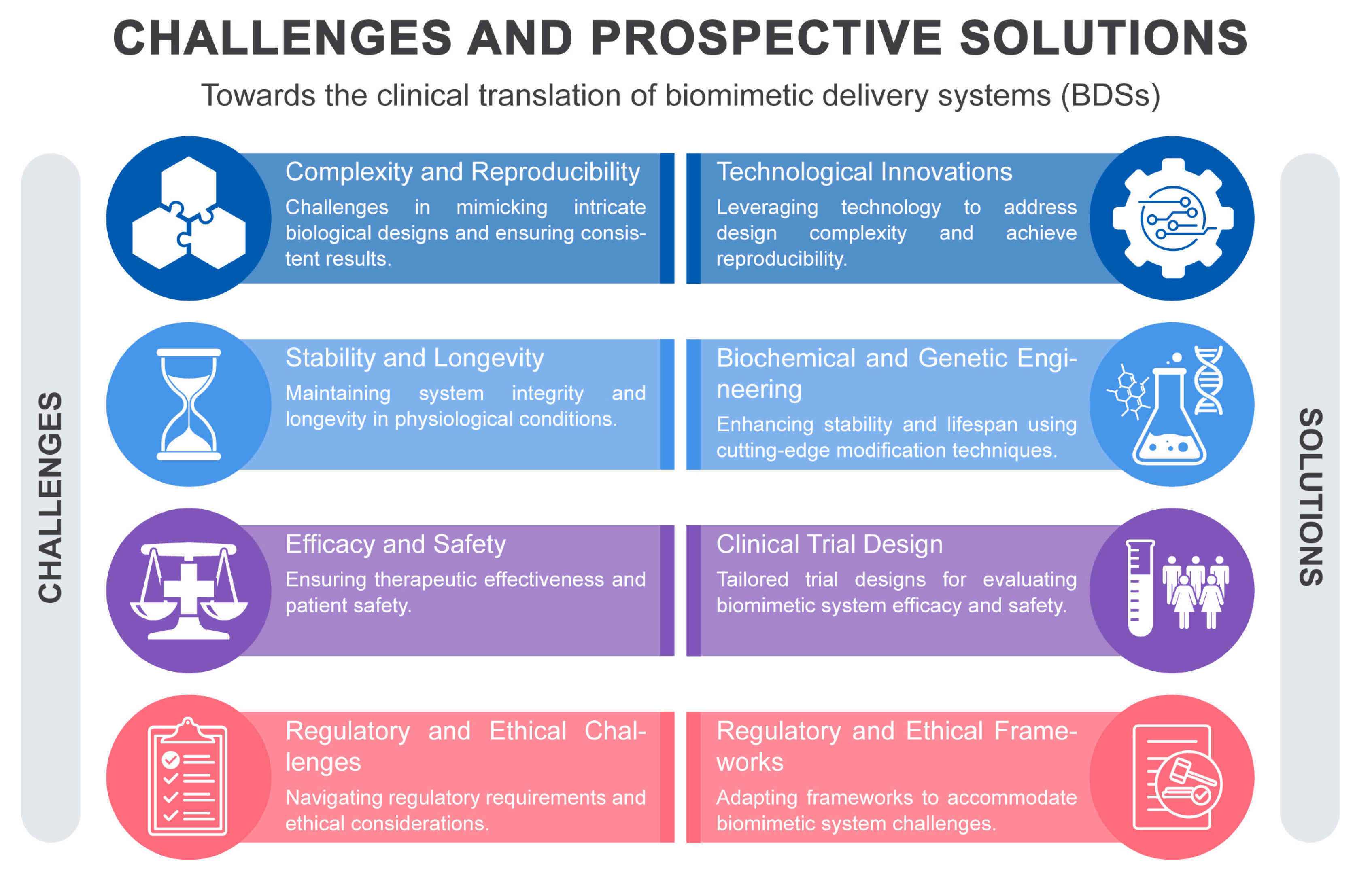
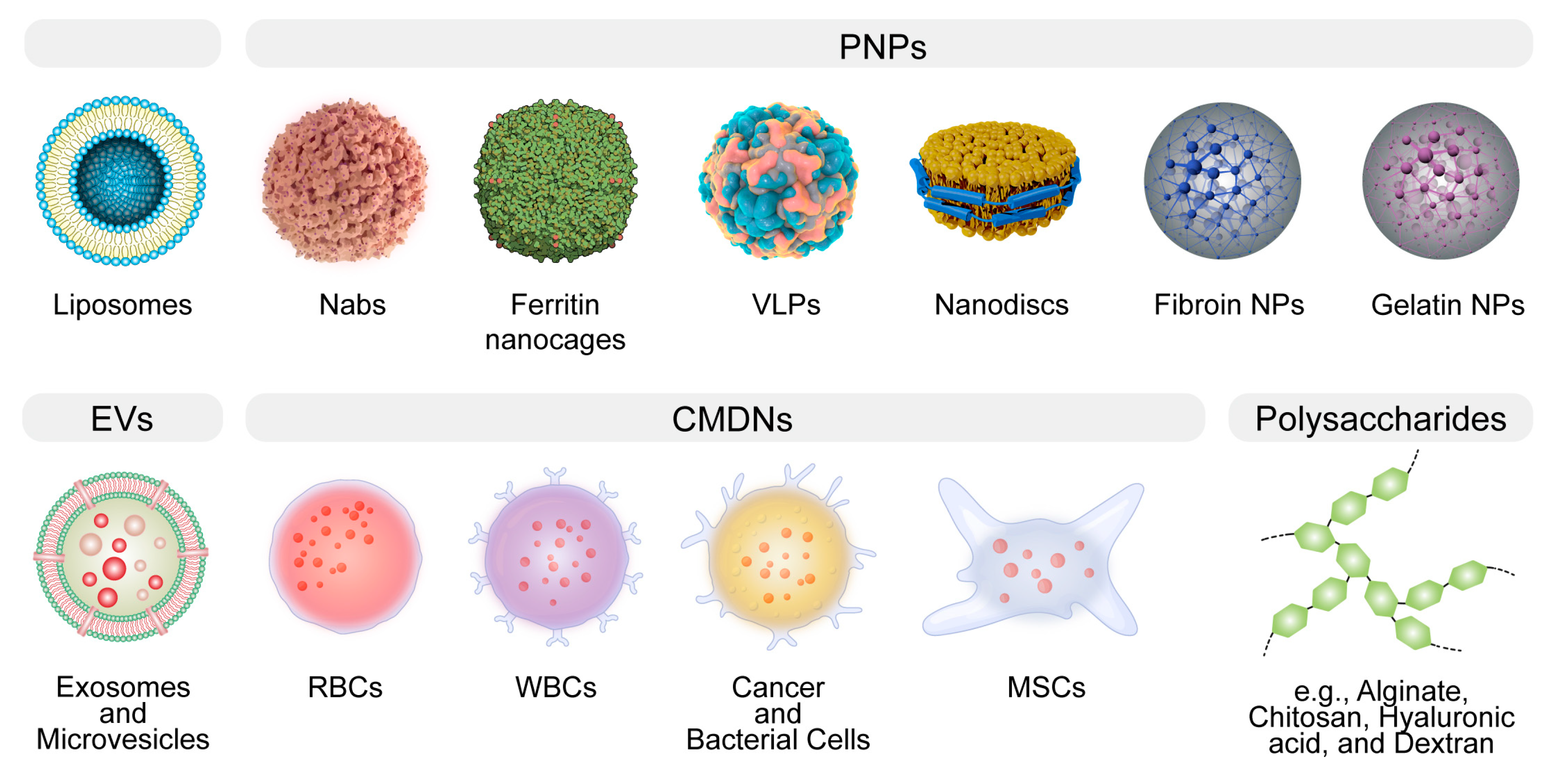
2. Challenges and Approaches in Clinical Translation of BDSs
2.1. Complexity and Reproducibility
| BDS | Complexity and Reproducibility | Prospective Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Liposomes | Diverse lipids induce variability. Sustained stability is challenging. Surface alterations cause variability. Scaling up adds variability. | Advanced lipid-mixing technologies. Freeze-thaw increases reproducibility. Advanced ligand conjugation methods. Automated production control. |
| Protein-based NPs | ||
| Albumin NPs | Influenced by albumin source. Uniform size & shape are hard to attain. Altered surface for specific targeting. Efficient drug encapsulation control. | High-pressure homogenization. Improved purification techniques. High Throughput Screening. Microfluidics and Computational Modeling. |
| Protein-based nanocages | Ensuring consistent protein folding. Reproducible encapsulation. Stable surface chemistry. Efficient drug encapsulation control. Consistent drug release profiles. | Advanced bioengineering methods. Monitoring protein folding in real-time. New modification methods for stability. Innovative drug-loading for consistency. Smart release systems for specific triggers. |
| VLPs | Complexity in VLP assembly. Attaining purity and reproducibility. Heterogeneous surface modifications. Inconsistent therapeutic encapsulation in VLPs. | Advanced purification like SEC. Genomic engineering for optimized production. Developed specific bioconjugation techniques. High-throughput techniques for optimal encapsulation. |
| NDs | Component multiplicity causes variability. Consistent size and shape. Adding functional groups increases complexity. Batch-to-batch variability | Synthesis and purification for uniformity. Advanced assembly techniques. Site-specific functionalization and modular design. Standardized protocols, real-time QC, and advanced characterization. |
| EVs | Heterogeneity of EV populations. Differentiating EV subtypes is challenging. Possible contamination with proteins. Ensuring efficient encapsulation. Controlling release kinetics. Maintaining EV properties post-modification. Ensuring targeting specificity. EV source depends on donor cells. | Advanced centrifugation. High-resolution imaging & flow cytometry. Improved purification processes. Sonication or electroporation. Covalent and non-covalent linking. Bio-orthogonal chemistry. Molecular imprinting techniques. Standardized cell lines/biofactories. |
| CMDNs | Potential heterogeneity due to cell sources. Unpredictable biological interactions. Batch-to-batch differences. Enhancing nanocarrier functionality/specificity. | Improved cell culture techniques. Predictive molecular modeling & simulation. Controlled nanocarrier production via microfluidics. Surface engineering, genetic modifications, molecular tethering strategies. |
| Polysaccharides | ||
| Alginate | Variability in alginate source/purity. Gelation process control. Encapsulation efficiency variability. | Advanced chromatography for purification. Microfluidics for consistent gel bead formation. Advanced sonication/emulsification. |
| Chitosan | Molecular weight influences properties. Degree of deacetylation influences properties. Replicating desired structures is challenging. Crosslinking variability affects stability. Uniform surface properties are challenging. | Advanced chromatographic techniques to standardize molecular weight. Spectroscopy for precise deacetylation. High-resolution microscopy & automated synthesis. Advanced controlled crosslinking techniques. Advanced surface characterization. |
| Hyaluronic acid | Variability in sources. Consistent molecular weight is crucial. | Microbial synthesis of HA for consistency. Real-time molecular weight monitoring. |
| Dextran | Variability in molecular weight distribution. Branching variation affects behavior. Functional group variation. Achieving consistent size/morphology is challenging. | Controlled polymerization methods. Detailed structure analysis via spectroscopy. Controlled enzymatic/chemical modifications. Microfluidics for controlled and reproducible nanosystem generation. |
2.2. Stability and Longevity
| BDS | Stability and Longevity Challenges | Prospective Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Liposomes | Sensitivity to oxidation and hydrolysis. Fusion/aggregation in serum. Rapid clearance from circulation. | Liposome coating (e.g., PEGylation). Incorporation of cholesterol. Antioxidant inclusion. |
| Protein-Based NPs | ||
| Albumin nanoparticles | Instability in harsh environments (e.g., acidic pH). Enzymatic degradation. | Cross-linking of albumin molecules. Encapsulation with protective polymers. Surface modifications. |
| Protein-based nanocages | Structural disintegration at non-optimal conditions. Immune recognition and clearance. | Chemical surface modifications. Incorporation of stability-enhancing ligands. Fusion with other stable proteins. |
| VLPs | Potential immunogenicity. Stability issues due to dynamic protein structures. | Genetic modifications. Encapsulation within protective matrices. Surface modifications to reduce immunogenicity. |
| NDs | Sensitivity to physiologic conditions, leading to structural alteration. Potential immune recognition. | Use of stable lipids. Protective protein inclusion. Surface modification. |
| Fibroin and Gelatin | Sensitivity to temperature and pH. Enzymatic degradation in vivo. | Chemical cross-linking. Incorporation into composite materials. Coating with protective polymers. |
| EVs | Susceptibility to clearance mechanisms. Sensitivity to physiologic conditions leading to vesicle disruption. | Surface modifications. PEGylation. Encapsulation within biomaterials. Cryopreservation techniques. |
| CMDNs | Potential immunogenicity. Sensitivity to in vivo degradation mechanisms. | Immune camouflage techniques. Genetic modifications for enhanced stability. Surface modifications. |
| Polysaccharides | ||
| Alginate | Rapid degradation in vivo. Instability in the presence of divalent cations. | Cross-linking with divalent cations. Incorporation into composite materials. Layer-by-layer assembly. |
| Chitosan | Solubility issues in neutral and basic pH. Rapid degradation in vivo. | Chemical modifications for solubility. Cross-linking. Layer-by-layer assembly. |
| Hyaluronic acid | Rapid enzymatic degradation in vivo. Instability under harsh conditions. | Derivatization and cross-linking. Hydrogel formulations. Composite materials incorporation. |
| Dextran | Sensitivity to oxidative conditions. Enzymatic degradation. | Cross-linking. Encapsulation within protective matrices. Blend with other stable polymers. |
2.3. Efficacy and Safety
2.4. Regulatory and Ethical Challenges
| Categories | Insights |
|---|---|
| Regulatory Challenges |
|
| Regulatory Frameworks |
|
| Ethical Challenges |
|
| Ethical Frameworks |
|
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sheikhpour, M.; Barani, L.; Kasaeian, A. Biomimetics in drug delivery systems: A critical review. J. Control. Release 2017, 253, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, J.F.V. Biomimetics — a review. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part H: Journal of Engineering in Medicine 2009, 223, 919–939.
- Vincent, J.F.V.; Bogatyreva, O.A.; Bogatyrev, N.R.; et al. Biomimetics: its practice and theory. J. R. Soc. Interface 2006, 3, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, S.; E Byrne, M.; A Peppas, N.; Hilt, J.Z. Applications of biomimetic systems in drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2005, 2, 1085–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuta, T.; Kogure, K. Biomimetic Nanoparticle Drug Delivery Systems to Overcome Biological Barriers for Therapeutic Applications. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2022, 70, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-X.; Wei, C.-X.; Lyu, Y.-Q.; Chen, H.-Z.; Jiang, G.; Gao, X.-L. Biomimetic drug-delivery systems for the management of brain diseases. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 1073–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Hong, W.; Ren, W.; Xu, T.; Qian, Z.; He, Z. Recent progress in targeted delivery vectors based on biomimetic nanoparticles. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, T.; Nabeel, F.; Raza, A.; Bilal, M.; Iqbal, H. Biomimetic nanostructures/cues as drug delivery systems: a review. Mater. Today Chem. 2019, 13, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Du, Y.; Wang, S.; Chen, B. A Review of Biomimetic Nanoparticle Drug Delivery Systems Based on Cell Membranes. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2020, ume 14, 5495–5503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrawati, R.; Caruso, F. Biomimetic Liposome- and Polymersome-Based Multicompartmentalized Assemblies. Langmuir 2012, 28, 13798–13807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tariq, H.; Batool, S.; Asif, S.; Ali, M.; Abbasi, B.H. Virus-Like Particles: Revolutionary Platforms for Developing Vaccines Against Emerging Infectious Diseases. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 790121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nooraei, S.; Bahrulolum, H.; Hoseini, Z.S.; Katalani, C.; Hajizade, A.; Easton, A.J.; Ahmadian, G. Virus-like particles: preparation, immunogenicity and their roles as nanovaccines and drug nanocarriers. J. Nanobiotechnology 2021, 19, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banskota, S.; Raguram, A.; Suh, S.; et al. Engineered virus-like particles for efficient in vivo delivery of therapeutic proteins. Cell 2022, 185, 250–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geckil, H.; Xu, F.; Zhang, X.; Moon, S.; Demirci, U. Engineering hydrogels as extracellular matrix mimics. Nanomedicine 2010, 5, 469–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Gao, J. The engineering and application of extracellular matrix hydrogels: a review. Biomater. Sci. 2023, 11, 3784–3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Díaz, E.C.; Varghese, S. Hydrogels as extracellular matrix analogs. Gels 2016, 2, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vader, P.; Mol, E.A.; Pasterkamp, G.; Schiffelers, R.M. Extracellular vesicles for drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 106, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, I.K.; Wood, M.J.A.; Fuhrmann, G. Extracellular vesicles as a next-generation drug delivery platform. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2021, 16, 748–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzykantov, V.R. Drug delivery by red blood cells: vascular carriers designed by mother nature. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2010, 7, 403–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, C.H.; Anselmo, A.C.; Mitragotri, S.; Muzykantov, V. Red blood cells: Supercarriers for drugs, biologicals, and nanoparticles and inspiration for advanced delivery systems. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 106, 88–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Pol, E.; Böing, A. N.; Harrison, P.; Sturk, A.; Nieuwland, R. , Classification, Functions, and Clinical Relevance of Extracellular Vesicles. Pharmacol. Rev. 2012, 64, 676–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V.S. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science 2020, 367, eaau6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raposo, G.; Stoorvogel, W. Extracellular vesicles: Exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 200, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muralidharan-Chari, V.; Clancy, J.W.; Sedgwick, A.; D'Souza-Schorey, C. Microvesicles: mediators of extracellular communication during cancer progression. J. Cell Sci. 2010, 123, 1603–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Théry, C.; Zitvogel, L.; Amigorena, S. Exosomes: composition, biogenesis and function. Nature Reviews Immunology 2002, 2, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’brien, K.; Breyne, K.; Ughetto, S.; Laurent, L.C.; Breakefield, X.O. RNA delivery by extracellular vesicles in mammalian cells and its applications. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 585–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, C.H.; Cines, D.B.; Siegel, D.L.; Muzykantov, V. Erythrocytes as Carriers for Drug Delivery in Blood Transfusion and Beyond. Transfus. Med. Rev. 2017, 31, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Hou, X.; Feng, N. Red blood cell membrane-camouflaged nanoparticles: a novel drug delivery system for antitumor application. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2019, 9, 675–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glassman, P.M.; Villa, C.H.; Ukidve, A.; Zhao, Z.; Smith, P.; Mitragotri, S.; Russell, A.J.; Brenner, J.S.; Muzykantov, V.R. Vascular Drug Delivery Using Carrier Red Blood Cells: Focus on RBC Surface Loading and Pharmacokinetics. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujita, M.; Wolska, A.; Gutmann, D.A.; Remaley, A.T. Reconstituted Discoidal High-Density Lipoproteins: Bioinspired Nanodiscs with Many Unexpected Applications. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2018, 20, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, T. Phospholipid nanodisc engineering for drug delivery systems. Biotechnol. J. 2012, 7, 762–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bariwal, J.; Ma, H.; Altenberg, G.A.; Liang, H. Nanodiscs: a versatile nanocarrier platform for cancer diagnosis and treatment. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 1702–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traughber, C.A.; Opoku, E.; Brubaker, G.; Major, J.; Lu, H.; Lorkowski, S.W.; Neumann, C.; Hardaway, A.; Chung, Y.-M.; Gulshan, K.; et al. Uptake of high-density lipoprotein by scavenger receptor class B type 1 is associated with prostate cancer proliferation and tumor progression in mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 8252–8261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranova, I.N.; Kurlander, R.; Bocharov, A.V.; Vishnyakova, T.G.; Chen, Z.; Remaley, A.T.; Csako, G.; Patterson, A.P.; Eggerman, T.L. Role of Human CD36 in Bacterial Recognition, Phagocytosis, and Pathogen-Induced JNK-Mediated Signaling. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 7147–7156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Wang, J.; Lv, P.; Liu, G. Biomimetic synthesis of nanovesicles for targeted drug delivery. Sci. Bull. 2018, 63, 663–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, R.S.; Tirrell, M. Bottom-up design of biomimetic assemblies. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2004, 56, 1537–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, X.; Huang, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z. Harnessing Protein Corona for Biomimetic Nanomedicine Design. Biomimetics 2022, 7, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Kong, N.; Liu, C.; Chen, W.; Huang, X.; Xu, D.; Ouyang, J.; Feng, C.; Wang, C.; et al. Nano-bio interfaces effect of two-dimensional nanomaterials and their applications in cancer immunotherapy. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 3447–3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Xiong, Q.; Hornburg, D.; Tao, W.; Farokhzad, O.C. Nano–Bio Interactions in Cancer: From Therapeutics Delivery to Early Detection. Accounts Chem. Res. 2021, 54, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, X.; Liu, G.; Han, K.; Chen, J.; Wang, J. Editorial: The Application of Nanoengineering in Advanced Drug Delivery and Translational Research. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 886109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, J.; Kong, H.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, G. Functional biomimetic nanoparticles for drug delivery and theranostic applications in cancer treatment. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2018, 19, 771–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, A.Z.; Lv, P.; Tao, W.; Liu, G. Advancing the Pharmaceutical Potential of Bioinorganic Hybrid Lipid-Based Assemblies. Adv. Sci. 2018, 5, 1800564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guido, C.; Maiorano, G.; Cortese, B.; D’amone, S.; Palamà, I.E. Biomimetic Nanocarriers for Cancer Target Therapy. Bioengineering 2020, 7, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabu, C.; Rejo, C.; Kotta, S.; Pramod, K. Bioinspired and biomimetic systems for advanced drug and gene delivery. J. Control. Release 2018, 287, 142–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Yu, J.-M.; Gan, Y.-C.; Qiu, X.-Z.; Gao, Z.-C.; Wang, H.; Chen, S.-X.; Xiong, Y.; Liu, G.-H.; Lin, S.-E.; et al. Biomimetic natural biomaterials for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine: new biosynthesis methods, recent advances, and emerging applications. Mil. Med Res. 2023, 10, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Chen, G.; Zhang, J. A Review of Liposomes as a Drug Delivery System: Current Status of Approved Products, Regulatory Environments, and Future Perspectives. Molecules 2022, 27, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández, V.A.; Karlsson, G.; Edwards, K. Intrinsic Heterogeneity in Liposome Suspensions Caused by the Dynamic Spontaneous Formation of Hydrophobic Active Sites in Lipid Membranes. Langmuir 2011, 27, 4873–4883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maritim, S.; Boulas, P.; Lin, Y. Comprehensive analysis of liposome formulation parameters and their influence on encapsulation, stability and drug release in glibenclamide liposomes. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 592, 120051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, L.D.; Tai, L.C.L.; Ko, D.S.C.; et al. Influence of Vesicle Size, Lipid Composition, and Drug-to-Lipid Ratio on the Biological Activity of Liposomal Doxorubicin in Mice1. Cancer Research 1989, 49, 5922–5930. [Google Scholar]
- Crowe, J.H.; Crowe, L.M. Factors affecting the stability of dry liposomes. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes 1988, 939, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senior, J.H. Fate and behavior of liposomes in vivo: a review of controlling factors. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst. 1987, 3, 123–193. [Google Scholar]
- Sułkowski, W.W.; Pentak, D.; Nowak, K.; et al. The influence of temperature, cholesterol content and pH on liposome stability. Journal of Molecular Structure 2005, 744-747, 737–747.
- Hupfeld, S.; Holsæter, A.M.; Skar, M.; et al. Liposome Size Analysis by Dynamic/Static Light Scattering upon Size Exclusion-/Field Flow-Fractionation. Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology 2006, 6, 3025–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyen, C.; Larquet, E.; Coureux, P.-D.; Frances, O.; Herman, F.; Sablé, S.; Burnouf, J.-P.; Sizun, C.; Lescop, E. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy: A Multifaceted Toolbox to Probe Structure, Dynamics, Interactions, and Real-Time In Situ Release Kinetics in Peptide-Liposome Formulations. Mol. Pharm. 2021, 18, 2521–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siriwardane, D.A.; Wang, C.; Jiang, W.; Mudalige, T. Quantification of phospholipid degradation products in liposomal pharmaceutical formulations by ultra performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS). Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 578, 119077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, A.; Vorauer-Uhl, K. Liposome Technology for Industrial Purposes. J. Drug Deliv. 2010, 2011, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carugo, D.; Bottaro, E.; Owen, J.; Stride, E.; Nastruzzi, C. Liposome production by microfluidics: potential and limiting factors. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parchekani, J.; Allahverdi, A.; Taghdir, M.; Naderi-Manesh, H. Design and simulation of the liposomal model by using a coarse-grained molecular dynamics approach towards drug delivery goals. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jämbeck, J.P.M.; Eriksson, E.S.E.; Laaksonen, A.; Lyubartsev, A.P.; Eriksson, L.A. Molecular Dynamics Studies of Liposomes as Carriers for Photosensitizing Drugs: Development, Validation, and Simulations with a Coarse-Grained Model. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2014, 10, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langer, K.; Anhorn, M.G.; Steinhauser, I.; Dreis, S.; Celebi, D.; Schrickel, N.; Faust, S.; Vogel, V. Human serum albumin (HSA) nanoparticles: Reproducibility of preparation process and kinetics of enzymatic degradation. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 347, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertucci, C.; Domenici, E. Reversible and covalent binding of drugs to human serum albumin: methodological approaches and physiological relevance. Curr. Med. Chem. 2002, 9, 1463–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galisteo-González, F.; Molina-Bolívar, J.A. Systematic study on the preparation of BSA nanoparticles. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces 2014, 123, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciążek-Jurczyk, M.; Szkudlarek, A.; Chudzik, M.; Pożycka, J.; Sułkowska, A. Alteration of human serum albumin binding properties induced by modifications: A review. Spectrochim. Acta Part A: Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2018, 188, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hornok, V. Serum Albumin Nanoparticles: Problems and Prospects. Polymers 2021, 13, 3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Isiah, R.; Backianathan, S.; Jagan, L.; Rajesh, B.; Subhashini, J. Nanotechnology in oncology: Characterization and in vitro release kinetics of cisplatin-loaded albumin nanoparticles: Implications in anticancer drug delivery. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2011, 43, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulig, K.; Ziąbka, M.; Pilarczyk, K.; Owczarzy, A.; Rogóż, W.; Maciążek-Jurczyk, M. Physicochemical Study of Albumin Nanoparticles with Chlorambucil. Processes 2022, 10, 1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baler, K.; Martin, O.A.; Carignano, M.A.; Ameer, G.A.; Vila, J.A.; Szleifer, I. Electrostatic Unfolding and Interactions of Albumin Driven by pH Changes: A Molecular Dynamics Study. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narwal, M.; Kumar, D.; Mukherjee, T.K.; Bhattacharyya, R.; Banerjee, D. Molecular dynamics simulation as a tool for assessment of drug binding property of human serum albumin. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2018, 45, 1647–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaboli, S.F.; Mehrnejad, F.; Nematollahzadeh, A. Molecular modeling prediction of albumin-based nanoparticles and experimental preparation, characterization, and in-vitro release kinetics of prednisolone from the nanoparticles. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 64, 102588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirinasab, M.; Dehestani, M. Theoretical aspects of interaction of the anticancer drug cytarabine with human serum albumin. Struct. Chem. 2023, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthu, M.S.; Wilson, B. Challenges posed by the scale-up of nanomedicines. Nanomedicine 2012, 7, 307–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrimal, P.; Jadeja, G.; Patel, S. A review on novel methodologies for drug nanoparticle preparation: Microfluidic approach. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2020, 153, 728–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakala, T.A.; Davies, S.; Toprakcioglu, Z.; et al. A Microfluidic Co-Flow Route for Human Serum Albumin-Drug–Nanoparticle Assembly. Chemistry – A European Journal 2020, 26, 5965–5969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, V.T.G.; Kragh-Hansen, U.; Otagiri, M. Pharmaceutical Strategies Utilizing Recombinant Human Serum Albumin. Pharm. Res. 2002, 19, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Mohanty, R.P.; Maier, E.Y.; Peng, X.; Wulfe, S.; Looney, A.P.; Aung, K.L.; Ghosh, D. Controlled loading of albumin-drug conjugates ex vivo for enhanced drug delivery and antitumor efficacy. J. Control. Release 2020, 328, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadami, S.A.; Ahmadi, Z.; Moosavi-Nejad, Z. The albumin-based nanoparticle formation in relation to protein aggregation. Spectrochim. Acta Part A: Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2021, 252, 119489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawoud, M.H.S.; Abdel-Daim, A.; Nour, M.S.; Sweed, N.M. A Quality by Design Paradigm for Albumin-Based Nanoparticles: Formulation Optimization and Enhancement of the Antitumor Activity. J. Pharm. Innov. 2023, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sønderby, P.; Bukrinski, J.T.; Hebditch, M.; Peters, G.H.J.; Curtis, R.A.; Harris, P. Self-Interaction of Human Serum Albumin: A Formulation Perspective. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 16105–16117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, V.; Langer, K.; Balthasar, S.; et al. Characterization of serum albumin nanoparticles by sedimentation velocity analysis and electron microscopy. Berlin, Heidelberg, 2002, pp. 31–36.
- Spada, A.; Emami, J.; Tuszynski, J.A.; Lavasanifar, A. The Uniqueness of Albumin as a Carrier in Nanodrug Delivery. Mol. Pharm. 2021, 18, 1862–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesarova, B.; Musilek, K.; Rex, S.; Heger, Z. Taking advantage of cellular uptake of ferritin nanocages for targeted drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2020, 325, 176–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Orner, B.P. Self-Assembly in the Ferritin Nano-Cage Protein Superfamily. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 5406–5421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimi, K.H.; Hagedoorn, P.-L.; Hagen, W.R. Unity in the Biochemistry of the Iron-Storage Proteins Ferritin and Bacterioferritin. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 295–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stühn, L.; Auernhammer, J.; Dietz, C. pH-depended protein shell dis- and reassembly of ferritin nanoparticles revealed by atomic force microscopy. Sci Rep 2019, 9: 17755.
- Nakahara, Y.; Endo, Y.; Inoue, I. Construction Protocol of Drug-Protein Cage Complexes for Drug Delivery System. In Protein Cages: Design, Structure, and Applications, Ueno, T., Lim, S., Xia, K., Eds.; Springer US: New York, NY, 2023; pp. 335–347. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, G. Reassembly Design of Ferritin Cages. In Protein Cages: Design, Structure, and Applications, Ueno, T., Lim, S., Xia, K., Eds.; Springer US: New York, NY, 2023; pp. 69–78. [Google Scholar]
- Wade, V.J.; Levi, S.; Arosio, P.; et al. Influence of site-directed modifications on the formation of iron cores in ferritin. Journal of Molecular Biology 1991, 221, 1443–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Tang, G.; He, J.; Yan, X.; Fan, K. Ferritin nanocage: A promising and designable multi-module platform for constructing dynamic nanoassembly-based drug nanocarrier. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 176, 113892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang Caiyun, C.C. , Cai Yao, Zhang Tongwei, Pan Yongxin. The Surface Modification of Ferritin and Its Applications. Progress in Chemistry 2016, 28, 91–102. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, C.; Li, Z.; Yin, S.; Wang, Q.; Guo, F.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, R.; Liu, Y.; Su, Z. Extending Half Life of H-Ferritin Nanoparticle by Fusing Albumin Binding Domain for Doxorubicin Encapsulation. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zang, J.; Chen, H.; et al. The Size Flexibility of Ferritin Nanocage Opens a New Way to Prepare Nanomaterials. Small 2017, 13: 1701045.
- Giddings, J.; Yang, F.J.; Myers, M.N. Flow field-flow fractionation as a methodology for protein separation and characterization. Anal. Biochem. 1977, 81, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Hughes, S.; Vanden-Hehir, S.; et al. Structural characterization of encapsulated ferritin provides insight into iron storage in bacterial nanocompartments. eLife 2016, 5, e18972. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Maity, B.; Hishikawa, Y.; Ueno, T.; Lu, D. Importance of the Subunit–Subunit Interface in Ferritin Disassembly: A Molecular Dynamics Study. Langmuir 2022, 38, 1106–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anjum, F.; Shahwan, M.; Alhumaydhi, F.A.; Sharaf, S.E.; Al Abdulmonem, W.; Shafie, A.; Bilgrami, A.L.; Shamsi, A.; Ashraf, G.M. Mechanistic insight into the binding between Ferritin and Serotonin: Possible implications in neurodegenerative diseases. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 351, 118618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banskota, S.; Raguram, A.; Suh, S.; Du, S.W.; Davis, J.R.; Choi, E.H.; Wang, X.; Nielsen, S.C.; Newby, G.A.; Randolph, P.B.; et al. Engineered virus-like particles for efficient in vivo delivery of therapeutic proteins. Cell 2022, 185, 250–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lua, L.H.L.; Middelberg, A.P.J.; Sun, Y.; Connors, N.K. Biomolecular engineering of virus-like particles aided by computational chemistry methods. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 8608–8618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlton Hume, H.K.; Vidigal, J.; Carrondo, M.J.T.; Middelberg, A.P.J.; Roldão, A.; Lua, L.H.L. Synthetic biology for bioengineering virus-like particle vaccines. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2019, 116, 919–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuenmayor, J.; Gòdia, F.; Cervera, L. Production of virus-like particles for vaccines. New Biotechnol. 2017, 39, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santi, L.; Huang, Z.; Mason, H. Virus-like particles production in green plants. Methods 2006, 40, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohr, J.; Chuan, Y.P.; Wu, Y.; Lua, L.H.; Middelberg, A.P. Virus-like particle formulation optimization by miniaturized high-throughput screening. Methods 2013, 60, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huhti, L.; Blazevic, V.; Nurminen, K.; Koho, T.; Hytönen, V.P.; Vesikari, T. A comparison of methods for purification and concentration of norovirus GII-4 capsid virus-like particles. Arch. Virol. 2010, 155, 1855–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, J.M. Aqueous two-phase systems and monolithic chromatography as alternative technological platforms for virus and virus-like particle purification. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2021, 96, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchel, M.; Niewisiewicz, J.; Coroadinha, A.S.; Marrucho, I.M. Purification of virus-like particles using aqueous biphasic systems composed of natural deep eutectic solvents. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 252, 117480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Effio, C.L.; Oelmeier, S.A.; Hubbuch, J. High-throughput characterization of virus-like particles by interlaced size-exclusion chromatography. Vaccine 2016, 34, 1259–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, P.P.; González-Domínguez, I.; Schneider, T.A.; Gòdia, F.; Cervera, L.; Jungbauer, A. At-line multi-angle light scattering detector for faster process development in enveloped virus-like particle purification. J. Sep. Sci. 2019, 42, 2640–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durous, L.; Rosa-Calatrava, M.; Petiot, E. Advances in influenza virus-like particles bioprocesses. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2019, 18, 1285–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denisov, I.G.; Grinkova, Y.V.; Lazarides, A.A.; Sligar, S.G. Directed Self-Assembly of Monodisperse Phospholipid Bilayer Nanodiscs with Controlled Size. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 3477–3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xu, W.; Wang, X.; Lv, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wu, M.; Liu, G.; et al. Reconfigurable Peptide Analogs of Apolipoprotein A-I Reveal Tunable Features of Nanodisc Assembly. Langmuir 2023, 39, 1262–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wade, J.H.; Jones, J.D.; Lenov, I.L.; Riordan, C.M.; Sligar, S.G.; Bailey, R.C. Microfluidic platform for efficient Nanodisc assembly, membrane protein incorporation, and purification. Lab a Chip 2017, 17, 2951–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goluch, E.D.; Shaw, A.W.; Sligar, S.G.; Liu, C. Microfluidic patterning of nanodisc lipid bilayers and multiplexed analysis of protein interaction. Lab a Chip 2008, 8, 1723–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Chen, X.; Chen, Z.; Lv, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Xu, W.; Mo, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, Z.; et al. An in Silico Approach to Reveal the Nanodisc Formulation of Doxorubicin. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 859255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsen, T.; Holm, V.L.; Kjølbye, L.R.; et al. Structure and dynamics of a nanodisc by integrating NMR, SAXS and SANS experiments with molecular dynamics simulations. eLife 2020, 9, e56518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourmousa, M.; Pastor, R.W. Molecular dynamics simulations of lipid nanodiscs. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes 2018, 1860, 2094–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, J.-i.; Nagaki, A.; Yamada, D. Continuous flow synthesis. Drug Discovery Today: Technologies 2013, 10: e53-e59.
- Julien, J.A.; Fernandez, M.G.; Brandmier, K.M.; et al. Rapid preparation of nanodiscs for biophysical studies. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics 2021, 712, 109051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrazzani, R.; Ceretti, E.; Zerbini, I.; Casale, R.; Gozio, E.; Bertanza, G.; Gelatti, U.; Donato, F.; Feretti, D. Biodegradability, toxicity and mutagenicity of detergents: Integrated experimental evaluations. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 84, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobrino-Figueroa, A.S. Evaluation of oxidative stress and genetic damage caused by detergents in the zebrafish Danio rerio (Cyprinidae). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A: Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2013, 165, 528–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justesen, B.H.; Günther-Pomorski, T. Chromatographic and electrophoretic methods for nanodisc purification and analysis. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2014, 33, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, F.H.; Gao, Z.; Mansor, H.B.; et al. Silk Fibroin Nanoparticles: A Biocompatible Multi-Functional Polymer for Drug Delivery. 2023.
- Foox, M.; Zilberman, M. Drug delivery from gelatin-based systems. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 2015, 12, 1547–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elzoghby, A.O. Gelatin-based nanoparticles as drug and gene delivery systems: Reviewing three decades of research. J. Control. Release 2013, 172, 1075–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasmin, R.; Shah, M.; Khan, S.A.; Ali, R. Gelatin nanoparticles: a potential candidate for medical applications. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2017, 6, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.P.; Nguyen, Q.V.; Nguyen, V.-H.; Le, T.-H.; Huynh, V.Q.N.; Vo, D.-V.N.; Trinh, Q.T.; Kim, S.Y.; Van Le, Q. Silk Fibroin-Based Biomaterials for Biomedical Applications: A Review. Polymers 2019, 11, 1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baci, G.-M.; Cucu, A.-A.; Giurgiu, A.-I.; Muscă, A.-S.; Bagameri, L.; Moise, A.R.; Bobiș, O.; Rațiu, A.C.; Dezmirean, D.S. Advances in Editing Silkworms (Bombyx mori) Genome by Using the CRISPR-Cas System. Insects 2022, 13, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aznar-Cervantes, S.D.; Vicente-Cervantes, D.; Meseguer-Olmo, L.; Cenis, J.L.; Lozano-Pérez, A.A. Influence of the protocol used for fibroin extraction on the mechanical properties and fiber sizes of electrospun silk mats. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 1945–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeBari, M.K.; King, C.I., III; Altgold, T.A.; et al. Silk Fibroin as a Green Material. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 2021, 7, 3530–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A. Mini-Review: Opportunities and challenges in the techniques used for preparation of gelatin nanoparticles. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci 2020, 33, 221–228. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, M.A.; Al-Kahtani, H.A.; Jaswir, I.; AbuTarboush, H.; Ismail, E.A. Extraction and characterization of gelatin from camel skin (potential halal gelatin) and production of gelatin nanoparticles. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 1596–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Regenstein, J.M. Effects of Alkaline and Acid Pretreatments on Alaska Pollock Skin Gelatin Extraction. J. Food Sci. 2005, 70, c392–c396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggert, S.; Kahl, M.; Bock, N.; Meinert, C.; Friedrich, O.; Hutmacher, D.W. An open-source technology platform to increase reproducibility and enable high-throughput production of tailorable gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) - based hydrogels. Mater. Des. 2021, 204, 109619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Xu, R.; Ye, S.; Yan, J.; Kumar, P.; Zhang, P.; Zhao, X. Microfluidic Formulation of Curcumin-Loaded Multiresponsive Gelatin Nanoparticles for Anticancer Therapy. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2023, 9, 3402–3413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomun, J.I.; Totten, J.D.; Wongpinyochit, T.; Florence, A.J.; Seib, F.P. Manual Versus Microfluidic-Assisted Nanoparticle Manufacture: Impact of Silk Fibroin Stock on Nanoparticle Characteristics. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 2796–2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahanshahi, M.; Sanati, M.H.; Hajizadeh, S.; Babaei, Z. Gelatin nanoparticle fabrication and optimization of the particle size. Phys. Status solidi (a) 2008, 205, 2898–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madkhali, O.; Mekhail, G.; Wettig, S.D. Modified gelatin nanoparticles for gene delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 554, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gharehnazifam, Z.; Dolatabadi, R.; Baniassadi, M.; Shahsavari, H.; Kajbafzadeh, A.-M.; Abrinia, K.; Baghani, M. Computational analysis of vincristine loaded silk fibroin hydrogel for sustained drug delivery applications: Multiphysics modeling and experiments. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 609, 121184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hathout, R.M.; Metwally, A.A.; Woodman, T.J.; Hardy, J.G. Prediction of Drug Loading in the Gelatin Matrix Using Computational Methods. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 1549–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmelo-Luna, F.J.; Mendoza-Wilson, A.M.; Montfort, G.R.-C.; Lizardi-Mendoza, J.; Madera-Santana, T.; Lardizábal-Gutiérrez, D.; Quintana-Owen, P. Synthesis and experimental/computational characterization of sorghum procyanidins–gelatin nanoparticles. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2021, 42, 116240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordanaba-Florit, G.; Royo, F.; Kruglik, S.G.; Falcón-Pérez, J.M. Using single-vesicle technologies to unravel the heterogeneity of extracellular vesicles. Nat. Protoc. 2021, 16, 3163–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingato, D.; Lee, J.U.; Sim, S.J.; Kwon, Y.J. Good things come in small packages: Overcoming challenges to harness extracellular vesicles for therapeutic delivery. J. Control. Release 2016, 241, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkach, M.; Théry, C. Communication by Extracellular Vesicles: Where We Are and Where We Need to Go. Cell 2016, 164, 1226–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, R.; Coumans, F.A.W.; Maltesen, R.G.; Böing, A.N.; Bonnington, K.E.; Broekman, M.L.; Broom, M.F.; Buzás, E.I.; Christiansen, G.; Hajji, N.; et al. A standardized method to determine the concentration of extracellular vesicles using tunable resistive pulse sensing. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2016, 5, 31242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales-Kastresana, A.; Telford, B.; Musich, T.A.; McKinnon, K.; Clayborne, C.; Braig, Z.; Rosner, A.; Demberg, T.; Watson, D.C.; Karpova, T.S.; et al. Labeling Extracellular Vesicles for Nanoscale Flow Cytometry. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Amreddy, N.; Pareek, V.; Chinnappan, M.; Ahmed, R.; Mehta, M.; Razaq, M.; Munshi, A.; Ramesh, R. Progress in extracellular vesicle biology and their application in cancer medicine. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechnology 2020, 12, e1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allelein, S.; Medina-Perez, P.; Lopes, A.L.H.; Rau, S.; Hause, G.; Kölsch, A.; Kuhlmeier, D. Potential and challenges of specifically isolating extracellular vesicles from heterogeneous populations. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, I.K.; Shukla, N.; Borrelli, D.A.; Patel, T. Use of a Hollow Fiber Bioreactor to Collect Extracellular Vesicles from Cells in Culture. In Extracellular RNA: Methods and Protocols; Patel, T., Ed.; Springer New York: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 35–41. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, H.; Bae, Y.; Kwon, Y.; Kim, S.; Park, J. Extracellular Vesicles Generated Using Bioreactors and their Therapeutic Effect on the Acute Kidney Injury Model. Adv. Heal. Mater. 2022, 11, 2101606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, R.T.; Kim, J.; Jang, S.C.; Choi, E.-J.; Gho, Y.S.; Park, J. Microfluidic filtration system to isolate extracellular vesicles from blood. Lab a Chip 2012, 12, 5202–5210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholizadeh, S.; Draz, M.S.; Zarghooni, M.; Sanati-Nezhad, A.; Ghavami, S.; Shafiee, H.; Akbari, M. Microfluidic approaches for isolation, detection, and characterization of extracellular vesicles: Current status and future directions. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 91, 588–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Görgens, A.; Corso, G.; Hagey, D.W.; Wiklander, R.J.; Gustafsson, M.O.; Felldin, U.; Lee, Y.; Bostancioglu, R.B.; Sork, H.; Liang, X.; et al. Identification of storage conditions stabilizing extracellular vesicles preparations. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2022, 11, e12238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Jiang, W.; Shen, J.; Yao, X.; He, X.; Li, L.; Fu, B.; Liu, X. Biological Features of Extracellular Vesicles and Challenges. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 816698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenkenschuh, E.; Richter, M.; Heinrich, E.; Koch, M.; Fuhrmann, G.; Friess, W. Enhancing the Stabilization Potential of Lyophilization for Extracellular Vesicles. Adv. Heal. Mater. 2022, 11, 2100538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-de-Mariscal, E.; Maška, M.; Kotrbová, A.; et al. Deep-Learning-Based Segmentation of Small Extracellular Vesicles in Transmission Electron Microscopy Images. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 13211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourgeaux, V.; Lanao, J.M.; Bax, B.E.; Godfrin, Y. Drug-loaded erythrocytes: on the road toward marketing approval. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2016, 10, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chugh, V.; Krishna, K.V.; Pandit, A. Cell Membrane-Coated Mimics: A Methodological Approach for Fabrication, Characterization for Therapeutic Applications, and Challenges for Clinical Translation. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 17080–17123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, L.; Cai, B.; Bu, L.-L.; Liao, Q.-Q.; Guo, S.-S.; Zhao, X.-Z.; Dong, W.-F.; Liu, W. Microfluidic Electroporation-Facilitated Synthesis of Erythrocyte Membrane-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles for Enhanced Imaging-Guided Cancer Therapy. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 3496–3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.-C.; Waldman, R.Z.; Chen, Z.; Darling, S.B. Atomic layer deposition for membrane interface engineering. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 20505–20513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.-L.; Nie, W.; Zhang, J.; Xie, H.-Y. Cell-Membrane-Based Biomimetic Systems with Bioorthogonal Functionalities. Accounts Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, N.; Tufenkji, N. Probing the Interaction between Nanoparticles and Lipid Membranes by Quartz Crystal Microbalance with Dissipation Monitoring. Front. Chem. 2016, 4, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonnell, J.M. Surface plasmon resonance: towards an understanding of the mechanisms of biological molecular recognition. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2001, 5, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, R.H.; Kroll, A.V.; Gao, W.W.; Zhang, L.F. Cell Membrane Coating Nanotechnology. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1706759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, E.; Park, J.; Shah, R.; Riley, B.; Brorson, K.; Rathore, A. Process analytical technology (PAT) for biopharmaceutical products: Part I. concepts and applications. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2010, 105, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Ma, G.; Wei, W. Simulation of nanoparticles interacting with a cell membrane: probing the structural basis and potential biomedical application. NPG Asia Mater. 2021, 13, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.V.; Maharjan, R.-S.; Kanase, A.; Siewert, K.; Rosenkranz, D.; Singh, R.; Laux, P.; Luch, A. Machine-Learning-Based Approach to Decode the Influence of Nanomaterial Properties on Their Interaction with Cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 1943–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barclay, T.G.; Day, C.M.; Petrovsky, N.; Garg, S. Review of polysaccharide particle-based functional drug delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 221, 94–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Montes, E. Dextran: Sources, Structures, and Properties. Polysaccharides 2021, 2, 554–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Khor, E.; Lim, L.-Y. Uptake and Cytotoxicity of Chitosan Molecules and Nanoparticles: Effects of Molecular Weight and Degree of Deacetylation. Pharm. Res. 2004, 21, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, D.S.; Svechkarev, D.A.; Bapat, A.; Patil, P.; Hollingsworth, M.A.; Mohs, A.M. Sulfation Modulates the Targeting Properties of Hyaluronic Acid to P-Selectin and CDACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 3585–3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mena-García, A.; Ruiz-Matute, A.; Soria, A.; Sanz, M. Green techniques for extraction of bioactive carbohydrates. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 119, 115612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Chen, F.; Yang, W.; Huang, H. Preparation, deproteinization and comparison of bioactive polysaccharides. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 109, 564–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Yang, K.; Nie, Z. Engineering heterogeneity of precision nanoparticles for biomedical delivery and therapy. View 2021, 2, 20200067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plucinski, A.; Lyu, Z.; Schmidt, B.V.K.J. Polysaccharide nanoparticles: from fabrication to applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 7030–7062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galmarini, S.; Hanusch, U.; Giraud, M.; Cayla, N.; Chiappe, D.; Von Moos, N.; Hofmann, H.; Maurizi, L. Beyond Unpredictability: The Importance of Reproducibility in Understanding the Protein Corona of Nanoparticles. Bioconjugate Chem. 2018, 29, 3385–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastogne, T. Quality-by-design of nanopharmaceuticals – a state of the art. Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biol. Med. 2017, 13, 2151–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnitzer, E.; Pinchuk, I.; Bor, A.; Leikin-Frenkel, A.; Lichtenberg, D. Oxidation of liposomal cholesterol and its effect on phospholipid peroxidation. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2007, 146, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnitzer, E.; Pinchuk, I.; Lichtenberg, D. Peroxidation of liposomal lipids. European Biophysics Journal 2007, 36, 499–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inglut, C.T.; Sorrin, A.J.; Kuruppu, T.; Vig, S.; Cicalo, J.; Ahmad, H.; Huang, H.-C. Immunological and Toxicological Considerations for the Design of Liposomes. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyothi, V.G.S.; Bulusu, R.; Rao, B.V.K.; Pranothi, M.; Banda, S.; Bolla, P.K.; Kommineni, N. Stability characterization for pharmaceutical liposome product development with focus on regulatory considerations: An update. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 624, 122022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnadas-Rodrı́guez, R.; Sabés, M. Factors involved in the production of liposomes with a high-pressure homogenizer. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 213, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karn, P.R.; Cho, W.; Park, H.J.; Park, J.S.; Hwang, S.J. Characterization and Stability Studies of a Novel Liposomal Cyclosporin A Prepared Using the Supercritical Fluid Method: Comparison with the Modified Conventional Bangham Method. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb; Harasym, T. ; Masin, D.; Bally, M.; Mayer, L. Sphingomyelin-cholesterol liposomes significantly enhance the pharmacokinetic and therapeutic properties of vincristine in murine and human tumour models. Br. J. Cancer 1995, 72, 896–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, B.; Guha, P.; Bhattarai, R.; Nahak, P.; Karmakar, G.; Chettri, P.; Panda, A.K. Influence of Lipid Composition, pH, and Temperature on Physicochemical Properties of Liposomes with Curcumin as Model Drug. 6th Asian Conference on Colloid and Interface Science (ACCIS). LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, COUNTRYDATE OF CONFERENCE; pp. 399–411.
- Grit, M.; Crommelin, D.J. Chemical stability of liposomes: implications for their physical stability. Chem. Phys. Lipids 1993, 64, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arouri, A.; Hansen, A.H.; Rasmussen, T.E.; et al. Lipases, liposomes and lipid-prodrugs. Current Opinion in Colloid & Interface Science 2013, 18, 419–431. [Google Scholar]
- Flaten, G.E.; Chang, T.-T.; Phillips, W.T.; Brandl, M.; Bao, A.; Goins, B. Liposomal formulations of poorly soluble camptothecin: drug retention and biodistribution. J. Liposome Res. 2013, 23, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basáñez, G.; Goñi, F.M.; Alonso, A. Poly(ethylene glycol)-lipid conjugates inhibit phospholipase C-induced lipid hydrolysis, liposome aggregation and fusion through independent mechanisms. FEBS Letters 1997, 411, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mickova, A.; Buzgo, M.; Benada, O.; Rampichova, M.; Fisar, Z.; Filova, E.; Tesarova, M.; Lukas, D.; Amler, E. Core/Shell Nanofibers with Embedded Liposomes as a Drug Delivery System. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 952–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, N.; Fenske, D.B.; Cullis, P.R. Developments in liposomal drug delivery systems. Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy 2001, 1, 923–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, V.; Heath, R.J. Structural and Biochemical Features of Human Serum Albumin Essential for Eukaryotic Cell Culture. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebedeva, N.S.; Yurina, E.S.; Gubarev, Y.A.; et al. Molecular mechanisms causing albumin aggregation. The main role of the porphyrins of the blood group. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 2021, 246, 118975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-L.; Lin, S.-Y.; Li, M.-J.; Wei, Y.-S.; Hsieh, T.-F. Temperature effect on the structural stability, similarity, and reversibility of human serum albumin in different states. Biophys. Chem. 2005, 114, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliva, A.; Santoveña, A.; Llabres, M.; et al. Stability Study of Human Serum Albumin Pharmaceutical Preparations. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 2010, 51, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AA Aljabali, A.; A. Bakshi, H.; L. Hakkim, F.; et al. Albumin Nano-Encapsulation of Piceatannol Enhances Its Anticancer Potential in Colon Cancer Via Downregulation of Nuclear p65 and HIF-1α. Cancers 2020, 12, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayana, S.; Ahmed, M.G.; Nasrine, A. Effect of nano-encapsulation using human serum albumin on anti-angiogenesis activity of bevacizumab to target corneal neovascularization: Development, optimization and in vitro assessment.CONFERENCE NAME, LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, COUNTRYDATE OF CONFERENCE; pp. 93–104.
- Fahrländer, E.; Schelhaas, S.; Jacobs, A.H.; Langer, K. PEGylated human serum albumin (HSA) nanoparticles: preparation, characterization and quantification of the PEGylation extent. Nanotechnology 2015, 26, 145103–145103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niknejad, H.; Mahmoudzadeh, R. Comparison of Different Crosslinking Methods for Preparation of Docetaxel-loaded Albumin Nanoparticles. Iranian journal of pharmaceutical research: IJPR.
- Anhorn, M.G.; Mahler, H.-C.; Langer, K. Freeze drying of human serum albumin (HSA) nanoparticles with different excipients. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 363, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anraku, M.; Kouno, Y.; Kai, T.; Tsurusaki, Y.; Yamasaki, K.; Otagiri, M. The role of N-acetyl-methioninate as a new stabilizer for albumin products. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 329, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, R.; Zhu, H.; Deng, P.; Li, M.; Ji, Q.; He, H.; Jin, L.; Wang, B. Research progress on albumin-based hydrogels: Properties, preparation methods, types and its application for antitumor-drug delivery and tissue engineering. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Xie, H.; Zhao, Q.; Zhao, M. Molecular imprinting of doxorubicin by refolding thermally denatured bovine serum albumin and cross-linking with hydrogel network. React. Funct. Polym. 2021, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Hao, Y.; Tian, X.; Liang, Y.; He, X.; Gao, R.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y. Multi-stimuli responsive molecularly imprinted nanoparticles with tailorable affinity for modulated specific recognition of human serum albumin. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 6634–6643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, S.T.K.; Thiruselvi, T.; Mandal, A.B.; Gnanamani, A. pH and redox sensitive albumin hydrogel: A self-derived biomaterial. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Wang, L.; Gao, C. pH-sensitive bovine serum albumin nanoparticles for paclitaxel delivery and controlled release to cervical cancer. Applied Nanoscience 2022, 12, 4047–4057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshnejad, M.; Parhiz, H.; Shuvaev, V.V.; Dmochowski, I.J.; Muzykantov, V.R. Ferritin-based drug delivery systems: Hybrid nanocarriers for vascular immunotargeting. 15th International Nanomedicine and Drug Delivery Symposium (NanoDDS). LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, COUNTRYDATE OF CONFERENCE; pp. 13–24.
- Yin, S.; Davey, K.; Dai, S.; Liu, Y.; Bi, J. A critical review of ferritin as a drug nanocarrier: Structure, properties, comparative advantages and challenges. Particuology 2022, 64, 65–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houser, K.V.; Chen, G.L.; Carter, C.; Crank, M.C.; Nguyen, T.A.; Florez, M.C.B.; Berkowitz, N.M.; Mendoza, F.; Hendel, C.S.; Gordon, I.J.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of a ferritin nanoparticle H2 influenza vaccine in healthy adults: a phase 1 trial. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morikawa, K.; Oseko, F.; Morikawa, S. A Role for Ferritin in Hematopoiesis and the Immune System. Leuk. Lymphoma 1995, 18, 429–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Hong, Y.; Gong, Y.; Zheng, S.; Xie, D. Bioengineered Ferritin Nanocarriers for Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Singhal, B. Role of Machine Learning in Bioprocess Engineering: Current Perspectives and Future Directions. In Design and Applications of Nature Inspired Optimization: Contribution of Women Leaders in the Field, Singh, D., Garg, V., Deep, K., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2022; pp. 39–54. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, R.; Arora, K.; Roy, S.S.; Joseph, A.; Rastogi, R.; Arora, N.M.; Kundu, P.K. Platforms, advances, and technical challenges in virus-like particles-based vaccines. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1123805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, P.; Liu, X.; Chen, X.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Chu, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Liu, G. Genetically Engineered Cell Membrane Nanovesicles for Oncolytic Adenovirus Delivery: A Versatile Platform for Cancer Virotherapy. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 2993–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suffian, I.F.; Al-Jamal, K.T. Bioengineering of virus-like particles as dynamic nanocarriers for in vivo delivery and targeting to solid tumours. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2022, 180, 114030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biabanikhankahdani, R.; Alitheen, N.B.M.; Ho, K.L.; et al. pH-responsive Virus-like Nanoparticles with Enhanced Tumour-targeting Ligands for Cancer Drug Delivery. 3: Sci Rep 2016, 6, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.; Steinmetz, N.F. Doxorubicin-Loaded Physalis Mottle Virus Particles Function as a pH-Responsive Prodrug Enabling Cancer Therapy. 2: Biotechnology Journal 2020, 15, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Serradell, M.C.; Rupil, L.L.; Martino, R.A.; Prucca, C.G.; Carranza, P.G.; Saura, A.; Fernández, E.A.; Gargantini, P.R.; Tenaglia, A.H.; Petiti, J.P.; et al. Efficient oral vaccination by bioengineering virus-like particles with protozoan surface proteins. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Ganguillet, S.; Turgay, Y.; et al. Surface crosslinking of virus-like particles increases resistance to proteases, low pH and mechanical stress for mucosal applications. bioRxiv 2023: 2023.2007.2029. 5502. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, L.; Sanyal, G.; Ni, A.; Luo, Z.; Doshna, S.; Wang, B.; Graham, T.L.; Wang, N.; Volkin, D.B. Stabilization of human papillomavirus virus-like particles by non-ionic surfactants. J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 94, 1538–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, J.; Bacic, T.; Staritzbichler, R.; et al. Enhanced stability of a chimeric hepatitis B core antigen virus-like-particle (HBcAg-VLP) by a C-terminal linker-hexahistidine-peptide. 3: Journal of Nanobiotechnology 2018, 16, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gleiter, S.; Lilie, H. Coupling of antibodies via protein Z on modified polyoma virus-like particles. Protein Sci. 2001, 10, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segel, M.; Lash, B.; Song, J.; Ladha, A.; Liu, C.C.; Jin, X.; Mekhedov, S.L.; Macrae, R.K.; Koonin, E.V.; Zhang, F. Mammalian retrovirus-like protein PEG10 packages its own mRNA and can be pseudotyped for mRNA delivery. Science 2021, 373, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himbert, S.; Rheinstädter, M. Erythro-VLP: Erythrocyte Virus-Like-Particles. 1: Biophysical Journal 2021, 120, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Grushin, K.; White, M.A.; Stoilova-McPhie, S. Reversible stacking of lipid nanodiscs for structural studies of clotting factors. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2017, 6, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoi, K.K.; Robinson, C.V.; Marty, M.T. Unraveling the Composition and Behavior of Heterogeneous Lipid Nanodiscs by Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 6199–6204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiati, S.; Scheberl, A.; Zayni, S.; Damiati, S.A.; Schuster, B.; Kompella, U.B. Albumin-bound nanodiscs as delivery vehicle candidates: Development and characterization. Biophys. Chem. 2019, 251, 106178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Pan, F.; Luo, G.; Jiang, K.; Wang, H.; Ding, T.; Li, W.; Zhan, C.; Wei, X. Morphology-driven protein corona manipulation for preferential delivery of lipid nanodiscs. Nano Today 2022, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dane, E.L.; Belessiotis-Richards, A.; Backlund, C.; Wang, J.; Hidaka, K.; Milling, L.E.; Bhagchandani, S.; Melo, M.B.; Wu, S.; Li, N.; et al. STING agonist delivery by tumour-penetrating PEG-lipid nanodiscs primes robust anticancer immunity. Nat. Mater. 2022, 21, 710–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Sun, J.; Liu, Y.; Tao, M.; Ai, X.; Su, X.; Cai, C.; Tang, Y.; Feng, Z.; Yan, X.; et al. PEG-Stabilized Bilayer Nanodisks As Carriers for Doxorubicin Delivery. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 3279–3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Gu, L. Effects of Mass Ratio, pH, Temperature, and Reaction Time on Fabrication of Partially Purified Pomegranate Ellagitannin−Gelatin Nanoparticles. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 2011, 59, 4225–4231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammel, A.S.; Hu, X.; Park, S.-H.; Kaplan, D.L.; Scheibel, T.R. Controlling silk fibroin particle features for drug delivery. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 4583–4591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.-B.; Zhang, Y.-Q.; Ma, Y.-L.; Zhou, L.-X. Biosynthesis of insulin-silk fibroin nanoparticles conjugates and in vitro evaluation of a drug delivery system. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2009, 11, 1937–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leo, E.; Vandelli, M.A.; Cameroni, R.; Forni, F. Doxorubicin-loaded gelatin nanoparticles stabilized by glutaraldehyde: Involvement of the drug in the cross-linking process. Int. J. Pharm. 1997, 155, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaul, G.; Amiji, M. Long-Circulating Poly(Ethylene Glycol)-Modified Gelatin Nanoparticles for Intracellular Delivery. Pharm. Res. 2002, 19, 1061–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totten, J.D.; Wongpinyochit, T.; Carrola, J.; Duarte, I.F.; Seib, F.P. PEGylation-Dependent Metabolic Rewiring of Macrophages with Silk Fibroin Nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 14515–14525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, A.S.C.; Rodrigues, C.F.; Fernandes, N.; de Melo-Diogo, D.; Ferreira, P.; Moreira, A.F.; Correia, I.J. IR780 loaded gelatin-PEG coated gold core silica shell nanorods for cancer-targeted photothermal/photodynamic therapy. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2022, 119, 644–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, L.; Guo, L.; Zhu, J.; Ma, Y. Stability and cytocompatibility of silk fibroin-capped gold nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 43, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curcio, M.; Altimari, I.; Spizzirri, U.G.; et al. Biodegradable gelatin-based nanospheres as pH-responsive drug delivery systems. 1: Journal of Nanoparticle Research 2013, 15, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, N.; Lei, R.; Xu, J.; et al. Fabricated porous silk fibroin particles for pH-responsive drug delivery and targeting of tumor cells. Journal of Materials Science 2019, 54, 3319–3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deveci, S.S.; Basal, G. Preparation of PCM microcapsules by complex coacervation of silk fibroin and chitosan. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2009, 287, 1455–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yang, H.; Liu, X.; et al. Electrospinning of carboxyethyl chitosan/poly(vinyl alcohol)/silk fibroin nanoparticles for wound dressings. Int J Biol Macromol 2013, 53, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathollahipour, S.; Mehrizi, A.A.; Ghaee, A.; Koosha, M. Electrospinning of PVA/chitosan nanocomposite nanofibers containing gelatin nanoparticles as a dual drug delivery system. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2015, 103, 3852–3862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, S.; Basak, P.; Tibarewala, D. Synthesis of gelatin nano/submicron particles by binary nonsolvent aided coacervation (BNAC) method. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 59, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Fan, D.; Li, Y.; He, X.; Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, J.; Xu, G.; Wu, X.; Lan, P. Supercritical carbon dioxide-developed silk fibroin nanoplatform for smart colon cancer therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 7751–7761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rnjak-Kovacina, J.; DesRochers, T.M.; Burke, K.A.; Kaplan, D.L. The Effect of Sterilization on Silk Fibroin Biomaterial Properties. Macromol. Biosci. 2015, 15, 861–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeyaram, A.; Jay, S.M. Preservation and Storage Stability of Extracellular Vesicles for Therapeutic Applications. AAPS J. 2017, 20, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Li, Y.-M.; Wang, Z. Preserving extracellular vesicles for biomedical applications: consideration of storage stability before and after isolation. Drug Deliv. 2021, 28, 1501–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midekessa, G.; Godakumara, K.; Ord, J.; Viil, J.; Lättekivi, F.; Dissanayake, K.; Kopanchuk, S.; Rinken, A.; Andronowska, A.; Bhattacharjee, S.; et al. Zeta Potential of Extracellular Vesicles: Toward Understanding the Attributes that Determine Colloidal Stability. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 16701–16710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, E.; Karagianni, A.; Koch, M.; Fuhrmann, G. Hot EVs – How temperature affects extracellular vesicles. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2020, 146, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, M.I.; Amorim, M.G.; Gadelha, C.; Milic, I.; Welsh, J.A.; Freitas, V.M.; Nawaz, M.; Akbar, N.; Couch, Y.; Makin, L.; et al. Technical challenges of working with extracellular vesicles. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 881–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemmens, H.; Lambert, D.W. Extracellular vesicles: translational challenges and opportunities. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2018, 46, 1073–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melling, G.E.; Carollo, E.; Conlon, R.; Simpson, J.C.; Carter, D.R.F. The Challenges and Possibilities of Extracellular Vesicles as Therapeutic Vehicles. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 144, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahr, M.M.; Amer, M.S.; Abo-El-Sooud, K.; Abdallah, A.N.; El-Tookhy, O.S. Preservation techniques of stem cells extracellular vesicles: a gate for manufacturing of clinical grade therapeutic extracellular vesicles and long-term clinical trials. Int. J. Veter- Sci. Med. 2020, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, K.; Li, Q.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, Z.; Zhao, J.; Lin, X.; Wang, J.; Zhu, K.; Xiao, C.; et al. Incorporation of small extracellular vesicles in sodium alginate hydrogel as a novel therapeutic strategy for myocardial infarction. Theranostics 2019, 9, 7403–7416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piffoux, M.; Silva, A.K.A.; Wilhelm, C.; Gazeau, F.; Tareste, D. Modification of Extracellular Vesicles by Fusion with Liposomes for the Design of Personalized Biogenic Drug Delivery Systems. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 6830–6842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, M.; Vader, P.; Fuhrmann, G. Approaches to surface engineering of extracellular vesicles. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 173, 416–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardiner, C.; Di Vizio, D.; Sahoo, S.; Théry, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Wauben, M.; Hill, A.F. Techniques used for the isolation and characterization of extracellular vesicles: Results of a worldwide survey. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2016, 5, 32945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jong, O.G.; Kooijmans, S.A.A.; Murphy, D.E.; Jiang, L.; Evers, M.J.W.; Sluijter, J.P.G.; Vader, P.; Schiffelers, R.M. Drug Delivery with Extracellular Vesicles: From Imagination to Innovation. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 1761–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, S.; Dumoga, S.; Singh, N. Red blood cells membrane-derived nanoparticles: Applications and key challenges in their clinical translation. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechnology 2022, 14, e1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parambath, A. Engineering of Biomaterials for Drug Delivery Systems; Elsevier BV: Amsterdam, NX, Netherlands, 2018; ISBN 9780081017500. [Google Scholar]
- Doshi, N.; Zahr, A.S.; Bhaskar, S.; Lahann, J.; Mitragotri, S. Red blood cell-mimicking synthetic biomaterial particles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2009, 106, 21495–21499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, N.; Fang, R.H.; Zhang, L. Engineering of stimuli-responsive self-assembled biomimetic nanoparticles. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 179, 114006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.-M.J.; Fang, R.H.; Zhang, L. Erythrocyte-Inspired Delivery Systems. Adv. Heal. Mater. 2012, 1, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, K.L.; Lecak, J.; Acker, J.P. Biopreservation of Red Blood Cells: Past, Present, and Future. Transfusion Medicine Reviews 2005, 19, 127–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Quan, G.B.; Liu, X.Z.; Ma, E.P.; Liu, A.; Jin, P.; Cao, W. Improved preservation of human red blood cells by lyophilization. Cryobiology 2005, 51, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Mooney, D.J. Alginate: Properties and biomedical applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 106–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.N.V.R.; Muzzarelli, R.A.A.; Muzzarelli, C.; Sashiwa, H.; Domb, A.J. Chitosan Chemistry and Pharmaceutical Perspectives. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 6017–6084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, K. THE BIOLOGICAL SIGNIFICANCE OF HYALURONIC ACID AND HYALURONIDASE. Physiol. Rev. 1947, 27, 335–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirisha, V.; D’Souza, J.S. Polysaccharide-based nanoparticles as drug delivery systems. Marine OMICS 2016, 18, 663–702. [Google Scholar]
- Moosavian, S.A.; Bianconi, V.; Pirro, M.; Sahebkar, A. Challenges and pitfalls in the development of liposomal delivery systems for cancer therapy. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2019, 69, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sercombe, L.; Veerati, T.; Moheimani, F.; Wu, S.Y.; Sood, A.K.; Hua, S. Advances and Challenges of Liposome Assisted Drug Delivery. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawant, R.R.; Torchilin, V.P. Challenges in Development of Targeted Liposomal Therapeutics. AAPS J. 2012, 14, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, J.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Lou, M.; Qian, J.; Lu, W.; Zhan, C. Enhanced immunocompatibility of ligand-targeted liposomes by attenuating natural IgM absorption. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muro, S. Challenges in design and characterization of ligand-targeted drug delivery systems. J. Control. Release 2012, 164, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, H. Toward a full understanding of the EPR effect in primary and metastatic tumors as well as issues related to its heterogeneity. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2015, 91, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshpande, P.P.; Biswas, S.; Torchilin, V.P. Current trends in the use of liposomes for tumor targeting. Nanomedicine 2013, 8, 1509–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallmann, P.; Bedding, A.W.; Choodari-Oskooei, B.; et al. Adaptive designs in clinical trials: why use them, and how to run and report them. 2: BMC Medicine 2018, 16, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Meunier, F.; Prentice, H.G.; Ringden, O. Liposomal amphotericin B (AmBisome): safety data from a phase II/III clinical trial. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1991, 28, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, N.R.H.; Bicanic, T.; Salim, R.; et al. Liposomal Amphotericin B (AmBisome®): A Review of the Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamics, Clinical Experience and Future Directions. Drugs 2016, 76, 485–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, M.K.B.; Barthel, F.M.-S.; Sydes, M.; Langley, R.; Kaplan, R.; Eisenhauer, E.; Brady, M.; James, N.; Bookman, M.A.; Swart, A.-M.; et al. Speeding up the Evaluation of New Agents in Cancer. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2008, 100, 1204–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wason, J.M.S.; Jaki, T. Optimal design of multi-arm multi-stage trials. Statistics in Medicine 2012, 31, 4269–4279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burcu, M.; Manzano-Salgado, C.B.; Butler, A.M.; Christian, J.B. A Framework for Extension Studies Using Real-World Data to Examine Long-Term Safety and Effectiveness. Ther. Innov. Regul. Sci. 2021, 56, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, R.E.; Anderson, S.A.; Dal Pan, G.J.; et al. Real-World Evidence — What Is It and What Can It Tell Us? New England Journal of Medicine 2016, 375, 2293–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kianfar, E. Protein nanoparticles in drug delivery: animal protein, plant proteins and protein cages, albumin nanoparticles. J. Nanobiotechnology 2021, 19, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollazadeh, S.; Yazdimamaghani, M.; Yazdian-Robati, R.; Pirhadi, S. New insight into the structural changes of apoferritin pores in the process of doxorubicin loading at an acidic pH: Molecular dynamics simulations. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 141, 105158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arosio, P.; Levi, S. Ferritin, iron homeostasis, and oxidative damage1, 2 1Guest Editor: Mario Comporti 2This article is part of a series of reviews on “Iron and Cellular Redox Status. ” The full list of papers may be found on the homepage of the journal. Free Radical Biology and Medicine 2002, 33, 457–463. [Google Scholar]
- Harro, C.D.; Pang, Y.-Y.S.; Roden, R.B.S.; Hildesheim, A.; Wang, Z.; Reynolds, M.J.; Mast, T.C.; Robinson, R.; Murphy, B.R.; Karron, R.A.; et al. Safety and Immunogenicity Trial in Adult Volunteers of a Human Papillomavirus 16 L1 Virus-Like Particle Vaccine. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2001, 93, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carissimi, G.; Montalbán, M.G.; Fuster, M.G.; et al. Silk Fibroin Nanoparticles: Synthesis and Applications as Drug Nanocarriers. 2: 21st Century Nanostructured Materials: Physics, Chemistry, Classification, and Emerging Applications in Industry, Biomedicine, and Agriculture 2022, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, W.; He, C.; Hao, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, L.; Zhu, G. Prospects and challenges of extracellular vesicle-based drug delivery system: considering cell source. Drug Deliv. 2020, 27, 585–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, Q.-V.; Lee, J.; Lee, H.; Shim, G.; Oh, Y.-K. Cell membrane-derived vesicles for delivery of therapeutic agents. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 2096–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noren Hooten, N.; Yáñez-Mó, M.; DeRita, R.; et al. Hitting the Bullseye: Are extracellular vesicles on target? e: J Extracell Vesicles 2020, 10, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz, A. Not all extracellular vesicles were created equal: clinical implications. Ann. Transl. Med. 2017, 5, 111–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghodsi, M.; Cloos, A.-S.; Mozaheb, N.; et al. Variability of extracellular vesicle release during storage of red blood cell concentrates is associated with differential membrane alterations, including loss of cholesterol-enriched domains. 1: Frontiers in Physiology 2023, 14, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Loch-Neckel, G.; Matos, A.T.; Vaz, A.R.; Brites, D. Challenges in the Development of Drug Delivery Systems Based on Small Extracellular Vesicles for Therapy of Brain Diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 839790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravasco, J.M.J.M.; Paiva-Santos, A.C.; Conde, J. Technological challenges of biomembrane-coated top-down cancer nanotherapy. Nat. Rev. Bioeng. 2023, 1, 156–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, A.; Rubens, M.; Ramamoorthy, V.; Zhang, Z.; Ahmed, A.; McGranaghan, P.; Das, S.; Veledar, E. A Brief Overview of Adaptive Designs for Phase I Cancer Trials. Cancers 2022, 14, 1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angus, D.C.; Alexander, B.M.; Berry, S.; et al. Adaptive platform trials: definition, design, conduct and reporting considerations. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery 2019, 18, 797–807. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, P.; Liu, L.; Senchaudhuri, P.; et al. Design and monitoring of multi-arm multi-stage clinical trials. Biometrics 2017, 73, 1289–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.J.H.; Hsu, G.; Siden, E.G.; Thorlund, K.; Mills, E.J.; Msc, J.J.H.P.; Msc, G.H.; Frcp(Edin), E.J.M. An overview of precision oncology basket and umbrella trials for clinicians. CA: A Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidwell, K.M.; Almirall, D. Sequential, Multiple Assignment, Randomized Trial Designs. JAMA 2023, 329, 336–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.M. Get SMART — Understanding Sequential Multiple Assignment Randomized Trials. NEJM Évid. 2023, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, T.; Wang, J.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, G.; Chen, X. Polysaccharide-Based Controlled Release Systems for Therapeutics Delivery and Tissue Engineering: From Bench to Bedside. Adv. Sci. 2018, 5, 1700513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasmin, F.; Chen, X.; Eames, B.F. Effect of Process Parameters on the Initial Burst Release of Protein-Loaded Alginate Nanospheres. J. Funct. Biomater. 2019, 10, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannon, G.; Prina-Mello, A. Endotoxin contamination of engineered nanomaterials: Overcoming the hurdles associated with endotoxin testing. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechnology 2021, 13, e1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paull, J. A Prospective Study of Dextran-induced Anaphylactoid Reactions in 5745 Patients. Anaesth. Intensiv. Care 1987, 15, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegemann, S.; Klingmann, V.; Reidemeister, S.; Breitkreutz, J. Patient-centric drug product development: Acceptability across patient populations – Science and evidence. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2023, 188, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasti, S.; Lee, I.H.; Kim, S.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, H. Ethical and legal challenges in nanomedical innovations: a scoping review. Front. Genet. 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradise, J. Regulating Nanomedicine at the Food and Drug Administration. AMA J. Ethic- 2019, 21, E347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allon, I.; Ben-Yehudah, A.; Dekel, R.; et al. Ethical issues in nanomedicine: Tempest in a teapot? Medicine, Health Care and Philosophy 2017, 20, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belfiore, L.; Saunders, D.N.; Ranson, M.; Thurecht, K.J.; Storm, G.; Vine, K.L. Towards clinical translation of ligand-functionalized liposomes in targeted cancer therapy: Challenges and opportunities. J. Control. Release 2018, 277, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, D.P.; Pazdernik, N.J. Chapter 21 - Viral and Prion Infections. In Biotechnology (Second Edition), Clark, D.P., Pazdernik, N.J., Eds.; Academic Cell: Boston, 2016; pp. 663–685. [Google Scholar]
- Mittal, M.; Banerjee, M.; Lua, L.H.; Rathore, A.S. Current status and future challenges in transitioning to continuous bioprocessing of virus-like particles. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2021, 97, 2376–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, M.T.; Kuhlmann, M.; Hvam, M.L.; Howard, K.A. Albumin-based drug delivery: harnessing nature to cure disease. Mol. Cell. Ther. 2016, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohovie, M.J.; Nagasawa, M.; Swartz, J.R. Virus-like particles: Next-generation nanoparticles for targeted therapeutic delivery. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2017, 2, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





