1. Introduction
Liver fibrosis is a chronic and progressive liver disease characterized by excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix proteins, which leads to impaired liver function and ultimately liver failure. This condition is a growing global health concern, as it is associated with various liver diseases such as viral hepatitis, alcoholic liver disease, and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis [
1]. Despite extensive research, effective treatment options for liver fibrosis remain limited, highlighting the urgent need for novel therapeutic strategies.
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), particularly adipose-derived stem cells (ASCs), have shown promising potential for liver regeneration due to their ability to differentiate into various cell types, secrete bioactive factors, and modulate immune responses. However, the optimization of their regenerative potential is crucial for successful therapeutic applications, as their efficacy can be influenced by factors such as donor age, tissue source, and culture conditions. One of the key factors determining the characteristics of MSCs is the appropriate balance between intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and scavenging by antioxidant enzymes [
2,
3]. Elevated ROS levels are associated with cellular damage and impaired regenerative potential, while controlled ROS levels play a vital role in maintaining cellular homeostasis and promoting tissue repair [
4,
5]. Thus, modulating the intracellular redox state of MSCs could potentially enhance their therapeutic efficacy.
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator 1α (PGC-1α) is a potent regulator of mitochondrial biogenesis and function, and its overexpression leads to increased expression of mitochondrial antioxidant enzymes, thereby reducing oxidative stress and cell death [
6,
7,
8]. Additionally, PGC-1α has been implicated in the regulation of various cellular processes, such as energy metabolism, inflammation, and cell survival, which are relevant to tissue repair and regeneration. In this study, we aimed to enhance the antifibrogenic potential of adipose-derived stem cells (ASCs) by transfecting them with PGC-1α and investigate the therapeutic potential of the secretome released from these PGC-ASCs in a mouse model of liver fibrosis. By leveraging the beneficial effects of PGC-1α-driven upregulation of mitochondrial proliferation, we hypothesize that the secretome of PGC-ASCs will exhibit improved antifibrogenic and regenerative properties compared to the secretome of unmodified ASCs. This investigation will provide valuable insights into the development of cell-based therapies for liver fibrosis and other fibrotic diseases, as well as contribute to the growing body of knowledge on the mechanisms underlying MSC-mediated tissue repair.
3. Discussion
This study investigates the therapeutic potential of the secretome released from PGC-1α-overexpressing adipose-derived stem cells (PGC-Sec) in liver fibrosis treatment. Using in vitro and in vivo models, we demonstrate that PGC-Sec enhances cell viability, reduces mitochondrial oxidative stress, lowers serum liver enzyme levels, and attenuates pro-inflammatory cytokine concentrations. Furthermore, PGC-Sec significantly modulates the expression of fibrosis-related markers and improves liver histology. Immunohistochemistry confirms the upregulation of mitochondrial function markers, such as OPA1, in the PGC-Sec group, indicating a strong association between PGC-1α-driven mitochondrial proliferation and the antifibrogenic potential of the secretome. Collectively, our findings reveal the promise of PGC-Sec as a novel therapeutic strategy for liver fibrosis management.
PGC-1α is a transcriptional coactivator that plays a pivotal role in regulating cellular energy metabolism, particularly in the context of mitochondrial biogenesis, oxidative phosphorylation, and fatty acid oxidation [
6,
7,
8]. As a master regulator of energy homeostasis, PGC-1α is essential in maintaining metabolic flexibility in various tissues, such as the liver, skeletal muscle, and heart [
9,
10]. Its influence on mitochondrial function has profound implications for numerous physiological processes, including cellular respiration, thermogenesis, and overall energy balance [
6]. Additionally, PGC-1α is implicated in various disease conditions, such as obesity, diabetes, and neurodegenerative disorders, where mitochondrial dysfunction and energy imbalance are key features [
7]. Consequently, PGC-1α has garnered significant attention as a potential therapeutic target for a wide range of metabolic and degenerative diseases, highlighting its remarkable significance in the fields of cell biology, metabolism, and human health.
PGC-1α has emerged as a potential player in the context of liver fibrosis, a chronic liver disease characterized by excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix components, ultimately leading to impaired liver function [
11,
12]. As a key regulator of mitochondrial biogenesis and function, PGC-1α has been implicated in modulating the processes associated with liver fibrosis progression and resolution. Dysregulated energy metabolism and mitochondrial dysfunction have been observed in fibrotic livers, with PGC-1α potentially serving as a therapeutic target to counteract these changes. By enhancing mitochondrial function, oxidative phosphorylation, and fatty acid oxidation, PGC-1α could alleviate inflammation, oxidative stress, and hepatic stellate cell activation, which are hallmarks of liver fibrosis [
13,
14,
15]. Moreover, PGC-1α has been shown to regulate the expression of various fibrosis-related markers, further underscoring its potential in controlling the fibrogenic process [
16,
17,
18]. Therefore, a better understanding of PGC-1α's role in liver fibrosis may provide novel insights into the development of effective therapeutic strategies to manage and treat this debilitating liver disease.
The use of PGC-Sec presents several advantages over direct PGC-1α administration for the treatment of liver fibrosis. First, the secretome contains a rich array of bioactive molecules, including growth factors, cytokines, and extracellular vesicles, which can act in concert to promote tissue repair, modulate inflammation, and mitigate fibrosis [
19,
20]. This multifaceted approach may offer a more effective therapeutic outcome compared to targeting PGC-1α alone. Second, utilizing the secretome takes advantage of the paracrine effects of stem cells, circumventing potential challenges associated with stem cell engraftment, survival, and differentiation. Third, the use of PGC-Sec may reduce the risk of off-target effects or unintended consequences associated with direct PGC-1α manipulation. Lastly, PGC-Sec administration is a cell-free therapy, which may simplify production, storage, and transportation, ultimately expediting its translation to clinical settings. Collectively, these advantages suggest that PGC-Sec holds promise as a novel therapeutic strategy for the treatment of liver fibrosis, warranting further investigation into its efficacy and safety.
The potential mechanism through which PGC-Sec improves liver fibrosis involves several key processes. First, PGC-Sec contains various growth factors, cytokines, and extracellular vesicles, which together contribute to a multifaceted regenerative environment. This environment promotes hepatocyte viability and proliferation, leading to the restoration of damaged liver tissue. Additionally, PGC-Sec is thought to modulate the immune response by reducing the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6 and TNF-α, thereby alleviating inflammation associated with liver fibrosis. Furthermore, given the critical role PGC-1α plays in liver disease pathogenesis [
6,
8], it is plausible that PGC-Sec could serve as a promising therapeutic approach for ameliorating liver fibrosis. In a study by Sugden et al. (2010), the authors demonstrated that mice lacking hepatic PGC-1α developed hepatic steatosis and inflammation when fed a high-fat diet [
21]. Moreover, in another study by Koliaki et al. (2015), the authors reported that hepatic PGC-1α expression was significantly reduced in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which are both conditions that can progress to liver fibrosis [
22]. Lastly, the enhancement of mitochondrial biogenesis and function by PGC-1α overexpression in PGC-Sec-treated cells might help to ameliorate the metabolic disturbances that contribute to the progression of liver fibrosis [
23,
24]. Altogether, these combined actions of PGC-Sec create a multifaceted therapeutic approach to improve liver fibrosis.
In conclusion, our findings reveal the secretome from PGC-1α-overexpressing adipose-derived stem cells (PGC-Sec) as a promising therapeutic candidate for liver fibrosis treatment, by decreasing proliferation of activated HSC cells, reducing oxidative stress, modulating fibrosis-related markers, and improving liver histology. Furthermore, the observed upregulation of mitochondrial function markers, such as OPA1, highlights the critical role of PGC-1α-driven mitochondrial proliferation in contributing to the antifibrogenic potential of the secretome. Collectively, these results underscore the promise of PGC-Sec as a novel and effective therapeutic strategy for liver fibrosis management, paving the way for future research and clinical applications.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
LX2 human hepatic stellate cells (HSC cells) were kindly donated by Dr. Won-il Jeong of KAIST Biomedical Research of Korea and cultured in high-glucose Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium (DMEM; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Carlsbad, CA) supplemented with 10% FBS, 100 U/mL of penicillin, and 0.1 mg/mL of streptomycin. Human adipose-derived stem cells (ASCs) were donated by Hurim BioCell Co. Ltd. (Seoul, Korea) (IRB number 700069-201407-BR-002-01) and cultured in low-glucose DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS, 100 U/mL of penicillin, and 0.1 mg/mL of streptomycin. Cells were incubated at 37℃ in a CO2 incubator (Thermo).
4.2. Preparation of PGC-Secretome
ASCs were grown in 100 mm cell dishes (Corning Glass Works, Corning, NY). After reaching 70–80% confluence, ASCs were transiently transfected with 4 μg pcDNA-PGC-1α. Twenty-four hours later, 1.0 × 106 ASCs were cultured in 7 mL serum-free low-glucose DMEM for 24 h. The conditioned media were concentrated 25-fold using ultrafiltration units with a 3-kDa molecular weight cutoff (Amicon Ultra-PL 3; Millipore, Bedford, MA) to obtain 0.28 mL of secretome from 1.0 × 106 ASCs. Mice were injected with 0.1 mL of secretome and PGC-secretome, equivalent to the secretome obtained from 5 × 105 ASCs. The normal secretome was obtained from empty vector-transfected ASCs, while PGC-secretome was obtained from pcDNA-PGC-1 α transfected ASCs.
4.3. Cell Proliferation Assay
Cell proliferation of LX2 cells was evaluated using the EZ-Cytox Cell Proliferation Assay kit (Itsbio, Seoul, Republic of Korea) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
4.4. Animal Experiments
Animal studies were carried out in compliance with the guidelines of the Institute for Laboratory Animal Research, Korea (IRB No: CUMC-2020-0125-03). Seven-week-old male C57BL/6J mice (Central Laboratory Animal Inc., Seoul, Korea) were used. An in vivo model of liver fibrosis was generated using methionine/choline-deficient diets (MCD diet; ENVIGO, Seoul, Korea). Mice freely consumed a MCD diet ad libitum for two weeks, which was continued until the fourth week of the experiment. Mice were divided into four experimental groups: control (n = 5), MCD diet + saline injection (n = 8), MCD diet + control-secretome (Ctrl-Sec) injection (n = 8), and MCD diet + PGC-1α-boosted secretome (PGC-Sec) (n = 8). After 14 days on the MCD diet, mice were administered intravenous injections of 0.1 mL of saline, Ctrl-Sec, or PGC-Sec three times per week for a duration of two weeks (totaling six injections). At the beginning of the fifth week, mice were euthanized for the collection of blood and liver samples.
4.5. Real-Time PCR
Total RNA was extracted using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen, CA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Reverse transcription was performed with 1 µg RNA using an RT-premix kit (TOYOBO, Osaka, Japan) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. SYBR Green real-time quantitative PCR was conducted with primers specific to mouse Collagen1, TGF-β1, and GAPDH. The reaction was performed using an Applied Biosystems Step One Plus Real-Time PCR system (Thermo). Expression levels for each target gene were calculated using the comparative threshold cycle method after normalization to the GAPDH gene. Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD) from three independent experiments.
4.6. Western Blot Analysis
Liver specimens from mice were lysed using the EzRIPA Lysis kit (ATTO Corporation; Tokyo, Japan) and protein concentrations were quantified using Bradford reagent (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA). Proteins were analyzed by western blot using primary antibodies against TIMP1 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, MA), CollagenA1 (Novus Bio, CO), and β-actin (Cell Signaling Technology, MA) at a 1:1000 dilution, followed by HRP-conjugated secondary antibodies (1:2000 dilution) from Vector Laboratories (Burlingame, CA). Specific immune complexes were detected using the Western Blotting Plus Chemiluminescence Reagent (Millipore, Bedford, MA).
4.7. Serology Test and Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
Blood samples were collected from each mouse, and the concentrations of liver injury markers, including aspartate transaminase (AST) and alanine transaminase (ALT), were measured using an IDEXX VetTest Chemistry Analyzer (IDEXX Laboratories, Inc., Westbrook, ME, USA). Mouse interleukin (IL)-6 and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α concentrations were measured by sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (Abbkine, China) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
4.8. Immunohistochemistry and Sirius Red Staining
Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue sections were deparaffinized, rehydrated, and subjected to epitope retrieval using standard procedures. Antibodies against Collagen1α (Santa Cruz Biotechnology), PGC-1α (Novus Biologicals, CO), PPAR-α (Cell Signaling Technology), and OPA-1 (Santa Cruz Biotechnology) were used for immunochemical staining. Sirius red staining was performed using the Sirius Red Staining Kit (Polysciences, Warrington, PA, United Kingdom) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Samples were examined under a laser-scanning microscope (Eclipse TE300; Nikon, Tokyo, Japan).
4.9. Quantification of Mitochondrial Superoxide by Flow Cytometry
Mitochondrial superoxide was detected in cells stained with MitoSOX (Thermo Fisher Scientific, MA). After incubation for 10 min in the dark at 25°C, cells were analyzed using an Attune NxT Acoustic Focusing Cytometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, MA).
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Data were analyzed using SPSS 11.0 software (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL) and are presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD). Statistical comparisons among groups were determined using the Kruskal–Wallis test. Probability values of P < 0.05 were regarded as statistically significant.
Figure 1.
PGC-Sec enhances cell viability and reduces mitochondrial oxidative stress in an in vitro model of liver injury. (A) Schematic representation of PGC-1α-overexpressing adipose-derived stem cells (ASCs) generation by transfecting a plasmid encoding PGC-1α. (B) Cell viability assessment of control AML12 hepatocytes without treatment, and those treated with either Ctrl-Sec or PGC-Sec, showing a significant increase in cell viability upon PGC-Sec treatment in TAA-induced liver injury. (C) MitoSOX flow cytometry analysis of mitochondrial superoxide production in control AML12 cells and TAA-induced liver injury cells, indicating a significant reduction in MitoSOX fluorescence in both Ctrl-Sec and PGC-Sec treatment groups compared to the No Treatment group, with a more pronounced reduction in the PGC-Sec treatment group. Values are presented as mean ± standard deviation of three independent experiments; * P < 0.05. Abbreviations: ASCs, adipose-derived stem cells; Ctrl-Sec, Control-secretome, PGC-Sec, PGC-1α-secretome; TAA, thioacetamide; MitoSOX, mitochondrial superoxide indicator.
Figure 1.
PGC-Sec enhances cell viability and reduces mitochondrial oxidative stress in an in vitro model of liver injury. (A) Schematic representation of PGC-1α-overexpressing adipose-derived stem cells (ASCs) generation by transfecting a plasmid encoding PGC-1α. (B) Cell viability assessment of control AML12 hepatocytes without treatment, and those treated with either Ctrl-Sec or PGC-Sec, showing a significant increase in cell viability upon PGC-Sec treatment in TAA-induced liver injury. (C) MitoSOX flow cytometry analysis of mitochondrial superoxide production in control AML12 cells and TAA-induced liver injury cells, indicating a significant reduction in MitoSOX fluorescence in both Ctrl-Sec and PGC-Sec treatment groups compared to the No Treatment group, with a more pronounced reduction in the PGC-Sec treatment group. Values are presented as mean ± standard deviation of three independent experiments; * P < 0.05. Abbreviations: ASCs, adipose-derived stem cells; Ctrl-Sec, Control-secretome, PGC-Sec, PGC-1α-secretome; TAA, thioacetamide; MitoSOX, mitochondrial superoxide indicator.
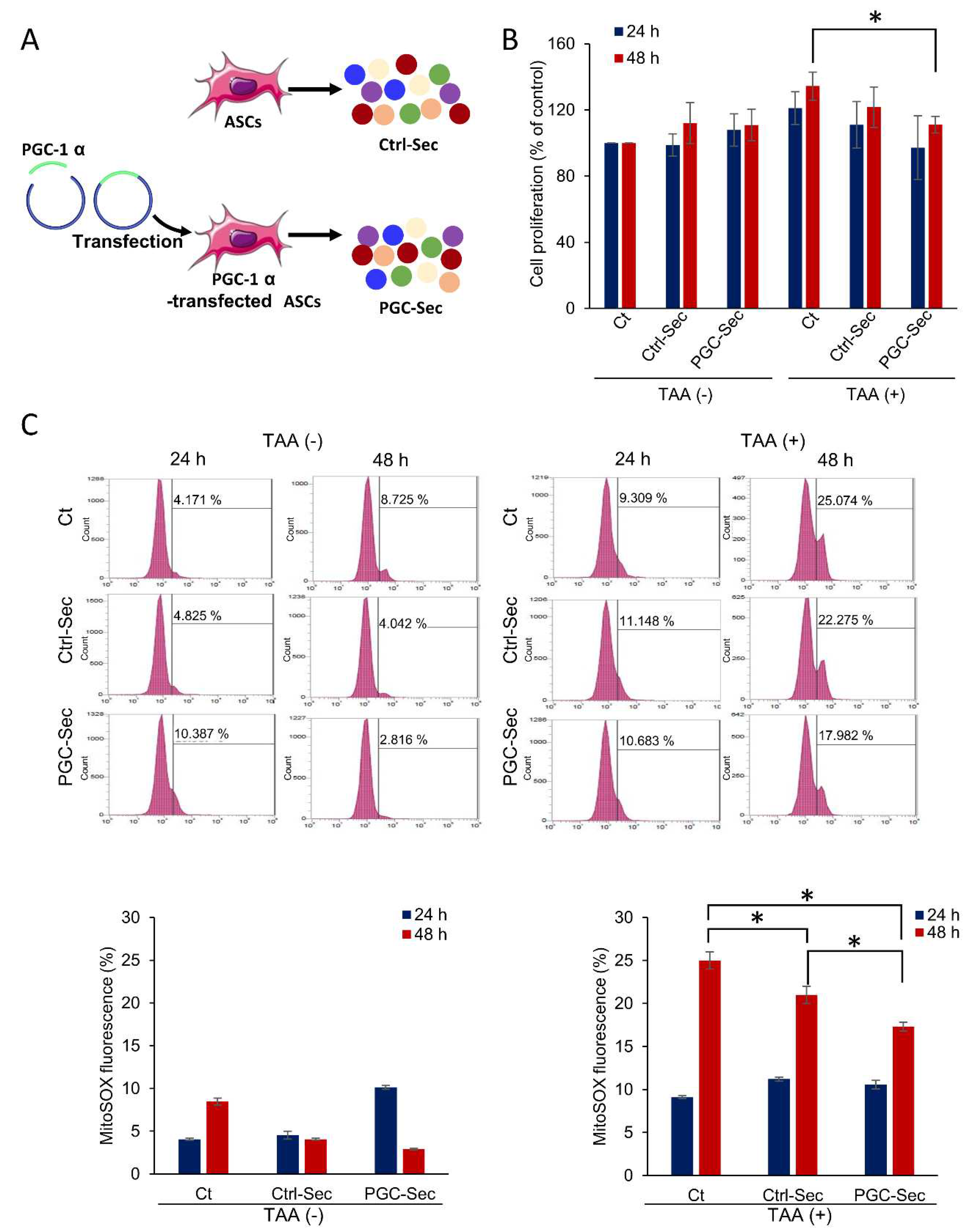
Figure 2.
In vivo effects of PGC-Sec on hepatic enzyme activity and serum inflammatory cytokine concentrations in a mouse model of liver fibrosis. (A) Schematic representation of the experimental design, involving a methionine-choline-deficient (MCD) diet and secretome injections. (B) Serum liver enzyme levels (AST and ALT) demonstrating significant reductions in the secretome-treated groups (Ctrl-Sec & PGC-Sec) compared to the control group, with the PGC-Sec group exhibiting significantly lower levels than the Ctrl-Sec group. (C) Serum pro-inflammatory cytokine concentrations (IL-6 and TNF-α) showing significant decreases in the secretome-treated groups (Ctrl-Sec & PGC-Sec) compared to the control group, and a more pronounced reduction in the PGC-Sec group relative to the Ctrl-Sec group. Values are presented as mean ± standard deviation of three independent experiments; * P < 0.05. Abbreviations: MCD, methionine-choline-deficient diet; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; IL-6, interleukin-6; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-alpha; Ctrl-Sec, Control-secretome; PGC-Sec, PGC-1α-secretome.
Figure 2.
In vivo effects of PGC-Sec on hepatic enzyme activity and serum inflammatory cytokine concentrations in a mouse model of liver fibrosis. (A) Schematic representation of the experimental design, involving a methionine-choline-deficient (MCD) diet and secretome injections. (B) Serum liver enzyme levels (AST and ALT) demonstrating significant reductions in the secretome-treated groups (Ctrl-Sec & PGC-Sec) compared to the control group, with the PGC-Sec group exhibiting significantly lower levels than the Ctrl-Sec group. (C) Serum pro-inflammatory cytokine concentrations (IL-6 and TNF-α) showing significant decreases in the secretome-treated groups (Ctrl-Sec & PGC-Sec) compared to the control group, and a more pronounced reduction in the PGC-Sec group relative to the Ctrl-Sec group. Values are presented as mean ± standard deviation of three independent experiments; * P < 0.05. Abbreviations: MCD, methionine-choline-deficient diet; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; IL-6, interleukin-6; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-alpha; Ctrl-Sec, Control-secretome; PGC-Sec, PGC-1α-secretome.
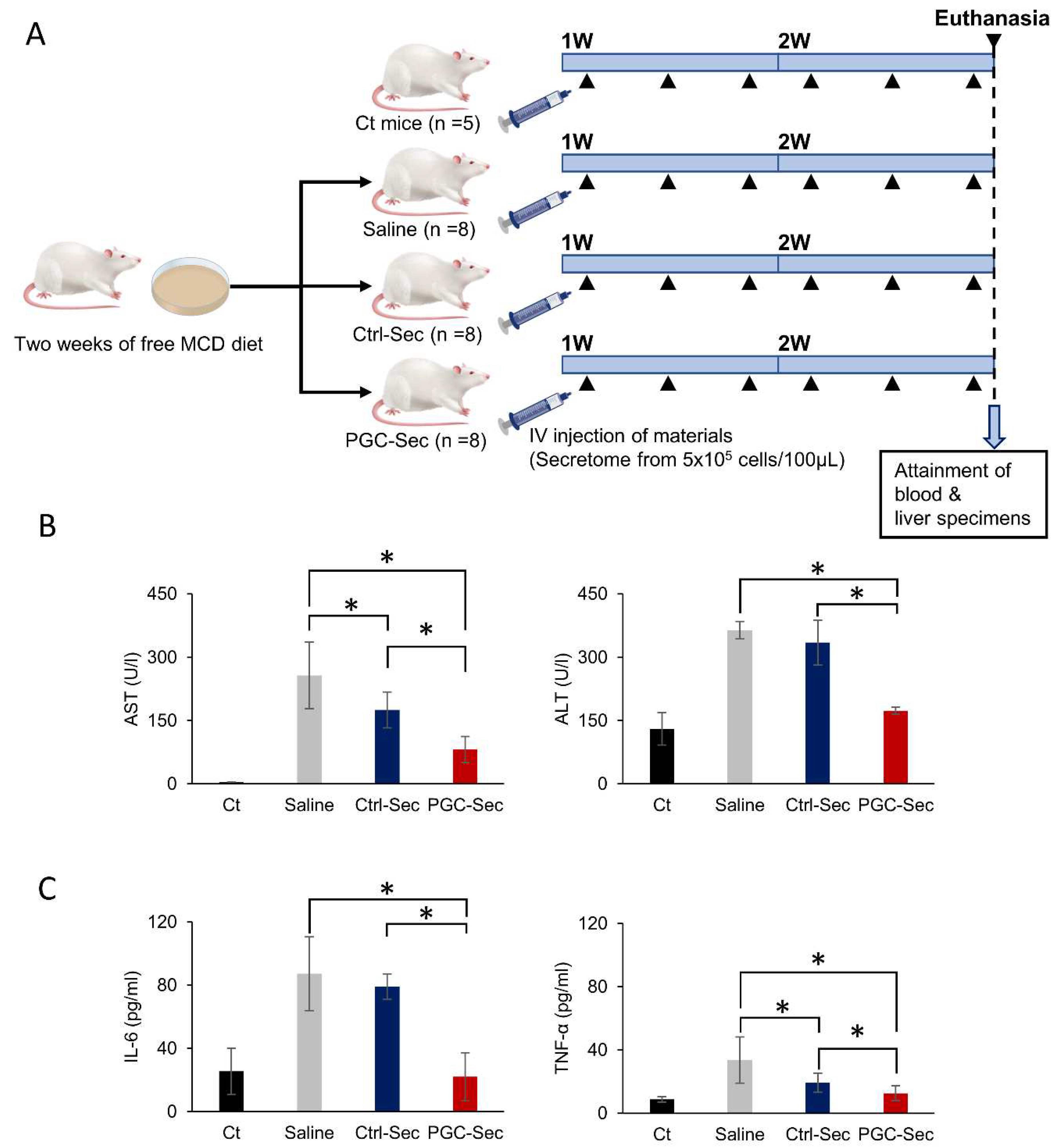
Figure 3.
In vivo effects of PGC-Sec on the expression of fibrosis-related markers and liver histology in a mouse model of liver fibrosis. (A) Quantitative real-time PCR analysis of pro-fibrogenic markers (collagen and TGF-β mRNA) showing significant reductions in the secretome injection groups (Ctrl-Sec & PGC-Sec) compared to the saline injection group, with a more pronounced decrease in the PGC-Sec group relative to the Ctrl-Sec group. (B) Western blot analysis of ColA1 (pro-fibrogenic) and TIMP (anti-fibrogenic) protein levels, demonstrating significantly lower ColA1 expression and higher TIMP expression in the secretome injection groups (Ctrl-Sec & PGC-Sec) compared to the saline injection group, and increased TIMP expression in the PGC-Sec group relative to the Ctrl-Sec group. The relative densities had been quantified using Image J software and then were normalized to the density of β-actin in each group. (C) Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of liver specimens revealing a significant reduction in liver fibrosis severity in the secretome injection groups (Ctrl-Sec & PGC-Sec) compared to the saline injection group, with the greatest reduction observed in the PGC-Sec group. (D) Sirius red staining, showing a significant reduction in liver fibrosis in the secretome injection groups (Ctrl-Sec & PGC-Sec) compared to the saline injection group, with the most substantial reduction in the PGC-Sec group. Values are presented as mean ± standard deviation of three independent experiments; * P < 0.05. Abbreviations: mRNA, messenger RNA; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-beta; ColA1, collagen type 1 alpha 1; TIMP, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases; H&E, hematoxylin and eosin; Ctrl-Sec, Control-secretome; PGC-Sec, PGC-1α-secretome.
Figure 3.
In vivo effects of PGC-Sec on the expression of fibrosis-related markers and liver histology in a mouse model of liver fibrosis. (A) Quantitative real-time PCR analysis of pro-fibrogenic markers (collagen and TGF-β mRNA) showing significant reductions in the secretome injection groups (Ctrl-Sec & PGC-Sec) compared to the saline injection group, with a more pronounced decrease in the PGC-Sec group relative to the Ctrl-Sec group. (B) Western blot analysis of ColA1 (pro-fibrogenic) and TIMP (anti-fibrogenic) protein levels, demonstrating significantly lower ColA1 expression and higher TIMP expression in the secretome injection groups (Ctrl-Sec & PGC-Sec) compared to the saline injection group, and increased TIMP expression in the PGC-Sec group relative to the Ctrl-Sec group. The relative densities had been quantified using Image J software and then were normalized to the density of β-actin in each group. (C) Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of liver specimens revealing a significant reduction in liver fibrosis severity in the secretome injection groups (Ctrl-Sec & PGC-Sec) compared to the saline injection group, with the greatest reduction observed in the PGC-Sec group. (D) Sirius red staining, showing a significant reduction in liver fibrosis in the secretome injection groups (Ctrl-Sec & PGC-Sec) compared to the saline injection group, with the most substantial reduction in the PGC-Sec group. Values are presented as mean ± standard deviation of three independent experiments; * P < 0.05. Abbreviations: mRNA, messenger RNA; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-beta; ColA1, collagen type 1 alpha 1; TIMP, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases; H&E, hematoxylin and eosin; Ctrl-Sec, Control-secretome; PGC-Sec, PGC-1α-secretome.
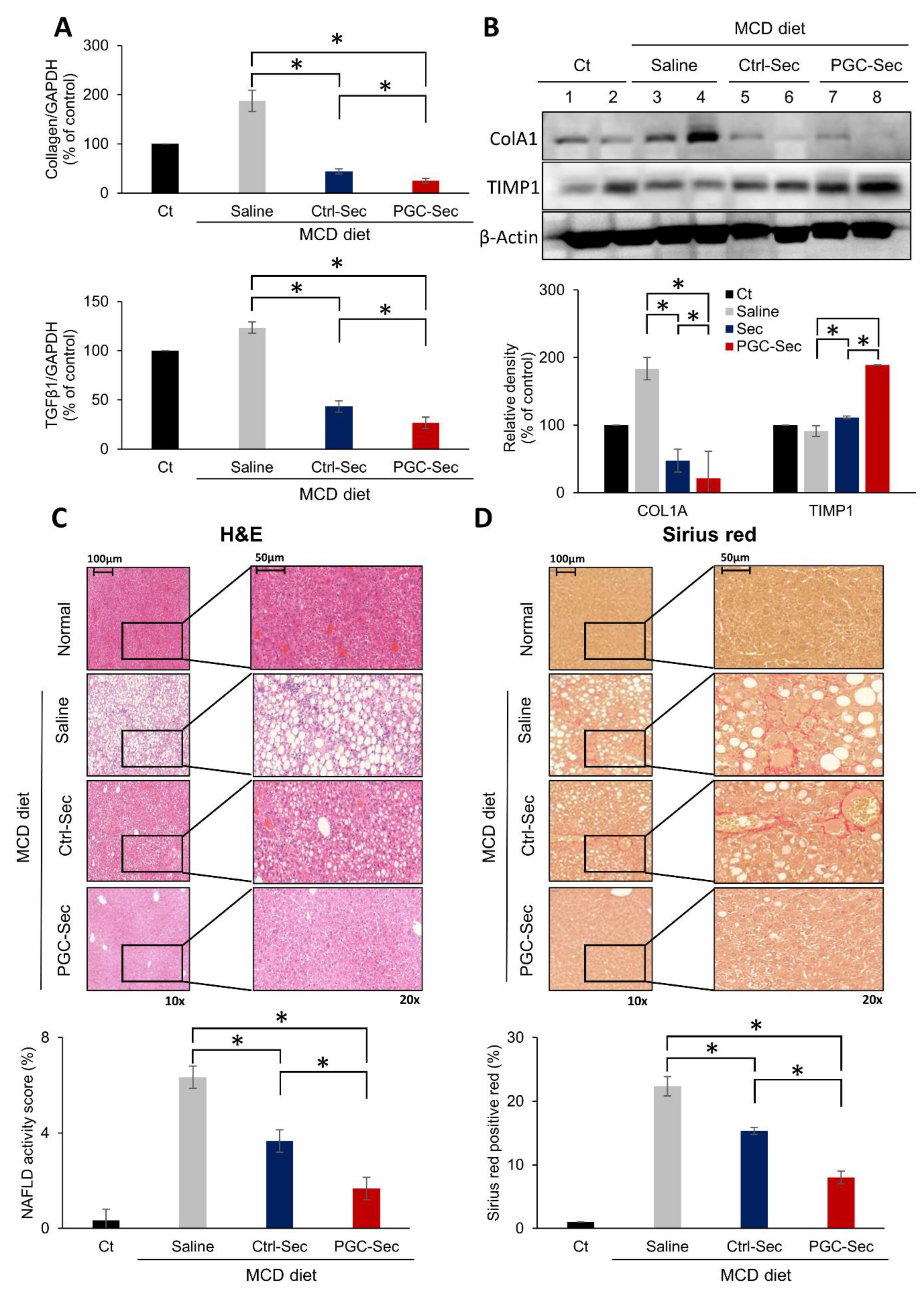
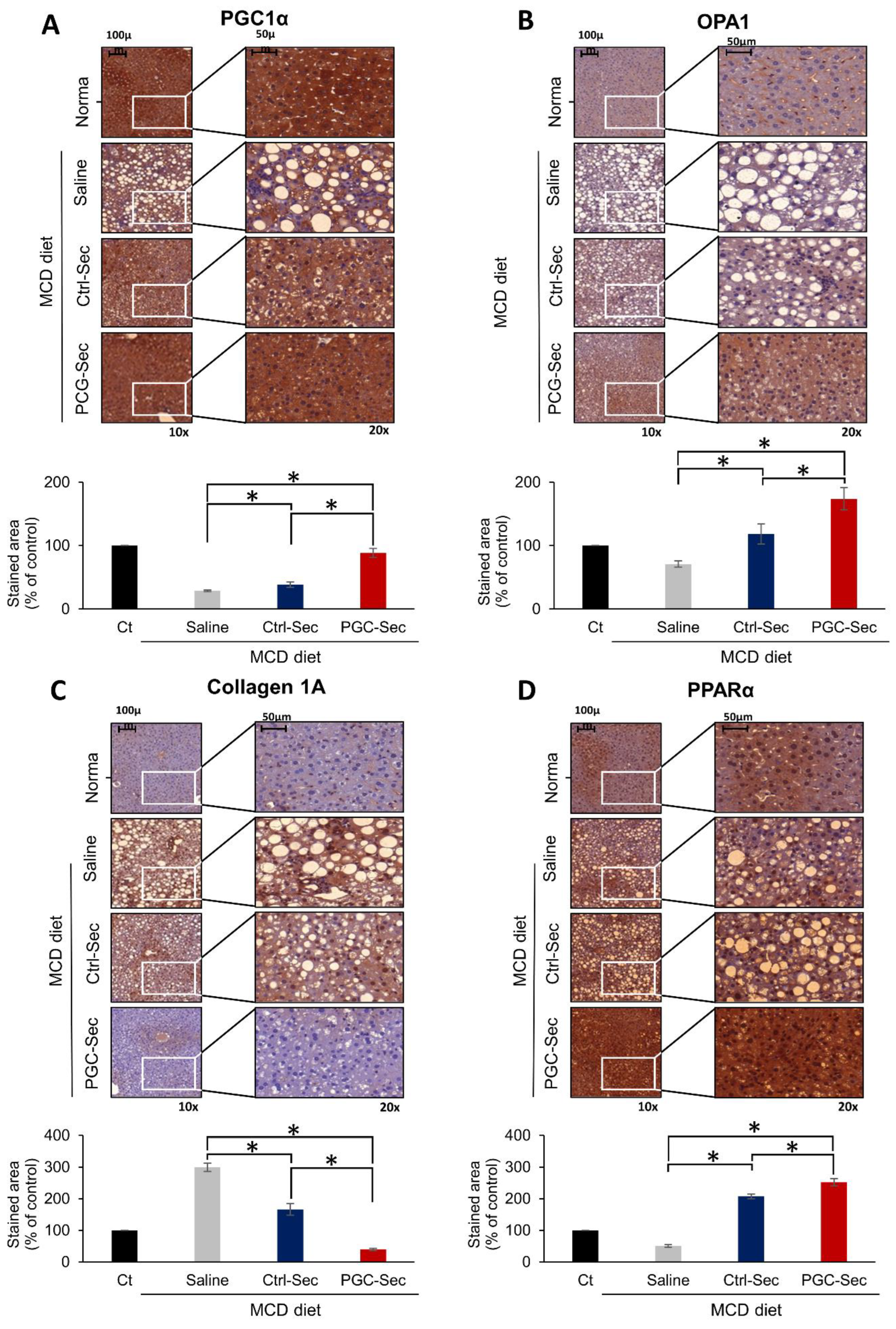
Figure 4.
Immunohistochemistry validating the antifibrogenic effects of PGC-Sec in a mouse model of liver fibrosis. (A) PGC1α immunohistochemistry showing significantly elevated PGC1α expression in the PGC-Sec group. (B) OPA1 expression comparison across different groups, with the highest OPA1 expression observed in the PGC-Sec group, indicating enhanced mitochondrial function. (C) Collagen 1A immunohistochemistry revealing markedly reduced expression of the pro-fibrogenic marker in the PGC-Sec group. (D) PPARα immunohistochemistry showing significantly increased expression of the anti-fibrogenic marker in the PGC-Sec group (P < 0.05). These findings emphasize the profound impact of PGC-Sec treatment on enhancing mitochondrial biogenesis and function, as well as promoting anti-fibrosis processes, collectively highlighting its potential as a novel therapeutic strategy for liver fibrosis. Percentages of immunoreactive areas were measured using NIH image J and expressed as relative values to those in normal livers. Abbreviations: PGC1α, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha; OPA1, optic atrophy 1; Collagen 1A, collagen type 1 alpha 1; PPARα, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha; Ctrl-Sec, Control-secretome; PGC-Sec, PGC-1α-secretome.
Figure 4.
Immunohistochemistry validating the antifibrogenic effects of PGC-Sec in a mouse model of liver fibrosis. (A) PGC1α immunohistochemistry showing significantly elevated PGC1α expression in the PGC-Sec group. (B) OPA1 expression comparison across different groups, with the highest OPA1 expression observed in the PGC-Sec group, indicating enhanced mitochondrial function. (C) Collagen 1A immunohistochemistry revealing markedly reduced expression of the pro-fibrogenic marker in the PGC-Sec group. (D) PPARα immunohistochemistry showing significantly increased expression of the anti-fibrogenic marker in the PGC-Sec group (P < 0.05). These findings emphasize the profound impact of PGC-Sec treatment on enhancing mitochondrial biogenesis and function, as well as promoting anti-fibrosis processes, collectively highlighting its potential as a novel therapeutic strategy for liver fibrosis. Percentages of immunoreactive areas were measured using NIH image J and expressed as relative values to those in normal livers. Abbreviations: PGC1α, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha; OPA1, optic atrophy 1; Collagen 1A, collagen type 1 alpha 1; PPARα, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha; Ctrl-Sec, Control-secretome; PGC-Sec, PGC-1α-secretome.