Submitted:
18 September 2023
Posted:
19 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
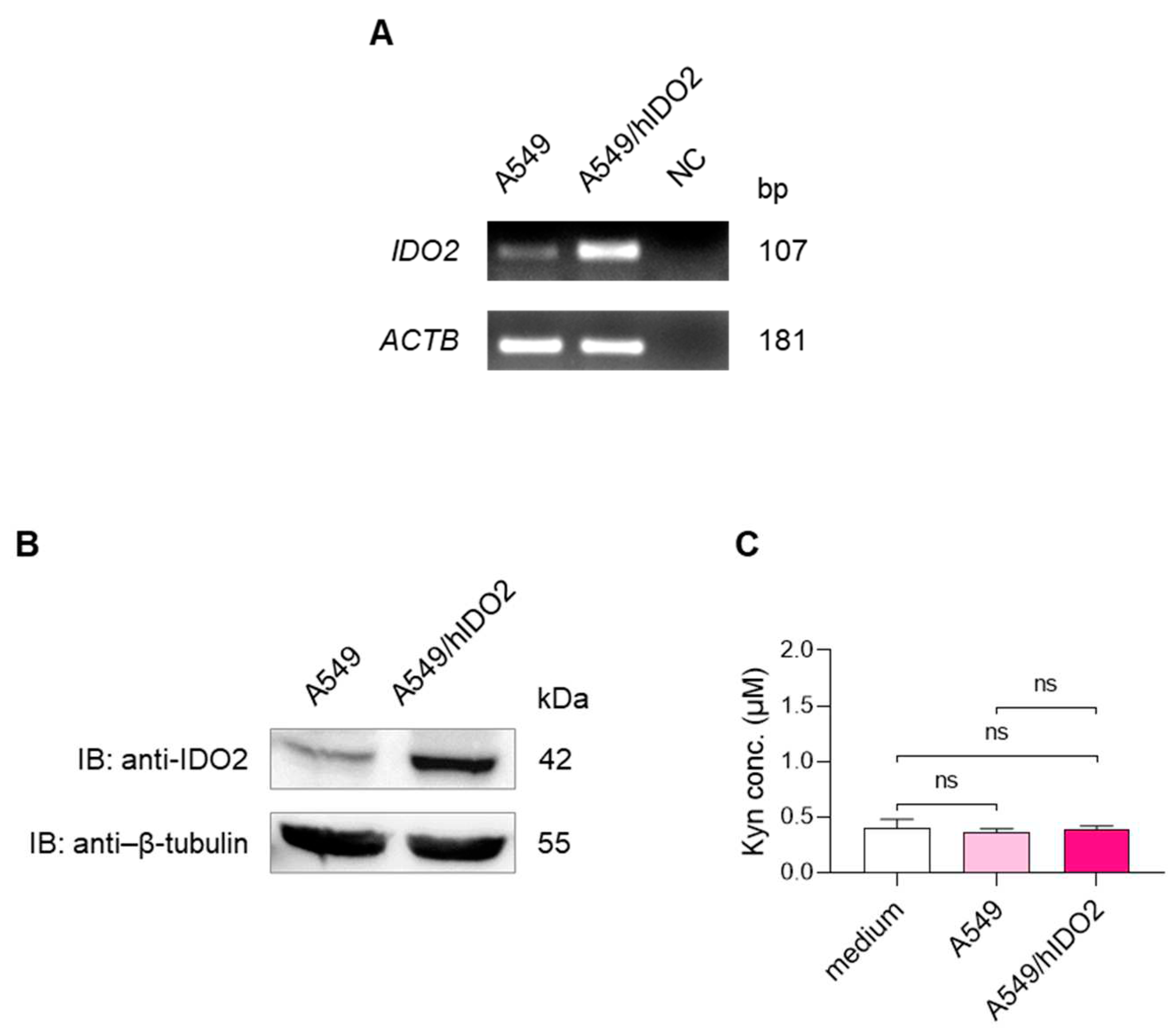
2.1. A549 Cells Basally Express IDO2
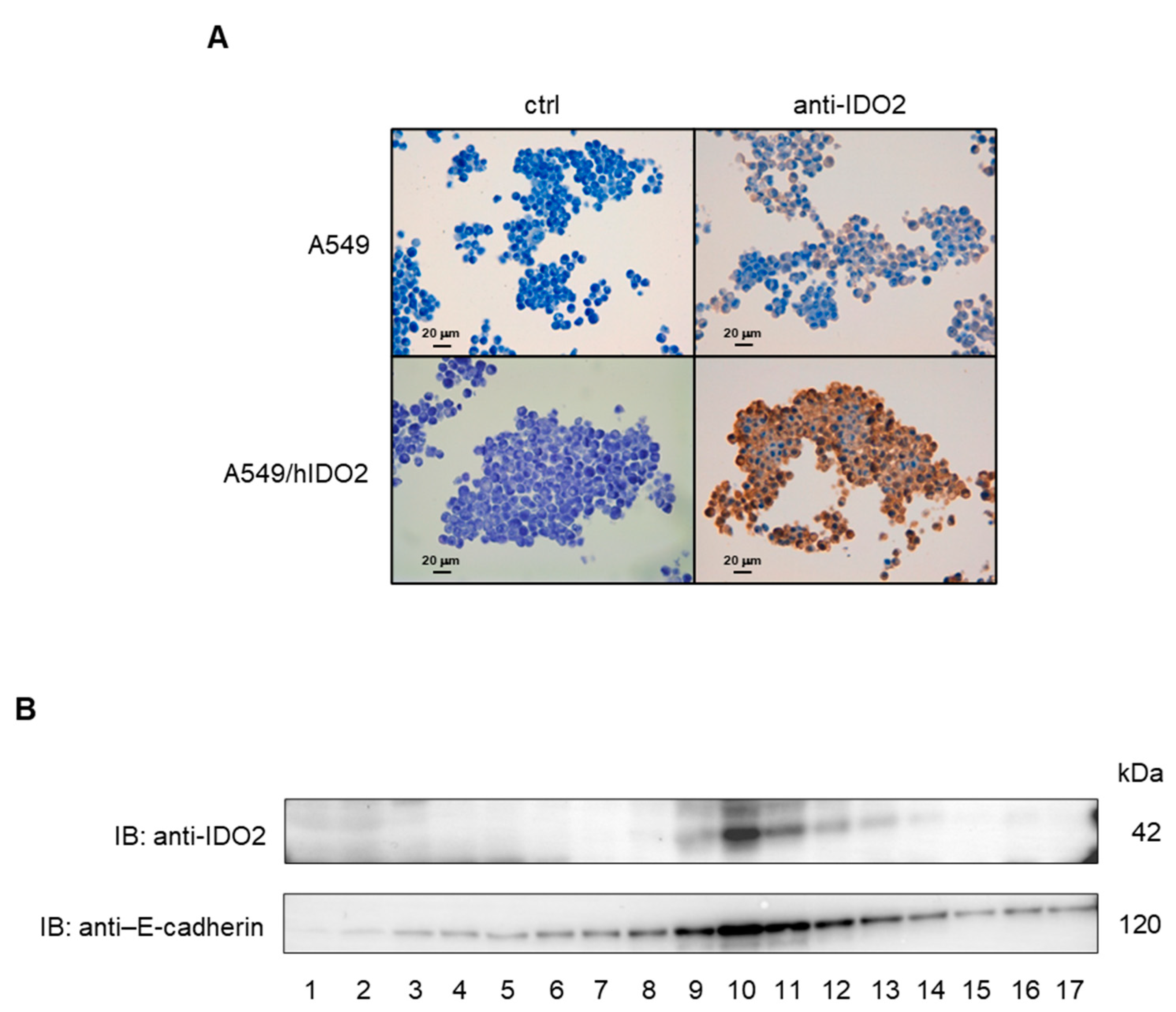
2.2. IDO2 Is Localized at the Membrane Level in A549 Cells
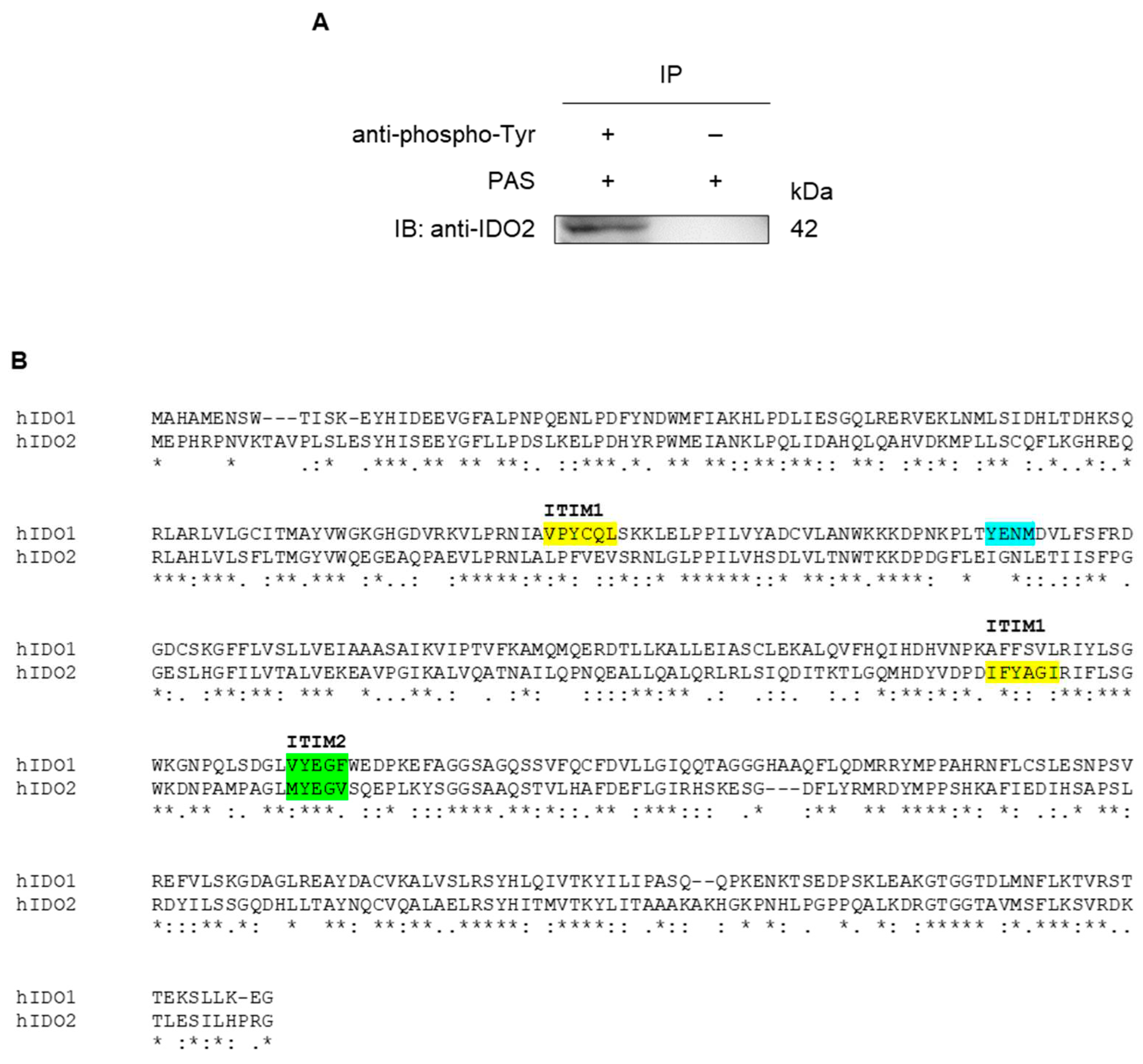
2.3. IDO2 Is Tyrosine-Phosphorylated in A549 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and End-Point RT-PCR
4.2. Kyn Determination
4.3. Western Blotting and Immunoprecipitation
4.4. Immunocytochemical Analysis
4.5. Immunocytochemical Analysis
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fiore, A.; Murray, P.J. Tryptophan and indole metabolism in immune regulation. Current opinion in immunology 2021, 70, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grohmann, U.; Mondanelli, G.; Belladonna, M.L.; Orabona, C.; Pallotta, M.T.; Iacono, A.; Puccetti, P.; Volpi, C. Amino-acid sensing and degrading pathways in immune regulation. Cytokine & growth factor reviews 2017, 35, 37–45. [Google Scholar]
- Gargaro, M.; Scalisi, G.; Manni, G.; Briseño, C.G.; Bagadia, P.; Durai, V.; Theisen, D.J.; Kim, S.; Castelli, M.; Xu, C.A.; et al. Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 activation in mature cDC1 promotes tolerogenic education of inflammatory cDC2 via metabolic communication. Immunity 2022, 55, 1032–1050.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ball, H.J.; Sanchez-Perez, A.; Weiser, S.; Austin, C.J.; Astelbauer, F.; Miu, J.; McQuillan, J.A.; Stocker, R.; Jermiin, L.S.; Hunt, N.H. Characterization of an indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-like protein found in humans and mice. Gene 2007, 396, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuasa, H.J.; Takubo, M.; Takahashi, A.; Hasegawa, T.; Noma, H.; Suzuki, T. Evolution of vertebrate indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenases. Journal of molecular evolution 2007, 65, 705–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metz, R.; Duhadaway, J.B.; Kamasani, U.; Laury-Kleintop, L.; Muller, A.J.; Prendergast, G.C. Novel tryptophan catabolic enzyme IDO2 is the preferred biochemical target of the antitumor indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase inhibitory compound D-1-methyl-tryptophan. Cancer research 2007, 67, 7082–7087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Théate, I.; van Baren, N.; Pilotte, L.; Moulin, P.; Larrieu, P.; Renauld, J.C.; Hervé, C.; Gutierrez-Roelens, I.; Marbaix, E.; Sempoux, C.; et al. Extensive profiling of the expression of the indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 protein in normal and tumoral human tissues. Cancer immunology research 2015, 3, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prendergast, G.C.; Metz, R.; Muller, A.J.; Merlo, L.M.; Mandik-Nayak, L. IDO2 in Immunomodulation and Autoimmune Disease. Frontiers in immunology 2014, 5, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jusof, F.F.; Bakmiwewa, S.M.; Weiser, S.; Too, L.K.; Metz, R.; Prendergast, G.C.; Fraser, S.T.; Hunt, N.H.; Ball, H.J. Investigation of the tissue distribution and physiological roles of indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase-2. International Journal of Tryptophan Research 2017, 10, 1178646917735098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukunaga, M.; Yamamoto, Y.; Kawasoe, M.; Arioka, Y.; Murakami, Y.; Hoshi, M.; Saito, K. Studies on Tissue and Cellular Distribution of Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase 2: The Absence of IDO1 Upregulates IDO2 Expression in the Epididymis. Journal of Histochemistry & Cytochemistry 2012, 60, 854–860. [Google Scholar]
- Pantouris, G.; Serys, M.; Yuasa, H.J.; Ball, H.J.; Mowat, C.G. Human indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-2 has substrate specificity and inhibition characteristics distinct from those of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-1. Amino Acids 2014, 46, 2155–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Li, Y.; Yang, D.; Hu, N.; Guo, Z.; Kuang, C.; Yang, Q. Establishment of a human indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase 2 (hIDO2) bioassay system and discovery of tryptanthrin derivatives as potent hIDO2 inhibitors. European journal of medicinal chemistry 2016, 123, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuasa, H.J.; Stocker, R. Methylene blue and ascorbate interfere with the accurate determination of the kinetic properties of IDO2. The FEBS journal 2021, 288, 4892–4904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuasa, H.J.; Ball, H.J.; Ho, Y.F.; Austin, C.J.D.; Whittington, C.M.; Belov, K.; Maghzal, G.J.; Jermiin, L.S.; Hunt, N.H. Characterization and evolution of vertebrate indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenases: IDOs from monotremes and marsupials. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part B: Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 2009, 153, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Baren, N.; Van den Eynde, B.J. Tryptophan-degrading enzymes in tumoral immune resistance. Frontiers in immunology 2015, 6, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metz, R.; Smith, C.; DuHadaway, J.B.; Chandler, P.; Baban, B.; Merlo, L.M.; Pigott, E.; Keough, M.P.; Rust, S.; Mellor, A.L.; et al. IDO2 is critical for IDO1-mediated T-cell regulation and exerts a non-redundant function in inflammation. International immunology 2014, 26, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlo, L.M.F.; Pigott, E.; DuHadaway, J.B.; Grabler, S.; Metz, R.; Prendergast, G.C.; Mandik-Nayak, L. IDO2 is a critical mediator of autoantibody production and inflammatory pathogenesis in a mouse model of autoimmune arthritis. Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2014, 192, 2082–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlo, L.M.F.; DuHadaway, J.B.; Montgomery, J.D.; Peng, W.D.; Murray, P.J.; Prendergast, G.C.; Caton, A.J.; Muller, A.J.; Mandik-Nayak, L. Differential Roles of IDO1 and IDO2 in T and B Cell Inflammatory Immune Responses. Frontiers in immunology 2020, 11, 1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, K.; Yamamoto, Y.; Mizutani, Y.; Saito, K.; Seishima, M. Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase 2 Deficiency Exacerbates Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-Like Skin Inflammation. International journal of molecular sciences 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandarano, M.; Bellezza, G.; Belladonna, M.L.; Vannucci, J.; Gili, A.; Ferri, I.; Lupi, C.; Ludovini, V.; Falabella, G.; Metro, G.; et al. Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase 2 Immunohistochemical Expression in Resected Human Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: A Potential New Prognostic Tool. Frontiers in immunology 2020, 11, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevler, A.; Muller, A.J.; Sutanto-Ward, E.; DuHadaway, J.B.; Nagatomo, K.; Londin, E.; O'Hayer, K.; Cozzitorto, J.A.; Lavu, H.; Yeo, T.P.; et al. Host IDO2 Gene Status Influences Tumor Progression and Radiotherapy Response in KRAS-Driven Sporadic Pancreatic Cancers. Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 2019, 25, 724–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witkiewicz, A.K.; Costantino, C.L.; Metz, R.; Muller, A.J.; Prendergast, G.C.; Yeo, C.J.; Brody, J.R. Genotyping and expression analysis of IDO2 in human pancreatic cancer: a novel, active target. Journal of the American College of Surgeons 2009, 208, 781–787; discussion 787-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Xu, W.; Liu, F.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, L.; Ding, Z.; Liang, H.; Song, J. The emerging roles of IDO2 in cancer and its potential as a therapeutic target. Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine & pharmacotherapie 2021, 137, 111295. [Google Scholar]
- Löb, S.; Königsrainer, A.; Zieker, D.; Brücher, B.L.; Rammensee, H.G.; Opelz, G.; Terness, P. IDO1 and IDO2 are expressed in human tumors: levo- but not dextro-1-methyl tryptophan inhibits tryptophan catabolism. Cancer immunology, immunotherapy CII 2009, 58, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, P.; Ling, B.; Ma, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, W.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chi, J.; Ruan, X.; Zheng, X.; et al. Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 2 immunohistochemical expression in medullary thyroid carcinoma: implications in prognosis and immunomodulatory effects. BMC cancer 2022, 22, 1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Li, Q.; Yuan, K.; Zhou, N.; Yu, Y.; Song, N.; et al. Gene silencing of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 2 in melanoma cells induces apoptosis through the suppression of NAD+ and inhibits in vivo tumor growth. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 32329–32340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlo, L.M.F.; Peng, W.; DuHadaway, J.B.; Montgomery, J.D.; Prendergast, G.C.; Muller, A.J.; Mandik-Nayak, L. The Immunomodulatory Enzyme IDO2 Mediates Autoimmune Arthritis through a Nonenzymatic Mechanism. Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2022, 208, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondanelli, G.; Mandarano, M.; Belladonna, M.L.; Suvieri, C.; Pelliccia, C.; Bellezza, G.; Sidoni, A.; Carvalho, A.; Grohmann, U.; Volpi, C. Current Challenges for IDO2 as Target in Cancer Immunotherapy. Frontiers in immunology 2021, 12, 679953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacono, A.; Pompa, A.; De Marchis, F.; Panfili, E.; Greco, F.A.; Coletti, A.; Orabona, C.; Volpi, C.; Belladonna, M.L.; Mondanelli, G.; et al. Class IA PI3Ks regulate subcellular and functional dynamics of IDO1. EMBO reports 2020, 21, e49756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlo, L.M.F.; Peng, W.; Mandik-Nayak, L. Impact of IDO1 and IDO2 on the B Cell Immune Response. Frontiers in immunology 2022, 13, 886225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetzel, L.A.; Hurtado, M.; MacDowell Kaswan, Z.A.; McCusker, R.H.; Steelman, A.J. Deletion of indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase (Ido)1 but not Ido2 exacerbates disease symptoms of MOG35-55-induced experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Brain, Behavior, & Immunity - Health 2020, 7, 100116. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Yamasuge, W.; Imai, S.; Kunisawa, K.; Hoshi, M.; Fujigaki, H.; Mouri, A.; Nabeshima, T.; Saito, K. Lipopolysaccharide shock reveals the immune function of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 2 through the regulation of IL-6/stat3 signalling. Scientific Reports 2018, 8, 15917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uyttenhove, C.; Pilotte, L.; Théate, I.; Stroobant, V.; Colau, D.; Parmentier, N.; Boon, T.; Van den Eynde, B.J. Evidence for a tumoral immune resistance mechanism based on tryptophan degradation by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase. Nature medicine 2003, 9, 1269–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, Y.; Kato, S.; Nesline, M.K.; Conroy, J.M.; DePietro, P.; Pabla, S.; Kurzrock, R. Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) inhibitors and cancer immunotherapy. Cancer treatment reviews 2022, 110, 102461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meireson, A.; Devos, M.; Brochez, L. IDO Expression in Cancer: Different Compartment, Different Functionality? Frontiers in immunology 2020, 11, 531491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prendergast, G.C.; Malachowski, W.J.; Mondal, A.; Scherle, P.; Muller, A.J. Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase and Its Therapeutic Inhibition in Cancer. International review of cell and molecular biology 2018, 336, 175–203. [Google Scholar]
- Pallotta, M.T.; Rossini, S.; Suvieri, C.; Coletti, A.; Orabona, C.; Macchiarulo, A.; Volpi, C.; Grohmann, U. Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1): an up-to-date overview of an eclectic immunoregulatory enzyme. The FEBS journal 2022, 289, 6099–6118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.F.; Yang, L.Q.; Shi, Z.H.; Li, X.M.; Qiu, H.Y. An updated patent review of IDO1 inhibitors for cancer (2018-2022). Expert opinion on therapeutic patents 2022, 32, 1145–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orecchini, E.; Belladonna, M.L.; Pallotta, M.T.; Volpi, C.; Zizi, L.; Panfili, E.; Gargaro, M.; Fallarino, F.; Rossini, S.; Suvieri, C.; et al. The signaling function of IDO1 incites the malignant progression of mouse B16 melanoma. Oncoimmunology 2023, 12, 2170095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallotta, M.T.; Orabona, C.; Volpi, C.; Vacca, C.; Belladonna, M.L.; Bianchi, R.; Servillo, G.; Brunacci, C.; Calvitti, M.; Bicciato, S.; et al. Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase is a signaling protein in long-term tolerance by dendritic cells. Nature immunology 2011, 12, 870–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albini, E.; Rosini, V.; Gargaro, M.; Mondanelli, G.; Belladonna, M.L.; Pallotta, M.T.; Volpi, C.; Fallarino, F.; Macchiarulo, A.; Antognelli, C.; et al. Distinct roles of immunoreceptor tyrosine-based motifs in immunosuppressive indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1. Journal of cellular and molecular medicine 2017, 21, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessede, A.; Gargaro, M.; Pallotta, M.T.; Matino, D.; Servillo, G.; Brunacci, C.; Bicciato, S.; Mazza, E.M.; Macchiarulo, A.; Vacca, C.; et al. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor control of a disease tolerance defence pathway. Nature 2014, 511, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpi, C.; Mondanelli, G.; Pallotta, M.T.; Vacca, C.; Iacono, A.; Gargaro, M.; Albini, E.; Bianchi, R.; Belladonna, M.L.; Celanire, S.; et al. Allosteric modulation of metabotropic glutamate receptor 4 activates IDO1-dependent, immunoregulatory signaling in dendritic cells. Neuropharmacology 2016, 102, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondanelli, G.; Bianchi, R.; Pallotta, M.T.; Orabona, C.; Albini, E.; Iacono, A.; Belladonna, M.L.; Vacca, C.; Fallarino, F.; Macchiarulo, A.; et al. A Relay Pathway between Arginine and Tryptophan Metabolism Confers Immunosuppressive Properties on Dendritic Cells. Immunity 2017, 46, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




