Submitted:
04 July 2023
Posted:
05 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
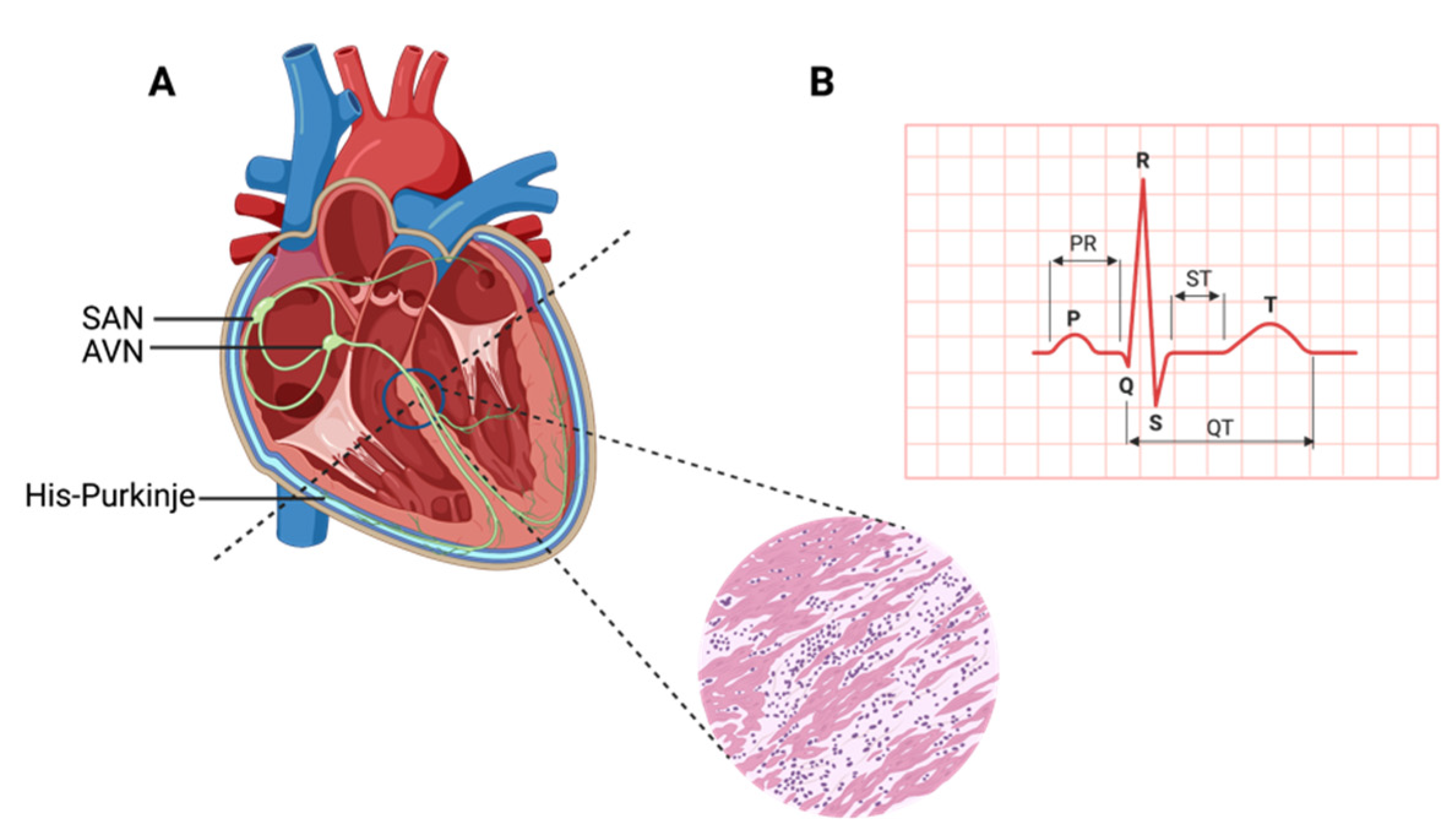
1. Contracting Cardiac Muscle
2. Key Transcription factors involved in Cardiac Conduction System development
2.1. Short stature homeobox 2 (SHOX2) and bone morphogenic protein 4 (BMP4)
2.2. T-box transcription factor 5 (TBX5), NK2 Homeobox 5 (NDX2-5) and Inhibitor of DNA binding 2 (ID2)
2.3. T-Box Transcription Factor 3 (TBX3)
2.4. T-box transcription factor 18 (TBX18)
2.5. ISLET-1 (ISL1)
2.6. GATA4
2.7. HAND1
2.8. IRX3
3. Key Signalling pathways involved in CCS development
3.1. Notch signalling
3.2. BMP signalling pathway
3.3. Wnt signalling
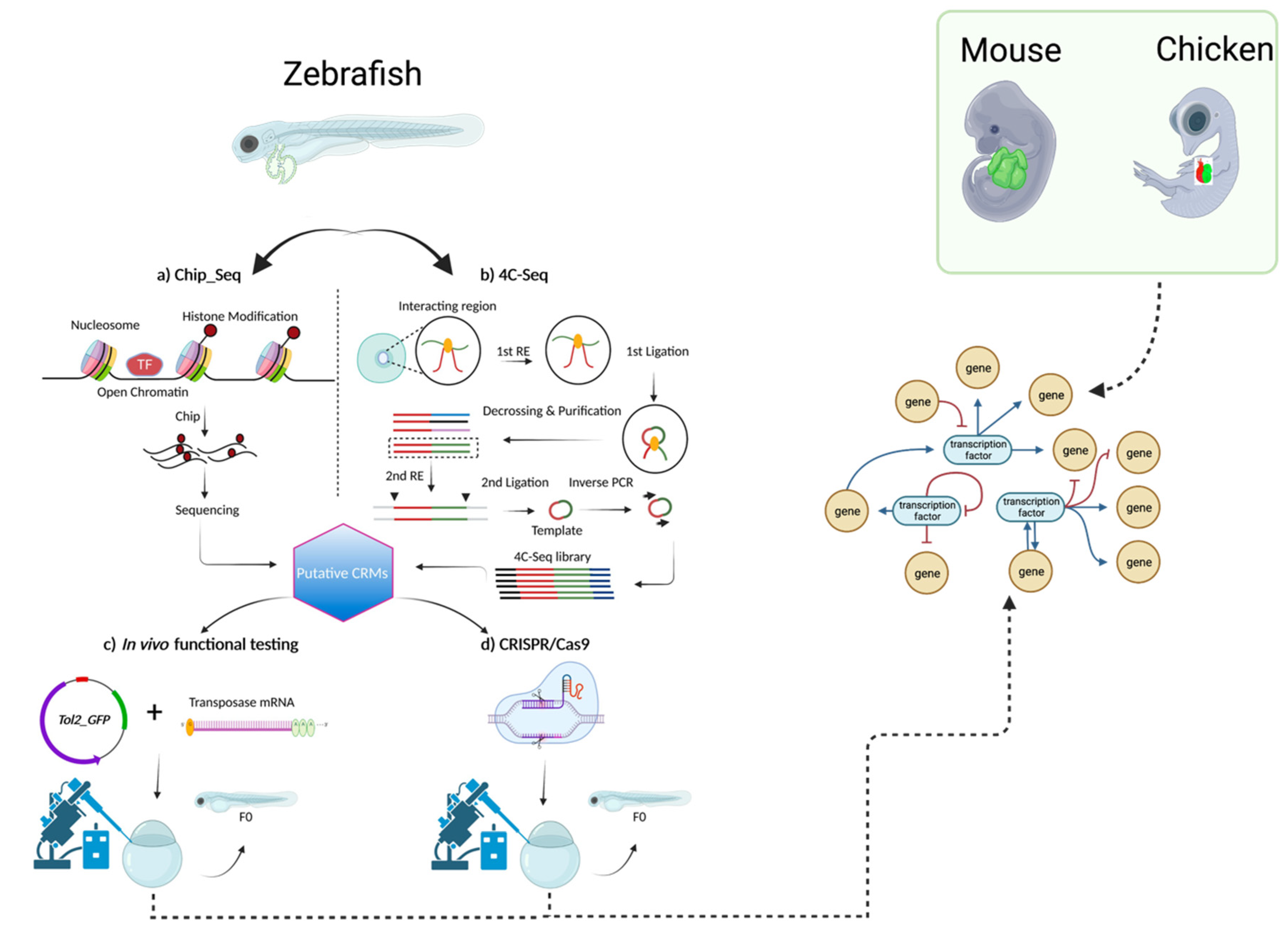
4. The genetic network of CCS development
5. Conclusion and future directions
References
- Alasti, M. , Machado, C., Rangasamy, K., Bittinger, L., Healy, S., Kotschet, E., Adam, D., Alison, J., 2018. Pacemaker-mediated arrhythmias. J Arrhythm 34, 485-492.
- Anderson, R.H.; Yanni, J.; Boyett, M.R.; Chandler, N.J.; Dobrzynski, H. The anatomy of the cardiac conduction system. Clin. Anat. 2009, 22, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrés-Delgado, L.; Mercader, N. Interplay between cardiac function and heart development. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) - Mol. Cell Res. 2016, 1863, 1707–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakker, M. , Boukens, B., Mommersteeg, M., Brons, J., Wakker, V., Moorman, A., Christoffels, V.M., 2008. Transcription Factor TBX3 Is Required for the Specification of the Atrioventricular Conduction System. Circulation Research 102, 1340-1349.
- Barbuti, A.; Baruscotti, M.; Difrancesco, D. The Pacemaker Current: From Basics to the Clinics. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2007, 18, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaschke, R.J.; Hahurij, N.D.; Kuijper, S.; Just, S.; Wisse, L.J.; Deissler, K.; Maxelon, T.; Anastassiadis, K.; Spitzer, J.; Hardt, S.E.; et al. Targeted Mutation Reveals Essential Functions of the Homeodomain Transcription Factor Shox2 in Sinoatrial and Pacemaking Development. Circulation 2007, 115, 1830–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs, L.E.; Takeda, M.; Cuadra, A.E.; Wakimoto, H.; Marks, M.H.; Walker, A.J.; Seki, T.; Oh, S.P.; Lu, J.T.; Sumners, C.; et al. Perinatal Loss of Nkx2-5 Results in Rapid Conduction and Contraction Defects. Circ. Res. 2008, 103, 580–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhard, S.B. , Bakkers, J., 2018. Spatially resolved RNA-sequencing of the embryonic heart identifies a role for Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in autonomic control of heart rate. Elife 7.
- Callis, T.E. , Cao, D., Wang, D.-Z. Bone Morphogenetic Protein Signaling Modulates Myocardin Transactivation of Cardiac Genes. Circ. Res. 2005, 97, 992–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Litchenberg, W.H.; Cole, G.J.; Mikawa, T.; Thompson, R.P.; Gourdie, R.G. Development of the cardiac conduction system involves recruitment within a multipotent cardiomyogenic lineage. Development 1999, 126, 5041–5049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.C. Pacing the Heart with Genes: Recent Progress in Biological Pacing. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2015, 17, 65–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cingolani, E.; Goldhaber, J.I.; Marbán, E. Next-generation pacemakers: from small devices to biological pacemakers. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2017, 15, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohle, S.D.; Suarez-Mier, M.P.; Aguilera, B. Sudden Death Resulting from Lesions of the Cardiac Conduction System. Am. J. Forensic Med. Pathol. 2002, 23, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, D.L.; Arruda, E.P.; Agarwal, P.; Kim, K.-H.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, W.; Lebel, M.; Cheng, C.W.; Park, C.Y.; Pierce, S.A.; et al. The Homeodomain Transcription Factor Irx5 Establishes the Mouse Cardiac Ventricular Repolarization Gradient. Cell 2005, 123, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, F. THE CONDUCTING SYSTEM OF THE VERTEBRATE HEART. Hear. 1942, 4, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Pater, E.; Clijsters, L.; Marques, S.R.; Lin, Y.-F.; Garavito-Aguilar, Z.V.; Yelon, D.; Bakkers, J. Distinct phases of cardiomyocyte differentiation regulate growth of the zebrafish heart. Development 2009, 136, 1633–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efe, J.A.; Hilcove, S.; Kim, J.; Zhou, H.; Ouyang, K.; Wang, G.; Chen, J.; Ding, S. Conversion of mouse fibroblasts into cardiomyocytes using a direct reprogramming strategy. Nature 2011, 13, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Eif, V.W.W.; Devalla, H.D.; Boink, G.J.J.; Christoffels, V.M. Transcriptional regulation of the cardiac conduction system. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2018, 15, 617–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firulli, B.A.; Fuchs, R.K.; Vincentz, J.W.; Clouthier, D.E.; Firulli, A.B. Hand1 phosphoregulation within the distal arch neural crest is essential for craniofacial morphogenesis. Development 2014, 141, 3050–3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firulli, B.A.; George, R.M.; Harkin, J.; Toolan, K.P.; Gao, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Field, L.J.; Liu, Y.; Shou, W.; et al. HAND1 loss-of-function within the embryonic myocardium reveals survivable congenital cardiac defects and adult heart failure. Cardiovasc. Res. 2019, 116, 605–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraidenraich, D.; Stillwell, E.; Romero, E.; Wilkes, D.; Manova, K.; Basson, C.T.; Benezra, R.; Lisci, M.; Barton, P.R.; Lezmy, J.; et al. Rescue of Cardiac Defects in Id Knockout Embryos by Injection of Embryonic Stem Cells. Science 2004, 306, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galang, G.; Mandla, R.; Ruan, H.; Jung, C.; Sinha, T.; Stone, N.R.; Wu, R.S.; Mannion, B.J.; Allu, P.K.; Chang, K.; et al. ATAC-Seq Reveals an Isl1 Enhancer That Regulates Sinoatrial Node Development and Function. Circ. Res. 2020, 127, 1502–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharibeh, L.; Yamak, A.; Whitcomb, J.; Lu, A.; Joyal, M.; Komati, H.; Liang, W.; Fiset, C.; Nemer, M. GATA6 is a regulator of sinus node development and heart rhythm. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2020, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greulich, F.; Rudat, C.; Kispert, A. Mechanisms of T-box gene function in the developing heart. Cardiovasc. Res. 2011, 91, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harst, P.v.d. , Setten, J.v., Verweij, N., Vogler, G., Franke, L., Maurano, M.T., Wang, X., Leach, I.M., Eijgelsheim, M., Sotoodehnia, N., et al. 2016. 52 Genetic Loci Influencing Myocardial Mass. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 68, 1435-1448.
- Hoogaars, W.M.H. , Tessari, A., Moorman, A.F.M., Boer, P.A.J.d., Hagoort, J., Soufan, A.T., Campione, M., Christoffels, V.M., 2004. The transcriptional repressor Tbx3 delineates the developing central conduction system of the heart. Cardiovascular Research 62, 489-499.
- Hu, W.; Xin, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, J. Shox2: The Role in Differentiation and Development of Cardiac Conduction System. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2018, 244, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Xin, Y.; Hu, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, Y. Inhibitor of DNA binding in heart development and cardiovascular diseases. Cell Commun. Signal. 2019, 17, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jay, P.Y. , Harris, B.S., Maguire, C.T., Buerger, A., Wakimoto, H., Tanaka, M., Kupershmidt, S., Roden, D.M., Schultheiss, T.M., O’Brien, T.X., Gourdie, R.G., Berul, C.I., Izumo, S., 2004. Nkx2-5 mutation causes anatomic hypoplasia of the cardiac conduction system. The Journal of Clinical Investigation 113, 1130-1137.
- Kapoor, N.; Liang, W.; Marbán, E.; Cho, H.C. Direct conversion of quiescent cardiomyocytes to pacemaker cells by expression of Tbx18. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 31, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, A. , Finlay, D.D., Guldenring, D., Bond, R., Moran, K., McLaughlin, J., 2016. The Cardiac Conduction System: Generation and Conduction of the Cardiac Impulse. Critical Care Nursing Clinics of North America 28, 269-279.
- Kim, K.-H.; Rosen, A.; Hussein, S.M.I.; Puviindran, V.; Korogyi, A.S.; Chiarello, C.; Nagy, A.; Hui, C.-C.; Backx, P.H. Irx3 is required for postnatal maturation of the mouse ventricular conduction system. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, srep19197–19197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.Y.C.; Cook, A.C.; Lovering, R.C. GOing Forward With the Cardiac Conduction System Using Gene Ontology. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 802393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Han, P.; Kim, E.H.; Mak, J.; Zhang, R.; Torrente, A.G.; Goldhaber, J.I.; Marbán, E.; Cho, H.C. Canonical Wnt signaling promotes pacemaker cell specification of cardiac mesodermal cells derived from mouse and human embryonic stem cells. STEM CELLS 2019, 38, 352–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Cattaneo, P.; Zhuang, S.; Gong, X.; Spann, N.J.; Jiang, C.; Cao, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, X.; et al. Transcription factor ISL1 is essential for pacemaker development and function. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 3256–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsey, S.E.; Butcher, J.T.; Yalcin, H.C. Mechanical regulation of cardiac development. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Fang, Y.; Hou, X.; Yan, Y.; Xiao, H.; Zuo, D.; Wen, J.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Z.; Dang, X.; et al. Enrichment differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cells into sinoatrial node-like cells by combined modulation of BMP, FGF, and RA signaling pathways. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2020, 11, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Fang, Y.; Hou, X.; Yan, Y.; Xiao, H.; Zuo, D.; Wen, J.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Z.; Dang, X.; et al. Enrichment differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cells into sinoatrial node-like cells by combined modulation of BMP, FGF, and RA signaling pathways. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2020, 11, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luxan, G. , D’Amato, G., Pompa, J.L.d.l., Nakanishi, T., Markwald, R.R., Baldwin, H.S., Keller, B.B., Srivastava, D., Yamagishi, H., 2016. Intercellular Signaling in Cardiac Development and Disease: The NOTCH pathway, Etiology and Morphogenesis of Congenital Heart Disease: From Gene Function and Cellular Interaction to Morphology, 1 ed. Springer, Tokyo.
- Martinsen, B.J. Reference guide to the stages of chick heart embryology. Dev. Dyn. 2005, 233, 1217–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNally, E.M.; Svensson, E.C. Setting the pace: Tbx3 and Tbx18 in cardiac conduction system development. Circulation Research 2009, 104, 285–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meilhac, S.M.; Esner, M.; Kelly, R.G.; Nicolas, J.-F.; Buckingham, M.E. The Clonal Origin of Myocardial Cells in Different Regions of the Embryonic Mouse Heart. Dev. Cell 2004, 6, 685–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minhas, R.; Loeffler-Wirth, H.; Siddiqui, Y.H.; Obrębski, T.; Vashisht, S.; Abu Nahia, K.; Paterek, A.; Brzozowska, A.; Bugajski, L.; Piwocka, K.; et al. Transcriptome profile of the sinoatrial ring reveals conserved and novel genetic programs of the zebrafish pacemaker. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minhas, R.; Paterek, A.; Łapiński, M.; Bazała, M.; Korzh, V.; Winata, C.L. A novel conserved enhancer at zebrafish zic3 and zic6 loci drives neural expression. Dev. Dyn. 2019, 248, 837–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, R. , Boukens, B.J., Christoffels, V.M., 2017. Lineages of the Cardiac Conduction System. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease 4, 5.
- Molkentin, J.D.; Lin, Q.; Duncan, S.A.; Olson, E.N. Requirement of the transcription factor GATA4 for heart tube formation and ventral morphogenesis. Genes Dev. 1997, 11, 1061–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moorman, A.F.; de Jong, F.; Denyn, M.M.; Lamers, W.H. Development of the Cardiac Conduction System. Circ. Res. 1998, 82, 629–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskowitz, I.P.; Kim, J.B.; Moore, M.L.; Wolf, C.M.; Peterson, M.A.; Shendure, J.; Nobrega, M.A.; Yokota, Y.; Berul, C.; Izumo, S.; et al. A Molecular Pathway Including Id2, Tbx5, and Nkx2-5 Required for Cardiac Conduction System Development. Cell 2007, 129, 1365–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskowitz, I.P.G.; Pizard, A.; Patel, V.V.; Bruneau, B.G.; Kim, J.B.; Kupershmidt, S.; Roden, D.; Berul, C.I.; Seidman, C.E.; Seidman, J.G. The T-Box transcription factor Tbx5 is required for the patterning and maturation of the murine cardiac conduction system. Development 2004, 131, 4107–4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munshi, N.V. Gene Regulatory Networks in Cardiac Conduction System Development. Circ. Res. 2012, 110, 1525–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, A.; Nakashima, Y.; Yanez, D.A.; Touma, M.; Nakano, H.; Jarodzewicz, A.; Jordan, M.C.; Pellegrini, M.; Roos, K.P. Abstract 13: Nkx2-5-notch Signaling Axis Regulates The Proliferation Of The Atrial Myocytes And Conduction System. Circ. Res. 2014, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeufer, A.; van Noord, C.; Marciante, K.D.; Arking, D.E.; Larson, M.G.; Smith, A.V.; Tarasov, K.V.; Müller, M.; Sotoodehnia, N.; Sinner, M.F.; et al. Genome-wide association study of PR interval. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puskaric, S.; Schmitteckert, S.; Mori, A.D.; Glaser, A.; Schneider, K.U.; Bruneau, B.G.; Blaschke, R.J.; Steinbeisser, H.; Rappold, G. Shox2 mediates Tbx5 activity by regulating Bmp4 in the pacemaker region of the developing heart. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2010, 19, 4625–4633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Mondragon, R. , Galindo, C.A., Avila, G., 2008. Role of TGF-β on cardiac structural and electrical remodeling. Vascular Health and Risk Management 4, 1289-1300.
- Ren, J.; Miao, D.; Li, Y.; Gao, R. Spotlight on Isl1: A Key Player in Cardiovascular Development and Diseases. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rentschler, S.; Yen, A.H.; Lu, J.; Petrenko, N.B.; Lu, M.M.; Manderfield, L.J.; Patel, V.V.; Fishman, G.I.; Epstein, J.A. Myocardial Notch Signaling Reprograms Cardiomyocytes to a Conduction-Like Phenotype. Circulation 2012, 126, 1058–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schram, G. , Pourrier, M., Melnyk, P., Nattel, S., 2002. Differential distribution of cardiac ion channel expression as a basis for regional specialization in electrical function. Circ Res 90, 939-950.
- van Setten, J.; Brody, J.A.; Jamshidi, Y.; Swenson, B.R.; Butler, A.M.; Campbell, H.; Del Greco, F.M.; Evans, D.S.; Gibson, Q.; Gudbjartsson, D.F.; et al. PR interval genome-wide association meta-analysis identifies 50 loci associated with atrial and atrioventricular electrical activity. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotoodehnia, N.; Isaacs, A.; Bakker, P.I.W.d.; Dörr, M.; Newton-Cheh, C.; Nolte, I.M.; van der Harst, P.; Müller, M.; Eijgelsheim, M.; Alonso, A.; et al. Common variants in 22 loci are associated with QRS duration and cardiac ventricular conduction. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 1068–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessadori, F.; van Weerd, J.H.; Burkhard, S.B.; Verkerk, A.O.; de Pater, E.; Boukens, B.J.; Vink, A.; Christoffels, V.M.; Bakkers, J. Identification and Functional Characterization of Cardiac Pacemaker Cells in Zebrafish. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Eif, V.W.W.; Stefanovic, S.; van Duijvenboden, K.; Bakker, M.; Wakker, V.; Vries, C.d.G.-D.; Zaffran, S.; Verkerk, A.O.; Boukens, B.J.; Christoffels, V.M. Transcriptome analysis of mouse and human sinoatrial node cells reveals a conserved genetic program. Development 2019, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Weerd, J.H. , Christoffels, V.M., 2016. The formation and function of the cardiac conduction system. Development 143, 197-210.
- Vedantham, V. , Galang, G., Evangelista, M., Deo, R.C., Srivastava, D. RNA Sequencing of Mouse Sinoatrial Node Reveals an Upstream Regulatory Role for Islet-1 in Cardiac Pacemaker Cells. Circ. Res. 2015, 116, 797–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verweij, N. , Mateo Leach, I., van den Boogaard, M., van Veldhuisen, D.J., Christoffels, V.M., LifeLines Cohort, S., Hillege, H.L., van Gilst, W.H., Barnett, P., de Boer, R.A., van der Harst, P., 2014. Genetic determinants of P wave duration and PR segment. Circ Cardiovasc Genet 7, 475-481.
- Vincentz, J.W.; Toolan, K.P.; Zhang, W.; Firulli, A.B. Hand factor ablation causes defective left ventricular chamber development and compromised adult cardiac function. PLOS Genet. 2017, 13, e1006922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Greene, S.B.; Bonilla-Claudio, M.; Tao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Bai, Y.; Huang, Z.; Black, B.L.; Wang, F.; Martin, J.F. Bmp Signaling Regulates Myocardial Differentiation from Cardiac Progenitors Through a MicroRNA-Mediated Mechanism. Dev. Cell 2010, 19, 903–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, P.; Jiang, L.; Wu, B.; Zhou, B. Control of sinus venous valve and sinoatrial node development by endocardial NOTCH1. Cardiovasc. Res. 2019, 116, 1473–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitcomb, J.; Gharibeh, L.; Nemer, M. From embryogenesis to adulthood: Critical role for GATA factors in heart development and function. IUBMB Life 2019, 72, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiese, C.; Grieskamp, T.; Airik, R.; Mommersteeg, M.T.M.; Gardiwal, A.; Vries, C.D.G.-D.; Schuster-Gossler, K.; Moorman, A.F.M.; Kispert, A.; Christoffels, V.M. Formation of the Sinus Node Head and Differentiation of Sinus Node Myocardium Are Independently Regulated by Tbx18 and Tbx3. Circ. Res. 2009, 104, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittig, J.G.; Münsterberg, A. The Chicken as a Model Organism to Study Heart Development. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2019, 12, a037218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Du, J.; Jing, X.; Yan, Y.; Deng, S.; Hao, Z.; She, Q. Bone morphogenetic protein 4 promotes the differentiation of Tbx18-positive epicardial progenitor cells to pacemaker-like cells. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 17, 2648–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Meng, Z.; Ruan, H.; Yin, W.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, T. Heart Development and Regeneration in Non-mammalian Model Organisms. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousefi, F.; Shabaninejad, Z.; Vakili, S.; Derakhshan, M.; Movahedpour, A.; Dabiri, H.; Ghasemi, Y.; Mahjoubin-Tehran, M.; Nikoozadeh, A.; Savardashtaki, A.; et al. TGF-β and WNT signaling pathways in cardiac fibrosis: non-coding RNAs come into focus. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020, 18, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Erhardt, S.; Ai, D.; Wang, J. Bmp Signaling Regulates Hand1 in a Dose-Dependent Manner during Heart Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Yang, H.; Shi, J.; Zhang, M.; Yang, S.; Wang, N.; Sun, R.; Wang, Z.; Fei, J. Fate Tracing of Isl1+Cells in Adult Mouse Hearts under Physiological and Exercise Conditions. Int. J. Sports Med. 2019, 40, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




