1. Introduction
Nanomaterials (NMs) are one of the most versatile products but due to their intrinsic physicochemical properties they can interact with various biological molecules or cells causing alterations in the organism. ZnO nanoparticles exhibit promising biomedical applications based on its biological activities [
1]. Nevertheless, when in contact with living organisms, nanoparticles interact with proteins, bind them to form the protein corona and their biological activity is modulated [
2].
In vitro studies offer the possibility to evaluate such NMs before to address more complex and toxicological preclinical studies.
In vitro methods offer the capacity to evaluate the potential hazards related to the administration of nanoparticles and understand the mechanism of adverse effects.
ZnO nanoparticles (NPs) are extended used as biosensor [
3], cosmetics [
4,
5], optical devices [
6] and different biomedical application [
7] such as drug delivery [
8,
9] among others. However, there are still concerns about the potential risk for human health. Then the study of its cytotoxic effect is of interest.
Interactions of nanomaterials with blood or blood components is a preliminary step to characterize their cytotoxic profile. However, the composition of media, the temperature or other are fundamental parameters than can lead to erroneous conclusions [
10]. Here we study the influence of different parameters on the potential hemolysis induced by commercial ZnO micro and nanoparticles (<50 nm and <100 nm) and the effect of these materials on the coagulation process.
It is known that colloid suspensions tend to adsorb proteins on their surface leading the formation of a superficial layer known as protein-corona. The protein corona can alter the physiological properties of NPs and their interaction with other molecules once in contact with the biological environment [
11]. Depending on the NP size, chemistry, the protein can present different affinity for the NP surface. The proteins adsorbed on NPs can affect aggregation, transference, and intracellular uptake of NPs [
12]. As serum albumin and fibrinogen were the most abundant two proteins in the corona formed on both bulk and nano ZnO [
13], it is necessary to study the influence of these two proteins. In this sense, we have studied the influence of different particle size (micrometric, <50 nm and <100 nm) of commercially available ZnO on the formation of protein corona and coagulation assay.
To study the toxicity of nanoparticles
in vitro it is important the selection of the appropriate cell type considering the via of entry in the body and the most relevant cytotoxicity assay [
14,
15]. In this sense, the purpose of this work is also to evaluate the potential cytotoxic effect of ZnO micro and nano particles on two human cell lines. The cell lines studied are the HaCaT as representative of normal cells of the epidermis, considering topical administration and, A549 as model of lung epithelium for potential aerial penetration. The cytotoxicity has been evaluated using three different endpoints, namely MTT, NRU and LDH.
This comparative in vitro cytotoxic study will increase the knowledge on how metal oxide nanoparticles develop adverse effects.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. ZnO particles and Reagents
ZnO in nano (50 nm and 100 nm) and micro forms were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Products are defined by manufacturer as ZnO nanopowder <50 nm particle size ZnO nanopowder, <100 nm particle size, both with a purity > 95%, and ZnO micro as ACS reagent 99%.
Al2O3 powder (99.8%) and nanopowder (13 nm, 99.8%) also were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA).
Phosphate Buffered Saline at pH 7.4 was prepared in house with extra pure potassium dihydrogen phosphate, synthesis grade sodium chloride (Scharlau, Sentmenat, Spain) and di-Sodium hydrogen phosphate anhydrous (Panreac, Castellar del Vallés, Spain).
For the SDS-PAGE electrophoresis, acrylamide (40%), bisacrylamide (2%), tetramethylethylenediamine (TEMED), ammonium persulfate, β-mercaptoethanol and bromophenol blue were obtained at GE Healthcare Bio-Sciences AB (Uppsala, Sweden); Sodium Dodecyl Sulphate (SDS) was purchased at (Sigma-Aldrich, Sant Louis, MO, USA) and Precision Plus Protein™ Standard (ranging from 10 to 250 kDa) at Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc. (CA, USA).
Dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO), Neutral Red Solution, Thiazolyl Blue Tetrazolium Bromide (MTT), and Trypan Blue Solution 0.4% were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Catalyst solution (Diaphorase/NAD+) and dye (INT/Na-lactate) were from Takara, Clontech Laboratories (Kyoto, Japan).
Bovine Serum Albumin (≥96%) and fibrinogen (50-70% protein, ≥80% of protein is clottable) were acquired at Sigma-Aldrich (Sant Louis, MO, USA, ≥96%); Coomassie brilliant blue G-250 (BioRad); D(+)-Sucrose was from Carlo Erba Reagents (RPE-for analysis-ACS).
2.2. Characterization of ZnO particles
2.2.1. Atomic Force Microcopy (AFM)
To characterize the topography and particle size of the ZnO nanoparticles a droplet (about 40 μL) of a ZnO-PBS solution (100 μg/mL) was deposited on a mica substrate previously cracked. Then, samples are quickly dried with N2, and finally observed with a Bruker Nanoscope V Multimode 8 (USA) at the Centres Científics i Tecnològics of Universitat de Barcelona (CCiT UB).
2.2.2. Transmission Electron Microcopy (TEM)
In this case, ZnO nanoparticles of 50 nm or 100 nm were suspended at a final concentration of 100 μg/mL in PBS, 0.9% NaCl and ethanol. Suspension was obtained from dilution and ultrasonication of a previous ultrasonicated suspension of 1.0 mg/mL of the sample. Observation and analysis were carried out in a JEOL JEM LaB6-2100 microscope of one drop (5 µL)) deposited and dried on a Holey Carbon- Cu grid (CCiT UB).
2.2.3. Dynamic Light Scattering
The mean hydrodynamic diameter (HD) and the polydispersity index (PDI) of the particles were determined by dynamic light scattering (DLS) using a Malvern Zetasizer ZS (Malvern Instruments, Malvern, UK) at a scattering angle of 173° and with a refractive index of 2.003 specific of ZnO. Briefly, the metal oxide particles at a final concentration of 1.0 mg/mL were incubated in phosphate buffered saline (PBS, pH 7.4), in PBS containing albumin or fibrinogen (2 mg/mL) or in DMEM 5% FBS for 2h and 24h at 37°C. Each measurement, made with a 10x10mm quartz cuvette (Hellma Analytics, Müllheim, Germany) consisted of three series of 5 readings. Finally, results were expressed as the mean of three independent experiments.
In addition, after incubation samples were centrifuged (15,300g x 5 min) and the amount of protein in the supernatant was determined by the Bradford assay [
16] to calculate the protein adsorbed by subtraction from the amount determined before incubation using Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) as standard.
2.3. Study of ZnO albumin interactions by spectrometric analysis
The interaction between ZnO of different sizes and albumin was investigated using Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) at physiological pH (7.4). A stock solution of BSA was prepared at a concentration of 4 mg/mL; different concentrations of ZnO were added to 3 mL of BSA to obtain a final concentration of 2 mg BSA/mL. This mixture was homogenized and kept for 30 min for incubation. The same assay was repeated with a previous incubation of 18 hours. After incubation, UV-Visible absorption spectra were recorded in the wavelength range of 250-330 nm (Shimadzu UV-Vis 160, Japan) using a 1 cm path length quartz cuvette [
17].
Moreover, fluorescence measurements (Luminescence Spectrometer, Aminco Bowman) were recorded in the wavelength range of 310-430 nm using a 1 cm path length quartz cuvette. The excitation wavelength was set at 278 nm and emission was measured in the range of 275-475 nm [
17].
2.4. Hemocompatibility studies
2.4.1. Blood collection and preparation of erythrocyte suspension
Fresh human blood was extracted from healthy voluntaries by venopunction and draw into tubes containing EDTA or sodium citrate, after informed consent and approval of Bioethics Committee at University of Barcelona, Spain (15 February 2021).
Blood extracted with EDTA was centrifuged for 10 min at 3,000 rpm to remove plasma traces, buffy coat, and platelets to stay only with erythrocytes. Immediately, the isolated red blood cells (RBC) or erythrocytes were suspended in twice volume of saline solution (PBS pH=7.4) and the washing procedure (centrifugation/discarding plasma/washing with PBS) was carried out three more times till a transparent and colorless supernatant was obtained. The final RBC suspension was adjusted by adding the adequate of PBS to obtain a maximal hemoglobin absorbance at 575 nm of 1.8-2.1.
2.4.2. Potential media interaction on hemoglobin adsorption
Before study the hemolytic behavior of ZnO particles the potential existence of interactions with hemoglobin, and if these interactions were due to pH, the media composition or the metal oxide nanoparticles studied was investigated [
18]. According to the isoelectric point of hemoglobin protein (6.8), studies were performed at pH 7.4 and 5.7 in PBS, 0.9% NaCl 0.9% solution and tris(hydroxymethhyl)aminomethane – maleate (tris–maleate) buffer solution. Besides, Al
2O
3 nanosized particles were chosen for comparative purposes.
PBS solution (pH 7.4) was acidified with HCl 0.1 M to obtain PBS at pH 5.7 whereas in the case of 0.9% NaCl (pH 5.7) addition of NaOH 0.1 M allows to increase the pH at 7.4. Finally, tris–maleate buffer solution, was obtained mixing 0.2 M solution of Tris acid maleate aminomethane (A) and 0.2 M of NaOH (B). The appropriated amount of each solution to obtain the desired pH values was given by the formula:
Adsorption of hemoglobin was assessed by incubation of a fixed concentration of the metal oxides 1.0 mg/mL with an aliquot of human erythrocyte suspension or human hemoglobin solution during 30 minutes at room temperature (RT) in the presence of the different media. Then samples were centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 5 min (Nahita Blue, high-speed centrifuge 2624/2, Sudelab S.L., Spain) and finally, the supernatants of the samples were qualitative observed to assess if the hemoglobin had been adsorbed by the metal oxide.
2.4.3. Hemolytic Activity: effect of temperature and albumin
To study the membrane-lytic activity, various concentrations of ZnO oxide particles (0.2 mg/mL – 1,6 mg/mL) at final volume of 1 mL were prepared from freshly stock solutions of 10 mg/mL in PBS. Then, an aliquot of 25 μL of the erythrocyte suspension was introduced to each tube and the tubes were placed in a rotary shaker for incubation at RT or 37°C for a period of 24 h. At the end of incubation samples were centrifuged (10,000 rpm for 5 min) in a Nahita Blue, high-speed centrifuge 2624/2 (Sudelab S.L., Spain) and supernatant absorption was determined at 540 nm (Shimadzu UV-Vis 160, Japan). Each experiment was repeated almost three times in triplicate and appropriate controls consisting in RBC incubated in PBS pH 7.4 (negative control or basal hemolysis) and in deionized water (positive control or total hemolysis) were included. [
19].
The percentage of RBC hemolysis was calculated using the following formula [
20]:
where
AS is the absorbance obtained for each sample,
AC the absorbance of negative control (basal hemolysis) and
A100 the absorbance of positive control or total hemolysis (100%).
The effect of potential protective effect of albumin on hemolysis was also studied. It has now been well established that proteins from body fluids bind to NP surfaces upon their exposure to an organism, forming a so-called “protein corona” around the NPs [
21]. Albumin is the most abundant protein in the human body. Moreover, previous studies have demonstrated that the addition of 0.5 mg/mL of albumin in PBS (pH 7.4) decreases the hemolytic behavior of Al
2O
3 nanoparticles [
22]. In this case, negative controls (A
C) consist in RBC incubated in PBS pH 7.4 containing 0.5 mg/mL of albumin.
2.4.3.1. Effects of ZnO on erythrocyte morphology
Evaluation of ZnO particles over erythrocyte morphology was studied by Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM). In a similar way as in section 2.3.2, RBC were exposed to 0.2 mg/mL of each ZnO particles or PBS as a control of morphology and incubated at 3 or 24 hours at RT. Then samples were centrifuged at high speed (10,000 rpm for 5 min), the supernatant was discarded, and 1 mL of 2.5% glutaraldehyde in PBS was added. Fixed samples were washed with PBS solution, post-fixed with 1% osmium tetroxide, placed over a glass coverslip, dehydrated in an ascending series of ethyl alcohol (50–100%), air-dried using the critical point drying method in a CPD 7501 apparatus (Polaron, Watford, UK), and finally mounted on a carbon stub. The resulting specimens were observed at CCiT UB in a Hitachi 2300 electron microscope operating at 15 kV.
2.4.4. Coagulation Assays
Fresh human plasma was obtained from whole blood extracted with sodium citrate (see section
2.3.1) and posteriorly centrifuged to separate plasma form cellular elements. Then, plasma was incubated with each the three ZnO particles for a period of 30 minutes at 37°C under soft rotation before to evaluate the effects on coagulation time [
23]. Effects on coagulation was studied by the determination of the prothrombin time (PT) using RecombiPlasTin 2G (HemosIL kit, Werfen, Spain) and activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) using SynthASil (HemosIL kit, Werfen, Spain) following the protocol provided by the manufacturer.
Different concentrations of ZnO particles were assessed in each run, namely 0.1, 0.5 and 1.0 mg/mL in quadruplicate. In each independent experiment, control samples of coagulation time consisting in plasma incubated with vehicle (PBS pH 7.4) were included. Each experiment was repeated almost three times with plasma of different donors.
Finally, protein adsorption onto ZnO particles after incubation with human plasma was quantitatively and qualitatively evaluated on the pellets by the Bradford assay, SDS-PAGE and TEM (Transmission electron microscopy).
After incubation of ZnO particles in human plasma adsorption of protein was also explored with TEM. For this reason, before observation samples were diluted at a final concentration of 0.02 µg/mL in mere H2O (MiliQ quality) and dyed with phosphotungstic acid to reveal the presence of protein. Observation and analysis were carried out in a JEOL JEM LaB6-2100 microscope of one drop deposited and dried on a Holey Carbon- Cu grid. Complementary analysis of elemental composition by Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) was performed to confirm the presence of plasma proteins, ZnO particles and the staining agent.
2.4.5. Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis of human plasma protein: SDS-PAGE
As a preliminary study the different proteins involved in the protein coronas SDS-PAGE experiments were performed. Thus, human plasma samples were incubated 30 minutes at 37°C with ZnO particles at a concentration 10 times higher than those used in section 2.3.3. and then centrifuged (13,000 rpm, 5 min.) to separate the pellet from the supernatant and study them separately. Pellets were washed three times with a solution of Sucrose 0.7 M in PBS according to facilitate pellets separation from the supernatant [
24]. Finally, the amount of protein on both supernatants and pellets was determined by the Bradford assay as previously stated [
25]. Controls without particles were included for qualitative comparative purposes.
The following process was used to perform SDS–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis on 18 micrograms of extracted protein: the method reported by [
26] was followed and a Mini-PROTEAN Tetra Cell unit from Bio-Rad (Hercules, CA, USA) was used. The gel used consisted of two parts: a 7.5% polyacrylamide resolving gel and a 5% polyacrylamide stacking gel. The extracted protein was mixed with 2x SDS sample buffer, heated for 5 minutes at 95°C, and then loaded onto the gel. Electrophoresis was run for 10 minutes at 60 V and then continued for 40 minutes at 200V. The protein bands were stained with Coomassie Blue R-250 for 40 minutes while gently shaking and then the excess of stain was removed by a mixture of 7.5% methanol and 10% acetic acid. The molecular weight of plasma proteins was estimated based on a molecular size marker ranging from 10-250 kDa.
2.5. Cell culture and cytotoxicity studies
Two cell lines have been studied: a human keratinocyte cell line HaCaT (Eucellbank, Barcelona) and an A549 line originating from the lung epithelium (European Collection of Cell Cultures, EACC, Salisbury, England). Cells were grown and maintained in DMEM medium (4.5 g/L glucose) supplemented with 10% (v/v) FBS (Fetal Bovine Serum), 2 mM L-glutamine, 100 U/mL penicillin and 100 µg/mL streptomycin in an incubator at 37°C, 5% CO2. All culture reagents were purchased at Lonza (Verviers, Belgium) except FBS HyClone® that was acquired at Thermo Scientific (Northumberland, UK).
Briefly, when cultures reached 80% confluence, culture medium was discarded and cells were detached with trypsin-EDTA (Lonza, Verviers, Belgium). From the cell suspension obtained, cell density was determined in an aliquot treated with the vital dye Trypan Blue (Sigma-Aldrich, Madrid, Spain). Cell density was adjusted at 1 x 10
5 cells/mL and cells were seeded in 96 well plates and maintained for 24 hours in an incubator at 37°C, 5% CO
2. Then, cytotoxic activity was investigated exposing cells 24 hours at different concentrations of ZnO particles ranging from 0.78 to 100 µg/mL prepared from a freshly solution of 1.0 mg/mL [
27] in DMEM medium with 5% FBS, 2 mM L-glutamine, and 1% antibiotic. Before applying the treatment, the medium was aspirated, and then the cells were exposed to the compounds at decreasing concentrations. For each plate and experiment untreated cells remaining with DMEM medium as controls of viability were included. Finally, the plates were incubated for 24 hours at 37°C and 5% CO
2. The assessment of the cytotoxic potential of ZnO particles was performed using three different methods: lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) determination, reduction of the 2,5 diphenyl-3-(4,5-dimethyl-2-thiazolyl) tetrazolium bromide (MTT) dye, and the neutral red uptake (NRU) assay.
To avoid surface nanoparticle adsorption LDH was detected in cell free supernatant without previous centrifugation [
28]. Thus, supernatant of each sample was introduced in a clear plate and mixed with the same volume of the reaction mixture following the instructions of a commercially available kit (Takara, Japan). The plate was incubated at Room Temperature protected from light for up 30 minutes and finally absorbance at 492 nm was measured in a Tecan Sunrise microplate reader (Männedorf, Switzerland). Viable cells were calculated as percentage of cell viability according to the following formula:
where
AC is the absorbance of untreated cells,
AB the background absorbance (medium without cells) and
AT the absorbance obtained for treated cells.
In the case of MTT, we have followed the protocol of Mosmann [
29] with slightly modifications [
30]. Thus, after extracting the supernatant, 100 µL of a solution of 0.5 mg/mL MTT in serum free DMEM without phenol red was introduced in each well and the plate was incubated for at least 3 h at 37°C and 5% CO
2. The formazan crystals formed were dissolved in 100 µL of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and the plate was agitated for 10 minutes at 100 rpm/min to homogenize the well content. For the uptake of NR uptake, similar steps were followed as for the MTT and according to Babich and Borenfreund [
31]. In this case, a 0.05 mg/mL NR in serum free DMEM without phenol red solution is used and a destain solution containing an acidic ethanol solution was added to dissolve the NR uptake by viable cells. Finally, absorbance was measured at 550 nm in a Tecan Sunrise microplate reader (Männedorf, Switzerland), and cell viability was calculated as percentage considering that untreated cells as 100% viability.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
Each experiment was repeated at least three times including triplicates for each condition, and results are expressed as mean ± standard error. Unpaired Student’s t-test or a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) were used to determine the differences between the data set, followed by a Scheffé post-hoc test for multiple comparisons using the SPSS® program (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) Differences were considered significant for p< 0.05 as indicated in figure or table footnotes.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of ZnO particles.
3.1.1. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM).
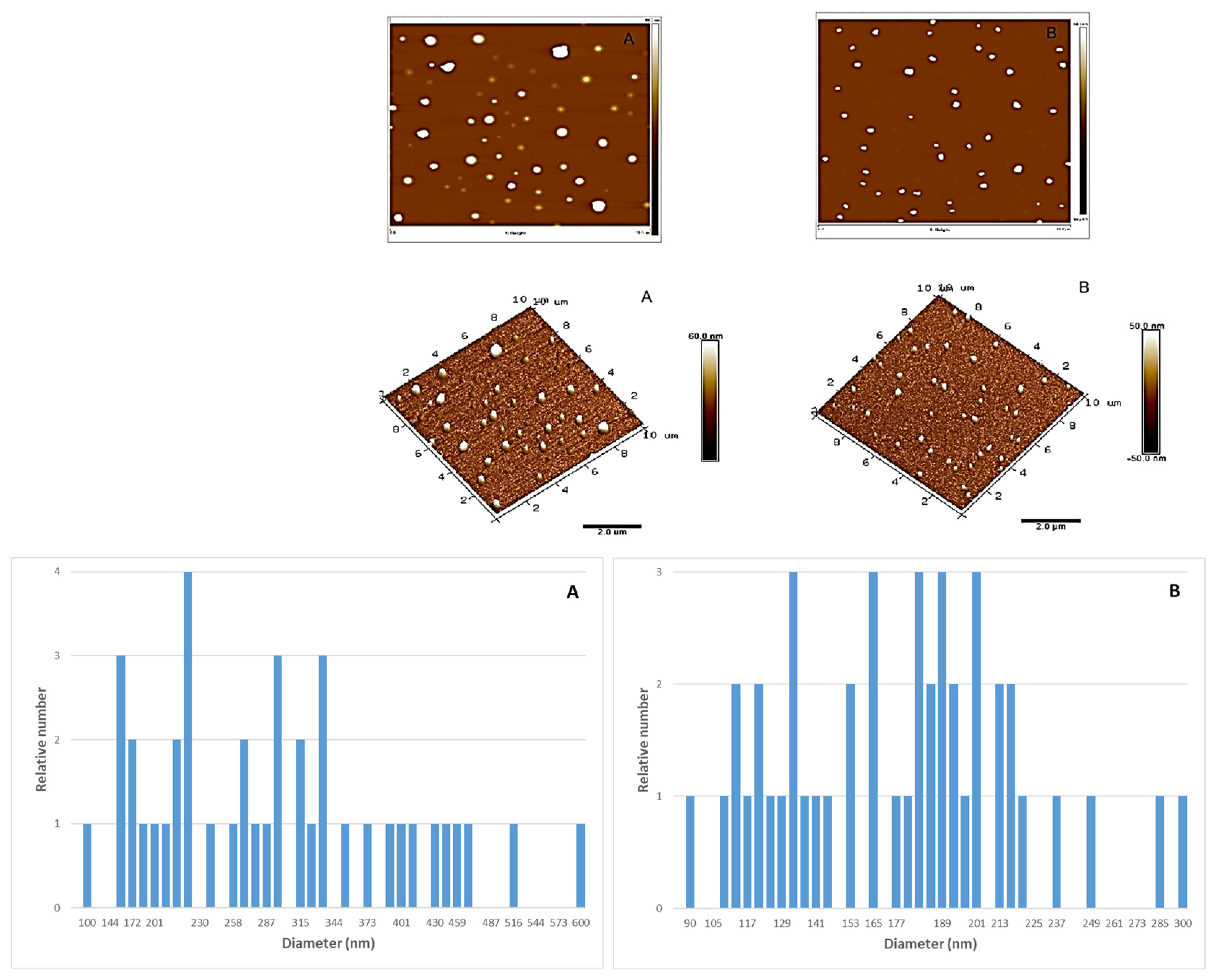
Topographical images of the ZnO nanoparticles are shown in
Figure 1. From AFM characterization it was possible to determine the relative abundance of the ZnO particles different size and the mean size could be determined, being 373.5 ± 114.2 nm for the ZnO 50 nm nanoparticles and 173.2 ± 43.8 for the 100 nm nanoparticles. Thus, particle size of ZnO provided by AFM differ from those provided by the manufacturer, meanly those of 50 nm. These much higher values indicate a trend of nanoparticles to aggregate when they are put in solution. In agreement with their smaller size, this trend is much more important for 50 nm particles.
3.1.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
TEM is a very powerful technique to study a nanosized system, since it allows to analyze size and crystallographic characteristics [
32]. However, here we have used TEM images to qualitatively analyze the behavior of ZnO nanoparticles in different media and to compare with AFM outcomes. In this sense,
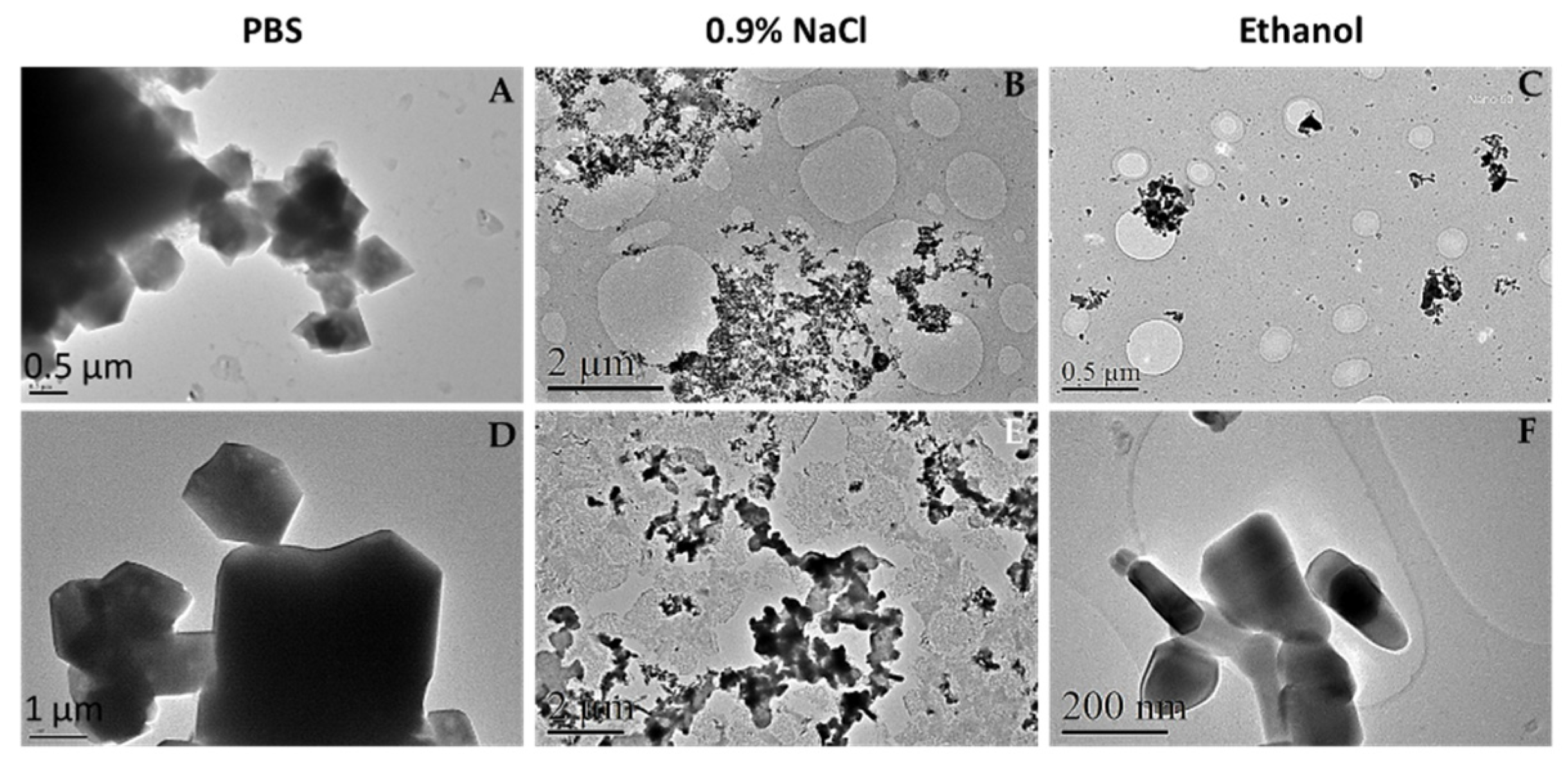
Figure 2 shows that in the case of PBS (A and D) NPs formed great polyhedral aggregates as indicated previously by AFM images and confirmed by its chemical nature with energy-dispersive X-Ray spectroscopy and selected area diffraction analysis (
Figure S1 and S2, Table S1). Moreover, these observations agree with previous studies reporting that in physiological medium NPs have the trend to agglomerate to form micro-sized particles that are more stable are more stable in such environment [
33].
When the nanoparticles were suspended in 0.9% NaCl (B, E), it was observed that newly aggregates at the micro size scale were also formed. These aggregates are bigger for ZnO 50 nm than ZnO 100 nm particles and qualitatively smaller than the formed in PBS (about 3 to 5 times). Finally, the NPs were observed dissolved in ethanol to know the real size of the particles. It was thought that this medium being a very volatile one, no aggregation would occur therein. However, as shown in images C and F of
Figure 2, aggregates of ZnO NPs are also observed, although in a smaller size than the observed in the other two media. Moreover, in a similar way that happens in the saline 0.9% NaCl medium, 50 nm ZnO form larger aggregates than ZnO 100 nm, as also observed here with AFM characterization.
3.1.3. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
The population of ZnO NPs in PBS solution, as measured with dynamic light scattering method, was heterogeneous in size due to the formation of large aggregates [
34]. Consequently, this method measures de sizes of the clustered particles rather than individual particles [
32].
Hydrodynamic diameter (HD) obtained by DLS for ZnO particles in PBS are presented in
Table 1. As observed, HD obtained at 24h are greater than at 2 h indicating that, to a greater or lesser degree, particles agglomerate [2, 27], being such agglomerates at two hours fifteen to twenty times larger than the primary particles [
33]. When considering HD values after 10 minutes incubation (
Table S2) as well as AFM and TEM observations it can be concluded that NPs aggregate immediately after introducing them in physiological media.
We have also observed that ZnO 50 nm tend to form bigger aggregates than 100 nm and that using other media as 0.9% NaCl or ethanol does not prevent the tendency of NPs to agglomerate. SEM images of ZnO 100 nm obtained by Jung et al. in 2021, also demonstrated this aggregation but allow to determine a particle size that resembles that described for the provider [
35].
These measurements have the added problem of the fast sedimentation of the NPs, but they agree with those obtained with the previous techniques showing the strong agglomeration of the ZnO particles [
34]. For this reason, hydrodynamic size of ZnO particles is only qualitatively relevant due to the extremely high polydispersity index that we have obtained (from 0.426 to 0.851). It can be concluded that, when immersed in aqueous media, homogenic suspension is unstable and our particles quickly agglomerate and form random sized clusters. All results obtained to characterize the NPs in PBS indicate that the behavior of metal oxides in biological medium is poorly predictable since they aggregate, agglomerate, and even degrade under neutral medium.
3.1.4. Influence of proteins on hydrodynamic diameter
Jung et al., [
35] indicate that the presence of proteins increases the hydrodynamic size of NPs, however this author has compared values obtained by different techniques, SEM and DLS. Therefore, the role of proteins on nanoparticle size is investigated by DLS and specifically we have studied BSA and fibrinogen, as well as DMEM 5% FBS (
Table 2).
In the case of proteins, our results reveal that in a similar way as described for PBS, HD increases with time when BSA is present in the medium. However, HD values are in general statistical significantly lower than those shown in
Table 1 and, in the case of fibrinogen, attaining the lowest values recorded. This decrease in size has been attributed to the effect of preventing the aggregation of particles, providing greater stability to the system [
36]. However, at 24 hours this stabilization is basically attributed to fibrinogen as in the case of BSA is only observed for ZnO 50 nm. In the case of DMEM also there is an increase of HD with time, except for micro-sized particles, and values are statistical significantly lower than in the case of PBS but higher than those reported previously by other authors [27, 33, 35].
In summary, we can conclude that similar behavior among the three different particle size is observed, the maximum particle size and increase in HD is determined in PBS, then in BSA and DMEM and finally fibrinogen. Regarding ZnO micro-sized, there are certain discrepancies with its behavior because its HD seems most affected by the presence of BSA the reason remains that micrometric materials compared to nanometric ones have different properties [
33].
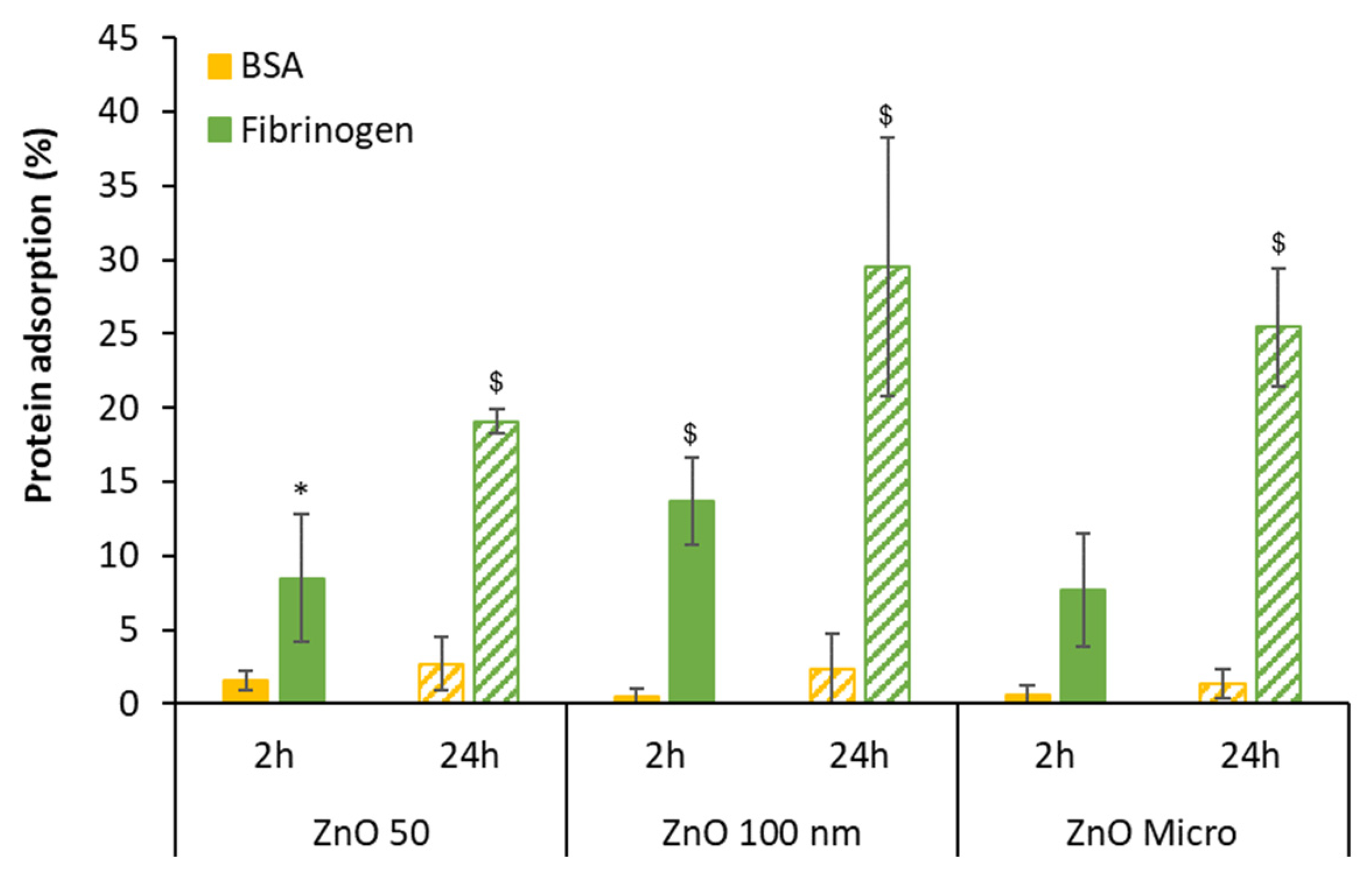
The quantification of total protein after incubation with BSA and fibrinogen was done using the Bradford method and finally the percentage of protein adsorbed was calculated.
Figure 3 reveals that the percentage of protein adsorption after incubation is very low in the case of BSA (up to 2.7%) while this percentage is considerably significant for fibrinogen at 24 hours [
2]. In this later case, the percentage of fibrinogen adsorption increases with time suggesting the formation of a protein corona around the nanoparticle [2, 37].
3.4. ZnO albumin interactions
3.4.1. UV-Visible spectrophotometry
Interaction between albumin and ZnO was studied by using absorption spectroscopy and fluorescence techniques, the most powerful techniques to investigate the interaction between nanostructured inorganic particles and biological molecules. Bovine serum albumin (BSA) has been used to study this potential interaction [
38].
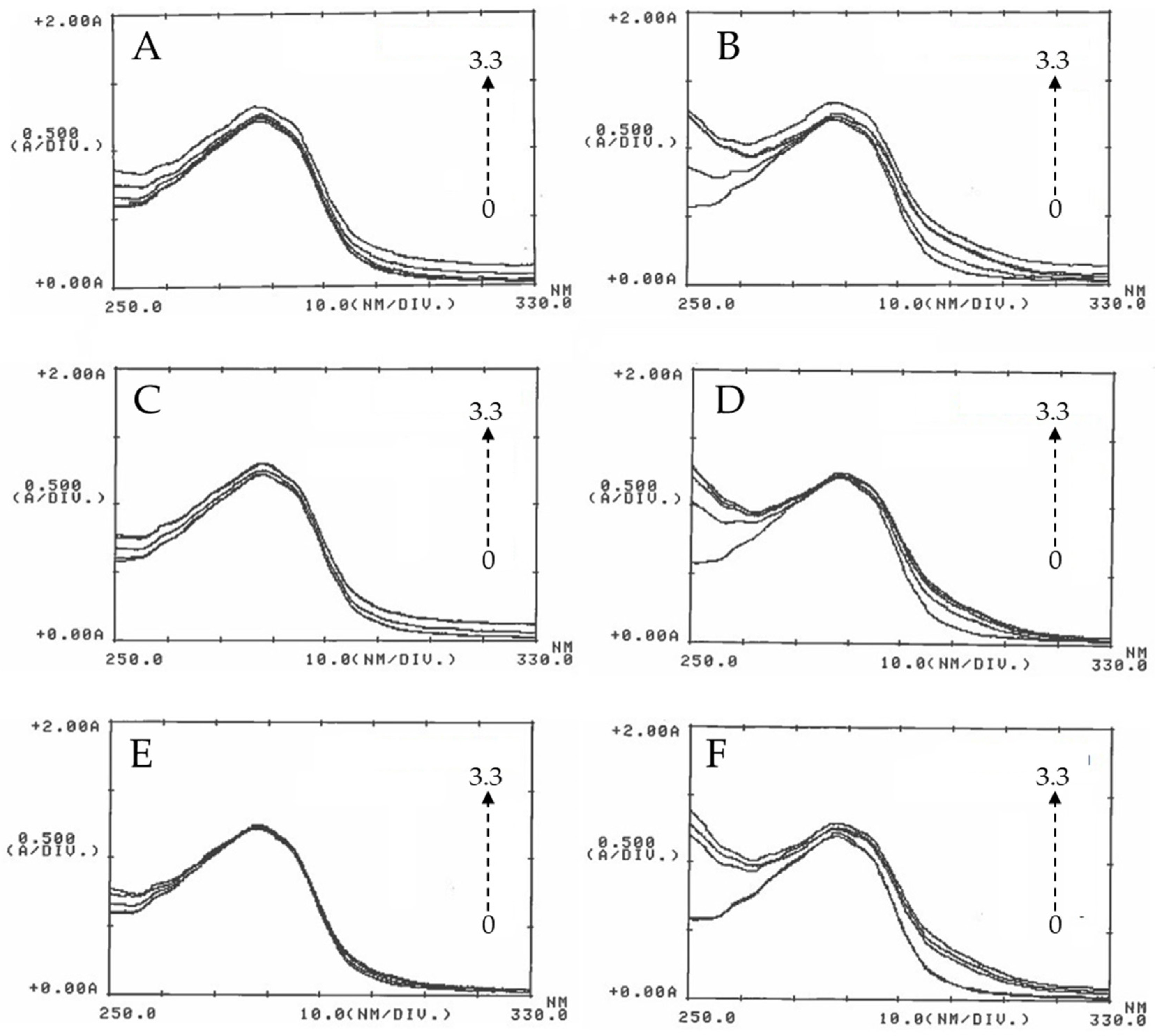
UV-Vis spectroscopy was used to investigate the interaction between BSA and the ZnO particles; different assays were performed in absence and in presence of ZnO NPs at different concentration. As shown in
Figure 4, the absorption band of BSA at 280 nm slightly increases with the concentration of ZnO. Since ZnO NPs do not display absorption band around 280 nm, the increase in the intensity of the peak at 280 nm of BSA with the addition of ZnO NPs, is attributed to the formation of a complex due to the ZnO-BSA interaction [
38].
Another highlight is that the interval between the concentrations increases significantly as the particle size decreases. The absorbance spectra at 30 min show that the band at 280 nm increases more with the concentration of 50 nm ZnO than that obtained with 100 nm ZnO, and this last more than that of micro ZnO; in that case absorbance was almost invariable. As shown in the figure, the behavior at 18h is similar and it does not provide additional information than that obtained at 30 min. Therefore, it could be said that the absorbance not only depends on the concentration, but also on the particle size, since the behavior of the three zinc oxides is slightly different. On the other hand, incubation time has not influence on the BSA absorbance. This behavior has been observed in other cases where different concentration of ZnO have been used [
38].
Other studies performed in the literature use the variation of the λmax of ZnO NPs at 375 nm by adding different amounts of BSA. The absorbance variations observed with this procedure also reveal formation of a complex BSA-ZnO particles [
39].
3.4.2. Fluorescence measurements
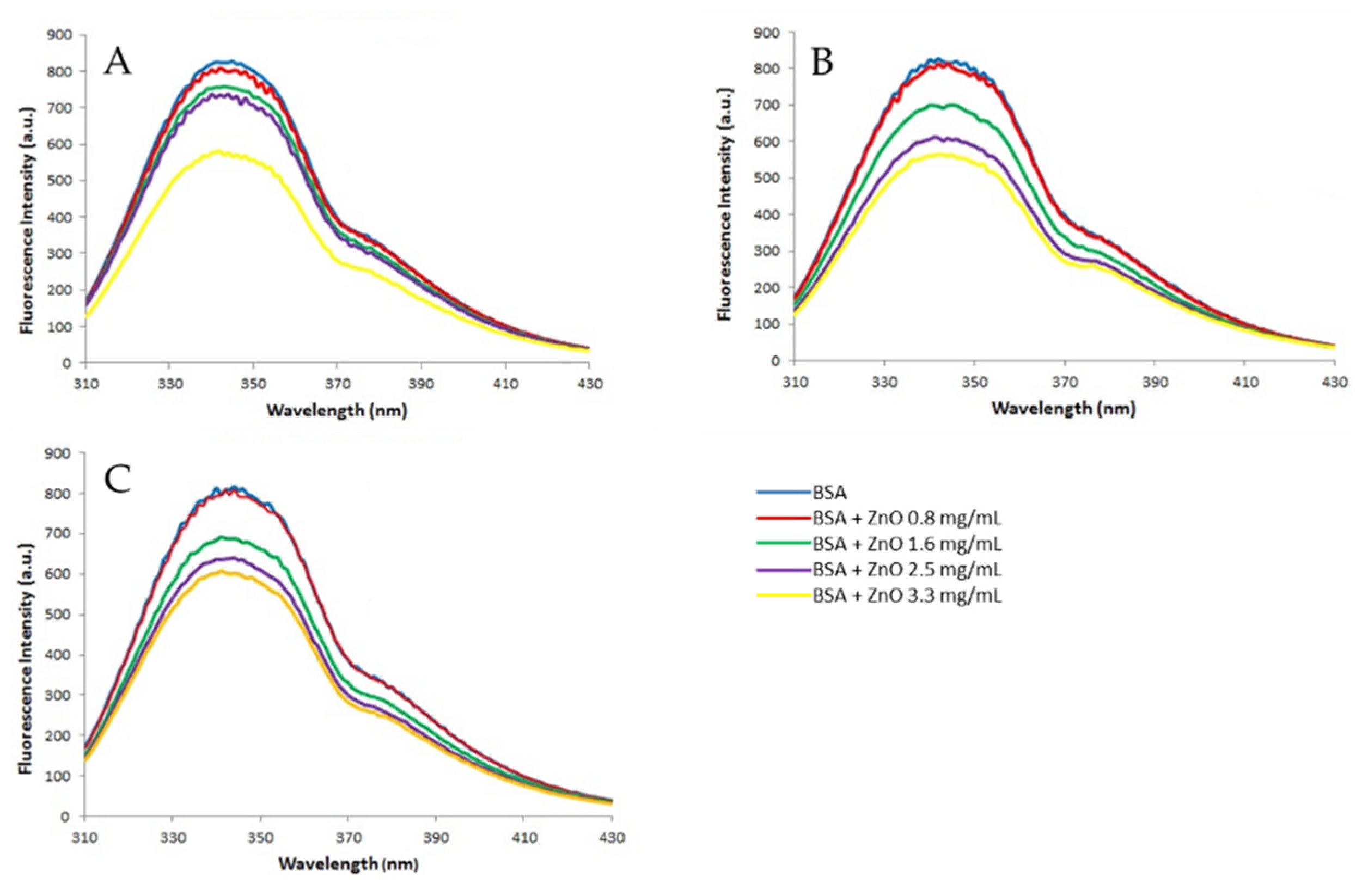
The fluorescence spectra (
Figure 5) obtained after incubating BSA (2 mg/mL) with different concentrations of ZnO (0, 0.8, 1.6, 2.5 and 3.3 mg/mL) show that BSA has a strong emission band at 340 nm when excited with 278 nm wavelength (blue line). The presence of ZnO particles causes a decrease on fluorescence intensity inversely dependent of ZnO concentration which suggest the formation of certain complex by the binding between ZnO NPs and BSA [
38].
The fluorescence quenching refers to any process that decreases the fluorescence intensity of a sample, in this case of the albumin. A variety of molecular interactions can result in quenching, that include excited state reactions, energy transfer, ground state complex formation and collisional quenching [
20]. Depending on the kind of interaction between quencher and BSA, the fluorescence quenching can occur by two different mechanisms, which are usually classified into dynamic and static quenching. Dynamic quenching occurs when excited state fluorophore (a fluorescent chemical compound that can re-emit light upon light excitation) of BSA is deactivated upon contact with the quencher molecule in solution. Static quenching occurs due to the formation of a nonfluorescent complex between the fluorophore and the quencher [
38]. In this case the interaction between ZnO and BSA occurs through static quenching mechanism.
In almost all referred studies, the fluorescence quenching is studied at different temperatures. As the temperature increases the stability of complexes decreases and therefore, the static quenching is attenuated. This is because the binding between ZnO and BSA at high temperatures to form a complex is destabilized, and then this unstable complex can decompose [
38].
As has been mentioned above, ZnO interacts with albumin reducing the fluorescence intensity. The shoulder that appears at about 377 nm becomes slightly clearer with the addition of particles and this could be attributed to a partial denaturation of the protein or to a protein conformational change. Since this change has not been observed with any of the other metal oxide tested, it appears that ZnO NPs act as a denaturing agent. Other NPs such as TiO
2, CeO
2 and Al
2O
3 also caused an important decrease in the fluorescence intensity of the BSA, although alumina was the most inert metal oxide NPs [
40].
About the two techniques used to study the interaction between albumin and zinc oxide, both reveal the formation of a BSA-ZnO complex, but the variations are much more important in the fluorescence, demonstrating that this technique would be the best to study this phenomenon.
3.5. Hemolytic activity of Zn
3.5.1. Media interaction on hemoglobin adsorption
Previous studies with different metallic nanoparticles fail to determine the potential hemolytic activity of ZnO indicating its high binding affinity with hemoglobin [18, 41]. In this sense, the ability of ZnO nanoparticles to capture hemoglobin protein was assessed using three different solutions (PBS, 0.9% NaCl and tris-maleate) at two different pH (pH 7.4 and pH 5.7). Moreover, for comparative purposes, Al
2O
3 were included. After incubation of the nano and micros-sized metal oxides, the disappearance of the characteristic red color provided by the hemoglobin in solution was observed. In
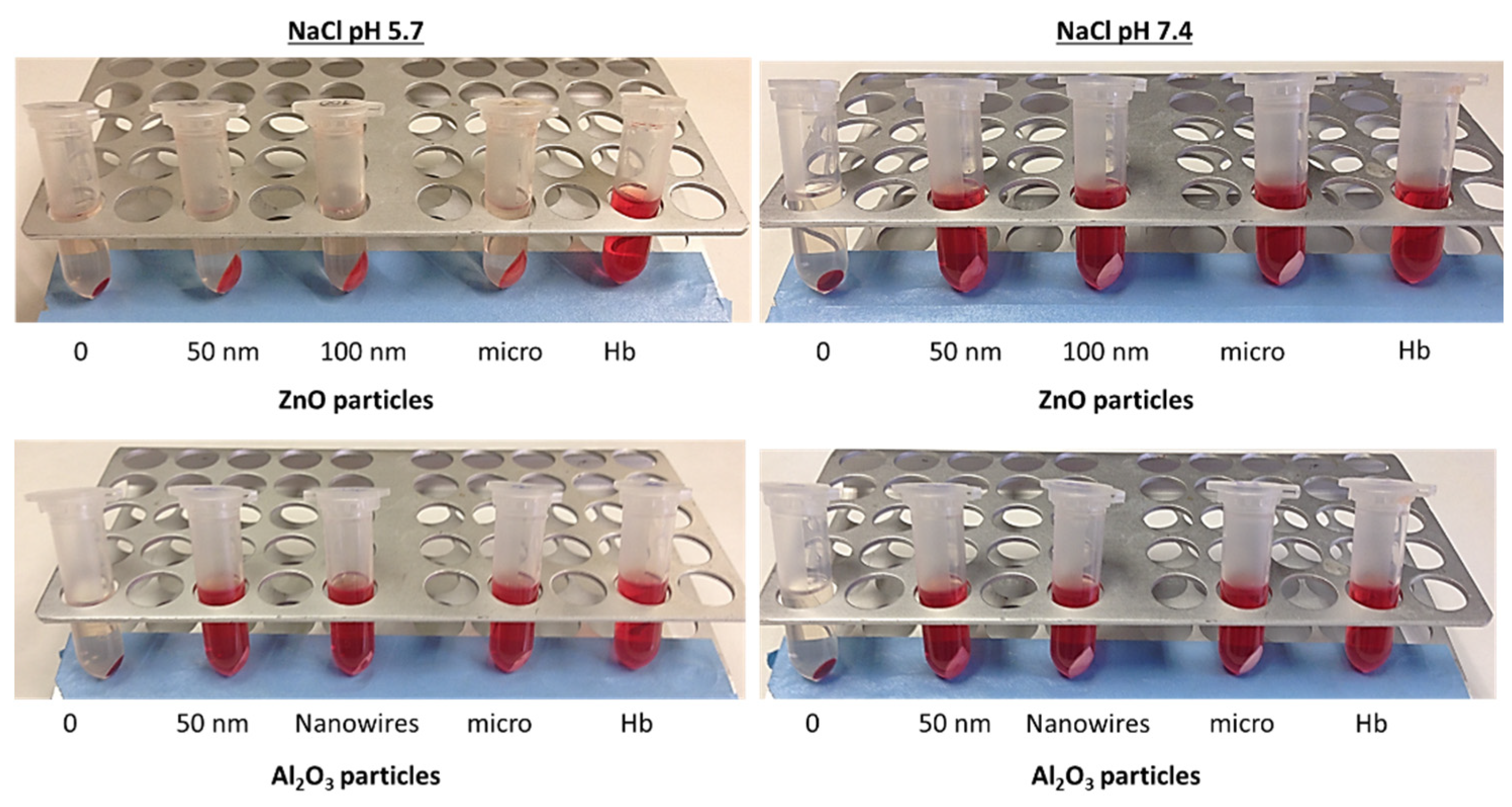
Table 3, a comparison of the behavior of both metal oxides in the different media and pH conditions is presented. The data indicates that adsorption of hemoglobin is only recorded for zinc oxide in tris-maleate, independently of the pH of the buffer solution, and in 0.9% NaCl at pH 5.7. Moreover, this behavior is not dependent of ZnO particle size. For this reason, posterior hemolytic studies were performed in PBS at pH 7.4.
According to these interferences we conclude that election of adequate working media to study the hemolytic activity of metal oxide nanoparticles is crucial for a good interpretation of data and depends upon the characteristics of the specific metal. As an example,
Figure 6 shows how ZnO adsorbs hemoglobin protein at acidic 0.9% NaCl (pH 5.7) whereas this behavior is not observed for Al
2O
3.
This phenomenon could be explained by the importance of pH on the hemoglobin protein behavior. The isoelectric point of hemoglobin is 6.8 and the isoelectric point of ZnO is 7.3 but the pH of the 0.9% NaCl medium is 5.7. For this reason, we hypothesize that at this acidic pH, hemoglobin has a positive charge, while, according to the literature, the zeta potential of zinc oxide at this same pH is negative 26.27 (not demonstrated in 0.9% NaCl). So, the adsorption may be due to electrostatic attraction among particles however to corroborate this hypothesis zeta potential of the zinc oxide particles in 0.9% NaCl should be determined.
3.5.2. Hemolytic activity in PBS media pH 7.4.
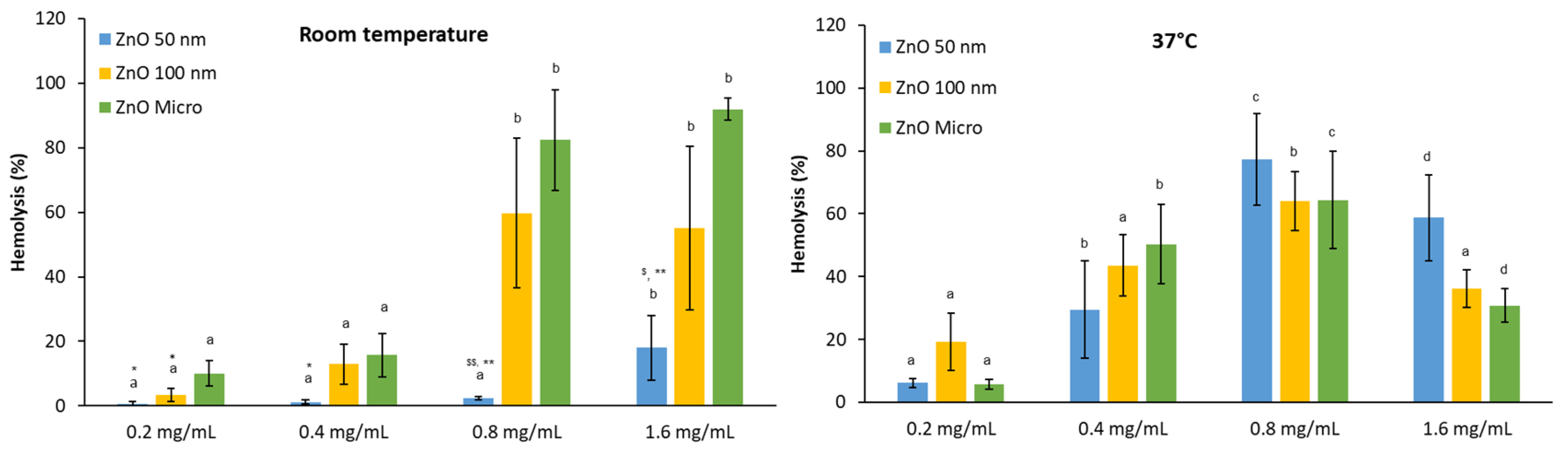
For particles in contact with human body, it is essential to understand their behavior at physiological conditions. For this reason, we have studied the potential hemolytic activity effect of the three zinc oxides (50 nm, 100 nm and micro) at various concentrations (0.2, 0.4, 0.8 and 1.6 mg/mL) with human RBC at Room Temperature (RT) and physiological body temperature as 37°C (
Figure 7).
At RT, it is observed that there is an increase in hemolysis in presence of ZnO micro and 100 nm in parallel with the concentration assessed, being maximal hemolysis recorded at 0.8 mg/mL. In contrast, for ZnO 50 nm particles at the maximal concentration studied less than 20% of hemolysis is recorded. In the case of 37°C, maximal hemolysis was attained in all three cases at 0.8 mg/mL followed by a decrease at 1.6 mg/mL. However, previous studies of our group revealed from the hemoglobin spectra that this protein suffers denaturalization (
Figure S3), and thus the hemolytic activity of these metal oxides nanoparticles can be underestimated. Studies from [
33] comparing the potential toxicity of different metal oxides indicate that ZnO 100 nm was the most toxic of these metal oxides. Here, we found that these nanoparticles are not more toxic than the micro sized material. Nevertheless, at low concentrations of ZnO, which are intended to be administered as drug, would not be damaging [
42].
Results obtained at room and physiological temperatures show that hemolysis increases with increasing temperature [
43]. This observation suggests that red blood cells at RT can behave in a different way as expected because not only temperature had been lower than the physiological one but also with greater fluctuations during the day. Moreover, these temperature fluctuations can correlate well with the highest error bars encountered especially in the case of ZnO 100 nm particles.
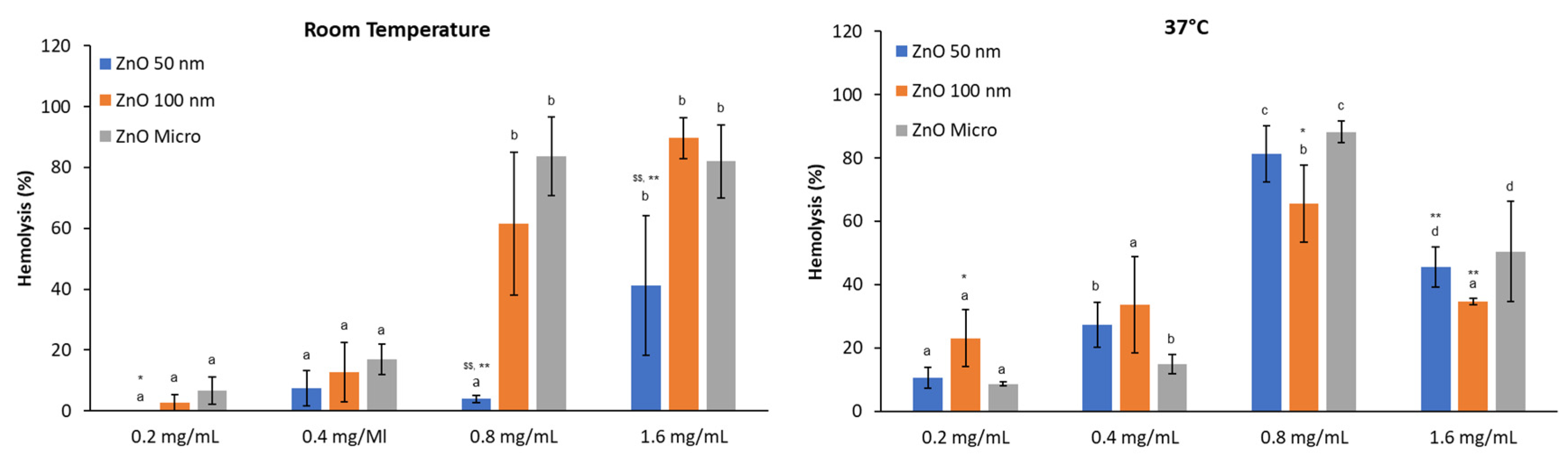
The hemolytic activity of ZnO particles when albumin protein is included in the media (
Figure 8), shows a similar behavior than PBS pH 7.4 alone. At RT hemolysis increases in a dose dependent manner and more dispersion is observed, while at physiological temperature hemolysis decreases at 1.6 mg/mL indicating that hemoglobin is suffering denaturation as stated before. Data values are also like those in
Figure 7 and no statistical differences were found when comparing with hemolysis without albumin. These results suggest that higher concentrations of albumin are required to interact with ZnO nanoparticles [
36] and thus that protein corona is not formed at 0.5 mg/mL of BSA.
Then, it can be concluded that ZnO cause dose-dependent hemolytic activity that also depends on temperature. Although the mechanism of membrane perturbation by ZnO is not clear [
44], these data suggest that this ZnO could enter cells, induce morphologic alteration, and subsequently produce the rupture of cells membrane.
3.5.3. Effects of ZnO on erythrocyte morphology
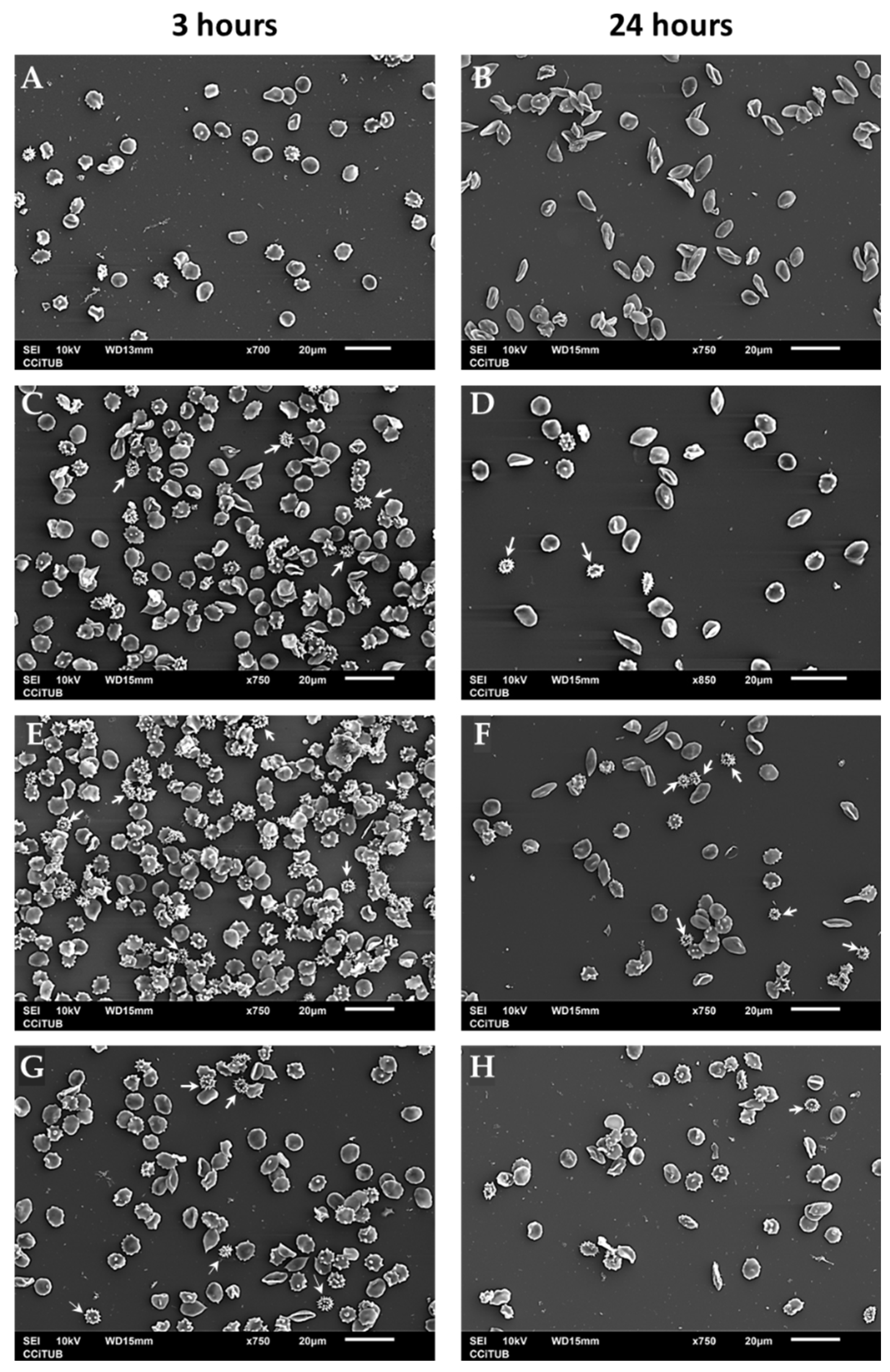
The interaction between ZnO particles and human erythrocytes was observed by Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM). Healthy and young erythrocytes have a biconcave disc shape morphology called discocyte. Alterations in cytoskeletal structures result in membrane deformability’s which conduct to modified shapes as echinocytes, erythrocytes with abnormal cell membrane characterized by many evenly spaced thorny projections [
45]. Incubation for 3 hours of erythrocytes in the presence of ZnO induces an increase in the number of echinocytes at different stages. But the presence of late echinocyte shapes, spherical bodies with spicules distributed over its surface, are easily identified (
Figure 9, white arrows). At 24 hours of incubation the number of red blood cells decreases because ZnO particles (nano and micro) can cause rupture of the membrane as mentioned before, but still crenated shapes of echinocytes are observed (
Figure 9, white arrows). In these images, the effect of time incubation is more evident in the case of nanosized particles than micro particles.
3.6. Coagulation studies and plasma protein interactions
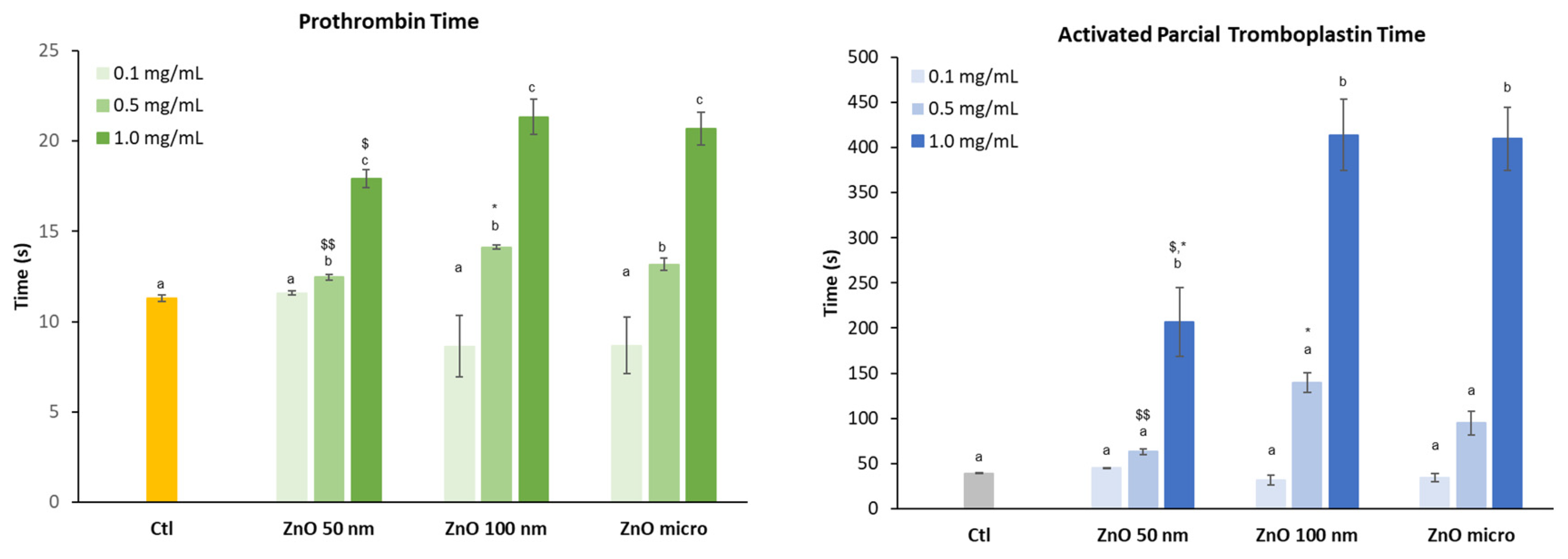
3.6.1. Coagulation: Prothrombin time and activated partial thromboplastin time.
Prothrombin time (PT) and activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) are used to evaluate the extrinsic and intrinsic pathway of coagulation, respectively [
46]. The purpose of this test is to determine how ZnO particles affect the coagulation time if they reach body fluids.
Figure 10 shows the effect of the three zinc oxides on the intrinsic and extrinsic pathway of coagulation.
Data obtained for PT at the highest concentration assessed, shows that in the case of the intrinsic route coagulation time increases when the diameter of the particle is greater (microsized particles) unlike the extrinsic route. Previous studies have shown that blood clotting is closely related to particle size. It was the case of silicon NPs where the intrinsic pathway of coagulation increased significantly as the size of these particles increased. The results obtained showed that the small-sized particles were practically inert while the larger ones did present significant differences while determining coagulation [
47].
As the concentration of the different zinc oxides increases, the coagulation time, both in the case of the extrinsic (PT) and intrinsic (aPTT) pathways, also increases. In the case of aPTT, this increase is already evident at the concentration of 0.5 mg/mL in particular for ZnO 100 nm and micro-sized particles, although not statistical different from control samples. Statistical analysis also revealed that nanoparticles affect in a similar way coagulation time as ZnO micro-sized and being ZnO 50 NPs slightly less toxic at the highest concentration assayed.
Some authors suggest that the fact that the intrinsic pathway is more affected than the extrinsic pathway is probably due to the structural loss of factor XII (FXII, a key pro-enzyme of the coagulation cascade) when it comes into contact with the particles [
48], that is, to a denaturation caused by structural and functional changes of the native protein [
47].
3.6.2. Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis of human plasma protein: SDS-PAGE
Differential behavior among particles could be attributed to their size and particle curvature and surface area [
49]. This statement agrees with the amount of protein determined from particle’s pellet presented in
Figure 11.A, as a clear correlation between total protein adsorbed and particle size is observed; as the particle size diminishes, surface area and particle curvature increase and so does the total amount of protein adsorb.
Herein, only the most abundant proteins with characteristic and easy recognized stained bands, such as albumin and fibrinogen, could be reliably identified (
Figure 11.B). Our findings show how certain proteins were adsorbed on particles with greater affinity than others (see
Table S3). For instance, in lane 7 that correspond to 50 nm particle’s pellet, subunits β and γ [
50] can be easily identified among the stained protein bands. Moreover, these bands present more intense staining than the one that corresponds to albumin, meaning that fibrinogen is present in greater concentration in the protein corona. In normal conditions, human plasma albumin is found in concentrations 20 times higher than fibrinogen as it can be observed in lane 1 (human plasma) which reveals a great stain band mainly constituted by albumin while the ones from fibrinogen β and γ remain regular sized. In conclusion, it can be assumed that fibrinogen has more affinity to ZnO particles than albumin, especially to ZnO 50 nm. It should be noted that the albumin/fibrinogen relation varies with particle size, lane 5 (ZnO micro-sized) shows more albumin than fibrinogen.
Fibrinogen presence on the protein corona could explain the delays on plasma coagulation reported here; if fibrinogen is trapped in the protein corona, it cannot perform its coagulation role as ZnO particles could be deactivating or denaturalizing it, as reported in previous studies to happen to numerous proteins [
10]. Even though, this would imply that the particles that adsorbed the most fibrinogen caused the greatest delays of plasma coagulation, which contradicts our findings of PT and aPTT. ZnO micro seems to adsorb less fibrinogen, although their effects on plasma coagulation were more significant than those observed for ZnO 50 nm, that seemed to adsorb more fibrinogen. This suggests the importance of further analysis and gel digestion, in order to accurately know each protein that was adsorbed on the particles that could alter physiological processes like plasma coagulation.
Differences among particle sizing are also well observed. For instance, lane 7 from
Figure 11.B reveals much greater fibrinogen β and γ stains than lane 5 and 6, thus meaning that fibrinogen has much more affinity to Zn 50 nm than it does to the other ones. Moreover, most stains seem to pale as particle size grows, as global protein-particle affinity lowers with bigger particles (
Figure 11.A), although it is not the case for albumin/fibrinogen α stain that seems to gain significance.
3.6.3. Observation of protein corona by TEM
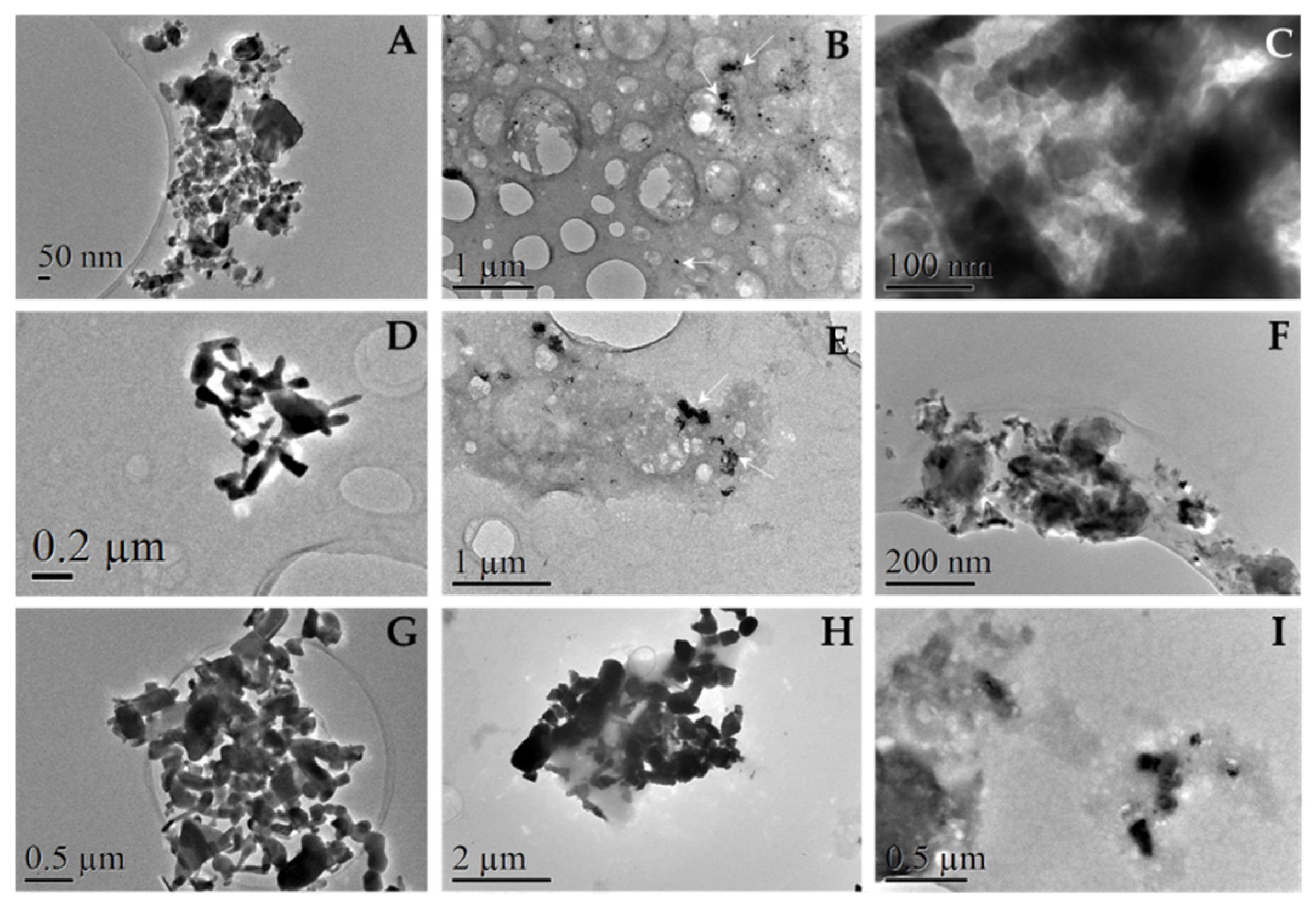
TEM observations revealed protein accumulations around our particles, as can be seen in
Figure 12 (B, C, E, F, H and I). Black spots correspond to particles, shadowy staining corresponds to plasma proteins. These findings should be compared to images A, D and G of
Figure 12.
Organic substances are degraded by the electron beam while the observation takes place; as time went by, nanoparticles seemed to move as the surrounding protein media that coated them was altered. Altogether, this degradation process proved protein presence. Protein presence was corroborated by elemental analysis (EDX) from the same TEM instrument by the presence of Tungsten in the shadowy staining around the particles (
Figure S4).
Differences among particles were significant. ZnO 50 nm NPs revealed large and dense stains of protein where our particles were immersed preventing to find them sometimes. Similar pattern was observed in the case of 100 nm NPs, although protein stains were lighter and clearer. On the other hand, micro sized particles revealed clear protein coating and no individual protein stains were found. These phenomena agree with the total protein adsorbed calculated after incubation with human plasma in section 3.3.2.
3.7. Cytotoxity of ZnO particles in HaCaT and A549
The purpose of cytotoxic studies is to predict the toxicity of a certain substance on cells. The fact of working with nanomaterials can pose a risk to the worker, since they are such small particles, they can be suspended in the air and, consequently, can be easily inhaled and therefore deposited in the tract respiratory tract crossing the lung epithelium or penetrated through the skin's protective membrane causing an inflammatory response or other possible adverse effects [
51]. Based on this explanation, in vitro cytotoxicity has been determined in two human cell lines: keratinocytes (HaCaT) and lung epithelial cells (A549).
Evaluation of cytotoxicity was assessed after exposing the two cell lines to serial concentrations of ZnO particles for 24 hours by MTT, NRU and LDH. The MTT assay allows to evaluate the metabolic activity of the mitochondria while the cellular property that determines the uptake of NR and the release of lactate dehydrogenase is the integrity of the lysosomal and plasma membrane, respectively [
52].
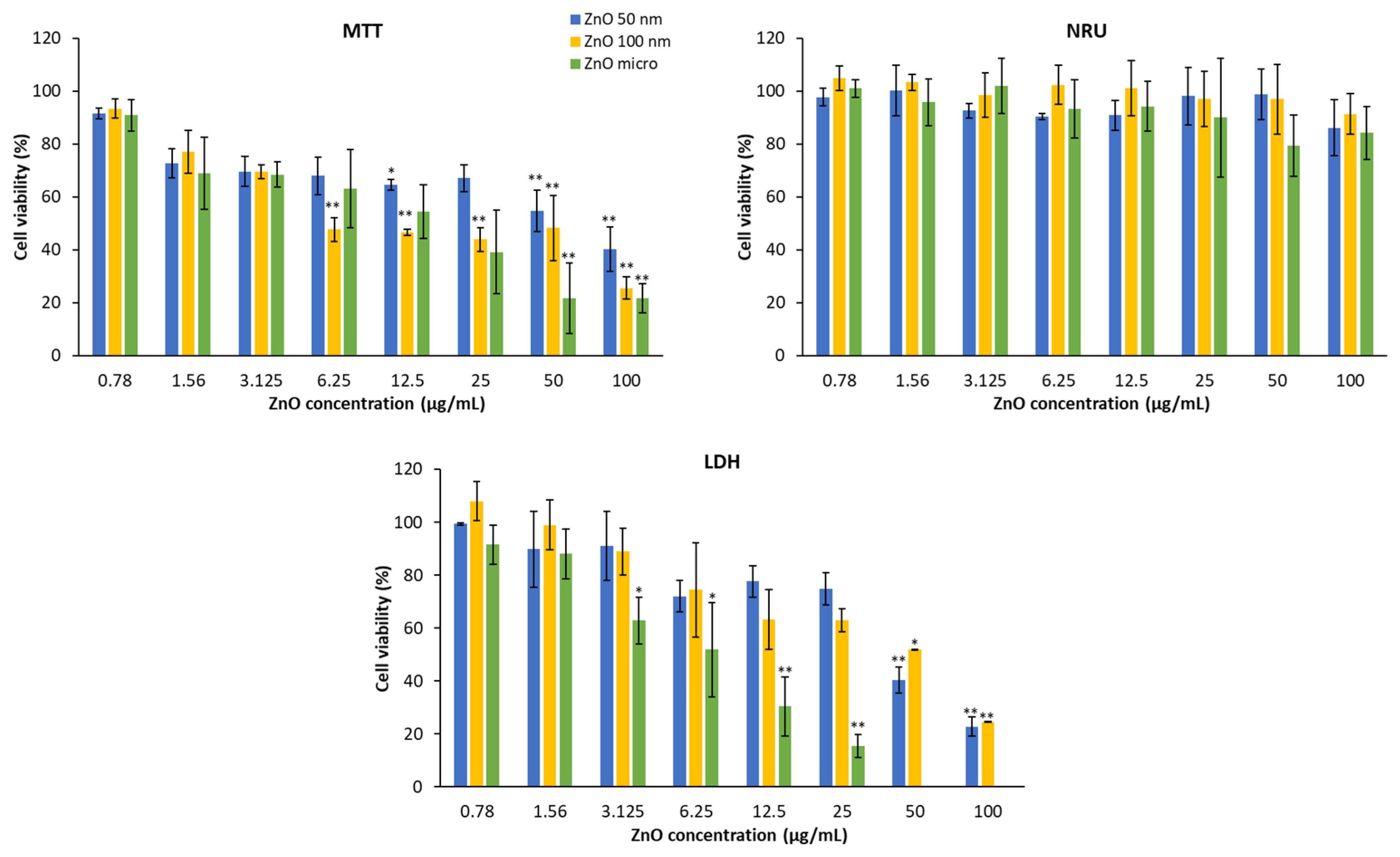
Figure 13 shows HaCaT cell viability in the presence of the three types of zinc oxides. It can be deduced that these products mainly affect mitochondrial activity (MTT) and the plasma membrane (LDH). The lysosomal membrane is practically not altered; only a slight decrease can be observed at the highest concentration.
To avoid potential interferences of the NPs with the final spectrometric readouts of LDH we followed the recommendations of [
28]., Moreover, previous studies also indicated the suitability of MTT and NRU as no interferences were found [2, 53].
Cytotoxicity is demonstrated by a decrease in cell viability. Thus, in the MTT assay, cytotoxicity increases as the concentration does, in a dose-dependent manner [
54]. This fact is more visible if we look at a certain concentration, for example at 100 μg/mL, micrometric ZnO produces a reduction of mitochondrial function by about 80% compared to 50 nm ZnO which causes 60% of the reduction, on the other hand at a concentration of 0.78 μg/mL the effects are practically insignificant with respect to mitochondrial function [
55]. With reference to particle size, ZnO 50 nm is the one with the least toxicity, while micrometric ZnO at concentrations greater than 25 μg/mL is the most cytotoxic [
2].
This behavior is very similar to the LDH test, the higher the concentration, the more amount of lactate dehydrogenase is released into the medium and therefore, the lower the cell viability. Regarding the size of the particles, it can be observed that the micrometric size causes greater damage to the plasma membrane than ZnO 100 nm and this greater than ZnO 50 nm.
There are studies showing that some ZnO NPs after 6 hours of incubation already show a decrease in mitochondrial function and LDH release [
55]. Other articles also suggest that the size of the particles is directly related to their cytotoxicity [
56].
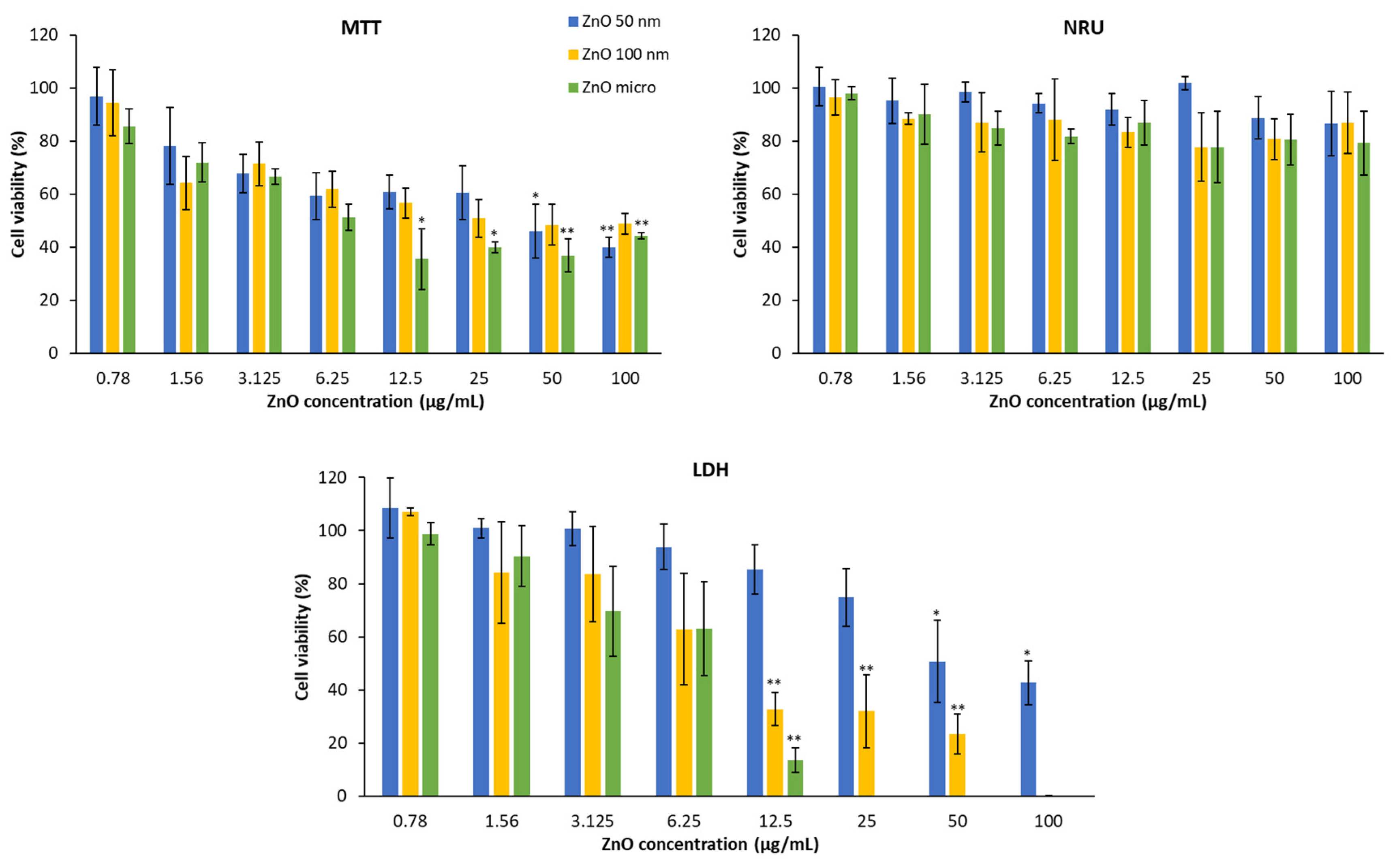
In
Figure 14 it is shown A549 cell viability treated with zinc oxide after 24 hours of exposure and obtained by different methods. In the same way as the HaCaT, the lysosomal function of the lung cells only presents significant differences at concentrations higher than 50 μg/mL [
52].
In the case of the MTT test, it is also observed that the higher the concentration, the lower the cell viability. In this case, if we analyze the percentage of living cells at 100 μg/mL, all the compounds affect mitochondrial activity practically equally (the functional reduction of the mitochondria of ZnO 50 nm, 100 nm and the micrometric is of 60%, 52% and 56% respectively).
In the same way, the test that allows to evaluate the integrity of the membrane has a dose-dependent effect where the higher concentration presents a lower viability, since the amount of enzyme released in the medium is greater and therefore, there is a greater number of damaged cells. In this case, micrometric zinc oxide is also the one with the greatest cytotoxicity, followed by ZnO 100 nm and ZnO 50 nm. There are studies that postulate the idea that the integrity of the plasma membrane depends directly on the structure of the compound studied [
52] but here the most distinctive feature is particle size.
Based on the cytotoxicity data, the inhibitory concentration (IC
50) has been calculated, which allows us to make comparisons between the different products and between the different cell lines in the most effective way. This value is obtained by fitting the data obtained to the best curve. In
Table 4, the IC
50 of the three zinc products in the two cell lines (HaCaT and A549) determined by the MMT and LDH method can be compared. In the case of the NRU test, the IC
50 could not be calculated, since at the maximum tested concentration (100 μg/mL) cell viability is approximately 80% in both cell lines. It is observed that the IC
50 of all zinc oxides is lower than 100 μg/mL. Regarding the MTT and LDH test, if we compare the different zinc oxides in the keratinocyte cell line, it can be seen, as we mentioned previously, that micrometric ZnO is the most cytotoxic, followed by ZnO 100 nm and 50 nm. In the case of lung epithelial cells, ZnO 50 nm is also the least cytotoxic. If we compare between the cell lines, the integrity of the cell membrane in the case of ZnO 50 nm is more affected in the keratinocyte line than in the lung epithelial line.
4. Conclusions
In conclusion, the study presented in this research study provides valuable insights into the behavior of ZnO nanoparticles (NPs) in physiological media and their impact on various biological processes. Despite challenges in characterizing ZnO NPs in PBS, it was observed that ZnO NPs tend to form aggregates and agglomerates. However, the presence of proteins potentially avoid NPs agglomeration and aggregation effects as can be concluded from the decrease of hydrodynamic diameter and protein adsorption capacity of nanoparticles with time, with fibrinogen being the most adsorbed protein. The interaction between albumin and ZnO NPs was confirmed through absorption and fluorescence techniques, with fluorescence results proving to be more accurate.
Moreover, our study also highlighted that pH and media can interfere with hemolysis determination, leading to misinterpretations if potential hemoglobin adsorption is not previously assessed. According to this, PBS pH 7.4 is an adequate medium to conclude that hemolytic activity of ZnO NPs is dose-dependent and temperature-dependent, with no evidence that nanosized ZnO was more hemolytic than micro-sized particles. However, the presence of 0.5 mg/mL of albumin failed to prevent this hemolytic activity suggesting that a "protein corona" may not form under these conditions although previously the formation of a complex between albumin and ZnO NPs is described but at highest albumin concentration.
Coagulation process was also affected by ZnO NPs, with the extrinsic pathway being the most influenced. As stated, ZnO NPs can agglomerate rapidly in aqueous media, but agglomeration was mitigated in plasma. The presence of protein corona on ZnO NPs was visually confirmed through TEM observations, and the hydrodynamic diameter of ZnO NPs in the presence of proteins was found to decrease, avoiding agglomeration effects as also described when ZnO NPs were in presence of fibrinogen alone.
Cytotoxicity studies revealed that ZnO NPs exhibited similar behavior in MTT and LDH methods, with micrometric-sized particles being more cytotoxic and exhibiting a lower IC50. Overall, the relationship between nanometer size and toxicity cannot be directly attributed.
In summary, the results of this study highlight the complex interactions between ZnO NPs and biological systems, including their aggregation behavior, hemolytic activity, protein corona formation, coagulation effects, and cytotoxicity. These findings contribute to a better understanding of the potential impacts of ZnO NPs on human health and suggest the need for further investigations to elucidate the underlying mechanisms and optimize the safe use of ZnO NPs in various applications.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org., Figure S1: Example of EDX elemental analysis for ZnO 100 nm in ethanol used to confirm the chemical nature of the aggregates observed; Figure S2. Example of selected area diffraction analysis (SAED) for ZnO 100 nm in ethanol used to confirm the chemical nature of the aggregates observed. Figure S3. Spectra of human hemoglobin; Figure S4. Example of EDX elemental analysis for ZnO 50 nm after 30 minutes incubation in human plasma to confirm the presence of protein corona; Table S1. Values of theoretical and experimental lattice distance and their Miller indexes; Table S2. DLS characterization of nanoparticles at room temperature; Table S3. Qualitative SDS-PAGE band proteins and tentative protein identification.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.P.V. and M.M.; methodology, L.M., M.B., A.M. and J.JP.; formal analysis, L.M., M.B., A.M. and J.JP.; investigation, L.M., M.B., A.M. and J.JP.; resources, M.P.V. and M.M; writing—original draft preparation, M.P.V. and M.M; writing—review and editing, M.P.V. and M.M; supervision, M.P.V. and M.M.; funding acquisition, M.P.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad–Spain and FEDER, the European Union, grant number MAT2012-38047-C02-01”.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be available upon valid request.
Acknowledgments
The authors Jordi Diaz and Joan Mendoza from the Centres Científics i Tecnològics of Universitat de Barcelona (CCiT UB) for their help and assistance on the microscopy studies.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Jiang, J.; Pi, J.; Cai, J. The Advancing of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2018, 1062562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allouni, Z. E.; Gjerdet, N. R.; Cimpan, M. R.; i Høl, P. J. The effect of blood protein adsorption on cellular uptake of anatase TiO2 nanoparticles. Int J Nanomedicine 2015, 10, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fritea, L.; Banica, F.; Costea, T.O.; Moldovan, L.; Dobjanschi, L.; Muresan, M.; Cavalu, S. Metal Nanoparticles and Carbon-Based Nanomaterials for Improved Performances of Electrochemical (Bio)Sensors with Biomedical Applications. Materials (Basel) 2021, 14, 6319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramaniam, V.D.; Prasad, S.V.; Banerjee, A.; Gopinath, M.; Murugesan, R.; Marotta, F.; Sun, X.F.; Pathak, S. Health hazards of nanoparticles: understanding the toxicity mechanism of nanosized ZnO in cosmetic products. Drug. Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 42, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, R.; Kumar, A.; Tripathi, R.; Kumar, A. Advancing of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles for Cosmetic Applications. In Handbook of Consumer Nanoproducts; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 1057–1072. [Google Scholar]
- Sha, R.; Basak, A.; Maity, P.C.; Badhulika, S. ZnO nano-structured based devices for chemical and optical sensing applications, Sensors Actuat. Rep. 2022, 4, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Z.; Xu, Y.; Gao, J.; Wang, X. Research progress of stimuli-responsive ZnO-based nanomaterials in biomedical applications. Biomater. Sci. 2022, 11, 76–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alavi, N.; Maghami, P.; Fani Pakdel, A.; Rezaei, M.; Avan, A. The advance anticancer role of polymeric core-shell ZnO nanoparticles containing oxaliplatin in colorectal cancer. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2023, e23325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, B.A.; Abuçafy, M.P.; Barbosa, T.W.L.; da Silva, B.L.; Fulindi, R.B.; Isquibola, G.; da Costa, P.I.; Chiavacci, L.A. ZnO@ZIF-8 Nanoparticles as Nanocarrier of Ciprofloxacin for Antimicrobial Activity. Pharmaceutics. 2023, 15, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, P.; Liptrott, N.J.; Bremer, S. Overview of the blood compatibility of nanomedicines: A trend analysis of in vitro and in vivo studies. Wiley Interdiscip. Ver. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 11, e1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopac, C. Protein corona, understanding the nanoparticle interactions and future prespectives: A critical review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 169, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satzer, P.; Svec, F.; Sekot, G.; Jungbauer, A. Protein adsorption onto nanoparticles induces conformational changes: Particle size dependency, kinetics, and mechanisms. Eng. Life Sci. 2016, 16, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu J, Kim HJ, Go MR, Bae SH, Choi SJ. ZnO Interactions with Biomatrices: Effect of Particle Size on ZnO-Protein Corona. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2017, 7, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, B.; Seog, J.H.; Graham, L.M.; Lee, S.B. Experimental considerations on the cytotoxicity of nanoparticles. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2011, 6, 929–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jedrzejczak-Silicka, M.; Mijowska, E. General Cytotoxicity and Its Application in Nanomaterial Analysis [Internet]. Cytotoxicity. InTech. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruger, N.J. The Bradford Method for Protein Quantitation. In: The Protein Protocols Handbook. Springer Protocols Handbooks. Walker, J.M. (eds). Humana Press, Totowa, NJ. 2009. [CrossRef]
- Mariam, J.; Dongre, P. M.; Kothari, D. C. Study of Interaction of Silver Nanoparticles with Bovine Serum Albumin Using Fluorescence Spectroscopy. J. Fluoresc. 2011, 21, 2193–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, W.; Duffin, R.; Bradley, M.; Megson, I. L.; Macnee, W.; Lee, J. K.; Jeong, J.; Donaldson, K. Predictive Value of in Vitro Assays Depends on the Mechanism of Toxicity of Metal Oxide Nanoparticles. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2013, 10, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, D. R.; Mitjans, M.; Infante, M. R.; Vinardell, M. P. The Role of Counterions in the Membrane-Disruptive Properties of pH-Sensitive Lysine-Based Surfactants. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 2846–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Lan, J.; Xu, Z.; Chen, T. Toxicity and Biodistribution of Aqueous Synthesized ZnS and ZnO Quantum Dots in Mice. Nanotoxicol. 2014, 8, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treuel, L.; Brandholt, S.; Maffre, P.; Wiegele, S.; Shang, L.; Nienhaus, G.U. Impact of protein modification on the protein corona on nanoparticles and nanoparticle-cell interactions. ACS Nano. 2014, 8, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinardell, M. P.; Sordé, A.; Díaz, J.; Baccarin, T.; Mitjans, M. Comparative Effects of Macro-Sized Aluminum Oxide and Aluminum Oxide Nanoparticles on Erythrocyte Hemolysis: Influence of Cell Source, Temperature, and Size. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2015, 17, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, T.M.; Rodriguez, J.C.; Neun, B.W.; Ilinskaya, A.N.; Cedrone, E.; Dobrovolskaia, M.A. In Vitro Assessment of Nanoparticle Effects on Blood Coagulation. Methods Mol Biol. 2018, 1682, 103–124. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tenzer, S.; Docter, D.; Kuharev, J.; Musyanovych, A.; Fet, V.; Hecht, R.; Schlenk, F.; Fischer, D.; Kiouptsi, K.; Reinhardt, C.; Landfester, K.; Schild, H.; Maskos, M.; Knauer, S. K.; Stauber, R. H. Rapid formation of plasma protein corona critically affects nanoparticle pathophysiology. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2013, 8, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kielkopf, C.L.; Bauer, W.; Urbatsch, I.L. Bradford Assay for Determining Protein Concentration. Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2020, 2020, 102269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laemmli, U.H. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinardell, M.P.; Llanas, H.; Marics, L.; Mitjans, M. In Vitro Comparative Skin Irritation Induced by Nano and Non-Nano Zinc Oxide. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guadagnini, R.; Halamoda, B.; Walker, L.; Pojana, G.; Magdolenova, Z.; Bilanicova, D.; Saunders, L.; Juillerat-Jeanneret, L.; Marcomini, A.; Huk, A.; Dusinska, M.; Fjellsbo, L.; Marano, F.; Boland, S. Toxicity screenings of nanomaterials: challenges due to interference with assay processes and components of classic in vitro tests. Nanotoxicol. 2015, 9, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanette, C.; Pelin, M.; Crosera, M.; Adami, G.; Bovenzi, M.; Larese, F.F.; Florio, C. Silver nanoparticles exert a long-lasting antiproliferative effect on human keratinocyte HaCaT cell line. Toxicol Vitro. 2011, 25, 1053–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babich, H.; Borenfreund, E. Applications of the neutral red cytotoxicity assay to risk assessment of aquatic contaminants: an overview, Landis,W.G., Hughes, J.S., Lewis, M.A. (Eds.), Environ. Tox. Risk Asses. 1993, 215-216.
- Dhawan, A.; Sharma, V. Toxicity assessment of nanomaterials: methods and challenges. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 398, 589–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. Q.; Yin, L. H.; Tang, M.; Pu, Y. P. ZnO, TiO2, SiO2 and Al2O3 Nanoparticles-Induced Toxic Effects on Human Fetal Lung Fibroblasts. Biomed Env. Sci. 2011, 24, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimundić, M.; Drašler, B.; Šuštar, V.; Zupanc, J.; Štukelj, R.; Makovec, D.; Erdogmus, D.; Hägerstrand, H.; Drobne, D.; Kralj-Iglič, V. Effect of engineered TiO2 and ZnO nanoparticles on erythrocytes, platelet-rich plasma and giant unilamelar phospholipid vesicles. BMC Vet Res. 2013, 9, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, E.B.; Yu, J.; Choi, S.J. Interaction between ZnO Nanoparticles and Albumin and Its Effect on Cytotoxicity, Cellular Uptake, Intestinal Transport, Toxicokinetics, and Acute Oral Toxicity. Nanomaterials. 2021, 11, 2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornaguera, C.; Calderó, G.; Mitjans, M.; Vinardell, M. P.; Solans, C.; Vauthier, C. Interactions of PLGA nanoparticles with blood components: protein adsorption, coagulation, activation of the complement system and hemolysis studies. Nanoscale. 2015, 7, 6045–6058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bihari, P.; Vippola, M.; Schultes, S.; Praetner, M.; Khandoga, A. G.; Reichel, C. A.; Coester, C.; Tuomi, T.; Rehberg, M.; Krombach, F. Optimized dispersion of nanoparticles for biological in vitro and in vivo studies. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2008, 5, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhogale, A.; Patel, N.; Sarpotdar, P.; Mariam, J.; Dongre, P. M.; Miotello, A.; Kothari, D. C. Systematic Investigation on the Interaction of Bovine Serum Albumin with ZnO Nanoparticles Using Fluorescence Spectroscopy. Colloids Surf. B. Biointerfaces 2013, 102, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasidharan, N. Interaction of Colloidal Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles with Bovine Serum Albumin and its Adsorption Isotherms and Kinetics. Colloids Sur. B Biointerfaces. 2013, 102, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simón-Vázquez, R.; Lozano-Fernández, T.; Peleteiro-Olmedo, M.; González-Fernández, Á. Conformational Changes in Human Plasma Proteins Induced by Metal Oxide Nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B. Biointerfaces. 2014, 113, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Duffin, R.; Poland, C.; Daly, P.; Murphy, F.; Drost, E.; Macnee, W.; Stone, V.; Donaldson, K. Efficacy of simple short-term in vitro assays for predicting the potential of metal oxide nanoparticles to cause pulmonary inflammation. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 10, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemmar, A.; Beegam, S.; Yuvaraju, P. Interaction of Amorphous Silica Nanoparticles with Erythrocytes in Vitro: Role of Oxidative Stress. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 34, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, M.; Abdelmonem, A.M.; Behzadi, S.; Clement, J.H.; Dutz, S.; Ejtehadi, M.R.; Hartmann, R.; Kantner, K.; Linne, U.; Maffre, P.; Metzler, S.; Moghadam, M.K.; Pfeiffer, C.; Rezaei, M.; Ruiz-Lozano, P.; Serpooshan, V.; Shokrgozar, M.A.; Nienhaus, G.U.; Parak, W.J. Temperature: the "ignored" factor at the NanoBio interface. ACS Nano. 2013, 7, 6555–6562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aisaka, Y.; Kawaguchi, R.; Watanabe, S. Hemolysis Caused by Titanium Dioxide Particles. Inhal. Toxicol. 2008, 20, 891–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geekiyanage, N.M.; Balanant, M.A.; Sauret, E.; Saha, S.; Flower, R.; Lim, C.T.; Gu, Y. A coarsegrained red blood cell membrane model to study stomatocyte-discocyte-echinocyte morphologies. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neun, B. W.; Rodriguez, J.; Ilinskaya, A.; Dobrovolskaia, M. NCL Method ITA-12 Coagulation assays, 2015, 1-8. https://ncihub.cancer.gov/publications/147/?v=1 (accessed 3 may 2023).
- Kushida, T.; Saha, K.; Subramani, C.; Nandwana, V.; Rotello, V. M. Effect of nano-scale curvature on the intrinsic blood coagulation system. Nanoscale, 2014, 6, 14484–14487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.; Zhu, D.; Liu, L.; Dong, X.; Zhang, H.; Leng, X. Evaluation of the coagulation properties of arginine-chitosan/DNA nanoparticles. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B: Appl. Biomater. 2010, 95, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duran, N.; Silveira, C. P.; Duran, M.; Martinez, D. S. T. Silver nanoparticle protein corona and toxicity: a mini-review. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2015, 13, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tennent, G. A.; Brennan, S. O.; Stangou, A. J.; O’Grady, J.; Hawkins, P. N.; Pepys, M. B. Human plasma fibrinogen is synthesized in the liver. Blood, 2007, 109, 1971–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verstraelen, S.; Remy, S.; Casals, E.; De Boever, P.; Witters, H.; Gatti, A.; Puntes, V.; Nelissen, I. Gene expression profiles reveal distinct immunological responses of cobalt and cerium dioxide nanoparticles in two in vitro lung epithelial cell models. Toxicol. Lett. 2014, 228, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, D. R.; Morán, M. C.; Mitjans, M.; Martínez, V.; Pérez, L.; Vinardell, M. P. New cationic nanovesicular systems containing lysine-based surfactants for topical administration: toxicity assessment using representative skin cell lines. Eur J. Pharm Biopharm. 2013, 83, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farcal, L.; Torres Andón, F.; Di Cristo, L.; Rotoli, B.M.; Bussolati, O.; Bergamaschi, E.; et al. Comprehensive In Vitro Toxicity Testing of a Panel of Representative Oxide Nanomaterials: First Steps towards an Intelligent Testing Strategy. PLoSONE, 2015, 10, e0127174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Jin, C.; Tang, Y.; Wang, F.; Ma, C.; Yang, Y. Cytotoxicity of silica nanoparticles on HaCaT cells. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2014, 34, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeng, H. A.; Swanson, J. Toxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles in mammalian cells. J. Environ. Sci. Health A. 2006, 41, 2699–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Fujita, D.; Kajiwara, S.; Minowa, T.; Li, X.; Takemura, T.; Iwai, H.; Hanagata, N. Contribution of physicochemical characteristics of nano-oxides to cytotoxicity. Biomat. 2010, 31, 8022–8031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Figure 1.
Topographical AFM images (2D and 3D) and particle size histograms of ZnO 50 nm (A) and ZnO 100 nm (B).
Figure 1.
Topographical AFM images (2D and 3D) and particle size histograms of ZnO 50 nm (A) and ZnO 100 nm (B).
Figure 2.
TEM microphotographs of commercial ZnO nanoparticles in different media. ZnO nanoparticles of 50 nm (A-C) or 100 nm (D-F) were suspended at a final concentration of 100 μg/mL in PBS (A and D), 0.9% NaCl (B and E) and ethanol (C and F). Suspension was obtained from dilution and ultrasonication of a previous ultrasonicated suspension of 1mg/mL of the sample. Observation and analysis were carried out in a JEOL JEM LaB6-2100 microscope of one drop deposited and dried on a Holey Carbon- Cu grid, at CCiT UB.
Figure 2.
TEM microphotographs of commercial ZnO nanoparticles in different media. ZnO nanoparticles of 50 nm (A-C) or 100 nm (D-F) were suspended at a final concentration of 100 μg/mL in PBS (A and D), 0.9% NaCl (B and E) and ethanol (C and F). Suspension was obtained from dilution and ultrasonication of a previous ultrasonicated suspension of 1mg/mL of the sample. Observation and analysis were carried out in a JEOL JEM LaB6-2100 microscope of one drop deposited and dried on a Holey Carbon- Cu grid, at CCiT UB.
Figure 3.
Particle protein adsorption after 2 and 24 hours of incubation. Results are expressed as mean ± standard error of n=3 independent experiments. For statistical analysis, unpaired Student’s t-test was used assuming differences for p < 0.05; *denotes statistical differences between 2 and 24 hours for the same protein; $indicates statistical differences between media containing BSA versus media containing fibrinogen at the same time incubation.
Figure 3.
Particle protein adsorption after 2 and 24 hours of incubation. Results are expressed as mean ± standard error of n=3 independent experiments. For statistical analysis, unpaired Student’s t-test was used assuming differences for p < 0.05; *denotes statistical differences between 2 and 24 hours for the same protein; $indicates statistical differences between media containing BSA versus media containing fibrinogen at the same time incubation.
Figure 4.
UV-Visible absorption spectra of BSA in the presence of ZnO particles. 2 mg BSA/mL were incubated with ZnO 50 nm (A-B), ZnO 100 nm (C-D) and ZnO micro (E-F) at concentrations of 0, 0.8, 1.6, 2.5 and 3.3 mg/mL (arrow) at 30 minutes (left) and 18h (right). After incubation, UV-Vis absorption spectra were recorded in the wavelength range of 250-330 nm using a 1 cm path length quartz cuvette.
Figure 4.
UV-Visible absorption spectra of BSA in the presence of ZnO particles. 2 mg BSA/mL were incubated with ZnO 50 nm (A-B), ZnO 100 nm (C-D) and ZnO micro (E-F) at concentrations of 0, 0.8, 1.6, 2.5 and 3.3 mg/mL (arrow) at 30 minutes (left) and 18h (right). After incubation, UV-Vis absorption spectra were recorded in the wavelength range of 250-330 nm using a 1 cm path length quartz cuvette.
Figure 5.
Fluorescence spectra of BSA in the presence of ZnO particles. 2 mg BSA/mL were incubated with ZnO 50 nm (A), ZnO 100 nm (B) and ZnO micro (C) at concentrations of 0, 0.8, 1.6, 2.5 and 3.3 mg/mL. Fluorescence measurements were recorded in the wavelength range of 310-430 nm using a 1 cm path length quartz cuvette. The excitation wavelength was set at 278 nm and emission was measured in the range of 275-475 nm.
Figure 5.
Fluorescence spectra of BSA in the presence of ZnO particles. 2 mg BSA/mL were incubated with ZnO 50 nm (A), ZnO 100 nm (B) and ZnO micro (C) at concentrations of 0, 0.8, 1.6, 2.5 and 3.3 mg/mL. Fluorescence measurements were recorded in the wavelength range of 310-430 nm using a 1 cm path length quartz cuvette. The excitation wavelength was set at 278 nm and emission was measured in the range of 275-475 nm.
Figure 6.
Hemoglobin adsorption in the presence of ZnO and Al2O3 particles in 0.9% NaCl at pH 5.7 and pH 7.4. A solution of hemoglobin was incubated in the presence of the different particles at a concentration of 1 mg/mL for 30 minutes, posteriorly were centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 5 min. Finally, the samples were observed to know if the hemoglobin had been adsorbed by the metal oxide, and thus if the hemolysis assays can be performed at the conditions studied. RBC incubated with 0.9% NaCl without particles was used as a control of negative hemoglobin solution (0). Hb: hemoglobin solution incubated with the different media.
Figure 6.
Hemoglobin adsorption in the presence of ZnO and Al2O3 particles in 0.9% NaCl at pH 5.7 and pH 7.4. A solution of hemoglobin was incubated in the presence of the different particles at a concentration of 1 mg/mL for 30 minutes, posteriorly were centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 5 min. Finally, the samples were observed to know if the hemoglobin had been adsorbed by the metal oxide, and thus if the hemolysis assays can be performed at the conditions studied. RBC incubated with 0.9% NaCl without particles was used as a control of negative hemoglobin solution (0). Hb: hemoglobin solution incubated with the different media.
Figure 7.
Hemolytic activity of ZnO at different concentrations at Room Temperature and 37°C. Results are expressed as Mean ± ES of almost 4 independent experiments in triplicate. A one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and a Scheffe post hoc assay have been performed. a-ddenoted statistical differences among concentrations at p < 0.05 or p <0.01; Differences among particle size were considered at *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01 between nano 50 or 100 nm and micro-sized ZnO and $p < 0.05; $$p < 0.01 between 50 nm and 100 nm ZnO.
Figure 7.
Hemolytic activity of ZnO at different concentrations at Room Temperature and 37°C. Results are expressed as Mean ± ES of almost 4 independent experiments in triplicate. A one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and a Scheffe post hoc assay have been performed. a-ddenoted statistical differences among concentrations at p < 0.05 or p <0.01; Differences among particle size were considered at *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01 between nano 50 or 100 nm and micro-sized ZnO and $p < 0.05; $$p < 0.01 between 50 nm and 100 nm ZnO.
Figure 8.
Effect of BSA over hemolytic activity of ZnO at different concentrations at Room Temperature and 37°C. Results are expressed as Mean ± ES of almost 4 independent experiments in triplicate. A one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and a Scheffe post hoc assay have been performed. a-ddenoted statistical differences among concentrations at p < 0.05 or p <0.01; Differences among particle size were considered at *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01 between nano 50 or 100 nm and micro-sized ZnO and $p < 0.05; $$p < 0.01 between 50 nm and 100 nm ZnO.
Figure 8.
Effect of BSA over hemolytic activity of ZnO at different concentrations at Room Temperature and 37°C. Results are expressed as Mean ± ES of almost 4 independent experiments in triplicate. A one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and a Scheffe post hoc assay have been performed. a-ddenoted statistical differences among concentrations at p < 0.05 or p <0.01; Differences among particle size were considered at *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01 between nano 50 or 100 nm and micro-sized ZnO and $p < 0.05; $$p < 0.01 between 50 nm and 100 nm ZnO.
Figure 9.
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images of human erythrocytes. Erythrocytes were incubated for 3 or 24 hours in PBS (pH 7.4) for (A-B), 0.2 mg/mL ZnO 50 nm (C-D), 0.2 mg/mL ZnO 100 nm (E-F) or 0.2 mg/mL ZnO micro (G-H).
Figure 9.
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images of human erythrocytes. Erythrocytes were incubated for 3 or 24 hours in PBS (pH 7.4) for (A-B), 0.2 mg/mL ZnO 50 nm (C-D), 0.2 mg/mL ZnO 100 nm (E-F) or 0.2 mg/mL ZnO micro (G-H).
Figure 10.
Effect of the different zinc oxides on prothrombin and partial activated thromboplastin time. Results are expressed as Mean ± ES of almost 3 independent experiments in triplicate. A one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and a Scheffe post hoc assay have been performed. a-cdenoted statistical differences compared to plasma control at p < 0.05 or p <0.01; Differences among particle size were considered at *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01 between nano and micro-sized ZnO and $p < 0.05; $$p < 0.01 between 50 nm and 100 nm ZnO.
Figure 10.
Effect of the different zinc oxides on prothrombin and partial activated thromboplastin time. Results are expressed as Mean ± ES of almost 3 independent experiments in triplicate. A one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and a Scheffe post hoc assay have been performed. a-cdenoted statistical differences compared to plasma control at p < 0.05 or p <0.01; Differences among particle size were considered at *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01 between nano and micro-sized ZnO and $p < 0.05; $$p < 0.01 between 50 nm and 100 nm ZnO.
Figure 11.
ZnO protein adsorption after incubation of ZnO micro and nano-sized particles with human plasma. A: Total protein adsorbed. B: SDS-PAGE electrophoresis. ZnO particles (10 mg/mL) were incubated with human plasma for 30 minutes and then centrifuged and washed with a solution of Sucrose 0.7 M in PBS. Protein extracted (18 µg) was finally running by using a Mini-PROTEAN Tetra Cell unit (Bio-Rad, Hercules CA, USA). The slab gel consisted of a 7.5% polyacrylamide resolving gel and a 5% polyacrylamide stacking gel. Electrophoresis was carried out for 10 min at 60 V and then at 200 V. Protein bands were stained with Coomassie Blue R-250 under gentle shaking and destained with a mixture of 7.5% methanol and 10% acetic acid. The molecular weight of the membrane proteins was estimated from the molecular size marker (10–250 kDa). Lane 1: human plasma; Lanes 2-4: first supernatant obtained from micro, 100 nm and 50 nm ZnO samples after centrifugation, respectively; Lane 5: pellet from ZnO microparticles; Lane 6: pellet form ZnO 100 nm particles; Lane 7: pellet ZnO 50 nm particles; Lane 8: molecular weight-marker.
Figure 11.
ZnO protein adsorption after incubation of ZnO micro and nano-sized particles with human plasma. A: Total protein adsorbed. B: SDS-PAGE electrophoresis. ZnO particles (10 mg/mL) were incubated with human plasma for 30 minutes and then centrifuged and washed with a solution of Sucrose 0.7 M in PBS. Protein extracted (18 µg) was finally running by using a Mini-PROTEAN Tetra Cell unit (Bio-Rad, Hercules CA, USA). The slab gel consisted of a 7.5% polyacrylamide resolving gel and a 5% polyacrylamide stacking gel. Electrophoresis was carried out for 10 min at 60 V and then at 200 V. Protein bands were stained with Coomassie Blue R-250 under gentle shaking and destained with a mixture of 7.5% methanol and 10% acetic acid. The molecular weight of the membrane proteins was estimated from the molecular size marker (10–250 kDa). Lane 1: human plasma; Lanes 2-4: first supernatant obtained from micro, 100 nm and 50 nm ZnO samples after centrifugation, respectively; Lane 5: pellet from ZnO microparticles; Lane 6: pellet form ZnO 100 nm particles; Lane 7: pellet ZnO 50 nm particles; Lane 8: molecular weight-marker.
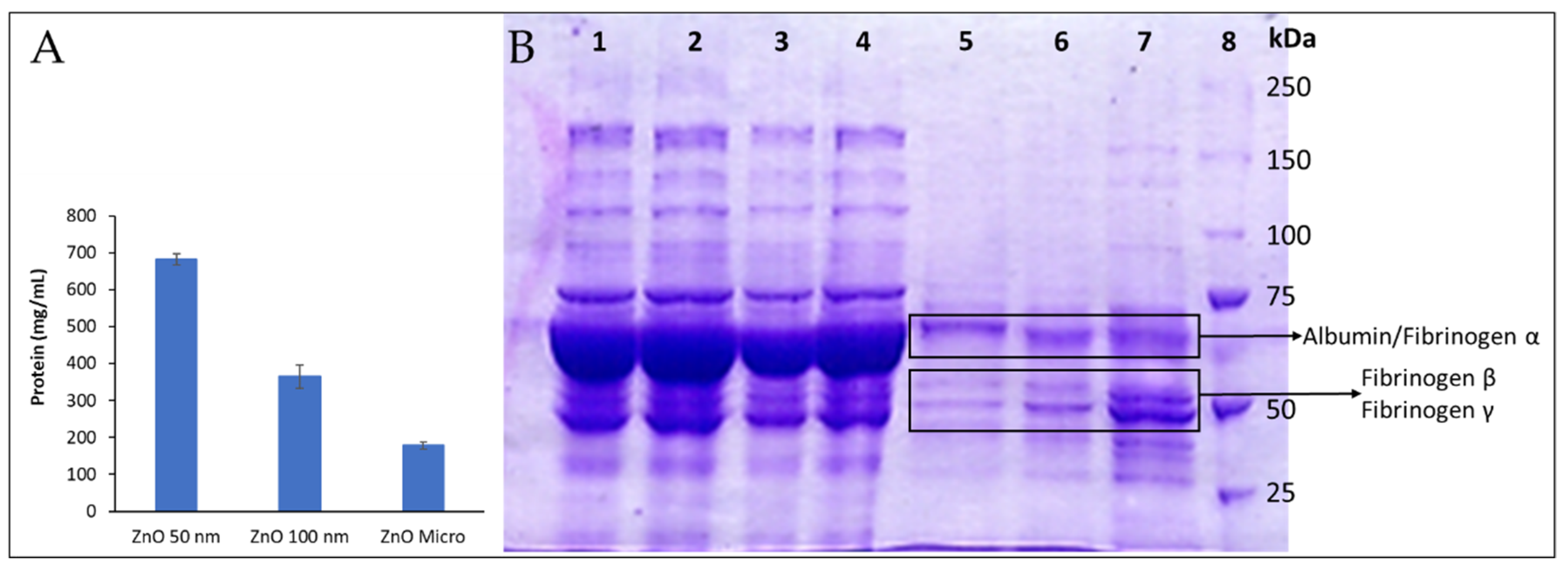
Figure 12.
Protein corona images after incubation of ZnO particles with human plasma. ZnO of 50 nm (A-C), 100 nm (D-F) or micro (G-I) particles were suspended in MiliQ water before and after 30 minutes incubation with human plasma. One sample drop was deposited and dried on a Holey Carbon- Cu grid and protein were revealed by adding phosphotungstic acid. Observation and analysis were carried out in a JEOL JEM LaB6-2100 microscope at CCiT UB.
Figure 12.
Protein corona images after incubation of ZnO particles with human plasma. ZnO of 50 nm (A-C), 100 nm (D-F) or micro (G-I) particles were suspended in MiliQ water before and after 30 minutes incubation with human plasma. One sample drop was deposited and dried on a Holey Carbon- Cu grid and protein were revealed by adding phosphotungstic acid. Observation and analysis were carried out in a JEOL JEM LaB6-2100 microscope at CCiT UB.
Figure 13.
Viability of HaCaT cells in the presence of different concentrations of zinc oxide particles obtained by three different methods (MTT, NRU and LDH). Results are expressed as mean ± standard error of n=3 independent experiments. A one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and a Scheffe post hoc assay have been performed. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01 denoted statistical differences among concentrations.
Figure 13.
Viability of HaCaT cells in the presence of different concentrations of zinc oxide particles obtained by three different methods (MTT, NRU and LDH). Results are expressed as mean ± standard error of n=3 independent experiments. A one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and a Scheffe post hoc assay have been performed. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01 denoted statistical differences among concentrations.
Figure 14.
Viability of A549 cells in the presence of different concentrations of zinc oxide particles obtained by three different methods (MTT, NRU and LDH). Results are expressed as mean ± standard error of n=3 independent experiments. A one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and a Scheffe post hoc assay have been performed. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01 denoted statistical differences among concentrations.
Figure 14.
Viability of A549 cells in the presence of different concentrations of zinc oxide particles obtained by three different methods (MTT, NRU and LDH). Results are expressed as mean ± standard error of n=3 independent experiments. A one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and a Scheffe post hoc assay have been performed. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01 denoted statistical differences among concentrations.
Table 1.
Hydrodynamic diameter (nm) of ZnO NPs in PBS at 2 h and 24 h.
Table 1.
Hydrodynamic diameter (nm) of ZnO NPs in PBS at 2 h and 24 h.
| ZnO particles |
2 hours1
|
24 hours1
|
| 50 nm |
1,014.9 ± 90.5 |
2,165.0 ± 237.6$$
|
| 100 nm |
940.5 ± 72.4 |
1,354.0 ± 62.2$
|
| Micro |
721.1 ± 12.3 |
916.0 ± 43.2$
|
Table 2.
Hydrodynamic diameter (nm) of ZnO NPs after incubation in PBS containing 2 mg/mL of bovine serum albumin (BSA) or fibrinogen and DMEM at 2 h and 24 h.
Table 2.
Hydrodynamic diameter (nm) of ZnO NPs after incubation in PBS containing 2 mg/mL of bovine serum albumin (BSA) or fibrinogen and DMEM at 2 h and 24 h.
| ZnO particles |
2 hours1
|
24 hours1
|
| BSA |
Fibrinogen |
DMEM2
|
BSA |
Fibrinogen |
DMEM2
|
| 50 nm |
806.5 ± 52.6**
|
30.0 ± 7.2**
|
772.2 ± 34.1**
|
995.9 ± 171.3**, $
|
25.6 ± 0.2**
|
1199.0 ± 188.2**, $$
|
| 100 nm |
709.5 ± 15.8**
|
53.3 ± 3.6**
|
614.90 ± 12.7**
|
1334.5 ± 262.3$$
|
173.9 ± 50.1**
|
827.5 ± 102.0**, $
|
| Micro |
625.9 ± 104.7*
|
120.4 ± 78.8**
|
470.30 ± 20.6**
|
1802.0 ± 49.5**, $$
|
214.0 ± 91.1**
|
507.6 ± 36.2**
|
Table 3.
Hemoglobin adsorption after incubation of metal oxide particles in different media.
Table 3.
Hemoglobin adsorption after incubation of metal oxide particles in different media.
| Incubation media |
ZnO |
Al2O3
|
0.9% NaCl
pH 5.7
pH 7.4 |
Adsorption
No adsorption |
No adsorption
No adsorption |
PBS
pH 5.7
pH 7.4 |
No adsorption
No adsorption |
No adsorption
No adsorption |
Tris-maleate
pH 5.7
pH 7.4 |
Adsorption
Adsorption |
No adsorption
No adsorption |
Table 4.
Inhibitory concentration 50 (IC50) for ZnO in HaCaT and A549.
Table 4.
Inhibitory concentration 50 (IC50) for ZnO in HaCaT and A549.
| ZnO particles |
HaCaT |
A549 |
| MTT1
|
LDH |
MTT |
LDH |
| 50 nm |
68.7 ± 5.9 |
38.9 ± 1.6 |
33.1 ± 1.7 |
91.5 ± 9.3 |
| 100 nm |
13.1 ± 1.4 |
16.1 ± 4.7 |
42.9 ± 5.6 |
10.3 ± 0.3 |
| Micro |
11.3 ± 1.0 |
6.2 ± 1.3 |
10.4 ± 0.2 |
6.3 ± 0.8 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).