Submitted:
17 April 2024
Posted:
18 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
2.2. Investigation of the Grain Development and Grain-Filling Rate
2.3. RNA Sequencing and Transcriptomic Profiling Analysis
2.4. Metabolome Profiling Analysis
2.5. Conjoint Analysis of Transcriptome and Metabolome
2.6. Quantitative qRT-PCR
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
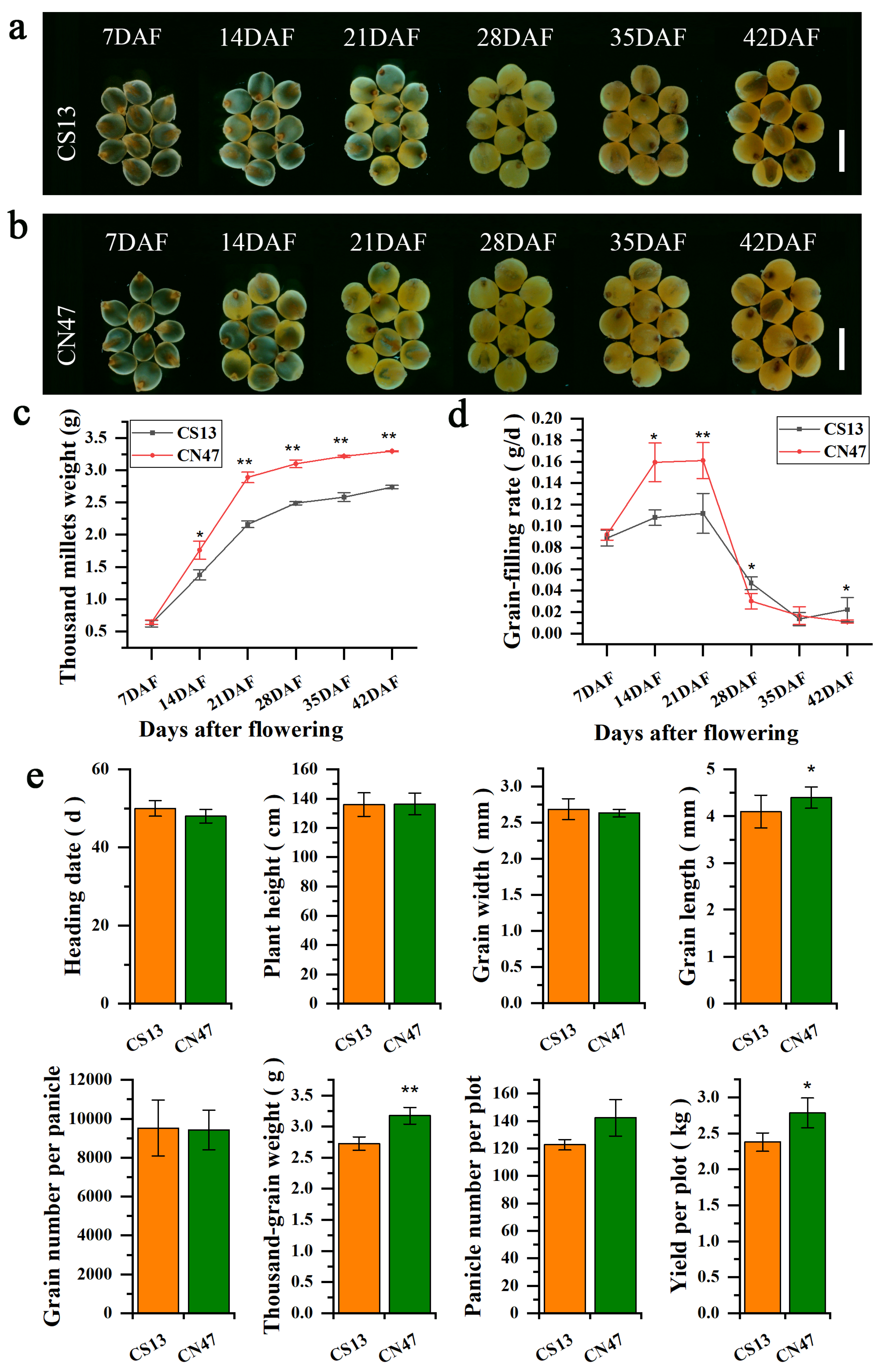
3.1. Characterization of Grain Filling Rate-Related Phenotypes in Foxtail Millet
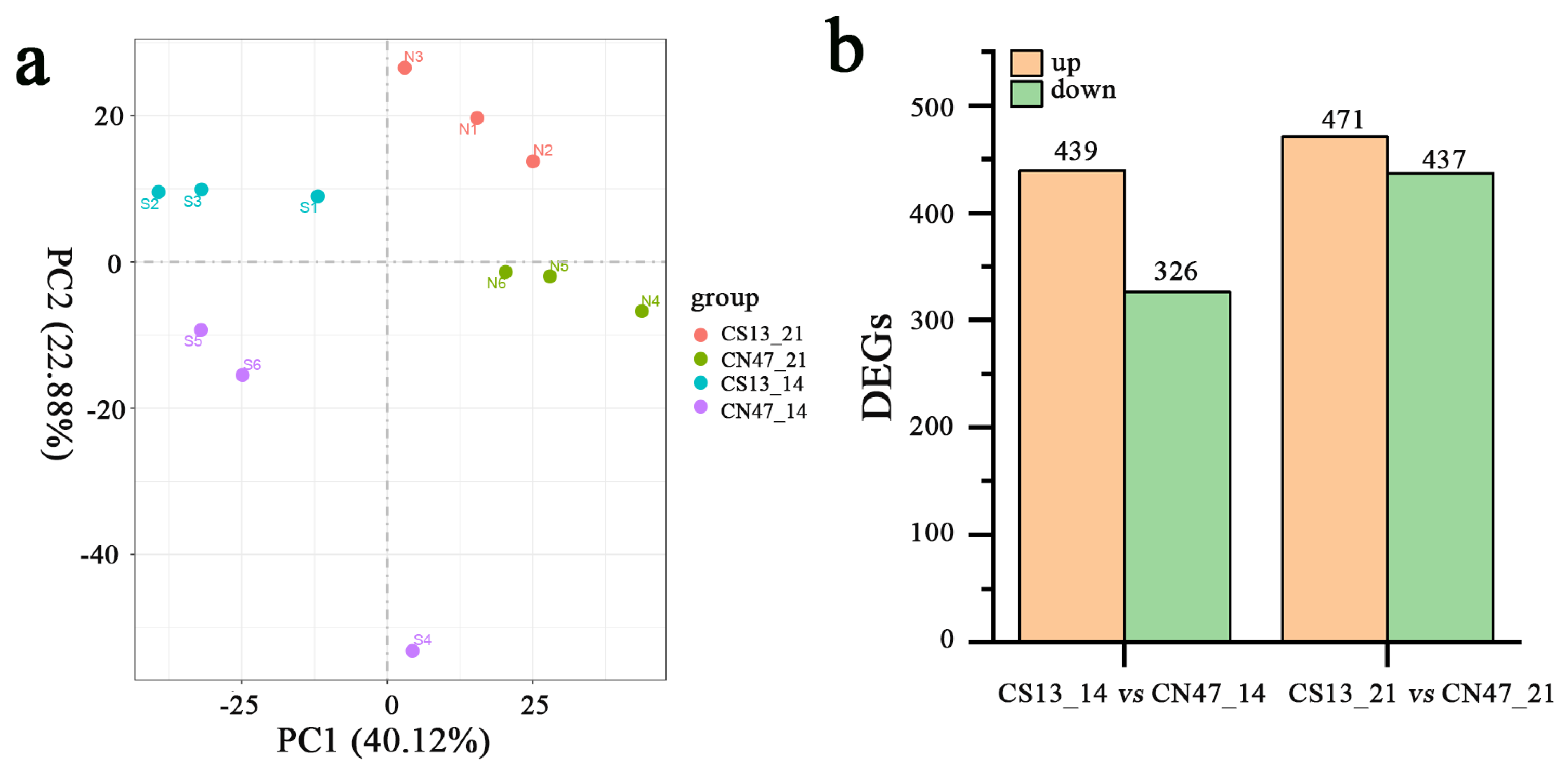
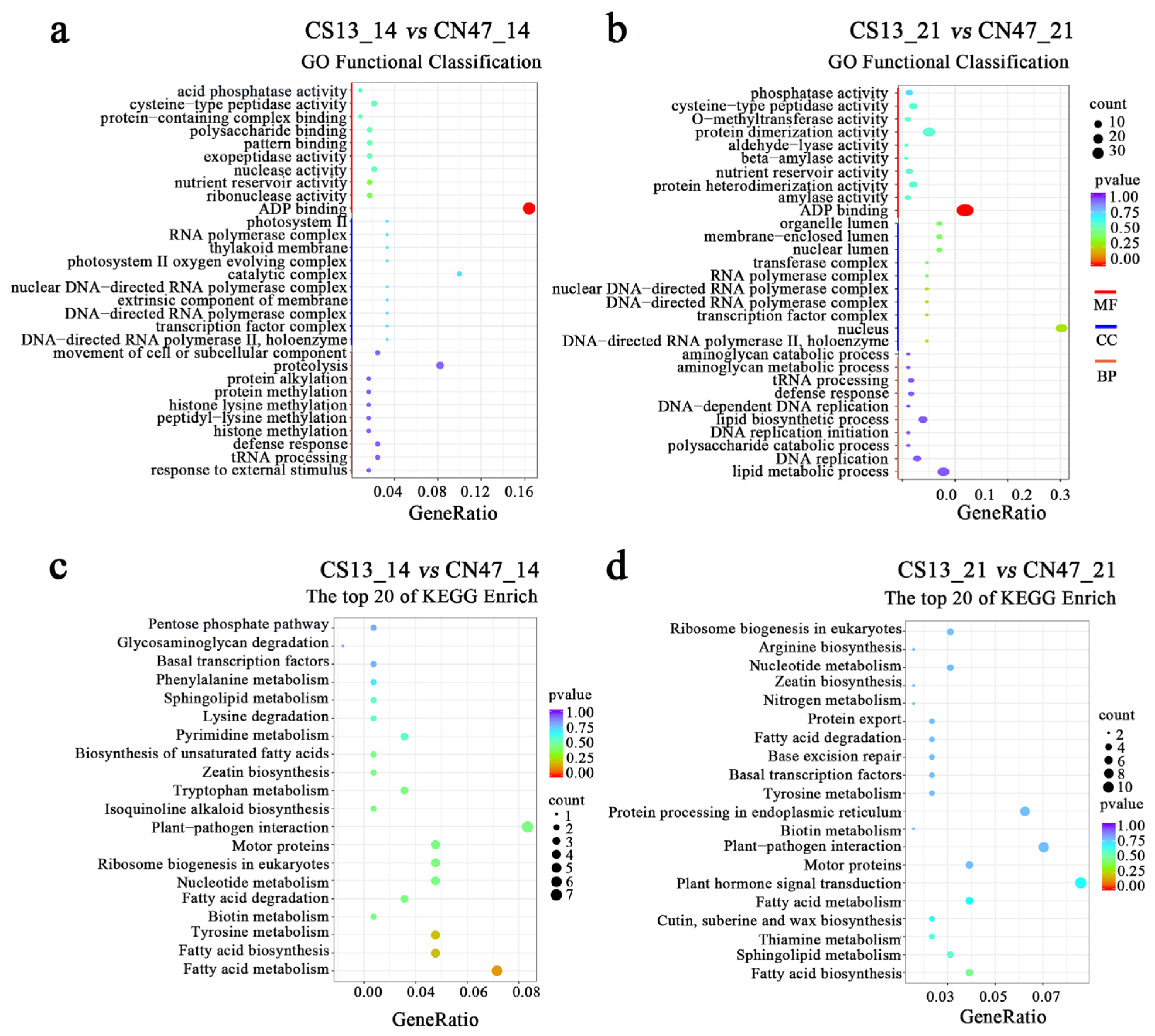
3.2. Transcriptomic Difference in the Grains during Grain-Filling Stages between Foxtail Millet Cultivars
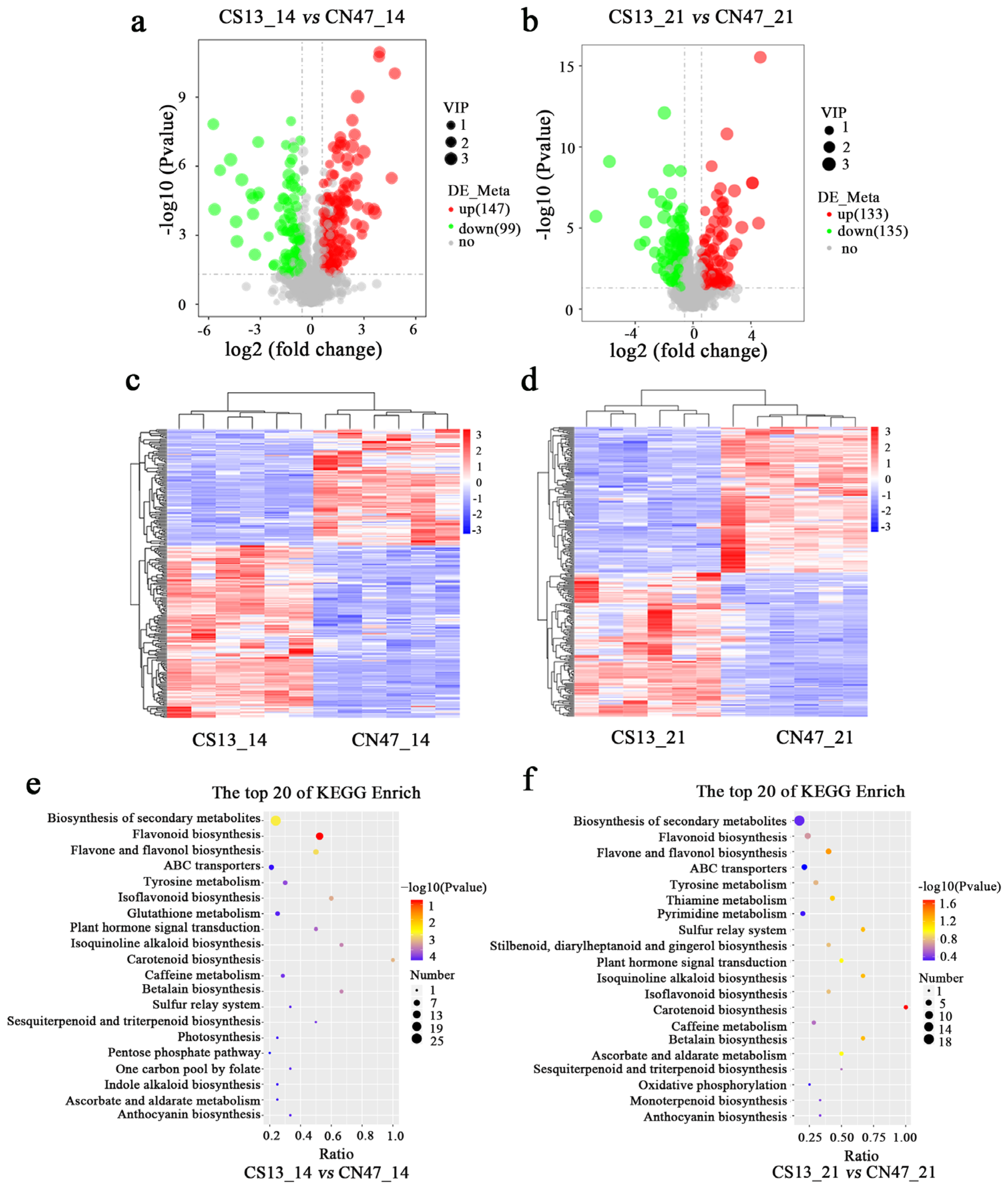
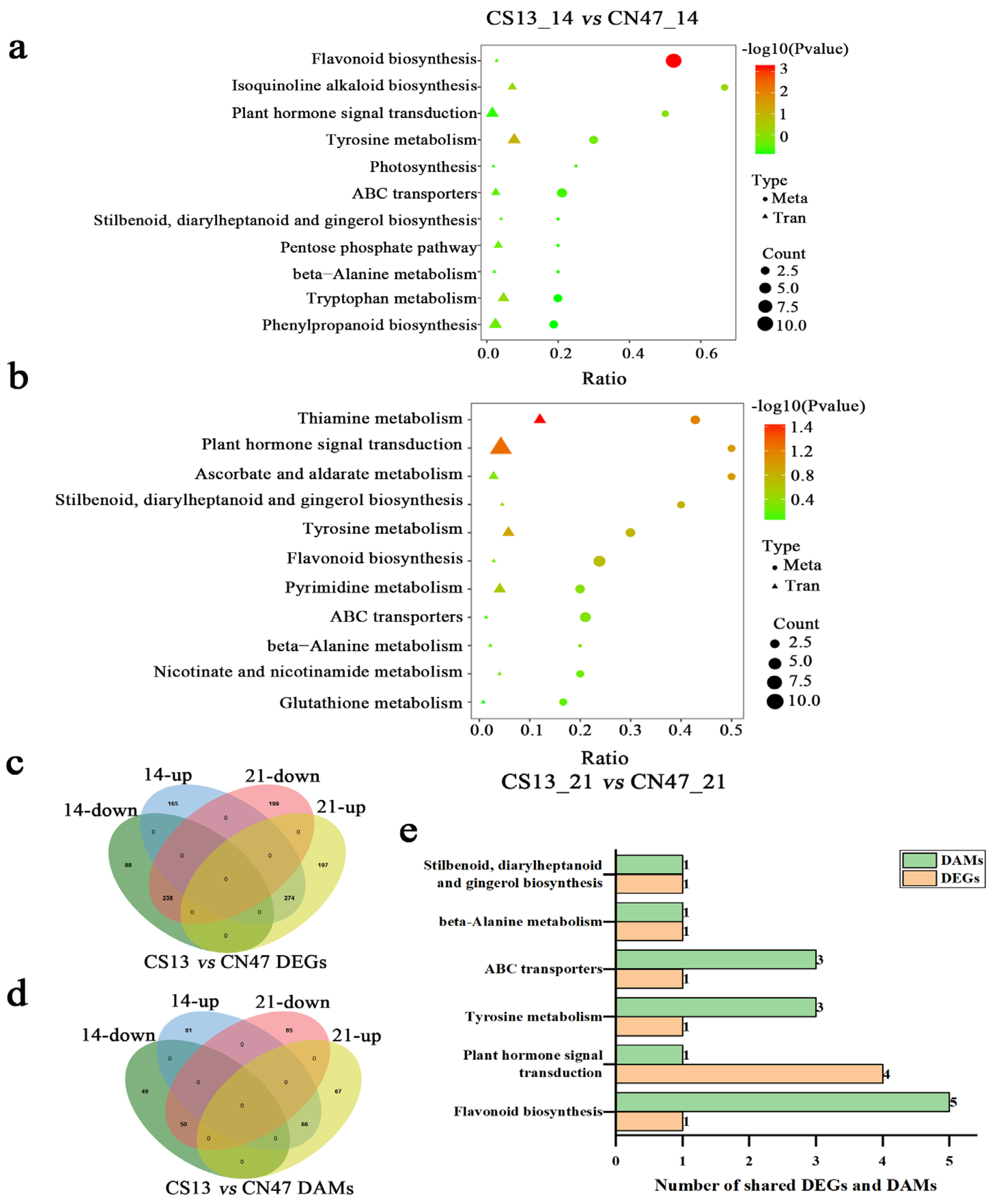
3.3. Metabolite Difference in the Grains during Grain-Filling Stages between Foxtail Millet Cultivars
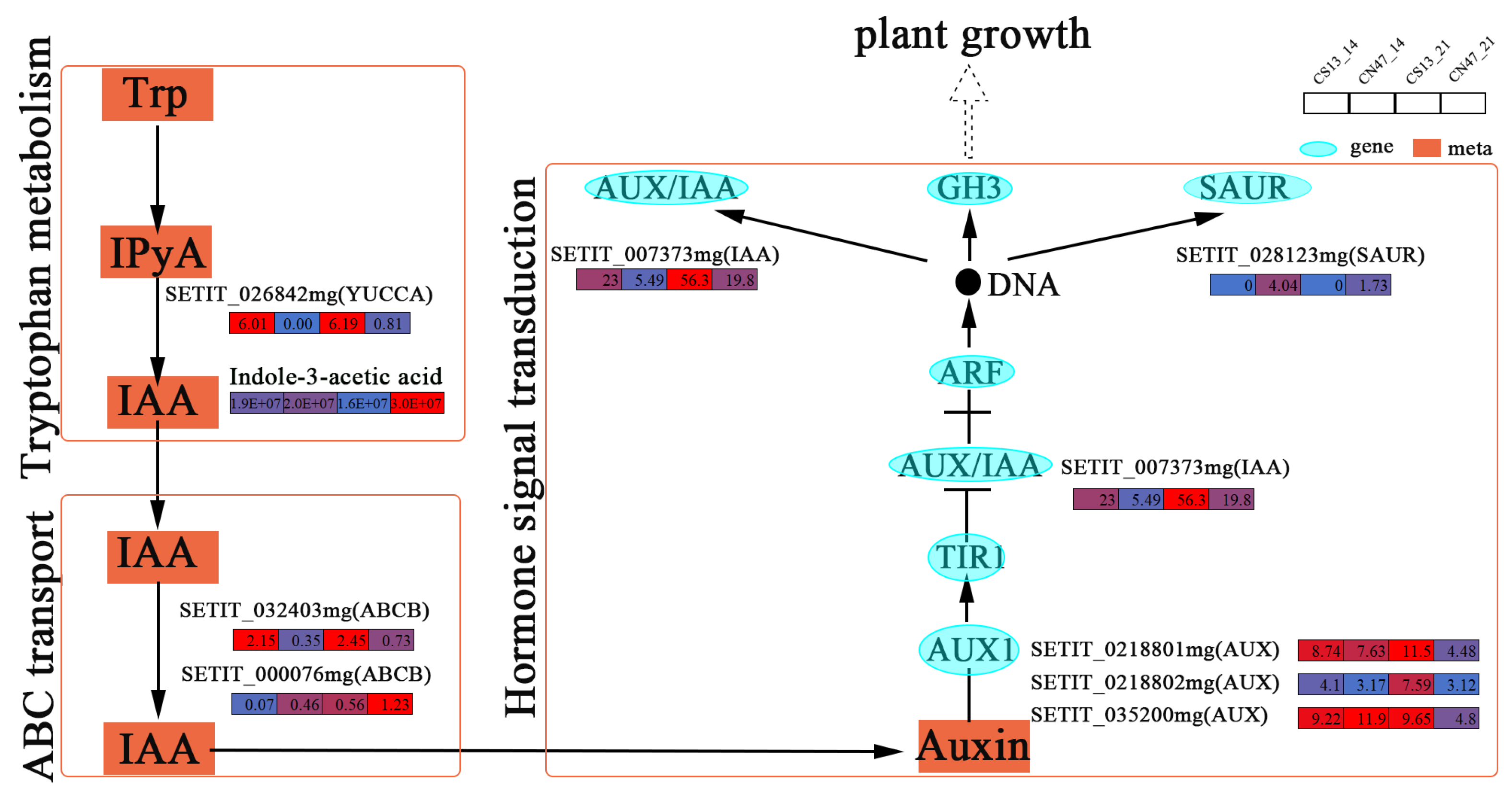
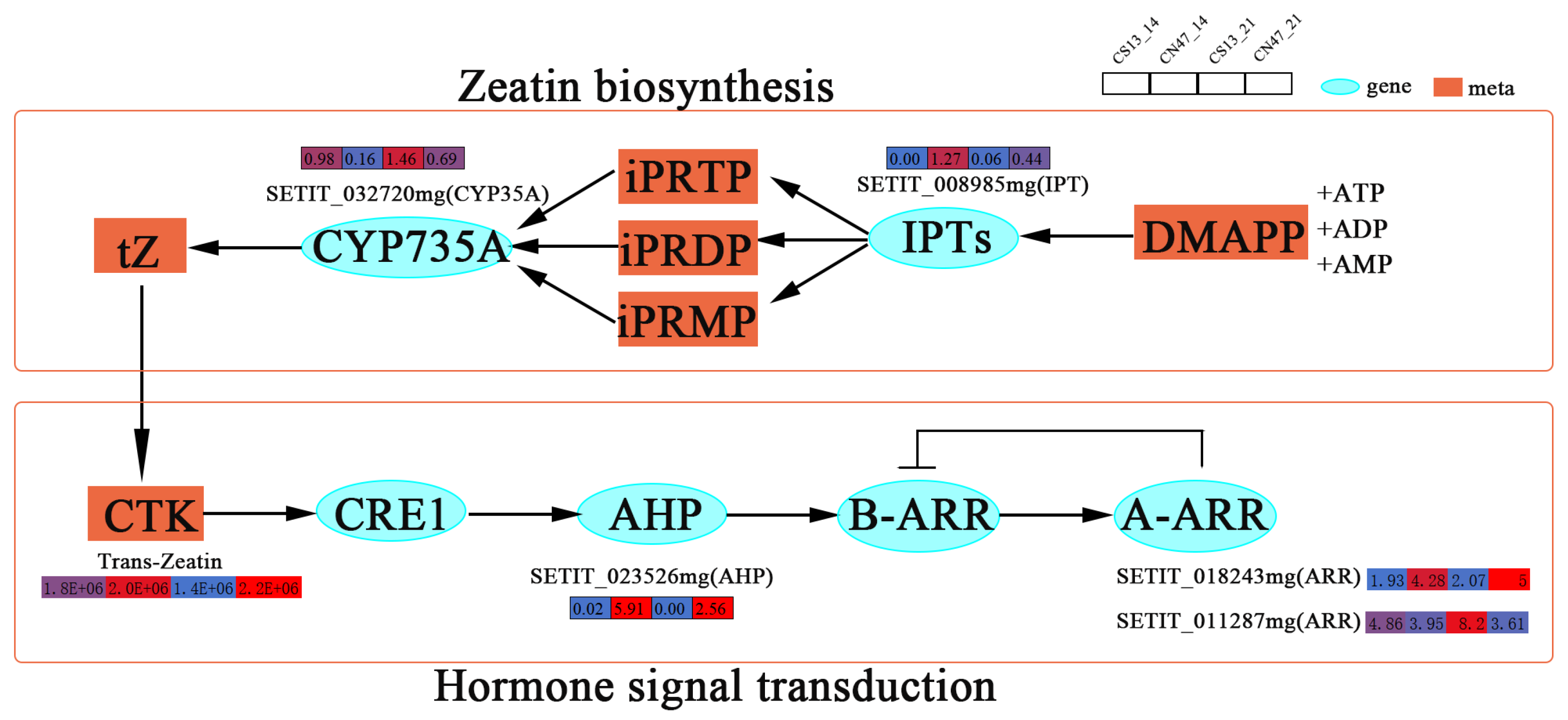
3.4. Integrated Transcriptome and Metabolome Analysis
3.5. Many Hormones Were Key Regulators of the Grain Filling Rate
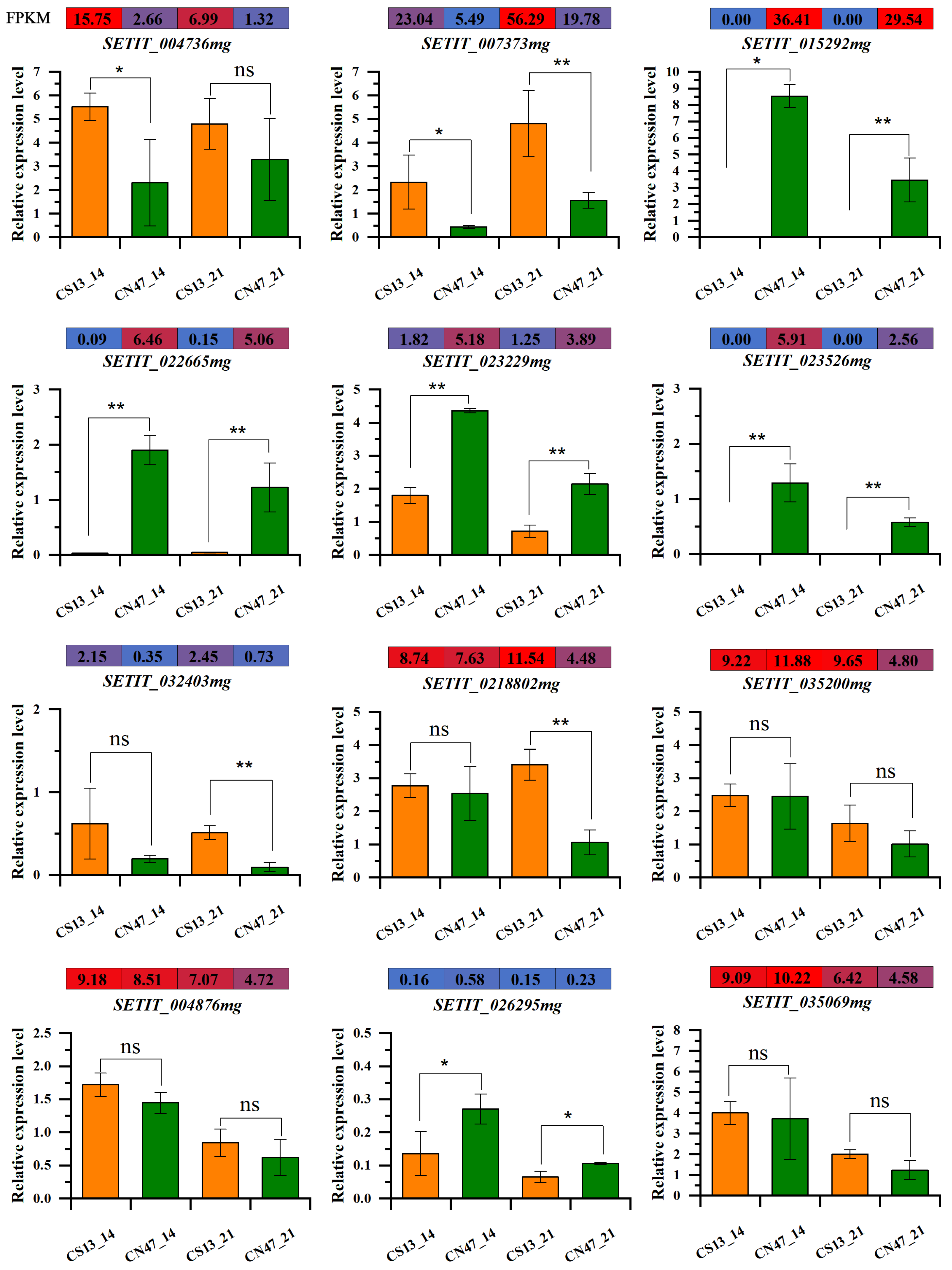
3.6. qRT-PCR Verification of RNA-seq Data
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lata, C.; Gupta, S.; Prasad, M. Foxtail millet: a model crop for genetic and genomic studies in bioenergy grasses. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2012, 33, 328–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Memariani, Z.; Abbas, S.Q.; ul Hassan, S.S.; Ahmadi, A.; Chabra, A. Naringin and naringenin as anticancer agents and adjuvants in cancer combination therapy: Efficacy and molecular mechanisms of action, a comprehensive narrative review. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 171, 105264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, P.; Purewal, S.S.; Sandhu, K.S.; Kaur, M.; Salar, R.K. Millets: a cereal grain with potent antioxidants and health benefits. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2018, 13, 793–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachdev, N.; Goomer, S.; Singh, L.R. Foxtail millet: a potential crop to meet future demand scenario for alternative sustainable protein. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 101, 831–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shyamli, P.S.; Rana, S.; Suranjika, S.; Muthamilarasan, M.; Parida, A.; Prasad, M. Genetic determinants of micronutrient traits in graminaceous crops to combat hidden hunger. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2021, 134, 3147–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amadou, I.; Amza, T.; Shi, Y.; Le, G. Chemical analysis and antioxidant properties of foxtail millet bran extracts. SJST. 2011, 33, 509−15 http://rdopsuacth/sjstweb/indexphp. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, S.; Yang, G.; Ma, Y. Chemical Characteristics and Fatty Acid Profile of Foxtail Millet Bran Oil. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2009, 87, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Niranjan, K. Foxtail millet: Properties, processing, health benefits, and uses. Food Rev. Int. 2017, 34, 329–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Su, M.; Hao, J.-H.; Li, Z.-D.; Dong, S.; Yuan, X.; Li, X.; Gao, L.; Chu, X.; Yang, G.; et al. Dynamic transcriptome landscape of foxtail millet grain development. Seed Biol. 2023, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Zhang, Q. Genetic and Molecular Bases of Rice Yield. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2010, 61, 421–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Pan, Z. A study on the grain filling characteristic of different weight wheat. Rev China Agric Sci Technol. 2005, 7, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, S.; Hara, T. Effects of air temperature and light on grain filling of an indica and a japonica rice (Oryza sativaL.) under controlled environmental conditions. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 1977, 23, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegand, C.L.; Cuellar, J.A. Duration of Grain Filling and Kernel Weight of Wheat as Affected by Temparature1. Crop. Sci. 1981, 21, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Ming, D.; Ma, W.; Xu, F. Effects of different nitrogen application periods on rice starch accumulation and starch synthesis Studies on the activity changes of related enzymes. Scientia Agricultura Sinica. 2005, 38, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Chen, T.; Zhang, H.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J. Abscisic acid and the key enzymes and genes in sucrose-to-starch conversion in rice spikelets in response to soil drying during grain filling. Planta 2015, 241, 1091–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Sanford, D.A. Variation in Kernel Growth Characters Among Soft Red Winter Wheats1. Crop. Sci. 1985, 25, 626–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashiringwani, N.A.; Mashingaidze, K.; Kangai, J.; Olsen, K. Genetic basis of grain filling rate in wheat (Triticum aestivum L. emend. Thell.). Euphytica 1994, 76, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.B.; Peterson, M.L.; Geng, S. Association Between Grain Filling Rate and Duration and Yield Components in Rice1. Crop. Sci. 1979, 19, 641–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Peng, T.; Sun, H.; Teotia, S.; Wen, H.; Du, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Tang, G.; Xue, H.; et al. miR1432-OsACOT (Acyl-CoA thioesterase) module determines grain yield via enhancing grain filling rate in rice. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2018, 17, 712–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Wang, H.; Liu, D.; Gao, D.; Lu, G.; Wang, J.; Gao, Z.; Lu, C. Characteristics of grain filling and dehydration in wheat. Scientia Agricultura Sinica. 2019, 52, 4251–4261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Jiao, G.; Lin, H.; Sheng, Z.; Shao, G.; Xie, L.; Tang, S.; Xu, Q.; Hu, P. GRAIN INCOMPLETE FILLING 2 regulates grain filling and starch synthesis during rice caryopsis development. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2017, 59, 134–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibashi, Y.; Okamura, K.; Miyazaki, M.; Phan, T.; Yuasa, T.; Iwaya-Inoue, M. Expression of rice sucrose transporter gene OsSUT1 in sink and source organs shaded during grain filling may affect grain yield and quality. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2014, 97, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, A.-N.; Lu, X.-D.; Li, D.-Q.; Liu, J.-X.; Liu, C.-M. NF-YB1-regulated expression of sucrose transporters in aleurone facilitates sugar loading to rice endosperm. Cell Res. 2015, 26, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sosso, D.; Luo, D.; Li, Q.-B.; Sasse, J.; Yang, J.; Gendrot, G.; Suzuki, M.; E Koch, K.; McCarty, D.R.; Chourey, P.S.; et al. Seed filling in domesticated maize and rice depends on SWEET-mediated hexose transport. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1489–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, Y. Transactivation of Sus1 and Sus2 by Opaque2 is an essential supplement to sucrose synthase-mediated endosperm filling in maize. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 1897–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, E.; Wang, J.; Zhu, X.; Hao, W.; Wang, L.; Li, Q.; Zhang, L.; He, W.; Lu, B.; Lin, H.; et al. Control of rice grain-filling and yield by a gene with a potential signature of domestication. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 1370–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuanar, S.R.; Molla, K.A.; Chattopadhyay, K.; Sarkar, R.K.; Mohapatra, P.K. Introgression of Sub1 (SUB1) QTL in mega rice cultivars increases ethylene production to the detriment of grain- filling under stagnant flooding. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Ye, N.; Yang, J.; Peng, X.; Zhang, J. Regulation of expression of starch synthesis genes by ethylene and ABA in relation to the development of rice inferior and superior spikelets. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 3907–3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Cao, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, J.; Xu, G.; Gu, J.; Liu, L.; Wang, Z.; Yang, J.; Zhang, H. Grain Filling Characteristics and Their Relations with Endogenous Hormones in Large- and Small-Grain Mutants of Rice. PLOS ONE 2016, 11, e0165321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, B.B.; Sekhar, S.; Dash, S.K.; Behera, L.; Shaw, B.P. Biochemical and molecular characterisation of exogenous cytokinin application on grain filling in rice. BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shen, J.; Chen, H.; Zhang, L.; Lü, B.; Liang, G.; Liang, J. The Rice G Protein γ Subunit DEP1/qPE9–1 Positively Regulates Grain-Filling Process by Increasing Auxin and Cytokinin Content in Rice Grains. Rice 2019, 12, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, E.; Zeng, S.; Zhu, S.; Liu, Y.; Wu, G.; Zhao, K.; Liu, X.; Liu, Q.; Dong, Z.; Dang, X.; et al. Favorable Alleles of GRAIN-FILLING RATE1 Increase the Grain-Filling Rate and Yield of Rice. Plant Physiol. 2019, 181, 1207–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Jiang, X.; Tao, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, Z.; Wu, F.; Liu, S.; Li, C.; Deng, M.; Ma, J.; et al. Identification and validation of stable quantitative trait loci for grain filling rate in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2020, 133, 2377–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennetzen, J.L.; Schmutz, J.; Wang, H.; Percifield, R.; Hawkins, J.; Pontaroli, A.C.; Estep, M.; Feng, L.; Vaughn, J.N.; Grimwood, J.; et al. Reference genome sequence of the model plant Setaria. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, G.; Huang, X.; Zhi, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Li, W.; Chai, Y.; Yang, L.; Liu, K.; Lu, H.; et al. A haplotype map of genomic variations and genome-wide association studies of agronomic traits in foxtail millet (Setaria italica). Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 957–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Song, H.; Li, P.; Wei, Y.; Hu, N.; Chen, Z.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Zhang, B.; Peng, R. Transcriptome Analysis Provides Insights into Grain Filling in Foxtail Millet (Setaria italica L.). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wang, S.; Tong, Y.; Wei, Y.; Li, P.; Hu, N.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, H.; et al. Spatiotemporal dynamics of the foxtail millet transcriptome during grain filling. Physiol. Plant. 2024, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Xing, L.; Song, H.; Wei, Y.; Li, P.; Lu, Q.; Hu, N.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, J.; et al. Large-scale metabolome analysis reveals dynamic changes of metabolites during foxtail millet grain filling. Food Res. Int. 2023, 165, 112516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Lu, Q.; Song, H.; Hu, N.; Wei, Y.; Li, P.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhang, B.; et al. DNA Methylation and RNA-Sequencing Analysis Show Epigenetic Function During Grain Filling in Foxtail Millet (Setaria italica L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Wang, T.; Li, L.; Xing, L.; Xie, H.F.; Feng, B.L.; Liu, J.R. Comparative transcriptome analysis provides insights into grain filling commonalities and differences between foxtail millet [Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv.] varieties with different panicle types. PeerJ 2022, 10, e12968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anders, S.; Huber, W. Differential expression analysis for sequence count data. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.A.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Davis, A.P.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.S.; Eppig, J.T.; et al. Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S.; Kawashima, S.; Okuno, Y.; Hattori, M. The KEGG resource for deciphering the genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, D277–D280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Want, E.J.; Masson, P.; Michopoulos, F.; Wilson, I.D.; Theodoridis, G.; Plumb, R.S.; Shockcor, J.; Loftus, N.; Holmes, E.; Nicholson, J.K. Global metabolic profiling of animal and human tissues via UPLC-MS. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 8, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, B.; Mei, Z.; Zeng, C.; Liu, S. metaX: a flexible and comprehensive software for processing metabolomics data. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Tan, G.; Yang, L.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, B. Hormones in the grains and roots in relation to post-anthesis development of inferior and superior spikelets in japonica/indica hybrid rice. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2009, 47, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y. Auxin Biosynthesis: A Simple Two-Step Pathway Converts Tryptophan to Indole-3-Acetic Acid in Plants. Mol. Plant 2012, 5, 334–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Dai, S.; Qin, N.; Zhu, C.; Qin, J.; Li, J. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the SAUR gene family in foxtail millet (Setaria italica L.). BMC Plant Biol. 2023, 23, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, M. Cytokinins and plant development—an overview. In Cytokinins, ed. Mok MC. Boca Raton: CRC Press. 2019, pp. 15–66. [CrossRef]
- Ishimaru, T.; Matsuda, T.; Ohsugi, R.; Yamagishi, T. Morphological development of rice caryopses located at the different positions in a panicle from early to middle stage of grain filling. Funct. Plant Biol. 2003, 30, 1139–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Zhao, H.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, G.; Cao, S.; Yin, W.; Qian, Y.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, S.; et al. A cryptic inhibitor of cytokinin phosphorelay controls rice grain size. Mol. Plant 2021, 15, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y. Essential Roles of Local Auxin Biosynthesis in Plant Development and in Adaptation to Environmental Changes. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2018, 69, 417–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Slafer, G.; Foulkes, M.J.; Reynolds, M.P.; Murchie, E.H.; Carmo-Silva, E.; Flavell, R.; Gwyn, J.; Sawkins, M.; Griffiths, S. A ‘wiring diagram’ for sink strength traits impacting wheat yield potential. J. Exp. Bot. 2022, 74, 40–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Kang, M.S.; Moreno, O. Genetic analyses of grain-filling rate and duration in maize. Field Crop. Res. 1999, 61, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Cui, Z.; Hu, Y.; Wang, B.; Tang, J. Genetic Analysis of Grain Filling Rate Using Conditional QTL Mapping in Maize. PLOS ONE 2013, 8, e56344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, X.; Wang, G.; Wang, X.; Yang, H.; Cheng, Q. ; Qin,Y. Breeding and cultivation techniques of millet variety Changsheng 13 suitable for mechanized production. China Seed Industry. 2019, 10, 74–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, A.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, R.; Guo, E. Breeding of high-quality herbicide-resistant millet variety Changnong 47 and its high-yield cultivation techniques. Journal of Hebei Agricultural Sciences. 2022, 26, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Garg, R.; Jain, M. RNA-Seq for Transcriptome Analysis in Non-model Plants. In Legume Genomics; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2013; Volume 1069, pp. 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gao, J.; Song, J.; Guo, K.; Hou, S.; Wang, X.; He, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; et al. Multi-omics analyses of 398 foxtail millet accessions reveal genomic regions associated with domestication, metabolite traits, and anti-inflammatory effects. Mol. Plant 2022, 15, 1367–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, J.; Qie, Q.; Yang, Y.; Hou, S.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Han, Y. Comparative Analysis of Flavonoid Metabolites in Foxtail Millet (Setaria italica) with Different Eating Quality. Life 2021, 11, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, H.L.; Blumenthal, R.M.; Cheng, X. Many paths to methyltransfer: a chronicle of convergence. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2003, 28, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rea, P.A. Plant ATP-Binding Cassette Transporters. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2007, 58, 347–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, S.; Kahla, A.; Arunachalam, C.; Perochon, A.; Khan, M.R.; Scofield, S.R.; Doohan, F.M. A wheat ABC transporter contributes to both grain formation and mycotoxin tolerance. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 2583–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhati, K.K.; Alok, A.; Kumar, A.; Kaur, J.; Tiwari, S.; Pandey, A.K. Silencing ofABCC13transporter in wheat reveals its involvement in grain development, phytic acid accumulation and lateral root formation. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 4379–4389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Cao, X.; Li, X.; Bian, Z.; Zhang, Q.-Q.; Fang, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, Q.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, L.; et al. Two ABCI family transporters, OsABCI15 and OsABCI16, are involved in grain-filling in rice. J. Genet. Genom. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Wang, K.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, P.; Shi, Z.; Luo, J.; Jiang, D.; Fan, F.; Zhu, Y.; et al. Blocking miR396 increases rice yield by shaping inflorescence architecture. Nat. Plants 2015, 2, 15196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashikari, M.; Sakakibara, H.; Lin, S.; Yamamoto, T.; Takashi, T.; Nishimura, A.; Angeles, E.R.; Qian, Q.; Kitano, H.; Matsuoka, M. Cytokinin Oxidase Regulates Rice Grain Production. Science 2005, 309, 741–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Lv, Q.; Deng, J.; Huang, J.; Cai, F.; Liang, C.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, X.; et al. Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Key Seed-Development Genes in Common Buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; E, Z.; Zhang, D.; Yun, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Niu, B.; Chen, C. OsYUC11-mediated auxin biosynthesis is essential for endosperm development of rice. Plant Physiol. 2020, 185, 934–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhang, M.; Liang, J. RGB1 Regulates Grain Development and Starch Accumulation Through Its Effect on OsYUC11-Mediated Auxin Biosynthesis in Rice Endosperm Cells. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forestan, C.; Meda, S.; Varotto, S. ZmPIN1-Mediated Auxin Transport Is Related to Cellular Differentiation during Maize Embryogenesis and Endosperm Development. Plant Physiol. 2009, 152, 1373–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamowski, M.; Friml, J. PIN-Dependent Auxin Transport: Action, Regulation, and Evolution. Plant Cell 2015, 27, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Bailly, A.; Zwiewka, M.; Sovero, V.; Di Donato, M.; Ge, P.; Oehri, J.; Aryal, B.; Hao, P.; Linnert, M.; et al. TWISTED DWARF1 Mediates the Action of Auxin Transport Inhibitors on Actin Cytoskeleton Dynamics. Plant Cell 2016, 28, 930–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchant, A.; Kargul, J.; May, S.T.; Muller, P.; Delbarre, A.; Perrot-Rechenmann, C.; Bennett, M.J. AUX1 regulates root gravitropism in Arabidopsis by facilitating auxin uptake within root apical tissues. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 2066–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, M.; Lee, Z.-W.; Cho, H.-T. ATP-Binding Cassette B4, an Auxin-Efflux Transporter, Stably Associates with the Plasma Membrane and Shows Distinctive Intracellular Trafficking from That of PIN-FORMED Proteins. Plant Physiol. 2012, 159, 642–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, F.; Zhang, F.; Zhu, Y.; Lan, D.; Yan, P.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Hu, J.; Niu, F.; et al. Auxin signaling module OsSK41-OsIAA10-OsARF regulates grain yield traits in rice. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2023, 65, 1753–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, F.; Huang, Y.; Qi, P.; Lian, G.; Hu, X.; Han, N.; Wang, J.; Zhu, M.; Qian, Q.; Bian, H. Functional analysis of auxin receptor OsTIR1/OsAFB family members in rice grain yield, tillering, plant height, root system, germination, and auxinic herbicide resistance. New Phytol. 2020, 229, 2676–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Lu, Z.; Zhai, L.; Li, N.; Yan, H. The Small Auxin-Up RNA SAUR10 Is Involved in the Promotion of Seedling Growth in Rice. Plants 2023, 12, 3880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Sun, C.; Shen, C.; Wang, S.; Liu, F.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, C.; Qian, Q.; Aryal, B.; et al. The auxin transporter, OsAUX1, is involved in primary root and root hair elongation and in Cd stress responses in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant J. 2015, 83, 818–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




