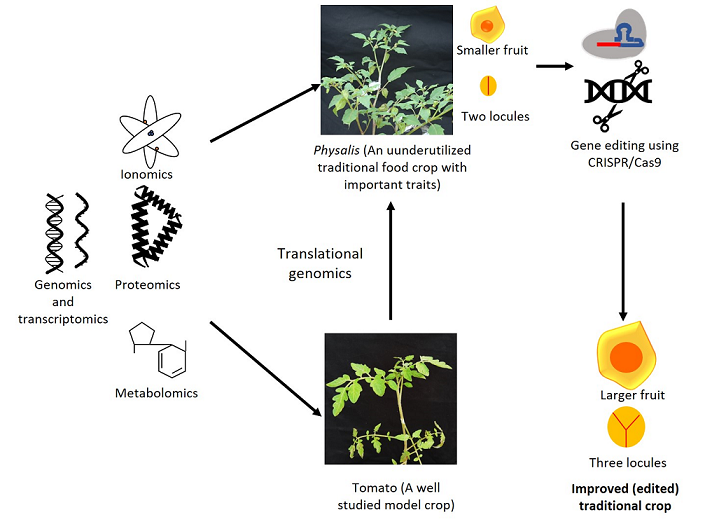
The indigenous communities across the globe especially in the rural areas consume locally available plants known as Traditional Food Plants (TFPs) for their nutritional and health-related needs. Recent research shows that many of the traditional food plants are highly nutritious as they contain health beneficial metabolites, vitamins, mineral elements and other nutrients. Excessive reliance on the mainstream staple crops has its own disadvantages. TFPs are nowadays considered important crops of the future and can act as supplementary foods for the burgeoning global population. They can also act as emergency foods in times of pandemics and other situations like COVID-19. The current situation necessitates locally available alternative nutritious TFPs for sustainable food production. To increase the cultivation or improve the traits in TFPs, it is essential to understand the molecular basis of the genes that regulate some important traits such as nutritional components and resilience to biotic and abiotic stresses. The integrated use of modern omics and gene editing technologies provide great opportunities to better understand the genetic and molecular basis of superior nutrient content, climate-resilient traits and adaptation to local agroclimatic zones. Recently, realising the importance and benefits of TFPs, scientists have shown interest in the prospection and sequencing of traditional food plants for their improvements, further cultivation and mainstreaming. Integrated omics such as genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, metabolomics and ionomics are successfully used in plants and have provided a comprehensive understanding of gene-protein-metabolite networks. Combined use of omics and editing tools has led to successful editing of beneficial traits in few TFPs. This suggests that there is ample scope of integrated use of modern omics and editing tools/techniques for improvement of TFPs and their use for sustainable food production. In this article, we highlight the importance, scope and progress towards improvement of TFPs for valuable traits by integrated use of omics and gene editing techniques.