I. Introduction
Several countries in sub-Sahara Africa rely on renewable energy to meet their growing electricity needs in a sustainable, cost-effective, and environmentally-friendly manner. The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) is located in a very high ‘sun belt’ with insolation values between 3.6 and 4.8kWh/m2/day[
1,
2], making the construction of photovoltaic systems and the usage of thermal solar systems economically viable. Diesel fuel for diesel generators is the key component of the power plant, accounting for roughly 80 % of the overall energy expenses in off-grid and bad-grid regions areas [
3]. Diesel generator operators and owners must therefore assess design configuration, operation and maintenance, energy efficiency, greenhouse gas emissions, and equipment lifespan [
4]. In addition to assisting in the fight against climate change (particularly through the reduction of greenhouse gases emissions from electricity and heat generation), PV power is also poised to play a pivotal role in the imminent transition from a centralised to distributed generation scheme. In fact, thanks to the easily scalable small modular units on which PV power relies, microgrid implementation is now seen as viable and, in some cases, the best available solution. This is because PV power is able to improve energy system reliability, decrease CO2 emissions and electricity generation costs, generate new employment opportunities and re-evaluate local resources that are undervalued in rural areas [
5,
6].
Diesel power plants, also known as engine-generators, are a more practical option for providing electricity to rural areas[
7]. However, a low load factor (below 40-50% of the generator's rated capacity) is inefficient for diesel generators and can reduce the generator's lifespan and increase maintenance expenses. Furthermore, incomplete combustion and carbon deposits on the cylinder walls induce premature engine wear due to low combustion temperatures during periods of operation with light loads [
9,
10,
11]. Thus, a hybrid diesel-PV power system (integration of a PV plant with a diesel generator as a back-up system for reducing the PV component sizes) supplies generally intermittent power from the PV plant to decrease the operating time of the generator and reduce its fuel consumption, operation and maintenance costs, and replacement costs. The generator only runs during periods when a minimum load is exceeded [
10,
11].
To confirm the widespread applicability of converting a pure diesel generator in Lubumbashi (the capital of Haut Katanga) of Congo Region into such a hybrid system, we analysed the effects of incorporating a photovoltaic (PV) battery and a diesel generator, and then simulated the system's performance. The data was analyzed to: (1) show that a hybrid diesel-PV power system will be the most efficient way for grid operators and diesel generator owners to reduce the emissions, and (2) estimate how much carbon emissions can be cut by incorporating solar PV into the power distribution network. Advocating for a hybrid PV/battery/diesel power system will aid sustainable and economic growth of the Congo Region.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Overview of carbon emissions and renewable energy in developing countries
Due to their fast-growing economies and populations, developing countries have become increasingly responsible for a rising proportion of global carbon emissions in recent years. The renewable energy sector in these nations, particularly solar, wind, and hydro power, has enormous untapped potential, though. Setting renewable energy targets, giving financial incentives for the development of renewable energy, and establishing carbon pricing mechanisms are just a few of the policies that many developing countries are enacting to stimulate the adoption of renewable energy and reduce carbon emissions. To further aid developing countries in making the switch to renewable energy sources and cutting their carbon emissions, international organizations and developed nations have been offering financial and technical assistance.
An integrated method for optimizing the economic dispatch and commitment (EDC) problems of hybrid thermosolar concentrating power generating systems was reported by Papazis et al. (2022) utilizing matrix mathematics and matlab programming in northwest Greece. After analyzing data from seven different thermal units, found that carbon dioxide emissions were reduced when the units were not run at full capacity. However, fuel usage and, eventually, fuel cost impacted the operation cost to generate adequate energy via concentrated solar power (CSP) into the power generation system. Thus, the benefits of producing greener energy with a smaller carbon footprint still have to contend with the issue of operating at the lowest possible cost. New energy generation technologies, such as zero-carbon power plants that reduce carbon dioxide emissions and the effects of global warming, are being developed as part of the transition to sustainable energy systems [
19,
21].
Iñigo-Labairu et al. (2022) simulated various hybrid power generation configurations on seven different sites by modifying their design parameters within specific boundary conditions to find the optimal configurations for both optimized systems and operation cost of using renewable energy sources (RES) coupled with conventional power generation systems. He concluded that PV-CSP hybrid power plants were the most efficient and cost the least to run compared to alternative configurations like standalone CSP plants and PV-battery energy system storage (BESS). Additionally, their approach utilized a techno-economic analysis with the levelized cost of electricity (LCOE) and the percentage of electricity during the night as independent variables. By projecting each configuration into the future in the year 2030, Iñigo-Labairu et al. (2022) were able to examine the impact of the system costs. The analysis concludes that hybrid power plants are more cost-effective than pure CSP plant layouts, mostly as a result of the decreased cost of PV power. Hybrid PV-CSP power plants have exhibit lower LCOE than PV-BESS for nighttime power fractions over 20-25% (corresponding to roughly 4-5h storage capacity).
Basheer et al. (2022) conducted a probability analysis of integrating hybrid energy into Pakistan's cement industry to cut down on GHG emissions from the sector's present reliance on thermal power while keeping cement production plants' overhead costs low. HOMER Pro was used for the analysis of hybrid energy models (HEMs). They collected primary data for analysis of five cement plants from four different types of HEMs: 1) a photovoltaic (PV), hydrogen tank, converter, electrolyzer, and fuel cell; 2) a single diesel generator; 3) a PV-converter-battery framework; and 4) a diesel generator, PV-converter. A 0% GHG was only possible with a PV, hydrogen tank, converter hybrid system or a diesel-PV-converter hybrid system. In the event of a power loss, however, the purchase of a single diesel generator remains the most cost-effective solution in terms of both installation and ongoing maintenance.
In off-grid isolated places and many underdeveloped countries, regular blackouts mean that diesel generators remain the most popular choice for emergency electricity backup. Burning hydrocarbons releases numerous pollutants into the air, some of which are harmful to humans and others of which have a significant impact on the ecosystem [
24]. Switching to greener forms of energy could end the global warming crisis. Making the switch to renewable energy sources may be a significant step in lowering atmospheric CO
2 concentrations[
25]. Integration of various energy sources into the power generating and distribution network is necessary to facilitate the growth and development of HESs [
26,
27,
28,
29]. Hybrid arrangements offer a number of advantages, including lower operating costs, lower carbon dioxide emissions, and a longer service life for Diesel generators (DG). The fuel consumption of the diesel generator can be cut by as much as 90% when a solar hybrid system is used. Power plant running and maintenance costs can be reduced by 90% as well. Reduced fossil fuel consumption also resulted in a 30–75% reduction in carbon footprint [
27,
28,
29,
30,
31,
32,
33]. In the case of conventional energy sources, power outages have decreased by 50% [
31,
34]. Reduced usage means longer intervals between diesel generator replacement [
35].
2.2. Potential benefits and challenges of implementing a hybrid diesel-PV power system in Lubumbashi, DR Congo
Some of the potential gains from installing a hybrid diesel-PV power system in Lubumbashi, DR Congo, are as follows: Hybrid systems offer greater energy security since they require less reliance on any one power source, such as diesel generators, which are susceptible to variations in fuel prices and supply. The adoption of a hybrid system may boost the availability of electricity in rural or distant places when connecting to the grid is not an option. Benefiting from steadily falling prices, PV systems are now cheaper to install and operate than conventional power plants. Over time, hybrid systems may also save money on gas. Greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution are reduced when PV systems are used, which is good for the environment and human health.
However, there may be obstacles to introducing a hybrid diesel-PV power system in Lubumbashi, DR Congo. Exorbitant outlay of capital in the outset: The initial outlay of cash needed to get a hybrid system up and running might be substantial. The system necessitates routine upkeep and repairs, which can be challenging to do due to a lack of technical experience and infrastructure in some regions. PV system output can be diminished by environmental factors like clouds and storms, making them less reliable. Storage capacity is limited in PV systems, which can reduce system dependability, especially during times of low sunlight. Optimal performance from a hybrid system demands thorough planning and design due to the complexity of system integration. Overall, a hybrid diesel-PV power system in Lubumbashi, DR Congo could provide a cost-effective and reliable option for improving access to energy in the region, but there are a number of considerations that need to be made before it is implemented.
3. Methodology
The HOMER Pro programme was used to assessed the best strategies for implementing renewable energy in the Lubumbashi area of the Democratic Republic of Congo. System emissions, necessary capital, payback duration, net present cost, and current value for each scenario were obtained by simulation, which are broken down into three stages: specifying input data, simulating each scenario, and analyzing outputs.
3.1. The Homer Pro software
The viability of renewable energy systems in terms of their technical, economic, and environmental aspects can be simulated using different tools [
36,
37,
38,
39,
40]. The hybrid optimization model electric renewable software (HOMER) has become increasingly popular among researchers in recent years as a tool for simulating different kinds of microgrids . To model and optimize the design of hybrid renewable energy systems, the HOMER Pro was employed in this study. The tool assists engineers, researchers, and energy experts in determining the ideal configurations for a given set of restrictions, as well as evaluating the technical and economic feasibility of various hybrid power systems[
41,
42,
43]. Multiple renewable energy sources (such as solar, wind, and hydro) can be modeled in a single HOMER Pro simulation, as can conventional generators, batteries, and other energy storage devices. Systems with load management and other energy-saving components can be modeled as well. System sizing, cost and financial analysis, sensitivity analysis, and system optimization are just few of the analyses that can be run with this software. We summarized the current study using the HOMER Pro to analyze multiple microgrid configurations in
Table 2 below.
Table 1.
Review of recent studies on microgrids configuration using HOMER Pro.
Table 1.
Review of recent studies on microgrids configuration using HOMER Pro.
| Configuration |
Investment Analysis |
References |
• Diesel generator with battery (DG + b)
• Fixed PV module with battery (FPV + b)
• Dual-Axis PV module tracker system with battery (DPV + b)
• Fixed PV module and wind turbine with battery (FPV + WT + b)
• Dual-Axis PV module tracker and wind turbine with battery (DPV + WT + b)
• 2 KW Pico-hydropower with battery (HP + b) |
The optimal layouts with the lowest net present cost (NPC) and cost of energy (COE) are (FPV + b) followed by HP + b. The NPC and COE costs of FPV + b and HP + b is 17.45%, 16.45%, 15.9%, and 15.5% lower than those of diesel generators with battery (DG + b), respectively. |
[44] |
• PV system only
• Wind turbine only
• A hybrid system of PV and wind turbine |
The PV technology achieved the best option as it has the lowest initial cost per kW, 1150 USD/kW, LCOE of 0.051 USD/kWh, and a simple payback period of 18.6 years. |
[45] |
•100% solar PV–battery system
•100% solar PV–P2H2P system
• 100% solar PV and hybrid battery-P2H2P system. |
The most cost-effective scenario is a hydrogen-battery hybrid energy storage system. It revealed that it has the lowest NPC and COE over the 25-year project lifespan. In comparison to a battery-based storage system, it uses less excess energy. |
[46] |
• Diesel-only
• Hybrid diesel/PV without battery
• Hybrid PV/diesel with battery system. |
The design of PV/diesel with a battery system is the recommended solution. The system’s initial capital cost and total NPC are USD 2,260,000 and USD 16,661,344, respectively. The COE of the system is USD 0.377/kWh. The design can save 14.3% of diesel fuel consumption, and a carbon footprint can be saved. The most expensive design in electricity generation is diesel-only, while the second most expensive is hybrid diesel-PV without a battery system. |
[47] |
• Hybrid PV/diesel with battery system.
• Hybrid diesel/PV without battery
• PV/battery system
• Diesel/battery System
|
PV/diesel with a battery system configuration is the ideal recommended hybrid System. The system’s initial capital cost and total NPC are USD 8336.13 and 5,794.18, respectively. With levelized COE of 0.1090$/KWh. Under the given local climate condition, the diesel generator can remain unused throughout the whole year (0% of fuel consumption). This hybrid system can emit lower to no emissions all year round compared to other configurations. |
Current study |
Different configurations of microgrids can be simulated, compared, and evaluated with HOMER. In this study, HOMER pro software was used to model a hybrid off-grid energy system and compare it to a diesel generator-only system under varying load conditions. When planning the system layout, it is important to factor in a number of different parameters. As part of its simulation, HOMER evaluates the hybrid system ability to meet the hybrid electric and thermal needs. By calculating the energy entering and leaving each part of the hybrid system, the system can ascertain whether or not a given setup is practical. The hybrid system electric and thermal demands are compared using modelling outputs from HOMER. Whether or not a proposed configuration is workable is determined by calculating the energy input and output of each part of the hybrid system.
The diesel generator, solar photovoltaics (PV), batteries, and converter were all a part of this study. This hybrid system was utilized to support the electricity demand in the specified area and to perform a study of the solar potential in developing countries in order to mitigate CO2 emissions based on the chosen location in the DR Congo. The economic feasibility of a system, including its operating hours, lifetime, and component attributes, as well as the system annual carbon print, were all taken into account by HOMER. The total net present cost (NPC) of the system, factoring in the annual real interest rate, is a representation of the system overall life-cycle expenses. Considering the linear depreciation factor used by HOMER, the salvage value is proportionate to the amount of time left before the asset is considered completely useless. When designing a system, it is important to consider how variables like component pricing and availability may affect the final product.
3.2. Input data and assumptions used in the analyses
By feeding the GPS coordinates into HOMER, we can model the solar resources using the surface meteorology and solar energy database. The average radiation followed a consistent pattern, and the annual radiation was greater than 4 kWh/m2/day [
48], so that the solar panels can reliably deliver electricity. In calculating the annual radiation readings, the peak month was found to be July in Lubumbashi.
3.3. Simulation of each scenario
The data is then imported into the HOMER programme, where it is simulated using a number of equations. With the help of the latitude, radiation value, and month of the year, HOMER can determine the clearness index, which is specified by equation (1). Atmospheric solar radiation at Earth's surface is given by the equation in HOMER as a solar radiation metre (2). After that, the HOMER Pro was used to determine the NPC using equation (3). As shown in equation (4) [
49,
50,
51], the CRF is a measure of how much of an investment is returned. Salvage value, payback duration, and present value were calculated for each system with the help of the HOMER software using equations (5), (6) and (7). The annual cost of the system components is calculated by HOMER by factoring in a number of different costs (including initial purchase price, cost per mile driven, cost per gallon of fuel, cost to scrap the system).
= The Earth’s monthly average radiation on its horizontal surface
= Extraterrestrial horizontal radiation – radiation on a horizontal surface at the top of the Earth’s atmosphere.
We used the equation below to calculate the intensity of solar radiation at the top of the earth's atmosphere with HOMER:
Where:
G_sc = Solar Constant [1.367 kw/m2]
n = The day of the year [a number between 1 and 365]
3.4. Further Analysis of the Outputs
In order to recommend the best system for the hybrid renewable energy system in the Lubumbashi region of the DR Congo, we ran simulations for each scenario and examined the payback period, components cost, current worth, and net present cost based on each configuration.
Where:
C_(ann,tot)=The total annual cost
i =The annual real interest rate (discount rate)
R_proj =The Project’s lifetime
CRF =The capital recovery factor
Where is the annual real interest rate and is the estimated number of years.
Using HOMER, we calculated the value of each component at the end of the project lifetime (salvage value (S)). HOMER uses the following equation to determine the salvage value [
50,
52].
Where: S = The salvage value; Crep = The cost of component replacement; Rrem = The Remaining life of the component; Rcomp = The overall lifetime of the component
3.5. Levelized Cost of Energy
The levelized cost of energy (LCOE), takes into account not only the estimated total expenses of operating a power plant but also its capital expenditures, costs of servicing, and return on investment. It also takes into consideration the expenses of operation and maintenance, the cost of fuel, as well as costs associated with CO
2 and other forms of emissions.
Where: E_t = The annual energy generation; F_t = Yearly fuel cost; I_t = Yearly investment; M_t = Yearly operation and maintenance cost; r = Discount rate
Homer's optimization depends on the generator being run 24/7/365, which is not always the case for private owners or grid operators. When optimizing, the majority of hybrid systems rotate between their various energy sources, with the renewable energy system taking precedence and the generator being the last configuration option [
48,
52].
DRC's chosen area is situated in the southern section of the country. Energy needs, solar radiation, and fuel costs were all taken into account while deciding on the hybrid diesel-PV-battery system. The results were analyzed based on four factors: 1. Investment, 2. Resource availability, 3. Location, and 4. Emissions.
3.6. Emissions
There are six main pollutants that were estimated within HOMER: carbon dioxide (CO2), carbon monoxide (CO), unburned hydrocarbons (UHC), particulate matter (PM), sulfur dioxide (SO2), and nitrogen oxides (NOX).
3.7. Modeling and simulating the hybrid diesel-PV power system
The components that make up the hybrid system are the diesel generator, PV array that houses the load, solar modules, converter, and batteries that are used for energy storage. The power that is produced by the diesel generator is delivered to the AC bus, where it is transformed into DC power before being distributed to the DC bus. The fuel cell and solar PV that together make up the DC power source are directly connected to the DC. The batteries are used to store the excess electricity during the day so that it can be utilized as the primary source of power throughout the night.
Figure 5 displays the HOMER Pro graphical representation of the system block diagram as it appears in the simulation.
Table 2.
Scenarios and Configurations.
Table 2.
Scenarios and Configurations.
| Scenario |
System configuration |
Limitations |
| PV provides the required energy to the power system and stores excess energy in the battery for night and low radiation use. The generator starts only in the start of complete discharge of the battery and absolutely no solar radiation resource |
|
Within HOMER Pro system, this type of scenario for the selected location of DR Congo has the diesel generator out of work due to the vast available solar radiation on daily basis and in all seasons. |
| Diesel generator only. In this scenario, power is fully provided from the diesel generator, which is used to make the comparison with the first scenario |
|
HOMER assumes that the diesel generator is on 24/7 throughout the whole year. This configuration gives a perspective that all diesel Gen owners emit the same amount of CO2 daily and simultaneously. |
3.8. Input parameters
The modelling procedure in HOMER primarily makes use of three input factors, which are the equipment cost, load needs, and power cost. These parameters are mutable in that they change depending on the locations and kinds of configurations. Due to the fact that the simulation is conducted in the same location and under the same conditions as the real-world scenario, costs associated with both of the available configurations have been standardized in this instance.
Table 4 provides a rundown of the prices associated with each of the individual components.
Table 3.
Summary of input cost for simulation results.
Table 3.
Summary of input cost for simulation results.
| System component |
Capacity (Kw/unit) |
Capital cost, USD |
Replacement cost (USD) |
Maintenance cost (hr/yr) |
| Diesel |
10 |
1000 |
400 |
20 |
| Battery |
1 |
81.80 |
81.80 |
0 |
| Solar PV |
0.3 |
82.75 |
30 |
5 |
| Converter |
3 |
439 |
300 |
0 |
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Technical performance of the hybrid diesel-PV power system
In conducting system comparisons, we utilized multiple indices, such as LCOE, energy production, solar PV system's energy contribution, solar PV adoption, fuel usage, fuel savings percentage, and carbon emissions. Our simulation results are shown below.
Table 4 illustrates the levelised cost of energy (LCOE) for the two different configurations based on the defined load of 11.27 kWh/d (2.39kW peak). From the table, the solar PV Battery systems are cost competitive for 2.39kW load on a lifetime basis. The LCOE for the 2.39 kW load is USD 0.08857/kWh comparing to USD 0.1090/kWh for diesel Hybrid PV and Battery System.
Table 4.
Levelised COE ($/Kwh) for Diesel-PV-Battery and PV Battery Systems.
Table 4.
Levelised COE ($/Kwh) for Diesel-PV-Battery and PV Battery Systems.
| Configuration |
LCOE |
Load |
| Diesel- PV- Battery |
$0.1090 |
11.27 kWh/d |
| PV-Battery |
0.8857 |
11.27 kWh/d |
However, operating a Solar PV battery systems alone have significant capital costs and, without affordable financing, meanwhile diesel generators require lower initial capital cost and are more accessible to the citizens in many developing countries. The cost of fuel for operating a single generator in Lubumbashi city is USD 1.34/l. If the operation cost of diesel generators and costs of components like the battery could be reduced, there would be a lower LCOE. The price of batteries, a major component of the PV system costs, is rapidly decreasing, majorly driven by the global quest for green energy transition. This will facilitate lower LCOEs for the PV system.
Table 5 shows the HOMER Pro optimized system results for the daily energy output of the hybrid system. Based on the solar irradiation resources in Lubumbashi. shows the optimized systems produced energy output. The system was simulated to run for 24 hours, from 01am. to 12 a.m., during the time when there is minimal or no sun exposure. The design results indicate that the photovoltaic (PV) and battery supply is available from 7:00 h to 22:00 h, with the solar radiation peak happening between noon and 2:00 p.m. The total daily solar irradiation in Lubumbashi is 2.5kw. with PV having a daily energy output of 2.3Kw while the battery system supplies 55.22kw of energy.
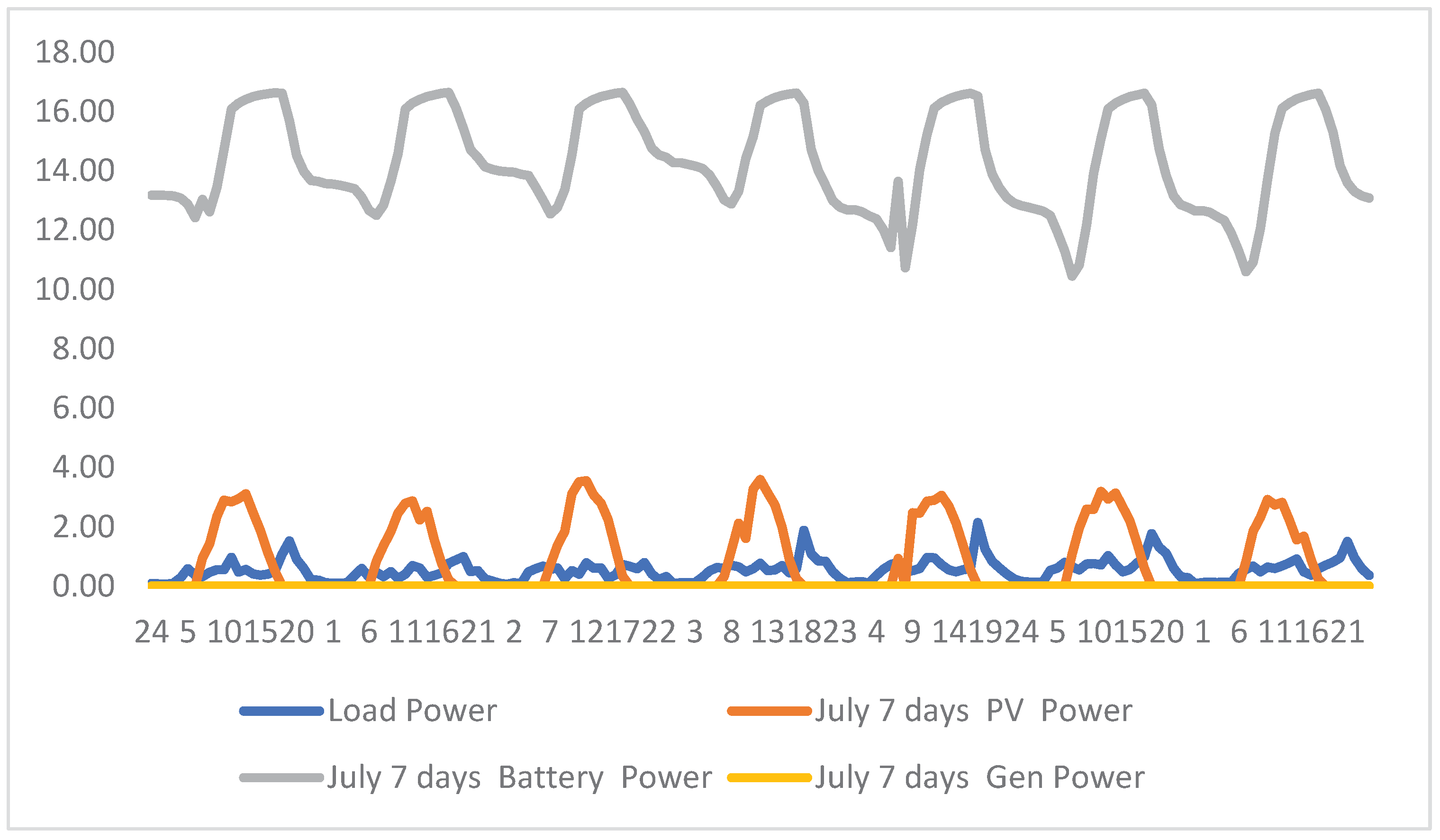
Figure 6 gives a summary of the overall daily Load output for seven days in the peak month of July.
The yearly energy consumption and percentage by the solar PV system after undergoing the Homer Optimization process is shown in
Table 6. As
Table 6 demonstrates, the solar PV system produces 100% of the energy, which is 7331kWh/yr. The excess energy produced is 2939kWh/yr, equaling 40.1% of the yearly AC consumption capacity of 4113kWh/yr. With the optimized 11.27kWh/day diesel-solar PV hybrid system proposed by Homer Pro, the renewable penetration rate reaches 2013%. Additionally, the constant non-operation of the diesel generator under the proposed system leads to fuel conservation, reduced carbon emissions, and an increased renewable energy penetration.
4.2. Economic analysis of the system, including costs and savings
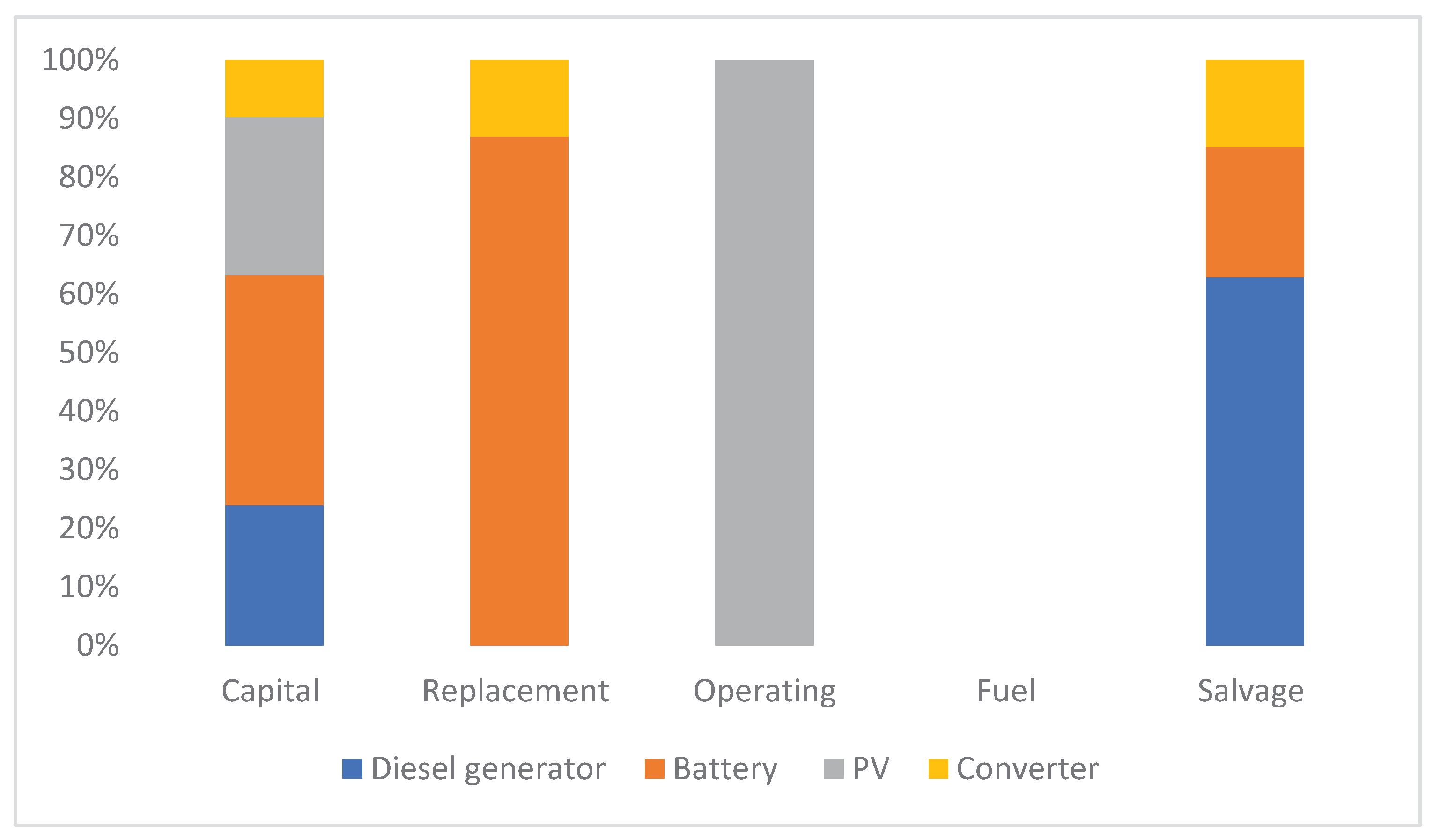
The cost analysis of the simulation results for the configuration is displayed in bar graphs and further described in the configurations that follow. The capital costs, replacement costs, and operation and maintenance costs (O&M) of the simulation are presented based on various optimization configurations proposed by Homer Pro software. A summary of the costs for the Solar PV Battery System and the Diesel PV-Battery System is provided in the
Table 6 and
Table 7 respectively
Figure .
Cost summary for Diesel –PV Battery Configuration.
Figure .
Cost summary for Diesel –PV Battery Configuration.
Table 6.
Cost summary for Diesel –PV Battery Configuration.
Table 6.
Cost summary for Diesel –PV Battery Configuration.
| Component of the system |
Capital |
Replacement |
Operating |
Fuel |
Salvage |
| Diesel generator |
1000 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
93.43 |
| Battery |
1636 |
776.04 |
0 |
0 |
32.92 |
| PV |
1128.42 |
0 |
881.43 |
0 |
0 |
| Converter |
403 |
117.03 |
0 |
0 |
22.03 |
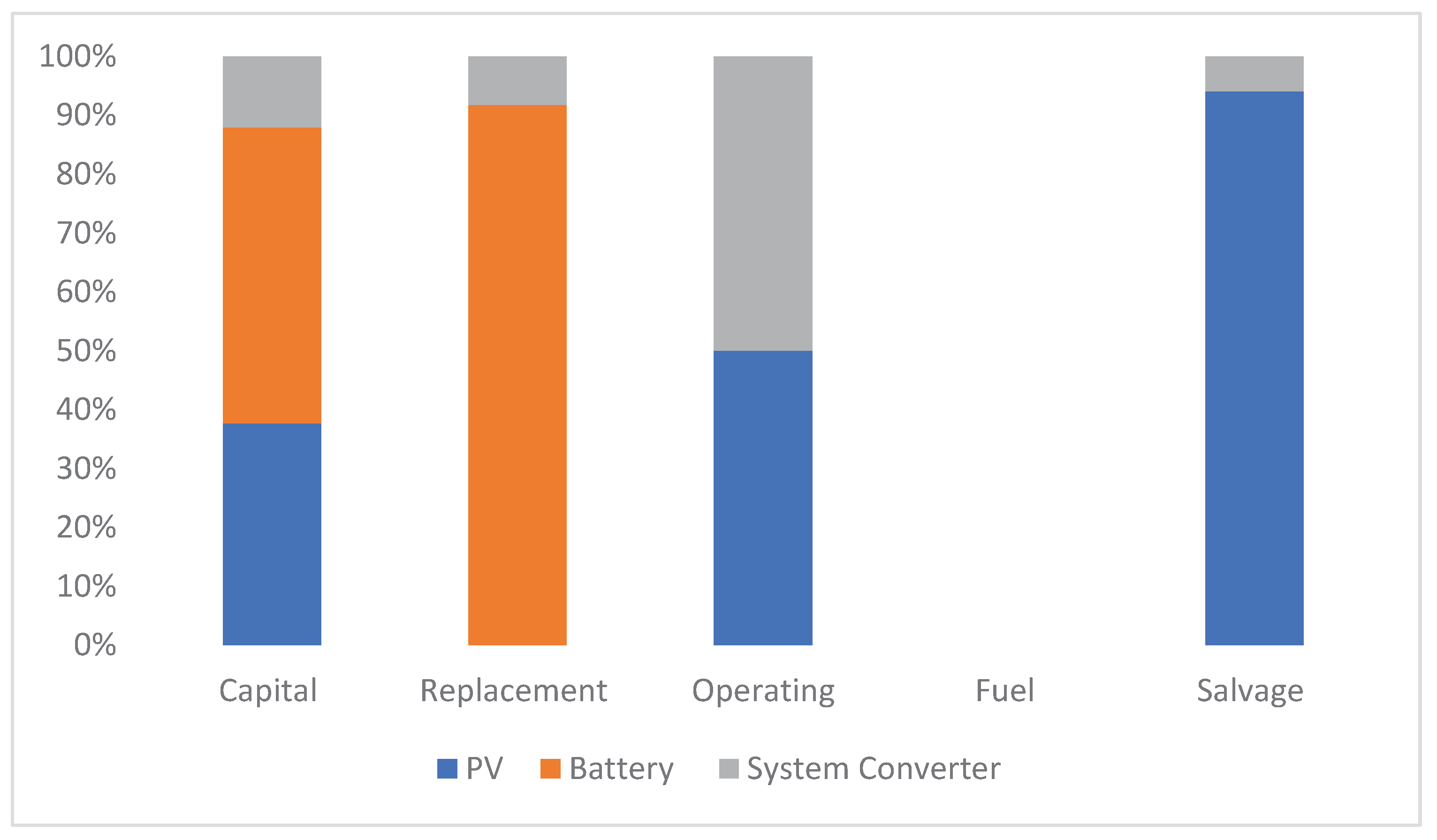
Figure 7.
Cost analysis results for PV-Battery Optimized system.
Figure 7.
Cost analysis results for PV-Battery Optimized system.
Table 7.
Cost summary for Diesel –PV-Battery Configuration.
Table 7.
Cost summary for Diesel –PV-Battery Configuration.
| |
Capital |
Replacement |
Operating |
Fuel |
Salvage |
| PV |
1102.98 |
0 |
861.56 |
0 |
306.07 |
| Battery |
1472.4 |
1138.74 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
| System Converter |
353.79 |
102.58 |
861.56 |
0 |
19.31 |
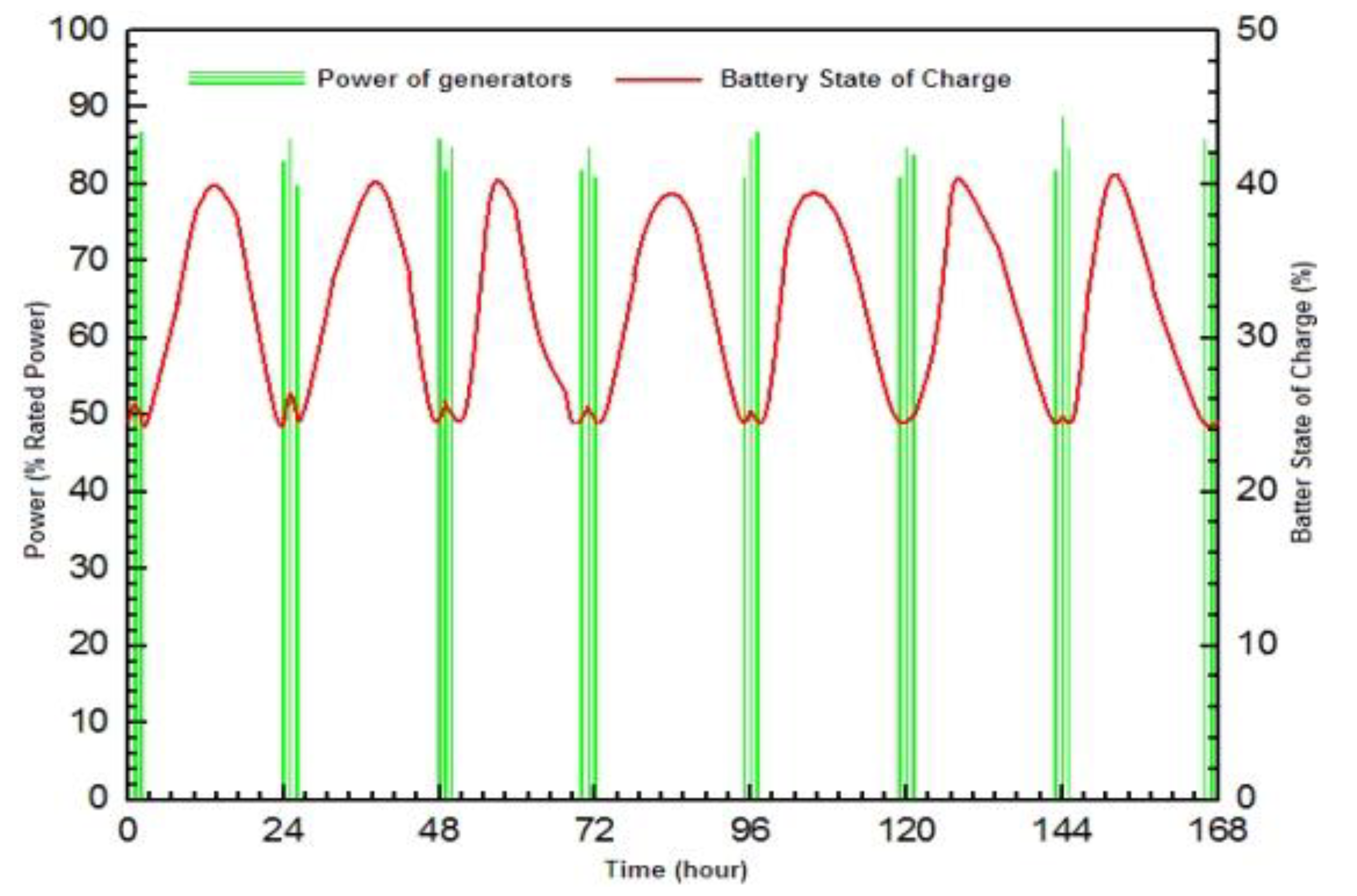
Figure 8 shows the performance of the hybrid power plant during a specific week of July, which was selected during the dry season due to its even power demand. The operation of the diesel generator is triggered when the battery charge reaches 25% during periods of increased demand. The diesel generator will not only supply power to customers but also recharge the battery. The generator operates for approximately 2.5 hours during nighttime and is supplemented by the PV generator during the day to recharge the battery. The diesel generator operates at an efficiency of between 82% and 92% of its nominal output, which results in improved efficiency and decreased fuel consumption from 4500 to 1600 liters every month, a reduction of 64%. This makes the hybrid power system an economical solution for residents in the developing Congo region, where centralized power supply is expensive.
5. Emissions
The system’s emissions are collected from the simulation results of Homer Pro-software to know the amount of each type of pollutant produced yearly by the power system in kg/year.
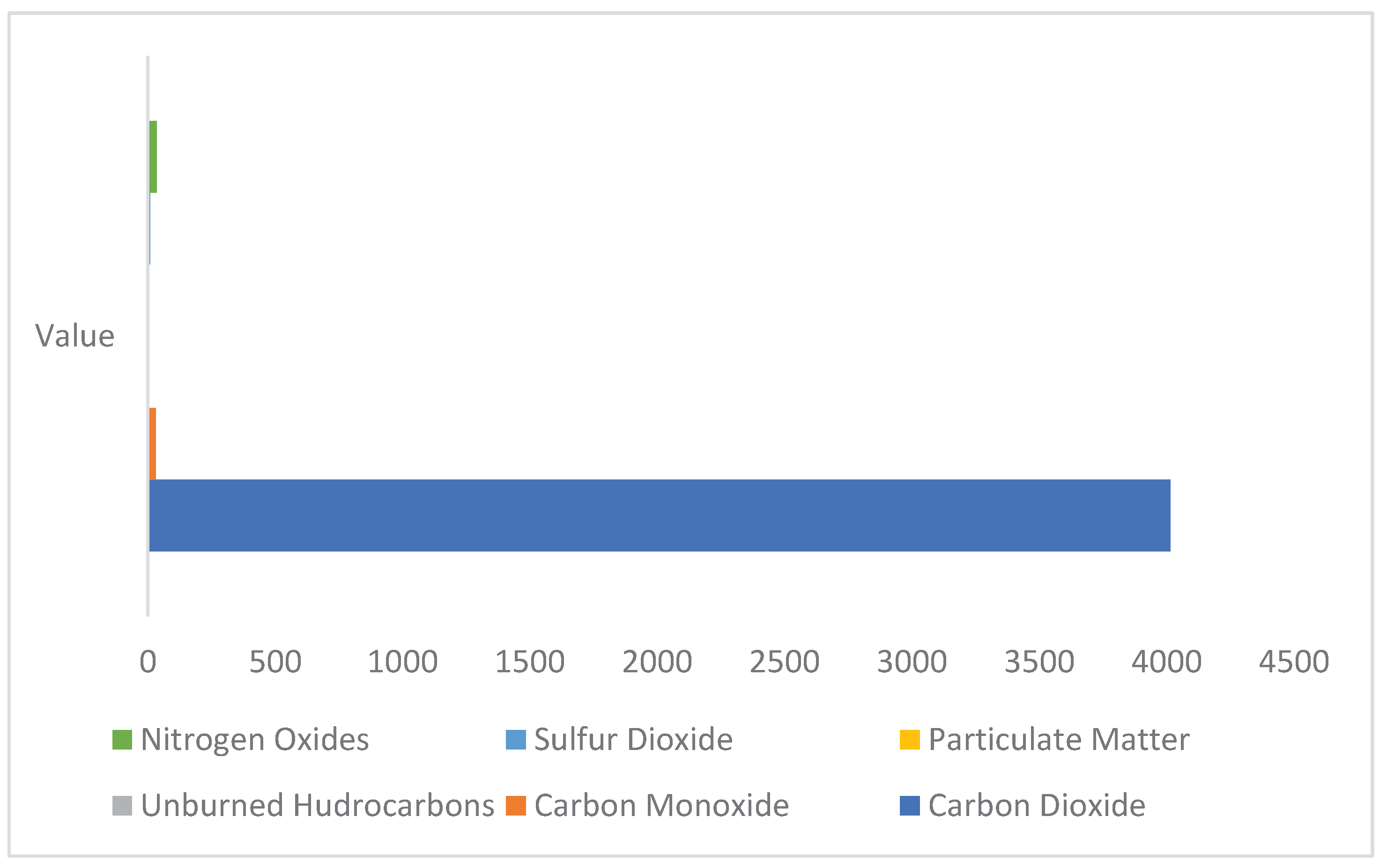
Figure 9 shows the emissions that have been produced for each of the systems in the simulation results. According to figure 9 Carbon Dioxide is the most dominant pollutant with 4014kg/yr for the Diesel and battery configurations, followed by the Nitrogen Oxides with 34.5 Kg/yr and 30.4 for the Carbon Monoxide.
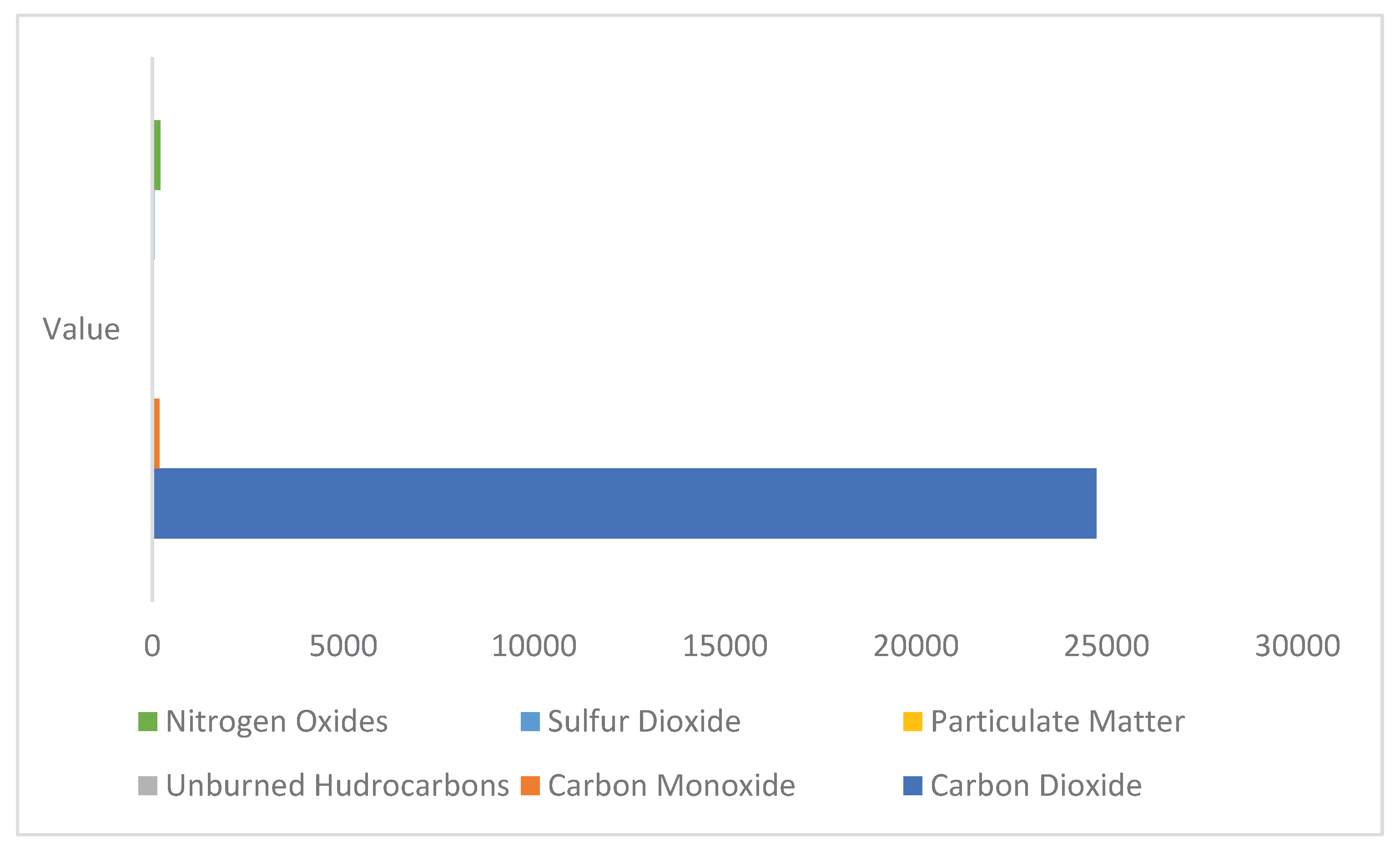
Figure 10 shows the emissions results from the Diesel-Solar PV- Converter with no energy storage system. The carbon dioxide yearly value is 24730 Kg/yr followed by the Nitrogen Oxides with 213kg/yr and Carbon Monoxide 187Kg/yr. However, when considering the Diesel-PV- Battery configuration as suggested by Homer Pro there is no emission recorded (
Figure 11). This is due to the fact that Homer Pro primarily optimizes and promote the use of renewable energy sources in Microgrids.
6. Conclusion and recommendations
Lubumbashi, the capital of Katanga in the Congo Region, relies heavily on diesel power plants due to frequent outages and a lack of access to the national grid. The diesel power plant efficiency is lower than that of newer plants, with expensive maintenance and operation expenses. Using the HOMER Pro software, we were able to establish the optimal hybridization of the power system for this specific geographic region. Results from hypothetical setups of solar photovoltaic panels, batteries, and diesel generators were analyzed.
The results from HOMER's simulations indicated that a PV, battery architecture would be most suited for a 4-kilowatt (kW) power plant. In other words, the results show that the solar PV system can generate 7166 KWh/yr, which is more than enough energy to meet the needs of households. Only 4111 KWh/hr of electricity per year are used by the AC primary load. About 38% of the energy is surplus, or 2777 KWh/hr each year. A meagre 2.24- KWh/hr per year (0.0544%) of electricity is going unused. It was suggested by HOMER that 18 batteries be put in parallel with 24v bus voltage to provide 100% of Lubumbashi's electricity needs, allowing the city to transition to renewable energy. This system provides an additional 2308 kWh/year despite only producing 2281 kWh/year overall. In terms of energy, the annual loss is 69.4- KWh/hr, or 37.4 KWh/hr for every full charge.
Given HOMER's emphasis on renewable energy, the diesel, solar photovoltaic, and battery configuration produces zero annual emissions. However, we generated sufficient emission data by simulating alternative setups. A combined solar PV and diesel Gen system generates 24730kg of CO2 per annum, compared to the 43711.0kg/year emitted only by the diesel generator. Subsequently, the combined output of a diesel and battery setup is 4014 kg of CO2 per year. Consequently, increasing the percentage of renewable energy in the electricity grid can lessen the burden on the environment, generate a quicker financial payback, and saves money. The NPC and CO2 emission of the renewable energy system are shown to be sensitive to the availability of renewable energy resources and the cost of capital in the sensitivity analysis.
Evidence suggests that the optimized solar PV-battery hybrid system is preferable to either a diesel and solar PV or a diesel and battery system hybrid in the southern DR Congo region, both in terms of energy economics and environmental friendliness. These analyses, however, have solely considered power consumption in homes. Power companies and smaller manufacturers should also assess the type of hybrid system that is most appropriate for their geographic location and power needs.
Implications for policy and future research
Policies and regulations from governments are a major boost in the development and deployment of renewable energy projects. Hybrid diesel-PV power systems are one example of a renewable energy source that could benefit from policy actions that promote its adoption. Capital constraints have stymied renewable energy growth in the DR Congo and other low-income countries. Consequently, it is crucial that renewable energy initiatives, such as hybrid diesel-PV power systems, have easier access to funding. The impact of hybrid diesel-PV power systems on livelihoods and economy of Lubumbashi city needs thorough consideration. Hybrid diesel-PV power system environmental impacts, including carbon emission reductions and air and water quality impacts, must be studied to understand their long-term viability. Integration of hybrid diesel-PV power systems into the current Congolese state grid infrastructure requires further study to evaluate its technical and economic viability.
Funding
The research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
The author would like to acknowledge all the help, providing the data and contributions of the Institute for Advanced Study, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen, China.
Conflicts of Interest
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
References
- Lamulamu, Augustin, et al. "Assessing the Predictive Power of Democratic Republic of Congo’s National Spaceborne Biomass Map over Independent Test Samples." Remote Sensing 2022, 14, 4126.
- Oviroh, Peter Ozaveshe, and Tien-Chien Jen. "The energy cost analysis of hybrid systems and diesel generators in powering selected base transceiver station locations in Nigeria." Energies 2018, 11, 687.
- Rozali, Nor Erniza Mohammad, et al. "Process integration of hybrid power systems with energy losses considerations." Energy 2013, 55, 38–45.
- Tsuanyo, David, et al. "Modeling and optimization of batteryless hybrid PV (photovoltaic)/Diesel systems for off-grid applications." Energy 2015, 86, 152–163.
- Alotaibi, Majed A., and Magdy MA Salama. "An incentive-based multistage expansion planning model for smart distribution systems." IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 2018m 33, 5469-5485.
- Abi Ghanem, Dana, and Sarah Mander. "Designing consumer engagement with the smart grids of the future: bringing active demand technology to everyday life." Technology Analysis & Strategic Management 2014, 26, 1163–1175.
- Charfi, Sana, Ahmad Atieh, and Maher Chaabene. "Modeling and cost analysis for different PV/battery/diesel operating options driving a load in Tunisia, Jordan and KSA." Sustainable cities and society 2016, 25, 49–56.
- Agarwal, Nitin, and Anoop Kumar. "Optimization of grid independent hybrid PV–diesel–battery system for power generation in remote villages of Uttar Pradesh, India." Energy for Sustainable Development 2013, 17, 210–219.
- Malheiro, André, et al. "Integrated sizing and scheduling of wind/PV/diesel/battery isolated systems." Renewable Energy 2015, 83, 646–657.
- Yap, Wai Kean, and Vishy Karri. "An off-grid hybrid PV/diesel model as a planning and design tool, incorporating dynamic and ANN modelling techniques." Renewable Energy 2015, 78, 42–50.
- Katsaprakakis, Dimitris Al, Pr Dimitris, and G. Christakis. "A wind parks, pumped storage and diesel engines power system for the electric power production in Astypalaia." EWEC 2006, 2006, 1–16.
- Khan, Mohammad Junaid, Amit Kumar Yadav, and Lini Mathew. "Techno economic feasibility analysis of different combinations of PV-Wind-Diesel-Battery hybrid system for telecommunication applications in different cities of Punjab, India." Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2017, 76, 577–607.
- Veerashekar, Kishan, Halil Askan, and Matthias Luther. "Qualitative and Quantitative Transient Stability Assessment of Stand-Alone Hybrid Microgrids in a Cluster Environment." Energies 2020, 13, 1286.
- International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA). Off-Grid Renewable Energy Systems:Status and Methodological Issues. Available online: https://www.irena.org/-/media/Files/IRENA/Agency/Publication/2015/IRENA_Off-grid_Renewable_Systems_WP_2015.pdf (accessed on 13 January 2020).
- Carnegie Mellon University (CMU). Available online: https://www.cmu.edu/ceic/assets/docs/publications/reports/2014/micro-grids-rural-electrification-critical-rev-best-practice.pdf (accessed on 13 January 2020).
- Motoren- und Turbinen-Union (MTU). Available online: https://www.mtu-solutions.com/eu/en/stories/power-generation/gas-generator-sets/microgrid-cooperation-with-qinous.html (accessed on 13 January 2020).
- Caterpillar. Available online: https://www.cat.com/en_US/by-industry/electric-power-generation/Articles/ White-papers/white-paper-hybrid-microgrids-the-time-is-now.html (accessed on 13 January 2020).
- Papazis, Stylianos A. "Integrated Economic Optimization of Hybrid Thermosolar Concentrating System Based on Exact Mathematical Method." Energies 2022, 15, 7019.
- Papazis, S.A.; Ioannides, M.G.; Fotilas, P.N. Development of an Information System for Wind Power Stations. In Enterprise Information Systems II; Sharp, B., Filipe, J., Cordeiro, J., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 101–107. [Google Scholar]
- Ioannides, M.G.; Tuduce, R.; Cristea, P.-D.; Papazis, S.A. Wind power generating systems based on double output induction machine: Considerations about control techniques. In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Systems, Signals and Image Processing (IWSSIP), Bucharest, Romania, 7–9 July 2013; pp. 103–107. [Google Scholar]
- Ioanides, M.G.; Stamelos, A.; Papazis, S.A.; Papoutsidakis, A.; Vikentios, V.; Apostolakis, N. IoT Monitoring System for Applications with Renewable Energy Generation and Electric Drives. Renew. Energy Power Qual. J. 2021, 19, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iñigo-Labairu, Javier, Jürgen Dersch, and Luca Schomaker. "Integration of CSP and PV Power Plants: Investigations about Synergies by Close Coupling." Energies 2022, 15, 7103.
- Analyzing the Prospect of Hybrid Energy in the Cement Industry of Pakistan, Using HOMER Pro.
- Turkdogan, S. Design and optimization of a solely renewable based hybrid energy system for residential electrical load and fuel cell electric vehicle. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2021, 24, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisale, S.W.; Mangani, P. Energy Audit and Feasibility of Solar PV Energy System: Case of a Commercial Building. J. Energy 2021, 2021, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdinc, O.; Uzunoglu, M. Optimum design of hybrid renewable energy systems: Overview of different approaches. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 1412–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huawei. Huawei Diesel Hybrid Power Solution; Huawei: Shenzhen, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Odoi-Yorke, Flavio, and Atchou Woenagnon. "Techno-economic assessment of solar PV/fuel cell hybrid power system for telecom base stations in Ghana." Cogent Engineering 2021, 8, 1911285.
- Oviroh, P.O.; Jen, T.-C.; Idusuyi, N.; Gbadeyan, O. Comparative Energy Cost Analysis of Hybrid System and Diesel Generator in Powering Selected Base Transceiver Stations in Nigeria. In Proceedings of the ASME 2017 International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, Tampa, FL, USA, 3–9 November 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.J.; Yadav, A.K.; Mathew, L. Techno economic feasibility analysis of different combinations of PV-Wind-Diesel-Battery hybrid system for telecommunication applications in different cities of Punjab, India. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 76, 577–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Advanced Hybrid Power. Available online: https://carrier.huawei.com/en/products/digital-power/telecom-energy/hybrid-power (accessed on 15 January 2023).
- Adaramola, M.S.; Paul, S.S.; Oyewola, O.M. Assessment of decentralized hybrid PV solar-diesel power system for applications in Northern part of Nigeria. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2014, 19, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajlan, A.; Tan, C.W.; Abdilahi, A.M. Assessment of environmental and economic perspectives for renewable-based hybrid power system in Yemen. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 75, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, I. Mitigating ICT Related Carbon Emissions: Using Renewable Energy to Power Base Stations in Africa’s Mobile Telecommunications Sector; Centre for Development Informatics (CDI) University of Manchester: Manchester, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ani, V.A. Design of a Reliable Hybrid (PV/Diesel) Power System with Energy Storage in Batteries for Remote Residential Home. J. Energy 2016, 2016, 6278138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green Tech: The Rise of Environment-Friendly Technologies |The Edge Markets. Available online: https://www.theedgemarkets. com/article/green-tech-rise-environmentfriendly-technologies (accessed on 15 January 2023).
- Vaka, M.; Walvekar, R.; Rasheed, A.K.; Khalid, M. A Review on Malaysia’s Solar Energy Pathway towards Carbon-Neutral Malaysia beyond COVID’19 Pandemic. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 273, 122834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albani, A.; Ibrahim, M.Z.; Taib, C.M.I.C.; Azlina, A.A. The Optimal Generation Cost-Based Tariff Rates for Onshore Wind Energy in Malaysia. Energies 2017, 10, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhtaruddin, R.N.S.R.; Rahman, H.A.; Hassan, M.Y. Economic Analysis of Grid-Connected Hybrid Photovoltaic-Wind System in Malaysia. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Clean Electrical Power (ICCEP), Alghero, Italy, 11–13 June 2013; pp. 577–583. [Google Scholar]
- Zailan, R.; Zaini, S.N.; Mohd Rashid, M.I.; Abdul Razak, A. Feasibility Study of Standalone PV-Wind-Diesel Energy Systems for Coastal Residential Application in Pekan, Pahang. MATEC Web Conf. 2017, 131, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plants, U.H.P.; Silva, A.R.; Estanqueiro, A. From Wind to Hybrid: A Contribution to the Optimal Design of Utility-Scale Hybrid Power Plants. Energies 2022, 15, 2560. [Google Scholar]
- Sinha, S.; Chandel, S.S. Review of Software Tools for Hybrid Renewable Energy Systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 32, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukarno, K.; Hamid, A.S.A.; Jackson, C.H.W.; Pien, C.F.; Dayou, J. Comparison of Power Output between Fixed and Perpendicular Solar Photovoltaic PV Panel in Tropical Climate Region. Adv. Sci. Lett. 2017, 23, 1259–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulmula, A.; Sopian, K.; Ludin, N.A.; Haw, L.C.; Elberki, A.; Aldawi, F.; Moria, H. Micropower System Optimization for the Telecommunication Towers Based on Various Renewable Energy Sources. Int. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2022, 12, 1069–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkassem, A.; Draou, A.; Alamri, A.; Alharbi, H. Design Analysis of an Optimal Microgrid System for the Integration of Renewable Energy Sources at a University Campus. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, F.; Shafiullah, G.M.; Anda, M. Stand-Alone Microgrid with 100% Renewable Energy: A Case Study with Hybrid Solar Pv-Battery-Hydrogen. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lao, C.; Chungpaibulpatana, S. Techno-Economic Analysis of Hybrid System for Rural Electrification in Cambodia. Energy Procedia 2017, 138, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HOMER Energy. HOMER®Pro Version 3.7-User Manual; HOMER Energy: Boulder, CO, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Alsharif, M.H. Techno-Economic Evaluation of a Stand-Alone Power System Based on Solar Power/Batteries for Global System for Mobile Communications Base Stations. Energies 2017, 10, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsharif, M.H. A Solar Energy Solution for Sustainable Third Generation Mobile Networks. Energies 2017, 10, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsharif, M.H. Comparative Analysis of Solar-Powered Base Stations for Green Mobile Networks. Energies 2017, 10, 1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalogirou, S.A. Solar Energy Engineering: Processes and Systems; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).