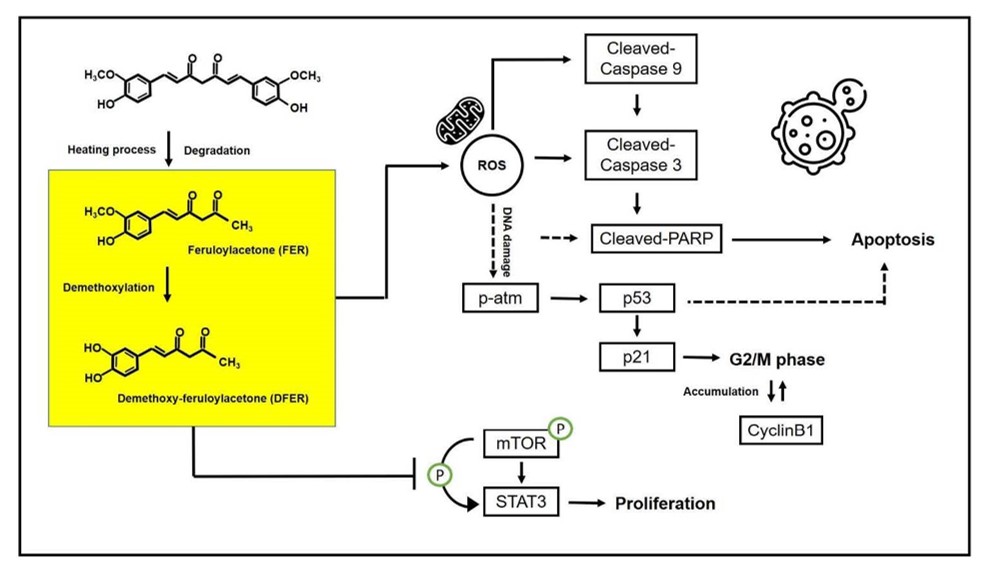
Feruloylacetone (FER) is a natural degradant of curcumin after heating, which structurally reserves some functional groups of curcumin. It is not as widely discussed as its original counterpart in previous studies and, therefore, its anti-cancer efficacy is investigated herein. This study focuses on the suppressive effect of FER on colon cancer, as the efficacious effect of curcumin on this typical cancer type has been well evidenced. In addition, demethoxy-feruloylacetone (DFER) was applied to compare the effect that might be brought on by the structural differences of the methoxy group. It was revealed that both FER and DFER inhibited the proliferation of HCT116 cells, possibly via suppression of the phosphorylated mTOR/STAT3 pathway. Notably, FER could significantly repress both the STAT3 phosphorylation and protein levels. Furthermore, both samples showed the capability of arresting HCT116 cells at the G2/M phase via the activation of p53/p21 and upregulation of cyclin-B. In addition, ROS elevation and changes in mitochondrial membrane potential were revealed, as indicated by p-atm elevation. The apoptotic rate rised to 36.9% and 32.2% after being treated by FER and DFER, respectively. In summary, both compounds exhibited an anti-cancer effect, and FER showed a greater pro-apoptotic effect, possibly due to the presence of the methoxy group on the aromatic ring.