Submitted:
31 March 2023
Posted:
03 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fly stocks and genetics
2.2. Expression of tagged remodelers by using UAS/Gal4 system
2.3. Cytological analyses and Immunofluorescence
2.4. Statistical Analysis
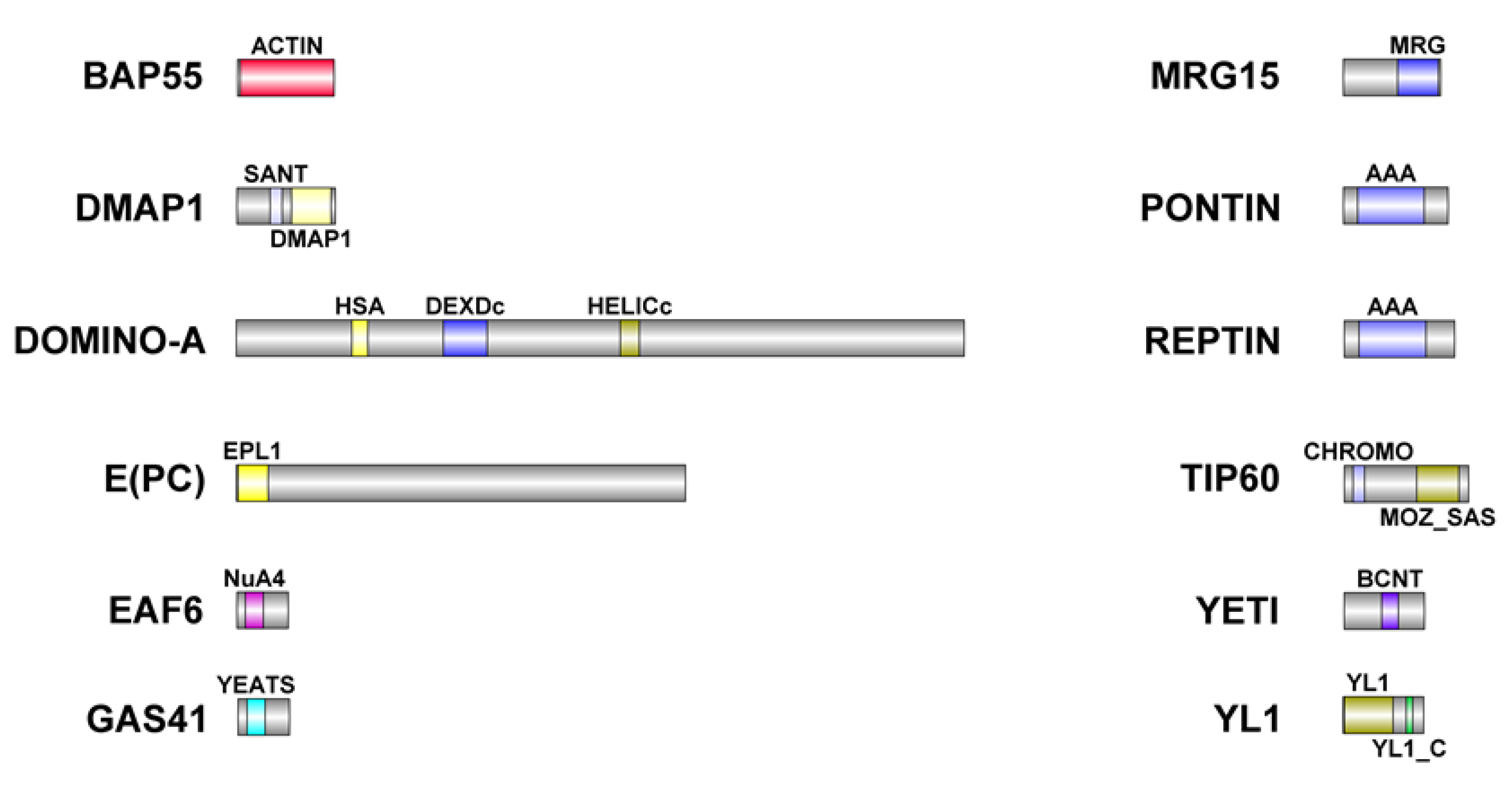
2.5. Bioinformatic analysis
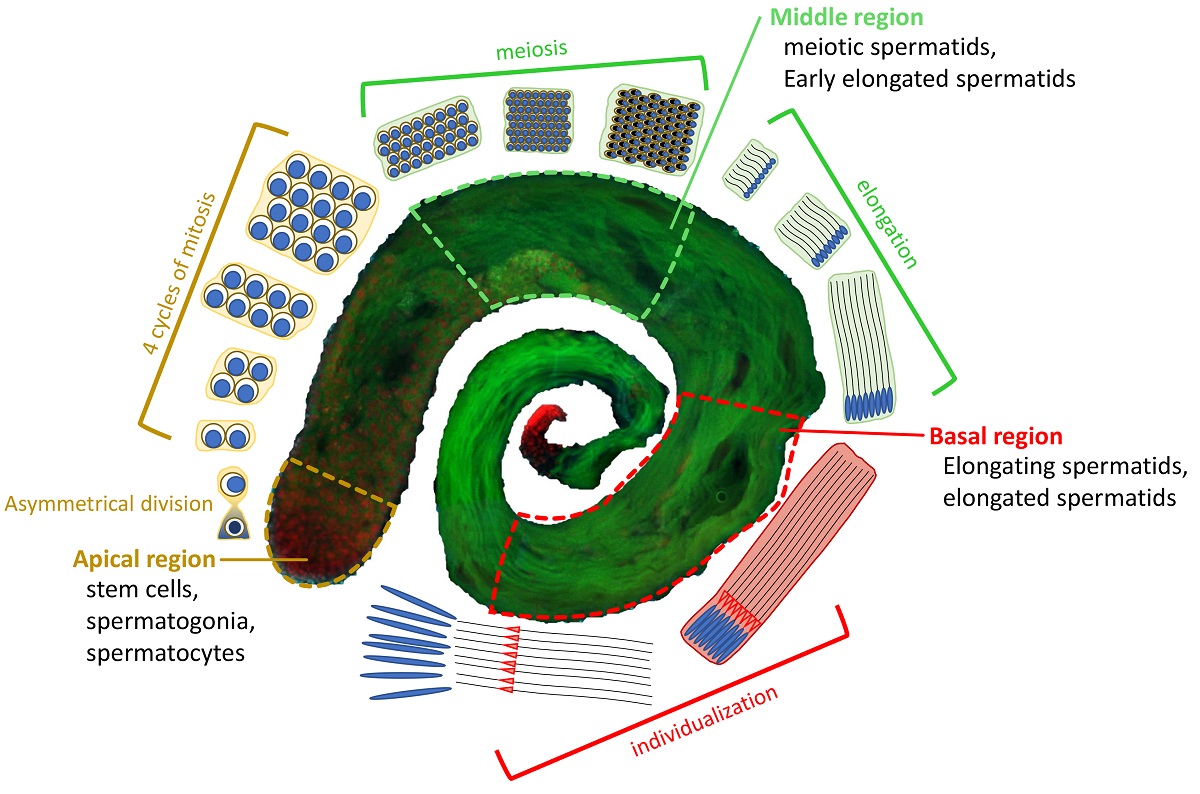
3. Results
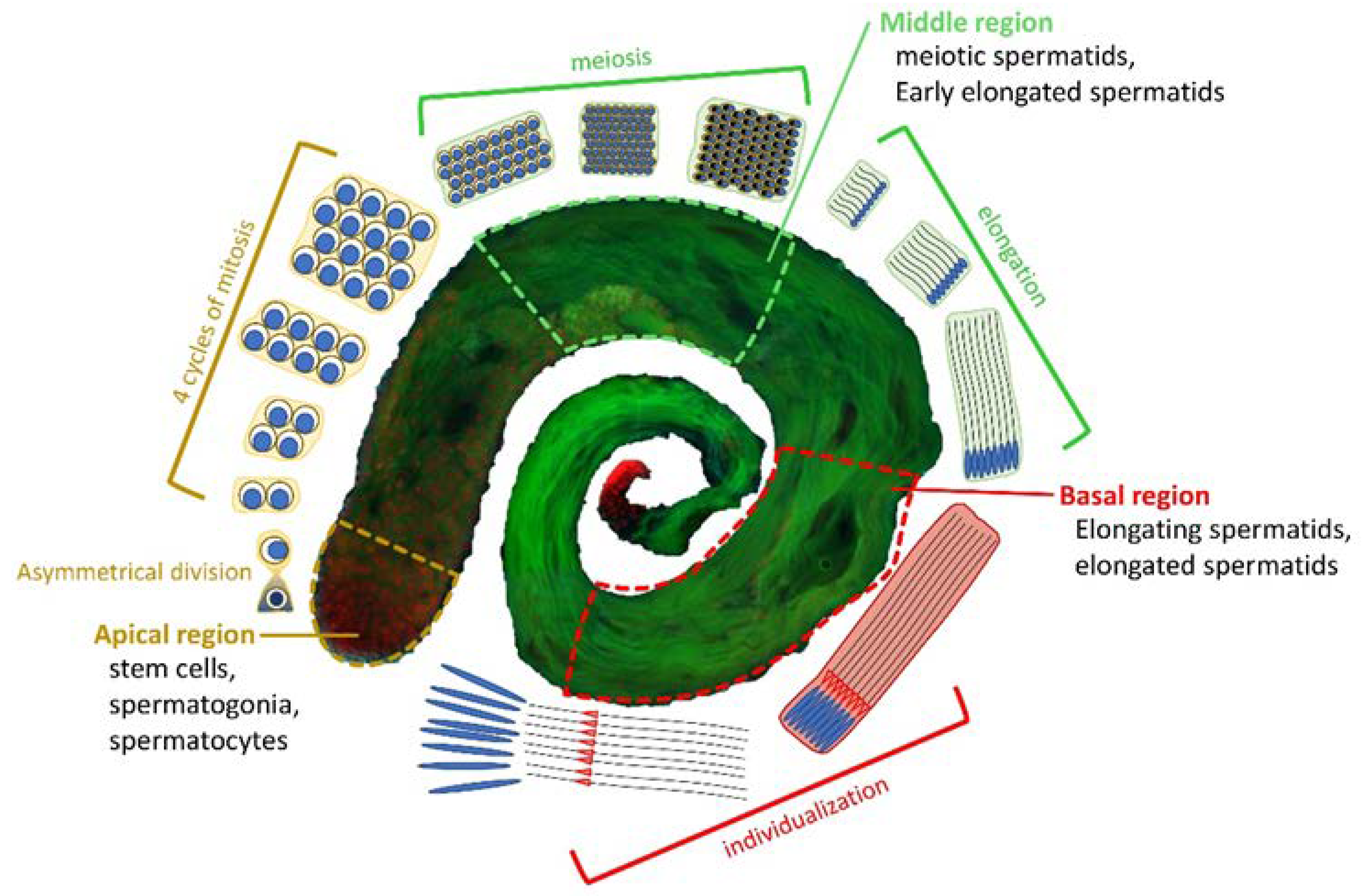
3.1. The subunits of DOM/TIP60 chromatin remodeling complex localize to the meiotic apparatus
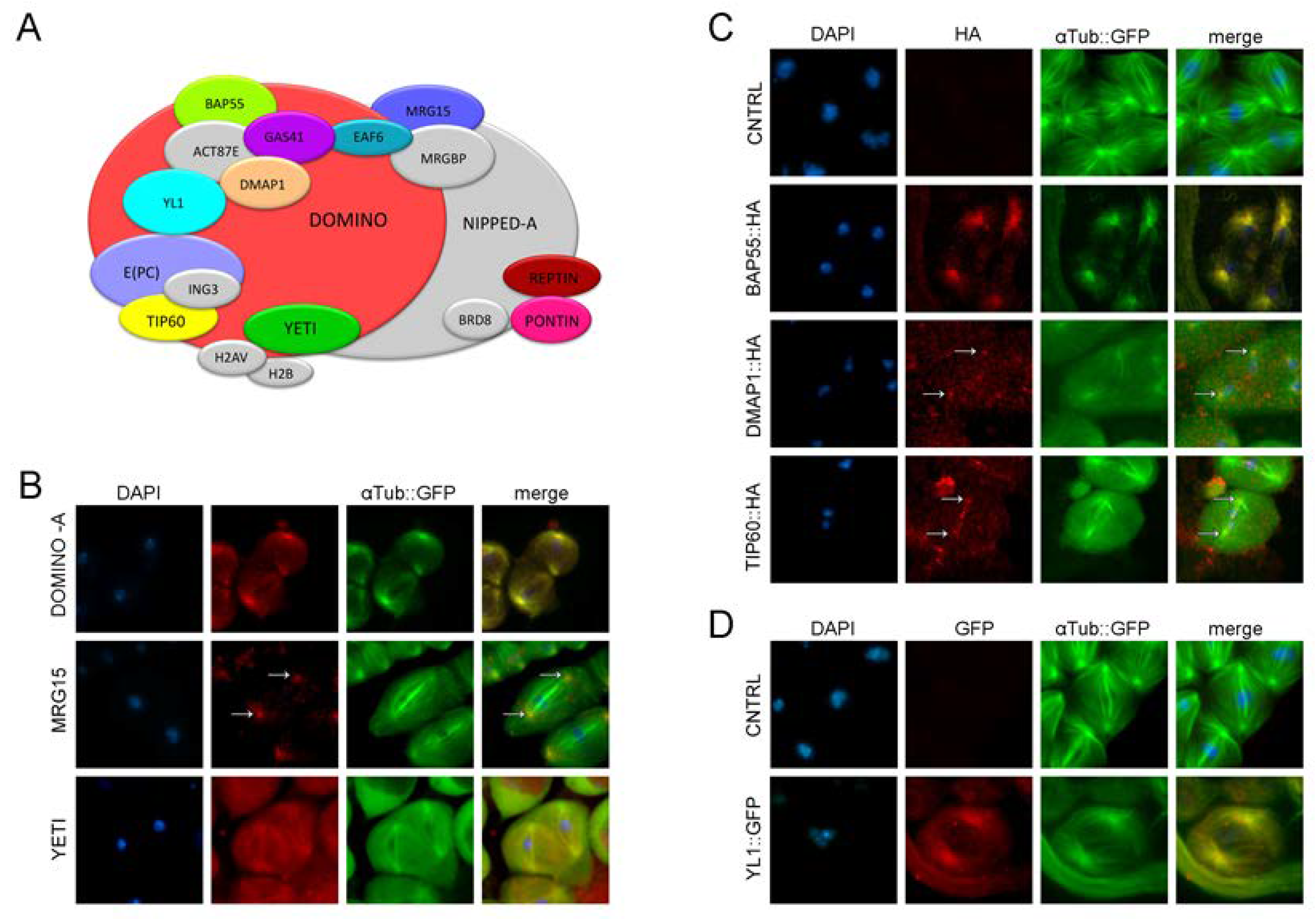
3.2. RNAi depletion of DOM/TIP60 complex subunits
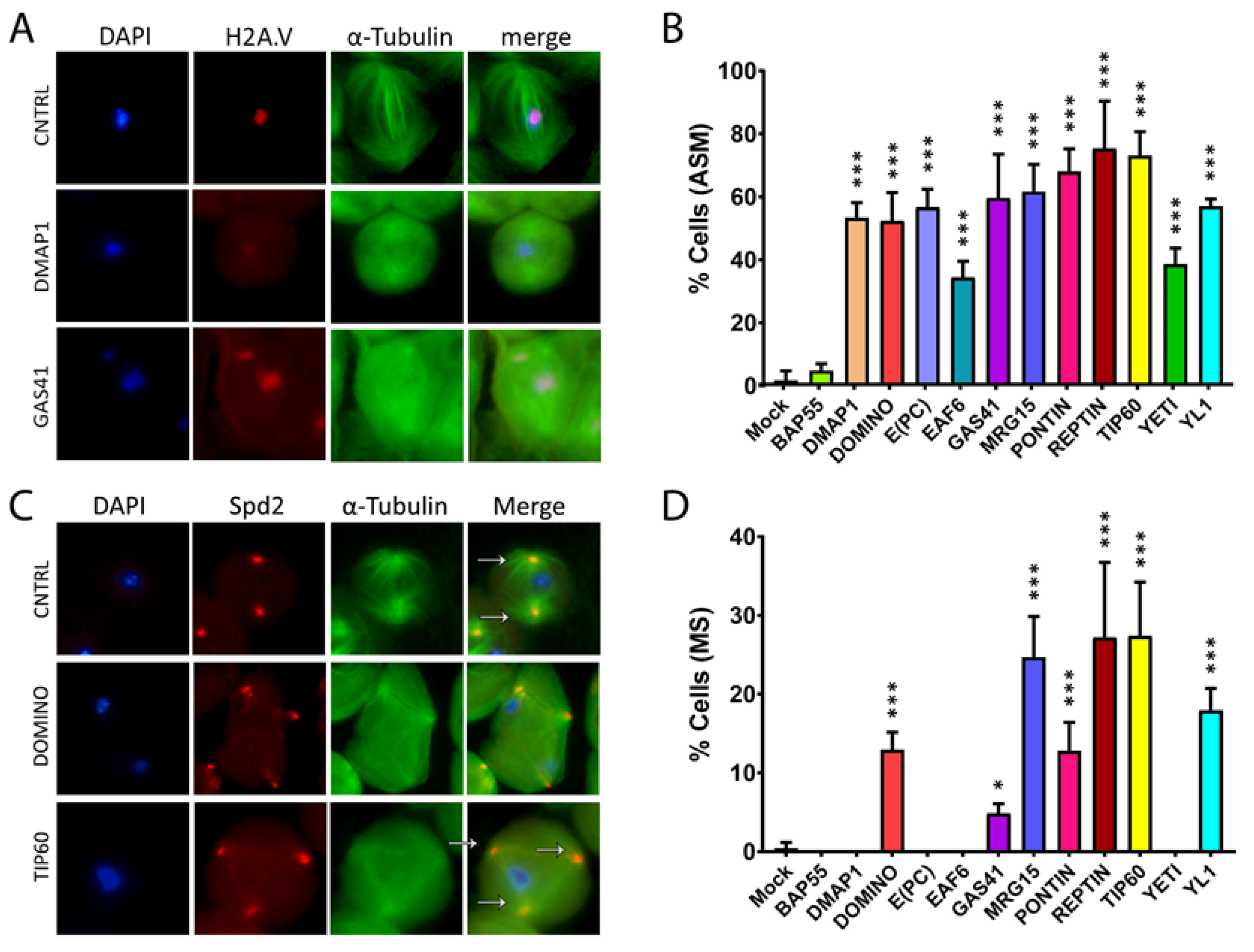
3.3. RNAi-mediated depletion of TIP60 subunits affects spindle integrity
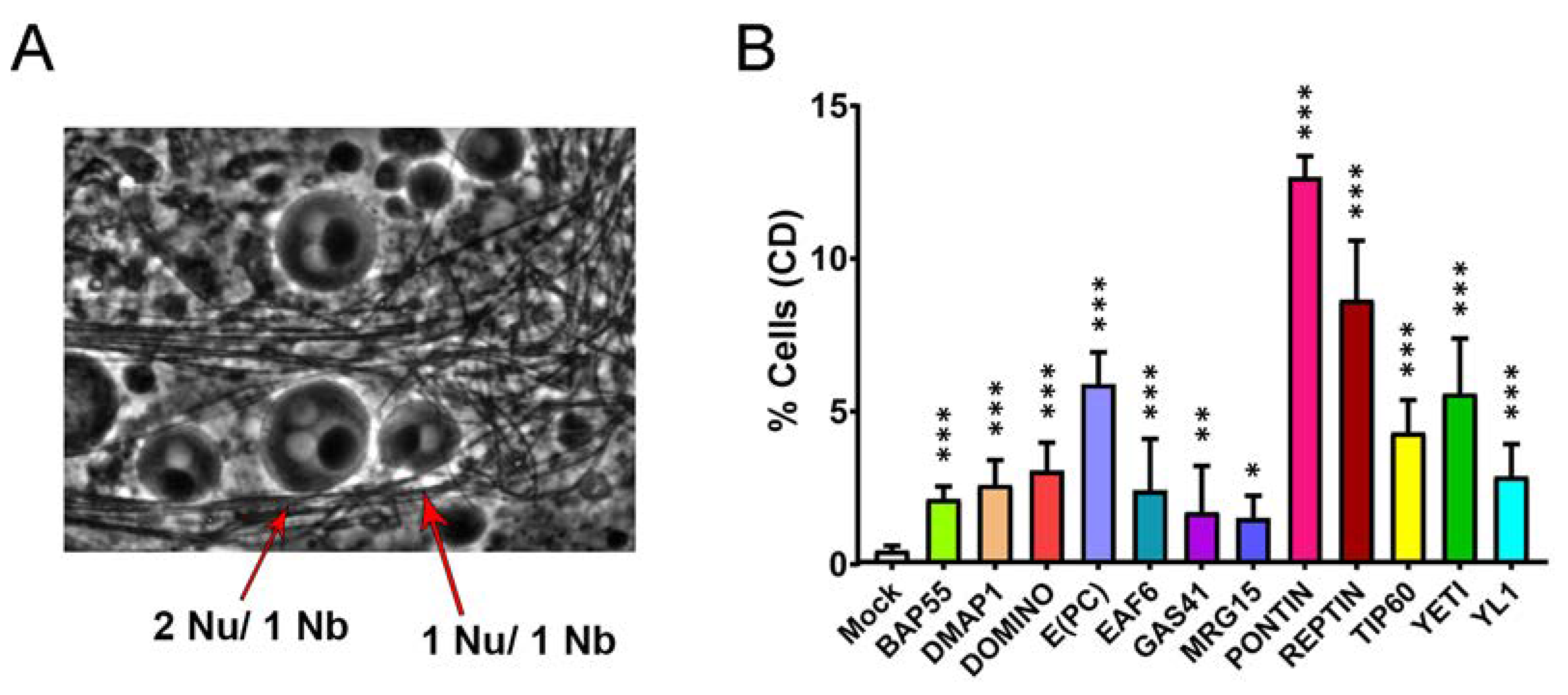
3.4. Cytokinesis Defects
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clapier, C.R.; Cairns, B.R. The biology of chromatin remodeling complexes. Annual review of biochemistry 2009, 78, 273–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yodh, J. ATP-Dependent Chromatin Remodeling. Advances in experimental medicine and biology 2013, 767, 263–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, M.; Demajo, S.; Jain, P.; Di Croce, L. Combinatorial assembly and function of chromatin regulatory complexes. Epigenomics 2011, 3, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prozzillo, Y.; Cuticone, S.; Ferreri, D.; Fattorini, G.; Messina, G.; Dimitri, P. In Vivo Silencing of Genes Coding for dTip60 Chromatin Remodeling Complex Subunits Affects Polytene Chromosome Organization and Proper Development in Drosophila melanogaster. International journal of molecular sciences 2021, 22, 4525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusch, T.; Florens, L.; Macdonald, W.H.; Swanson, S.K.; Glaser, R.L.; Yates, J.R., 3rd; Abmayr, S.M.; Washburn, M.P.; Workman, J.L. Acetylation by Tip60 is required for selective histone variant exchange at DNA lesions. Science 2004, 306, 2084–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuguchi, G.; Shen, X.; Landry, J.; Wu, W.H.; Sen, S.; Wu, C. ATP-driven exchange of histone H2AZ variant catalyzed by SWR1 chromatin remodeling complex. Science 2004, 303, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keogh, M.C.; Mennella, T.A.; Sawa, C.; Berthelet, S.; Krogan, N.J.; Wolek, A.; Podolny, V.; Carpenter, L.R.; Greenblatt, J.F.; Baetz, K.; et al. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae histone H2A variant Htz1 is acetylated by NuA4. Genes Dev 2006, 20, 660–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, L.; Lambert, J.P.; Gerdes, M.; Al-Madhoun, A.S.; Skerjanc, I.S.; Figeys, D.; Baetz, K. Functional dissection of the NuA4 histone acetyltransferase reveals its role as a genetic hub and that Eaf1 is essential for complex integrity. Mol Cell Biol 2008, 28, 2244–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morillo Prado, J.R.; Srinivasan, S.; Fuller, M.T. The histone variant His2Av is required for adult stem cell maintenance in the Drosophila testis. PLoS Genet 2013, 9, e1003903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borner, K.; Becker, P.B. Splice variants of the SWR1-type nucleosome remodeling factor Domino have distinct functions during Drosophila melanogaster oogenesis. Development 2016, 143, 3154–3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, G.; Damia, E.; Fanti, L.; Atterrato, M.T.; Celauro, E.; Mariotti, F.R.; Accardo, M.C.; Walther, M.; Verni, F.; Picchioni, D.; et al. Yeti, an essential Drosophila melanogaster gene, encodes a protein required for chromatin organization. J Cell Sci 2014, 127, 2577–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prozzillo, Y.; Delle Monache, F.; Ferreri, D.; Cuticone, S.; Dimitri, P.; Messina, G. The True Story of Yeti, the "Abominable" Heterochromatic Gene of Drosophila melanogaster. Frontiers in physiology 2019, 10, 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messina, G.; Celauro, E.; Atterrato, M.T.; Giordano, E.; Iwashita, S.; Dimitri, P. The Bucentaur (BCNT) protein family: a long-neglected class of essential proteins required for chromatin/chromosome organization and function. Chromosoma 2015, 124, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messina, G.; Prozzillo, Y.; Delle Monache, F.; Santopietro, M.V.; Atterrato, M.T.; Dimitri, P. The ATPase SRCAP is associated with the mitotic apparatus, uncovering novel molecular aspects of Floating-Harbor syndrome. BMC Biol 2021, 19, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messina, G.; Prozzillo, Y.; Monache, F.D.; Santopietro, M.V.; Dimitri, P. Evolutionary conserved relocation of chromatin remodeling complexes to the mitotic apparatus. BMC Biol 2022, 20, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messina, G.; Prozzillo, Y.; Bizzochi, G.; Marsano, R.M.; Dimitri, P. The Green Valley of Drosophila melanogaster Constitutive Heterochromatin: Protein-Coding Genes Involved in Cell Division Control. 2022, 11, 3058. [Google Scholar]
- Messina, G.; Celauro, E.; Marsano, R.M.; Prozzillo, Y.; Dimitri, P. Epigenetic Silencing of P-Element Reporter Genes Induced by Transcriptionally Active Domains of Constitutive Heterochromatin in Drosophila melanogaster. 2023, 14, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsano, R.M.; Giordano, E.; Messina, G.; Dimitri, P. A New Portrait of Constitutive Heterochromatin: Lessons from Drosophila melanogaster. Trends Genet 2019, 35, 615–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gartner, W.; Rossbacher, J.; Zierhut, B.; Daneva, T.; Base, W.; Weissel, M.; Waldhausl, W.; Pasternack, M.S.; Wagner, L. The ATP-dependent helicase RUVBL1/TIP49a associates with tubulin during mitosis. Cell motility and the cytoskeleton 2003, 56, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigala, B.; Edwards, M.; Puri, T.; Tsaneva, I.R. Relocalization of human chromatin remodeling cofactor TIP48 in mitosis. Exp Cell Res 2005, 310, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.J.; Hur, S.K.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, S.A.; Kwon, J. The human Ino80 binds to microtubule via the E-hook of tubulin: implications for the role in spindle assembly. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2011, 416, 416–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducat, D.; Kawaguchi, S.; Liu, H.; Yates, J.R., 3rd; Zheng, Y. Regulation of microtubule assembly and organization in mitosis by the AAA+ ATPase Pontin. Mol Biol Cell 2008, 19, 3097–3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.M.; Song, M.; Yang, T.Y.; Fan, R.; Liu, X.D.; Zhou, P.K. HIV-1 Tat impairs cell cycle control by targeting the Tip60, Plk1 and cyclin B1 ternary complex. Cell Cycle 2012, 11, 1217–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentili, C.; Castor, D.; Kaden, S.; Lauterbach, D.; Gysi, M.; Steigemann, P.; Gerlich, D.W.; Jiricny, J.; Ferrari, S. Chromosome Missegregation Associated with RUVBL1 Deficiency. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0133576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billmann, M.; Horn, T.; Fischer, B.; Sandmann, T.; Huber, W.; Boutros, M. A genetic interaction map of cell cycle regulators. Mol Biol Cell 2016, 27, 1397–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, G.; Atterrato, M.T.; Fanti, L.; Giordano, E.; Dimitri, P. Expression of human Cfdp1 gene in Drosophila reveals new insights into the function of the evolutionarily conserved BCNT protein family. Scientific reports 2016, 6, 25511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, G.; Atterrato, M.T.; Prozzillo, Y.; Piacentini, L.; Losada, A.; Dimitri, P. The human Cranio Facial Development Protein 1 (Cfdp1) gene encodes a protein required for the maintenance of higher-order chromatin organization. Scientific reports 2017, 7, 45022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echard, A.; Hickson, G.R.; Foley, E.; O'Farrell, P.H. Terminal cytokinesis events uncovered after an RNAi screen. Curr Biol 2004, 14, 1685–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scacchetti, A.; Schauer, T.; Reim, A.; Apostolou, Z.; Campos Sparr, A.; Krause, S.; Heun, P.; Wierer, M.; Becker, P.B. Drosophila SWR1 and NuA4 complexes are defined by DOMINO isoforms. eLife 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rust, K.; Tiwari, M.D.; Mishra, V.K.; Grawe, F.; Wodarz, A. Myc and the Tip60 chromatin remodeling complex control neuroblast maintenance and polarity in Drosophila. EMBO J 2018, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, S.L.; Hawley, R.S. Chromosome choreography: the meiotic ballet. Science 2003, 301, 785–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petronczki, M.; Siomos, M.F.; Nasmyth, K. Un menage a quatre: the molecular biology of chromosome segregation in meiosis. Cell 2003, 112, 423–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frappaolo, A.; Piergentili, R.; Giansanti, M.G. Microtubule and Actin Cytoskeletal Dynamics in Male Meiotic Cells of Drosophila melanogaster. Cells 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKee, B.D.; Yan, R.; Tsai, J.H. Meiosis in male Drosophila. Spermatogenesis 2012, 2, 167–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cenci, G.; Belloni, G.; Dimitri, P. 1(2)41Aa, a heterochromatic gene of Drosophila melanogaster, is required for mitotic and meiotic chromosome condensation. Genet Res 2003, 81, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zur Lage, P.; Stefanopoulou, P.; Styczynska-Soczka, K.; Quinn, N.; Mali, G.; von Kriegsheim, A.; Mill, P.; Jarman, A.P. Ciliary dynein motor preassembly is regulated by Wdr92 in association with HSP90 co-chaperone, R2TP. J Cell Biol 2018, 217, 2583–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Shi, Z.; Chen, X. Enhancer of polycomb coordinates multiple signaling pathways to promote both cyst and germline stem cell differentiation in the Drosophila adult testis. PLoS Genet 2017, 13, e1006571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, A.; Deiulio, A.; Martin, E.T.; Upadhyay, M.; Rangan, P. Tip60 complex promotes expression of a differentiation factor to regulate germline differentiation in female Drosophila. Mol Biol Cell 2018, 29, 2933–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Shi, Z.; Xie, J.; Ma, B.; Chen, X. Enhancer of polycomb maintains germline activity and genome integrity in Drosophila testis. Cell Death Differ 2018, 25, 1486–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldi, S.; Becker, P.B. The variant histone H2A.V of Drosophila-three roles, two guises. Chromosoma 2013, 122, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, E.F.; Pedersen, M.; Tiong, S.; White-Brown, S.K.; Paul, A.; Campbell, S.D.; McKim, K.S. Drosophila ATM and ATR have distinct activities in the regulation of meiotic DNA damage and repair. J Cell Biol 2011, 195, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bischof, J.; Bjorklund, M.; Furger, E.; Schertel, C.; Taipale, J.; Basler, K. A versatile platform for creating a comprehensive UAS-ORFeome library in Drosophila. Development 2013, 140, 2434–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischof, J.; Sheils, E.M.; Bjorklund, M.; Basler, K. Generation of a transgenic ORFeome library in Drosophila. Nat Protoc 2014, 9, 1607–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consortium, T.U. UniProt: the universal protein knowledgebase in 2021. Nucleic Acids Research 2020, 49, D480–D489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madeira, F.; Park, Y.M.; Lee, J.; Buso, N.; Gur, T.; Madhusoodanan, N.; Basutkar, P.; Tivey, A.R.N.; Potter, S.C.; Finn, R.D.; et al. The EMBL-EBI search and sequence analysis tools APIs in 2019. Nucleic Acids Res 2019, 47, W636–W641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Khedkar, S.; Bork, P. SMART: recent updates, new developments and status in 2020. Nucleic Acids Research 2020, 49, D458–D460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Wen, L.; Gao, X.; Jin, C.; Xue, Y.; Yao, X. DOG 1.0: illustrator of protein domain structures. Cell research 2009, 19, 271–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, J.B. GAL4 system in Drosophila: a fly geneticist's Swiss army knife. Genesis 2002, 34, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, D.A.; Brand, A.H. The GAL4 system : a versatile system for the expression of genes. Methods Mol Biol 2008, 420, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verni, F.; Cenci, G. The Drosophila histone variant H2A.V works in concert with HP1 to promote kinetochore-driven microtubule formation. Cell Cycle 2015, 14, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
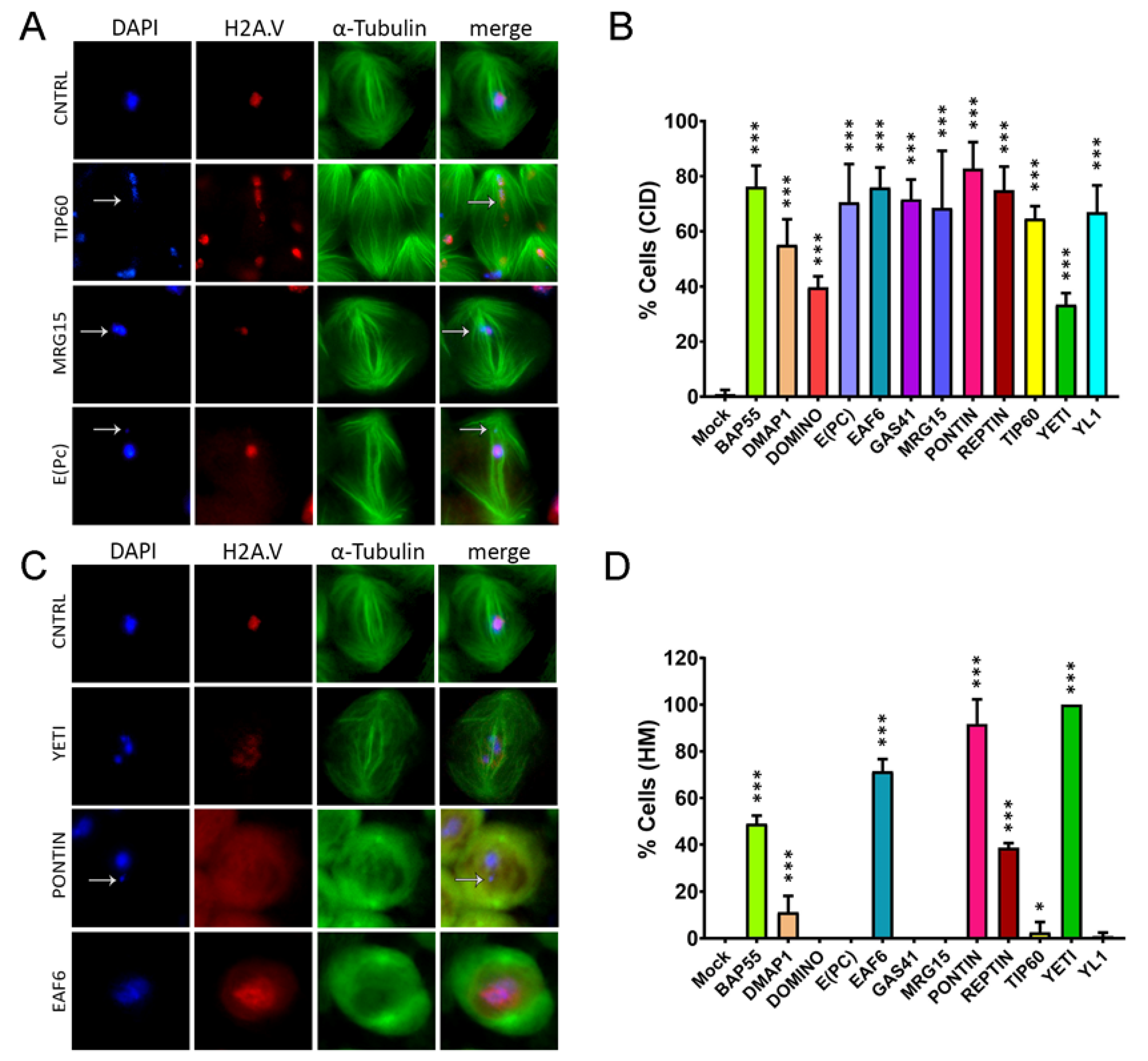
| Control. | BAP55 | DMAP1 | DOMINO | E(PC) | EAF6 | GAS41 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.90 ± 1.56 | 76.20 ± 7.64 | 55.14 ± 9.23 | 39.69 ± 4.00 | 70.47 ± 13.93 | 75.96 ± 7.20 | 71.59 ± 7.21 |
| MRG15 | PONTIN | REPTIN | TIP60 | YETI | YL1 | |
| 68.49 ± 20.73 | 82.80 ± 9.58 | 74.88 ± 8.63 | 64.63 ± 4.50 | 33.37 ± 4.23 | 66.93 ± 9.64 |
| Control | BAP55 | DMAP1 | DOMINO | E(PC) | EAF6 | GAS41 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 ± 0 | 0 ± 0 | 7.69 ± 4.44 | 0 ± 0 | 0 ± 0 | 71.41 ± 5.27 | 0 ± 0 |
| MRG15 | PONTIN | REPTIN | TIP60 | YETI | YL1 | |
| 0 ± 0 | 91.79 ± 10.47 | 38.66 ± 2.01 | 2.56 ± 4.44 | 100 ± 0 | 0.90 ± 1.56 |
| Control | BAP55 | DMAP1 | DOMINO | E(PC) | EAF6 | GAS41 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.75 ± 3.04 | 4.74 ± 2.26 | 53.42 ± 4.74 | 52.37 ± 8.98 | 56.67 ± 5.77 | 34.44 ± 5.09 | 59.60 ± 13.94 |
| MRG15 | PONTIN | REPTIN | TIP60 | YETI | YL1 | |
| 61.69 ± 8.63 | 68.14 ± 7.09 | 75.32 ± 15.10 | 73.04 ± 7.65 | 38.53 ± 5.18 | 56.98 ± 2.36 |
| Control | BAP55 | DMAP1 | DOMINO | E(PC) | EAF6 | GAS41 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.43 ± 0.74 | 0 ± 0 | 0 ± 0 | 12.93 ± 2.25 | 0 ± 0 | 0 ± 0 | 4.84 ± 1.25 |
| MRG15 | PONTIN | REPTIN | TIP60 | YETI | YL1 | |
| 24.72 ± 5.14 | 12.81 ± 3.60 | 27.18 ± 9.54 | 27.37 ± 6.88 | 0 ± 0 | 17.93 ± 2.81 |
| Control | BAP55 | DMAP1 | DOMINO | E(PC) | EAF6 | GAS41 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.44 ± 0.16 | 2.13 ± 0.41 | 2.60 ± 0.81 | 3.05 ± 0.93 | 5.89 ± 1.04 | 2.41 ± 0.63 | 1.70 ± 1.51 |
| MRG15 | PONTIN | REPTIN | TIP60 | YETI | YL1 | |
| 1.52 ± 0.72 | 12.68 ± 0.68 | 8.64 ± 1.94 | 4.31 ± 1.07 | 5.59 ± 1.80 | 2.87 ± 1.06 |
| D. melanogaster | H. sapiens | Domain | Identity (%) | Similarity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BAP55 (425aa) | ACTL6A (429aa) | ACTIN | 54 | 71,2 |
| DMAP1 (433aa) | DMAP1 (467aa) | SANT | 55,6 | 79,6 |
| DMAP1 | 47,4 | 68,6 | ||
| DOMINO-A (3198aa) | SRCAP (3230aa) | HSA | 47,2 | 72,2 |
| DEXDc | 86,1 | 93,3 | ||
| HELICc | 91,7 | 95,2 | ||
| E(PC) (1974aa) | EPC1 (834aa) | EPL1 | 1,4 | 2,8 |
| EPC2 (807aa) | EPL1 | 5,7 | 17,8 | |
| EAF6 (225aa) | MEAF6 (191aa) | NuA4 | 77,5 | 90 |
| GAS41 (227aa) | YEATS (227aa) | YEATS | 77,8 | 86,4 |
| MRG15 (424aa) | MORF4L1 (362aa) | MRG | 51,4 | 71,8 |
| Tudor-knot | 46,3 | 59,3 | ||
| PONTIN (456aa) | RUVBL1 (456aa) | AAA | 85,5 | 92,1 |
| REPTIN (481aa) | RUVBL2 (467aa) | AAA | 82,3 | 93,2 |
| TIP60 (543aa) | KAT5 (513aa) | CHROMO | 59,6 | 82,7 |
| MOZ_SAS | 81,1 | 86,5 | ||
| YETI (241aa) | CFDP1 (299aa) | BCNT | 49,3 | 76 |
| YL1 (351aa) | VPS72 (364aa) | YL1 | 46,6 | 60,2 |
| YL1_C | 50 | 70 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





