1. Introduction
Water stress is one of the main abiotic factors that reduce the development and yield of plants. Therefore, agricultural productivity and food security are threatened by water deficit [
1]. Plants are under water stress if the water supply to the roots is limited or exceeded by the rate of transpiration. However, other factors influence this process, so there is no conclusive definition [
2]. Because the fresh biomass of plants is composed of 85% water, drought severely affects physiological and biochemical processes [
3]. Some of these alterations include mineral absorption, photosynthesis, respiration rate, gas exchange in leaves, increase in reactive oxygen species (ROS), among others [
4,
5].
The physiological and biochemical modifications in response to drought stress in crops are given by the duration and intensity of the period to which they are subjected. In this way, tolerance mechanisms such as osmotic adjustment, cell wall modifications and activation of the antioxidant system arise as a response to stress [
6]. Therefore, the degree of tolerance to drought stress in plants depends on the efficacy in the activation of said mechanisms [
7].
Although plants can reduce the adverse effects of low water availability, reducing the transpiration cycle through stomatal closure, this also causes an alteration in the photosynthesis process, specifically in the availability of CO
2, which in turn, it would slow down the production of energy generation and structural biocomposites [
8]. Due to this, it is necessary to investigate the use of compounds that are effective in stimulating development and production in plants and that are also capable of enhancing responses against water stress.
One of the innovative proposals that has emerged in recent decades to increase crop growth and production, improve the efficient use of nutrients and promote tolerance against abiotic stress in an environmentally friendly way is the use of biostimulants in plants in low concentrations [
9]. Biostimulants have been defined as compounds obtained from different organic or inorganic substances and/or microorganisms, which can improve the growth and productivity of plants and reducing the negative effects of stress. Among the most common biostimulants are minerals such as zinc (Zn) and silicon (Si), vitamins, amino acids, poly and oligosaccharides, and some types of plant hormones [
10,
11,
12]. However, due to the wide range of products cataloged as biostimulants in development and the lack of published literature on the mechanisms of action in metabolism, it is necessary to investigate the effects of these compounds on physiological and biochemical modifications in plants. Therefore, the objective of this study was to evaluate the efficacy and differential physiological-biochemical response of biostimulants in green bean cv. Strike subjected to moderate and severe water stress.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Aerial, foliar, root and total biomass
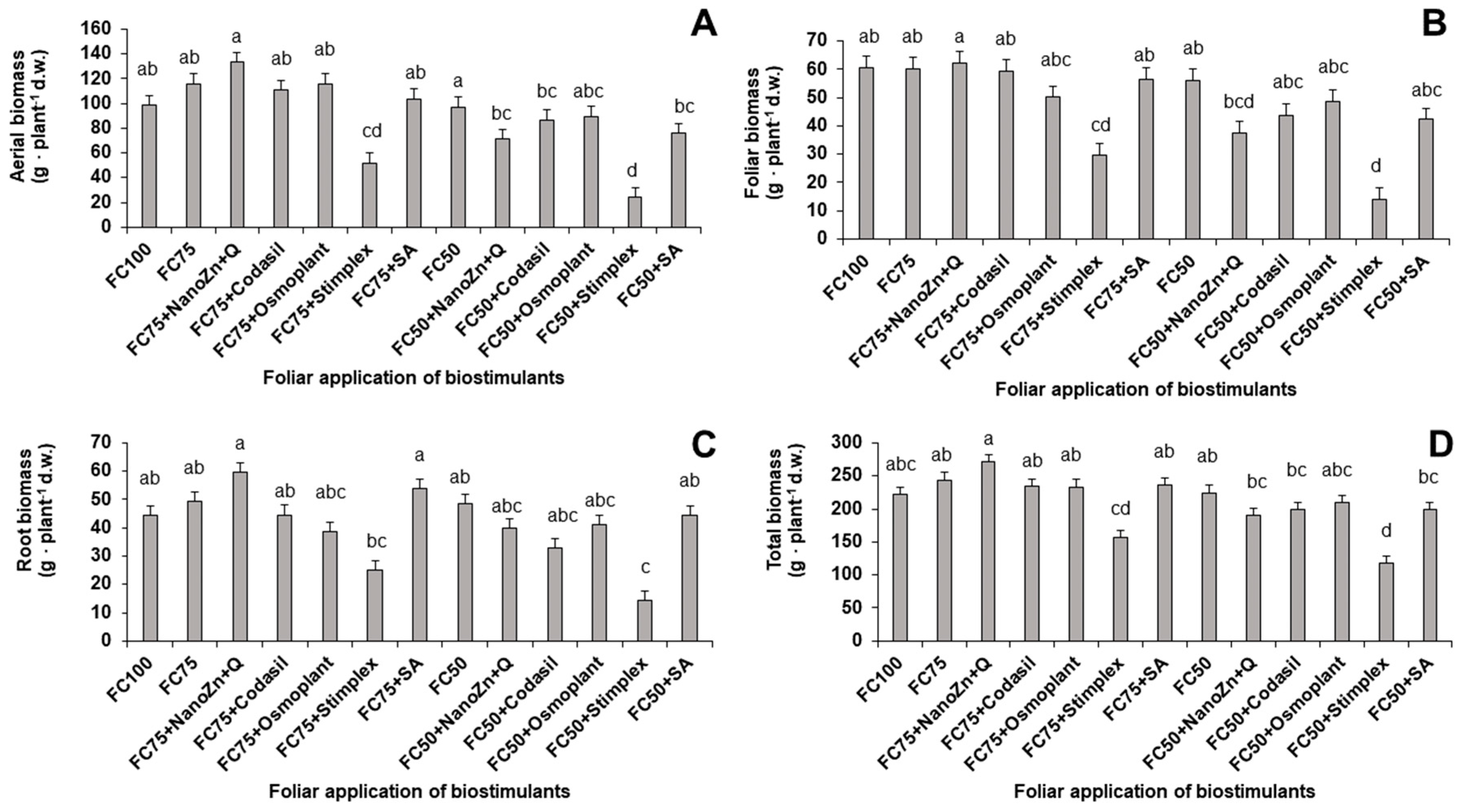
One of the key variables when analyzing the physiological state of plants is the accumulation of biomass [
7,
13]. In the present study, significant differences were found in the production of aerial, foliar, root and total biomass because of the application of water stress and biostimulants (
Figure 1). Regarding aerial biomass, the FC75+NanoZn+Q treatment presented the highest accumulation with an increase of 15.24% with respect to FC75, placing this combination as a viable biostimulant to reduce the effect of water stress on plants, even surpassing other biostimulants established commercial.
The same trend was recorded in leaf biomass, with FC75+NanoZn+Q being the best treatment with an increase of 91.2% with respect to FC75+Stimplex, which was the treatment that favored this parameter to a lesser extent when irrigation was reduced by 25%. Likewise, when the amount of water was reduced by 50%, the FC50 treatment obtained the highest yield, with an increase of 3 times the value of the FC50+Stimplex treatment, as the treatment with the lowest accumulation of foliar biomass (
Figure 1).
In the case of root biomass, when the amount of irrigation was reduced by 25%, the treatment that obtained the highest value was FC75+NanoZn+Q, presenting an increase of 136.8%, with respect to FC75+Stimplex, which was the least value treatment. As in the previous sections, when the amount of irrigation was reduced by 50%, the treatment that benefited the most was FC50, presenting an increase of 236.8% with respect to FC50+Stimplex with the least accumulation (
Figure 1).
Finally, in relation to the total biomass, when the amount of irrigation was reduced by 25%, the treatment that favored the accumulation was FC75+NanoZn+Q, with an increase of 73.7%, compared to FC75+Stimplex, the treatment with the least accumulation. In addition, when the irrigation reduction was 50%, the FC50 treatment presented the highest accumulation, increasing by 91.4% with respect to the treatment with the lowest accumulation, FC50+Stimplex (
Figure 1).
These results agree with [
14], who reported an increase in biomass of 23.77% when a combination of zinc and chitosan nanoparticles was added, compared to the control without application, and a decrease when only Zn nanoparticles were added, demonstrating the potential of these compounds together. This joint effect is related to the signaling reactions triggered by zinc nanoparticles and chitosan. These reactions include the generation of hormones such as ABA, which influences root architecture, increasing the adaptation of plants to resist water stress [
15].
The application of biostimulants did not favor the accumulation of biomass once the plants were subjected to FC at 50% with respect to the control, highlighting the FC50+Codasil and FC50+Osmoplant treatments as viable options when drought stress is severe. This phenomenon was caused by the decrease in stomatal density under severe drought conditions, which in turn affected the photosynthesis cycle, limiting plant growth and decreasing the absorption efficiency of foliar-applied biostimulants [
16].
2.2. Yield
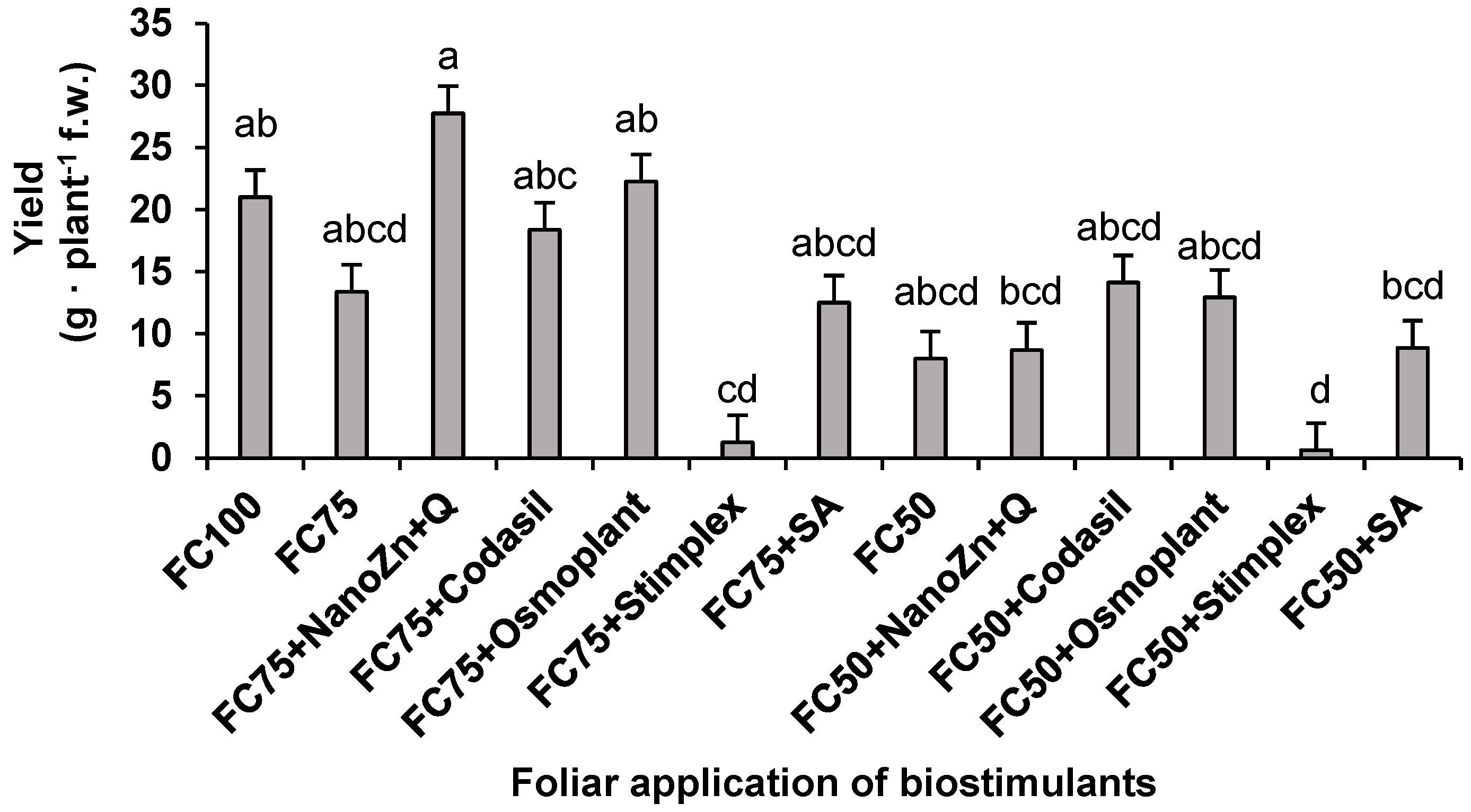
Yield is linked to biomass production and the physiological state of the plants, since part of the biomass generated is used for the formation of fruits [
17]. In the present study, significant differences in yield were found because of the application of water stress and biostimulants (
Figure 2). When the plants were subjected to 75% FC, the treatment that favored fruit production was FC75+NanoZn+Q, with an increase of 107.4% compared to the FC75 treatment and 32.1% compared to FC100 (control, without stress) water and without application of biostimulants). On the other hand, when the plants were subjected to a 50% irrigation reduction, the treatments that were shown to alleviate the effects of stress were FC50+Codasil and FC50+Osmoplant with increases of 76.6% and 59.2%, respectively, compared to FC50. These results show the relationship between total biomass productions (
Figure 1) and yield (
Figure 2). Treatments with higher biomass production were able to translocate the largest amount of assimilates to the fruits. In addition, the results show the decrease in fruit production when the plant is under conditions of moderate (FC75) and severe (FC50) water stress caused by the decrease in growth parameters such as root (
Figure 1) and stem elongation.
Finally, the results agree with [
18], who explain that plants subjected to water stress experience an induced deficiency of micronutrients such as Zn, Fe, Mn and Ca, which in vegetative stages are necessary for metabolic processes related to growth and development. The application of Zn in the form of nanoparticles, accompanied by chitosan at the recommended doses (100 pm) [
19], improved the accumulation of this micronutrient and, therefore, promoted a higher production through the improvement in the metabolic processes of the plant.
2.3. Nitrate reductase activity “in vivo”
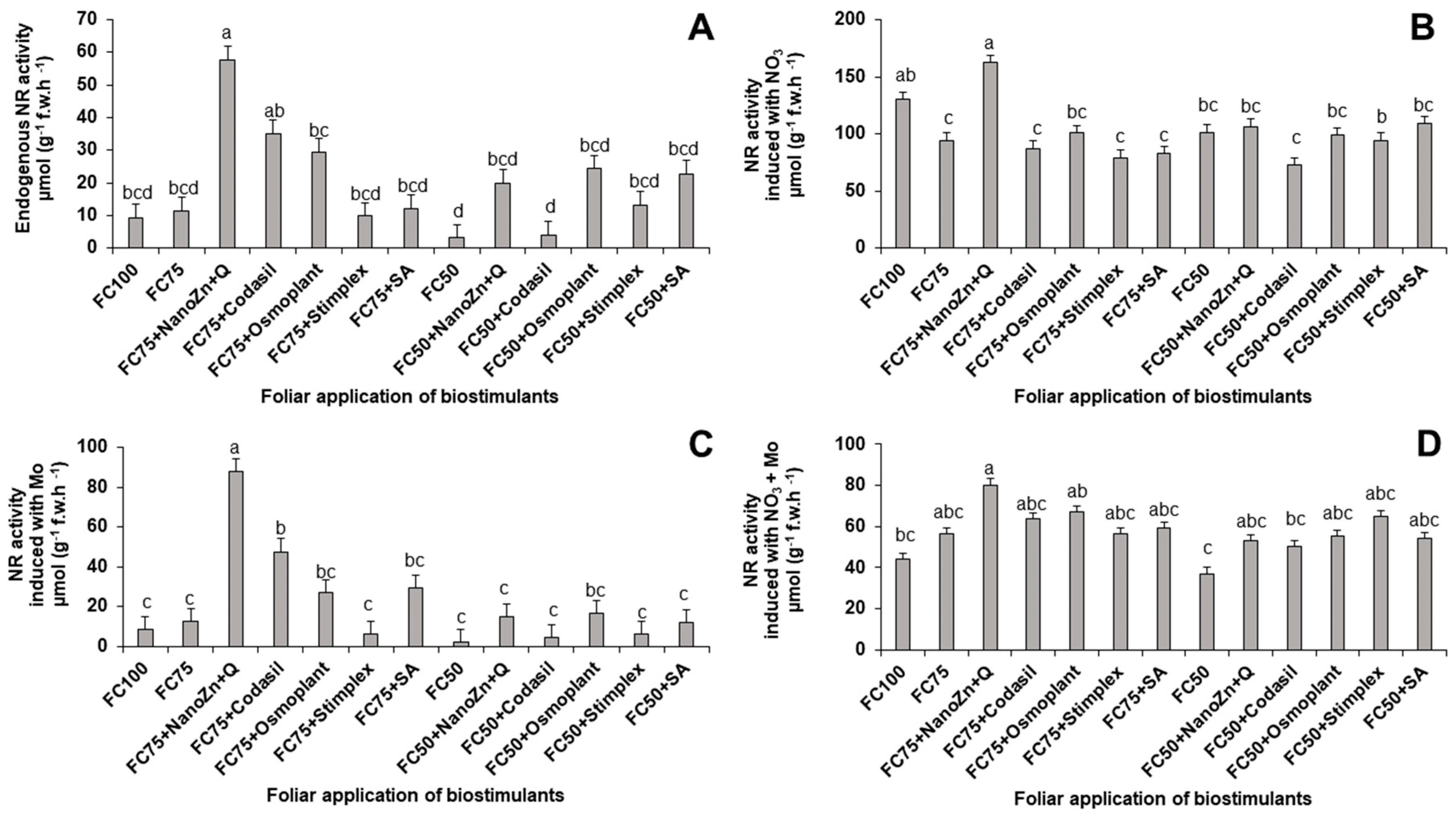
The enzyme nitrate reductase (NR) is the first step in the nitrate assimilation process in plants, since it reduces the absorbed nitrate into nitrite, which will later be incorporated into nitrogenous metabolites [
20]. In the present study, significant differences were found in the NR activity due to the effect of the application of hydric stress and biostimulants (
Figure 3). The treatment that presented the highest activity was FC75+NanoZn+Q, presenting increases of 490.7% with respect to FC75+Stimplex, as the treatment with the lowest activity when the plants were subjected to moderate stress (FC75). Once the amount of water applied was reduced by 50%, the treatments that benefited the most were FC50+Osmoplant, FC50+SA, FC50+NanoZn+Q and FC50+Stimplex, with no significant difference between them, with the highest being FC50 +Osmoplant, increasing 6.8 times with respect to FC50.
The data obtained agree with those found in the variables of biomass (
Figure 1) and yield (
Figure 2), where the most favored treatment was also FC75+NanoZn+Q. As indicated by [
21], the constant application of Zn nanoparticles tends to modify growth, yield, nutritional status and nitrogen assimilation in plants, making these physiological processes more efficient. These changes are due to the high participation of Zn in signaling, enzymatic cofactor and integral maintenance of DNA. In addition, the results agree with what was found by [
22], who report that the application of ZnO nanoparticles at doses of 25 and 100 ppm foliar-applied to cucumber crops increased growth, biomass accumulation and decreased the effects of water stress. These results place foliar ZnO nanoparticles as a viable option to mitigate the decrease in the nitrogen assimilation process caused by water stress in green bean plants.
2.4. Photosynthetic pigments
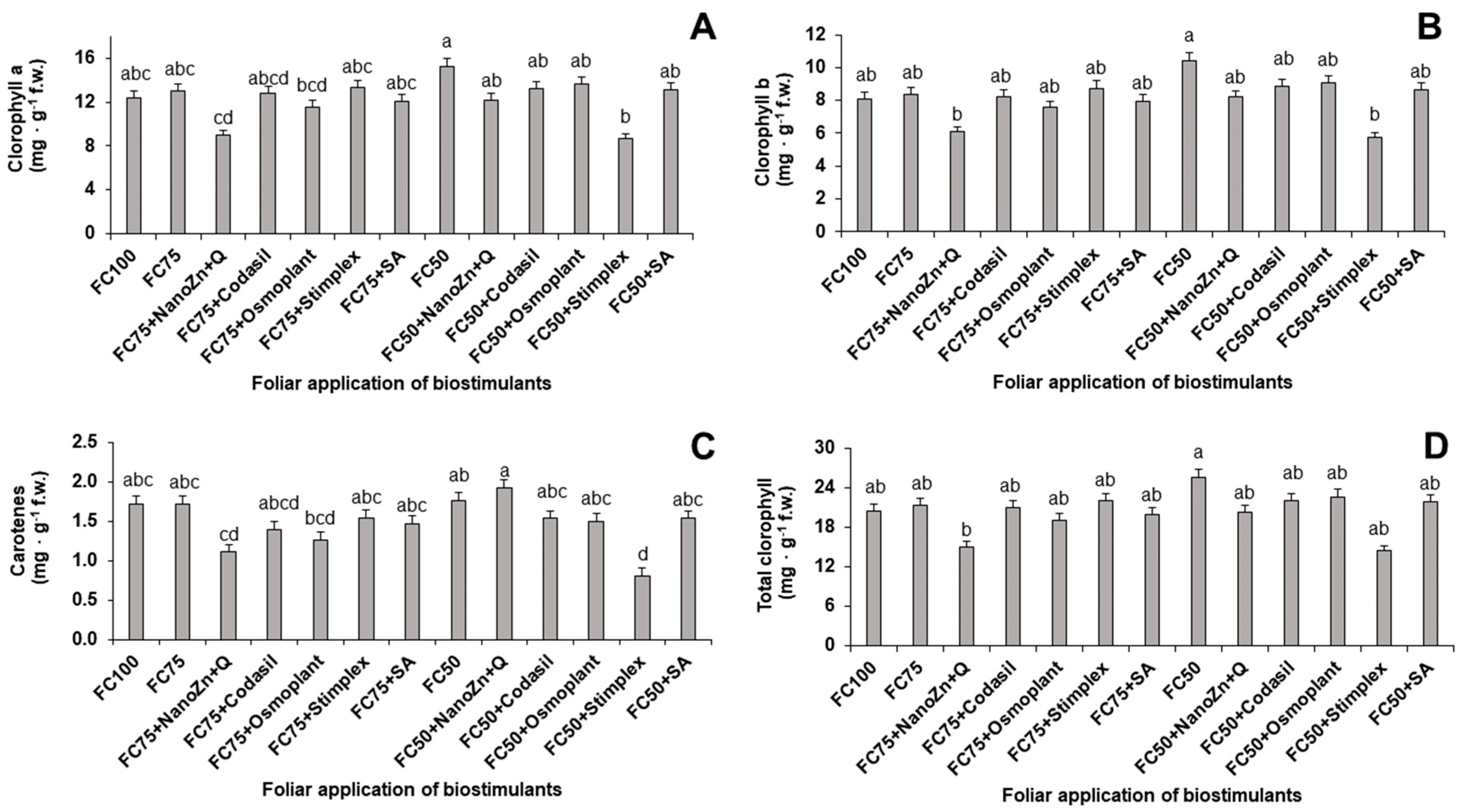
The study of the concentration of photosynthetic pigments in plants is a good indicator of the physiological state of crops [
23]. In the present study, significant differences were found in the concentration of photosynthetic pigments due to the application of water stress and biostimulants (
Figure 4). When subjecting the plants to a water stress of 25% (FC75), the treatment that showed the highest accumulation of total chlorophyll was FC75+Stimplex, with an increase of 3.23% compared to FC75, without significant difference with FC75+Codasil, FC75+Osmoplant and FC75+SA. Once water stress increased to 50% (FC50), the FC50 treatment obtained the highest values in total chlorophyll.
The results obtained are similar to those reported by [
24], who indicate that a simulated mild stress had no effect on the chlorophyll content in spinach. Other authors mention that in sage plants (
Salvia officinalis L.) with drought stress induction treated with algae extracts, the concentration of chlorophyll increased [
25]. The algae extract used in this experiment had the ability to improve the water relations of the leaves and reduce the closure of the stomata, which reduced the CO
2 fixation capacity, and promoted the synthesis of chlorophyll. This explanation agrees with what was obtained in the stomatal conductance parameter (Figure 10), where this treatment was the one that favored the efficiency of this process, facilitating water management through density and stomatal closure. The high concentration of chlorophyll in the FC50 treatment happened due to the development of chlorophylls to make the photosynthetic process more efficient, as explained by [
26].
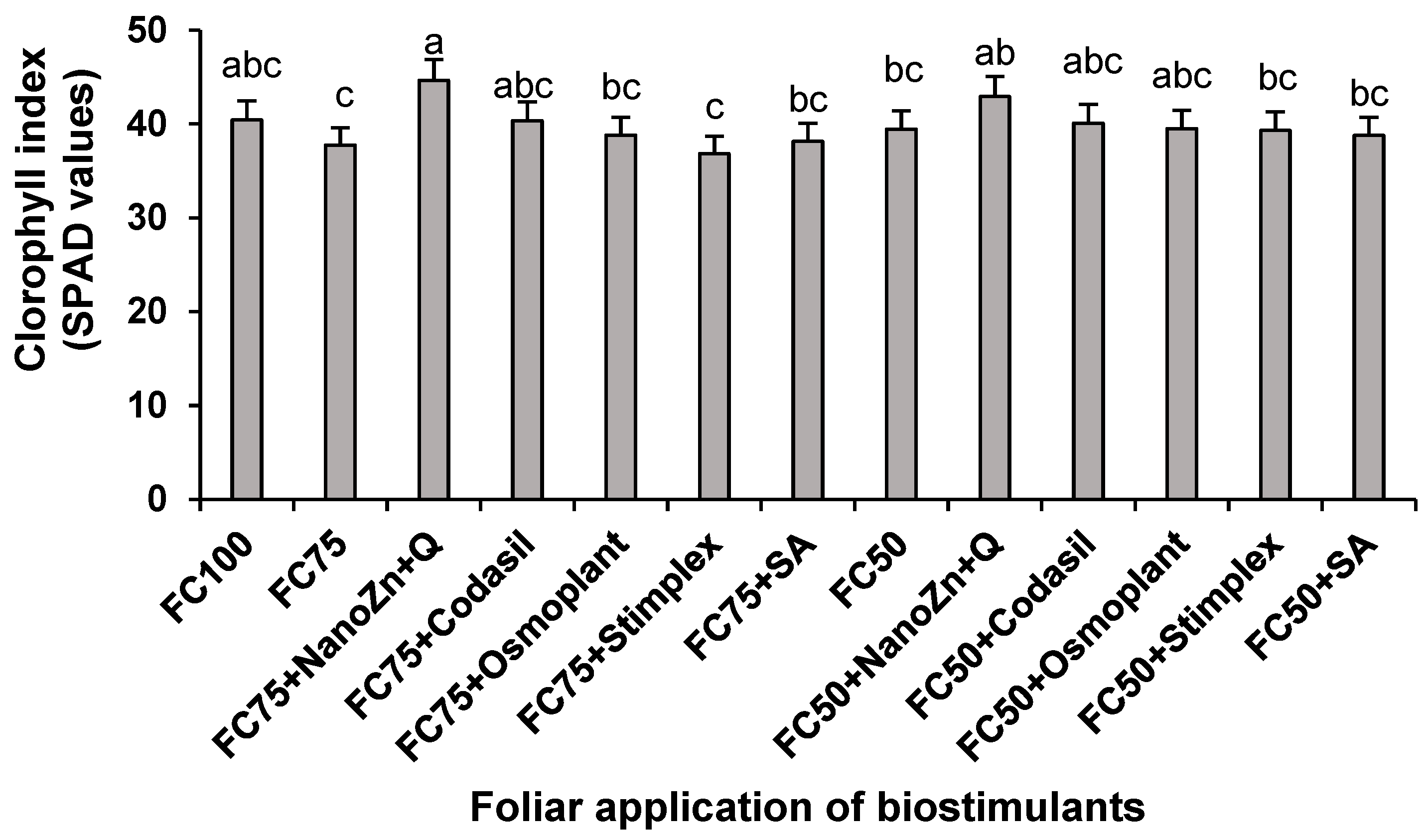
2.5. Chlorophyll index
The chlorophyll index (SPAD) is a rapid and non-destructive method to detect chlorophyll levels in plants and determine their nutritional status [
27]. In the present study, significant differences were found in the chlorophyll index because of the application of water stress and biostimulants (
Figure 5). The treatment that presented the highest SPAD values when irrigation was restricted by 25% (FC75) was FC75+NanoZn+Q, with an increase of 18.3% compared to FC75 and 10.4% compared to FC100. Similarly, when water stress was 50% water, the treatment that accumulated the highest SPAD value was FC50+NanZn+Q, with an increase of 8.85% with respect to FC50. These values correspond to what was published by [
13], who report an increase in SPAD values in bean crops of around 20% when ZnO nanoparticles + chitosan were applied to bean plants. In the same way, [
15], reported a similar trend when applying ZnO nanoparticles in eggplant, finding increases in SPAD values with respect to untreated plants, with doses of 50 and 100 ppm.
The increase in SPAD values (
Figure 5), along with yield (
Figure 2) and total biomass (
Figure 1) values, can be attributed to the role of zinc and chitosan application in maintaining the integrity of the membranes and the efficiency in the absorption of other micronutrients such as copper and boron that are key to inhibit the activity of chlorophyllase and the maintenance of the structure of the chloroplasts [
28].
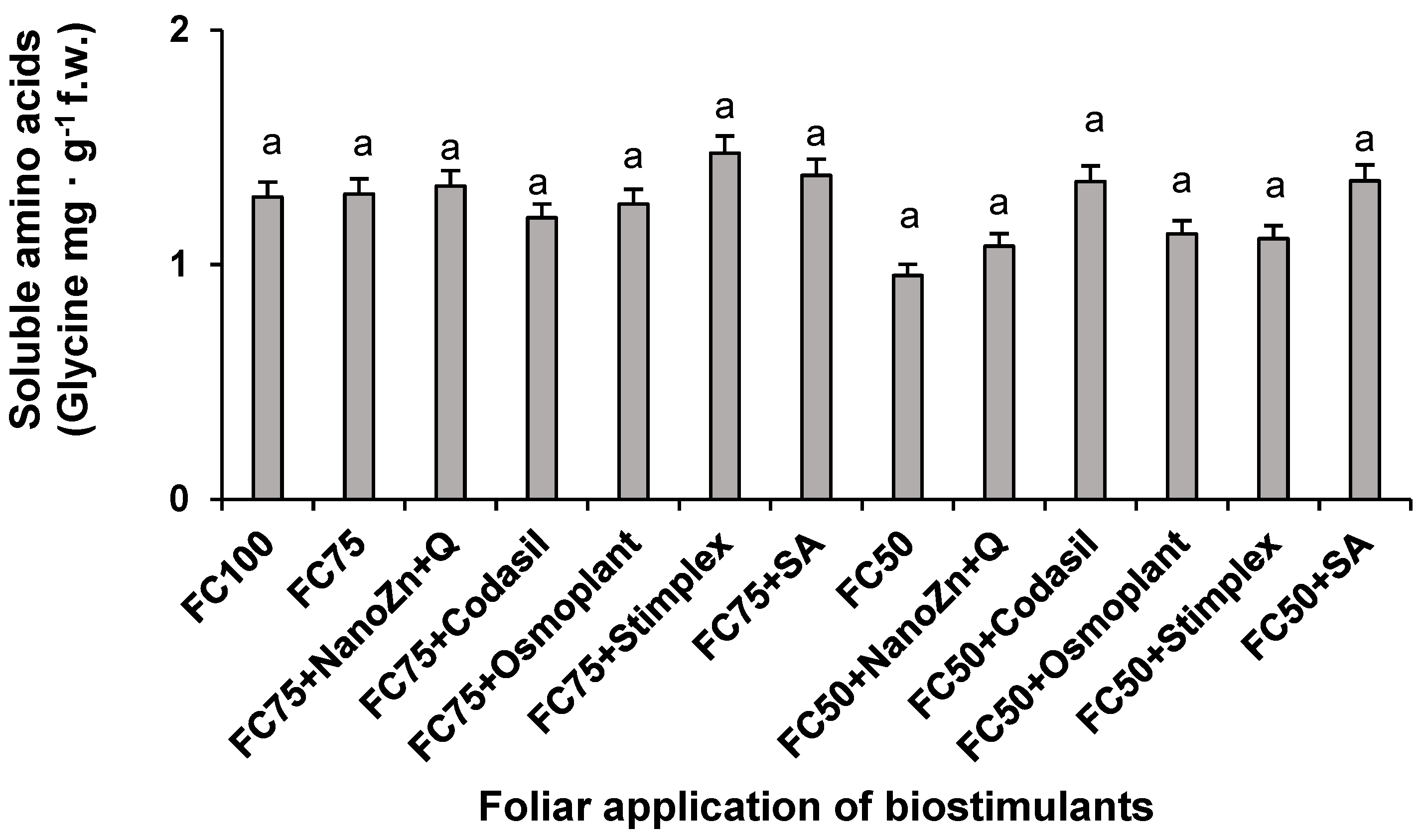
2.6. Amino Acids and Soluble Proteins
Amino acids are precursors of proteins, and both are part of the nitrogen assimilation process, so they are a biochemical indicator of the effectiveness of the applied treatments [
29]. In the present study, no significant differences were found in the concentration of soluble amino acids due to the application of water stress and biostimulants (
Figure 6). However, the FC75+Stimplex treatment favored the accumulation of amino acids with an increase of 13.8% with respect to FC75 when the plants were subjected to a 25% irrigation reduction. When the irrigation reduction was 50%, the treatment that stood out was FC50+SA, with an increase of 42.3%.
According to several authors, this effect was probably due to the composition of the seaweed extracts (
Ascophyllum nodosum L.), which in addition to containing hormones such as cytokinins and auxins that promote growth, contain protein hydrolysates and free amino acids. In addition to this, the additional source of N provided by the product derived from algae facilitates the assimilation and elaboration of metabolites [
30]. [
31] indicate that compounds such as amino acids and peptides contained in biostimulants are easily absorbed, increasing their concentration in plants and generating a defense against different types of stress.
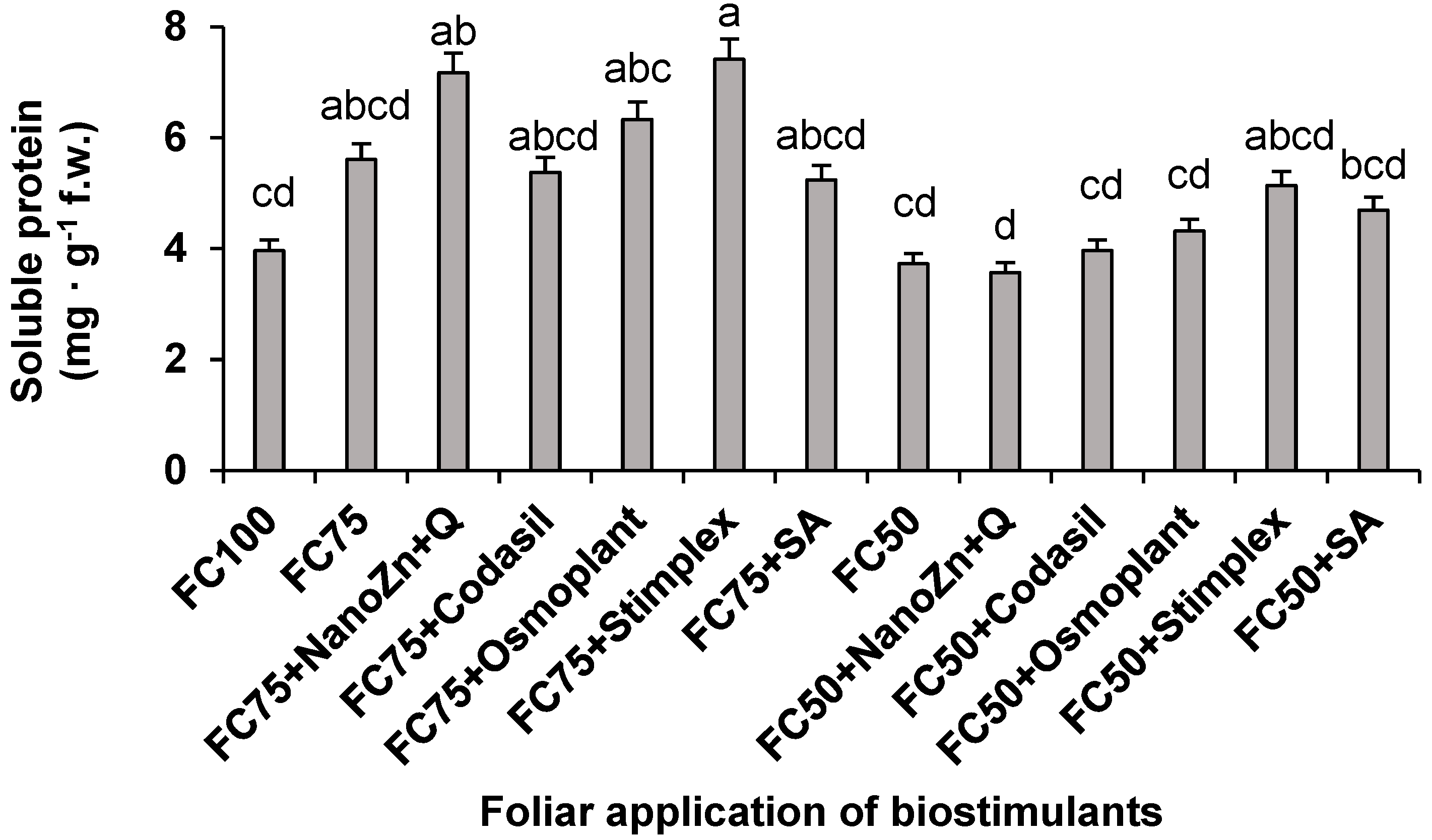
Regarding the content of soluble proteins (
Figure 7), in the same way the FC75+Stimplex treatment promoted the accumulation when a hydric stress of 25% of water was applied, having an increase of 32.1% with respect to FC75. Similarly, when the field capacity was at 50%, the FC50+Stimplex treatment increased by 37.8% compared to FC50, being the best treatment. These results agree with those obtained by [
32], who report an increase in protein content of 25 % compared to the control in snap beans cv. Paulista, when algae extracts (
Fucus spiralis and
Ulva rigida) were applied foliarly. Several authors have reported the relationship between the application of algae extracts by foliar route and improvement in the assimilation of growth hormones and other metabolites, in turn improving nitrate reductase activity, chlorophyll and protein content [
33].
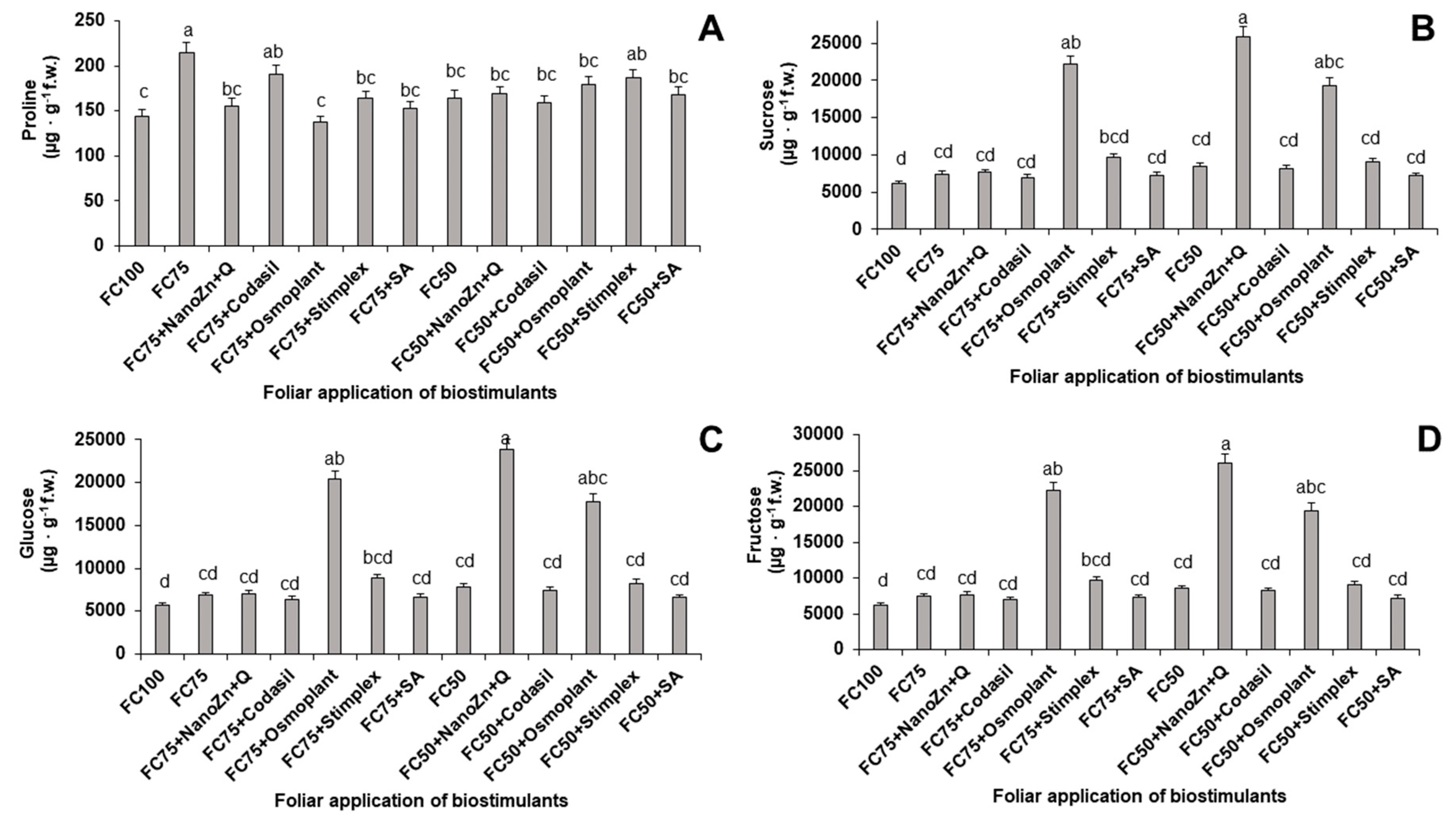
2.7. Content of proline, sucrose, glucose and fructose
One of the adaptive responses to abiotic stress in plants is the accumulation of compatible osmolytes such as sugars (sucrose and glucose) and amino acids (proline) that help protect cells [
34]. In the present study, significant differences were found in the contents of proline, sucrose, glucose and fructose because of the application of hydric stress and biostimulants (
Figure 8). Regarding the proline content, the treatment with the highest content was FC75, with an increase of 48.6% compared to FC100, evidencing the state of stress of the plants with a decrease in water to 25%. This increase was 13.9 % when the water application was reduced to 50 % (FC50) with respect to FC100 (control without water stress and without application of biostimulants).
When the amount of water was reduced by 25%, the treatment that decreased the proline content the most was FC75+Osmoplant, with a reduction of 36% compared to FC75. This treatment did not present significant differences (P= 0.05) with respect to FC100, which could indicate a better adaptation to stress in this group of plants. When irrigation was reduced by 50%, the treatment that reduced proline content the most was FC50+Codasil, with a reduction of 2.5%.
These results are similar to those of [
35], who indicate that the concentration of proline was higher in plants treated with commercial osmoregulator products compared to those not treated. When stress is induced by salinity or water deficit, the osmotic adjustment is the main response factor [
36]. The accumulation of proline in tissues, leaves, could play a protective role in drought conditions, together with osmoregulation. On the other hand, products such as Osmoplant® could mitigate water stress since the treated plants did not accumulate proline in leaves.
The accumulation in the plant of nonstructural carbohydrates such as glucose and its derivatives are a good indicator of the physiological state and stress, because it leads to a decrease in photosynthesis and respiration, which ultimately lead to carbon depletion [
37]. In the present study, the treatment that favored the accumulation of sucrose, glucose and fructose when the field capacity was at 75% was FC75+Osmoplant, with increases compared to FC75 of 198% in the three parameters (
Figure 6). The treatment that benefited the most in these variables when irrigation decreased by 50% was FC5+NanoZn+Q, which increased by 205.9% compared to FC50.
These results agree with those obtained by [
38], who reported that the application of ZnO nanoparticles at a dose of 100 mg · kg
-1 in pea plants increased the sucrose content by 1.8 times, however, no increases in reducing sugars such as glucose and fructose were recorded. The possible explanation for the increase in the concentrations of non-structural carbohydrates in both FC75+Osmoplant and FC50+NanoZn+Q is due to the participation of these compounds in the response to stress. The plants that showed the best adaptation were those treated with Osmoplant® and ZnO nanoparticles + chitosan, and it has been reported that sucrose, glucose and fructose can contribute to stress-related signaling pathways [
39]. Finally, it should be noted that these results are related to those obtained in fluorescence and photosynthetic activity (Figure 10). Previously, it was mentioned that water stress caused a decrease in photosynthesis efficiency, which would explain why the highest fluorescence values were obtained in the FC75+Osmoplant treatment, since the highest rate of electron exchange occurred in this treatment, which in turn triggered the biosynthesis of anti-stress signaling metabolites such as reducing sugars.
2.8. Content of proline, sucrose, glucose and fructose
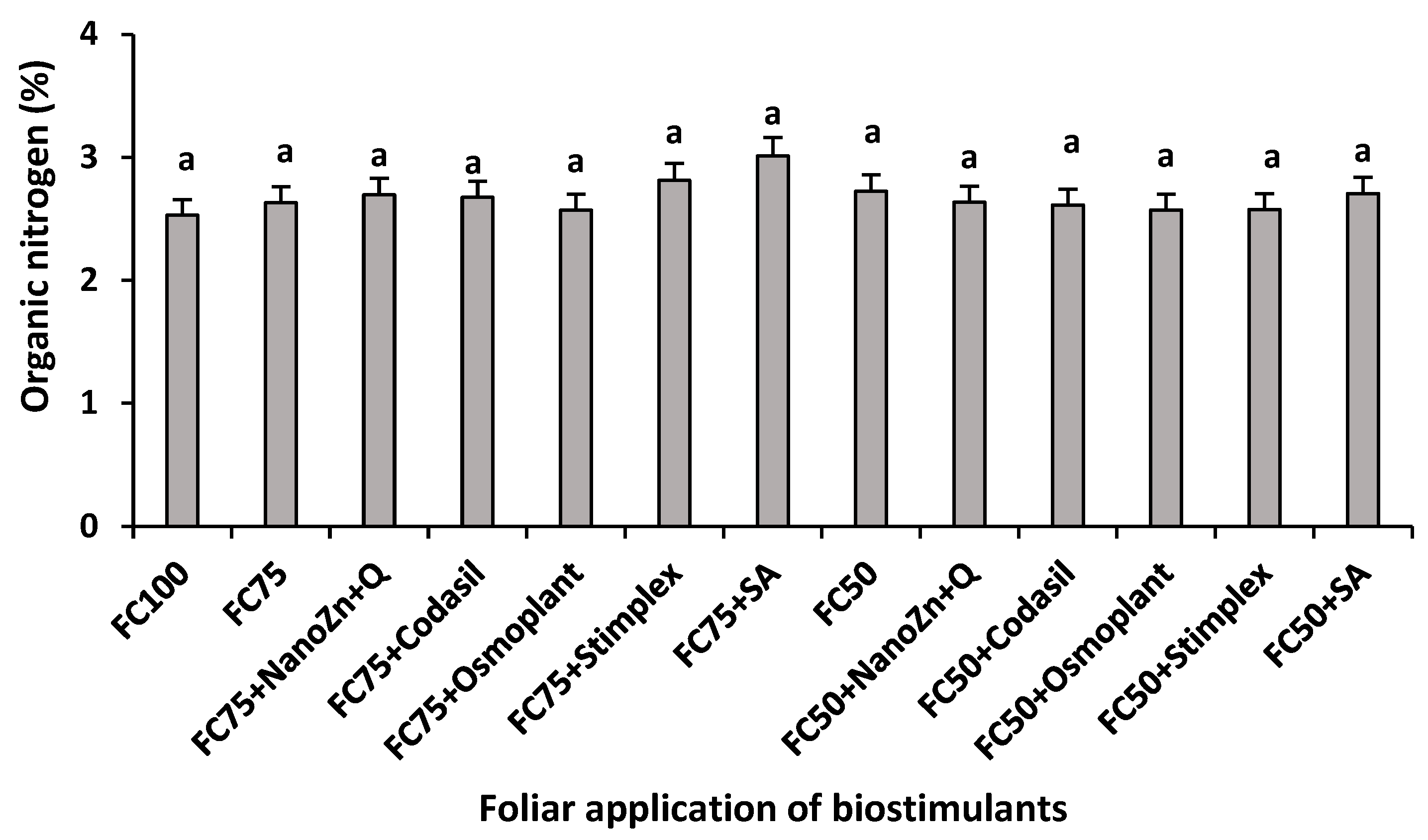
Organic nitrogen is, together with amino acids and proteins, one of the final products of the nitrogen assimilation process in plants. Therefore, it is a good indicator of the nutritional status of the plant [
40]. In the present research work, no significant differences were found (P= 0.05) with respect to the treatments used in the content of organic nitrogen in green bean plants cv. Strike (
Figure 9). The treatment that presented the highest organic nitrogen content when the amount of water was reduced by 25% was FC75+Stimplex, with an increase of 6.8% compared to FC75, although not significant. The plants to which an irrigation of 50% of water was applied showed a reduction in the content of organic nitrogen in all the treatments equally. However, the treatment that presented the least reduction and, therefore, the greatest capacity to cope with water stress was FC50+SA, with a reduction of only 0.7%.
As indicated by various authors, the applications of commercial products with
Ascophyllum nodosum extracts have a beneficial effect on the availability and assimilation of nutrients, including nitrogen [
41]. This effect can be attributed to the induction of the expression of glutamine synthetase and nitrate reductase, enzymes that convert inorganic ammonium to organic glutamine and reduce nitrate to nitrite, respectively [
42]. In the same way, the exogenous application of salicylic acid has been extensively studied in plants with beneficial effects on nitrogen accumulation, related to the increase in glutathione assimilation and content, as well as the increase in the concentration of photosynthetic pigments. Together, this plant response to salicylic acid application results in increased photosynthesis and development under several types of stress [
43,
44].
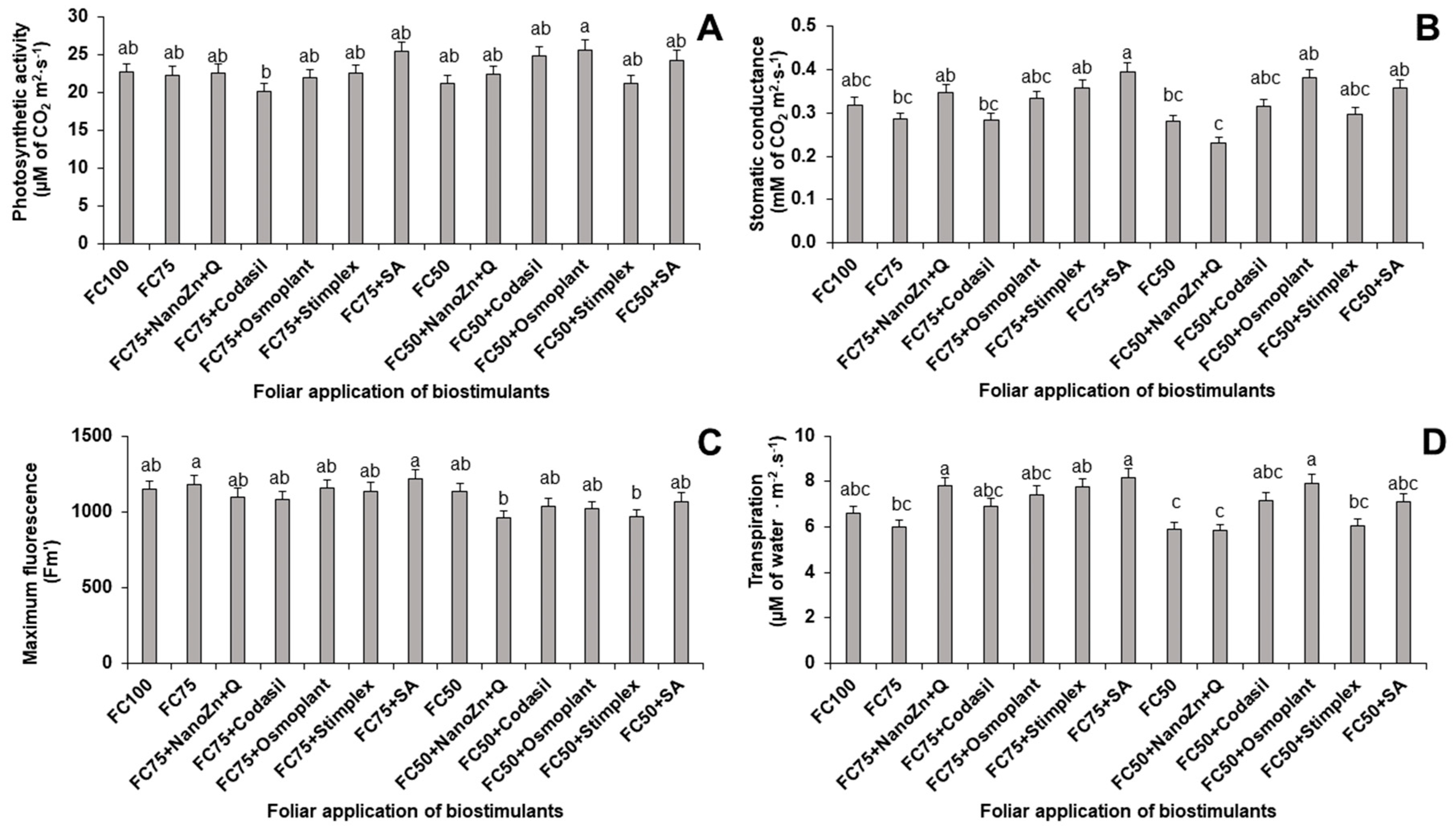
2.9. Photosynthetic activity, stomatal conductance, fluorescence and transpiration.
To obtain biomass and production, a correct balance between carbon assimilation and transpiration is necessary. In this process, gas exchange mediated by stomatal closure is decisive for the supply of CO
2, ATP, and NADPH [
45]. In the present study, significant differences were found in photosynthetic activity, stomatal conductance, fluorescence and transpiration due to the application of water stress and biostimulants (
Figure 10). The highest photosynthetic activity occurred when the amount of irrigation was reduced by 25% in the FC75+SA treatment, with an increase of 13.6% compared to FC75, however, the increase was not significant. On the other hand, when irrigation was reduced by 50%, the treatment that stood out was FC50+Osmoplant, increasing photosynthetic activity by 21.2% compared to FC50 (
Figure 10). Regarding stomatal conductance when irrigation was reduced by 25%, the treatment that benefited most was FC75+SA, with an increase of 38.8% compared to FC75. By supplying a 50% irrigation, the 27.8% increase of the FC50+SA treatment with respect to FC50 positioned it as the best treatment.
As the literature indicates, one of the processes most affected by drought is photosynthetic activity, due to the reduction of the photosynthetic area, stomatal closure, the reduction of the synthesis of chlorophyll pigments and the deterioration of the photosynthetic machinery [
46]. Within the mechanisms of action of commercial products called osmoregulators is the increase in the efficient use of water, through the restriction of transpiration, closing the stomata and reducing evaporation from the surface of the leaf to avoid the dehydration and preserve turgor [
47]. In the same way, the photoprotective effect of salicylic acid could be the reason photosynthetic activity remains stable even though the plant is under drought conditions.
On the other hand, these results, together with those obtained in total biomass (
Figure 1), yield (
Figure 2), total chlorophyll (
Figure 4) and chlorophyll index (
Figure 5), lead to the conclusion that the application of ZnO nanoparticles + chitosan have a beneficial effect on photosynthetic efficiency, which ultimately led to maintaining this process despite stress conditions due to reduced irrigation and allowed plants to root development and the accumulation of aerial biomass to finally obtain a high yield.
Maximum relative fluorescence quantification (Fm') is another essential element when considering photosynthetic efficiency. The energy that is absorbed by the photosynthetic pigments is sent to the reaction centers of photosystems I (PSI) and II (PSII) for transformation to photochemical energy or dissipated as fluorescence [
48]. In the present study, the highest value when the plants were subjected to a 25% decrease in irrigation was presented in the FC75+SA treatment with an increase of 3.4% with respect to FC75. On the other hand, once the amount of water decreased to 50%, the treatment with the highest fluorescence value was FC50, followed by the FC50+SA treatment (
Figure 10).
These results agree with what was reported by [
49], who found that the application of salicylic acid at a dose of 0.5 mM reduced the adverse effects of drought and increased photosynthetic efficiency. Other authors indicated that although the exogenous application of salicylic acid in broad bean plants improved CO
2 assimilation and chlorophyll content, it did not have significant effects on photoprotective compounds such as chlorophyll fluorescence [
50]. The values obtained can be related to the effect of salicylic acid in the protection of the photosynthetic machinery, since, during the light reactions in the leaves, one of the main processes of energy dissipation for the absorption of light by light-harvesting pigments is the fluorescence emission of chlorophyll.
Finally, the treatments with the highest values in transpiration were FC75+SA when irrigation was applied at 75%, with an increase of 36.2%, and FC50+Codasil, when irrigation was applied at 50% (
Figure 10). These data agree with what was mentioned above and with the production values obtained. Although the treatment with salicylic acid improved the response to water stress through an improvement in photosynthetic efficiency, it did not reach the highest values in production and biomass, due to its high rate of transpiration.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Crop management
The experiment was conducted at the facilities of the Food and Development Research Center in Delicias, Chihuahua, Mexico, during the months of August and September 2021. The experiment was established under greenhouse conditions at an average ambient temperature of 30.7 °C. Green bean seeds (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) cv. Strike, which were grown in 13.4 L plastic pots (two plants per pot) in a substrate mixture composed of vermiculite and perlite in a 2:1 ratio. The plants were watered with a complete nutrient solution composed of 6 mM NH4NO3, 1.6 mM K2HPO4, 0.3 mM K2SO4, 4 mM CaCl2, 1.4 mM MgSO4, 5 µM Fe-EDDHA, 2 µM MnSO4, 0.25 µM CuSO4, 0.5 µM H3BO3 and 0.3 µM Na2MoO4 with a pH of 6.0-6.1. The solution was applied depending on the amount of irrigation (100, 75 and 50%).
3.2. Experimental design
A completely randomized design with thirteen treatments and six repetitions was used (
Table 1). A control (FC100) was used at 100% field capacity (without water stress and without application of biostimulants). In addition, two water stress treatments were applied: FC75 with a water application restriction of 25% and FC50, with a water application restriction of 50%. Biostimulants were applied via foliar to both water stress conditions: ZnO nanoparticles + chitosan, Codasil®, Osmoplant®, Stimplex® and salicylic acid (
Table 1). Biostimulant treatments were applied 15 days after germination and the appearance of the first true leaves. The applications were made foliar, every seven days in a period of two months.
3.3. Plant sampling
Once the plants reached the state of physiological maturity at 60 days of crop development, the plant material was harvested. The collected material was washed with distilled water to remove residues and finally separated into organs (root, stem, leaves and fruit). The samples were divided into fresh and dry material. The fresh material was used for "in vivo" analyses, which included yield, nitrate reductase activity, photosynthetic pigments, amino acids and proteins, and proline, sucrose, glucose and fructose assays. The dry material was used for the quantification of biomass and organic nitrogen content.
3.4. Plant analysis
3.4.1. Aerial, foliar, root and total biomass
The production of aerial, foliar, root and total biomass of the plant were evaluated separately from the dry weight of the plant. To quantify the weight, an analytical balance (AND HR-120, San José, California, USA) was used, the weights were expressed as grams per plant based on dry weight (g plant-1 d.w.).
3.4.2. Biomass and Yield
The total fresh weight of fruits per plant was quantified. Ripe pods were harvested, and their weight was recorded using an analytical balance (AND HR-120, San José, California, USA). The results are expressed as grams of fresh weight per plant (g plant-1 f.w.).
3.4.3. Nitrate Reductase Activity “in vivo”
Nitrate Reductase (NR) activity “in vivo” (EC 1.6.6.1) was determined using the method proposed by Sánchez et al. (2004). The taleoles of the leaves were cut into 7 mm sections and placed in 10 mL of maceration buffer (100 mM K phosphate buffer, pH 7.5 and 1% (v/v) propanol). The samples were infiltrated at a pressure of 0.8 bar. They were incubated at 30 °C in the dark for 1 h, and finally placed in a boiling water bath to stop NR activity. Then, 1 mL of the enzyme extract was taken and 2 mL of 1% (p/v) sulfanilamide in 1.5 M HCl and 2 mL of 0.02% 1-naphthylenediamine N-dihydrochloride in 0.2 M (p/v) HCl were added. The resulting nitrite concentration was determined by spectrophotometry at 540 nm, against a standard curve of NO2-.
3.4.4. Photosynthetic pigments
For the quantification of photosynthetic pigments, the methodology described by [
53] was followed. From the fresh leaf material, specifically from the leaf blade, 7 mm taleole were obtained up to an approximate weight of 0.125 g. Four replicates per treatment were acquired and placed in test tubes. 10 mL of pure methanol (99%) (CH
3COH) were added to each tube and sealed with parafilm tape. It was left to stand in the dark for 24 h. Once this time had elapsed, the samples were shaken and the reading was carried out in a Genesis 10S UV-VIS spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, Massachusetts, USA) at three wavelengths: 666, 653 and 470 nm. Photosynthetic pigment concentrations were expressed as mg g
-1 f.w. and were calculated using the following formulas:
3.4.5. Chlorophyll index
For the quantification of the chlorophyll index, a Minolta SPAD 502 chlorophyll reader (Konica Minolta Sensing, Inc., Osaka, Japan) was obtained, which measures "
in situ" without causing damage to the leaf. Reading is achieved by projecting light through a sheet. The measurement was made on parts free of ribs. The results were expressed as SPAD units [
27].
3.4.6. Amino acids and soluble proteins
For the quantification of amino acids and soluble proteins, 0.5 g of fresh plant material were weighed and homogenized in cold 50 mM KH
2PO
4 buffer at pH 7. The sample was centrifuged at 12,000 g for 15 min. The supernatant obtained was obtained for the determination of total amino acids by the ninhydrin method with slight modifications [
54]. Total amino acids are expressed as mg g
−1 f.w. The soluble protein content was measured with the Bradford reagent [
55] and expressed as mg g
−1 f.w., using bovine serum albumin as standard.
3.4.7. Proline, sucrose, glucose and fructose assay
The extraction for the determination of the concentration of proline, sucrose, glucose and fructose was conducted following the methodology proposed by [
56] with modifications for the experiment proposed by [
57]. An amount between 0.25-0.5 of fresh plant material was homogenized with 5 mL of 96% ethanol and, subsequently, two rinses with 5 mL of 70% ethanol were applied. The resulting homogenate was centrifuged at 5,500 rpm for 10 min, and the resulting supernatant was used to determine the concentrations of proline and soluble sugars. The concentration of proline and soluble sugars were expressed as mg g
-1 f.w.
3.4.8. Organic nitrogen content
An organic elemental analyzer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, FLASH 2000, Massachusetts, United States) was used for total organic nitrogen quantification, following the methodology described by [
58], adapted for plant material. 0. 3 mg of the ground plant material was weighed over a soft tin microcontainer on an ultra-microbalance (Mettler Toledo, XP6 Excellence Plus XP, Ohio, United States), to which 9 mg of vanadium pentoxide (V
2O
5) was added and subsequently sealed. The sealed capsules were placed inside the automatic sampler carousel for analysis. The results were expressed as percentage of organic nitrogen (%).
3.4.9. Photosynthetic activity, stomatal conductance, maximum fluorescence and transpiration.
Photosynthetic activity and stomatal conductance were measured in the leaves when the plant reached its physiological maturity, in a time range from 10:00 am to 11:00 am. A portable meter LI-COR 6400 (Lincoln, Nebraska, USA) was used, a healthy leaf of homogeneous color and free of damage was selected on each plant. A concentration of 400 µmol per mol CO2 was used in the reference cell, while the sample cell was maintained at approximately 380 µmol per mL CO2. The air vapor pressure deficit in the sample chamber was less than 1.5 and the temperature of the block that housed the leaf was 25 °C. Photosynthetic activity was expressed as μM CO2 m2·s-1, stomatal conductance was reported as mM CO2 m2·s-1. Transpiration was reported as µmol H2O m-2·s-1 and maximum chlorophyll fluorescence was expressed as (Fm').
3.5. Statistical analysis
The data obtained were subjected to an analysis of variance and the significant differences in the means were determined by the test of significant differences (LSD) (P < 0.05), using the Statistical Software SAS 9.0.
4. Conclusions
The foliar application of the biostimulants with zinc oxide + chitosan nanoparticles was the foliar treatment that most benefited biomass accumulation and yield in green bean plants cv. Strike at a moderate level of water stress (FC75). When water stress was severe (FC50), with a 50% reduction in water application, the physiological and biochemical responses of the biostimulants used were modified, as well as the adaptive responses by the plant, now being the application of Codasil® and Osmoplant® the treatments that benefited the production and accumulation of biomass. The commercial product Stimplex® increased the accumulation of proteins and amino acids in the plant, however, the content of free sugars had a greater response with the application of zinc nanoparticles and Osmoplant®. A similar trend was found in gas exchange parameters, where, in general, the application of zinc nanoparticles + chitosan and Osmoplant® were the treatments that stood out, demonstrating the importance of osmoregulatory responses and micronutrients such as zinc in the carbon assimilation process. These results could indicate that the use of ZnO nanoparticles accompanied with chitosan can increase tolerance to moderate water stress in green bean plants cv. Strike. On the other hand, when water stress is severe, products that focus on osmotic balance such as Osmoplant® and Codasil® are a viable alternative to increase tolerance to this type of stress. Finally, it should be noted that more in-depth studies are required regarding the use of biostimulants in horticulture to elucidate the mechanisms of action at the physiological, biochemical and molecular levels that are involved in relieving and tolerating water stress in plants.
Author Contributions
K.I.H-F. and E.S.; designed the experiment, K.I.H-F., C.A.R-E., and E.M-M; conducted the experiment and collected the samples, E.S.; designed the methodology, D.L.O-B. and S.P-A.; made the formal analysis and data curation, K.I.H-F. and C.A.R-E.; writing—original draft preparation, E.S. and K.I.H-F.; writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
“This work was supported by the National Science and Technology Council (CONACYT, Méxi-co) under the project of the Call to Address National Problems: Project #1529 “Biofortification of basic agricultural crops representing the key to combat malnutrition and ensure food security in Mexico”.
Conflicts of Interest
“The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.”
References
- Haghighi, M.; Saadat, S.; Abbey, L. Effect of exogenous amino acids application on growth and nutritional value of cabbage under drought stress. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 272, 109561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kissel, E.; Van Asten, P.; Swennen, R.; Lorenzen, J.; Carpentier, S. C. Transpiration efficiency versus growth: exploring the banana biodiversity for drought tolerance. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 185, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seleiman, M.F.; Al-Suhaibani, N.; Ali, N.; Akmal, M.; Alotaibi, M.; Refay, Y.; Dindaroglu, T.; Abdul-Wajid, H.H.; Battaglia, M. L. Drought stress impacts on plants and different approaches to alleviate its adverse effects. Plants. 2021, 10(2), 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, G.; Asthir, B. Molecular responses to drought stress in plants. Biol. Plant. 2017, 61, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathobo, R.; Marais, D.; Steyn, J. M. The effect of drought stress on yield, leaf gaseous exchange and chlorophyll fluorescence of dry beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 180, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laxa, M.; Liebthal, M.; Telman, W.; Chibani, K.; Dietz, K. J. The role of the plant antioxidant system in drought tolerance. Antioxidants. 2019, 8(4), 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo-Santiago, L.; Navarro-León, E.; López-Moreno, F.J.; Arjó, G.; González, L.M.; Ruiz, J.M.; Blasco, B. The application of the silicon-based biostimulant Codasil® offset water deficit of lettuce plants. Sci. Hortic. 2021, 285, 110177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperdouli, I.; Moustaka, J.; Ouzounidou, G.; Moustakas, M. Leaf age-dependent photosystem II photochemistry and oxidative stress responses to drought stress in Arabidopsis thaliana are modulated by flavonoid accumulation. Molecules. 2021, 26(14), 4157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouphael, Y.; Colla, G. Biostimulants in agriculture. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulgari, R.; Franzoni, G.; Ferrante, A. Biostimulants application in horticultural crops under abiotic stress conditions. Agronomy. 2019, 9(6), 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Song, F.; Zhu, X.; Liu, S.; Liu, F.; Wang, Y.; Li, X. Nano-ZnO alleviates drought stress via modulating the plant water use and carbohydrate metabolism in maize. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2021, 67(2), 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Lu, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Chen, S. Response mechanism of plants to drought stress. Horticulturae. 2021, 7(3), 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacio-Márquez, A.; Ramírez-Estrada, C.A.; Gutiérrez-Ruelas, N.J.; Sánchez, E.; Ojeda-Barrios, D.L.; Chávez-Mendoza, C.; Sida-Arreola, J.P. Efficiency of foliar application of zinc oxide nanoparticles versus zinc nitrate complexed with chitosan on nitrogen assimilation, photosynthetic activity, and production of green beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Sci. Hortic. 2021, 288, 110297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.V.; Nath, M.; Bhatt, M.D.; Dobriyal, A.K.; Bhatt, D. Nanofomulation of zinc oxide and chitosan zinc sustain oxidative stress and alter secondary metabolite profile in tobacco. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 10, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semida, W.M.; Abdelkhalik, A.; Mohamed, G.F.; Abd El-Mageed, T.A.; Abd El-Mageed, S. A.; Rady, M. M.; Ali, E. F. Foliar application of zinc oxide nanoparticles promotes drought stress tolerance in eggplant (Solanum melongena L.). Plants. 2021, 10(2), 421. [CrossRef]
- De Micco, V.; Aronne, G. Morpho-anatomical traits for plant adaptation to drought. In Plant responses to drought stress, 1st ed.; Aroca, R. Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2012; pp. 37–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salcido-Martinez, A.; Sanchez, E., Licon-Trillo, L.P.; Perez-Alvarez, S.; Palacio-Marquez, A.; Amaya-Olivas, N.I.; Preciado-Rangel, P. Impact of the foliar application of magnesium nanofertilizer on physiological and biochemical parameters and yield in green beans. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. 2020, 48(4), 2167-2181. [CrossRef]
- Etienne, P.; Diquelou, S.; Prudent, M.; Salon, C.; Maillard, A.; Ourry, A. Macro and micronutrient storage in plants and their remobilization when facing scarcity: The case of drought. Agriculture. 2018, 8(1), 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Luo, X.; Wang, Y.; Feng, Y. Evaluation of zinc oxide nanoparticles on lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) growth and soil bacterial community. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 6026–6035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, C. P.; Merkt, N.; Zörb, C. Different nitrogen (N) forms affect responses to N form and N supply of rootstocks and grafted grapevines. Plant Sci. 2018, 277, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pejam, F.; Ardebili, Z.O.; Ladan-Moghadam, A.; Danaee, E. Zinc oxide nanoparticles mediated substantial physiological and molecular changes in tomato. Plos one. 2021, 16(3), e0248778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghani, M.I.; Saleem, S.; Rather, S.A.; Rehmani, M.S.; Alamri, S.; Rajput, V.D.; Kalaji, H.M.; Saleem, N.; Sail, T.A.; Liu, M. Foliar application of zinc oxide nanoparticles: An effective strategy to mitigate drought stress in cucumber seedling by modulating antioxidant defense system and osmolytes accumulation. Chemosphere. 2022, 289, 133202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista-Diaz, J.; Cruz-Alvarez, O.; Hernández-Rodríguez, O.A.; Sánchez-Chávez, E.; Jacobo-Cuellar, J.L.; Preciado-Rangel, P.; Ávila-Quezada, G.D.; Ojeda-Barrios, D.L. Zinc sulphate or zinc nanoparticle applications to leaves of green beans. Folia Hortic. 2021, 33(2), 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Leskovar, D.I. Effects of A. nodosum seaweed extracts on spinach growth, physiology and nutrition value under drought stress. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 183, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kaoaua, M.; Chernane, H.; Benaliat, A.; Neamallah, L. Seaweed liquid extracts effect on Salvia officinalis growth, biochemical compounds and water deficit tolerance. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 12(28), 4481–4489. [Google Scholar]
- Heidari, M.; Golpayegani, A. Effects of water stress and inoculation with plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) on antioxidant status and photosynthetic pigments in basil (Ocimum basilicum L.). J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2012, 11(1), 57-61. [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.; Brueck, H.; Asch, F. Chlorophyll index, photochemical reflectance index and chlorophyll fluorescence measurements of rice leaves supplied with different N levels. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B: Biol. 2012, 113, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seleiman, M.F.; Ahmad, A.; Battaglia, M.L.; Bilal, H.M.; Alhammad, B.A.; Khan, N. Zinc oxide nanoparticles: A unique saline stress mitigator with the potential to increase future crop production. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2023, 159, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegeder, M. Transporters for amino acids in plant cells: some functions and many unknowns. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2021, 15(3), 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertani, A.; Francioso, O.; Tinti, A.; Schiavon, M.; Pizzeghello, D.; Nardi, S. Evaluation of seaweed extracts from Laminaria and Ascophyllum nodosum spp. as biostimulants in Zea mays L. using a combination of chemical, biochemical and morphological approaches. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocira, S.; Szparaga, A.; Findura, P.; Treder, K. Modification of yield and fiber fractions biosynthesis in Phaseolus vulgaris L. by treatment with biostimulants containing amino acids and seaweed extract. Agronomy. 2020, 10(9), 1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latique, S.; Chernane, H.; Mansori, M.; El Kaoua, M. Seaweed liquid fertilizer effect on physiological and biochemical parameters of bean plant (Phaesolus vulgaris variety Paulista) under hydroponic system. Eur. Sci. J. 2013, 9(30), 174–191. [Google Scholar]
- Hidangmayum, A.; Sharma, R. Effect of different concentration of commercial seaweed liquid extract of Ascophylum nodosum on germination of onion (Allium cepa L.). Int. J. Sci. Res. 2017, 6(7), 1488-1491.
- Dar, M.I.; Naikoo, M.I.; Rehman, F.; Naushin, F.; Khan, F.A. Proline accumulation in plants: roles in stress tolerance and plant development. In Osmolytes and plants acclimation to changing environment. 1st ed.; Iqbal, N.; Nazar, R.; Khan, N.A.; Springer, New Delhi, India, 2016; pp. 155-166. [CrossRef]
- Jungklang, J.; Saengnil, K.; Uthaibutra, J. Effects of water-deficit stress and paclobutrazol on growth, relative water content, electrolyte leakage, proline content and some antioxidant changes in Curcuma alismatifolia Gagnep. cv. Chiang Mai Pink. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 24(7), 1505–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, P.S.; Jogeswar, G.; Rasineni, G.K.; Maheswari, M.; Reddy, A.R. , Varshney, R. K.; Kishor, P.K. Proline over-accumulation alleviates salt stress and protects photosynthetic and antioxidant enzyme activities in transgenic sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench]. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 94, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, F.I. Drought induces opposite changes in the concentration of non-structural carbohydrates of two evergreen Nothofagus species of differential drought resistance. Ann. For. Sci. 2011, 68(2), 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Latef, A.A.H.; Abu-Alhmad, M.F.; Abdelfattah, K.E. The possible roles of priming with ZnO nanoparticles in mitigation of salinity stress in lupine (Lupinus termis) plants. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2017, 36, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Deng, X.; Xiao, Q.; Han, Y.; Zhu, S.; Chen, J. IAA priming improves the germination and seedling growth in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) via regulating the endogenous phytohormones and enhancing the sucrose metabolism. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 155, 112788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran-Zuloaga, D.; Dippold, M.; Glaser, B.; Kuzyakov, Y. Organic nitrogen uptake by plants: Reevaluation by position-specific labeling of amino acids: Reevaluation of organic N uptake by plants by position-specific labeling. Biogeochemistry. 2015, 125, 359–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H.S.; Fleming, C.; Selby, C.; Rao, J.R.; Martin, T. Plant biostimulants: a review on the processing of macroalgae and use of extracts for crop management to reduce abiotic and biotic stresses. J. Appl. Phycol. 2014, 26, 465–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, P.S.; Mantin, E.G.; Adil, M.; Bajpai, S.; Critchley, A.T.; Prithiviraj, B. Ascophyllum nodosum-based biostimulants: Sustainable applications in agriculture for the stimulation of plant growth, stress tolerance, and disease management. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, M.; Hayat, S.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Fariduddin, Q.; Ahmad, A. Salicylic acid: physiological roles in plants. In Salicylic Acid: Plant Growth and Development, 1st ed.; Hayat, S.; Ahmad, A.; Alyemeni, M.N., Eds.; Springer, Dordrecht, Netherlands, 2013; pp. 15-30. [CrossRef]
- Wani, W.; Masoodi, K.Z.; Zaid, A.; Wani, S.H.; Shah, F.; Meena, V.S.; Wani, S.A.; Mosa, K.A. Engineering plants for heavy metal stress tolerance. Rend. Lincei Sci. Fis. Nat. 2018, 29, 709–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, J.S.; Vialet-Chabrand, S.R.; Lawson, T. Diurnal variation in gas exchange: the balance between carbon fixation and water loss. Plant Physiol. 2017, 174(2), 614–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sher, A.; Hussain, S.; Cai, L.J.; Ahmad, M.I.; Jamro, S.A.; Rashid, A. Significance of chemical priming on yield and yield components of wheat under drought stress. Am. J. Plant Sci. 2017, 8(06), 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, A.; Tuberosa, R. Dehydration survival of crop plants and its measurement. J. Exp. Bot. 2018, 69(5), 975–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.; Wang, Y.; Chi, Y.; Zhou, L.; Chen, J.; Zhou, W.; Song, J.; Zhao, N; Ding, J. Drought stress strengthens the link between chlorophyll fluorescence parameters and photosynthetic traits. PeerJ. 2020, 8, e10046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazar, R.; Umar, S.; Khan, N.A.; Sareer, O. Salicylic acid supplementation improves photosynthesis and growth in mustard through changes in proline accumulation and ethylene formation under drought stress. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2015, 98, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martel, A.B.; Qaderi, M.M. Does salicylic acid mitigate the adverse effects of temperature and ultraviolet-B radiation on pea (Pisum sativum) plants? Environ. Exp. Bot. 2016, 122, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, M.M.A.; Malek, M.A.; Puteh, A.B.; Ismail, M.R. Foliar application of chitosan on growth and yield attributes of mungbean (Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek). Bangladesh J. Bot. 2013, 42(1), 179-183.
- Sánchez-Chávez, E.; Barrera-Tovar, R.; Muñoz-Márquez, E.; Ojeda-Barrios, D.L.; Anchondo-Nájera, Á. Efecto del ácido salicílico sobre biomasa, actividad fotosintética, contenido nutricional y productividad del chile jalapeño. Rev. Chapingo Ser. Hortic. 2011, 17(SPE1), 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellburn, A.R. The spectral determination of chlorophylls a and b, as well as total carotenoids, using various solvents with spectrophotometers of different resolution. J. Plant Physiol. 1994, 144(3), 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, E.; Rivero, R.M.; Ruiz, J.M.; Romero, L. Changes in biomass, enzymatic activity and protein concentration in roots and leaves of green bean plants (Phaseolus vulgaris L. cv. Strike) under high NH4NO3 application rates. Sci. Hortic. 2004, 99(3-4), 237-248. [CrossRef]
- Kruger, N.J. The Bradford Method For Protein Quantitation. In The Protein Protocols Handbook, Walker, J.M., Eds.; Springer Protocols Handbooks. Humana Press, Totowa, New Jersey, United States. [CrossRef]
- Irigoyen, J.J.; Einerich, D.W.; Sánchez-Díaz, M. (1992). Water stress induced changes in concentrations of proline and total soluble sugars in nodulated alfalfa (Medicago sativa) plants. Physiol. Plant. 1992, 84(1), 55-60. [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, E.; Soto, J.M.; Núñez, A.; Ruiz, J.M.; Romero, L. Biosynthesis of non-structural carbohydrates and their distribution in greenbean plants (Phaseolus vulgaris L. Cv. Strike): deficiency vs toxicity of nitrogen. Rev. Fit. Mex. 2005, 28(1), 55-61.
- Krotz, L.; Giazzi, G. Nitrogen, Carbon and Sulfur Determination in Paper by Flash Combustion. 2014. Available online: http://tools.thermofisher.com/content/sfs/posters/PN-42211-Nitrogen-Carbon-Sulfur-Paper-Flash-Combustion-PN42211-EN.pdf.
Figure 1.
Effect of biostimulant application on aerial (A), foliar (B), root (C) and total (D) biomass production in plants of green bean cv. Strike under water stress conditions (FC75 and FC50) and a control (FC100, without water stress and without biostimulant application). Means with different letters indicate significant differences according to LSD test. (P <0.05).
Figure 1.
Effect of biostimulant application on aerial (A), foliar (B), root (C) and total (D) biomass production in plants of green bean cv. Strike under water stress conditions (FC75 and FC50) and a control (FC100, without water stress and without biostimulant application). Means with different letters indicate significant differences according to LSD test. (P <0.05).
Figure 2.
Effect of biostimulant application on yield in green bean plants cv. Strike under water stress conditions (FC75 and FC50) and a control (FC100, without water stress and without biostimulant application). Means with different letters indicate significant differences according to LSD test (P < 0.05).
Figure 2.
Effect of biostimulant application on yield in green bean plants cv. Strike under water stress conditions (FC75 and FC50) and a control (FC100, without water stress and without biostimulant application). Means with different letters indicate significant differences according to LSD test (P < 0.05).
Figure 3.
Effect of biostimulant application on NR activity in plants of green bean cv. Strike under water stress conditions (FC75 and FC50) and a control (FC100, without water stress and without biostimulant application). Means with different letters indicate significant differences according to LSD test (P < 0.05).
Figure 3.
Effect of biostimulant application on NR activity in plants of green bean cv. Strike under water stress conditions (FC75 and FC50) and a control (FC100, without water stress and without biostimulant application). Means with different letters indicate significant differences according to LSD test (P < 0.05).
Figure 4.
Effect of biostimulant application on chlorophyll a (A), chlorophyll b (B), carotenes (C) and total chlorophyll (D) content in green bean plants cv. Strike under water stress conditions (FC75 and FC50) and a control (FC100, without water stress and without biostimulant application). Means with different letters indicate significant differences according to LSD test (P < 0.05).
Figure 4.
Effect of biostimulant application on chlorophyll a (A), chlorophyll b (B), carotenes (C) and total chlorophyll (D) content in green bean plants cv. Strike under water stress conditions (FC75 and FC50) and a control (FC100, without water stress and without biostimulant application). Means with different letters indicate significant differences according to LSD test (P < 0.05).
Figure 5.
Effect of biostimulant application on the chlorophyll index (SPAD) in green bean plants cv. Strike under water stress conditions (FC75 and FC50) and a control (FC100, without water stress and without biostimulant application). Means with different letters indicate significant differences according to LSD test (P < 0.05).
Figure 5.
Effect of biostimulant application on the chlorophyll index (SPAD) in green bean plants cv. Strike under water stress conditions (FC75 and FC50) and a control (FC100, without water stress and without biostimulant application). Means with different letters indicate significant differences according to LSD test (P < 0.05).
Figure 6.
Effect of biostimulant application on soluble amino acid content in green bean plants cv. Strike under water stress conditions (FC75 and FC50) and a control (FC100, without water stress and without biostimulant application). Means with different letters indicate significant differences according to LSD test (P <0.05).
Figure 6.
Effect of biostimulant application on soluble amino acid content in green bean plants cv. Strike under water stress conditions (FC75 and FC50) and a control (FC100, without water stress and without biostimulant application). Means with different letters indicate significant differences according to LSD test (P <0.05).
Figure 7.
Effect of biostimulant application on soluble protein content in green bean plants cv. Strike under water stress conditions (FC75 and FC50) and a control (FC100, without water stress and without biostimulant application). Means with different letters indicate significant differences according to LSD test. (P <0.05).
Figure 7.
Effect of biostimulant application on soluble protein content in green bean plants cv. Strike under water stress conditions (FC75 and FC50) and a control (FC100, without water stress and without biostimulant application). Means with different letters indicate significant differences according to LSD test. (P <0.05).
Figure 8.
Effect of biostimulants application on proline (A) and sucrose (B), glucose (C) and fructose (D) content in green bean plants cv. Strike under water stress conditions (FC75 and FC50) and a control (FC100, without water stress and without biostimulants application). Means with different letters indicate significant differences according to LSD test. (P <0.05).
Figure 8.
Effect of biostimulants application on proline (A) and sucrose (B), glucose (C) and fructose (D) content in green bean plants cv. Strike under water stress conditions (FC75 and FC50) and a control (FC100, without water stress and without biostimulants application). Means with different letters indicate significant differences according to LSD test. (P <0.05).
Figure 9.
Effect of biostimulants application on organic nitrogen content in green bean plants cv. Strike under water stress conditions (FC75 and FC50) and a control (FC100, without water stress and without biostimulants application). Means with different letters indicate significant differences according to LSD test (P <0.05).
Figure 9.
Effect of biostimulants application on organic nitrogen content in green bean plants cv. Strike under water stress conditions (FC75 and FC50) and a control (FC100, without water stress and without biostimulants application). Means with different letters indicate significant differences according to LSD test (P <0.05).
Figure 10.
Effect of biostimulants application on photosynthetic activity (A), stomatal conductance (B), fluorescence (C) and transpiration (D) in green bean plants cv. Strike under water stress conditions (FC75 and FC50) and a control (FC100, without water stress and without biostimulants application). Means with different letters indicate significant differences according to LSD test (P <0.05).
Figure 10.
Effect of biostimulants application on photosynthetic activity (A), stomatal conductance (B), fluorescence (C) and transpiration (D) in green bean plants cv. Strike under water stress conditions (FC75 and FC50) and a control (FC100, without water stress and without biostimulants application). Means with different letters indicate significant differences according to LSD test (P <0.05).
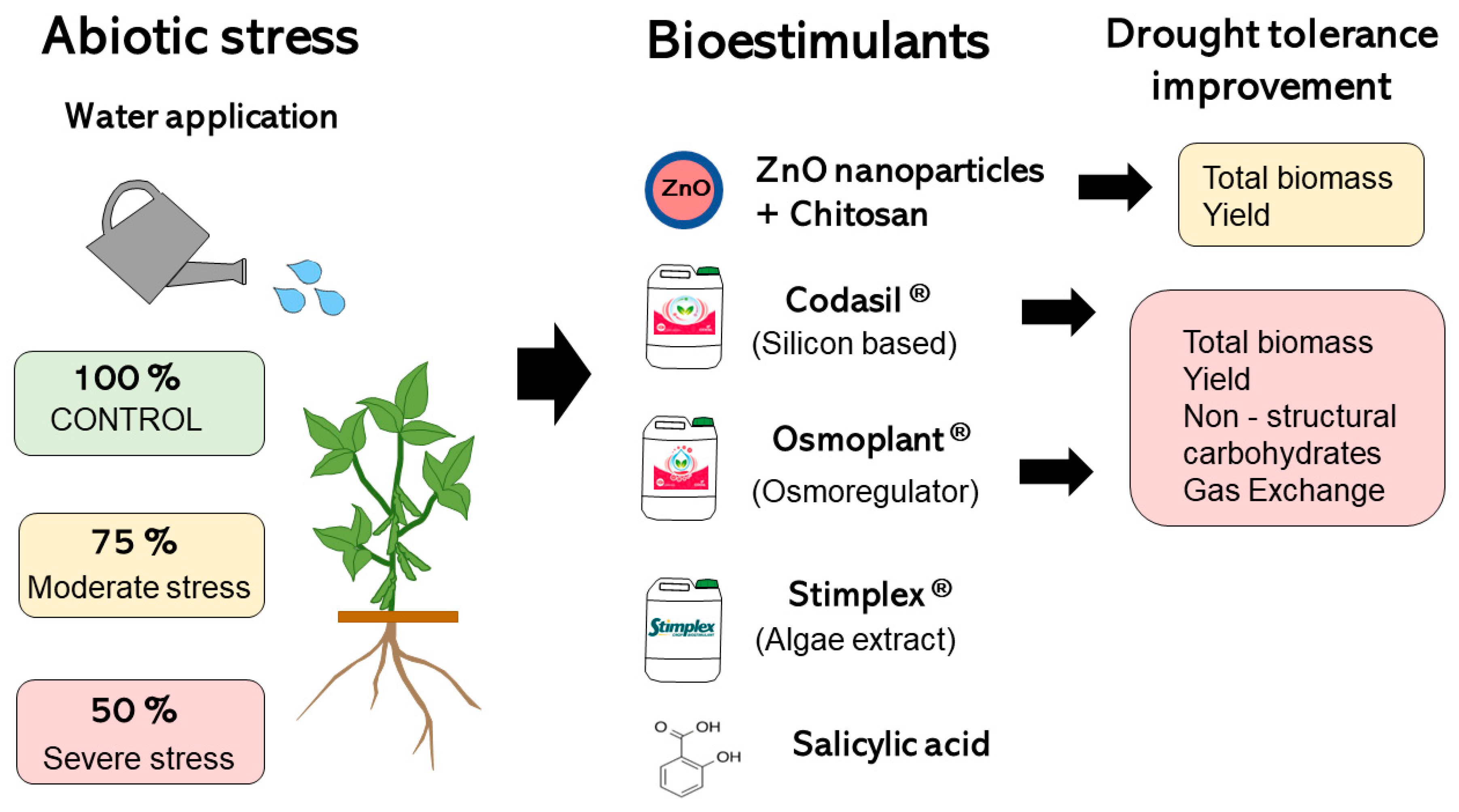
Figure 11.
Graphical summary of the treatments applied and the effect on the main variables measured under moderate (FC75) and severe (FC50) stress in ejotero bean plants cv. Strike.
Figure 11.
Graphical summary of the treatments applied and the effect on the main variables measured under moderate (FC75) and severe (FC50) stress in ejotero bean plants cv. Strike.
Table 1.
Treatment description.
Table 1.
Treatment description.
| Percentage of water applied (FC) |
Added biostimulant |
Doses of added biostimulant |
Code |
| 100 |
- |
- |
FC100 |
| 75 |
- |
- |
FC75 |
| 75 |
Nano ZnO + Chitosan |
100 ppm |
FC75+NanoZn+Q |
| 75 |
Codasil® |
200 ppm |
FC75+Codasil |
| 75 |
Osmoplant® |
200 ppm |
FC75+Osmoplant |
| 75 |
Stimplex® |
200 ppm |
FC75+Stimplex |
| 75 |
Salicylic Acid |
0.1 mM |
FC75+SA |
| 50 |
- |
- |
FC50 |
| 50 |
Nano ZnO + Chitosan |
100 ppm |
FC50+NanoZn+Q |
| 50 |
Codasil® |
200 ppm |
FC50+Codasil |
| 50 |
Osmoplant® |
200 ppm |
FC50+Osmoplant |
| 50 |
Stimplex® |
200 ppm |
FC50+Stimlex |
| 50 |
Salicylic Acid |
0.1 mM |
FC50+SA |
Table 2.
Chemical composition of biostimulants and doses applied on green bean plants cv. Strike under water stress.
Table 2.
Chemical composition of biostimulants and doses applied on green bean plants cv. Strike under water stress.
| Bioestimulant |
Chemical composition |
Doses |
| Codasil ® |
Liquid solution with a high concentration of soluble silicon composed of 20% silicon, 4% free amino acids and 11.20% potassium. |
2 mL/L (Manufacturer's recommendation). |
| Osmoplant ® |
Liquid solution composed of 6% free amino acids, 2.4% nitrogen, and 3.3% potassium. |
2 mL/L (Manufacturer's recommendation). |
| Stimplex ® |
Liquid solution, composed of Ascophyllum nodosum algae extract as its active ingredient at 0.34%, with a formulation of total nitrogen 0.1 % and soluble potassium (K2O) 4.0 %. |
2 mL/L (Manufacturer's recommendation). |
| Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles |
< 50 nm, 99.9% |
0.1246 g/L (100 ppm) [13]. |
| Chitosan (Poli-D-glucosamine) |
|
2 mL/L [51]. |
| Salicylic acid |
C7H6O3
|
0.0138 g/1 L (0.1 mM) [52]. |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).