Submitted:
16 June 2023
Posted:
19 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
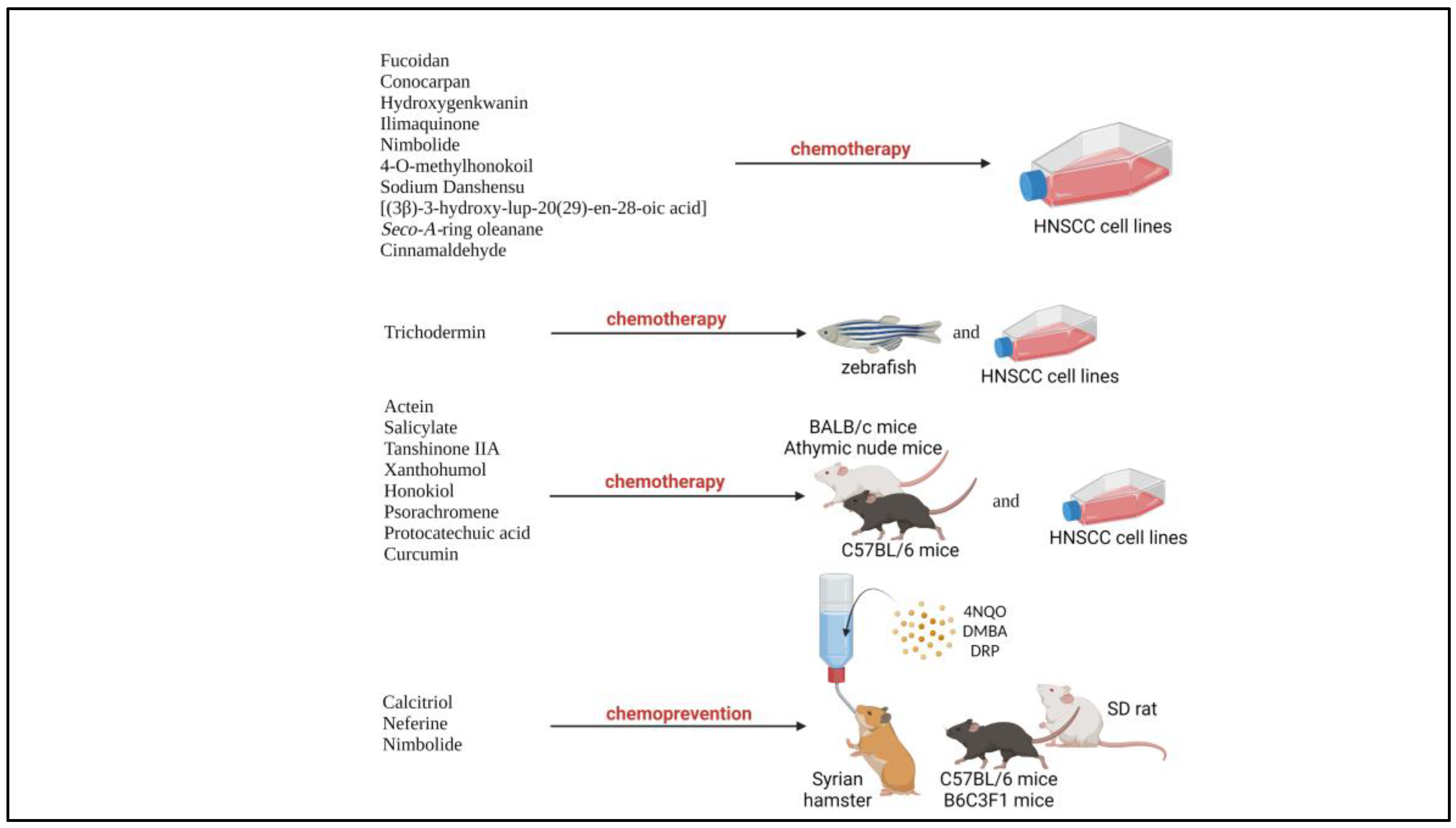
1. Introduction
2. Chemotherapeutic Properties of Natural Products Against Essential Pathway for HNSCC
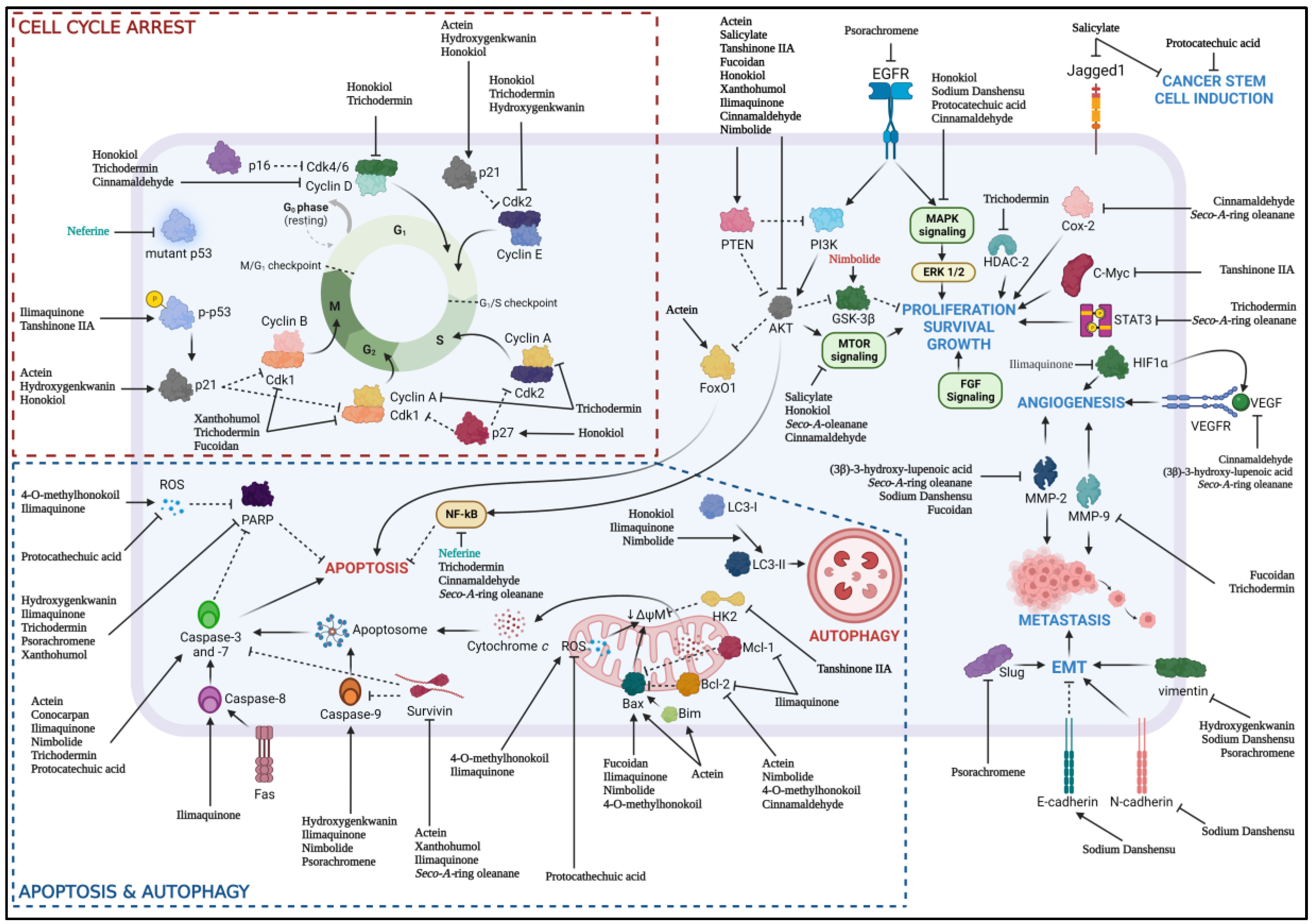
2.1. PI3K/Akt/mTOR Pathway
2.2. MAPK/ERK Pathway
2.3. NF- κB and STAT3 Transcription Factors
2.4. LC3-Dependent Autophagy
2.5. Bcl-2/Bax Signaling
2.6. Cell Cycle Arrest by Cyclin and CDK Signaling Pathway
2.7. Potential Natural Products as Therapeutic Agent for HNSCC
3. Chemoprevention Properties of Natural Products Against HNSCC Oral Carcinogenesis Mechanism
4. Limitation and Future Direction
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johnson, D.E.; Burtness, B.; Leemans, C.R.; Lui, V.W.Y.; Bauman, J.E.; Grandis, J.R. Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2020, 6. [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA. Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [CrossRef]
- Magnes, T.; Wagner, S.M.; Melchardt, T.; Weiss, L.; Rinnerthaler, G.; Huemer, F.; Kopp, M.; Gampenrieder, S.P.; Mayrbäurl, B.; Füreder, T.; et al. Postoperative Chemoradiotherapy with Cisplatin Is Superior to Radioimmunotherapy with Cetuximab and Radiotherapy Alone: Analysis of the Austrian Head and Neck Cancer Registry of the AGMT. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2021, 133, 1131–1136. [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2022. CA. Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 7–33. [CrossRef]
- Bonner, J.A.; Harari, P.M.; Giralt, J.; Cohen, R.B.; Jones, C.U.; Sur, R.K.; Raben, D.; Baselga, J.; Spencer, S.A.; Zhu, J.; et al. Radiotherapy plus Cetuximab for Locoregionally Advanced Head and Neck Cancer: 5-Year Survival Data from a Phase 3 Randomised Trial, and Relation between Cetuximab-Induced Rash and Survival. Lancet Oncol. 2010, 11, 21–28. [CrossRef]
- Ferris, R.L.; Blumenschein, G.; Fayette, J.; Guigay, J.; Colevas, A.D.; Licitra, L.; Harrington, K.; Kasper, S.; Vokes, E.E.; Even, C.; et al. Nivolumab for Recurrent Squamous-Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1856–1867. [CrossRef]
- Talamini, R.; Bosetti, C.; La Vecchia, C.; Dal Maso, L.; Levi, F.; Bidoli, E.; Negri, E.; Pasche, C.; Vaccarella, S.; Barzan, L.; et al. Combined Effect of Tobacco and Alcohol on Laryngeal Cancer Risk: A Case-Control Study. Cancer Causes Control 2002, 13, 957–964. [CrossRef]
- Lewin, F.; Norell, S.E.; Johansson, H.; Gustavsson, P.; Wennerberg, J.; Biörklund, A.; Rutqvist, L.E. Smoking Tobacco, Oral Snuff, and Alcohol in the Etiology of Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck A Population-Based Case-Referent Study in Sweden. Cancer 1998, 82, 1367–1375. [CrossRef]
- Hansson, B.G.; Rosenquist, K.; Antonsson, A.; Wennerberg, J.; Schildt, E.B.; Bladström, A.; Andersson, G. Strong Association between Infection with Human Papillomavirus and Oral and Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Population-Based Case-Control Study in Southern Sweden. Acta Otolaryngol. 2005, 125, 1337–1344. [CrossRef]
- Van Wyk, C.W.; Stander, I.; Padayachee, A.; Grobler-Rabie, A.F. The Areca Nut Chewing Habit and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma in South African Indians. A Retrospective Study. South African Med. J. 1993, 83, 425–429.
- Haddad, R.I.; Shin, D.M. Recent Advances in Head and Neck Cancer Reconstruction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 1143–1154. [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, N.; Yadav, J.; Chhakara, S.; Janjua, D.; Tripathi, T.; Chaudhary, A.; Chhokar, A.; Thakur, K.; Singh, T.; Bharti, A.C. Phytochemicals as Potential Chemopreventive and Chemotherapeutic Agents for Emerging Human Papillomavirus–Driven Head and Neck Cancer: Current Evidence and Future Prospects. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12. [CrossRef]
- Posner, M.R.; Hershock, D.M.; Blajman, C.R.; Mickiewicz, E.; Winquist, E.; Gorbounova, V.; Tjulandin, S.; Shin, D.M.; Cullen, K.; Ervin, T.J.; et al. Cisplatin and Fluorouracil Alone or with Docetaxel in Head and Neck Cancer Marshall. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 1705–1715. [CrossRef]
- Hashim, D.; Genden, E.; Posner, M.; Hashibe, M.; Boffetta, P. Head and Neck Cancer Prevention: From Primary Prevention to Impact of Clinicians on Reducing Burden. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 744–756. [CrossRef]
- Brockstein, B.; Haraf, D.J.; Rademaker, A.W.; Kies, M.S.; Stenson, K.M.; Rosen, F.; Mittal, B.B.; Pelzer, H.; Fung, B.B.; Witt, M.E.; et al. Patterns of Failure, Prognostic Factors and Survival in Locoregionally Advanced Head and Neck Cancer Treated with Concomitant Chemoradiotherapy: A 9-Year, 337-Patient, Multi-Institutional Experience. Ann. Oncol. 2004, 15, 1179–1186. [CrossRef]
- Bonner, J.A.; Harari, P.M.; Giralt, J.; Azarnia, N.; Shin, D.M.; Cohen, R.B.; Jones, C.U.; Sur, R.; Raben, D.; Jassem, J.; et al. Results of Radiotherapy plus Cetuximab for Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 567–578. [CrossRef]
- Naruse, T.; Yanamoto, S.; Matsushita, Y.; Sakamoto, Y.; Morishita, K.; Ohba, S.; Shiraishi, T.; Yamada, S.-I.; Asahina, I.; Umeda, M. Cetuximab for the Treatment of Locally Advanced and Recurrent/Metastatic Oral Cancer: An Investigation of Distant Metastasis. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 5, 246–252. [CrossRef]
- Sok, J.C.; Coppelli, F.M.; Thomas, S.M.; Lango, M.N.; Xi, S.; Hunt, J.L.; Freilino, M.L.; Graner, M.W.; Wikstrand, C.J.; Bigner, D.D.; et al. Mutant Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFRvIII) Contributes to Head and Neck Cancer Growth and Resistance to EGFR Targeting. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 5064–5073. [CrossRef]
- US Food and Drug Administration FDA Approves Pembrolizumab for First-Line Treatment of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-approves-pembrolizumab-first-line-treatment-head-and-neck-squamous-cell-carcinoma.
- US Food and Drug Administration Nivolumab for SCCHN. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/nivolumab-scchn.
- dos Santos, L. V.; Abrahão, C.M.; William, W.N. Overcoming Resistance to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 1–16. [CrossRef]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural Products as Sources of New Drugs over the Nearly Four Decades from 01/1981 to 09/2019. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 770–803. [CrossRef]
- National Cancer Institute Dictionary of Cancer Terms. Available online: https://www.cancer.gov/publications/dictionaries/cancer-terms (accessed on 26 September 2022).
- Wang, T.H.; Leu, Y.L.; Chen, C.C.; Shieh, T.M.; Lian, J.H.; Chen, C.Y. Psorachromene Suppresses Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Progression by Inhibiting Long Non-Coding RNA GAS5 Mediated Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Vincent-Chong, V.K.; DeJong, H.; Attwood, K.; Hershberger, P.A.; Seshadri, M. Preclinical Prevention Trial of Calcitriol: Impact of Stage of Intervention and Duration of Treatment on Oral Carcinogenesis. Neoplasia (United States) 2019, 21, 376–388. [CrossRef]
- Hashem, S.; Ali, T.A.; Akhtar, S.; Nisar, S.; Sageena, G.; Ali, S.; Al-Mannai, S.; Therachiyil, L.; Mir, R.; Elfaki, I.; et al. Targeting Cancer Signaling Pathways by Natural Products: Exploring Promising Anti-Cancer Agents. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 150, 113054. [CrossRef]
- Sever, R.; Brugge, J.S. Signal Transduction in Cancer. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2015, 5. [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Vega, F.; Mina, M.; Armenia Pathways, Oncogenic Signaling Cancer, The Atlas, Genome. 2019, 173, 321–337. [CrossRef]
- Crooker, K.; Aliani, R.; Ananth, M.; Arnold, L.; Anant, S.; Thomas, S.M. A Review of Promising Natural Chemopreventive Agents for Head and Neck Cancer; 2018; Vol. 11; ISBN 1913588467.
- Rahman, M.A.; Amin, A.R.M.R.; Shin, D.M. Chemopreventive Potential of Natural Compounds in Head and Neck Cancer. Nutr. Cancer 2010, 62, 973–987. [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.M.; Khuri, F.R.; Murphy, B.; Garden, A.S.; Clayman, G.; Francisco, M.; Liu, D.; Glisson, B.S.; Ginsberg, L.; Papadimitrakopoulou, V.; et al. Combined Interferon-Alfa, 13-Cis-Retinoic Acid, and Alpha-Tocopherol in Locally Advanced Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Novel Bioadjuvant Phase II Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2001, 19, 3010–3017. [CrossRef]
- Papadimitrakopoulou, V.A.; Lee, J.J.; William, W.N.; Martin, J.W.; Thomas, M.; Kim, E.S.; Khuri, F.R.; Shin, D.M.; Feng, L.; Waun, K.H.; et al. Randomized Trial of 13-Cis Retinoic Acid Compared with Retinyl Palmitate with or without Beta-Carotene in Oral Premalignancy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 599–604. [CrossRef]
- Tsao, A.S.; Liu, D.; Martin, J.; Tang, X.M.; Lee, J.J.; El-Naggar, A.K.; Wistuba, I.; Culotta, K.S.; Mao, L.; Gillenwater, A.; et al. Phase II Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial of Green Tea Extract in Patients with High-Risk Oral Premalignant Lesions. Cancer Prev. Res. 2009, 2, 931–941. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.L.; Hsu, C.H.; Lin, J.K.; Hse, M.W.; Ho, Y.F.; Shen, T.S.; Ko, J.Y.; Lin, J.T.; Lin, B.R.; Wu, M.S.; et al. Phase I Clinical Trial of Curcumin, a Chemopreventive Agent, in Patients with High-Risk or Pre-Malignant Lesions. Anticancer Res. 2001, 21, 2895–2900.
- Molinolo, A.A.; Hewitt, S.M.; Amornphimoltham, P.; Keelawat, S.; Rangdaeng, S.; García, A.M.; Raimondi, A.R.; Jufe, R.; Itoiz, M.; Gao, Y.; et al. Dissecting the Akt/Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Signaling Network: Emerging Results from the Head and Neck Cancer Tissue Array Initiative. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 4964–4973. [CrossRef]
- Freudlsperger, C.; Horn, D.; Weißfuß, S.; Weichert, W.; Weber, K.J.; Saure, D.; Sharma, S.; Dyckhoff, G.; Grabe, N.; Plinkert, P.; et al. Phosphorylation of AKT(Ser473) Serves as an Independent Prognostic Marker for Radiosensitivity in Advanced Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, 2775–2785. [CrossRef]
- Zumsteg, Z.S.; Morse, N.; Krigsfeld, G.; Gupta, G.; Higginson, D.S.; Lee, N.Y.; Morris, L.; Ganly, I.; Shiao, S.L.; Powell, S.N.; et al. Taselisib (GDC-0032), a Potent β-Sparing Small Molecule Inhibitor of PI3K, Radiosensitizes Head and Neck Squamous Carcinomas Containing Activating PIK3CA Alterations. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 2009–2019. [CrossRef]
- Iwase, M.; Yoshiba, S.; Uchid, M.; Takaoka, S.; Kurihara, Y.; Ito, D.; Hatori, M.; Shintani, S. Enhanced Susceptibility to Apoptosis of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells Subjected to Combined Treatment with Anticancer Drugs and Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase Inhibitors. Int. J. Oncol. 2007, 31, 1141–1147.
- Cantley, L.C. The Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase Pathway. Science (80-. ). 2002, 296, 1655–1657. [CrossRef]
- Sarbassov, D.D.; Guertin, D.A.; Ali, S.M.; Sabatini, D.M. Phosphorylation and Regulation of Akt/PKB by the Rictor-MTOR Complex. Science (80-. ). 2005, 307, 1098–1101. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zhang, Z.; Dai, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Ma, H. Actein Antagonizes Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Proliferation through Activating FoxO1. Pharmacology 2021, 106, 551–563. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, F.; Zeng, Y.; Zhu, X.; Peng, L.; Zhang, L.; Gu, J.; Han, H.; Yi, X.; Shi, J. Salicylate Sensitizes Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma to Chemotherapy through Targeting MTOR Pathway. Oral Dis. 2020, 26, 1131–1140. [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Gao, F.; Zhao, Q.; Zuo, H.; Liu, W.; Li, W. Tanshinone IIA Inhibits Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma via Reducing Akt-c-Myc Signaling-Mediated Aerobic Glycolysis. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11. [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Gao, F.; Yu, X.; Zhao, Q.; Zhou, L.; Liu, W.; Li, W. Promotion of Ubiquitination-Dependent Survivin Destruction Contributes to Xanthohumol-Mediated Tumor Suppression and Overcomes Radioresistance in Human Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 1–15. [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.J.; Kuo, C.H.; Chen, S.H.; Lin, C.Y.; Lee, Y.R. Honokiol Inhibits in Vitro and in Vivo Growth of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma through Induction of Apoptosis, Cell Cycle Arrest and Autophagy. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 1894–1908. [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.W.; Bai, L.Y.; Su, J.H.; Chiu, C.F.; Lin, W.Y.; Huang, W.T.; Shih, M.C.; Huang, Y.T.; Hu, J.L.; Weng, J.R. Ilimaquinone Induces Apoptosis and Autophagy in Human Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 1–11. [CrossRef]
- Sophia, J.; Kowshik, J.; Dwivedi, A.; Bhutia, S.K.; Manavathi, B.; Mishra, R.; Nagini, S. Nimbolide, a Neem Limonoid Inhibits Cytoprotective Autophagy to Activate Apoptosis via Modulation of the PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β Signalling Pathway in Oral Cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9. [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, S.; Bhadana, K.; Singh, B.; Rawat, M.; Mohammad, T.; Al-Keridis, L.A.; Alshammari, N.; Hassan, M.I.; Das, S.N. Cinnamomum Zeylanicum Extract and Its Bioactive Component Cinnamaldehyde Show Anti-Tumor Effects via Inhibition of Multiple Cellular Pathways. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1–14. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Gao, L.; Ren, W.; Li, S.; Zhang, D.; Song, X.; Zhao, C.; Zhi, K. Fucoidan Affects Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cell Functions in Vitro by Regulating FLNA-Derived Circular RNA. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2020, 1462, 65–78. [CrossRef]
- Aswathy, M.; Banik, K.; Parama, D.; Sasikumar, P.; Harsha, C.; Joseph, A.G.; Sherin, D.R.; Thanathu, M.K.; Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Vasu, R.K. Exploring the Cytotoxic Effects of the Extracts and Bioactive Triterpenoids from Dillenia Indica against Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Scientific Interpretation and Validation of Indigenous Knowledge. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2021, 4, 834–847. [CrossRef]
- Schulz, L.; Pries, R.; Lanka, A.S.; Drenckhan, M.; Rades, D.; Wollenberg, B. Inhibition of GSK3α/β Impairs the Progression of HNSCC. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 27630–27644. [CrossRef]
- Ugolkov, A. V.; Matsangou, M.; Taxter, T.J.; O’halloran, T. V.; Cryns, V.L.; Giles, F.J.; Mazar, A.P. Aberrant Expression of Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3β in Human Breast and Head and Neck Cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 6437–6444. [CrossRef]
- Marconi, G.D.; Della Rocca, Y.; Fonticoli, L.; Melfi, F.; Rajan, T.S.; Carradori, S.; Pizzicannella, J.; Trubiani, O.; Diomede, F. C-Myc Expression in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Molecular Mechanisms in Cell Survival and Cancer Progression. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1–14. [CrossRef]
- Bancroft, C.C.; Chen, Z.; Dong, G.; Sunwoo, J.B.; Yeh, N.; Park, C.; Van Waes, C. Coexpression of Proangiogenic Factors IL-8 and VEGF by Human Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Involves Coactivation by MEK-MAPK and IKK-NF-ΚB Signal Pathways. Clin. Cancer Res. 2001, 7, 435–442.
- Kumar, V.B.; Lin, S.H.; Mahalakshmi, B.; Lo, Y.S.; Lin, C.C.; Chuang, Y.C.; Hsieh, M.J.; Chen, M.K. Sodium Danshensu Inhibits Oral Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion by Modulating P38 Signaling Pathway. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne). 2020, 11, 1–10. [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Cao, L.; Yang, C.; Liu, T.; Zhao, H.; Luo, X.; Chen, Q. Protocatechuic Acid-Based Supramolecular Hydrogel Targets SerpinB9 to Achieve Local Chemotherapy for OSCC. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Gkouveris, I.; Nikitakis, N.; Karanikou, M.; Rassidakis, G.; Sklavounou, A. JNK1/2 Expression and Modulation of STAT3 Signaling in Oral Cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 12, 699–706. [CrossRef]
- O-charoenrat, P.; Rhys-Evans, P.H.; Eccles, S.A. Expression of Matrix Metalloproteinases and Their Inhibitors Correlates With Invasion and Metastasis in Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2001, 127, 813–820.
- Carmeliet, P. VEGF as a Key Mediator of Angiogenesis in Cancer. Oncology 2005, 69, 4–10. [CrossRef]
- Pepper, M.S.; Ferrara, N.; Orci, L.; Montesano, R. Potent Synergism between Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor in the Induction of Angiogenesis in Vitro. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1992, 189, 824–831.
- Zhang, Y.H.; Wei, W.; Xu, H.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wu, W.X. Inducing Effects of Hepatocyte Growth Factor on the Expression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Human Colorectal Carcinoma Cells through MEK and PI3K Signaling Pathways. Chin. Med. J. (Engl). 2007, 120, 743–748. [CrossRef]
- Lun, M.; Zhang, P.L.; Pellitteri, P.K.; Law, A.; Kennedy, T.L.; Brown, R.E. Nuclear Factor-KappaB Pathway as a Therapeutic Target in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Pharmaceutical and Molecular Validation in Human Cell Lines Using Velcade and SiRNA/NF-ΚB. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2005, 35, 251–258.
- Oeckinghaus, A.; Ghosh, S. The NF-ΚB Family of Transcription Factors and Its Regulation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1–15.
- Wang, J.; Hu, Y.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Alahmadi, T.A.; Ali Alharbi, S.; Zhuang, Z.; Wu, F. Chemomodulatory Effect of Neferine on DMBA-Induced Squamous Cell Carcinogenesis: Biochemical and Molecular Approach. Environ. Toxicol. 2021, 36, 460–471. [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Lo, Y.; Lin, C.; Lee, T.; Leung, W.; Wang, S.; Lin, I.; Lin, M.; Lee, C. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy Trichodermin Inhibits the Growth of Oral Cancer through Apoptosis-Induced Mitochondrial Dysfunction and HDAC-2-Mediated Signaling. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 153, 113351. [CrossRef]
- Ihle, J.N. The Stat Family in Cytokine Signaling. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2001, 13, 211–217. [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.S.; Zhou, X.; Huang, Y.Y.; Kong, L.P.; Mei, M.; Guo, W.Y.; Zhao, M.H.; Ren, Y.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, L. Targeting STAT3/MiR-21 Axis Inhibits Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition via Regulating CDK5 in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 1–11. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Ren, Y.; Liu, A.; Han, L.; Zhang, K.; Li, S.; Li, P.; Li, P.; Kang, C.; Wang, X.; et al. STAT3 Inhibitor WP1066 Attenuates MiRNA-21 to Suppress Human Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Growth in Vitro and in Vivo. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 31, 2173–2180. [CrossRef]
- Riebe, C.; Pries, R.; Schroeder, K.N.; Wollenberg, B. Phosphorylation of STAT3 in Head and Neck Cancer Requires P38 MAPKinase, Whereas Phosphorylation of STAT1 Occurs via a Different Signaling Pathway. Anticancer Res. 2011, 31, 3819–3825.
- Zhao, C.; Yang, L.; Zhou, F.; Yu, Y.; Du, X.; Xiang, Y.; Li, C.; Huang, X.; Xie, C.; Liu, Z.; et al. Feedback Activation of EGFR Is the Main Cause for STAT3 Inhibition-Irresponsiveness in Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Oncogene 2020, 39, 3997–4013. [CrossRef]
- Ning, Y.; Cui, Y.; Li, X.; Cao, X.; Chen, A.; Xu, C.; Cao, J.; Luo, X. Co-Culture of Ovarian Cancer Stem-like Cells with Macrophages Induced SKOV3 Cells Stemness via IL-8/STAT3 Signaling. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 103, 262–271. [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liao, D.; Chen, C.; Liu, Y.; Chuang, T.H.; Xiang, R.; Markowitz, D.; Reisfeld, R.A.; Luo, Y. Tumor-Associated Macrophages Regulate Murine Breast Cancer Stem Cells through a Novel Paracrine Egfr/Stat3/Sox-2 Signaling Pathway. Stem Cells 2013, 31, 248–258. [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.Y.; Huang, S.Y.; Sheu, J.J.C.; Roth, M.M.; Chou, I.T.; Lien, C.H.; Lee, M.F.; Huang, C.Y. Transcription Factor HBP1 Is a Direct Anti-Cancer Target of Transcription Factor FOXO1 in Invasive Oral Cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 14537–14548. [CrossRef]
- Roh, J.L.; Kang, S.K.; Minn, I.; Califano, J.A.; Sidransky, D.; Koch, W.M. P53-Reactivating Small Molecules Induce Apoptosis and Enhance Chemotherapeutic Cytotoxicity in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2011, 47, 8–15. [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.; Tiwari, R.P.; Mulherker, R.; Sah, N.K.; Prasad, G.B.; Shrivastava, B.R.; Bisen, P.S. Detection of Survivin and P53 in Human Oral Cancer: Correlation with Clinicopathological Findings. Head Neck 2009, 31, 1039–1048. [CrossRef]
- The Cancer Genome Atlas Network Comprehensive Genomic Characterization of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Nature 2015, 517, 576–582. [CrossRef]
- Tanida, I.; Ueno, T.; Kominami, E. LC3 and Autophagy. Methods Mol. Biol. 2008, 445, 77–88. [CrossRef]
- Kabeya, Y.; Mizushima, N.; Ueno, T.; Yamamoto, A.; Kirisako, T.; Noda, T.; Kominami, E.; Ohsumi, Y.; Yoshimori, T. LC3, a Mammalian Homologue of Yeast Apg8p, Is Localized in Autophagosome Membranes after Processing. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 5720–5728. [CrossRef]
- Yun, C.W.; Lee, S.H. The Roles of Autophagy in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1–18. [CrossRef]
- Khan, T.; Relitti, N.; Brindisi, M.; Magnano, S.; Zisterer, D.; Gemma, S.; Butini, S.; Campiani, G. Autophagy Modulators for the Treatment of Oral and Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Med. Res. Rev. 2020, 40, 1002–1060. [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Nam, H.Y.; Kang, H.B.; Lee, W.H.; Lee, G.H.; Sung, G.J.; Han, M.W.; Cho, K.J.; Chang, E.J.; Choi, K.C.; et al. Epigenetic Regulation of P62/SQSTM1 Overcomes the Radioresistance of Head and Neck Cancer Cells via Autophagy-Dependent Senescence Induction. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12. [CrossRef]
- Eisenberg-Lerner, A.; Kimchi, A. The Paradox of Autophagy and Its Implication in Cancer Etiology and Therapy. Cell D 2009, 14, 376–391. [CrossRef]
- Garcia-medina, R.; Gounon, P.; Chiche, J.; Pouysse, J.; Mazure, N.M. Hypoxia-Induced Autophagy Is Mediated through Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Induction of BNIP3 and BNIP3L via Their BH3 Domains †. 2009, 29, 2570–2581. [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Wei, S.; Gan, B.; Peng, X.; Zou, W.; Guan, J. Suppression of Autophagy by FIP200 Deletion Inhibits Mammary Tumorigenesis. 2011, 1510–1527. [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.S.; Vats, S.; Chia, A.Y.; Zea, T.; Shuo, T.; Mei, D.; Ong, S.; Arfuso, F.; Yap, C.T.; Cher, B.; et al. Dual Role of Autophagy in Hallmarks of Cancer. Oncogene 2018, 1142–1158. [CrossRef]
- Muz, B.; Azab, A.K. The Role of Hypoxia in Cancer Progression , Angiogenesis , Metastasis , and Resistance to Therapy. 2015, 83–92.
- Oltval, Z.N.; Milliman, C.L.; Korsmeyer, S.J. Bcl-2 Heterodimerizes in Vivo with a Conserved Homolog, Bax, That Accelerates Programed Cell Death. Cell 1993, 74, 609–619. [CrossRef]
- Hockenbery, D.; Nuñez, G.; Milliman, C.; Schreiber, R.D.; Korsmeyer, S.J. Bcl-2 Is an Inner Mitochondrial Membrane Protein That Blocks Programmed Cell Death. Nature 1990, 348, 334–336.
- Loro, L.L.; Vintermyr, O.K.; Liavaag, P.G.; Jonsson, R.; Johannessen, A.C. Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Is Associated with Decreased Bcl-2/Bax Expression Ratio and Increased Apoptosis. Hum. Pathol. 1999, 30, 1097–1105. [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Henzel, W.J.; Liu, X. Apaf-1, a Human Protein Homologous to C. Elegans CED-4, Participates In. Cell 1997, 90, 405–413.
- Xiao, S.; Chen, F.; Gao, C. Antitumor Activity of 4-O-Methylhonokiol in Human Oral Cancer Cells Is Mediated via ROS Generation, Disruption of Mitochondrial Potential, Cell Cycle Arrest and Modulation of Bcl-2/Bax Proteins. J. B.U.ON. 2017, 22, 1577–1581.
- Liu, J.; Uematsu, H.; Tsuchida, N.; Ikeda, M.A. Essential Role of Caspase-8 in P53/P73-Dependent Apoptosis Induced by Etoposide in Head and Neck Carcinoma Cells. Mol. Cancer 2011, 10, 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Uematsu, H.; Tsuchida, N.; Ikeda, M.A. Association of Caspase-8 Mutation with Chemoresistance to Cisplatin in HOC313 Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 390, 989–994. [CrossRef]
- Coleman, S.C.; Stewart, Z.A.; Day, T.A.; Netterville, J.L.; Burkey, B.B.; Pietenpol, J.A. Analysis of Cell-Cycle Checkpoint Pathways in Head and Neck Cancer Cell Lines: Implications for Therapeutic Strategies. Arch. Otolaryngol. - Head Neck Surg. 2002, 128, 167–176. [CrossRef]
- Norbury, C.; Nurse, P. Animal Cell Cycles and Their Control. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1992, 61, 441–470. [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Connolly, T.; Futcher, B.; Beach, D. Human D-Type Cyclin. Cell 1991, 65, 691–699. [CrossRef]
- Matsushime, H.; Ewen, M.E.; Strom, D.K.; Kato, J.Y.; Hanks, S.K.; Roussel, M.F.; Sherr, C.J. Identification and Properties of an Atypical Catalytic Subunit (P34PSK-J3/Cdk4) for Mammalian D Type G1 Cyclins. Cell 1992, 71, 323–334. [CrossRef]
- Lea, N.C.; Orr, S.J.; Stoeber, K.; Williams, G.H.; Lam, E.W.-F.; Ibrahim, M.A.A.; Mufti, G.J.; Thomas, N.S.B. Commitment Point during G 0 →G 1 That Controls Entry into the Cell Cycle . Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 23, 2351–2361. [CrossRef]
- Duronio, R.J.; Brook, A.; Dyson, N.; O’Farrell, P.H. E2F-Induced S Phase Requires Cyclin E. Genes Dev. 1996, 10, 2505–2513. [CrossRef]
- Oakes, V.; Wang, W.; Harrington, B.; Lee, W.J.; Beamish, H.; Chia, K.M.; Pinder, A.; Goto, H.; Inagaki, M.; Pavey, S.; et al. Cyclin A/Cdk2 Regulates Cdh1 and Claspin during Late S/G2 Phase of the Cell Cycle. Cell Cycle 2014, 13, 3302–3311. [CrossRef]
- Vigneron, S.; Sundermann, L.; Labbé, J.C.; Pintard, L.; Radulescu, O.; Castro, A.; Lorca, T. Cyclin A-Cdk1-Dependent Phosphorylation of Bora Is the Triggering Factor Promoting Mitotic Entry. Dev. Cell 2018, 45, 637-650.e7. [CrossRef]
- Gavet, O.; Pines, J. Activation of Cyclin B1-Cdk1 Synchronizes Events in the Nucleus and the Cytoplasm at Mitosis. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 189, 247–259. [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhou, P.; Xu, K.; Chen, T.; Jiao, J.; Wei, H.; Yang, X.; Xu, W.; Wan, W.; Xiao, J. Metformin Induces Cell Cycle Arrest, Apoptosis and Autophagy through ROS/JNK Signaling Pathway in Human Osteosarcoma. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 74–84. [CrossRef]
- McConnell, B.B.; Gregory, F.J.; Stott, F.J.; Hara, E.; Peters, G. Induced Expression of P16 INK4a Inhibits Both CDK4- and CDK2-Associated Kinase Activity by Reassortment of Cyclin-CDK-Inhibitor Complexes . Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19, 1981–1989. [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.Q.; Livingston, D.M.; Kaelin, W.G.; Adams, P.D. Deregulated Transcription Factor E2F-1 Expression Leads to S-Phase Entry and P53-Mediated Apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1994, 91, 10918–10922. [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.C.; Lee, P.C.; Wang, J.J.; Hsu, Y.C. Anticancer Effect and Mechanism of Hydroxygenkwanin in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1–10. [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, A.C.C. da; de Queiroz, L.N.; Sales Felisberto, J.; Jessé Ramos, Y.; Mesquita Marques, A.; Wermelinger, G.F.; Pontes, B.; de Lima Moreira, D.; Robbs, B.K. Cytotoxic Effect of Pure Compounds from Piper Rivinoides Kunth against Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Nat. Prod. Res. 2021, 35, 6163–6167. [CrossRef]
- de Campos, P.S.; Matte, B.F.; Diel, L.F.; Jesus, L.H.; Bernardi, L.; Alves, A.M.; Rados, P.V.; Lamers, M.L. Low Doses of Curcuma Longa Modulates Cell Migration and Cell–Cell Adhesion. Phyther. Res. 2017, 31, 1433–1440. [CrossRef]
- Chourasia, N.R.; Borle, R.M.; Vastani, A. Concomitant Association of Oral Submucous Fibrosis and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Incidence of Malignant Transformation of Oral Submucous Fibrosis in a Population of Central India: A Retrospective Study. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. 2015, 14, 902–906. [CrossRef]
- Evren, I.; Brouns, E.R.; Wils, L.J.; Poell, J.B.; Peeters, C.F.W.; Brakenhoff, R.H.; Bloemena, E.; de Visscher, J.G.A.M. Annual Malignant Transformation Rate of Oral Leukoplakia Remains Consistent: A Long-Term Follow-up Study. Oral Oncol. 2020, 110, 105014. [CrossRef]
- Iocca, O.; Sollecito, T.P.; Alawi, F.; Weinstein, G.S.; Newman, J.G.; De Virgilio, A.; Di Maio, P.; Spriano, G.; Pardiñas López, S.; Shanti, R.M. Potentially Malignant Disorders of the Oral Cavity and Oral Dysplasia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Malignant Transformation Rate by Subtype. Head Neck 2020, 42, 539–555. [CrossRef]
- Lodi, G.; Franchini, R.; Warnakulasuriya, S.; Varoni, E.M.; Sardella, A.; Kerr, A.R.; Carrassi, A.; MacDonald, L.C.; Worthington, H. V.; Mauleffinch, L.F. Interventions for Treating Oral Leukoplakia to Prevent Oral Cancer (Review). Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016. [CrossRef]
- Papadimitrakopoulou, V.A.; William, W.N.; Dannenberg, A.J.; Lippman, S.M.; Lee, J.J.; Ondrey, F.G.; Peterson, D.E.; Feng, L.; Atwell, A.; El-Naggar, A.K.; et al. Pilot Randomized Phase II Study of Celecoxib in Oral Premalignant Lesions. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 2095–2101. [CrossRef]
- William, W.N.; Papadimitrakopoulou, V.; Lee, J.J.; Mao, L.; Cohen, E.E.W.; Lin, H.Y.; Gillenwater, A.M.; Martin, J.W.; Lingen, M.W.; Boyle, J.O.; et al. Erlotinib and the Risk of Oral Cancer the Erlotinib Prevention of Oral Cancer (EPOC) Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2016, 2, 209–216. [CrossRef]
- Gutkind, J.S.; Molinolo, A.A.; Wu, X.; Wang, Z.; Nachmanson, D.; Harismendy, O.; Alexandrov, L.B.; Wuertz, B.R.; Ondrey, F.G.; Laronde, D.; et al. Inhibition of MTOR Signaling and Clinical Activity of Metformin in Oral Premalignant Lesions. JCI Insight 2021, 6. [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Lyu, Y.; Yang, Y.G.; Hu, Z. Humanized Rodent Models for Cancer Research. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1–11. [CrossRef]
- Bouaoud, J.; De Souza, G.; Darido, C.; Tortereau, A.; Elkabets, M.; Bertolus, C.; Saintigny, P. The 4-NQO Mouse Model: An Update on a Well-Established in Vivo Model of Oral Carcinogenesis. Methods Cell Biol. 2021, 163, 197–229. [CrossRef]
- Schoop, R.A.L.; Noteborn, M.H.M.; Baatenburg De Jong, R.J. A Mouse Model for Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Mol. Histol. 2009, 40, 177–181. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Xia, Q.; Tian, Z.; Guan, X. Chemopreventive Effect of Modified Zengshengping on Oral Cancer in a Hamster Model and Assessment of Its Effect on Liver. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 255, 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Zhu, P.F.; Liu, H.; Li, X.C.; Zhu, Y.Y.; Liu, Y.Y.; Shi, X.L.; Chen, W. Di; Liu, Y.P.; Zhao, Y. li; et al. Discovery of Potent Immune-Modulating Molecule Taccaoside A against Cancers from Structures-Active Relationships of Natural Steroidal Saponins. Phytomedicine 2022, 104, 154335. [CrossRef]
- Cattaneo, C.M.; Dijkstra, K.K.; Fanchi, L.F.; Kelderman, S.; Kaing, S.; van Rooij, N.; van den Brink, S.; Schumacher, T.N.; Voest, E.E. Tumor Organoid–T-Cell Coculture Systems. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 15–39. [CrossRef]
- Neal, J.T.; Li, X.; Zhu, J.; Giangarra, V.; Grzeskowiak, C.L.; Ju, J.; Liu, I.H.; Chiou, S.H.; Salahudeen, A.A.; Smith, A.R.; et al. Organoid Modeling of the Tumor Immune Microenvironment. Cell 2018, 175, 1972-1988.e16. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Van der Jeught, K.; Fang, Y.; Yu, T.; Li, Y.; Ao, Z.; Liu, S.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Y.; Eyvani, H.; et al. An Organoid-Based Screen for Epigenetic Inhibitors That Stimulate Antigen Presentation and Potentiate T-Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 5, 1320–1335. [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Vincent-chong, V.K.; Dejong, H.; Hershberger, P.A.; Seshadri, M.; Park, R.; Cancer, C.; Park, R.; Cancer, C.; Prosthetics, M.; et al. Impact of Dietary Vitamin D on Initiation and Progression of Oral Cancer. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 2020, 199, 1–23. [CrossRef]
- Choudhari, A.S.; Mandave, P.C.; Deshpande, M.; Ranjekar, P.; Prakash, O. Phytochemicals in Cancer Treatment: From Preclinical Studies to Clinical Practice. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 10, 1–17. [CrossRef]
| No | Author | PMID | Natural product | Preclinical Model (cell lines) |
Findings | Pathway related |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Zhang et al. [49] |
31495936 | Fucoidan | In vitro (SCC15, SCC25) |
|
Akt Bax/Bcl-2 |
| 2 | Fonseca et al. [107] |
33078660 | Conocarpan | In vitro (SCC9, SCC4, SCC25) |
|
Caspase |
| 3 | Huang et al. [106] |
31620368 | Hydroxygenkwanin | In vitro (SAS & OECM1) |
|
Caspase |
| 4 | Lin et al. [46] |
32825464 | Ilimaquinone | In vitro (SCC4, SCC2095) |
|
Akt Caspase Bax/Bcl-2 |
| 5 | Sophia et al. [47] |
30352996 | Nimbolide | In vitro (SCC131, SCC4) |
|
PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β Caspase Bax/Bcl-2 |
| 6 | Xiao et al. [91] |
29332355 | 4-O-methylhonokoil | In vitro (PE/CA-PJ41) |
|
Bax/Bcl-2 |
| 7 | Kumar et al. [55] |
33101201 | Sodium Danshensu | In vitro (FaDu, CA9-22) |
|
MAPK/ERK |
| 8 | Aswathy et al. [50] |
33860206 | [(3β)-3-hydroxy-lup-20(29)-en-28-oic acid] | In vitro (SAS) |
|
Akt/mTOR JAK/STAT3 VEGF NF-κB |
| Seco-A-ring oleanane | In vitro (SAS) |
|
||||
| 9 | Aggarwal et al. [48] |
35774603 | Cinnamaldehyde | In vitro (SCC9, SCC25, SCC4) |
|
PI3K/Akt/mTOR NF-κB MAPK |
| No | Author | PMID | Natural product | Preclinical model |
Findings | Pathway related |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Zhao et al. [41] |
34175854 | Actein | In vitro (CAL27, SCC9) |
|
Akt/FoxO1 Bax/Bcl-2 |
|
In vivo (CAL27) C57BL/6 mice |
|
|||||
| 2 | Zhang et al. [42] |
32267053 | Salicylate | In vitro (SAS) |
|
Akt/mTOR |
|
In vivo (SAS) Nude mice |
|
|||||
| 3 | Li et al. [43] |
32424132 | Tanshinone IIA | In vitro (CAL27, SCC9, SCC15, SCC25) |
|
Akt/c-Myc |
|
In vivo (CAL27, SCC15) Athymic nude mice |
|
|||||
| 4 | Li et al. [44] |
32410646 | Xanthohumol | In vitro (CAL27, SCC9, SCC15, SCC25) |
|
Akt/Wee1/Cdk1 Bax/Bcl-2 Caspase |
|
In vivo (CAL27, SCC25) Athymic nude mice |
|
|||||
| 5 | Huang et al. [45] |
29363886 | Honokiol | In vitro (OC2, OCSL) |
|
Akt/mTOR MAPK |
|
In vivo (SAS) BALB/c nude mice, AnN.Cg-Foxn1nu/CrlNarl |
|
|||||
| 6 | Chen et al. [65] |
35785707 | Trichodermin | In vitro (Ca922, HSC3) |
|
HDAC-2 Caspase |
|
In vivo (HSC3) Zebrafish |
|
|||||
| 7 | Wang et al. [24] |
31750253 | Psorachromene | In vitro (SAS, OECM1) |
|
EGFR EMT-related Caspase SLUG |
|
In vivo (SAS) BALB/c nude mice |
|
|||||
| 8 | Li et al. [56] |
35904511 | Protocatechuic acid | In vitro (HSC3, CAL27) |
|
JNK/p38 Caspase |
|
In vivo (CAL27) Nude mice |
|
|||||
| 9 | de Compos et al. [108] |
28782139 | Curcumin |
In vitro (CAL27, SCC25, HACAT, NIH-3T3) |
|
|
|
In vivo (HNSCC Biopsy) BALB/c nude mice |
|
| No | Author | PMID | Natural product | Preclinical model |
Findings | Pathway related |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Vincent-Chong et al. [25] |
30875566 | Calcitriol |
In vivo (4NQO-induced carcinogenesis) C57BL/6NCr mice |
|
|
| 2 | Wang et al. [64] |
33156559 | Neferine |
In vivo (DMBA-induced carcinogenesis) Syrian hamster |
|
NF-κB |
| 3 | Sophia et al. [47] |
30352996 | Nimbolide |
In vivo (DMBA-induced carcinogenesis) Syrian hamster |
|
PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





