Submitted:
20 July 2023
Posted:
21 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
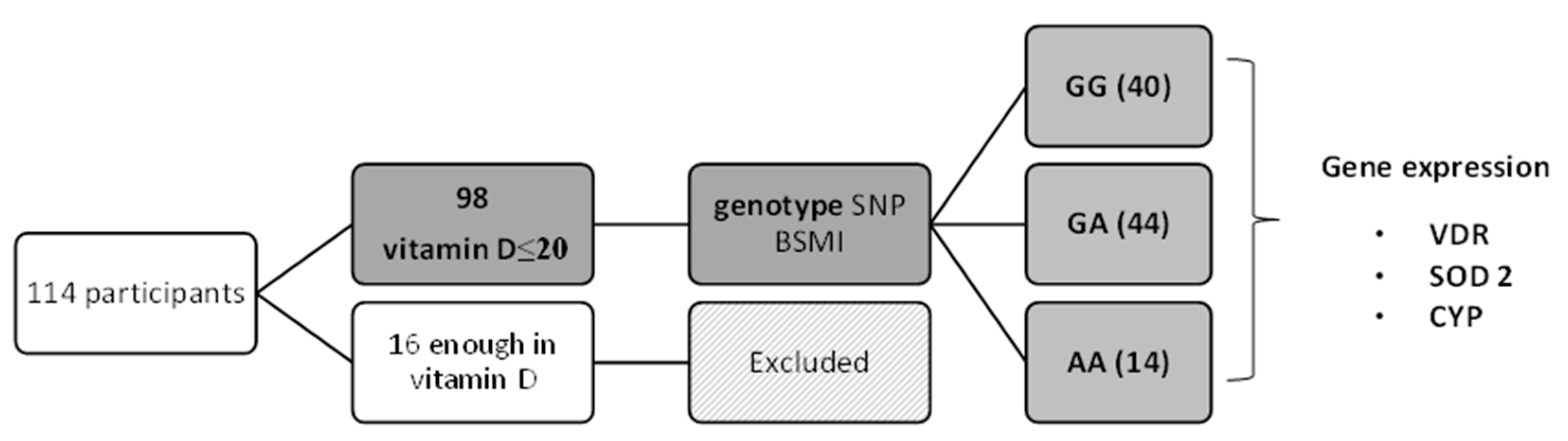
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Study Population and Design
2.3. Genetic-Molecular Analysis
2.3.1. DNA Extraction
2.3.2. Gene Amplification (04121019085)
2.4. Gene Expression by qRT-PCR
2.4.2. Anthropometric and Physiological Assays
2.5. Biochemical Assays
2.6. Vitamin D Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
2.8. Ethics
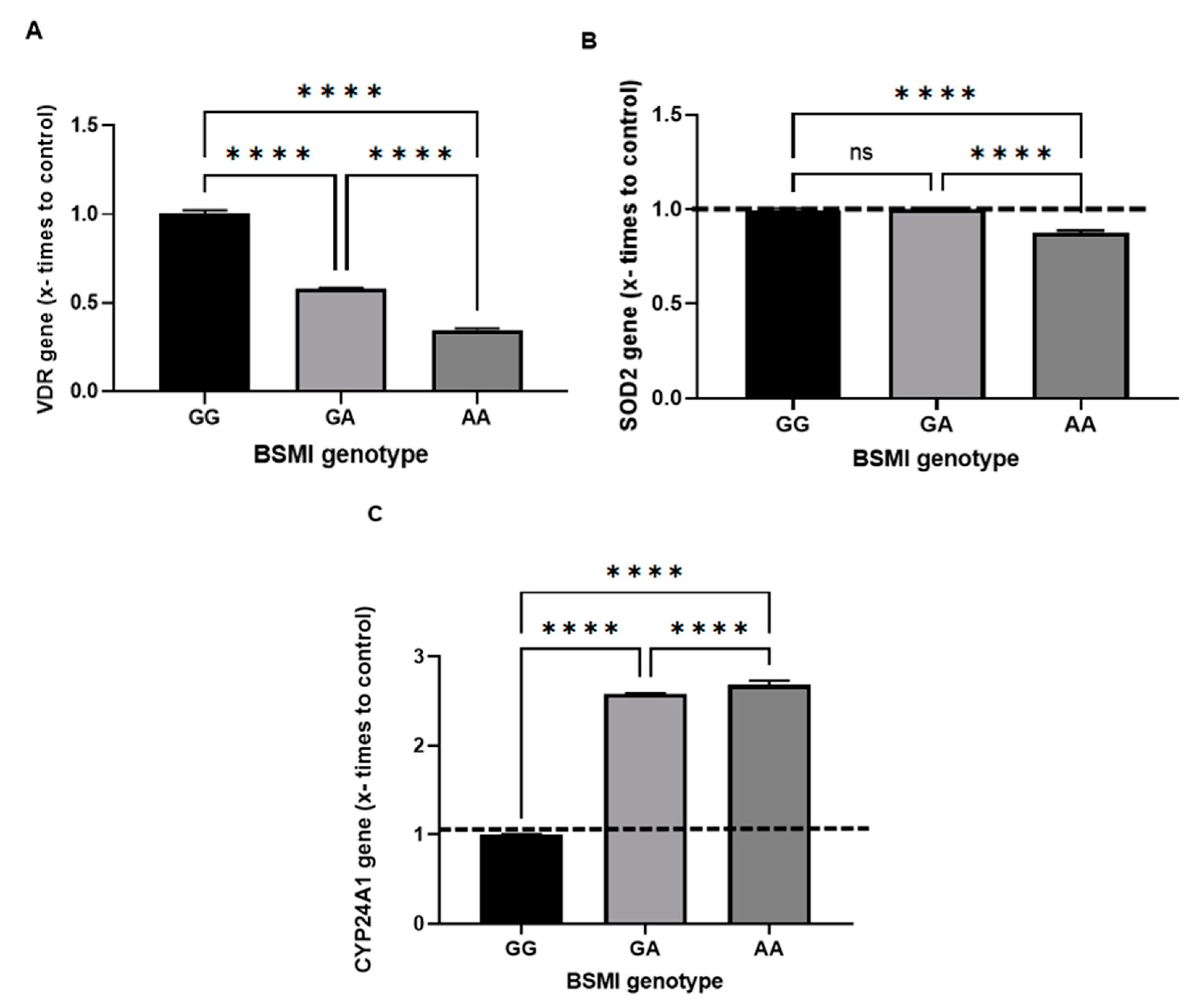
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
References
- Durak S, Gheybi A, Demirkol S, Arıkan S, et al., The effects of serum levels, and alterations in the genes of binding protein and receptor of vitamin D on gastric câncer. Molecular Biology Reports. Springer Nature B.V. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Saponaro F, Saba A, Zucchi R. An Update on Vitamin D Metabolism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6573. [CrossRef]
- Oczkowicz M, Szymczyk B, Swiątkiewicz M, Furgał-Dzier˙ zuk I, et al., Analysis of the effect of vitamin D supplementation and sex on Vdr, Cyp2r1 and Cyp27b1 gene expression in Wistar rats’ tissues. Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 212 (2021) 105918. [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, Carlos ES; Maeda, Sergio; Batista, Marcelo; et al., Consensus - Reference ranges of vitamin D [25(OH)D] from the Brazilian medical societies. Brazilian Society of Clinical Pathology/Laboratory Medicine (SBPC/ML) and Brazilian Society of Endocrinology and Metabolism (SBEM). Laboratory Medicine Journal Bras. Patol. Med. Lab. 53 (6) nov-dec 2017. [CrossRef]
- Zhumina A, Konstantin L, Konovalova A, Li Y et al., Plasma 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Levels and VDR Gene Expression in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells of Leukemia Patients and Healthy Subjects in Central Kazakhstan. Nutrients. 2020, 12, 1229. [CrossRef]
- Maeda SS, Borba VZ, Camargo MB, Silva DM, Borges JL, Bandeira F, Lazaretti-Castro M; Brazilian Society of Endocrinology and Metabology (SBEM). Recommendations of the Brazilian Society of Endocrinology and Metabology (SBEM) for the diagnosis and treatment of hypovitaminosis D. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol. 2014 Jul;58(5):411-33. [CrossRef]
- Quigley M, Rieger S, Capobianco E, Wang Z et al. Vitamin D Modulation of Mitochondrial Oxidative Metabolism and mTOR Enforces Stress Adaptations and Anticancer Responses. JBMR Plus 2021 Dec 1;6(1): e10572. [CrossRef]
- Mailhot G, White J. Vitamin D and Immunity in Infants and Children. Nutrients. 2020, 12, 1233. [CrossRef]
- Schuch, Natielen Jacques. Relação entre concentração sérica de vitamina D, polimorfismos do gene VDR e Síndrome Metabólica em indivíduos adultos. Tese de doutorado. Universidade de São Paulo. Faculdade de Saúde Pública. São Paulo. 2011. [CrossRef]
- Li HM, Liu Y, Zhang RJ, Ding JY, Shen CL. Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms and osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2021 Feb 1;60(2):538-548. [CrossRef]
- Shahbazi S, Alavi S, Majidzadeh-A K, Ghaffarpour M, Soleimani A, Mahdian R. BsmI but not FokI polymorphism of VDR gene is contributed in breast cancer. Med Oncol. 2013 Mar;30(1):393. [CrossRef]
- Lee YH, Gyu Song G. Vitamin D receptor FokI, BsmI, TaqI, ApaI, and EcoRV polymorphisms and susceptibility to melanoma: a meta-analysis. J BUON. 2015 Jan-Feb;20(1):235-43.
- Issa CT, Silva AS, Toscano LT, Medeiros MS, Persuhn DC, da Silva Diniz A, de Carvalho Costa MJ, Rodrigues Gonçalves Mda C. Relationship between cardiometabolic profile, vitamin D status and BsmI polymorphism of the VDR gene in non-institutionalized elderly subjects: Cardiometabolic profile, vitamin D status and BsmI polymorphism of the VDR gene in non-institutionalized elderly subjects. Exp Gerontol. 2016 Aug;81: 56-64. [CrossRef]
- Retamoso V, Feijoo L, Rubio D, Santos L et al. Black skin color but not VDR gene represent a risk factor for low serum levels of vitamin D in self-declared black individuals. Clinical Nutrition ESPEN 55 (2023) 230e237. [CrossRef]
- Khalid N, Mahjabeen I, Kayani MA, Akram Z. Association of arsenic-related AS3MT gene and antioxidant SOD2 gene expression in industrial workers occupationally exposed to arsenic. Toxicol Ind Health. 2020 Mar;36(3):161-169. [CrossRef]
- Maeda SS, Borba VZ, Camargo MB, Silva DM, Borges JL, Bandeira F, Lazaretti-Castro M; Brazilian Society of Endocrinology and Metabology (SBEM). Recommendations of the Brazilian Society of Endocrinology and Metabology (SBEM) for the diagnosis and treatment of hypovitaminosis D. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol. 2014 Jul;58(5):411-33. [CrossRef]
- Duarte T., Barbisan F., Prado-Lima P.A.S. do, V.F. Azzolin,et al., Ziprasidone, a second-generation antipsychotic drug, triggers a macrophage inflammatory response in vitro, Cytokine 106 (2018) 101–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto. 2017.10.017.World Health Organization. Obesity: preventing and managing the global epidemic. Report of a World Health Organization Consultation. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2000. p. 256. WHO Obesity Technical Report Series, n. 284.
- Brazilian Obesity Guidelines. Brazilian Association for the Study of Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome. Brazilian Obesity Guidelines 2016 ABESO-Brazilian Association for the Study of Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome. – 4 ed. - Itapevi, SP: AC Farmacêutica, ISBN 978-85-60549-15-3. 2016.
- Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics (IBGE). Brazilian Census 2022. Rio de Janeiro: IBGE, 2023.
- Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics (IBGE). Household budget survey (POF). Ministry of Economy. Rio de Janeiro. 2019.
- Rolizola P, Freiria C, Silva G, Brito T et al. Insuficiência de vitamina D e fatores associados: um estudo com idosos assistidos por serviços de atenção básica à saúde. Ciênc. saúde coletiva 27 (02) 02 Fev 2022. [CrossRef]
- Cheong W, Ji S, Gassiot A, Thu W et al. Predictors of circulating vitamin D levels in healthy mid-life Singaporean women. Archives of Osteoporosis. Springer p.1-9. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Oliveira AC, Magalhaes C, Loures C, Fraga V et al. BsmI polymorphism in the vitamin D receptor gene is associated with 25-hydroxy vitamin D levels in individuals with cognitive decline. Arq. Neuro-Psiquiatr. v.76p.11 Nov 2018. [CrossRef]
- Monteiro Junior FC, Mandarino N, Santos E, Santos A et al. Correlation between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and carotid intima-media thickness in a Brazilian population descended from African slaves. Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2018) 51(4): e7185. [CrossRef]
- Awasthi R, Manger P, Khare R. Fok I and Bsm I gene polymorphism of vitamin D receptor and essential hypertension: a mechanistic link. Clinical Hypertensio. V.29 n.5 p.2-12. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Dauletbaev N, Herscovitch K, Das M, Chen H, Bernier J, Matouk E, Bérubé J, Rousseau S, Lands LC. Down-regulation of IL-8 by high-dose vitamin D is specific to hyperinflammatory macrophages and involves mechanisms beyond up-regulation of DUSP1. Br J Pharmacol. 2015 Oct;172(19):4757-71. [CrossRef]
- Carlberg, C. Vitamin D and Its Target Genes. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene and gene ID | NCBI reference sequence | Location | Size (pb) | Primers |
| VDR - 7421 | NG_008731.1 | 12q13.11 | 4.738 | F- 5′CCTTCACCATGGACGACATG3’ R-5′CGGCTTTGGTCACGTCACT3′ |
| CYP24A1 - 1591 | NG_008334 | 20q12 | 37449 | F-5′CTCATGCTAAATACCCAGGTG-3′ R-5′TCGCTGGCAAAACGCGATGGG3′ |
| SOD-2 - 6648 | NG_008729 | 6q11 | 100213 | F-5’GCCCTGGAACCTCACATCAA-3’ R-5’GGTACTTCTCCTCGGTGACGTT3’ |
| Characteristic | N (98) | (%) |
| Sex | ||
| Female | 53 | 54.1 |
| Male | 45 | 45.9 |
| Self-declaration of color | ||
| Black | 20 | 20.4 |
| Brown | 25 | 25.5 |
| White | 53 | 54.1 |
| Education | ||
| Primary education (i) | 5 | 5.1 |
| Primary education (c) | 1 | 1.0 |
| Secondary education (i) | 1 | 1.0 |
| Secondary education (c) | 16 | 16.3 |
| Higher education (i) | 53 | 54.1 |
| Higher education (c) | 20 | 20.4 |
| Other (graduate degree) | 2 | 2.0 |
| Family income | ||
| 5–15 minimum wages | 24 | 24.5 |
| 3–5 minimum wages | 34 | 34.7 |
| 1–3 minimum wages | 39 | 38.8 |
| Up to 1 minimum wage | 1 | 1.0 |
| Marital status | ||
| Single | 66 | 67.3 |
| Married | 25 | 25.5 |
| Common-law marriage | 6 | 6.1 |
| Widowed | 1 | 1.0 |
| Performs physical activity | ||
| Yes | 48 | 49 |
| No | 50 | 51 |
| Smokes | ||
| Yes | 10 | 10.2 |
| No | 87 | 88.8 |
| Ex-smoker | 1 | 1.0 |
| Drinks alcohol | ||
| Yes | 63 | 63.3 |
| No | 35 | 35.7 |
| Marker | Mean | ±SD |
| Weight (kg) | 77.8 | 19.0 |
| Height (m) | 1.8 | 0.16 |
| BMI (kg/m)2 | 27.1 | 5.4 |
| CC (cm) | 88.2 | 14.7 |
| QC (cm) | 103.6 | 9.8 |
| % fat | 12.6 | 10.4 |
| Total col (mg/dL) | 177 | 47 |
| HDL-c (mg/dL) | 55.2 | 22.2 |
| LDL-c (mg/dL) | 94.9 | 41.2 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 146.1 | 142.2 |
| Vitamin D (ng/mL) | 17.03 | 4.04 |
| SNP BsmI | Participants (n = 98) | (%) | *p-value |
| Genotypic frequency | |||
| GG | 40 | 40.8 | 0.4 |
| GA | 44 | 44.9 | 0.46 |
| AA | 14 | 14.3 | 0.13 |
| Allelic frequency | |||
| Allele G | 102 | 67.1 | |
| Allele A | 50 | 32.9 | |
| Model | |||
| AA+GA | 54 | 55.1 | |
| GG | 40 | 44.9 |
| Genotype group BsmI VDR | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GG (40) | GA (44) | AA (14) | p | |
| Age | 29.8 ± 10.2 | 32.3 ± 11.4 | 29.8 ± 11.3 | 0.80 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 26.8 ± 5.2 | 26.8 ± 5.3 | 28.6 ± 6.2 | 0.51 |
| CC (cm) | 87.46 ± 15.3 | 87.5 ± 12.7 | 92.6 ± 18.7 | 0.49 |
| QC (cm) | 103.36 ± 9 | 102.7 ± 9.6 | 107.36 ± 12.2 | 0.29 |
| %fat | 12.26 ± 10.9 | 12.6 ± 9.96 | 13.7 ± 11.0 | 0.90 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 91.24 ± 21.9 | 84.07 ± 22.1 | 92.6 ± 24.12 | 0.25 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 182.5 ± 51.6 | 174.4 ± 47.3 | 169.8 ± 47.2 | 0.63 |
| HDL (mg/dL) | 58.16 ± 22.7 | 55.1 ± 22.6 | 45.34 ± 17.7 | 0.17 |
| LDL (mg/dL) | 95 ± 40.8 | 94.4 ± 44.8 | 96.17 ± 41.6 | 0.99 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 151.03 ± 149 | 135.91 ± 148.4 | 164.3 ± 104.8 | 0.78 |
| Vitamin D (ng/mL) | 17.45 ± 2.2 | 16.88 ± 4.3 | 16.34 ± 2.4 | 0.64 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





