1. Introduction
Breast cancer is the most common cause of female mortality from cancer around the globe [
1]. Based on the epidemiological reports during the past two decades, the rate of breast cancer-related deaths is markedly increasing worldwide [
2]. Breast cancer is generally categorized into three different subtypes that include estrogen/progesterone receptors positive, HER2-positive, and triple-negative forms [
3]. Each subtype of breast tumor harbors a specific risk profile. Hence, the patients are treated using a variety of approaches depending on the subtype of tumor, disease stage, and patient preferences [
4].
Classical methods of breast cancer therapy such as surgery, radiotherapy, hormone therapy, and chemotherapy are available in clinical settings [
4,
5]. However, therapy resistance and the development of adverse side effects following the use of conventional therapeutic methods are major drawbacks in breast cancer therapy causing disease recurrence and relapse. Consequently, there is an urgent need to seek more efficient therapeutic strategies with slight side effects for the treatment of patients with this disease [
6].
Metastasis is a multi-step process during tumor development leading to the spread of cancer cells to the secondary organs or tissues [
7]. Breast cancer is a highly metastatic cancer and represents a poor prognosis due to the development of a secondary tumor in the distant organ(s) [
8]. When breast cancer cells start the metastasis process, they undergo epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) to acquire invasive characteristics [
9]. EMT is a process of morphology alteration, by which epithelial cells acquire fibroblast-like characteristics typical of mesenchymal cells via orchestrating a set of transcriptional events [
10]. EMT is a pivotal process in morphogenetic alterations during embryonic development, wound repair, and cancer metastasis [
11]. Indeed, metastatic cancer cells usurp this developmental process to initiate a multi-step program leading to tumorigenesis and metastasis [
12]. Angiogenesis is an essential step in tumor development because tumor growth and metastasis rely on efficient angiogenesis [
13].
Rutin is a flavonoid compound found in a variety of plant sources. This compound has various medicinal effects, including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-diabetic, vascular protection, antimicrobial and anti-cancer activities [
14]. The anti-proliferative and anti-metastatic effects of rutin have been proven in various cancer cells. Indeed, this natural product has been shown to hamper the proliferation and migration of human lung and colon cancer cell lines [
15].
In breast cancer cell lines, data on rutin are more confusing. Indeed, one study performed on MB-MDA-231 and MCF-7 cells has shown that rutin does not possess anti-proliferative effect on these cells, at least up to 20 µM but was able to increase the cytotoxicity of two chemotherapy agents, cyclophosphamide and methotrexate. [
16]. On another hand, Elsayed, et al., reported that rutin inhibited triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by a mechanism involving c-Met kinase but using hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) to stimulate proliferation and migration of the cells [
17]. To the best of our knowledge, no previous study has investigated the effects of rutin on angiogenesis and EMT, as two pivotal steps in metastasis, in breast cancer cells. Therefore, the current study aimed to evaluate the effect of rutin on these two key processes in the metastasis of two different breast cancer cell lines, MB-MDA-231 and MCF-7.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Treatments
The breast cancer cell lines used in this present study, MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231, were purchased from Pasture Institute, Tehran, Iran. All the materials used for cell culture were purchased from Gibco, UK. MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cell lines were cultured and incubated in a humidified incubator at 37 °C and 5% CO2. Rutin was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (USA) and stock solution was prepared in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO).
2.2. Cell Viability
Both MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cell lines were seeded into 96-well cell culture plates at the density of 104 cells per well and allowed to adhere to the bottom of the wells. After 24 h, the seeded cells were treated with increasing concentrations of rutin (0, 6.25, 12.50, 25, 50, 100, 200, and 400 μM) for 24, 48, and 72 h. The control cell lines were treated with normal culture medium and vehicle (DMSO). Then, the viability of each cell line was assayed using 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) method. Briefly, at the end of the treatment period, the cell lines were incubated with 5mg/ml MTT solution for 4 h. Subsequently, the MTT solution was discarded and replaced by 100 µl of DMSO to allow the solubilization of a formazan product formed. After 15 min, the absorbance of the formazan product was read at 570 and 630 nm using a plate reader spectrophotometer (PerkinElmer, USA).
2.3. Wound Healing Assay
The effect of rutin treatment on the invasiveness and migratory capacity of MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cell lines was evaluated by the in-vitro scratch assay as previously described [
18]. Briefly, 2×10
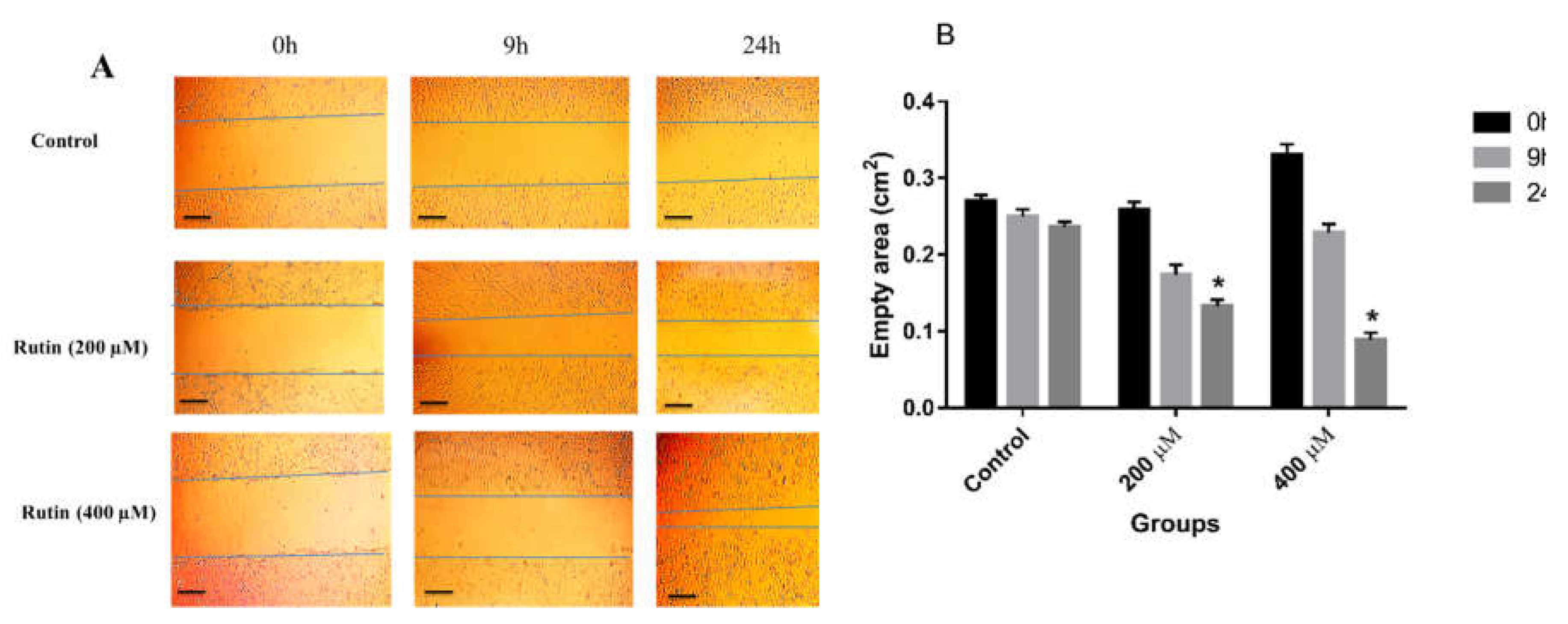
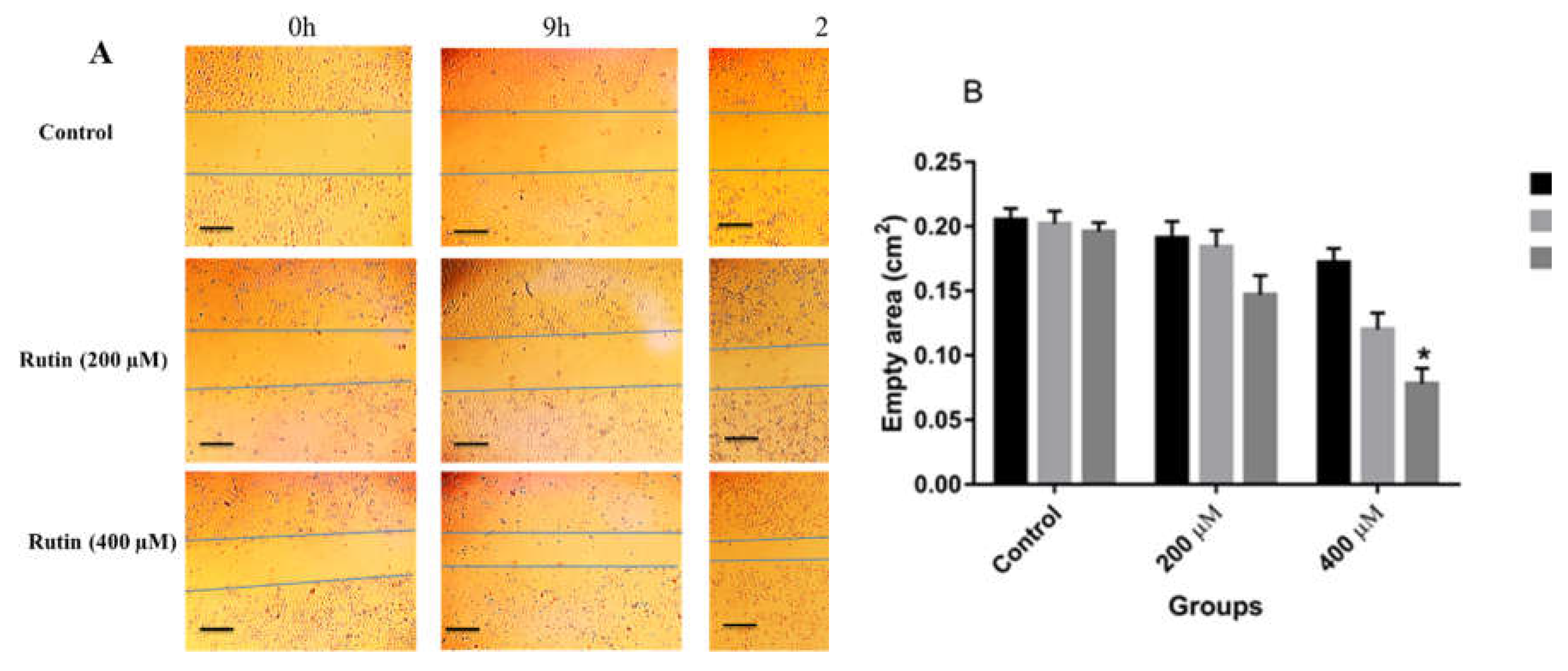
5 cells were seeded in a 6-well cell culture plate and allowed to adhere and grow to 50–60%. Subsequently, two horizontal scratches were created in the center of each well using 200 µl sterile pipette tips. One vertical line was created in each well to take photographs of scratches at the same point. Then, each well was washed with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) buffer solution (pH ~ 7.4) to remove cell debris. Afterward, three test wells were treated with 200 and 400 μM rutin compound and three control wells were treated with normal culture medium. Finally, the photographs of the wound healing capacity of both cell lines were captured at 0h, 9h, and 24h.
2.4. Real Time PCR Analysis
The effect of rutin on the gene markers of proliferation, EMT, and angiogenesis was evaluated by using the Quantitative Real-time-PCR technique. Following the treatment of MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cell lines with rutin at the concentration of 200 µM, for 48 h, the total RNAs were extracted from treated and control cells by an RNeasy mini kit (Qiagen Co., Korea). To estimate the concentration and quality of total RNA, the absorbance of the samples was measured by a Nanodrop 2000c spectrophotometer. Afterward, 2μg of total RNA sample was collected to synthesize cDNA molecules using a cDNA Synthesis Kit (BioFact, Korea). Then, ABI PRISM7900HT (Applied Biosystems, USA) qRT-PCR detection system with SYBR GREEN PCR master mix (Ampliqon, Denmark) was used to assess the expression levels of MKI67, CDH1, CDH2, VIM, FN1, VEGFA, and THBS1 genes. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) gene expression level was considered the internal control gene. The relative expression (fold changes) of the above-mentioned genes was calculated by the 2
-ΔΔCT formula.
Table 1 shows the primer sequences used for the amplification of the above-mentioned genes.
2.5. Western Blot Analysis
Both MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cell lines were seeded in 6-well culture plates at the density of 2×10
5 cells/well and allowed to adhere overnight. Then, the test cell lines were treated with 200 µM rutin for 48 h. The control cell lines were treated with culture medium. After 48 h, the treated cells were lysed using radioimmunoprecipitation assay (RIPA) buffer (Thomas Scientific Inc, USA). The protein content of the whole cell lysates was measured using the Bradford method [
19]. Consequently, the SDS-PAGE technique was used to separate 40 µg of total protein, and protein blots were transmitted onto PVDF membranes (Roche, Germany). The membranes were then blocked with 5% BSA (Sigma Aldrich, MO, USA) in 0.1% Tween 20 for 1 h. The blots were incubated with primary antibodies (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, USA) against E-cadherin, N-cadherin, Fibronectin 1, Vimentin, ki67, VEGF, Thrombospondin1, and β-actin at 4°C overnight. After extensive washes, the membranes were exposed to secondary antibodies conjugated with HRP for 1 h at room temperature. After further washes, the blots were visualized by adding enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL) substrate.
2.6. Data Analysis
The results of the present study were obtained from three independent experiments. The statistical analyses were done by GraphPad Prism software version 7. The data were analyzed using the one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) test followed by Duncan’s multiple range tests as the post hoc. P-values less than 0.05 and 0.01 were considered significant. All data are representative of the mean ± standard deviation (SD). Analysis of wound areas was performed by ImageJ software.
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Rutin on the Proliferation of MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 Cell Lines
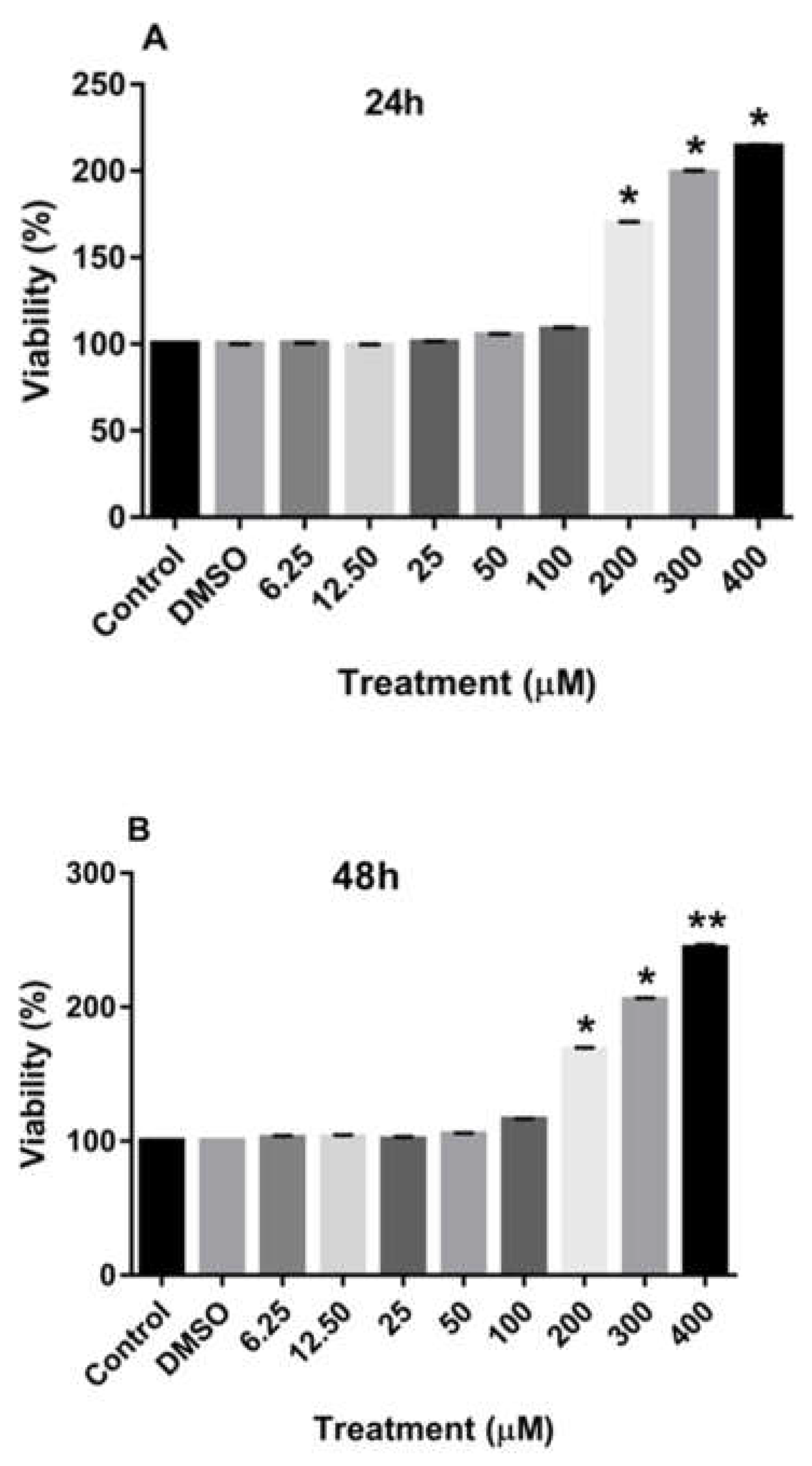
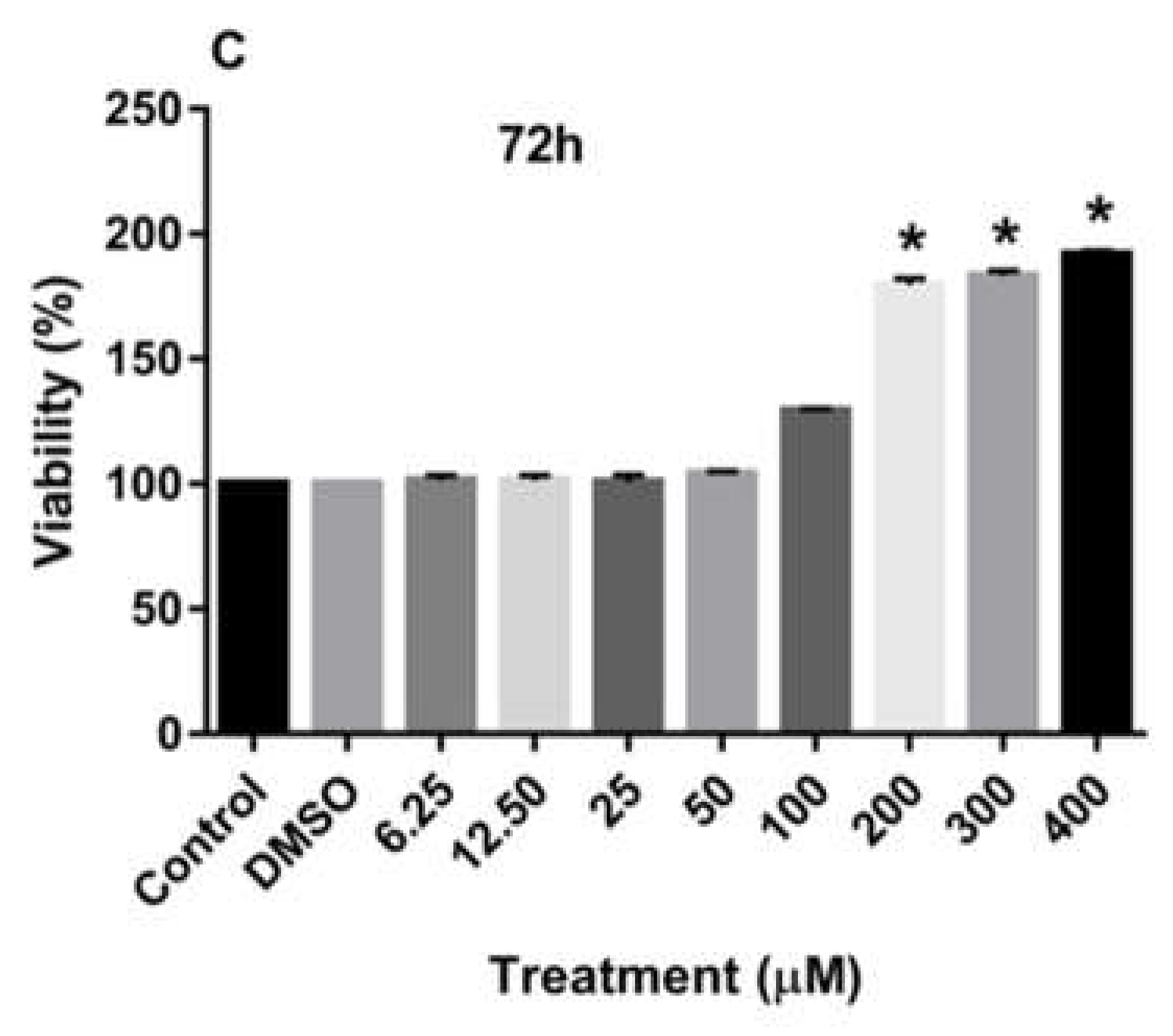
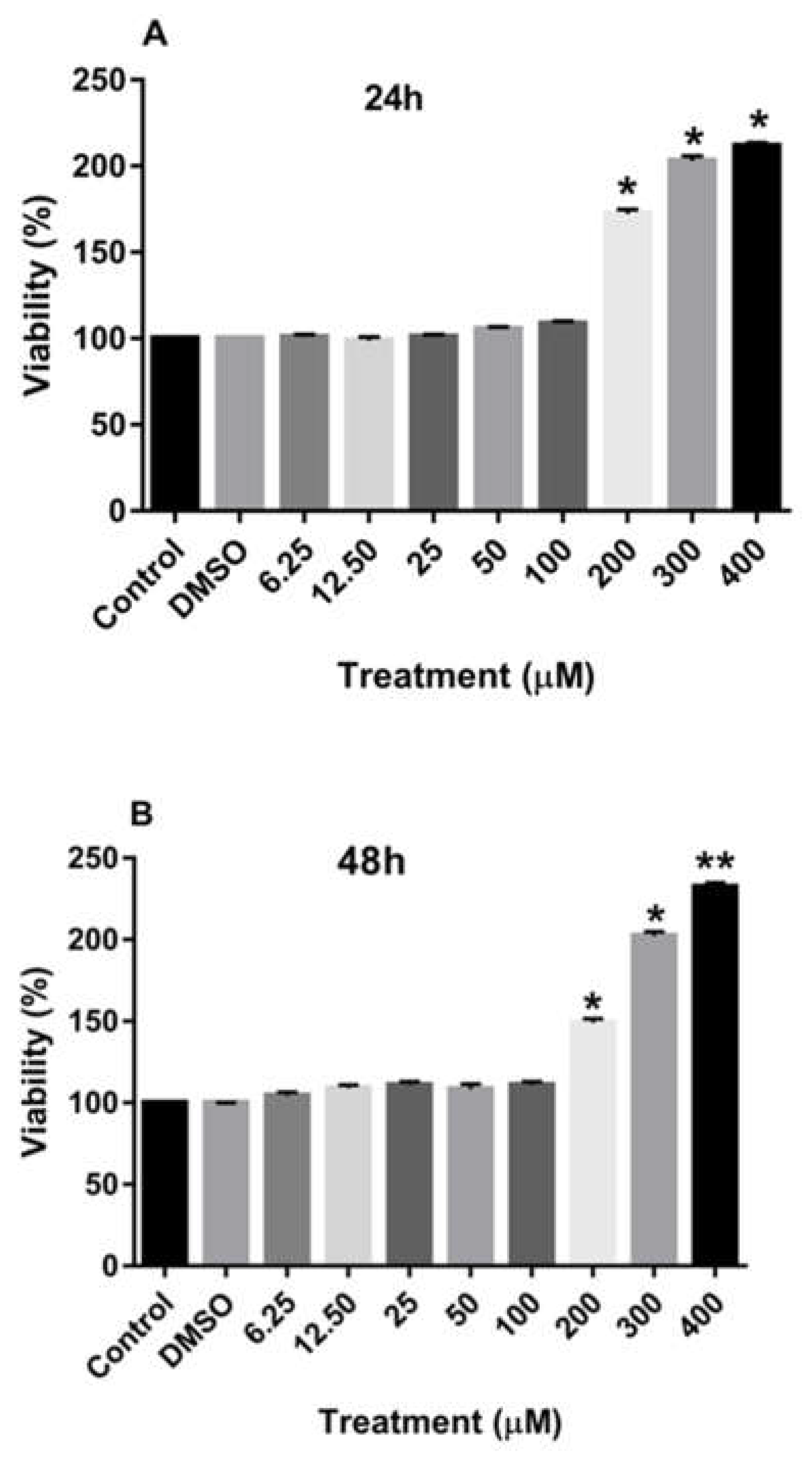
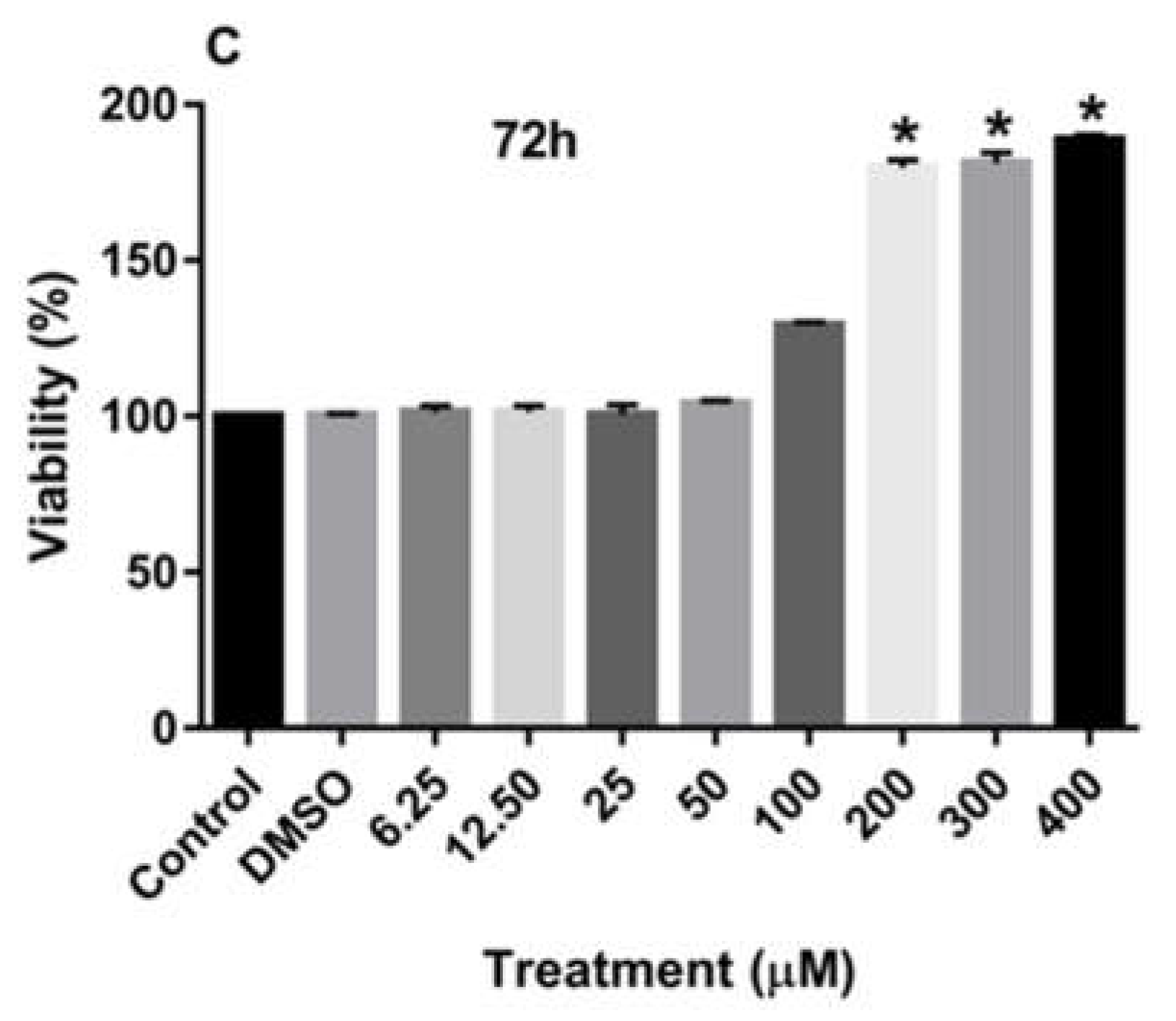
Treatment of MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cell lines with increasing concentrations of rutin for 24, 48, and 72 h promoted the proliferation of both cancer cell lines in a dose-dependent manner in comparison to the culture medium (control) and DMSO-treated cells. As depicted in
Figure 1A-C, treating the MDA-MB-231 cell line with rutin for 24, 48, and 72 h significantly increased the number of viable cells at concentrations of more than 200 µM.
Figure 2A-C also demonstrate that treatment of MCF-7 cells with increasing concentrations of rutin for 24, 48, and 72 h also significantly enhanced the proliferation of these cancer cells at the dose of more than 200 µM.
3.2. Effects of Rutin on the Invasion and Migration of MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 Cell Lines
To determine the effect of rutin on the invasion and migration of MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cell lines, the cells were seeded into 6 well plates and treated with 200 and 400 μM rutin. The results showed that rutin treatment promoted the invasion and migration of MDA-MB-231 cells at both concentrations of this natural compound (
Figure 3A). Indeed, in MDA-MB-231 cells, rutin (200 and 400 μM) significantly and time-dependently decreased the empty areas compared with untreated control (
Figure 3B).
Similarly, in MCF-7 cells, rutin, at concentrations of 200 and 400 μM, had a promoting effect on the invasion and migration of the treated cells in comparison to untreated controls (
Figure 4A and B), with a significant effect observed only at the dose of 400 μM in that case.
3.3. Effects of Rutin on Gene and Protein Expression in MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 Cell Lines
To evaluate the effect of rutin treatment on markers of proliferation, EMT, and angiogenesis, the expression levels of the corresponding gene markers in the MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cell lines were quantified.
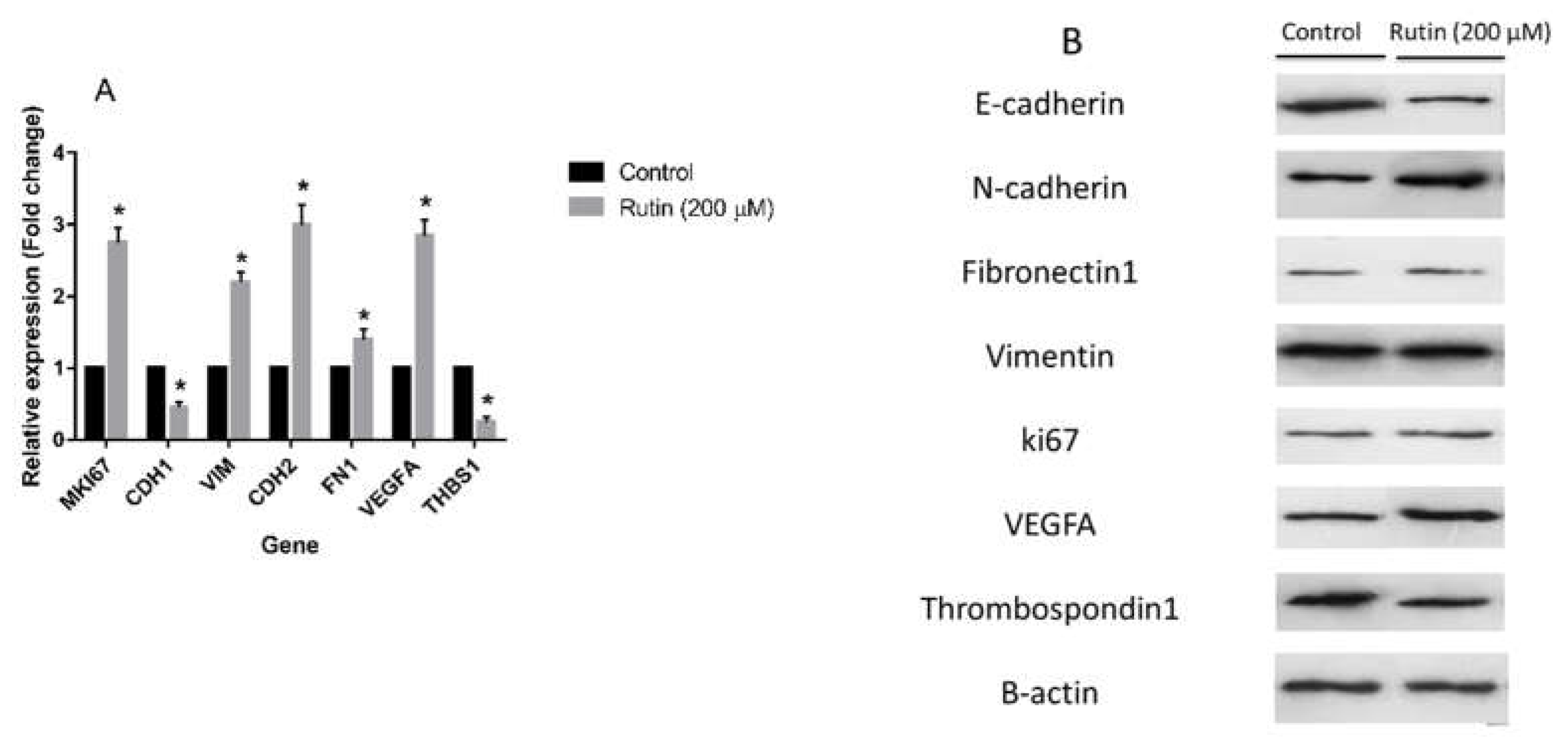
Figure 5A illustrates that rutin (200 μM) significantly amplified the mRNA expression of proliferation marker MKI67, pro-angiogenic marker VEGFA, and EMT markers VIM, CDH2, and FN1 in MDA-MB-231 cell line in comparison to the untreated control cells. In parallel, rutin downregulated mRNA expression of EMT marker CDH1 and anti-angiogenic marker THBS1 in this cancer cell line. As depicted in
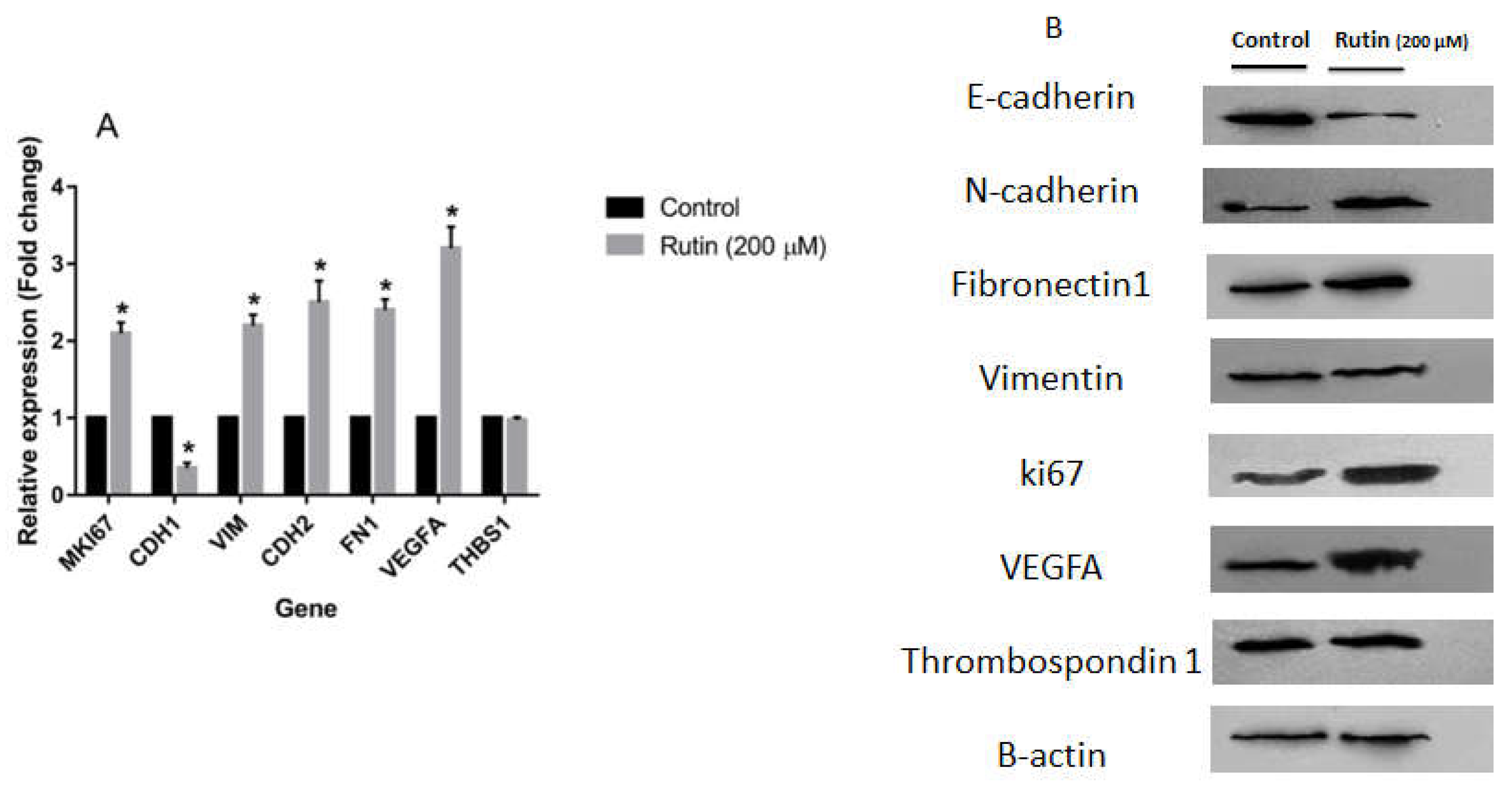
Figure 6A, rutin (200 μM) also significantly upregulated the expression of MKI67, as a proliferation marker, in MCF-7. Rutin also activated the EMT process in MCF-7 cells by suppressing the mRNA expression of CDH1 and increasing VIM, FN1, and CDH2 expression compared to the untreated control cells. Rutin at 200 µM also promoted the expression of the pro-angiogenic marker VEGFA in MCF-7 cells with no remarkable effect on the expression levels of the anti-angiogenic gene marker THBS1.
Treatment of the MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cell lines with rutin had a modulatory effect on the expression levels of various proteins involved in the angiogenesis and EMT process in these cancer cells. Thus, according to the results of western blotting analyses, rutin, at the concentration of 200 μM, had a possible effect on the EMT process in the MDA-MB-231 cell line by downregulating E-cadherin and upregulating N-cadherin in comparison to untreated control cells. However, it had no remarkable effect on the expression levels of Vimentin and Fibronectin 1 proteins compared with the controls. This natural compound also showed no significant effect on the protein levels of proliferation marker ki67 in the MDA-MB-231 cell line. Nonetheless, rutin activated angiogenesis by elevating the expression of the pro-angiogenic marker VEGFA and declining the anti-angiogenic marker Thrombospondin 1 (
Figure 5B).
Treatment of MCF-7 cells with rutin 200 µM decreased the protein expression of E-cadherin and increased the protein levels of ki67, N-cadherin, and Fibronectin 1 as compared with the untreated control with no significant effect on the protein level of Vimentin (
Figure 6B). As observed with MDA-MB-231 cells, in MCF-7 cells, rutin acted positively on angiogenesis process by upregulating VEGFA although no remarkable effect on anti-angiogenic Thrombospondin 1 was observed in that case.
4. Discussion
According to the literature, rutin has shown anti-proliferative and anti-metastatic effects in some cancer cell lines [
15]. For breast cancer cells, results were less evident, one study showing the absence of effect of rutin alone (at least for concentration of rutin up to 20 µM, the other study demonstrating an anti-proliferative effect on breast cancer cells pre-treated with hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) [
16,
17]. Therefore, we aimed to evaluate the potential effect of rutin flavonoid on the proliferation, invasion, migration, and angiogenesis in two metabolically different human breast cancer cell lines, MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7.
In the present study, the MTT assay results revealed that rutin stimulated the proliferation of both MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cancer cell lines at concentrations greater than 200 µM. Evaluation of the expression of ki67 also uncovered that rutin increased this marker in the MDA-MB-231 cell line at the mRNA level but had no effect on the expression of its protein product. In the MCF-7 cell line, rutin upregulated both mRNA and protein levels of ki67. Ki67 is known as a key marker of tumor proliferation and invasiveness [
20]. These data may suggest rutin as a proliferation stimulator in breast cancer cells.
The results of the wound scratch assay illustrated that rutin acts as an inducer of invasion and migration in the MDA-MB-231 cell line at doses of 200 and 400 µM. However, significant wound closure was observed in MCF-7 cells only following rutin treatment at a concentration of 400 µM. This difference may be due to the higher migratory activity of the MDA-MB-231 cell line in comparison to MCF-7 cells. The wound closure capacity of rutin may propose a potential metastatic-inducing activity of rutin in breast cancer cells.
Based on the results of the wound scratch assay, we decided to uncover the mechanism by which rutin has promoted the metastasis of MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Thus, the effect of rutin treatment on the expression levels of EMT markers in both cancer cell lines was evaluated. EMT is the leading event in the process of metastasis that allows an epithelial cell undergoes biochemical changes leading to a mesenchymal cell phenotype which is very invasive and metastatic [
21]. EMT is triggered by a loss of E-cadherin followed by increased levels of N-cadherin, vimentin, and Fibronectin [
22]. The data of real-time-PCR and western blotting methods of the present study showed that rutin may have triggered the EMT process in MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cells to promote the invasion and migration of these cancer cells. In MDA-MB-231 cells, rutin decreased the expression of E-cadherin and increased the levels of N-cadherin in comparison to control cells. In the MCF-7 cell line, rutin upregulated N-cadherin and Fibronectin 1 and downregulated E-cadherin. Rutin exerted no effect on the expression of vimentin in MCF-7 cells and vimentin and Fibronectin 1 in MDA-MB-231 cells. Rutin had a regulating effect on the expression of the pro-angiogenic marker VEGFA and anti-angiogenic marker Thrombospondin 1 in MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cell lines. It increased the expression of VEGFA and decreased the expression of Thrombospondin 1 in the MDA-MB-231 cell line. VEGFA expression was also increased due to the treatment of MCF-7 cells with rutin. However, it had no remarkable effect on the expression levels of Thrombospondin 1. Tumor angiogenesis is a pivotal step in the metastatic propagation of the tumor cells to distant organs [
23]. Therefore, it appears that rutin could effectively induce the angiogenic pathway to help the progression of breast tumors to secondary organs.
The present data on the effect of rutin on breast cancer is opposite to those reported in the literature. One possible explanation for these controversial results is based on the fact that rutin is a phytoestrogen compound with a variety of beneficial or adverse effects depending on the subject studied, the sex, the age, and the physiological status [
24]. Phytoestrogens have been shown to exert estrogenic effects by acting on estrogen receptors (ERs) [
25]. Some studies have proven that rutin elevates the estrogen concentration in plasma and mammary glands and upregulates the expression of ER in some tissues [
26]. Synthesis and metabolism of estrogens in steroid hormone-dependent organs by phytoestrogens may also disrupt the balance of local hormone levels leading to a variety of women's health issues, varying from altered menstrual cycle to hormone-dependent cancers [
25]. Phytoestrogens have been proven to inhibit estrogen inactivation and excretion leading to an increased bioavailability of endogenous estrogens and a disrupted endocrine balance [
27]. This pathological alteration may have a critical role in human susceptibility to breast cancer [
28]. In a previous in-vitro study, proliferation-stimulating activity of a phytoestrogen compound was evaluated. Yuan, et al provided evidence to highlight that genistein, a phytoestrogen, can induce cell growth in two human breast cancer cell lines (MCF-7 and T47D) in a concentration-dependent manner through ER activation [
29]. Whereas genistein promotes the proliferation of these cell lines at lower concentrations but suppresses their growth at higher doses [
29]. On the contrary, the present study revealed that rutin phytoestrogen stimulated cell growth at higher concentrations suggesting that the observed effect is not related to ER activation. Also in favor of this hypothesis, rutin was active both on ER/PR-positive MCF-7 and on triple-negative MDA-MB-231 cells further suggesting that the observed stimulatory effect of rutin does not depend on the steroid receptors.
An alternative scenario may arise from the intracellular metabolism of rutin in breast cancer cell lines. Harris, et al demonstrated that a variety of phytoestrogens act as potent inhibitors of sulfotransferases, which are enzymes that add a sulfate group to estrogens to inactivate them [
27]. Moreover, Yuan, et al observed that genistein, a phytoestrogen, was extensively conjugated with sulfate and glucuronide groups in breast cancer cells. Interestingly, these conjugated forms of genistein did not affect the proliferation stimulation of the breast cancer cell lines, and only unconjugated forms played an inducer of proliferation role [
29]. Comparing those data with the results of the present study may suggest the inhibition of sulfotransferases by rutin, as phytoestrogen, in MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cells, causing the blockage of rutin inactivation. This may have resulted in a high level of the active form of rutin in the intracellular space and the promotion of MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cells growth and metastasis. Elsayed, et al conducted a study to evaluate the effect of rutin on the proliferation, migration, and invasion of four different breast cancer cell lines. Oppositely to the present study, they reported that rutin could exert anti-proliferative and anti-metastatic effects on breast cancer cells. The comparison between our study and that of Elsayed, et al showed that different results may arise from the differences between the designs of the two studies [
17]. Indeed, in their study, Elsayed et al treated the breast cancer cells with hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), as a scatter factor, prior to treatment with rutin. This growth factor may interfere with the effects of rutin and pretreatment of the cells with it could render anti-proliferative and anti-metastatic activity to rutin. The use of rutin alone in the present study compared to the treatment by Elsayed et al., with rutin in the presence of HGF is certainly responsible for the opposite results obtained.
5. Conclusions
The present data unraveled the cancer-promoting effects of rutin on two different breast cancer cell lines. Contrary to the previously published data showing the anti-proliferative effect of rutin on HGF-treated breast cancer cells, the present study demonstrates that this natural phytoestrogen stimulated the proliferation, invasiveness, and pro-angiogenic capacity of breast cancer cells. Rutin induced invasion and migration of these cancer cell lines by a mechanism that involved the EMT process. It also stimulated the angiogenic pathway involved in the metastasis of breast cancer cells. Although rutin has been reported as an anti-cancer agent in the literature, these data suggest that it could act as a breast cancer-promoting or progressing natural compound. Although the present data is primary, it may pave the way to design more comprehensive studies for the evaluation of the effects of rutin phytoestrogen in a variety of cancers.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.R. and H.HM.; methodology, Z.T.; software, S.S.; validation, M.M., S.R. and Z.Z.; formal analysis, H.HM.; investigation, F.G.; resources, H.HM.; data curation, S.R.; writing—original draft preparation, H.HM.; writing—review and editing, S.R. and M.M.; visualization, Z.T.; supervision, S.R.; project administration, S.R.; funding acquisition, S.R. and M.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran, grant number 28658.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are a available upon request to corresponding authors.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the vice chancellor of research affairs Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran Iran.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Trayes, K.P.; Cokenakes, S.E.H. Breast Cancer Treatment. Am Fam Physician 2021, 104, 171–178. [Google Scholar]
- Azamjah, N.; Soltan-Zadeh, Y.; Zayeri, F. Global Trend of Breast Cancer Mortality Rate: A 25-Year Study. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 2019, 20, 2015–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, A.M.; Friebel-Klingner, T.; Ehsan, S.; He, W.; Welch, M.; Chen, J.; Kontos, D.; Domchek, S.M.; Conant, E.F.; Semine, A.; et al. Relationship of established risk factors with breast cancer subtypes. Cancer Med 2021, 10, 6456–6467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waks, A.G.; Winer, E.P. Breast Cancer Treatment: A Review. Jama 2019, 321, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahali, A.; Ghanadian, M.; Jafari, S.M.; Aghaei, M. Mitochondrial and caspase pathways are involved in the induction of apoptosis by nardosinen in MCF-7 breast cancer cell line. Res Pharm Sci 2018, 13, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Malik, J.A.; Ahmed, S.; Jan, B.; Bender, O.; Al Hagbani, T.; Alqarni, A.; Anwar, S. Drugs repurposed: An advanced step towards the treatment of breast cancer and associated challenges. Biomed Pharmacother 2022, 145, 112375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajabi, S.; Rajani, H.F.; Mohammadkhani, N.; Ramírez-Coronel, A.A.; Maleki, M.; Maresca, M.; Hajimehdipoor, H. Long Non-Coding RNAs as Novel Targets for Phytochemicals to Cease Cancer Metastasis. Molecules 2023, 28, 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.; Kim, D.; Ko, S.; Kim, A.; Mo, K.; Yoon, H. Breast Cancer Metastasis: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23, 6806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karamanou, K.; Franchi, M.; Vynios, D.; Brézillon, S. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and invadopodia markers in breast cancer: Lumican a key regulator. Semin Cancer Biol 2020, 62, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakib, H.; Rajabi, S.; Dehghan, M.H.; Mashayekhi, F.J.; Safari-Alighiarloo, N.; Hedayati, M. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in thyroid cancer: a comprehensive review. Endocrine 2019, 66, 435–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Xing, T.; Yang, Z.; Dudek, R.; Lu, Q.; Chen, Y.H. Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition in Embryonic Development, Tissue Repair and Cancer: A Comprehensive Overview. J Clin Med 2017, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malla, R.; Puvalachetty, K.; Vempati, R.K.; Marni, R.; Merchant, N.; Nagaraju, G.P. Cancer Stem Cells and Circulatory Tumor Cells Promote Breast Cancer Metastasis. Clin Breast Cancer 2022, 22, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabi, S.; Dehghan, M.H.; Dastmalchi, R.; Jalali Mashayekhi, F.; Salami, S.; Hedayati, M. The roles and role-players in thyroid cancer angiogenesis. Endocr J 2019, 66, 277–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caparica, R.; Júlio, A.; Araújo, M.E.M.; Baby, A.R.; Fonte, P.; Costa, J.G.; Santos de Almeida, T. Anticancer Activity of Rutin and Its Combination with Ionic Liquids on Renal Cells. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Sghaier, M.; Pagano, A.; Mousslim, M.; Ammari, Y.; Kovacic, H.; Luis, J. Rutin inhibits proliferation, attenuates superoxide production and decreases adhesion and migration of human cancerous cells. Biomed Pharmacother 2016, 84, 1972–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iriti, M.; Kubina, R.; Cochis, A.; Sorrentino, R.; Varoni, E.M.; Kabała-Dzik, A.; Azzimonti, B.; Dziedzic, A.; Rimondini, L.; Wojtyczka, R.D. Rutin, a Quercetin Glycoside, Restores Chemosensitivity in Human Breast Cancer Cells. Phytother Res 2017, 31, 1529–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsayed, H.E.; Ebrahim, H.Y.; Mohyeldin, M.M.; Siddique, A.B.; Kamal, A.M.; Haggag, E.G.; El Sayed, K.A. Rutin as A Novel c-Met Inhibitory Lead for The Control of Triple Negative Breast Malignancies. Nutr Cancer 2017, 69, 1256–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedayati, M.; Rajabi, S.; Nikzamir, A. Papillary Thyroid Cancer-Promoting Activities of Combined Oral Contraceptive Components. Galen Med J 2020, 9, e1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kielkopf, C.L.; Bauer, W.; Urbatsch, I.L. Bradford Assay for Determining Protein Concentration. Cold Spring Harb Protoc 2020, 2020, 102269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, S.; Yin, J. Radiomics of dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging parametric maps and apparent diffusion coefficient maps to predict Ki-67 status in breast cancer. Front Oncol 2022, 12, 847880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, X.; Li, Q.; Wu, F.; Lin, J.; Chen, J.; Zheng, H.; Guo, L. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Metabolic Switching in Cancer: Lessons From Somatic Cell Reprogramming. Front Cell Dev Biol 2020, 8, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, C.Y.; Chai, J.Y.; Tang, T.F.; Wong, W.F.; Sethi, G.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Chong, P.P.; Looi, C.Y. The E-Cadherin and N-Cadherin Switch in Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition: Signaling, Therapeutic Implications, and Challenges. Cells 2019, 8, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudley, A.C.; Griffioen, A.W. Pathological angiogenesis: mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Angiogenesis 2023, 1, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canivenc-Lavier, M.C.; Bennetau-Pelissero, C. Phytoestrogens and Health Effects. Nutrients 2023, 15, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Duursen, M.B.M. Modulation of estrogen synthesis and metabolism by phytoestrogens in vitro and the implications for women's health. Toxicol Res (Camb) 2017, 6, 772–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.-d.; Diao, Q.-y.; Wang, Y.-y.; Tu, Y.; Deng, K.-d.; Wang, X.-j.; Fu, T.; Yan, G.-l. The Effect of Administration of Rutin on Plasma Levels of Estrogen, Prolactin, Growth Hormone and Gene Expression of Their Receptors in Mammary Glands in Ovariectomized Rats. Jo Integ Agric 2012, 11, 1700–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, R.M.; Wood, D.M.; Bottomley, L.; Blagg, S.; Owen, K.; Hughes, P.J.; Waring, R.H.; Kirk, C.J. Phytoestrogens are potent inhibitors of estrogen sulfation: implications for breast cancer risk and treatment. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004, 89, 1779–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, C.J.; Harris, R.M.; Wood, D.M.; Waring, R.H.; Hughes, P.J. Do dietary phytoestrogens influence susceptibility to hormone-dependent cancer by disrupting the metabolism of endogenous oestrogens? Biochem Soc Trans 2001, 29, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, B.; Wang, L.; Jin, Y.; Zhen, H.; Xu, P.; Xu, Y.; Li, C.; Xu, H. Role of metabolism in the effects of genistein and its phase II conjugates on the growth of human breast cell lines. Aaps j 2012, 14, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Figure 1.
The effects of rutin on the proliferation of MDA-MB-231 cell line. The cells were treated with increasing concentrations of rutin (0, 6.25, 12.50, 25, 50, 100, 200, and 400 μM) for 24 (A), 48 (B), and 72 (C) h. The viability of the cells was estimated by MTT assay. The data are expressed as mean ± SD of three independent experiments. Significant differences were found between the treatment and control groups at *P<0.05 and **P<0.01.
Figure 1.
The effects of rutin on the proliferation of MDA-MB-231 cell line. The cells were treated with increasing concentrations of rutin (0, 6.25, 12.50, 25, 50, 100, 200, and 400 μM) for 24 (A), 48 (B), and 72 (C) h. The viability of the cells was estimated by MTT assay. The data are expressed as mean ± SD of three independent experiments. Significant differences were found between the treatment and control groups at *P<0.05 and **P<0.01.
Figure 2.
The effects of rutin on the proliferation of MCF-7 cell line. The cells were treated with various concentrations of rutin (0, 6.25, 12.50, 25, 50, 100, 200, and 400 μM) for 24 (A), 48 (B), and 72 (C) hours. The cell viabilities were determined using MTT assay method. The data are expressed as mean ± SD of three independent experiments. Significant differences were found between the treatment and control groups at *P<0.05 and **P<0.01.
Figure 2.
The effects of rutin on the proliferation of MCF-7 cell line. The cells were treated with various concentrations of rutin (0, 6.25, 12.50, 25, 50, 100, 200, and 400 μM) for 24 (A), 48 (B), and 72 (C) hours. The cell viabilities were determined using MTT assay method. The data are expressed as mean ± SD of three independent experiments. Significant differences were found between the treatment and control groups at *P<0.05 and **P<0.01.
Figure 3.
(A) The effect of rutin treatment on the migratory capacity of MDA-MB-231 cell line. The cultured cells were scratched with a sterile pipette tip followed by the treatment with 200 and 400 µM rutin. Photographs of wound closure process were captured at 0 h, 9 h and 24 h of post-treatment. (B) Data are expressed as cell migration area (cm2) compared with control (mean ± SD). *P<0.05 vs. control. The scale bar represents 100 µm.
Figure 3.
(A) The effect of rutin treatment on the migratory capacity of MDA-MB-231 cell line. The cultured cells were scratched with a sterile pipette tip followed by the treatment with 200 and 400 µM rutin. Photographs of wound closure process were captured at 0 h, 9 h and 24 h of post-treatment. (B) Data are expressed as cell migration area (cm2) compared with control (mean ± SD). *P<0.05 vs. control. The scale bar represents 100 µm.
Figure 4.
(A) The effect of rutin treatment on the migratory capacity of MCF-7 cell line. The cultured cells were scratched with a sterile pipette tip followed by the treatment with 200 and 400 µM rutin. Photographs of wound closure process were captured at 0 h, 9 h and 24 h of post-treatment. (B) Data are expressed as cell migration area (cm2) compared with control (mean ± SD). *P<0.05 vs. control. The scale bar represents 100 µm.
Figure 4.
(A) The effect of rutin treatment on the migratory capacity of MCF-7 cell line. The cultured cells were scratched with a sterile pipette tip followed by the treatment with 200 and 400 µM rutin. Photographs of wound closure process were captured at 0 h, 9 h and 24 h of post-treatment. (B) Data are expressed as cell migration area (cm2) compared with control (mean ± SD). *P<0.05 vs. control. The scale bar represents 100 µm.
Figure 5.
(A) The effect of rutin at the concentration of 200 µM for 48 h on the mRNA levels of proliferation, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and angiogenesis markers in MDA-MB231 cell line. The data represent as means ± SD for the three independent experiments (*P<0.05, compared with the control). (B) Effect of rutin (200 µM for 48 h) on the protein expression of above mentioned markers. Blots shown correspond to observed effects in three independent experiments.
Figure 5.
(A) The effect of rutin at the concentration of 200 µM for 48 h on the mRNA levels of proliferation, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and angiogenesis markers in MDA-MB231 cell line. The data represent as means ± SD for the three independent experiments (*P<0.05, compared with the control). (B) Effect of rutin (200 µM for 48 h) on the protein expression of above mentioned markers. Blots shown correspond to observed effects in three independent experiments.
Figure 6.
(A) The effect of ruin treatment at the concentration of 200 µM for 48 h on the expression of proliferation, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and angiogenesis gene markers in MCF-7 cell line. The data represent as means ± SD for the three separate experiments (*P<0.05, compared with the control). (B) Effect of rutin treatment (200 µM for 48 h) on the protein products of the mentioned markers in MCF-7 cell line. Blots shown correspond to observed effects in three independent experiments.
Figure 6.
(A) The effect of ruin treatment at the concentration of 200 µM for 48 h on the expression of proliferation, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and angiogenesis gene markers in MCF-7 cell line. The data represent as means ± SD for the three separate experiments (*P<0.05, compared with the control). (B) Effect of rutin treatment (200 µM for 48 h) on the protein products of the mentioned markers in MCF-7 cell line. Blots shown correspond to observed effects in three independent experiments.
Table 1.
Primer sequences used in the present study.
Table 1.
Primer sequences used in the present study.
| Gene name |
Forward primer |
Reverse primer |
| MKI67 |
5′-GCTACTCCAAAGAAGCCTGTG-3′ |
5’-AAGTTGTTGAGCACTCTGTAGG-3′ |
| CDH1 |
5'-GGGGTCTGTCATGGAAGGTG-3′ |
5'-CGACGTTAGCCTCGTTCTCA-3′ |
| CDH2 |
5'-GCGTCTGTAGAGGCTTCTGG-3′ |
5'-GCCACTTGCCACTTTTCCTG-3′ |
| FN1 |
5'-ACAAGCATGTCTCTCTGCCAA-3′ |
5'-TCAGGAAACTCCCAGGGTGA-3′ |
| VIM |
5'-TCCGCACATTCGAGCAAAGA-3′ |
5'-ATTCAAGTCTCAGCGGGCTC-3′ |
| VEGFA |
5'-GAGCAAGACAAGAAAATCCC-3′ |
5'-CCTCGGCTTGTCACATCTG-3′ |
| THBS1 |
5'-CCCTTGTGCTCAGAGTGGAT-3′ |
5'-GCCAGTAGAGAACAAATAAGCATGG-3′ |
| GAPDH |
5'-ACCCACTCCTCCACCTTTGA-3′ |
5'-CT GTTGCTGTAGCCAAATTCGT-3′ |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).