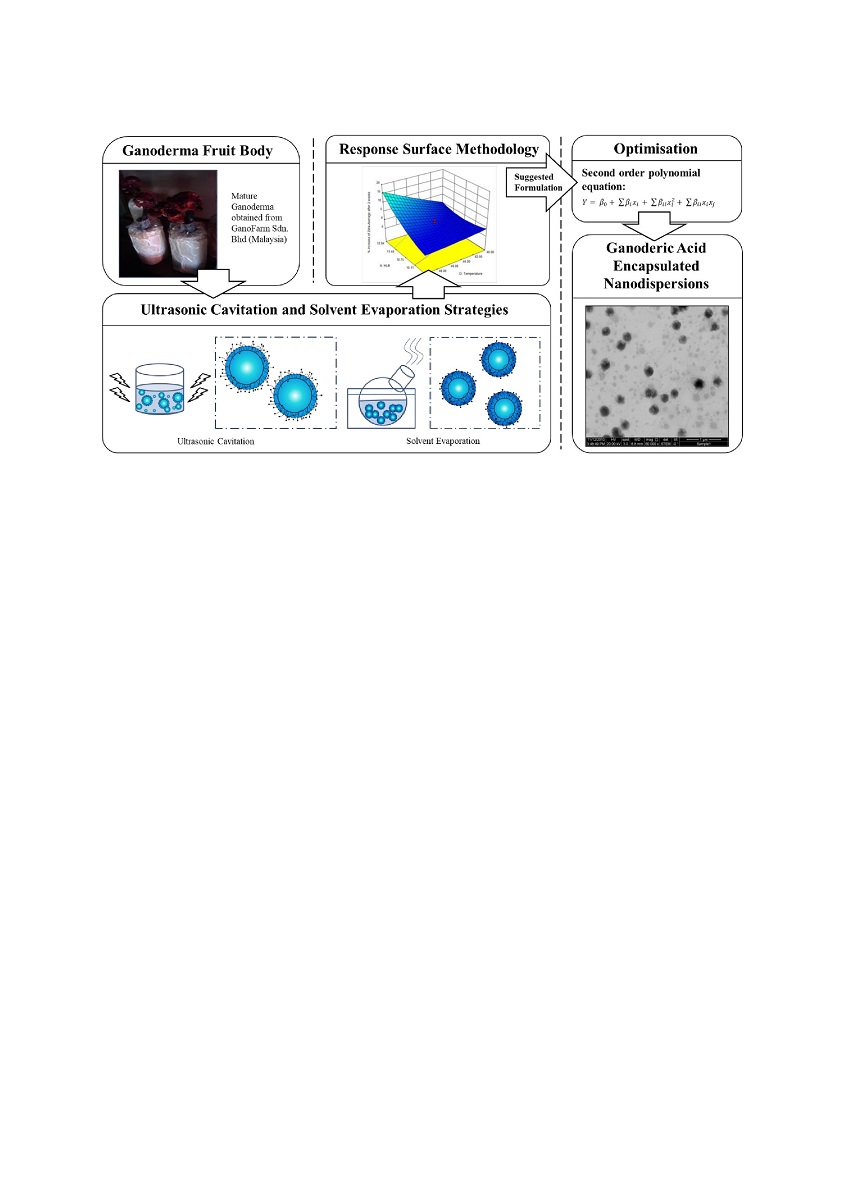
1. Introduction
For centuries, the medicinal fungi Ganoderma tsugae (
Figure 1) has been used in China, Japan, and other oriental countries as a folk remedy for preserving the well-being of humans. In Shen Nong's Herbal Classic, Ganoderma was mentioned as having "vital energy" as early as 100 B.C. However, the modern use of Ganoderma and intensive research into its pharmaceutical benefits has only increased in the Western hemisphere in recent decades. Ganoderma contains various bioactive ingredients, including polysaccharides, triterpenes/triterpenoids, amino acids, nucleosides, etc. Among the major bioactive ingredients isolated from Ganoderma tsugae (
Figure 1), ganoderic acids have been found to have significant potential either in preventing or in treating a variety of life-threatening diseases, including hepatitis B [
1], hypertension [
2], tumours [
3,
4], inflammation [
5], HIV [
6], cancer [
7], and many others.
As a result of its extremely low solubility in water, its limited bioavailability restricts its application in vivo. Dissolving Ganoderic acid in a solvent is generally necessary before administering it. As a result of the severe pain induced during injection [
8] and the possibility of hemolysis [
9], intravenous administration is not recommended. As a result of the development of new formulations, Ganoderic acid is now capable of presenting a favourable bioavailability. Nanocarriers have been extensively discussed to enhance the potential of hydrophobic compounds, including nanoemulsions [
10,
11], polymeric nanoparticles [
12], and liposomes [
13,
14]. Even so, there is still a great deal of uncertainty regarding the method of preparing Ganoderic acid in nanoformulation.
Ganoderic acids can be isolated from Ganoderma fruiting bodies by solvent extraction. Ganoderic acids have been separated from Ganoderma lucidum spores using methanol as a solvent, which is known to inhibit HIV-1 protease [
15] and to exhibit cytotoxicity against Meth-A and LLC tumor cells [
16]. Chin et al. [
17] have also extracted crude Ganoderic acids. They tested four different drying techniques, including freeze-drying, convective hot air drying, vacuum drying, and heat pump drying, on fruiting bodies weighing 36 ± 0.1 g on average. It has been found that vacuum-dried Ganoderma lucidum can preserve most of its active ingredients but requires a longer drying period. Accordingly, the heat pump required the shortest total drying time, yet it achieved an acceptable and relatively high concentration of Ganoderic acids and water-soluble polysaccharides.
Tan and Nakajima [
18,
19] produced β-carotene nanodispersion using emulsification and evaporation employing high-pressure homogenisation; it was suggested that process conditions, such as homogenisation pressures and cycles, could have significant effects on particle size and size distribution. In the following years, Tan and his group further investigated the synthesis of α-Tocopherol nanodispersions [
20], Astaxanthin nanodispersions [
21,
22] and Phytosterol nanodispersions [
23] with high-pressure homogenisation.
An important aspect of solvent removal is the evaporator temperature; the precipitation or recrystallisation rate of hydrophobic drug governed by temperature gradient significantly controls the size and shape of the particles. To combat insolubility, other methods have also been described for producing nanodispersions with properties similar to those of solutions [
24,
25,
26]. However, the complex processing conditions and the inability to achieve long-term physical stability limited their solemnity. The present study attempts to establish an efficient and reproducible method. The proposed route offers several advantages over conventional protocols, including conventional emulsification evaporation and reverse microemulsion template synthesis. A conventional emulsification method always involves a toxic solvent (e.g. hexane or chloroform), and low yields are frequently reported when a nanoprecipitation-reverse microemulsion template synthesis method is employed. In the present study, we have encapsulated crude Ganoderic acid using nanoemulsification via ultrasonic cavitation. In addition, Ganoderic acid nanodispersions have been generated by evaporating the solvent at reduced pressure. It is always important to consider the rheological behaviour of solid nanodispersion when ensuring particle stability. Solid nanoparticles interact with one another in an easy-to-understand manner. The attraction and repulsive forces between particles are the primary driving force behind agglomeration. In other successful cases, electrostatic surfactants have been included in formulations, or freeze-drying has been used to ensure stability.
Several efforts have been made to investigate the possibility of preparing Ganoderic acid-loaded nanodispersions using a modified protocol, as reported by Tan and Nakajima [
18,
19]. The process was then optimised using Response Surface Methodology (RSM). Several engineering applications have demonstrated the effectiveness of RSM as an optimisation tool [
28]. No reports have been published on optimising processes involving more than three control variables, especially for preparing drug-loaded nanoparticles. As a result, Central Composite Design (CCD) has been employed to investigate the impact of five control variables on the physical characteristics of the nanoformulations developed. Based on statistical experimental design, empirical models were developed with evidence of accuracy. Furthermore, process optimisation was conducted to obtain a formulation with the desired physical properties, including particle size, polydispersity index, zeta potential, and physical stability over two weeks. In order to confirm the particle morphology, the suggested optimum formulation was characterised by Scanning-Transmission Electron Microscopy (STEM). Furthermore, a size distribution study was conducted to investigate the effect of pH on nanodispersion particle size.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Span 20 and Brij 56 were obtained from Merck (Darmstadt, Germany). Ethanol (99.5%) was received from Fisher Scientific (Fair Lawn, NJ, USA). GanoFarm Sdn. Bhd (Malaysia) provided crude Ganoderic acid isolated from raw Ganoderma tsugae fruit bodies and used as received without further purification. Water was obtained from the Milli-Q water purification system (Millipore, MA, USA).
2.2. Preliminary screening of nanoemulsion formulations
A solution of Ganoderic acid (1% wt/wt) was prepared by dissolving crude Ganoderic acid in ethanol and preserving it in vials before formulation. Before encapsulating Ganoderic acid in nano vehicles, the solubilising potential of the solution (1%) was studied. After the solution was subjected to ultrasonic cavitation at room temperature, visual observations were recorded. To investigate emulsion phase behaviour, a predetermined water-surfactant mixture (or oil-surfactant mixture) was added to Ganoderic acid solution in vials. A titration of Ganoderic acid solution into a water-surfactant mixture (or oil-surfactant mixture) was conducted and stopped when turbidity was observed, indicating maximum solubilisation of surfactants. Formulations were then left at room temperature until equilibrium was reached.
2.3. Preparation of Ganoderic acid Nanodispersion
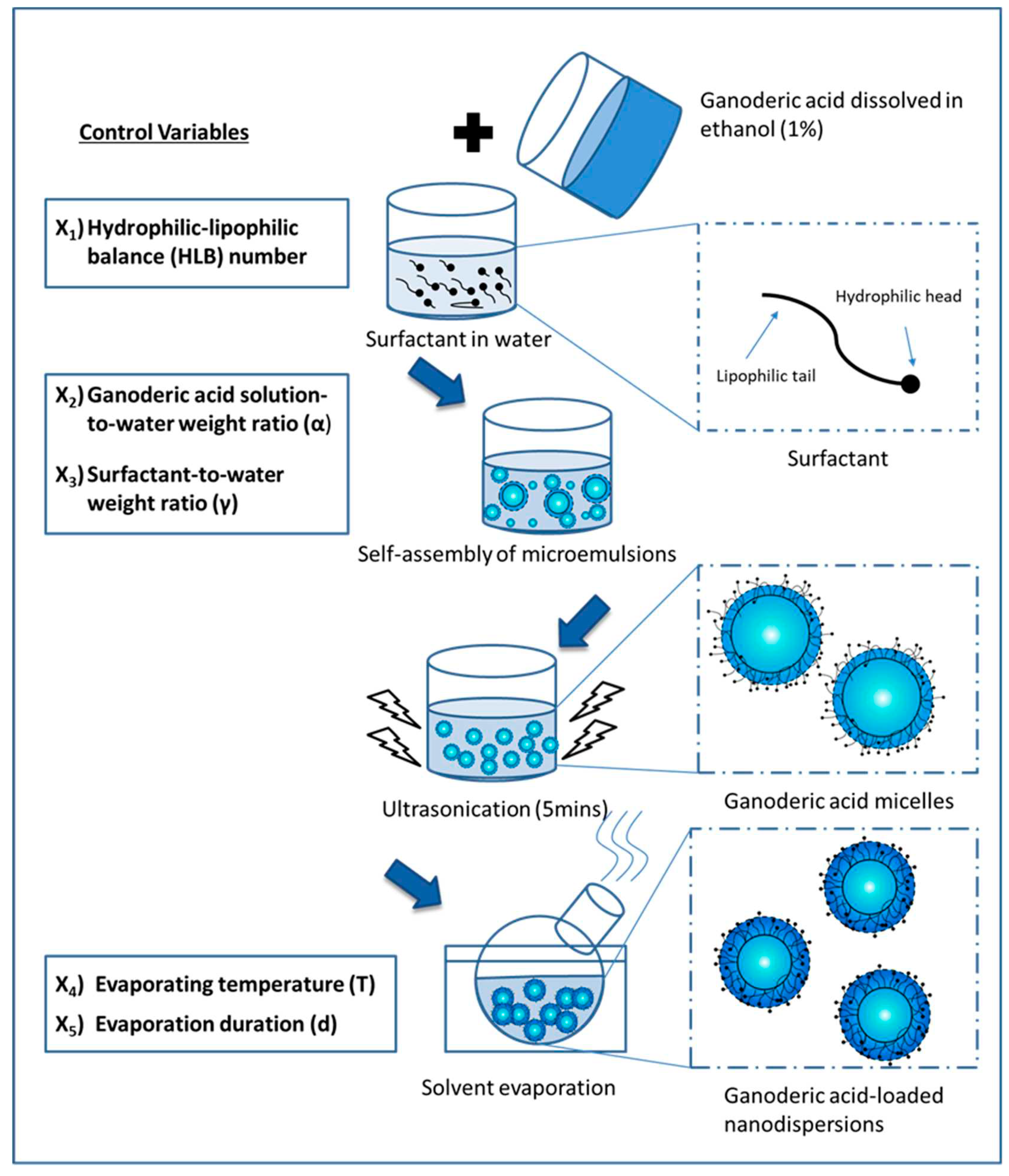
Figure 2 illustrates the ultrasonic cavitation and solvent evaporation techniques to prepare Ganoderic acid-loaded nanodispersion formulations. Response Surface Methodology (RSM) has been extensively used to study the importance of formulation composition and process conditions. In the first step, Ganoderic acid was extracted from the Ganoderma tsugae fruiting body using a modified isolation technique described by Chin et al. [
17]. The purified Ganoderic acid was redissolved in ethanol at 1 mg/g to produce Ganoderic acid-rich organic phases. To obtain the desired HLB, Brij 56 and Span 20 were mixed accordingly. The surfactant mixture, Ganoderic acid solution, and water were combined in the following steps until an isotropic micellar system was achieved. Following this step, a 5 min ultrasonic treatment (38 kHz, Ultrasonic RMS 140 W, Guyson International Ltd, UK) was conducted to induce homogenisation. To remove the organic phase from the Ganoderic acid micelles, the solvent was evaporated at reduced pressure (150 mbar). Temperature and evaporation time were controlled between 40 and 50 °C and 10 to 30 min, respectively. This process required the components to be mixed with an accuracy of +/- 0.005 g error.
2.4. Characterisation of Nanodispersion: Size distribution, Polydispersity index, Zeta-potential and Stability studies
Ganoderic acid-loaded nanodispersions were characterised by the Malvern Zetasizer-Nano instrument (Malvern Instrument Inc) regarding particle size, polydispersity index, and zeta potential. Immediately following preparation, nanodispersions were characterised at room temperature without dilution. The physical stability of the formulations was studied over a given storage period. As a result, the prepared emulsions were sealed after instant measurement on the first day of preparation. Following the preparation of the nanodispersion, 1 ml of it was withdrawn in order to monitor the growth of the particles.
2.5. Experimental design
A Central Composite Design (CCD) was used to approximate a quadratic model to construct an interactive relationship between the independent control variables. In a preliminary screening of product formulations, Ganoderic acid solution (1%), surfactant concentration, and the combination of two surfactants play an important role in determining the physical properties of an initial nanoemulsion. In order to study the synchronised effects of two surfactants, the Hydrophilic-Lipophilic Balance (HLB) number of mixed surfactants in the formulation could be described as follows:
Where N
HLB,mix is the HLB number of the mixed surfactant, N
HLB,SurfA is the HLB number of the surfactant A, W
surf A is the weight ratio of the surfactant A to the total weight of the surfactant, N
HLB,Surf B is the HLB number of the surfactant B, W
surf B is the weight ratio of the surfactant B to the total weight of the surfactant. A total of five independent variables, including the Hydrophilic-Lipophilic Balance number (X1, HLB), Ganoderic acid solution-to-water weight ratio (X2), surfactant-to-water weight ratio (X3), evaporation temperature (X4), and evaporation time (X5) were examined for their interaction. A summary of the factors that were evenly spaced to achieve this three-level orthogonal design can be found in
Table 1, where codes for low, medium and high were -1, 0 and +1, respectively. The 50 experiments designed by CCD, including five centre point replications, were run randomly according to the design configuration. Design-Expert 8.0 generated a quadratic function that was statistically analysed and validated using the Analysis of Variance (ANOVA). The following four response surface functions have been developed: particle size (Y1), polydispersity index (Y2), zeta-potential (Y3), and percentage increase in zeta-average after 14 days of storage (Y
4). A generalised response function could be used to describe them as follows:
Where Y is the respective response, β
0 is a constant, β
i, β
ij, and β
ii are linear, interaction and quadratic coefficients, respectively. A three-dimensional response surface was generated using the derived equation. As a result, process optimisation was achieved after each permutation of the multi-response quadratic function to achieve the smallest possible particle size and polydispersity index, the highest zeta potential, and the slowest particle growth.
2.6. Scanning-Transmission Electron Microscopy (STEM)
The surface morphology of ganoderic acid-loaded nanodispersions was investigated using Field Emission-Scanning Electron Microscopy (FE-SEM) in STEM mode. Drops of the optimised formulation were placed on a 50-mesh copper grid and allowed to dry naturally at room temperature for 5 min. During the STEM investigation, the nanodispersion was again left to stand in 3% Phosphotungstic Acid (PTA) for another 5 min.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Development of 3D surface function using Central Composite Design (CCD)
Table 2 summarises both experimental and response surface methodology (RSM) results for the physical characteristics of Ganoderic acid nanodispersion in terms of particle size (Y1), polydispersity index (Y2), zeta potential (Y3), and percentage increase in nanodispersion's zeta-average after two weeks of storage (Y4). According to the Analysis of Variance (ANOVA), the quadratic model is statistically significant in four responses at a 99% confidence level. Predicted values agree with the measured response data, as suggested by the approximating function. A coefficient of determination (R2) was calculated for the responses of particle size (Y1), polydispersity index (Y2), zeta-potential (Y3) and percentage increase in nanodispersion's zeta-average after two weeks of storage (Y4), respectively, to be 0.8822, 0.6583, 0.9652 and 0.7650.
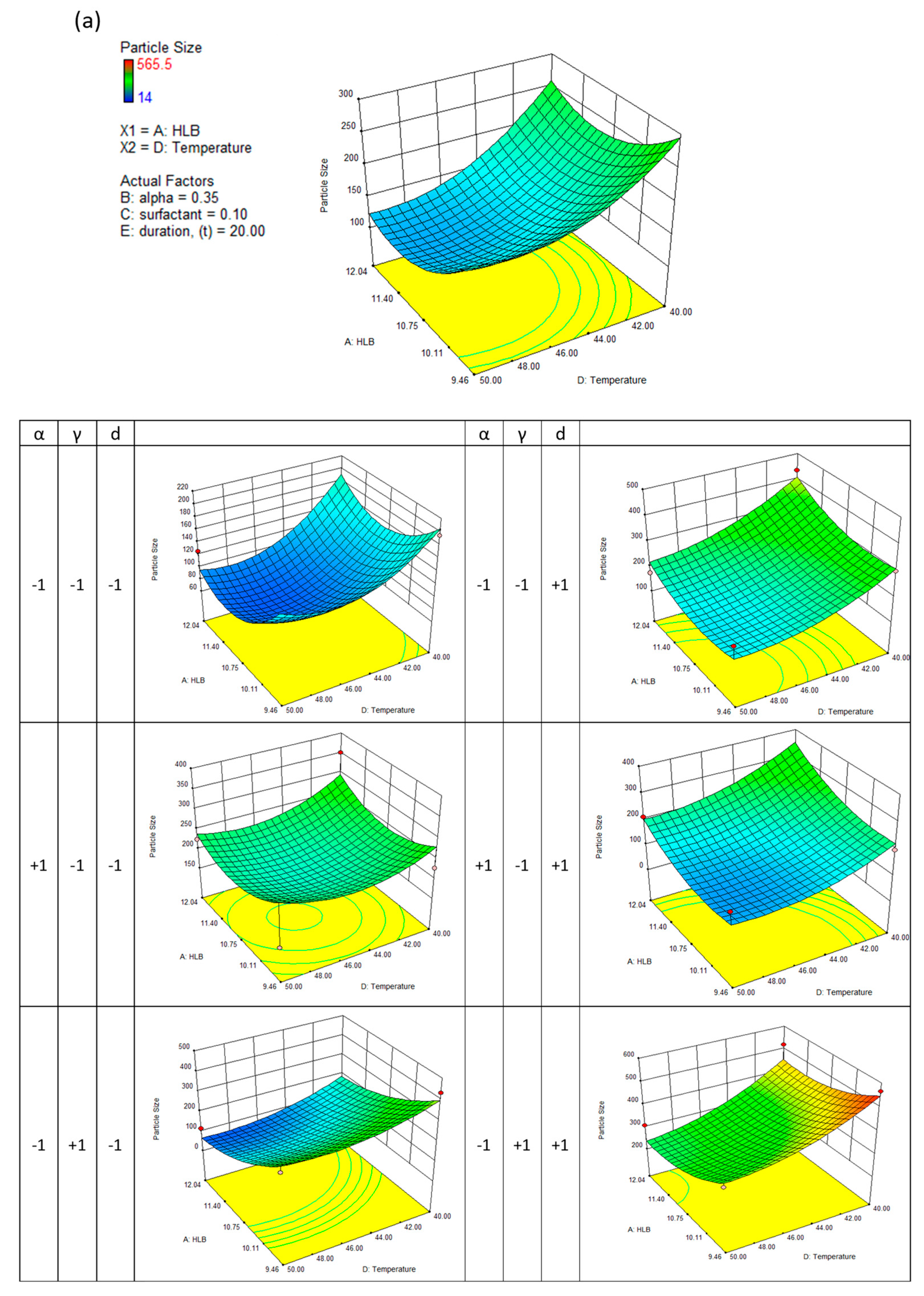
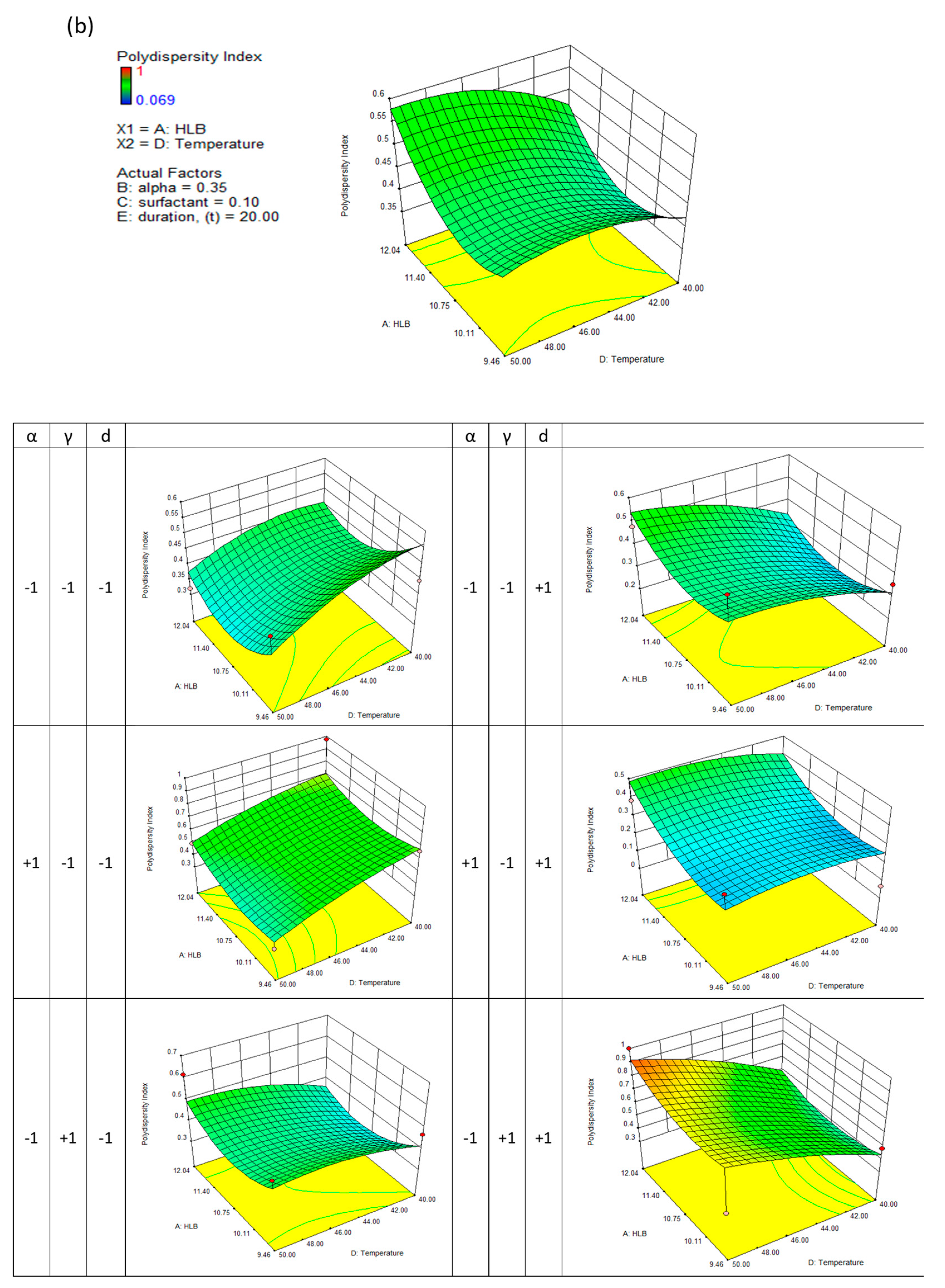
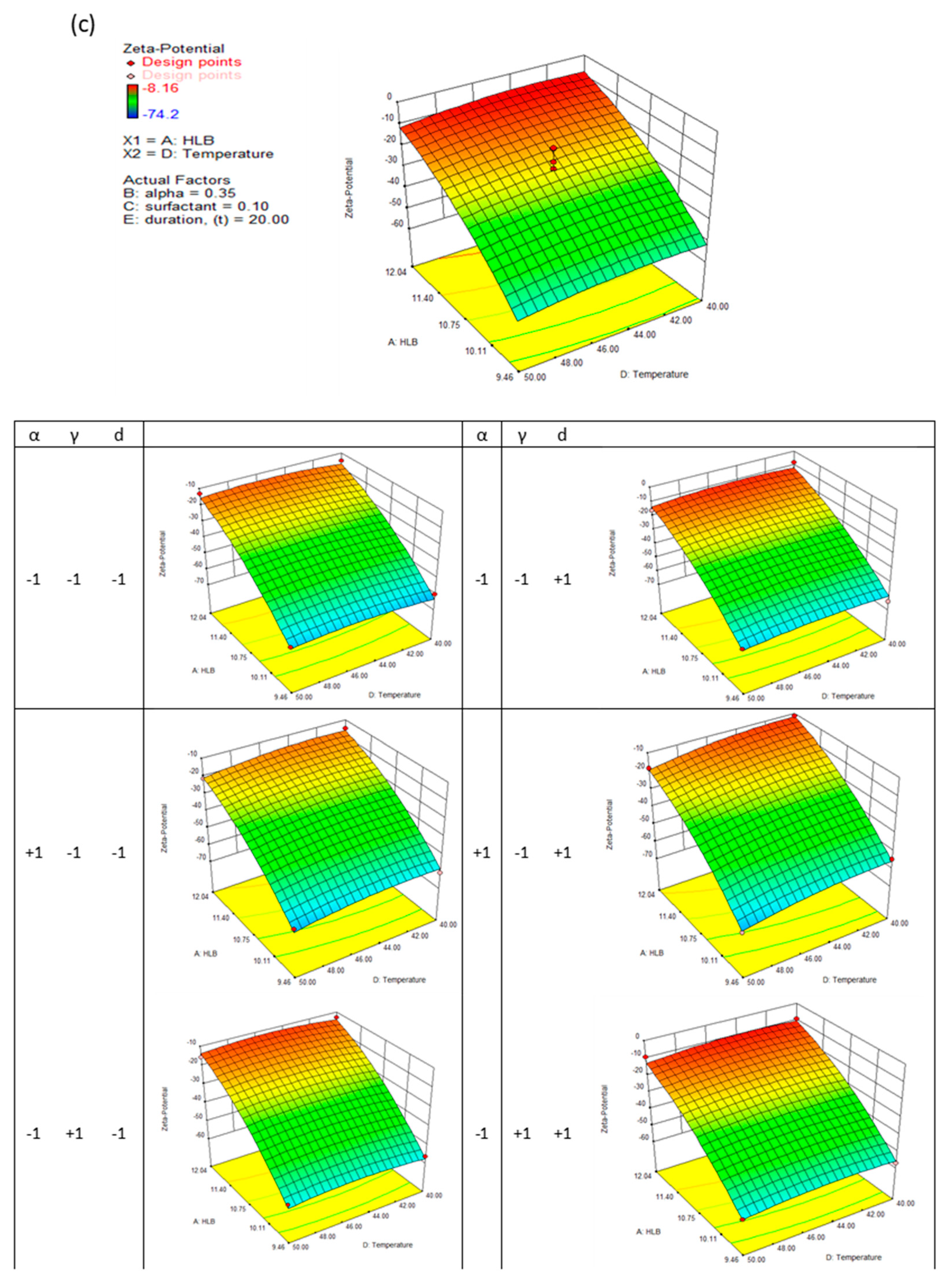
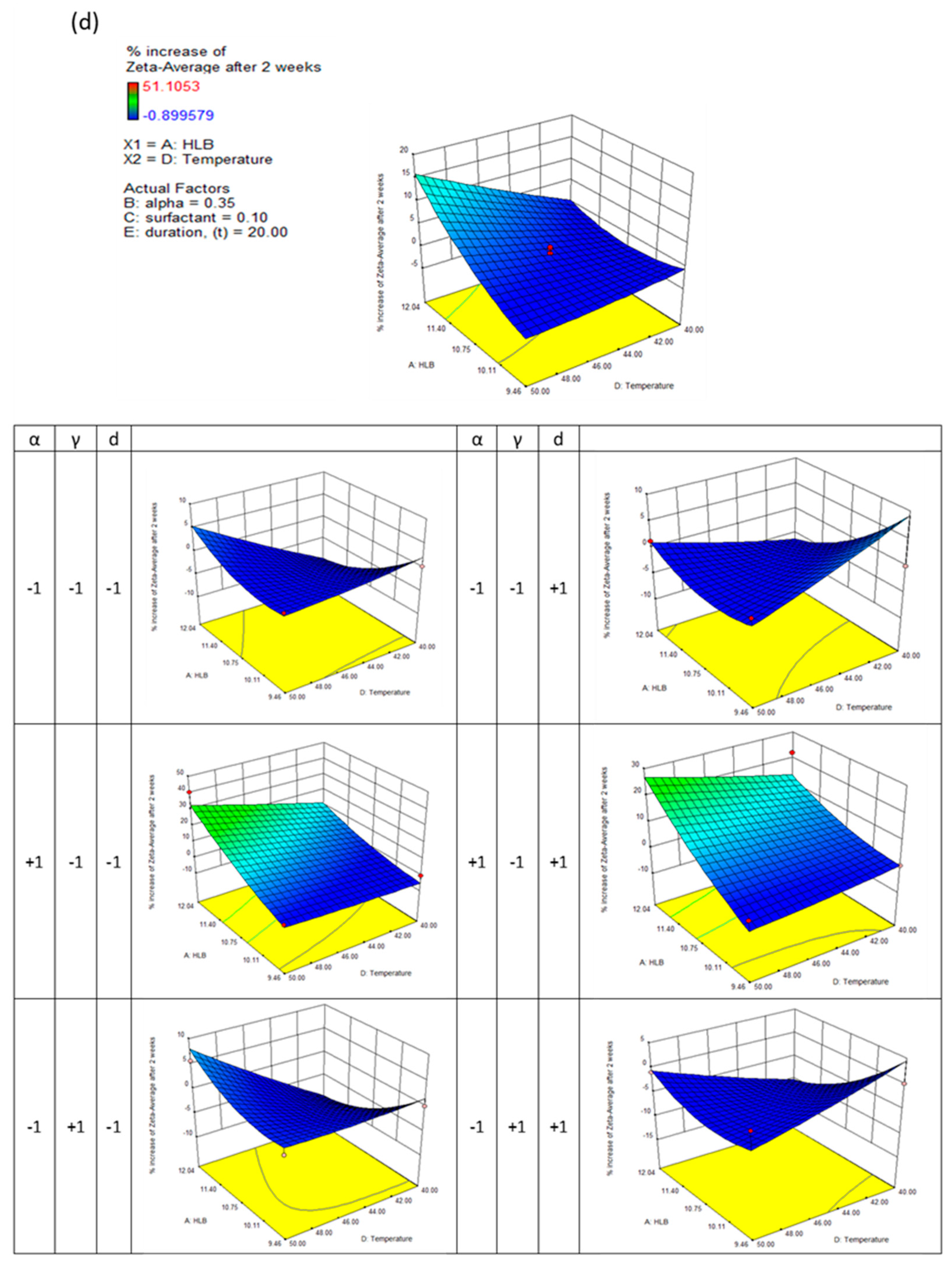
This generally results in a good approximation between the actual and predicted data. The quadric surfaces shown in
Figure 3a,b,c, and d illustrate the interactive relationship between five independent variables. For this purpose, a three-dimensional response surface has been developed, which shows the combined effect of the two most important independent variables while maintaining the values of the other three control variables at their center points. Following this, eight other quadric surfaces were constructed by varying the two most influential variables.
3.2. Effect of control variables on the response
Ganoderic acid nanodispersion in water was governed by gradient-driven solvent diffusion from the micelles' hydrophobic core into the continuous aqueous phase. Initially, the organic solvent stabilised by the surfactant forms drug-loaded micelles; however, after intensive removal of the organic solvent through evaporation at reduced pressure, the Ganoderic acid nanosphere crystallises. In most pharmaceutical practices, ethanol at low concentrations is acceptable. This study used ethanol to deliver Ganoderic acid to the hydrophobic core. Due to its ability to form azeotropes with water, excluding it from the formulation would generally be impractical. In the study of designed experimental data, it was determined that increasing the organic phase in the micelles promotes the formation of larger micelles, resulting in smaller nanodispersions with narrow particle sizes. Even so, after 14 days of storage, it rarely contributes to nanodispersion's surface charge or particle growth. Early precipitation of Ganoderic acid can be initiated by the movement of ethanol from the center of primary nanodroplets, which can be easily controlled within a boundary guided by a mixture of surfactant molecules. All the responses show statistical significance (p<0.05) for the choice of surfactant; however, the concentration of the surfactant appears to play a minor role in determining the particle's physical characteristics. The temperature gradient is the second most influential factor in this study. In this case, the high evaporation temperature of 50 °C could result in a substantial reduction in particle size due to the higher rate of solvent evaporation without destroying the formation of nanodispersions. Thus, the significance of each control variable in the formation of drug-loaded nanodispersions induced by chemical instability via solvent transport can be summarised in the following order: HLB number > evaporation temperature > Ganoderic acid (1%) concentration > surfactant concentration > evaporation duration.
3.3. Particle size distribution
Efficacious delivery of water-insoluble therapeutic substances can be achieved using the finest drug-loaded nanodispersions. For example, nanoparticles used for intravascular delivery should have a particle size no larger than 1 µm to prevent capillaries from becoming occluded in blood capillaries with a diameter of 4-7 µm. The prepared formulation must also be biocompatible, biodegradable, and sterile. According to the protocol above, Ganoderic acid-loaded nanodispersions are produced by intensively evaporating the solvent.
It can be seen in
Figure 3(a) that a decrease in evaporation temperature leads to the formation of nanodispersions with larger particle sizes; a reduction in evaporation duration can also result in larger particles, particularly when the formulation HLB number is low. A longer evaporating duration has no significant effect on particle size when the formulation's HLB number approaches a value of 12.04. In contrast, a lower HLB number may result in a greater reduction in particle size. Increasing the HLB number generally leads to smaller nanodispersions when the surfactant concentration is low. This is particularly true when the concentration of surfactant is low. When determining particle size, the ethanol concentration in the formulation showed the least impact. A higher diffusion rate of ethanol and satisfactory solvent removal during evaporation makes it advantageous to encapsulate more Ganoderic acid in the hydrophobic core without distinctly affecting the volume of the nanocarriers.
Similar results were observed when the polydispersity index of nanodispersions was considered. The polydispersity index describes the distribution of particle sizes within a medium. As a result, nanoparticulates with low polydispersity can ensure a consistent drug loading at the target site. As a result, the particle's surface active energy gradient is also reduced, significantly decreasing the ripening effect among tiny solid particles.
Figure 3(b) shows several saddle-like surfaces. A longer evaporation duration has been observed to result in a lower nanodispersion and a higher polydispersity index. By attaching amphiphilic molecules to the particle's surface, surfactants facilitate the detachment of the hydrophobic core. The surfactant concentration increases steadily, resulting in a steady nanodispersion; however, when a critical surfactant aggregation number was reached, micelles could no longer adsorb surfactant molecules, and therefore there was no change in the physical characteristics.
3.4. Physical stability
High surface area dispersions enhance dissolution rates and bioavailability. Following the reported findings, nanodispersions must be chemically or physically stabilised to ensure satisfactory drug delivery before reaching the targeted therapeutic area. Zeta potential is the electrokinetic potential on the particle surface, which greatly influences either an attractive or repulsive force between the particles, profoundly influencing the colloid's rheological behaviour. According to the response surface methodology, the linear terms of HLB number (X1), surfactant concentration (X3), and evaporation temperature (X4), and the quadratic terms of HLB number and evaporation temperature (X4) have significant effects on nanodispersion's zeta-potential, which have P-values of 0.0001, 0.0031, 0.0256, 0.0001 and 0.0042, respectively.
It can be seen from
Figure 3(c) that the HLB number of the formulation plays a dominant role in determining the zeta potential of nanodispersions. By increasing the formulation's HLB number, the zeta potential approaches zero. Theoretically, particles aggregate and coalesce at zeta potentials below 40 mV. Controlling the particles' growth for two weeks was possible by modifying the formulation composition and preparation conditions extensively. When the HLB number and evaporation temperature were at their maximum, a maximum increase in particle growth of 15% was observed. A relatively higher particle growth rate is obtained from nanodispersions prepared from micelles with a high ethanol content; up to 30% growth was measured for formulations with higher HLB numbers and higher evaporation temperatures. Further, varying the surfactant concentration and evaporation duration did not significantly affect the growth of the particles.
3.5. Optimisation of Ganoderic acid-loaded nanodispersions
Based on the desirability function, a multi-objective optimisation strategy can be described as transforming the predicted values of the response variables into a desirability value d
j, where 0≤d
i≤1; as shown below, increasing di indicates a more desirable response.
Simulation results indicate that the optimal solution in this study has a desirability of 0.624. After 25 min of solvent evaporation at 50 °C, nanodispersions formulated with 5% surfactant (Brij 56 and Span 20 weighted at three to seven) and 50% Ganoderic acid solution were estimated to have particle sizes, polydispersity indexes, zeta-potentials, and percentage increases in zeta-averages to be 126.01, 0.292, -51.11, and 0.2013, respectively after two weeks of storage. Verification of the proposed optimum solution, which is acceptable, was employed, as represented in Table 4. The repeated experiments have confirmed a good agreement, as described using Equation 4. For the response variables of particle size, polydispersity index, zeta-potential, and percentage increase in zeta-average after two weeks of storage, high accuracy was achieved, namely 97.57%, 98.97%, 89.81%, and 81.27%, respectively.
Table 3.
RSM prediction accuracy.
Table 3.
RSM prediction accuracy.
| Response Variable |
Predicted Value |
Experimental Value |
Accuracy (%) |
| Y1: Particle Size |
126.01 |
129.07 |
97.57% |
| Y2: Polydispersity Index |
0.292 |
0.289 |
98.97% |
| Y3: Zeta Potential |
-51.11 |
-45.9 |
89.81% |
| Y4: % increase in Zeta Average after 2 weeks of storage |
0.2013 |
0.239 |
81.27% |
In short, a more desirable formulation could be achieved if (1) the preparation is carried out using a surfactant mixture of Brij 56 and Span 20 in a weight ratio of 3:7, (2) the evaporation temperature applied is as high as possible, and (3) Ganoderic acid concentrations are maintained at a high level in order to maximise drug loading and to improve the integration of the hydrophobic core with the stabiliser barrier. Although evaporation duration and surfactant concentration are assumed to be insignificant process variables, it is always recommended to minimise energy consumption as well as formulation toxicity by reducing evaporation duration and surfactant concentration.
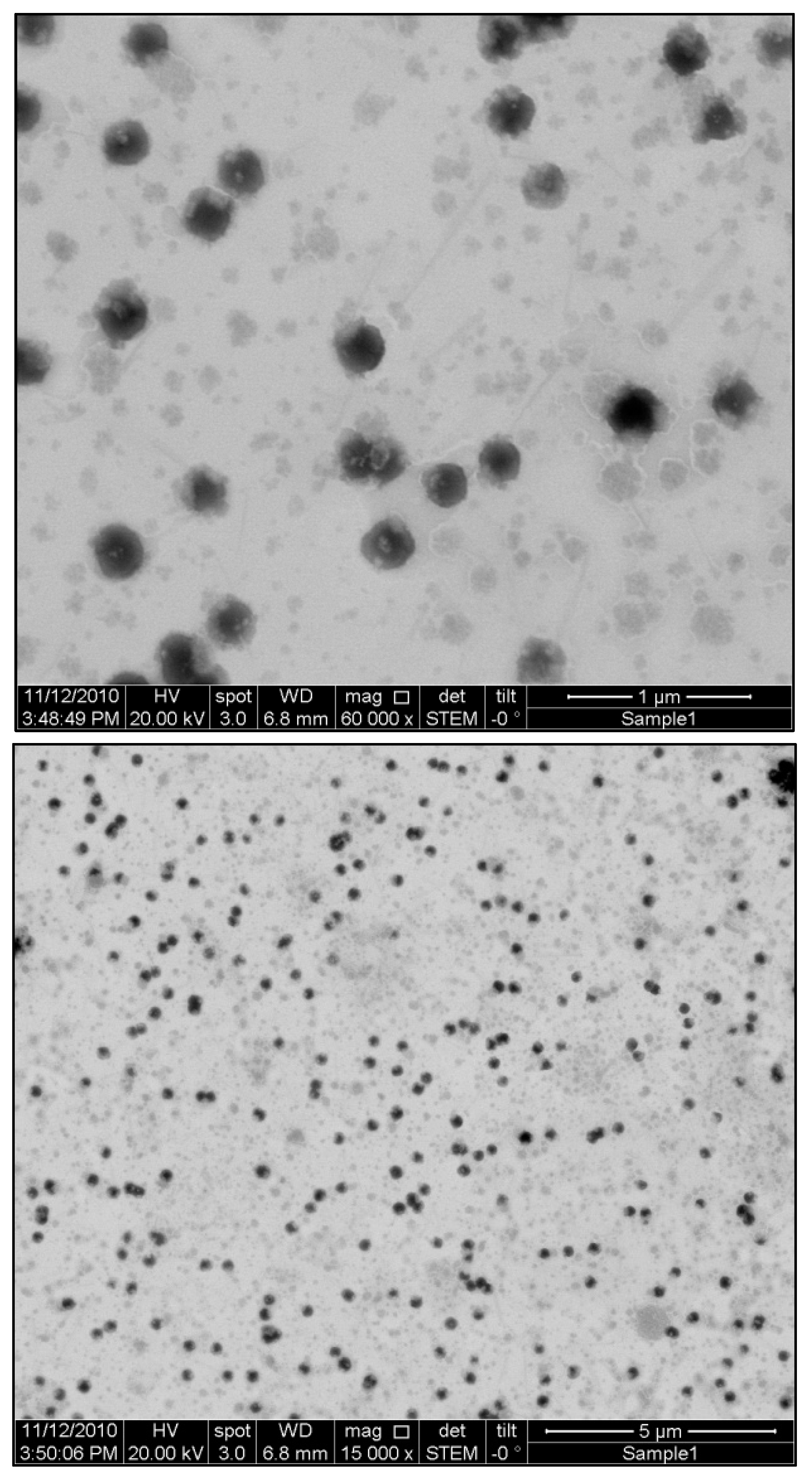
3.6. STEM Imaging
Using Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FESEM) in Scanning-Transmission Electron Microscopy (STEM) mode, we examined the surface morphology of Ganoderic acid-loaded nanodispersions. A picture of the optimal formulation of Ganoderic acid nanodispersion, as suggested by RSM, is illustrated in
Figure 4. Particles of nanodispersion appear to be spherical, with a diameter of no more than 200 nm and a very narrow particle distribution. The Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) technique results are consistent with the previous particle size measurements.
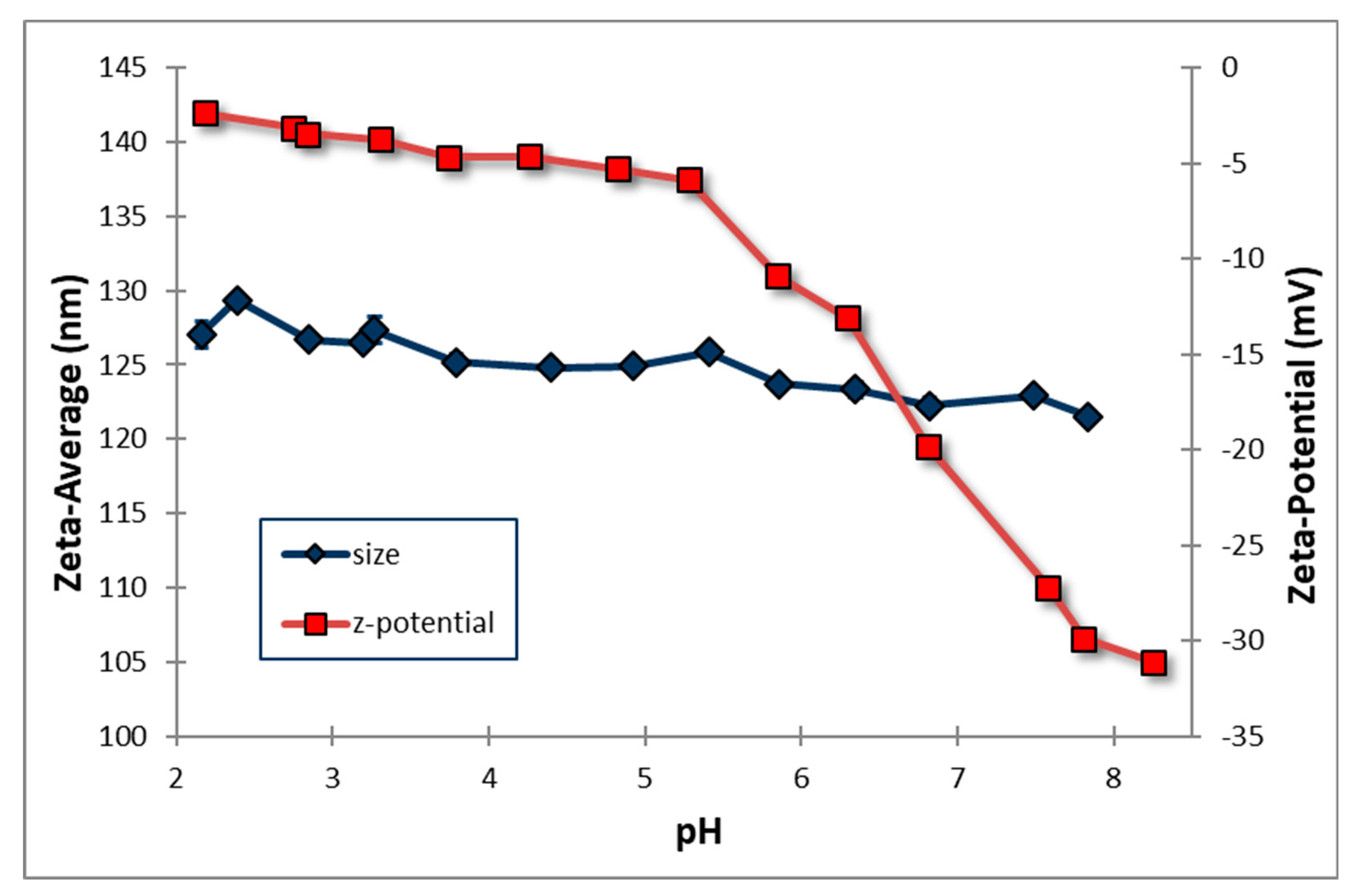
3.7. Effect of pH on the particle’s zeta average and zeta potential
As shown in
Figure 5, pH plays an important role in determining the zeta average and zeta potential of the particles of nanodispersion formulations. Increasing the pH of the solution instantly decreases the particle's zeta average; however, the intensity of the reduction seems to be very limited. When the solution pH changes from acid to alkaline, the zeta potential gradually decreases; however, when the pH reaches 5, a sudden decrease in the zeta potential occurs. Regarding zeta potential, the effective surface charge of particles determines their dispersion behaviour. As almost all particles contain surface species or functional groups that cause them to act as acids or bases, this effective surface charge can also be modified by pH. Particle stability is generally attributed to the negative charge on the particle surface. The electrostatic repulsion between the particles has been widely reported as providing a higher energy barrier against coalescence. Specifically, Ganoderic acid-loaded nanodispersions showed a lower negative zeta potential value (-3 mV to -31 mV) with a narrow particle size distribution. Under room conditions, they demonstrated excellent stability with minimal aggregation.
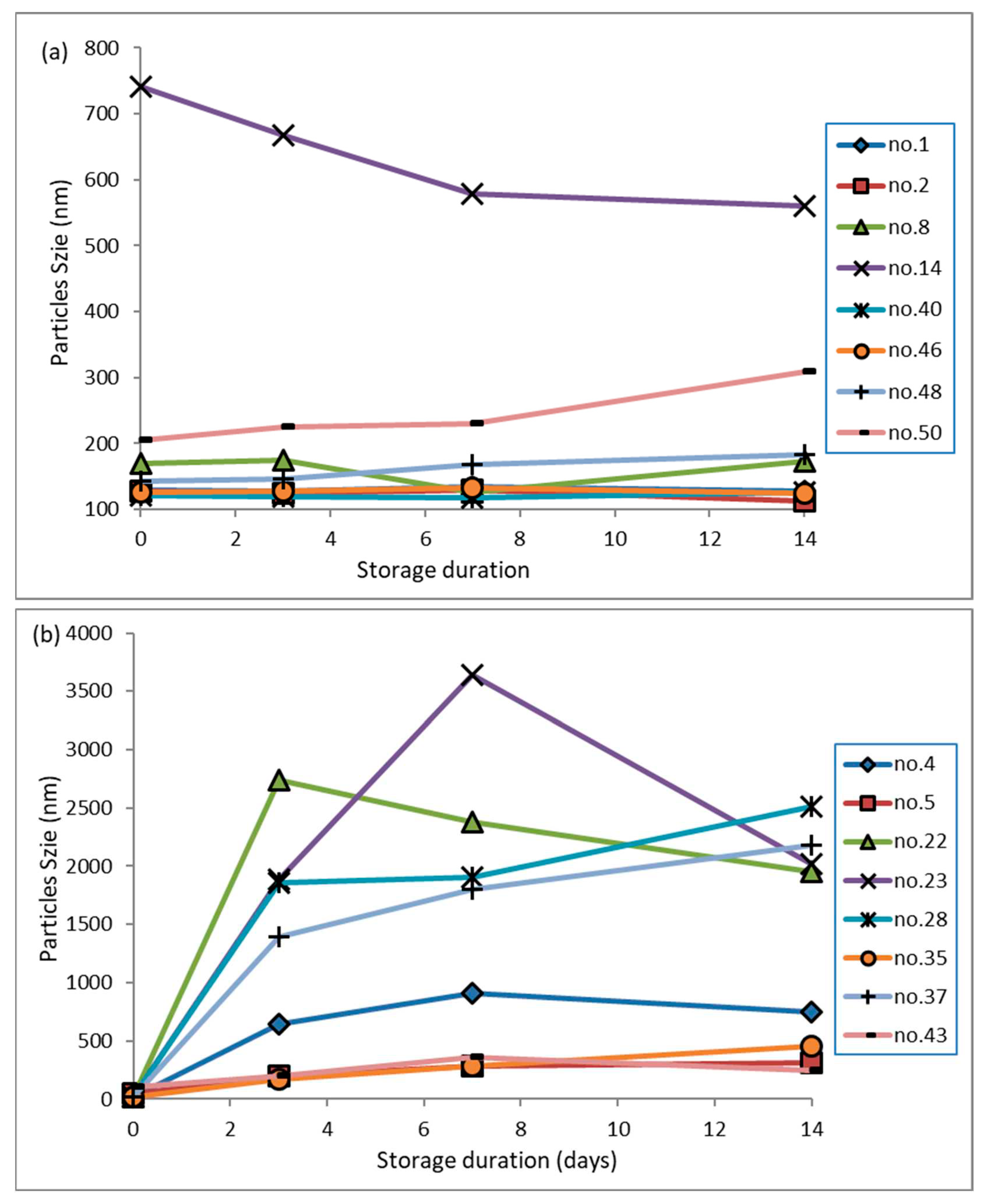
3.8. Stability during storage for 14 days
The physical stability of nanodispersions was evaluated based on particle size distribution over 14 days.
Figure 6(a) and 6(b) illustrate nanodispersions stabilised by surfactants with HLB numbers of 9.46 and 12.04, respectively. It has been found that the surfactant's HLB number has a predominant influence on particle growth. The nanodispersion formulated with a surfactant with a low HLB number (9.46) can moderately control particle growth over 14 days. In contrast, the nanodispersion generated using a surfactant with a higher HLB number (12.04) induces intense instability, resulting in an aggressive growth of up to 10 fold, observed after three days of storage. Additionally, it has been demonstrated that smaller particles have a superior ability to reduce particle growth. Smaller particles are more susceptible to Brownian motion; therefore, it is less likely that a group of such particles will adhere together. However, a restrained particle growth rate was observed for some of the nanodispersions (RSM runs 1, 8, 48 and 50 shown in
Figure 6(a)). A higher evaporating temperature during solvent evaporation could have caused satisfactory ethanol removal. As the residual ethanol left behind during evaporation is not removed sufficiently, it may diffuse from the hydrophobic core during storage, resulting in the size reduction of nanodispersions.
It could be noticed from
Figure 6(b) that nanodispersions obtained from micelles containing a lower amount of ethanol (organic core) are more susceptible to particle growth than others. A remarkable size increment has been observed in the RSM runs 22, 27 and 28, possibly due to a looser assembly of the drug hydrophobic core and stabiliser barrier, which has led particles to grow up to 10-fold in the first three days. As a result of the surface energy gradient of the smaller particles, molecules from such an assembly of hydrophobic drug cores and stabiliser barriers flow freely from one particle to another. Finally, this phenomenon contributes to the growth rate of larger particles. However, the growth rate of the particles was reduced once they had grown beyond 1500 nm.
4. Conclusion
Ganoderic acid-loaded nanodispersions can be produced using ultrasound and solvent evaporation techniques, an alternative to conventional methods. By developing the quadratic response function, we were able to determine the importance of each process variable and optimise the process conditions so that nanodispersions would possess favorable physical properties, namely a smaller particle size, a low polydispersity index, a high negative zeta potential, and a slow particle growth rate. According to the simulation results, a good formulation should have a low surfactant concentration and an HLB number of at least 10. Higher evaporation temperatures have been found to encourage the formation of nanodispersions with smaller particle sizes. At the same time, the micellar system's organic phase determines the particles' stability. Microscopy images revealed that the optimised Ganoderic acid-loaded nanodispersions displayed spherical morphology and narrow particle size distributions. The particle size distribution profile was not affected by the pH of the solution in general.
Author Contributions
Data curation, original draft preparation, writing revisions, editing, visualisation, W.K.C., and K.W.T.; resources and review, P.G.C., C.H.P., Y.T. and S.Y.T.; supervision and project administration, as well as review, S.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was conducted under the project “Novel Strategy of Ultrasonic Cavitation for the Generation of Nanoemulsions and Nanosuspensions in Pharmaceutical Preparations”. The financial assistance (Grant No. M0025.54.01) supported by the Ministry of Science, Technology and Innovation (MOSTI) and the Xiamen University Malaysia Research Fund (XMUMRF/2022-C10/IENG/0048) is gratefully acknowledged by the authors. A special acknowledgement to University of Nottingham as well as Andrew Yakin Sinit for his help in developing a distinct technique to capture the images of liquid nanodispersions with Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FESEM). .
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the study's design; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Li, Y.Q.; Wang, S.F. Anti-hepatitis B activities of ganoderic acid from Ganoderma lucidum. Biotechnol. Lett. 2006, 28, 837–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabir, Y.; Kimura, S.; Tamura, T. Dietary effect of Ganoderma lucidum mushroom on blood pressure and lipid levels in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR). J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 1988, 34, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Y.; Hsu, M.L.; Hsu, H.C.; Tzeng, C.H.; Lee, S.S.; Shiao, M.S.; Ho, C.K. The anti-tumor effect of Ganoderma lucidum is mediated by cytokines released from activated macrophages and T lymphocytes. Int. J. Cancer 1997, 70, 699–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhao, J.; Liu, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhong, J.J.; Tang, W. Enhancement of IL-2 and IFN-γ expression and NK cells activity involved in the anti-tumor effect of ganoderic acid Me in vivo. Int. Immunopharm. 2007, 7, 864–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, H.H.; Hung, C.F.; Wang, J.P.; Lin, C.N. Anti-inflammatory triterpenoids and steroids from Ganoderma lucidum and Ganoderma tsugae. Phytochem. 2008, 69, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Ma, C.M.; Hattori, M. Synthesis of dammarane-type triterpene derivatives and their ability to inhibit HIV and HCV proteases. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 3003–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Grieb, B.; Thyagarajan, A.; Sliva, D. Ganoderic acids suppress growth and invasive behavior of breast cancer cells by modulating AP-1 ad NF-kappaB signaling. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2008, 21, 577–584. [Google Scholar]
- Akers, M.J. Excipient-drug interactions in parenteral formulations. J. Pharm. Sci. 2002, 91, 2283–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krzyzaniak, J.F.; Raymond, D.M.; Yalkowsky, S.H. Lysis of human red blood cells 2: effect of contact time on cosolvent induced hemolysis. Int. J. Pharm. 1997, 152, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Y.W.; Huang, M.T.; Ho, C.T.; Huang, Q. Enhancing anti-inflammation activity of curcumin through O/W nanoemulsions. Food Chem. 2008, 108, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakulku, U.; Nuchuchua, O.; Uawongyart, N.; Puttipipatkhachorn, S.; Soottitantawat, A.; Ruktanonchai, U. Characterisation and mosquito repellent activity of citronella oil nanoemulsion. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 372, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, Y.B.; Toti, U.S.; Khadir, A.; Ma, L.; Panyam, J. Single-step surface functionalisation of polymeric nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Zhuang, C.; Wang, M.; Sun, X.; Nie, S.; Pan, W. Liposome coated with low molecular weight chitosan and its potential use in ocular drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 379, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anada, T.; Takeda, Y.; Honda, Y.; Sakurai, K.; Suzuki, O. Synthesis of calcium phosphate-binding liposome for drug delivery. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 4148–4150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, B.S.; Nakamura, N.; Miyashiro, H.; Bae, K.W.; Hattori, M. Triterpenes from the spores of Ganoderma lucidum and their inhibitory activity against HIV-1 protease. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1998, 46, 1607–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, B.S.; Gao, J.J.; Nakamura, N.; Hattori, M. Triterpenes from the spores of Ganoderma lucidum and their cytotoxicity against meth-A and LLC tumor cells. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2000, 48, 1026–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, S.K.; Law, C.L.; Cheng, P.G. Effect of drying on crude ganoderic acids and water-soluble polysaccharides content in Ganoderma lucidum. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 3, 38–43. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, C.P.; Nakajima, M. Effect of polyglycerol esters of fatty acids on physicochemical properties and stability of β-carotene nanodispersions prepared by emulsification/evaporation method. J. Sci. Food Agri. 2005, 85, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.P.; Nakajima, M. β-Carotene nanodispersions: preparation, characterisation and stability evaluation. Food Chem. 2005, 92, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheong, J.N.; Tan, C.P.; Man, Y.B.C.; Misran, M. α-Tocopherol nanodispersions: Preparation, characterisation and stability evaluation. J. Food Engg. 2008, 89, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anarjan, N.; Mirhosseini, H.; Baharin, B.S.; Tan, C.P. Effect of processing conditions on physicochemical properties of astaxanthin nanodispersions. Food Chem. 2010, 123, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anarjan, N.; Mirhosseini, H.; Baharin, B.S.; Tan, C.P. Effect of processing conditions on physicochemical properties of sodium caseinate-stabilised astaxanthin nanodispersions. LWT - Food Sci. Tech. 2011, 44, 1658–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, W.F.; Man, Y.B.C.; Lai, O.M.; Long, K.; Nakajima, M.; Tan, C.P. Effect of sucrose fatty acid esters on the particle characteristics and flow properties of phytosterol nanodispersions. J. Food Engg. 2011, 104, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, H.S.; Chu, B.S.; Ichikawa, S.; Nakajima, M. Preparation of nanodispersions containing β-carotene by solvent displacement method. Food Hydrocoll. 2008, 22, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Shukla, D.; Vuddanda, P.R.; Mishra, B.; Singh, S. Utilisation of adsorption technique in the development of oral delivery system of lipid based nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 81, 563–569. [Google Scholar]
- Margulis-Goshen, K.; Netivi, H.D.; Major, D.T.; Gradzielski, M.; Raviv, U.; Magdassi, S. Formation of organic nanoparticles from volatile microemulsions. J. Coll. Interface. Sci. 2010, 342, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffazick, S.R.; Pohlmann, A.R.; Dalla-Costa, T.; Guterres, S.S. Freeze-drying polymeric colloidal suspensions: nanocapsules, nanospheres and nanodispersion. A comparative study. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2003, 56, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra, M.A.; Santelli, R.E.; Oliveira, E.P.; Villar, L.S.; Escaleira, L.A. Response surface methodology (RSM) as a tool for optimisation in analytical chemistry. Talanta 2008, 76, 965–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).