Submitted:
12 June 2023
Posted:
12 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Experimental methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of α-MnO2 powders
2.3. Preparation of electrolytes
2.4. Preparation of electrode and battery assembly
2.5. Characterizations
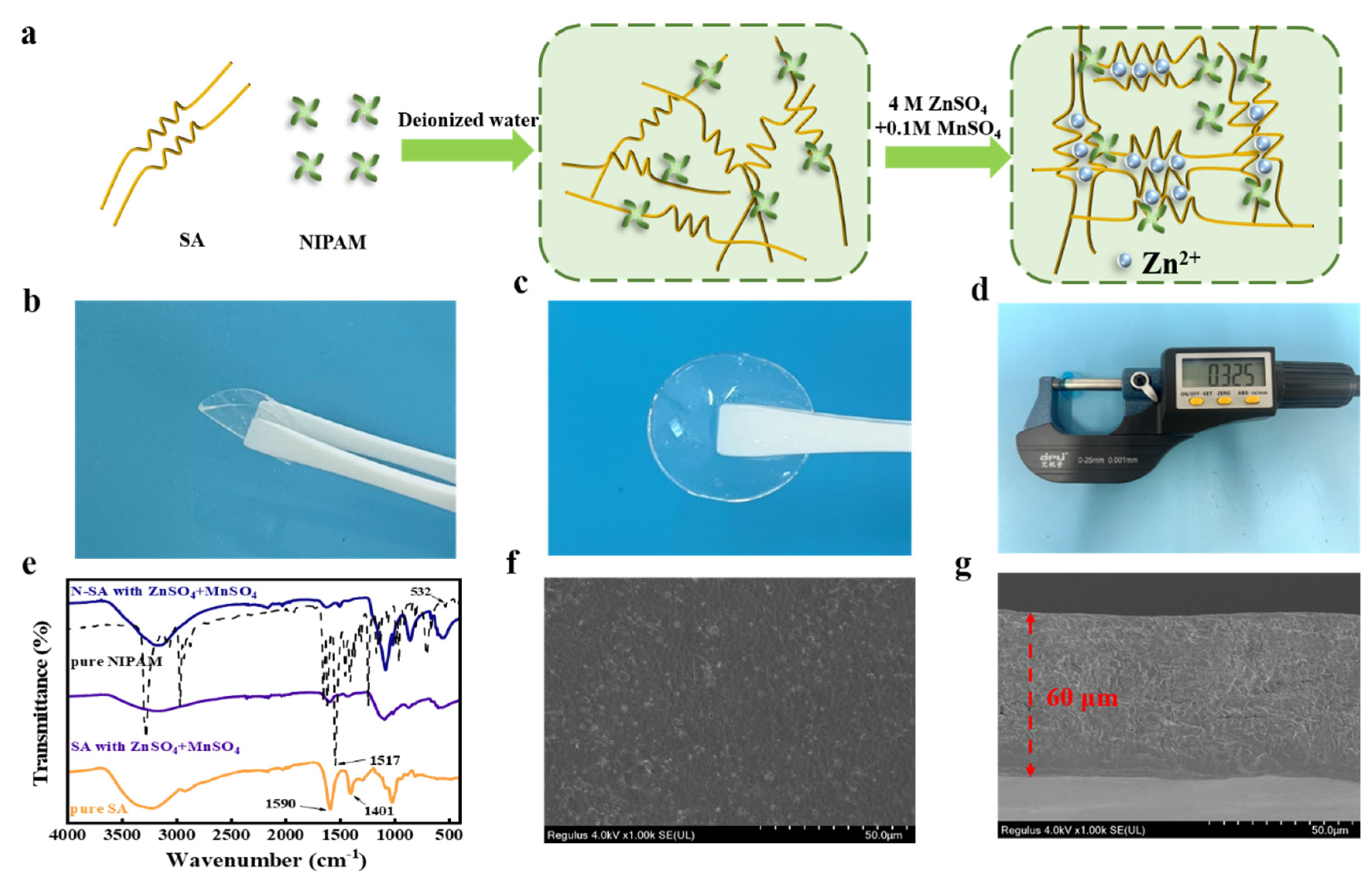
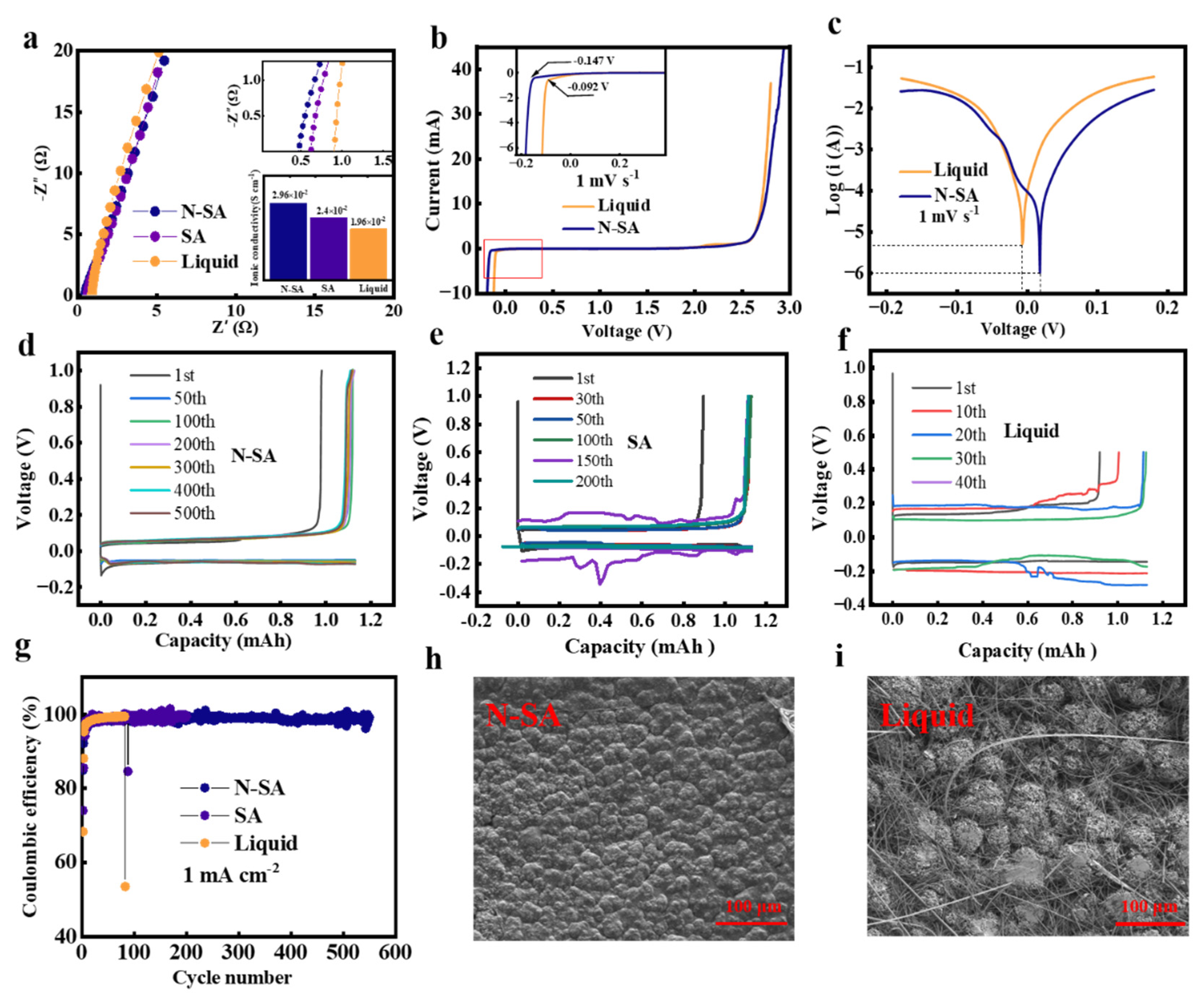
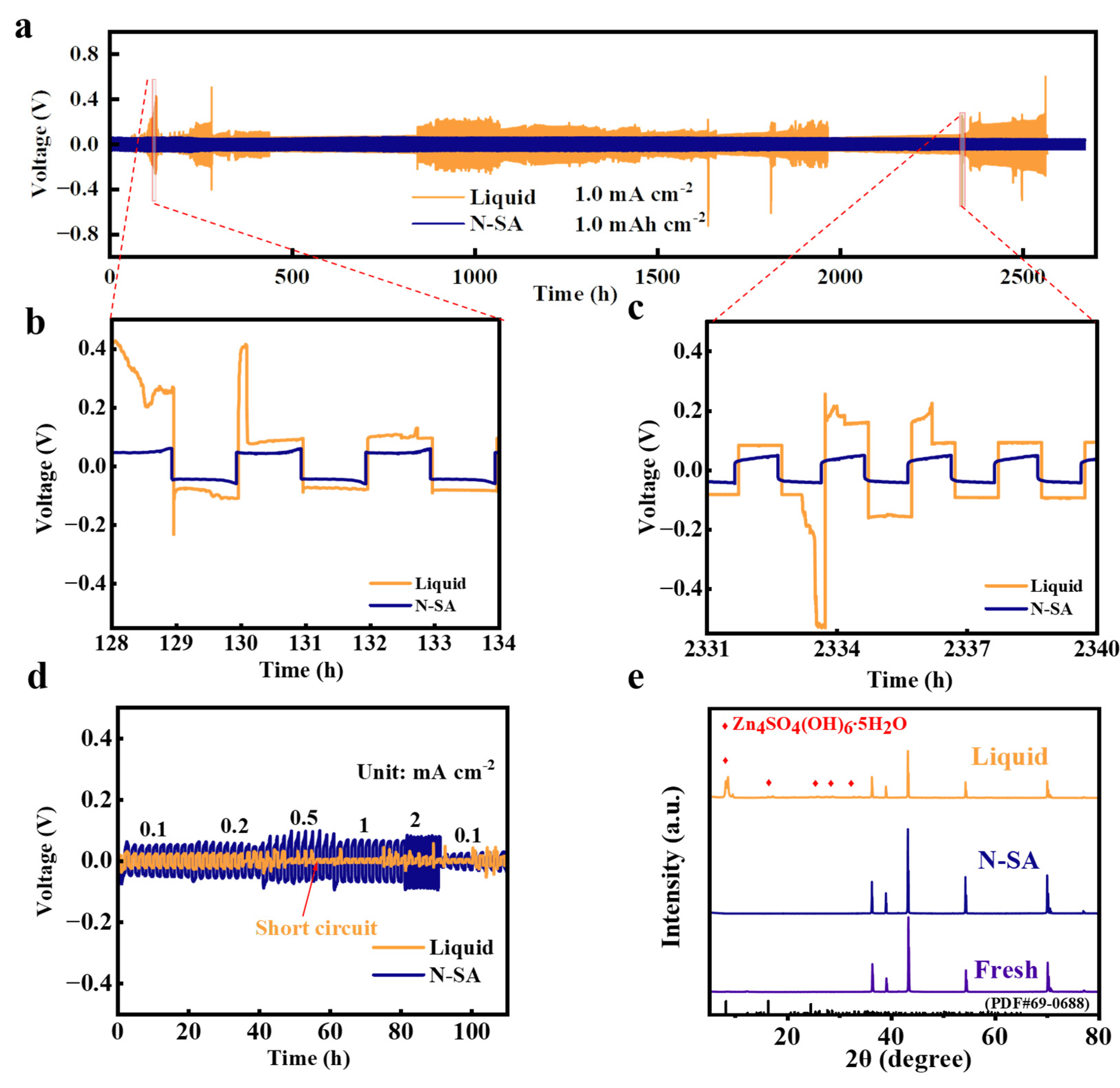
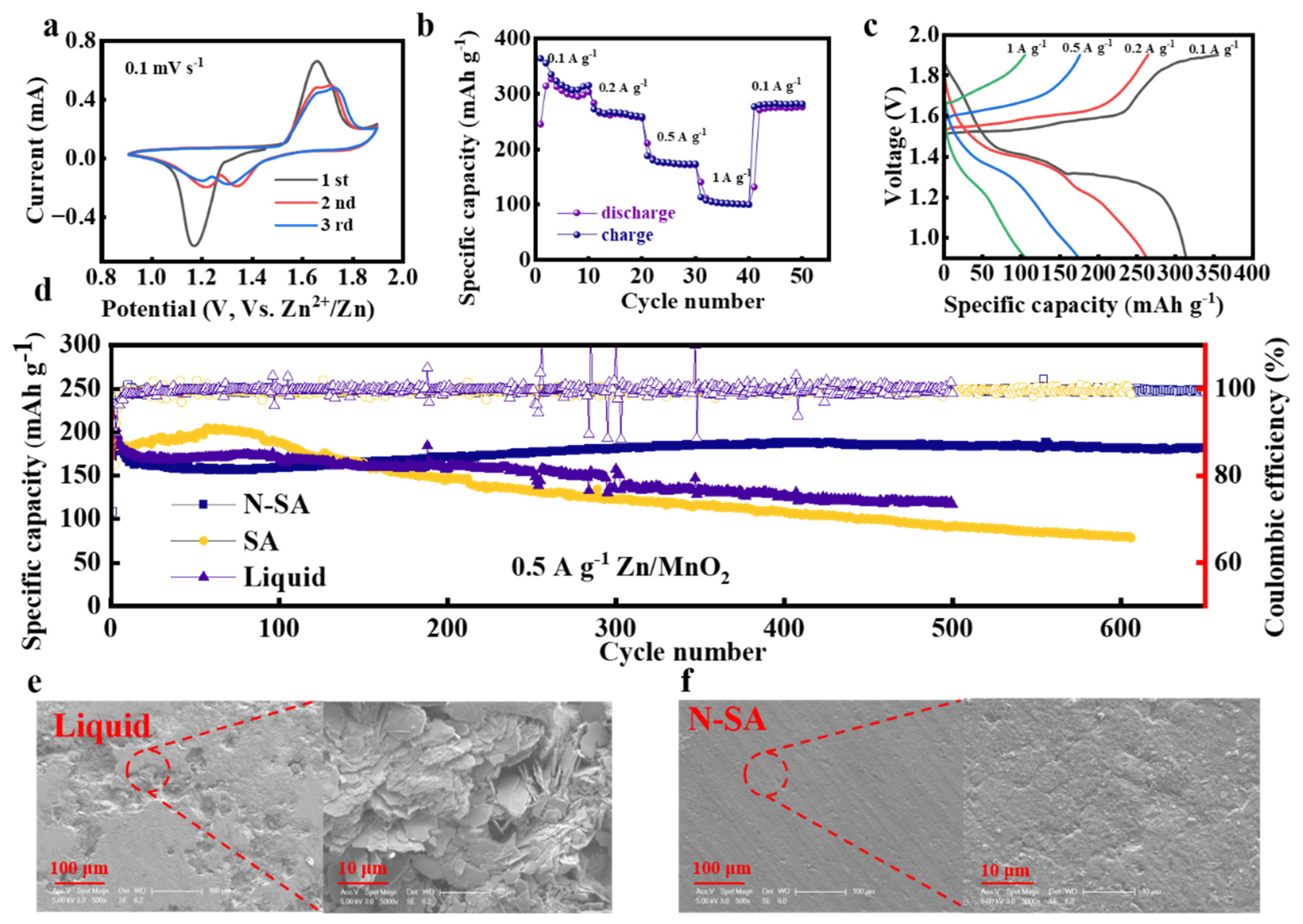
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, M.; Lu, J.; Chen, Z.; Amine, K. 30 Years of Lithium-Ion Batteries. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1800561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, B.; Shan, L.; Liang, S.; Zhou, J. Issues and Opportunities Facing Aqueous Zinc-Ion Batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 3288–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michail, A.; Silván, B.; Tapia-Ruiz, N. Progress in High-Voltage MgMn2O4 oxyspinel Cathode Materials for Mg Batteries. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2022, 31, 100817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Cano, Z.P.; Park, M.G.; Yu, A.; Fowler, M.; Chen, Z. Electrically Rechargeable Zinc-Air Batteries: Progress, Challenges, and Perspectives. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1604685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mainar, A.R.; Colmenares, L.C.; Blázquez, J.A.; Urdampilleta, I. A Brief Overview of Secondary Zinc Anode Development: The Key of Improving Zinc-Based Energy Storage Systems. Int. J. Energy Res. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Yao, M.; Huang, S.; Tian, J.; Niu, Z. Sustainable Dough-Based Gel Electrolytes for Aqueous Energy Storage Devices. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2009209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, T.; Fan, H.J. From Aqueous Zn-Ion Battery to Zn-MnO2 Flow Battery: A Brief Story. J. Energy Chem. 2021, 54, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Borodin, O.; Gao, T.; Fan, X.; Sun, W.; Han, F.; Faraone, A.; Dura, J.A.; Xu, K.; Wang, C. Highly Reversible Zinc Metal Anode for Aqueous Batteries. Nat. Mater. 2018, 17, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, X.; Jiang, B.; Wang, X.; Liu, W.; Dong, L.; Kang, F.; Xu, C. High-Performance Aqueous Zinc-Ion Batteries Realized by MOF Materials. Nano-Micro Lett. 2020, 12, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, J.F.; Chervin, C.N.; Pala, I.R.; Machler, M.; Burz, M.F.; Long, J.W.; Rolison, D.R. Rechargeable Nickel–3D Zinc Batteries: An Energy-Dense, Safer Alternative to Lithium-Ion. Science 2017, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhou, W.; Wang, A.; Huang, A.; Chen, J.; Xu, J.; Wong, C.-P. Anti-Freezing Flexible Aqueous Zn–MnO2 Batteries Working at −35 °C Enabled by a Borax-Crosslinked Polyvinyl Alcohol/Glycerol Gel Electrolyte. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 6828–6841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, F.; Liang, G.; Meng, Q.; Liu, Z.; Li, H.; Fan, J.; Zhi, C. A Flexible Rechargeable Aqueous Zinc Manganese-Dioxide Battery Working at −20 °C. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhou, W.; Wang, A.; Huang, A.; Chen, J.; Xu, J.; Wong, C.-P. Anti-Freezing Flexible Aqueous Zn–MnO2 Batteries Working at −35 °C Enabled by a Borax-Crosslinked Polyvinyl Alcohol/Glycerol Gel Electrolyte. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 6828–6841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaikwad, A.M.; Whiting, G.L.; Steingart, D.A.; Arias, A.C. Highly Flexible, Printed Alkaline Batteries Based on Mesh-Embedded Electrodes. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 3251–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhu, H.; Xie, X.; Gao, J.; Deng, C.; Han, M.; Liang, S.; Zhou, J. Ion-Confinement Effect Enabled by Gel Electrolyte for Highly Reversible Dendrite-Free Zinc Metal Anode. Energy Storage Mater. 2020, 27, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Li, Z.; Jin, S.; Li, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, H. Flexible and Stable Quasi-Solid-State Zinc Ion Battery with Conductive Guar Gum Electrolyte. Mater. Today Energy 2019, 14, 100349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, Y. A Flexible Zinc-Ion Battery Based on the Optimized Concentrated Hydrogel Electrolyte for Enhanced Performance at Subzero Temperature. Electrochemical Acta 2021, 395, 139178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Chi, X.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, B.; Yang, J.; Liu, Y. Durable, Flexible Self-Standing Hydrogel Electrolytes Enabling High-Safety Rechargeable Solid-State Zinc Metal Batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 23046–23054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, O.; Chen, G.; Gu, J.; Lu, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Hou, L.; Jiang, X. A Facile Preparation Method for Anti-Freezing, Tough, Transparent, Conductive and Thermoplastic Poly (Vinyl Alcohol)/Sodium Alginate/Glycerol Organohydrogen Electrolyte. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 2512–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Huang, Y.; Liu, B.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yang, G.; Hiralal, P.; Jin, S.; Zhou, H. Flexible and Anti-Freezing Zinc-Ion Batteries Using a Guar-Gum/Sodium-Alginate/Ethylene-Glycol Hydrogel Electrolyte. Energy Storage Mater. 2021, 41, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Li, J.; Zhao, S.; Jiao, Y.; Chen, J.; Tan, Y.; Brett, D.J.L.; He, G.; Parkin, I.P. Investigation of a Biomass Hydrogel Electrolyte Naturally Stabilizing Cathodes for Zinc-Ion Batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhu, T.; Xu, N.; Huang, K. A Semisolid Electrolyte for Flexible Zn-Ion Batteries. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2019, 2, 6904–6910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Zhou, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, M.; Yuan, X.; Hu, J.; Li, Z.; Li, C.; Li, R. High-Capacity Layered Magnesium Vanadate with Concentrated Gel Electrolyte toward High-Performance and Wide-Temperature Zinc-Ion Battery. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 15776–15785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, H.; Liu, H.-Y.; Lin, C.-C. Improving Gelation Efficiency and Cytocompatibility of Visible Light Polymerized Thiol-Norbornene Hydrogels via Addition of Soluble Tyrosine. Biomatter. Sci. 2017, 5, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Z.; Ding, J.; Liu, B.; Liu, X.; Han, X.; Deng, Y.; Hu, W.; Zhong, C. A Rechargeable Zn–Air Battery with High Energy Efficiency and Long Life Enabled by a Highly Water-Retentive Gel Electrolyte with Reaction Modifier. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1908127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.; Lee, H.R.; Kim, H.; Chung, K.Y.; Cho, B.W.; Oh, S.H. Elucidating the Intercalation Mechanism of Zinc Ions into α-MnO2 for Rechargeable Zinc Batteries. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 9265–9268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.-F.; Zhu, C.-Y.; Ye, Y.-W.; Zhang, Y.-H.; Cheng, F.; Li, H.-R. Synergistic Optimization Strategy Involving Sandwich-like MnO2 @rGO and Laponite-Modified PAM for High-Performance Zinc-Ion Batteries and Zinc Dendrite Suppression. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 25962–25971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhu, H.; Xie, X.; Gao, J.; Deng, C.; Han, M.; Liang, S.; Zhou, J. Ion-Confinement Effect Enabled by Gel Electrolyte for Highly Reversible Dendrite-Free Zinc Metal Anode. Energy Storage Mater. 2020, 27, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Meng, X.; Jiang, W.; Ling, M.; Yan, L.; Liang, C. In-Situ Constructing Polyacrylamide Interphase Enables Dendrite-Free Zinc Anode in Aqueous Batteries. Electrochimica Acta 2021, 378, 138106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Shen, P.; Zeng, N.; Wang, L.; Yan, D.; Cui, L.; Yang, K.; Zhai, C. Hybrid Hydrogel Electrolyte Based on Metal–Organic Supermolecular Self-Assembly and Polymer Chemical Cross-Linking for Rechargeable Aqueous Zn–MnO2 Batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 42285–42293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.; Ren, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Ji, D.; Hu, L. Bonding Interaction Regulation in Hydrogel Electrolyte Enable Dendrite-Free Aqueous Zinc-Ion Batteries from −20 to 60 °C. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 434, 134646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Chen, S.; Li, N.; Liu, Z.; Tang, Z.; Zapien, J.A.; Chen, S.; Fan, J.; Zhi, C. Hydrogen-Free and Dendrite-Free All-Solid-State Zn-Ion Batteries. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1908121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Z.; Ahmad, Z.; Viswanathan, V. Design Principles for Dendrite Suppression with Porous Polymer/Aqueous Solution Hybrid Electrolyte for Zn Metal Anodes. ACS Energy Lett. 2020, 5, 2466–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Liu, G.; Shim, G.Y.; Kim, H.; Lee, J.K. Functionalized Zn @ZnO Hexagonal Pyramid Array for Dendrite-Free and Ultrastable Zinc Metal Anodes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2004210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Shao, Y.; Yan, P.; Cheng, Y.; Han, K.S.; Nie, Z.; Wang, C.; Yang, J.; Li, X.; Bhattacharya, P.; et al. Reversible Aqueous Zinc/Manganese Oxide Energy Storage from Conversion Reactions. Nat. ENERGY 2016, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




