Submitted:
27 July 2023
Posted:
31 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Participants
Group variables
| Group | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Age | SES | FIV | HEV |
| Adults | ||||
| Mean | 23.95 | - | - | - |
| SD | 2.02 | - | - | - |
| Min | 20.83 | - | - | - |
| Max | 29.58 | - | - | - |
| Missing | - | - | - | - |
| Montessori-schooled | ||||
| Mean | 10.0 | 3.1 | 32.9 | 93.5 |
| SD | 3.1 | 0.5 | 4.0 | 10.2 |
| Min | 4.6 | 1.8 | 20.0 | 66.7 |
| Max | 18.0 | 4.0 | 36.0 | 100.0 |
| Missing | - | 5 | 4 | 6 |
| Traditional-schooled | ||||
| Mean | 10.91 | 3.05 | 32.83 | 91.89 |
| SD | 3.61 | 0.64 | 3.57 | 11.20 |
| Min | 3.4 | 1.75 | 19 | 58.33 |
| Max | 17.83 | 4 | 36 | 100 |
| Missing | - | 5 | 7 | 7 |
MRI Acquisition
MRI Preprocessing
Cortical Thickness Computation
Asymmetry Index Computation
Statistical Analysis
Group and demographic variables
Asymmetry index
Adult and students participants comparison
Montessori- and traditionally-schooled participants comparison
3. Results
Group and demographic variables
Asymmetry index
Adult and student participants comparison
Montessori- and traditionally-schooled participants comparison
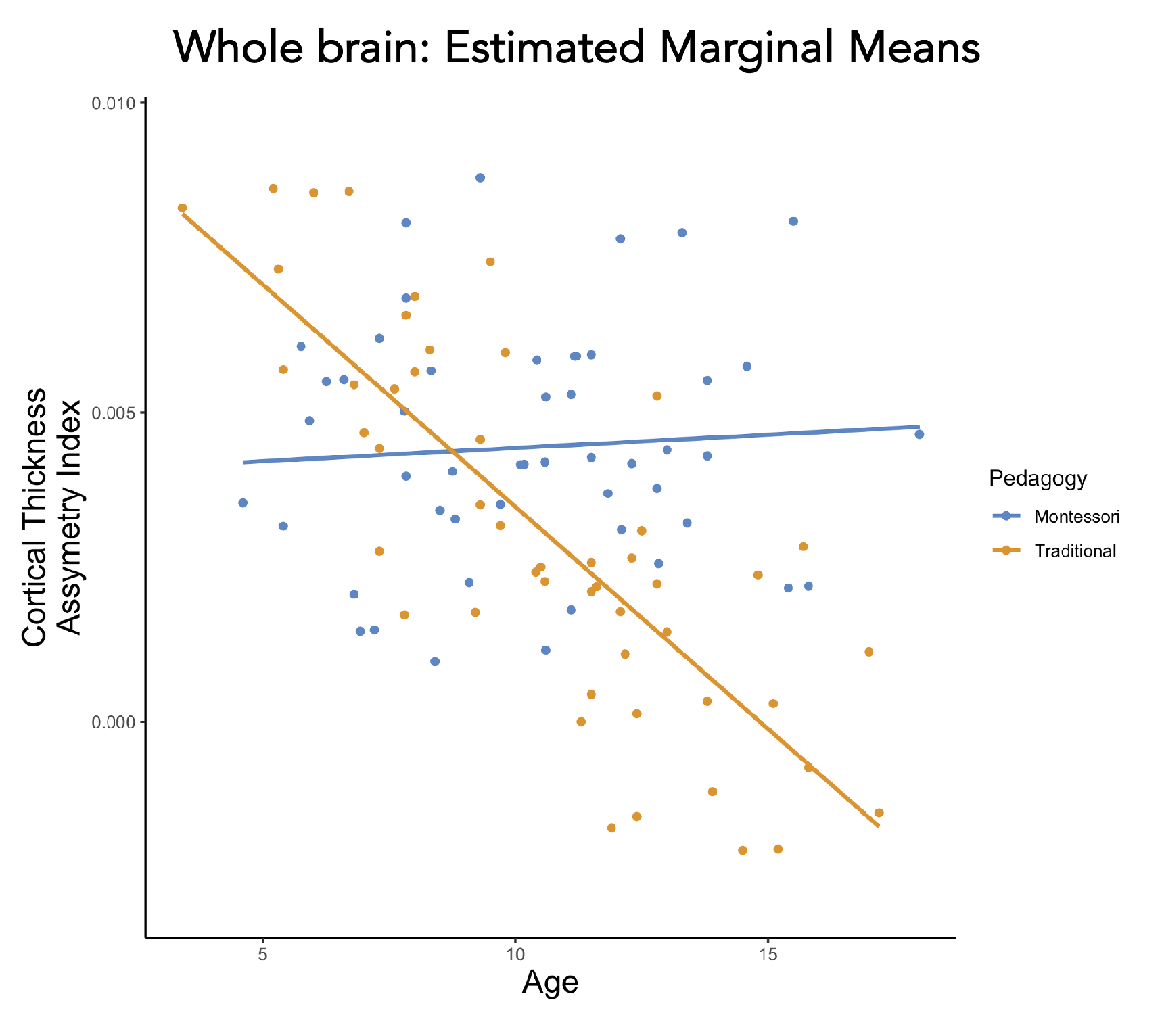
- Whole-brain analysis
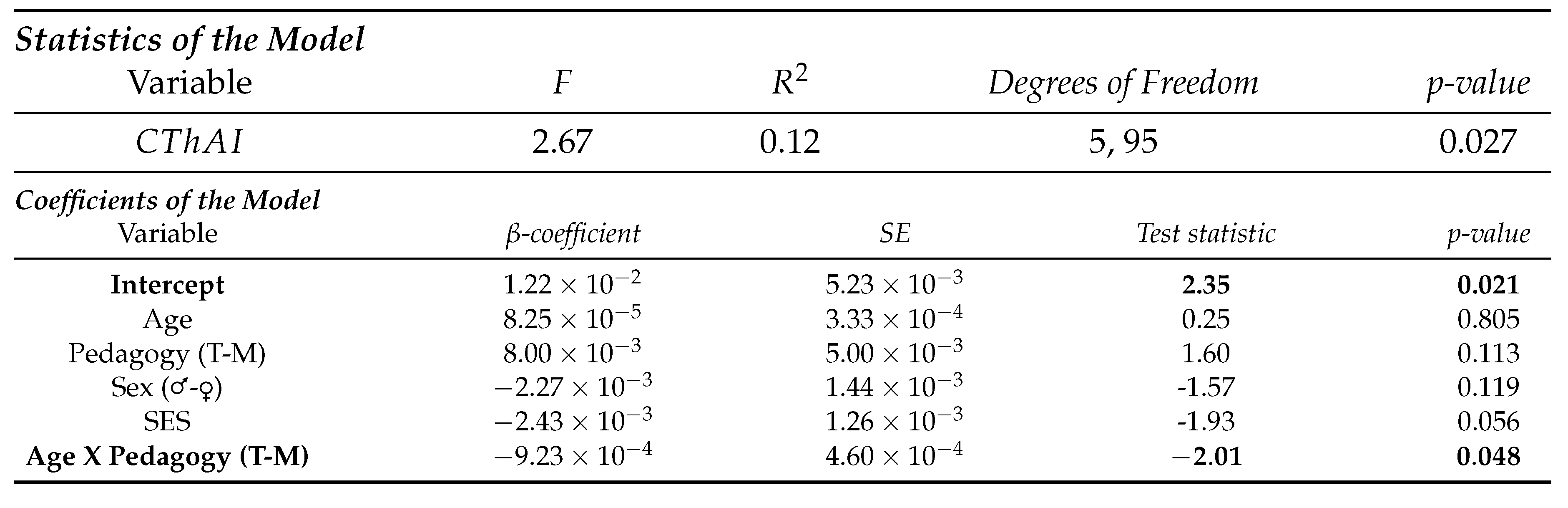
- 2.
- Lobe-wise analysis

- 3.
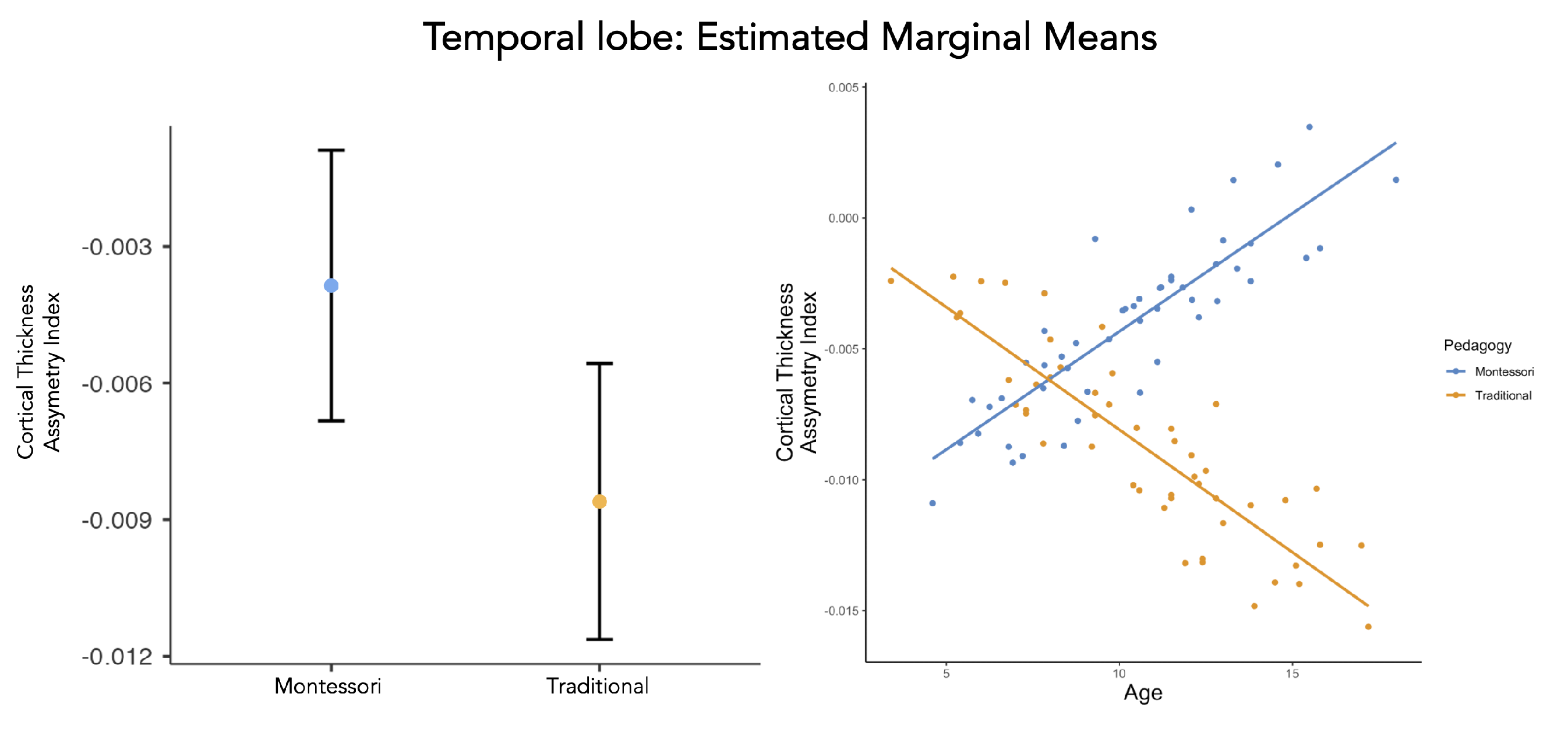
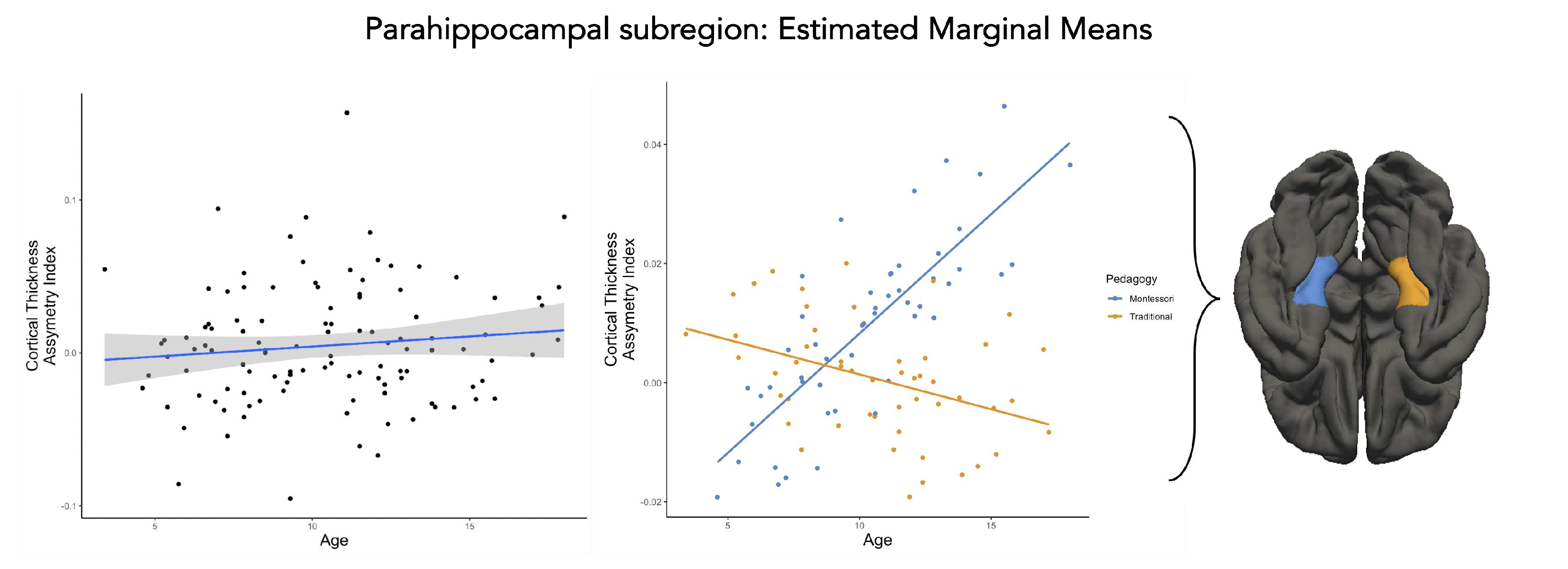
- Subregions of the temporal lobe
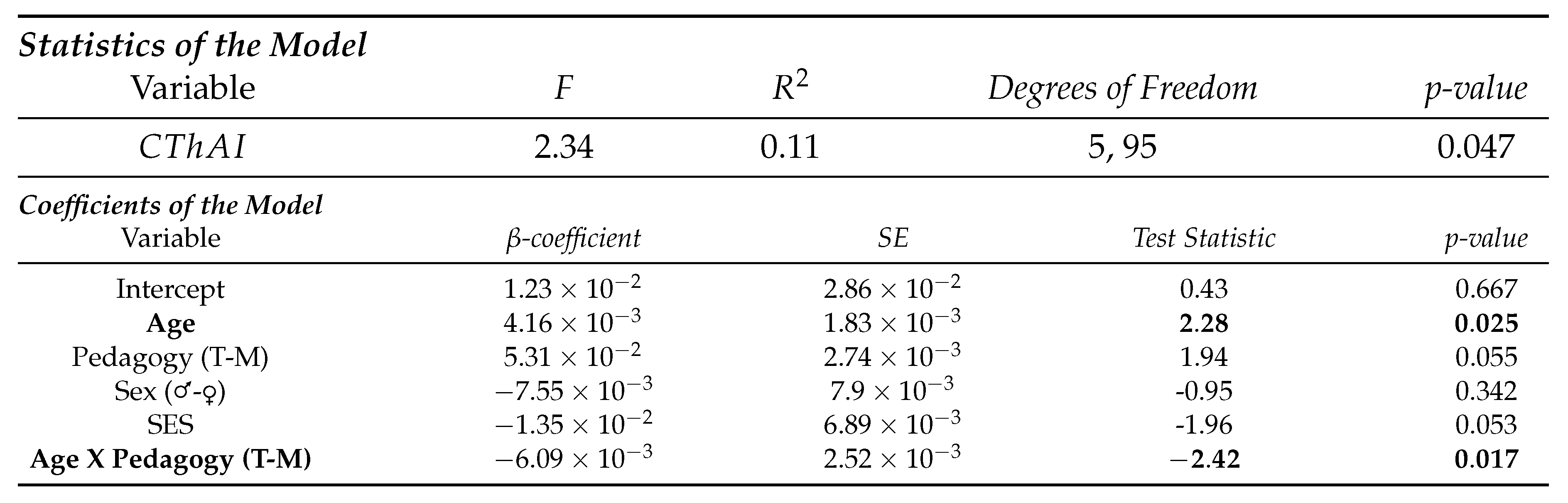
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ansari, A.; Winsler, A. The long-term benefits of Montessori pre-K for Latinx children from low-income families. Applied Developmental Science 2022, 26, 252–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillard, A.; Else-Quest, N. Evaluating montessori education. science 2006, 313, 1893–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courtier, P.; Gardes, M.l.; Van der Henst, J.B.; Noveck, I.A.; Croset, M.C.; Epinat-Duclos, J.; Léone, J.; Prado, J. Effects of montessori education on the academic, cognitive, and social development of disadvantaged preschoolers: a randomized controlled study in the French public-school system. Child Development 2021, 92, 2069–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denervaud, S.; Knebel, J.F.; Hagmann, P.; Gentaz, E. Beyond executive functions, creativity skills benefit academic outcomes: Insights from Montessori education. PloS one 2019, 14, e0225319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillard, A.S.; Heise, M.J.; Richey, E.M.; Tong, X.; Hart, A.; Bray, P.M. Montessori preschool elevates and equalizes child outcomes: A longitudinal study. Frontiers in psychology 2017, 8, 1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denervaud, S.; Christensen, A.P.; Kenett, Y.N.; Beaty, R.E. Education shapes the structure of semantic memory and impacts creative thinking. npj Science of Learning 2021, 6, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besançon, M.; Lubart, T. Differences in the development of creative competencies in children schooled in diverse learning environments. Learning and individual differences 2008, 18, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, D.J.; Culclasure, B.; Zhang, D. The Montessori model and creativity. Journal of Montessori Research 2019, 5, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denervaud, S.; Mumenthaler, C.; Gentaz, E.; Sander, D. Emotion recognition development: Preliminary evidence for an effect of school pedagogical practices. Learning and Instruction 2020, 69, 101353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiryaki, A.Y.; Findik, E.; Çetin Sultanoğlu, S.; Beker, E.; Biçakçi, M.Y.; Aral, N.; Özdoğan Özbal, E. A study on the effect of Montessori Education on self-regulation skills in preschoolers. Early Child Development and Care 2021, 191, 1219–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- İman, E.D.; Danişman, Ş.; Demircan, Z.A.; Yaya, D. The effect of the Montessori education method on pre-school children’s social competence–behaviour and emotion regulation skills. Early Child Development and Care 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lillard, A.S. Shunned and admired: Montessori, self-determination, and a case for radical school reform. Educational Psychology Review 2019, 31, 939–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denervaud, S.; Fornari, E.; Yang, X.F.; Hagmann, P.; Immordino-Yang, M.H.; Sander, D. An fMRI study of error monitoring in Montessori and traditionally-schooled children. NPJ science of learning 2020, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duval, P.E.; Fornari, E.; Décaillet, M.; Ledoux, J.B.; Beaty, R.E.; Denervaud, S. Creative thinking and brain network development in schoolchildren. Developmental Science 2023, p. e13389.
- Toga, A.W.; Thompson, P.M. Mapping brain asymmetry. Nature Reviews Neuroscience 2003, 4, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, X.Z.; Mathias, S.R.; Guadalupe, T.; Group, E.L.W.; Glahn, D.C.; Franke, B.; Crivello, F.; Tzourio-Mazoyer, N.; Fisher, S.E.; Thompson, P.M.; others. Mapping cortical brain asymmetry in 17,141 healthy individuals worldwide via the ENIGMA Consortium. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2018, 115, E5154–E5163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Gao, F.; Zheng, W.; You, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Lv, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhang, H.; Ji, C.; Wu, D. Diffusion MRI of the infant brain reveals unique asymmetry patterns during the first-half-year of development. NeuroImage 2021, 242, 118465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, P.; Lalonde, F.; Lepage, C.; Rabin, C.; Eckstrand, K.; Sharp, W.; Greenstein, D.; Evans, A.; Giedd, J.; Rapoport, J. Development of cortical asymmetry in typically developing children and its disruption in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Archives of general psychiatry 2009, 66, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, D.V. Cerebral asymmetry and language development: cause, correlate, or consequence? Science 2013, 340, 1230531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittling, R.; Schweiger, E.; Rizhova, L.; Vershinina, E.; Starup, L. A simple method for measuring brain asymmetry in children: Application to autism. Behavior research methods 2009, 41, 812–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avants, B.B.; Hackman, D.A.; Betancourt, L.M.; Lawson, G.M.; Hurt, H.; Farah, M.J. Relation of childhood home environment to cortical thickness in late adolescence: specificity of experience and timing. PloS one 2015, 10, e0138217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, S.W.; Kerr, C.E.; Wasserman, R.H.; Gray, J.R.; Greve, D.N.; Treadway, M.T.; McGarvey, M.; Quinn, B.T.; Dusek, J.A.; Benson, H.; others. Meditation experience is associated with increased cortical thickness. neuroreport 2005, 16, 1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogtay, N.; Giedd, J.N.; Lusk, L.; Hayashi, K.M.; Greenstein, D.; Vaituzis, A.C.; Nugent III, T.F.; Herman, D.H.; Clasen, L.S.; Toga, A.W.; others. Dynamic mapping of human cortical development during childhood through early adulthood. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2004, 101, 8174–8179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funahashi, S.; Andreau, J.M. Prefrontal cortex and neural mechanisms of executive function. Journal of Physiology-Paris 2013, 107, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squire, L.R.; Stark, C.E.; Clark, R.E. The medial temporal lobe. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2004, 27, 279–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Q.Y.; Sluming, V.; Mayes, A.; Keller, S.; Barrick, T.; Cezayirli, E.; Roberts, N. Voxel-based morphometry and stereology provide convergent evidence of the importance of medial prefrontal cortex for fluid intelligence in healthy adults. Neuroimage 2005, 25, 1175–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.S.; Pellecchia, G.; Aminian, K.; Ray, N.; Segura, B.; Obeso, I.; Strafella, A.P. Morphometric correlation of impulsivity in medial prefrontal cortex. Brain topography 2013, 26, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fried, P.J.; Rushmore III, R.J.; Moss, M.B.; Valero-Cabré, A.; Pascual-Leone, A. Causal evidence supporting functional dissociation of verbal and spatial working memory in the human dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. European Journal of Neuroscience 2014, 39, 1973–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Strien, N.; Cappaert, N.; Witter, M. The anatomy of memory: an interactive overview of the parahippocampal–hippocampal network. Nature reviews neuroscience 2009, 10, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, A.M.; Doyon, J.; Petrides, M.; Evans, A.C. Planning and spatial working memory: a positron emission tomography study in humans. European Journal of Neuroscience 1996, 8, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernier, M.; Gauvreau, C.; Theriault, D.; Madrolle, S.; Lepage, J.F.; Whittingstall, K. Increased BOLD activation in the left parahippocampal cortex after 1 year of medical school: an association with cumulative verbal memory learning. Neuroreport 2016, 27, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopelman, M.; Stevens, T.; Foli, S.; Grasby, P. PET activation of the medial temporal lobe in learning. Brain: a journal of neurology 1998, 121, 875–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Lu, S.; Zhong, N. The parahippocampal cortex mediates contextual associative memory: evidence from an fMRI study. BioMed research international 2016, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squire, L.R. Memory systems of the brain: a brief history and current perspective. Neurobiology of learning and memory 2004, 82, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raja, R.; Na, X.; Glasier, C.M.; Badger, T.M.; Bellando, J.; Ou, X. Associations between Cortical Asymmetry and Domain Specific Cognitive Functions in Healthy Children. 2021 43rd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC). IEEE, 2021, pp. 3127–3132.
- Takahashi, E.; Ohki, K.; Miyashita, Y. The role of the parahippocampal gyrus in source memory for external and internal events. Neuroreport 2002, 13, 1951–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yussen, S.R.; Mathews, S.; Knight, J.W. Performance of Montessori and traditionally schooled nursery children on social cognitive tasks and memory problems. Contemporary Educational Psychology 1980, 5, 124–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rummel, C.; Slavova, N.; Seiler, A.; Abela, E.; Hauf, M.; Burren, Y.; Weisstanner, C.; Vulliemoz, S.; Seeck, M.; Schindler, K.; others. Personalized structural image analysis in patients with temporal lobe epilepsy. Scientific reports 2017, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rummel, C.; Aschwanden, F.; McKinley, R.; Wagner, F.; Salmen, A.; Chan, A.; Wiest, R. A fully automated pipeline for normative atrophy in patients with neurodegenerative disease. Frontiers in neurology 2018, 8, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.Z.; Postema, M.C.; Guadalupe, T.; de Kovel, C.; Boedhoe, P.S.; Hoogman, M.; Mathias, S.R.; Van Rooij, D.; Schijven, D.; Glahn, D.C.; others. Mapping brain asymmetry in health and disease through the ENIGMA consortium. Human brain mapping 2022, 43, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Y.; Zhao, L.; Yu, S.; Sun, B.; Hou, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, Y.; Liu, S. Brain asymmetry differences between Chinese and Caucasian populations: a surface-based morphometric comparison study. Brain Imaging and Behavior 2020, 14, 2323–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duboc, V.; Dufourcq, P.; Blader, P.; Roussigné, M. Asymmetry of the brain: development and implications. Annu Rev Genet 2015, 49, 647–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, F.Y.; Fatemi, A.; Johnston, M.V. Cerebral plasticity: Windows of opportunity in the developing brain. European Journal of Paediatric Neurology 2017, 21, 23–48. Advances in Neuromodulation in Children. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genoud, P.A. Indice de position socioéconomique (IPSE): un calcul simplifié. Fribourg: Université de Fribourg 2011.
- Raven, J.C. Matrix tests. Mental Health 1940, 1, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Doucet, G.E.; Moser, D.A.; Rodrigue, A.; Bassett, D.S.; Glahn, D.C.; Frangou, S. Person-Based Brain Morphometric Similarity is Heritable and Correlates With Biological Features. Cerebral Cortex 2018, 29, 852–862, [https://academic.oup.com/cercor/article-pdf/29/2/852/27378719/bhy287.pdf]. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turesky, T.K.; Shama, T.; Kakon, S.H.; Haque, R.; Islam, N.; Someshwar, A.; Gagoski, B.; Petri, W.A.; Nelson, C.A.; Gaab, N. Brain morphometry and diminished physical growth in Bangladeshi children growing up in extreme poverty: A longitudinal study. Developmental Cognitive Neuroscience 2021, 52, 101029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desikan, R.; Segonne, F.; Fischl, B.; Quinn, B.; Dickerson, B.; Blacker, D.; Buckner, R.; Dale, A.; Maguire, R.; Hyman, B.; Albert, M.; Killiany, R. An Automated Labeling System for Subdividing the Human Cerebral Cortex on MRI Scans into Gyral Based Regions of Interest. NeuroImage 2006, pp. 968–980.
- Fischl, B.; Dale, A.M. Measuring the thickness of the human cerebral cortex from magnetic resonance images. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2000, 97, 11050–11055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutton, C.; De Vita, E.; Ashburner, J.; Deichmann, R.; Turner, R. Voxel-based cortical thickness measurements in MRI. Neuroimage 2008, 40, 1701–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilde, E.A.; Hyseni, I.; Lindsey, H.M.; Faber, J.; McHenry, J.M.; Bigler, E.D.; Biekman, B.D.; Hollowell, L.L.; McCauley, S.R.; Hunter, J.V.; others. A Preliminary DTI Tractography Study of Developmental Neuroplasticity 5–15 Years After Early Childhood Traumatic Brain Injury. Frontiers in Neurology 2021, 12, 2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.t.; Wu, C.y.; Liu, H.l.; Lin, K.c.; Wai, Y.y.; Chen, Y.l. Neuroplastic changes in resting-state functional connectivity after stroke rehabilitation. Frontiers in human neuroscience 2015, 9, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froeliger, B.; Garland, E.L.; McClernon, F.J. Yoga meditation practitioners exhibit greater gray matter volume and fewer reported cognitive failures: results of a preliminary voxel-based morphometric analysis. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlaug, G.; Forgeard, M.; Zhu, L.; Norton, A.; Norton, A.; Winner, E. Training-induced neuroplasticity in young children. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 2009, 1169, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Lee, S.J.; Roshchupkin, G.V.; Adams, H.H.; Schmidt, H.; Hofer, E.; Saba, Y.; Schmidt, R.; Hofman, A.; Amin, N.; van Duijn, C.M.; others. Gray matter heritability in family-based and population-based studies using voxel-based morphometry. Human Brain Mapping 2017, 38, 2408–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Ning, M.; Fang, P.; Xu, H. Sex differences in structural brain asymmetry of children with autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Integrative Neuroscience 2021, 20, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postema, M.C.; Van Rooij, D.; Anagnostou, E.; Arango, C.; Auzias, G.; Behrmann, M.; Calderoni, S.; Calvo, R.; Daly, E.; Deruelle, C.; others. Altered structural brain asymmetry in autism spectrum disorder in a study of 54 datasets. Nature communications 2019, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, J.; Dierker, D.; Neil, J.; Inder, T.; Knutsen, A.; Harwell, J.; Coalson, T.; Van Essen, D. A surface-based analysis of hemispheric asymmetries and folding of cerebral cortex in term-born human infants. Journal of neuroscience 2010, 30, 2268–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aminoff, E.M.; Kveraga, K.; Bar, M. The role of the parahippocampal cortex in cognition. Trends in Cognitive Sciences 2013, 17, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohbot, V.D.; Allen, J.J.; Dagher, A.; Dumoulin, S.O.; Evans, A.C.; Petrides, M.; Kalina, M.; Stepankova, K.; Nadel, L. Role of the parahippocampal cortex in memory for the configuration but not the identity of objects: converging evidence from patients with selective thermal lesions and fMRI. Frontiers in human neuroscience 2015, 9, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, S.; Schwabe, L. Learning and memory under stress: implications for the classroom. npj Science of Learning 2016, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwery, P.; Romascano, D.; Aleman Gomez, Y.; Messerli-Burgy, N.; Denervaud, S. The Effects of Mild but Chronic Stress at School on Brain Development: A Comparative Morphometric Study Between Traditionally and Montessori-schooled Children. Under Review.
| Statistic test | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Test Statistic | Degree of Freedom | p-value | Effect size |
| Sex | 2.68 | 1 | 0.10 | - |
| Handedness | 0.141 | 1 | 0.71 | - |
| Age | -1.39 | 109 | 0.17 | -0.26 |
| Socioeconomic Status | 0.40 | 99 | 0.70 | 0.08 |
| Fluid Intelligence | 0.95 | 98 | 0.95 | 0.01 |
| Home Environment | 0.45 | 96 | 0.45 | 0.15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




