Submitted:
03 May 2023
Posted:
04 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. PV power prediction model framework
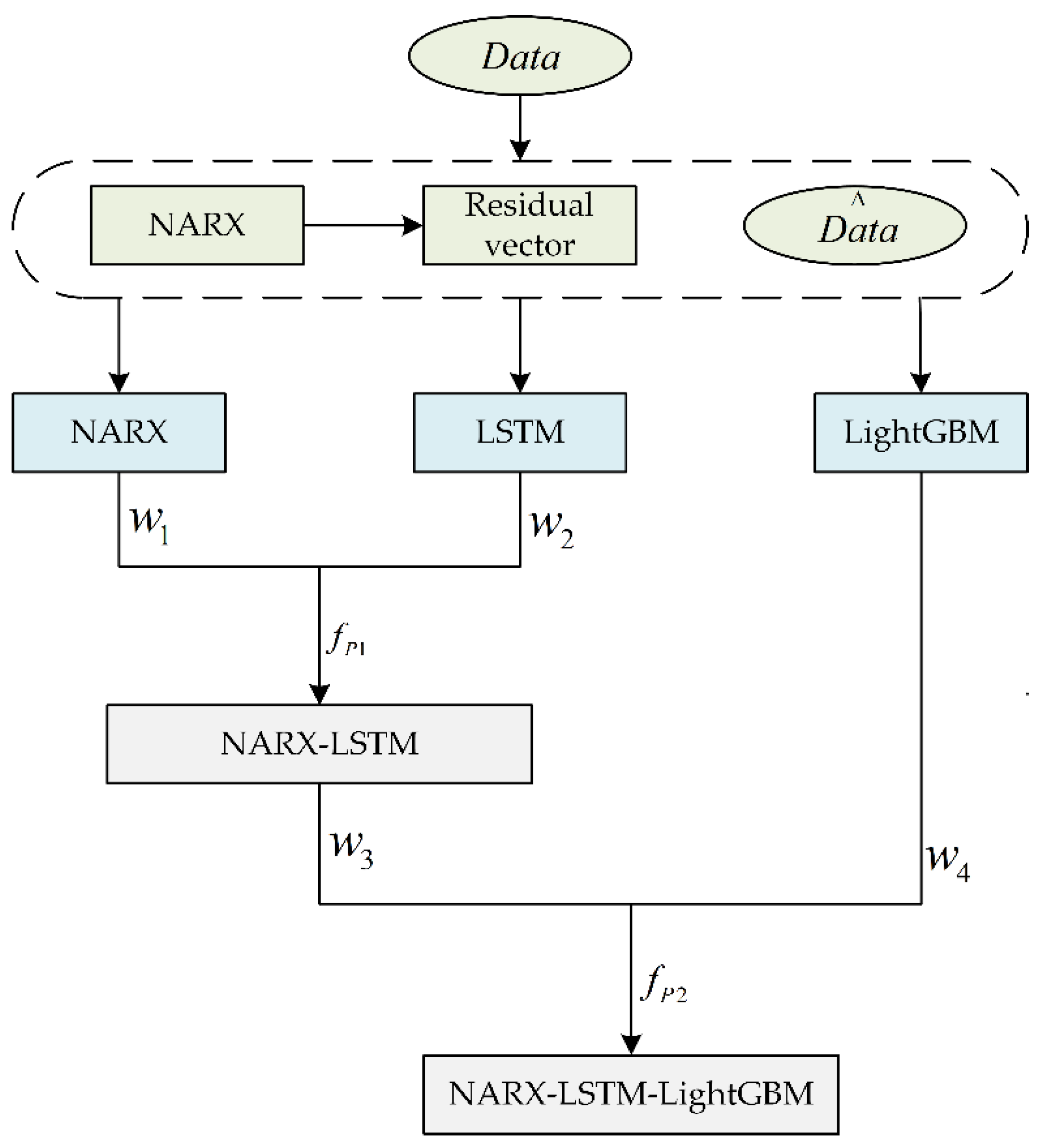
2.1. Method of the Optimal Weight Determination
2.2. Modal Decomposition
- Adding white noise with a standard normal distribution to the raw signal. ., The i-th signal is denoted as ,i=1,2…, I. EMD decomposes the timing signal to obtain the corresponding subsequence and the residual error vector :
- Adaptive white noise is added to the error and i times of experiments are performed each time the results are decomposed using EMD to obtain its first-order component . An error of the 2nd subsequence removed from the 2nd subsequence for CEEMDAN decomposition:
- To acquire the components that satisfy the conditions and the corresponding errors, the aforementioned decomposition procedure is repeated. The repetition comes to an end if the error is a monotonic function and cannot be broken down by EMD. The original signal can be expressed as:
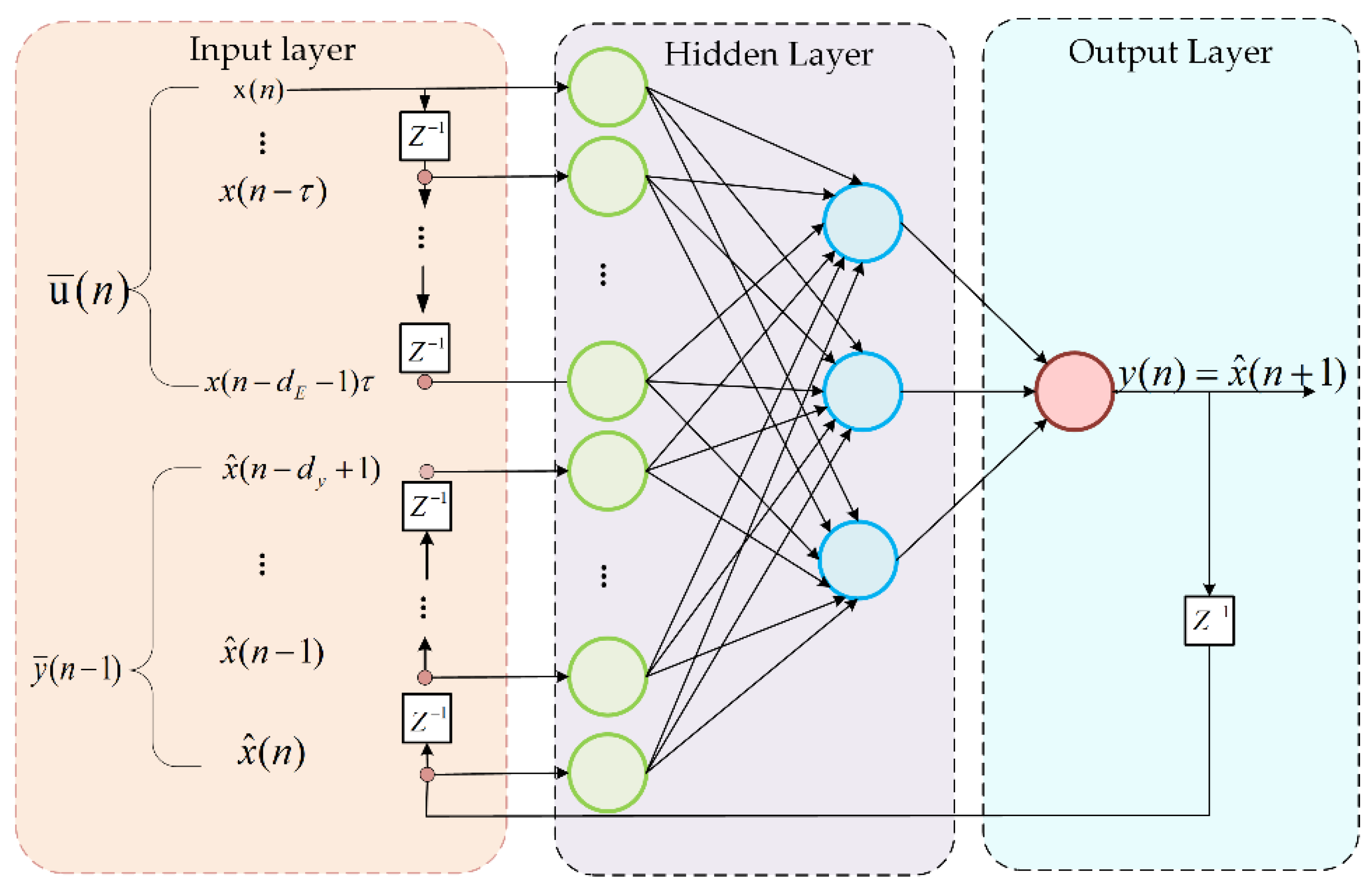
2.3. NARX Neural Network
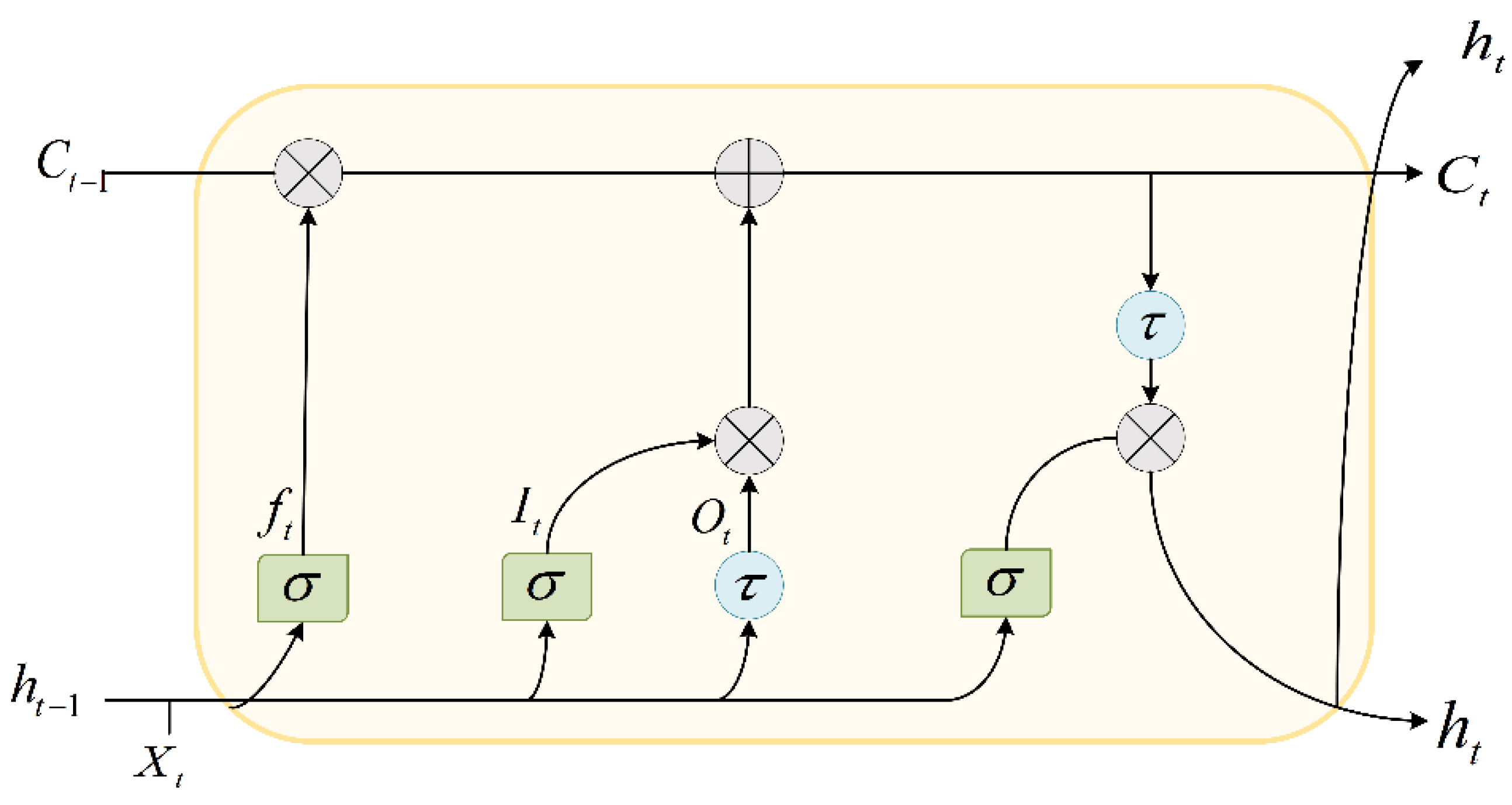
2.4. Long Short-Term Memory
2.5. LightGBM
2.6. Combined Forecasting Model and Process
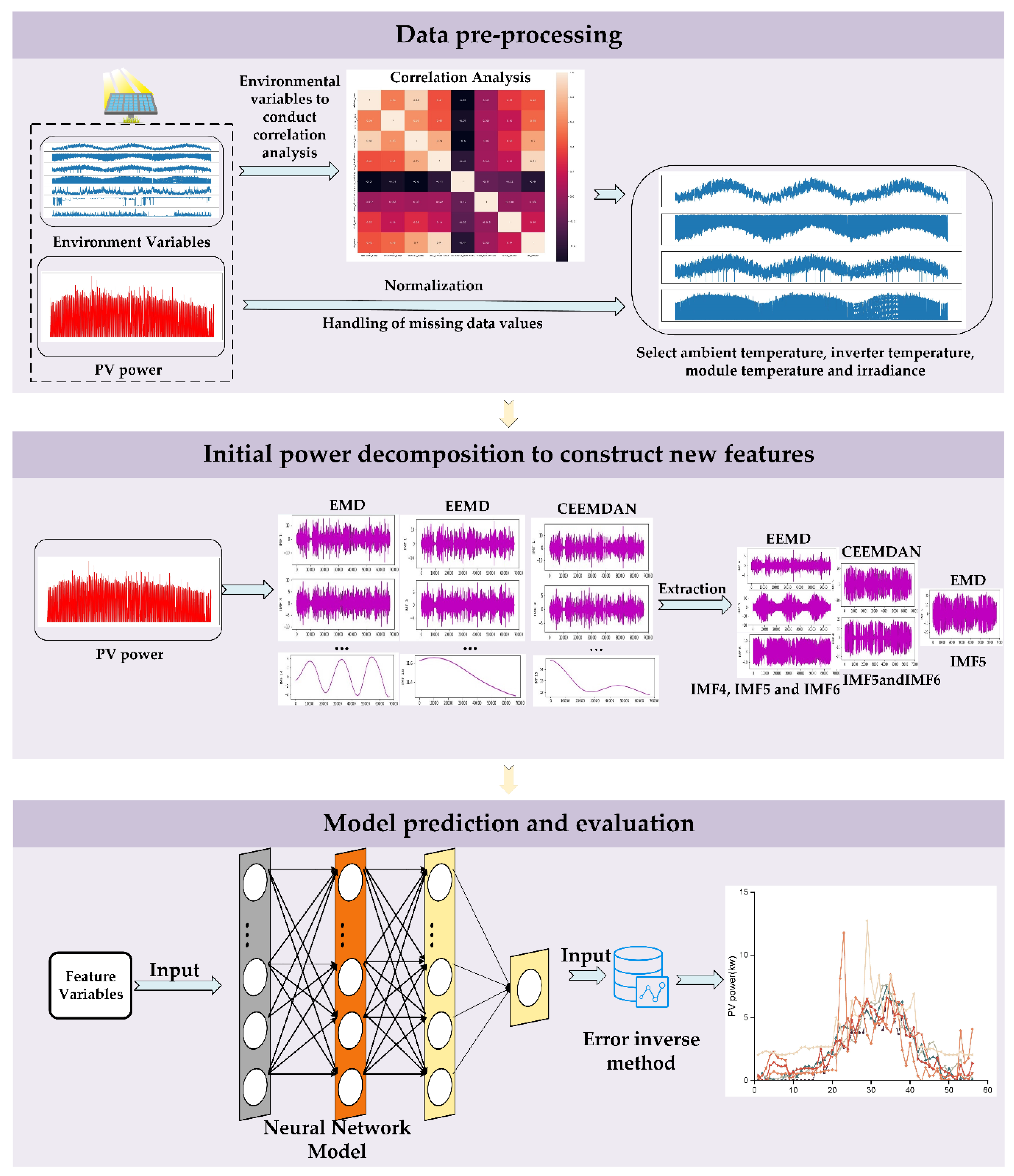
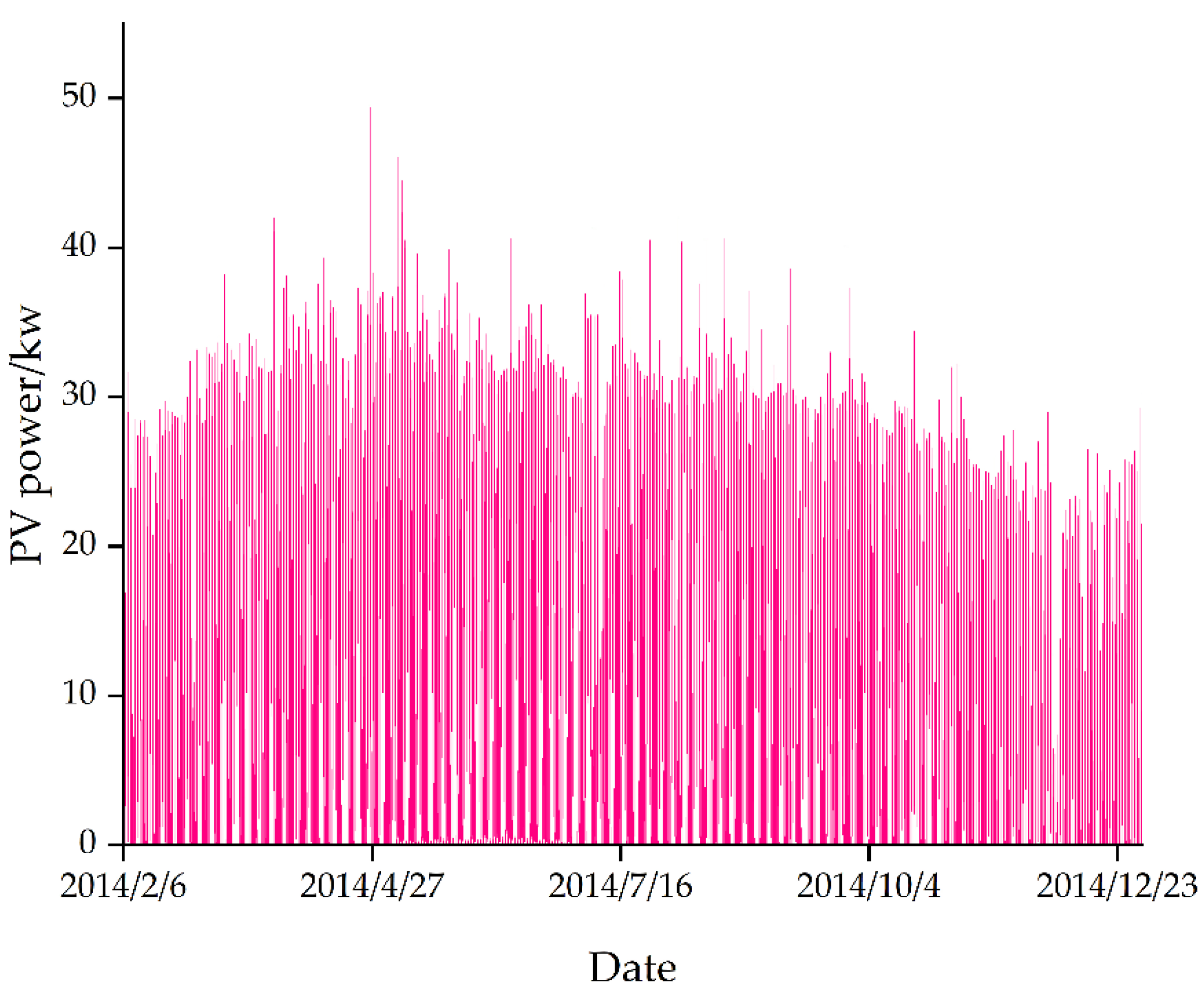
- After pre-processing the data, it only retains the data in the period of 5:00-20:00, analyzes the correlation of environmental features, selects the environmental variables with stronger correlation to be the features of the combined prediction model, and normalizes the features with higher correlation to improve the convergence speed and performance of the model.
- The EMD, EEMD, and CEEMDAN modal decomposition methods were selected to decompose the original PV power modalities, and the respective modal subseries were combined to construct the feature matrix for correlation analysis, and the subseries features with high correlation and environmental variables with strong correlation were selected to join the combined NARX-LSTM-LightGBM prediction model.
- Predictions are made by a combined modal decomposition NARX-LSTM-LightGBM model, and performance is evaluated.
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Model performance evaluation indicators
3.2. Data pre-processing
3.3. PV power characteristics correlation analysis
| Feature variables | Correlation factor | Correlation |
|---|---|---|
| Ambient temperature | 0.42 | Moderate |
| Inverter temperature | 0.50 | Moderate |
| Module temperature | 0.69 | Moderate |
| Irradiance | 0.96 | Strong |
| Relative humidity | -0.40 | Negative |
| Wind speed | 0.20 | weak |
| Wind direction | -0.039 | Negative |
3.4. Combinatorial decomposition to build new features
3.5. Model parameters setting
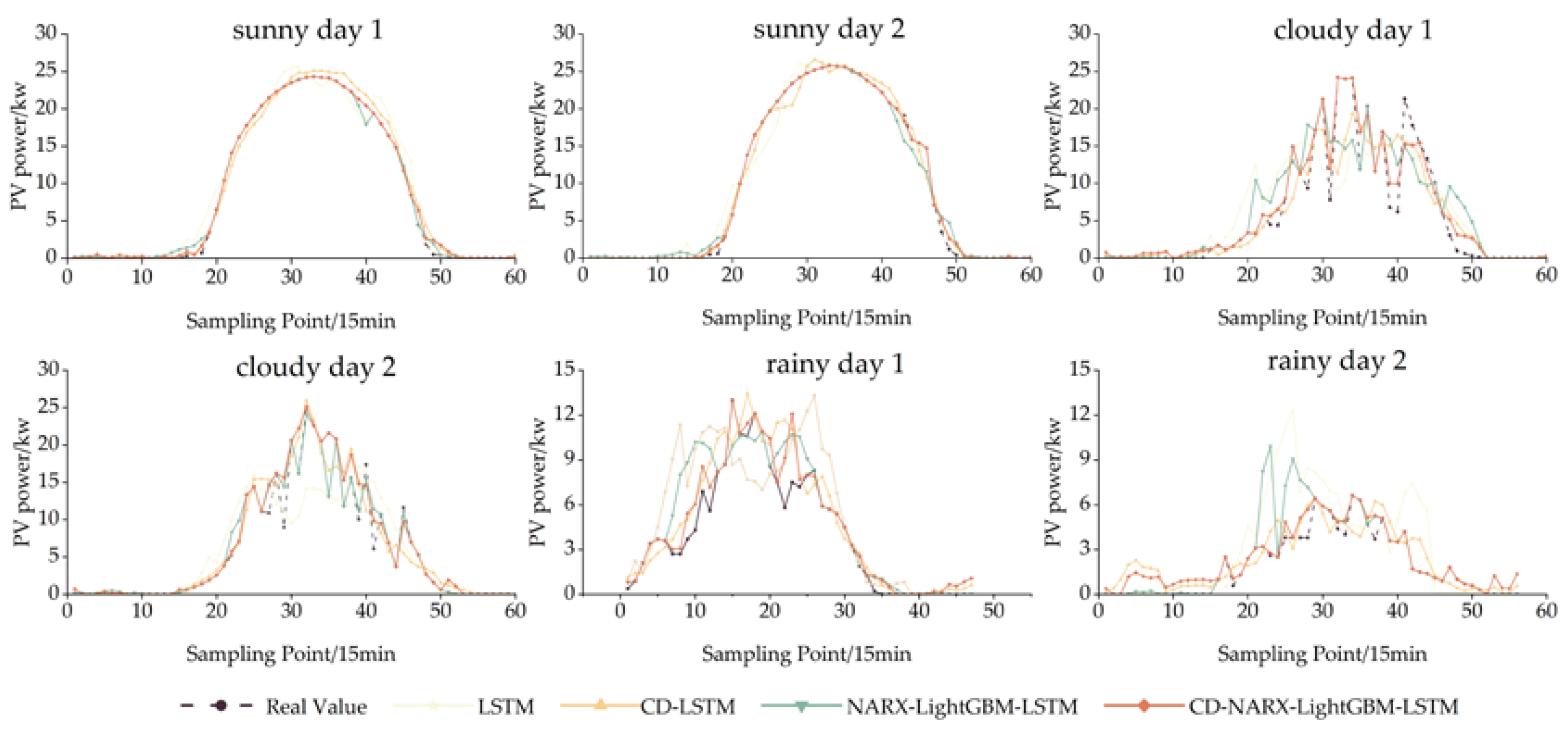
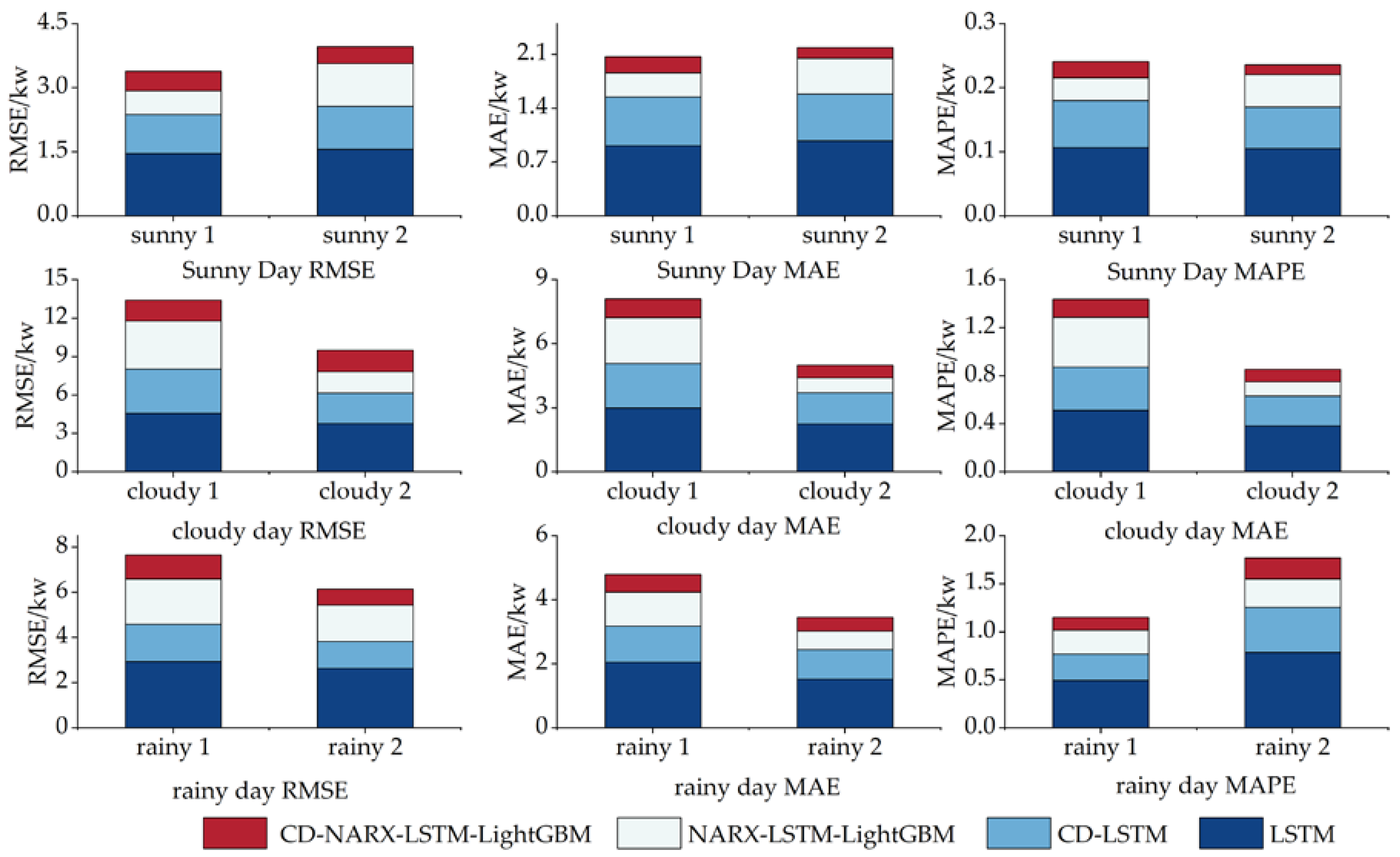
3.6. Validation of combined modal decomposition
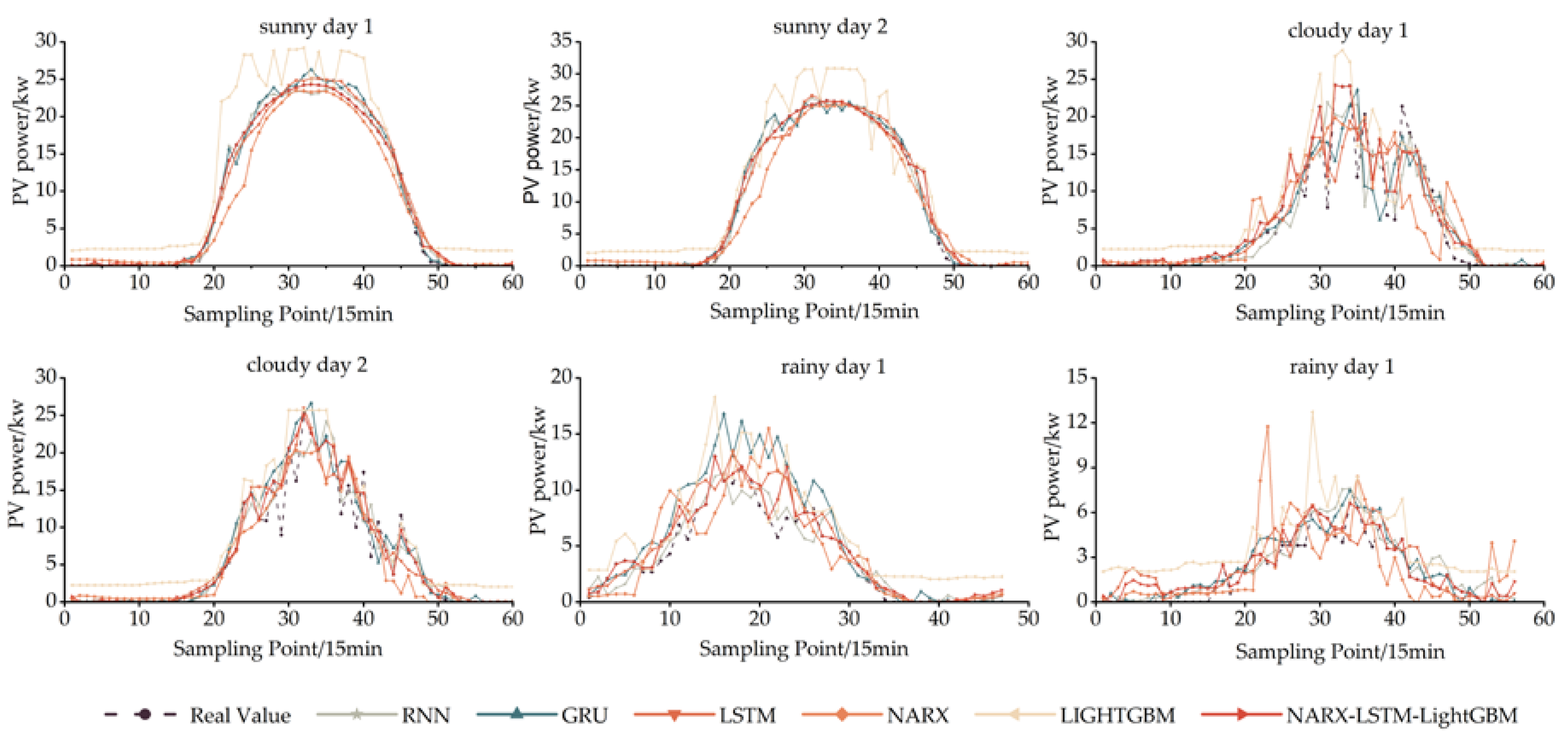
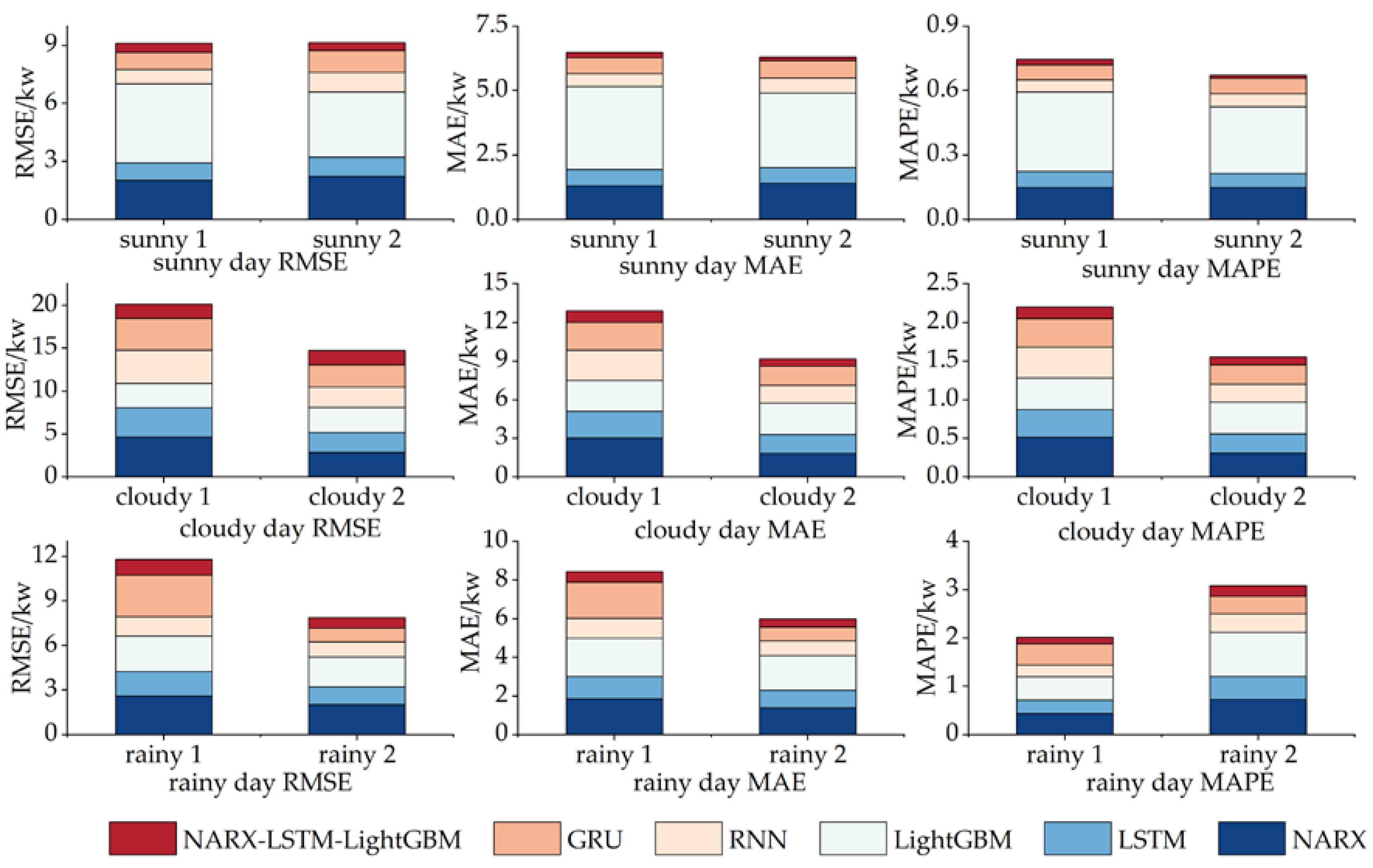
3.7. Validation of NARX-LSTM-LightGBM model
4. Conclusions
- The combination of EMD, EEMD, and CEEMDAN decomposes the original PV power, which can effectively reduce the original curve's nonlinearity and complexity, increase the positive correlation features, and improve the accuracy of PV power prediction.
- NARX, LSTM, and LightGBM models are based on different principles and mathematical models, each with excellent performance in time series data forecasting problems, and the combined NARX-LSTM-LightGBM forecasting model is better able to fully exploit the intrinsic information linkage of historical time series data.
- Compared with other single models, the combined prediction model based on CD- N.M. NARX-LSTM-LightGBM proposed in this paper has obvious advantages for the prediction of PV power, which has better and excellent prediction accuracy in both steady and non-steady weather, and it has the prospect and significance for application in other fields.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, G. K., Solar power generation by PV (photovoltaic) technology: A review - ScienceDirect. Energy 2013, 53, (5), 1-13.
- Zhou, J., Forecasting the Energy and Economic Benefits of Photovoltaic Technology in China's Rural Areas. Sustainability 2021, 13. [CrossRef]
- Kim, S. K.; Jeon, J. H.; Cho, C. H.; Kim, E. S.; Ahn, J. B., Modeling and simulation of a grid-connected PV generation system for electromagnetic transient analysis. Solar Energy 2009, 83, (5), 664-678. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Sun, W.; Zeng, J., A new short-term load forecasting method of power system based on EEMD and SS-PSO. Neural computing & applications 2014, (24-3/4). [CrossRef]
- Mellit, A.; Pavan, A. M.; Lughi, V., Deep learning neural networks for short-term photovoltaic power forecasting. Renewable Energy 2021, (2). [CrossRef]
- Almeida, M. P.; Perpinan, O.; Narvarte, L., PV power forecast using a nonparametric PV model. Solar Energy 2015, 115, 354-368. [CrossRef]
- Holland, N.; Pang, X.; Herzberg, W.; Karalus, S.; Bor, J.; Lorenz, E.; Ieee In Solar and PV forecasting for large PV power plants using numerical weather models, satellite data and ground measurements, IEEE 46th Photovoltaic Specialists Conference (PVSC), Chicago, IL, 2019 Jun 16-21, 2019; Chicago, IL, 2019; pp 1609-1614.
- Belmahdi, B.; Louzazni, M.; El Bouardi, A., A hybrid ARIMA-ANN method to forecast daily global solar radiation in three different cities in Morocco. European Physical Journal Plus 2020, 135, (11). [CrossRef]
- Bacher, P.; Madsen, H.; Nielsen, H. A., Online short-term solar power forecasting. Solar Energy 2009, 83, (10), 1772-1783.
- Kim, S.-G.; Jung, J.-Y.; Sim, M. K., A Two-Step Approach to Solar Power Generation Prediction Based on Weather Data Using Machine Learning. Sustainability 2019, 11, (5). [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Li, G.-Q.; Lin, K.-P.; Zhang, H.-J., Short-Term Wind Power Prediction Based on Improved Chicken Algorithm Optimization Support Vector Machine. Sustainability 2019, 11, (2). [CrossRef]
- Mo, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xian, Z.; Wang, H.; Iop In Photovoltaic (PV) Power Prediction Based on ABC - SVM, 1st International Conference on Environment Prevention and Pollution Control Technology (EPPCT), Tokyo Univ Sci, Tokyo, JAPAN, 2018 Nov 09-11, 2018; Tokyo Univ Sci, Tokyo, JAPAN, 2018.
- Gao, M.; Li, J.; Hong, F.; Long, D., Short-Term Forecasting of Power Production in a Large-Scale Photovoltaic Plant Based on LSTM. Applied Sciences-Basel 2019, 9, (15). [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Li, J.; Hong, F.; Long, D., Day-ahead power forecasting in a large-scale photovoltaic plant based on weather classification using LSTM. Energy 2019, 187. [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Qi, X.; Liu, H., Photovoltaic power forecasting based LSTM-Convolutional Network. Energy 2019, 189. [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Asemota, G. N. O.; Benimana, S.; Nduwamungu, A.; Bimenyimana, S.; Niyonteze, J. D. D.; Ieee In Comparison of Nonlinear Autoregressive Neural Networks Without and With External Inputs for PV Output Power Prediction, IEEE International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Information Systems (ICAIIS), Dalian, PEOPLES R CHINA, 2020 Mar 20-22, 2020; Dalian, PEOPLES R CHINA, 2020; pp 145-149.
- Louzazni, M.; Mosalam, H.; Khouya, A.; Amechnoue, K., A non-linear auto-regressive exogenous method to forecast the photovoltaic power output. Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments 2020, 38. [CrossRef]
- Ming, C.; Jie, S.; Peide, L.; Qing, B., Comparative analysis of three machine learning algorithms in regression application. Intelligent Computer and Applications 2022, 12, (8), 165-170.
- Guo, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y. In Study on the application of LSTM-LightGBM Model in stock rise and fall prediction, 2nd International Conference on Computer Science Communication and Network Security (CSCNS), Sanya, PEOPLES R CHINA, 2021 Dec 22-23, 2020; Sanya, PEOPLES R CHINA, 2020.
- Liang, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, W.; Cao, Y.; Zhong, B.; Chen, Z.; Li, Z.; Acm In Product Marketing Prediction based on XGboost and LightGBM Algorithm, 2nd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Pattern Recognition (AIPR), Beijing, PEOPLES R CHINA, 2019 Aug 16-18, 2019; Beijing, PEOPLES R CHINA, 2019; pp 150-153.
- Zhang, L.; Liu, M.; Qin, X.; Liu, G., Succinylation Site Prediction Based on Protein Sequences Using the IFS-LightGBM (BO) Model. Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine 2020, 2020.
- Wang, H.; Sun, J.; Wang, W., Photovoltaic Power Forecasting Based on EEMD and a Variable-Weight Combination Forecasting Model. Sustainability 2018, 10, (8). [CrossRef]
- Haiwang, T.; Qiliang, Y.; Jiangchun, X.; Kefeng, H.; Shuo2, Z.; Haoyu, H., Pgotovoltaic Power Prediction Based On Combined XGBoost-LSTM Model. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica 2022, 43, (8), 75-81.
- Zheng, Z.-W.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Zhou, X.-W.; Huo, M.-M.; Zhao, B.; Guo, M.-Y. In Short-term prediction model for a Grid-Connected Photovoltaic System using EMD and GABPNN, International Conference on Sustainable Energy and Environmental Engineering (ICSEEE 2012), Guangzhou, PEOPLES R CHINA, 2013 Dec 29-30, 2012; Guangzhou, PEOPLES R CHINA, 2012; pp 74-+. [CrossRef]
- Yue, Z.; Jie, G.; Lu, M., Photovoltaic power generation prediction model based on EMD-LSTM. Electric Power Engineering Technology 2020, 39, (02), 51-58.
- Zhongshan, L.; Jianhua, Y., Ultra-short term power prediction of photovoltaic power generation system based on EEMD-LSTM method China Measurement & Test 2022, 48, (12), 125-132.
- Wang, S.; Liu, S.; Guan, X., Ultra-Short-Term Power Prediction of a Photovoltaic Power Station Based on the VMD-CEEMDAN-LSTM Model. Frontiers in Energy Research 2022, 10. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Ren, Q.; Liu, G.; Guo, L.; Li, J., Short-term PV Output Power Forecasting Based on CEEMDAN-AE-GRU. Journal of Electrical Engineering & Technology 2022, 17, (2), 1183-1194. [CrossRef]
- Lilong, H.; Chao, Z.; Ping, Y.; Iop In Research on Power Load Forecast Based on Ceemdan Optimization Algorithm, 3rd International Conference on Computer Information Science and Application Technology (CISAT), Electr Network, 2020 Jul 17, 2020; Electr Network, 2020.
- Guihong, B.; Xin, Z.; Chenpeng, C.; Shilong, C.; Lu, L.; Xu, X.; Zhao, L., Ultra-short-term Prediction of Photovoltaic Power Generation Based on Multi-channel Input and PCNN-BiLSTM. Power System Technology 2022, 46, (9), 3463-3476.
- Massaoudi, M.; Chihi, I.; Sidhom, L.; Trabelsi, M.; Refaat, S. S.; Abu-Rub, H.; Oueslati, F. S., An Effective Hybrid NARX-LSTM Model for Point and Interval PV Power Forecasting. Ieee Access 2021, 9, 36571-36588. [CrossRef]
- Akhter, M. N.; Mekhilef, S.; Mokhlis, H.; Almohaimeed, Z. M.; Muhammad, M. A.; Khairuddin, A. S. M.; Akram, R.; Hussain, M. M., An Hour-Ahead PV Power Forecasting Method Based on an RNN-LSTM Model for Three Different PV Plants. Energies 2022, 15, (6). [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M. S.; Mahmood, H.; Ieee In Short-Term Photovoltaic Power Forecasting Using an LSTM Neural Network, IEEE-Power-and-Energy-Society Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Conference (ISGT), Washington, DC, 2020 Feb 17-20, 2020; Washington, DC, 2020.
- Ke, G.; Meng, Q.; Finley, T.; Wang, T.; Chen, W.; Ma, W.; Ye, Q.; Liu, T.-Y. In LightGBM: A Highly Efficient Gradient Boosting Decision Tree, 31st Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), Long Beach, CA, 2017 Dec 04-09, 2017; Long Beach, CA, 2017.
- Bentejac, C.; Csorgo, A.; Martinez-Munoz, G., A comparative analysis of gradient boosting algorithms. Artificial Intelligence Review 2021, 54, (3), 1937-1967. [CrossRef]
- Anbo, M.; Xuancong, X.; Jiaming, C.; Chenen, W.; Tianmin, Z.; Hao, Y., Ultra Short Term Photovoltaic Power Prediction Based on Reinforcement Learning and Combined Deep Learning Model. Power System Technology 2021, 45, (12), 4721-4728.
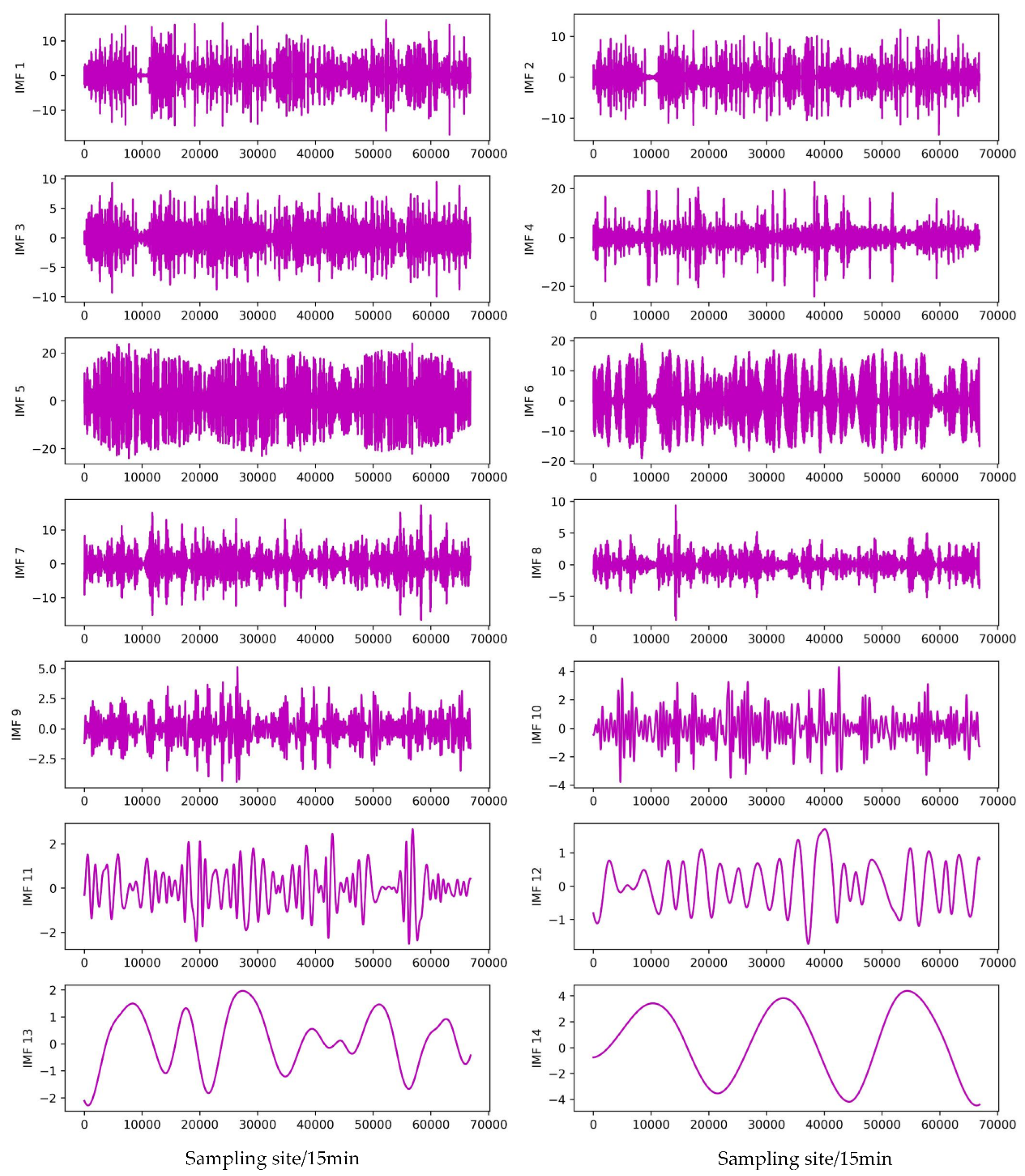
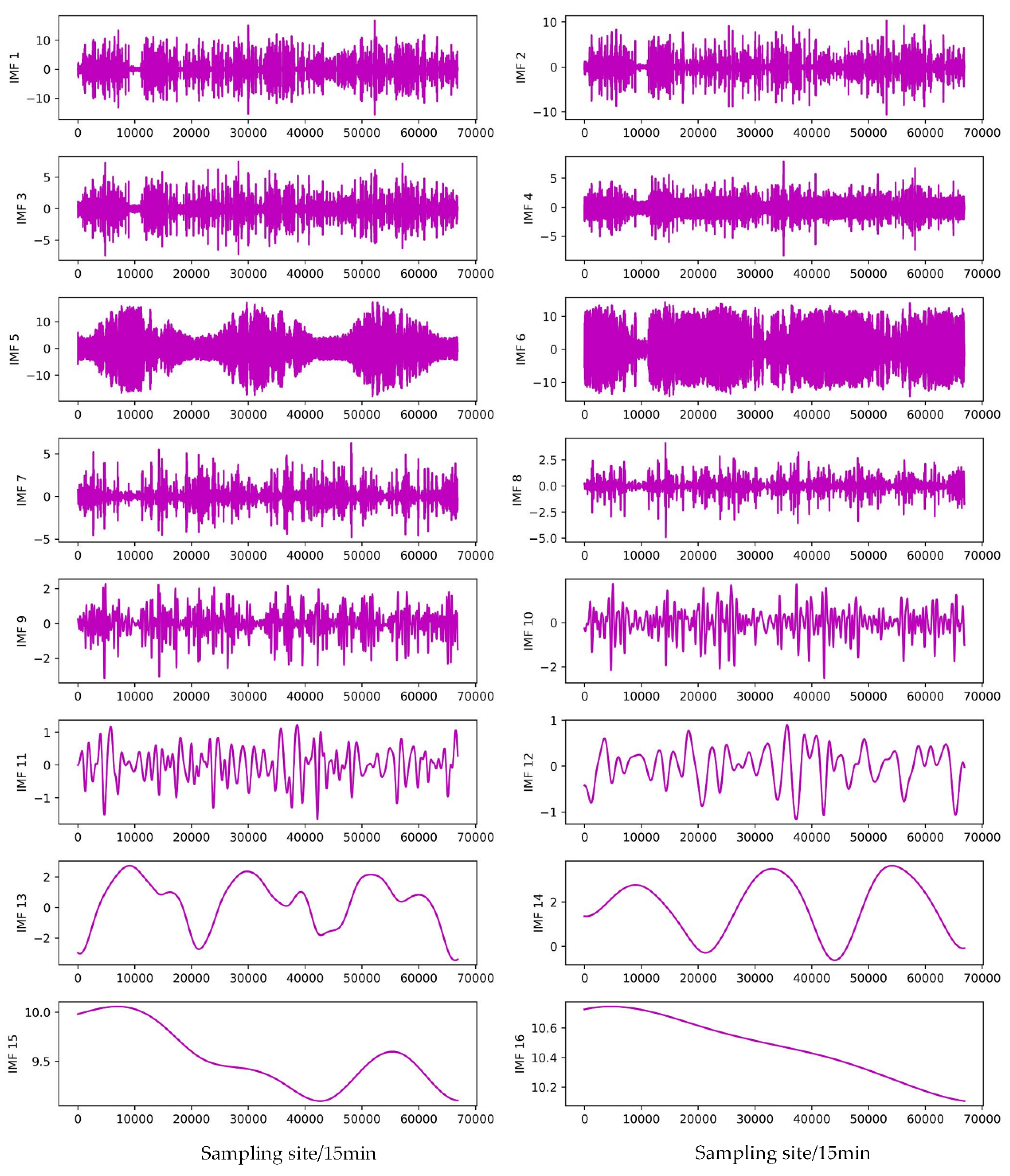
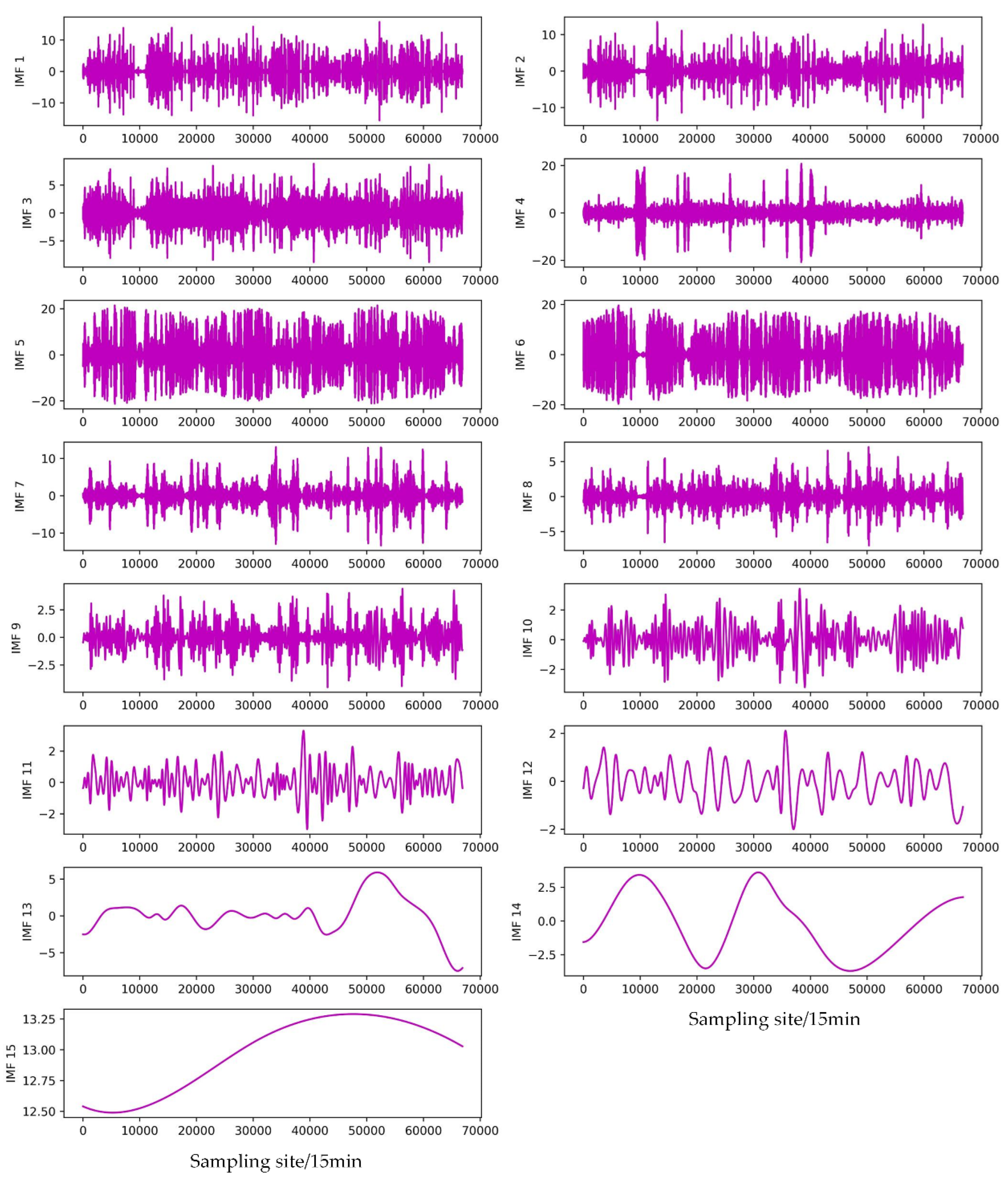
| Subsequence | EMD | EEMD | CEEMDAN |
|---|---|---|---|
| IMF1 | 0.073 | 0.13 | 0.078 |
| IMF2 | 0.069 | 0.13 | 0.073 |
| IMF3 | 0.083 | 0.14 | 0.066 |
| IMF4 IMF5 IMF6 |
0.34 0.8 0.31 |
0.61 0.92 0.47 |
0.31 0.68 0.57 |
| IMF7 | 0.15 | 0.33 | 0.15 |
| IMF8 | 0.062 | 0.12 | 0.072 |
| IMF9 IMF10 IMF11 IMF12 IMF13 IMF14 IMF15 IMF16 |
0.062 0.075 0.046 0.027 0.12 0.27 None None |
0.11 0.096 0.074 0.084 0.26 0.26 0.085 0.037 |
0.071 0.064 0.034 0.038 0.18 0.26 0.046 None |
| Test Day | Predictive Model | RMSE | MAE | MAPE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sunny day 1 | LSTM | 1.462 | 0.912 | 0.106 |
| CD-LSTM | 0.913 | 0.636 | 0.074 | |
| NARX-LSTM-LightGBM | 0.549 | 0.312 | 0.036 | |
| CD-NARX-LSTM-LightGBM | 0.465 | 0.213 | 0.025 | |
| sunny day 2 | LSTM | 1.560 | 0.977 | 0.105 |
| CD-LSTM | 1.006 | 0.605 | 0.065 | |
| NARX-LSTM-LightGBM | 1.003 | 0.471 | 0.051 | |
| CD-NARX-LSTM-LightGBM | 0.399 | 0.136 | 0.015 | |
| cloudy day 1 | LSTM | 4.571 | 2.981 | 0.513 |
| CD-LSTM | 3.443 | 2.092 | 0.360 | |
| NARX-LSTM-LightGBM | 3.764 | 2.147 | 0.414 | |
| CD-NARX-LSTM-LightGBM | 1.645 | 0.892 | 0.153 | |
| cloudy day 2 | LSTM | 3.775 | 2.242 | 0.383 |
| CD-LSTM | 2.375 | 1.467 | 0.250 | |
| NARX-LSTM-LightGBM | 1.675 | 0.698 | 0.119 | |
| CD-NARX-LSTM-LightGBM | 1.664 | 0.589 | 0.101 | |
| rainy day 1 | LSTM | 2.938 | 2.048 | 0.493 |
| CD-LSTM | 1.654 | 1.136 | 0.273 | |
| NARX-LSTM-LightGBM | 1.988 | 1.052 | 0.253 | |
| CD-NARX-LSTM-LightGBM | 1.071 | 0.553 | 0.133 | |
| rainy day 2 | LSTM | 2.636 | 1.527 | 0.783 |
| CD-LSTM | 1.183 | 0.918 | 0.471 | |
| NARX-LSTM-LightGBM | 1.628 | 0.578 | 0.296 | |
| CD-NARX-LSTM-LightGBM | 0.697 | 0.431 | 0.221 |
| Test Day | CD-Prediction Models | RMSE | MAE | MAPE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sunny 1 | NARX | 2.011 | 1.298 | 0.149 |
| LSTM | 0.913 | 0.636 | 0.074 | |
| LightGBM | 4.095 | 3.233 | 0.371 | |
| RNN | 0.735 | 0.491 | 0.056 | |
| GRU | 0.897 | 0.616 | 0.070 | |
| NARX-LSTM-LightGBM | 0.465 | 0.213 | 0.025 | |
| Sunny 2 | NARX | 2.223 | 1.405 | 0.149 |
| LSTM | 1.006 | 0.605 | 0.065 | |
| LightGBM | 3.364 | 2.902 | 0.310 | |
| RNN | 1.008 | 0.581 | 0.061 | |
| GRU | 1.148 | 0.679 | 0.072 | |
| NARX-LSTM-LightGBM | 0.399 | 0.136 | 0.015 |
| Test Day | CD-Prediction Models | RMSE | MAE | MAPE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NARX | 4.655 | 3.032 | 0.516 | |
| LSTM | 3.443 | 2.092 | 0.360 | |
| Cloudy 1 | LightGBM | 2.773 | 2.363 | 0.406 |
| RNN | 3.922 | 2.366 | 0.400 | |
| GRU | 3.690 | 2.155 | 0.365 | |
| NARX-LSTM-LightGBM | 1.645 | 0.892 | 0.153 | |
| NARX | 2.842 | 1.843 | 0.310 | |
| LSTM | 2.375 | 1.467 | 0.250 | |
| Cloudy 2 | LightGBM | 2.908 | 2.417 | 0.411 |
| RNN | 2.333 | 1.387 | 0.233 | |
| GRU | 2.620 | 1.487 | 0.250 | |
| NARX-LSTM-LightGBM | 1.664 | 0.589 | 0.101 |
| Test Day | CD-Prediction Models | RMSE | MAE | MAPE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rainy 1 | NARX | 2.585 | 1.862 | 0.442 |
| LSTM | 1.654 | 1.136 | 0.273 | |
| LightGBM | 2.390 | 1.992 | 0.481 | |
| RNN | 1.313 | 1.032 | 0.246 | |
| GRU | 2.776 | 1.868 | 0.440 | |
| NARX-LSTM-LightGBM | 1.071 | 0.553 | 0.133 | |
| Rainy 2 | NARX | 2.026 | 1.387 | 0.734 |
| LSTM | 1.183 | 0.918 | 0.471 | |
| LightGBM | 2.041 | 1.786 | 0.916 | |
| RNN | 1.004 | 0.756 | 0.382 | |
| GRU | 0.920 | 0.721 | 0.363 | |
| NARX-LSTM-LightGBM | 0.697 | 0.431 | 0.221 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





