2.3.1. Spectral Extraction of Remote Sensing Images
As the content of each component in the water body changes, the optical properties of the water body will also change accordingly, resulting in changes in the signals received by satellites. The implementation principle of remote sensing inversion of suspended sediment concentration is to invert the content of each component in the water body through the optical signal received by the sensor [
11].
When inverting the concentration of suspended sediment, it is necessary to extract the measured remote sensing images into different bands. Essentially, this involves using the measured spectral remote sensing reflectance to equivalently calculate the remote sensing reflectance values of each band range based on the different detection ranges of the sensor sensitivity of the remote sensing satellite [
12].
By consulting relevant literature, in this study, the satellite data of Landsat 8 was used for the inversion of suspended sediment concentration, and the four bands of B1, B2, B3 and B4 were adopted. Its wavelength range is generally OLI1/B1 (0.43-0.45μm), OLI2/B2 (0.45-0.51μm), OLI3/B3 (0.53-0.59μm), and OLI4/B4 (0.64-0.67μm). They respectively represent OLI1/B1 (Coastal band), OLI2/B2 (Blue band), OLI3/B3 (Green band), and OLI4/B4 (Red band).
Based on the four bands required for the inversion of suspended sediment concentration, and according to the different wavelength ranges of each band, the extraction of each band for each measurement point is carried out in ENVI5.2, and the equivalent reflectance is calculated. (
Table 3)
To enhance the accuracy, scientificity and universality of the experimental data, this study recalculated the different ratios of the four bands again to construct a multi-band combination model, with the aim of obtaining the most precise remote sensing inversion model. (
Table 4 and
Table 5)
2.3.2. Landsat 8 Remote Sensing Image Suspended Sediment Concentration Inversion Model
When using Landsat 8 for the inversion of suspended sediment concentration, it is necessary to establish the relevant functional relationship using the regression analysis method, and the accuracy of the model needs to be tested. This study mainly evaluates the quality of the relationship after model inversion using the correlation coefficient:
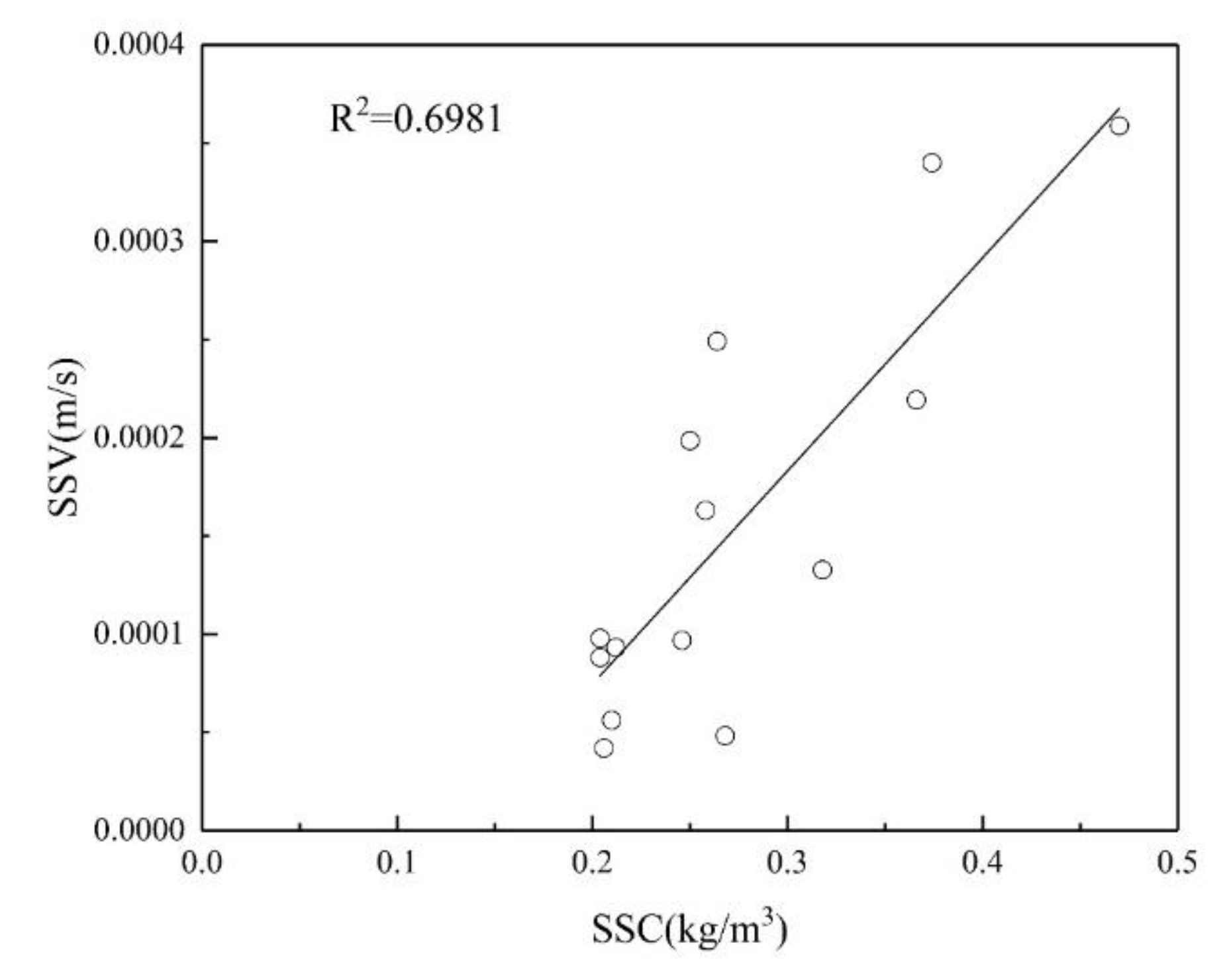
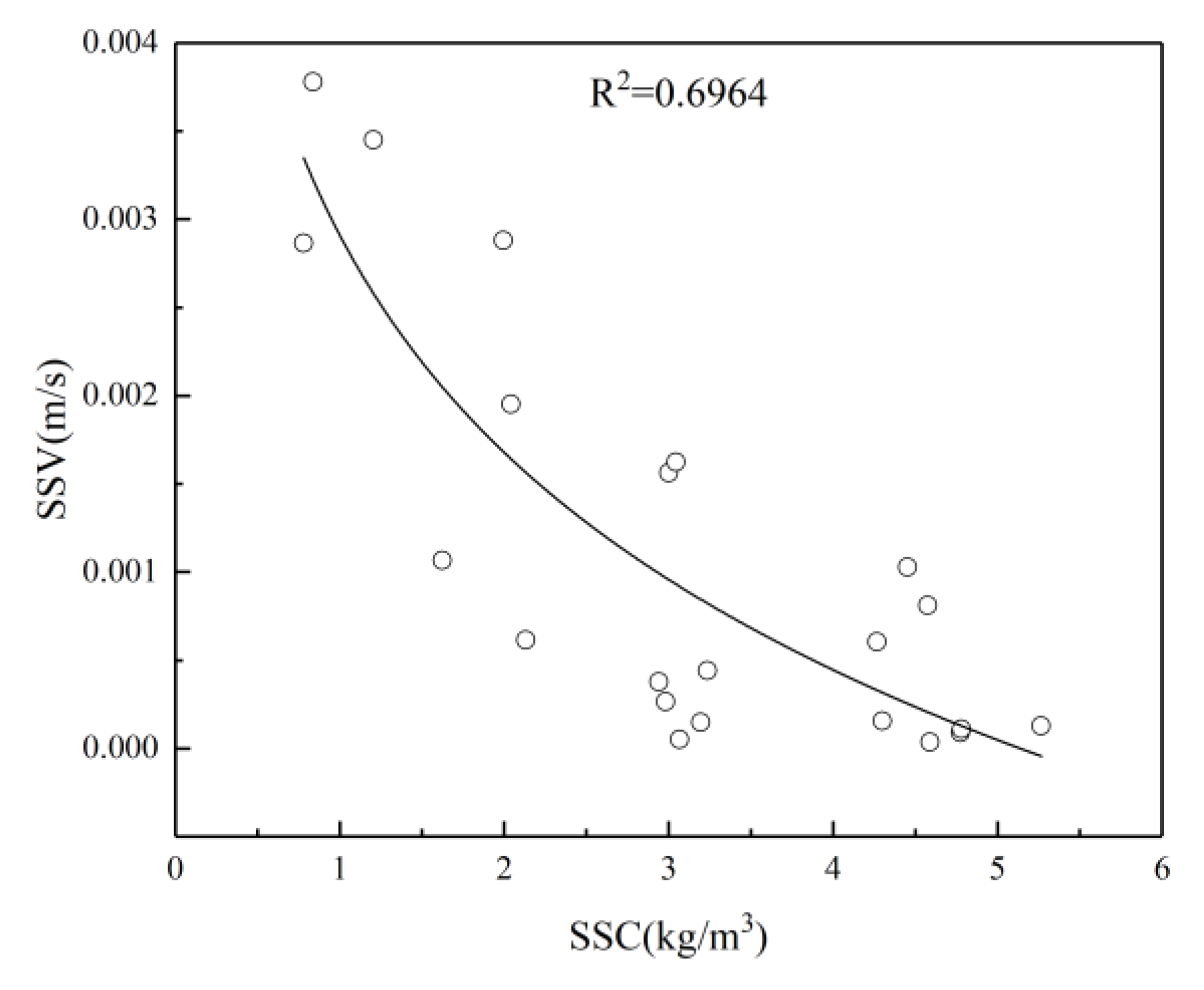
The correlation coefficient R2 is an evaluation index for the fitting regression results. The closer it is to 1, the better the fitting effect and the higher the degree of fit; the closer it is to 0, the worse the fitting regression effect and the lower the degree of fit. For the value of, 0.8 to 1.0 is highly correlated. 0.6 to 0.8 indicates a strong correlation. A correlation of 0.4 to 0.6 is considered moderate. 0.2 to 0.4 is a weak correlation. 0.0 to 0.2 indicates a very weak correlation or no correlation at all.
In Equation (1) : represents the measured value; It is the average value of the measured values; It is a simulated value; It is the number of samples.
(1) Landsat 8 single-band suspended sediment concentration inversion model.
In this study, in the calculation of the Landsat 8 single-band suspended sediment concentration inversion model, the remote sensing reflection values of the four single-band B1, B2, B3, and B4 were respectively taken as independent variables, and the suspended sediment concentration () was taken as the dependent variable. Thus, a single-band inversion model of remote sensing images can be established.
The models of each band are respectively shown in the following table:
By observing the above
Table 6,
Table 7,
Table 8 and
Table 9, it can be seen that the correlation coefficient of the linear function model inverted using B3 band data is relatively high, reaching 0.5195. Among the four different band inversion models of B1, B2, B3, and B4, the correlation between band 2 and band 3 is higher than that between band 1 and band 4.However, after observing the relationships and correlation coefficients of all the obtained function models, it was found that the effect of using a single band for the inversion of suspended sediment concentration was not very ideal. Therefore, using only a single band to invert the suspended sediment concentration in the nearshore sea area of Lianyungang lacks sufficient accuracy.
In the research on the inversion of suspended sediment concentration in Class II water bodies, factors that affect and can change the spectral characteristics of water bodies include not only suspended sediment concentration but also water color elements such as chlorophyll. These elements all have a certain impact on the accuracy of the local inversion of suspended sediment concentration using remote sensing images. Therefore, in order to overcome the possible interference of other factors on the accuracy of this study, it is necessary to conduct further inversion calculations using two or more remote sensing image bands.
(2) Landsat 8-band ratio suspended sediment concentration inversion model
In order to obtain more accurate band inversion results of suspended sediment concentration from remote sensing images, the ratio of two bands was further adopted as the independent variable to conduct the inversion calculation of suspended sediment concentration again.
Table 10.
Inversion model construction of the relationship between B4/B3 band and suspended sediment concentration and its correlation coefficients.
Table 10.
Inversion model construction of the relationship between B4/B3 band and suspended sediment concentration and its correlation coefficients.
| Band |
Model |
Relation |
|
| B4/B3 |
Linear function model of one order |
|
0.4638 |
| Quadratic polynomial function model |
|
0.4639 |
| Exponential function model |
|
0.451 |
| Logarithmic function model |
|
0.4496 |
Table 11.
Inversion model construction of the relationship betweenB4/ B2 band and suspended sediment concentration and its correlation coefficients.
Table 11.
Inversion model construction of the relationship betweenB4/ B2 band and suspended sediment concentration and its correlation coefficients.
| Band |
Model |
Relation |
|
| B4/B2 |
Linear function model of one order |
|
0.4875 |
| Quadratic polynomial function model |
|
0.4897 |
| Exponential function model |
|
0.4771 |
| Logarithmic function model |
|
0.4786 |
Table 12.
Inversion model construction of the relationship between B4/B1 band and suspended sediment concentration and its correlation coefficients.
Table 12.
Inversion model construction of the relationship between B4/B1 band and suspended sediment concentration and its correlation coefficients.
| Band |
Model |
Relation |
|
| B4/B1 |
Linear function model of one order |
|
0.5255 |
| Quadratic polynomial function model |
|
0.5285 |
| Exponential function model |
|
0.5091 |
| Logarithmic function model |
|
0.5148 |
Table 13.
Inversion model construction of the relationship between B3/B2 band and suspended sediment concentration and its correlation coefficients.
Table 13.
Inversion model construction of the relationship between B3/B2 band and suspended sediment concentration and its correlation coefficients.
| Band |
Model |
Relation |
|
| B3/B2 |
Linear function model of one order |
|
0.5687 |
| Quadratic polynomial function model |
|
0.5689 |
| Exponential function model |
|
0.5981 |
| Logarithmic function model |
|
0.5675 |
Table 14.
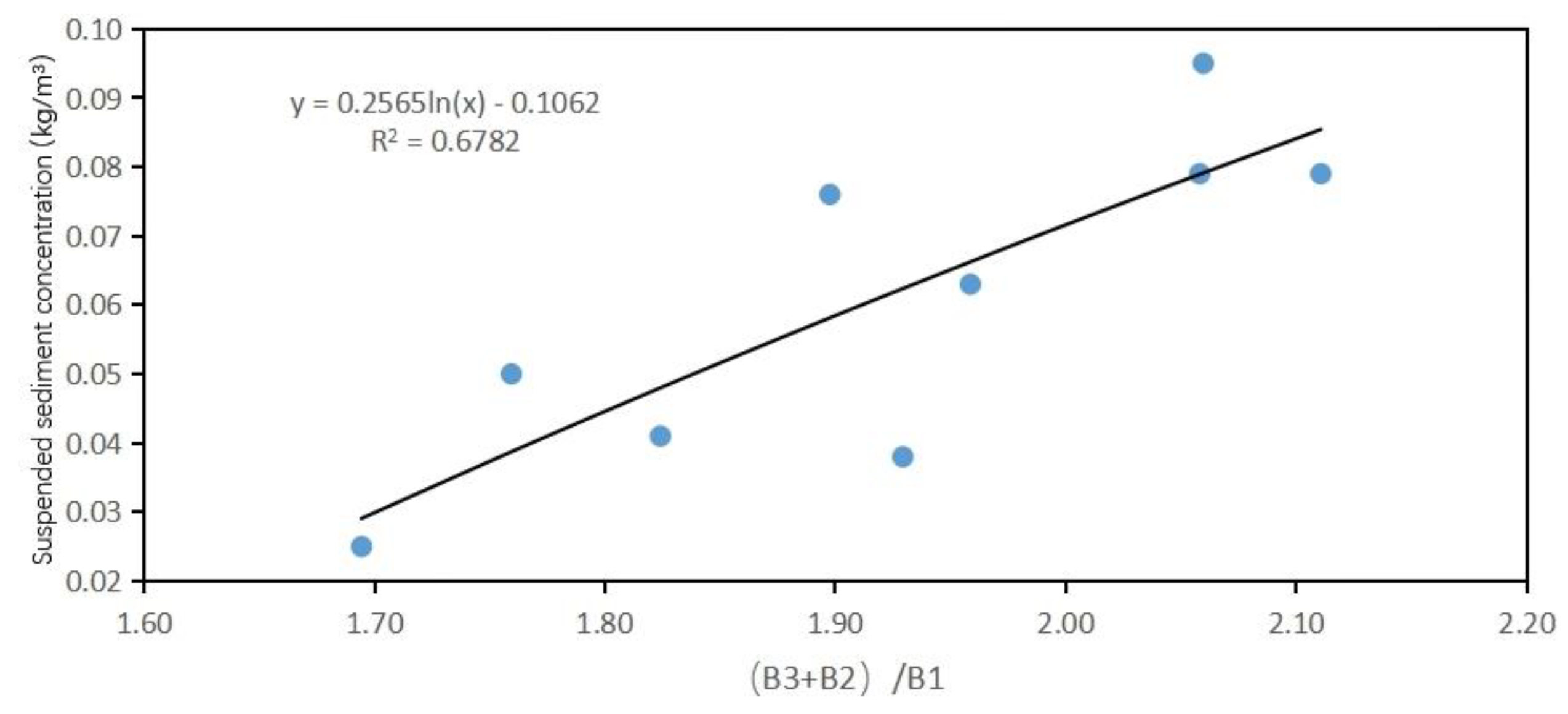
Inversion model construction of the relationship between B3/B1 band and suspended sediment concentration and its correlation coefficients.
Table 14.
Inversion model construction of the relationship between B3/B1 band and suspended sediment concentration and its correlation coefficients.
| Band |
Model |
Relation |
|
| B3/B1 |
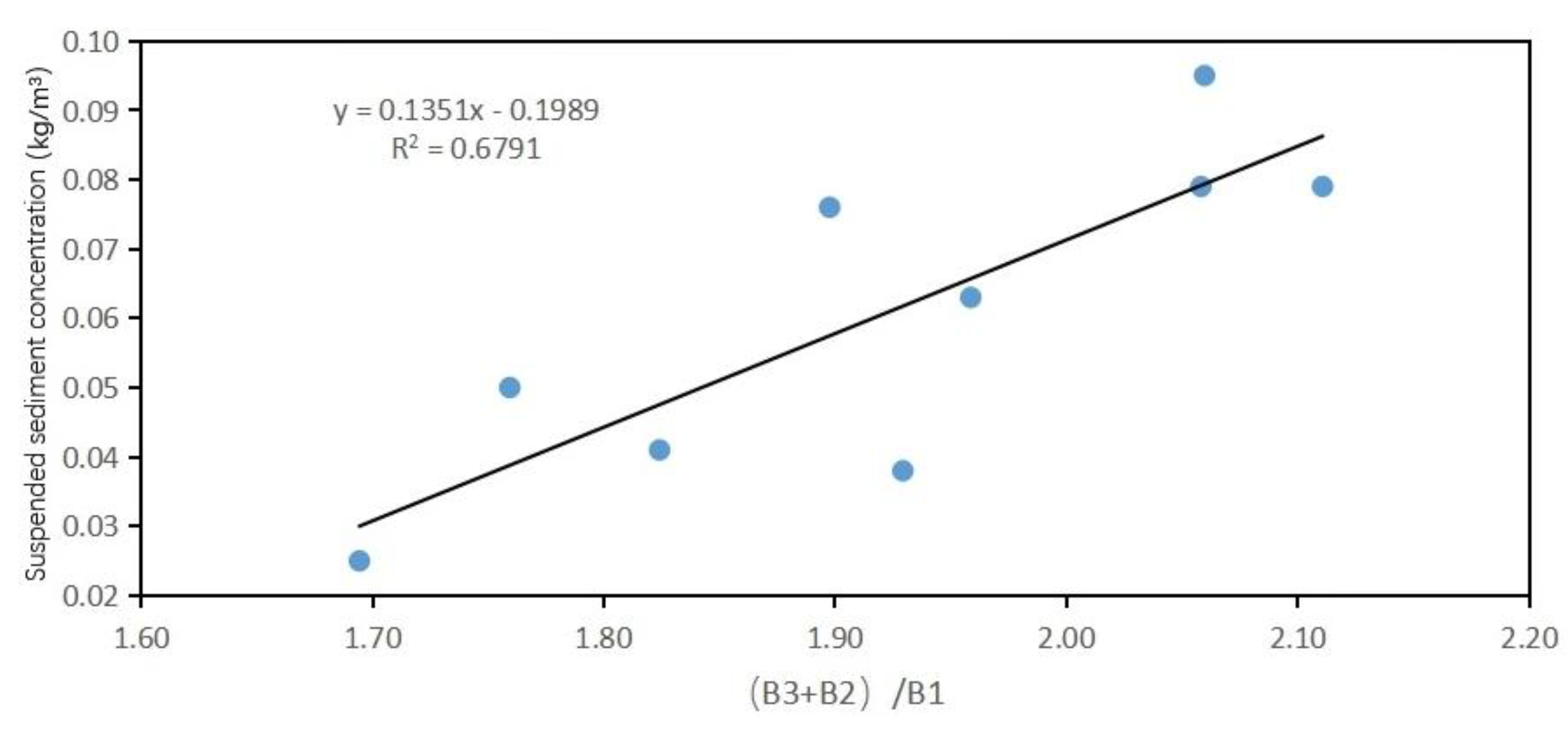
Linear function model of one order |
|
0.6604 |
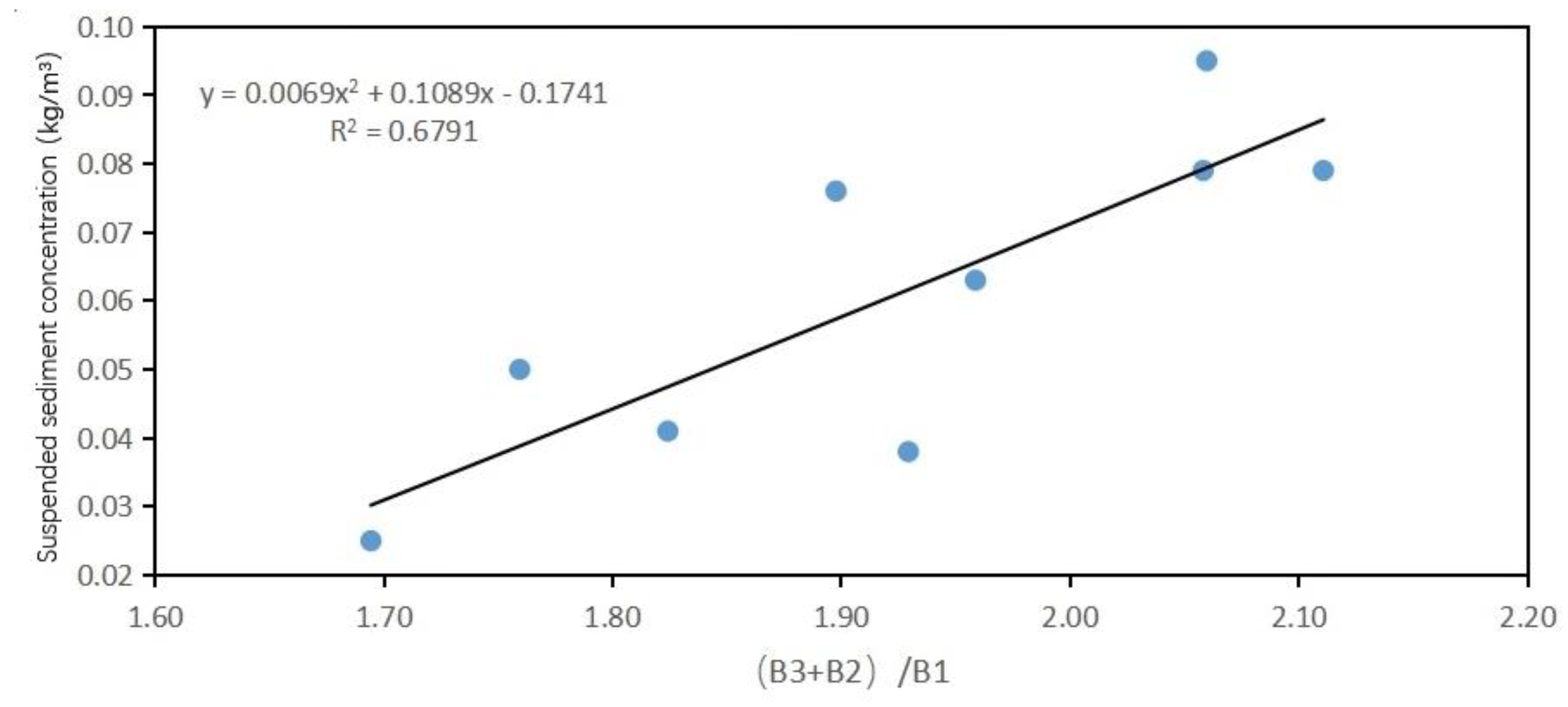
| Quadratic polynomial function model |
|
0.6604 |
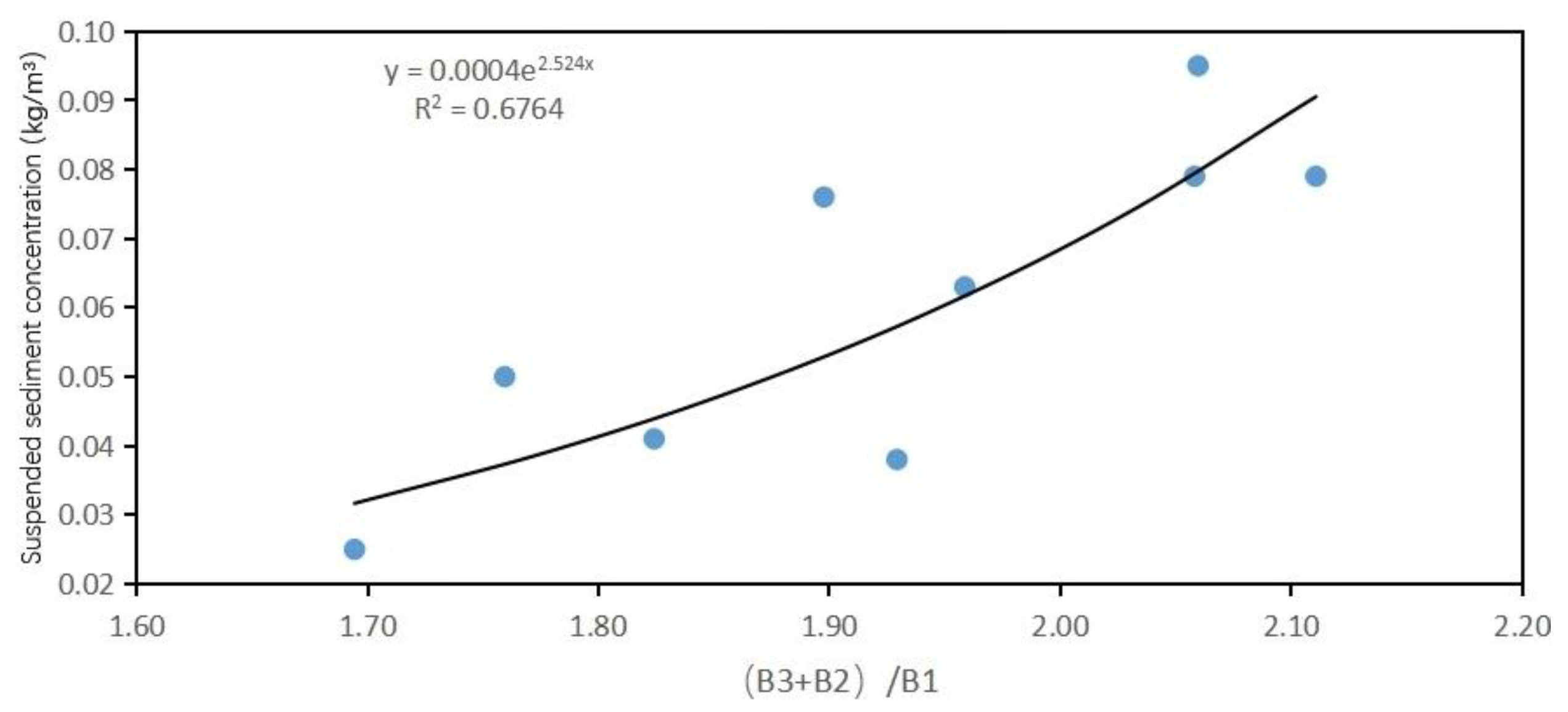
| Exponential function model |
|
0.6662 |
| Logarithmic function model |
|
0.6581 |
Table 15.
Inversion model construction of the relationship between B2/B1 band and suspended sediment concentration and its correlation coefficients.
Table 15.
Inversion model construction of the relationship between B2/B1 band and suspended sediment concentration and its correlation coefficients.
| Band |
Model |
Relation |
|
| B2/B1 |
Linear function model of one order |
|
0.6594 |
| Quadratic polynomial function model |
|
0.66 |
| Exponential function model |
|
0.6317 |
| Logarithmic function model |
|
0.659 |
By observing the above table, it can be seen that after combining the four bands B1, B2, B3 and B4 in pairs and solving the ratio, the obtained results are fitted with the measured suspended sediment concentration model. It is found that the maximum value of the correlation of the function model is higher than that of the single-band model, and the overall phenomenon is higher than that of the single-band model.
Among them, the correlation coefficient of the exponential function model of B3/B1 is the highest, reaching 0.6662. The correlation coefficients of linear functions, quadratic polynomials and logarithmic functions all reached above 0.6. The correlation coefficients of the linear function model, quadratic polynomial function model, exponential model and logarithmic model of B2/B1 have also reached above 0.6, which is better than the results of other band fitting models.Relatively speaking, in the inversion model fitting of B4/B2, a lower situation was presented.
It can be seen from this that the remote sensing inversion results of suspended sediment concentration using the two-band pairwise ratio as the independent variable are better than those calculated by the single-band method.
After conducting multi-band combinations and calculations on four different bands, namely B1, B2, B3, and B4, the correlation inversion model was calculated with the measured concentration of suspended sediment in the nearshore sea area, and the regression equation was constructed. According to the results of the fitting calculation, it is found that the correlation coefficients of the combination of band 1, band 2, and band 3 are slightly higher than those of other function models. Consistent with the data in the previous text, the correlation of the model combining band 4 with other bands remains poor. Therefore, the correlation regression equation between the concentration of suspended sediment in the nearshore waters of Haizhou Bay and the remote sensing band does not use the function model involving band 4 for inversion calculation.
2.3.3. Improvement of Existing Theory
The Rouse equation of diffusion theory is widely used due to its simple form and clear concept. It is often chosen when studying the vertical distribution of sediment concentration and the sedimentation rate of suspended sediment. When the horizontal flow velocity and the horizontal gradient of suspended sediment are relatively small, and the sediment exchange between the bottom bed and the upper water body reaches equilibrium, the vertical distribution law of suspended sediment concentration can be approximately expressed by Rouse's formula.
The Rouse equation method for determining the vertical distribution of sediment concentration is widely used in constant-flow rivers. Due to the particularly complex conditions of the dynamic field in the nearshore waters, the research on the vertical distribution of sediment concentration and sediment transport under non-constant flow conditions and multi-force coupling is still in the theoretical exploration stage, and there is no accurate description method. However, combining the theory of sediment motion mechanics with multivariate statistical analysis is a better solution.
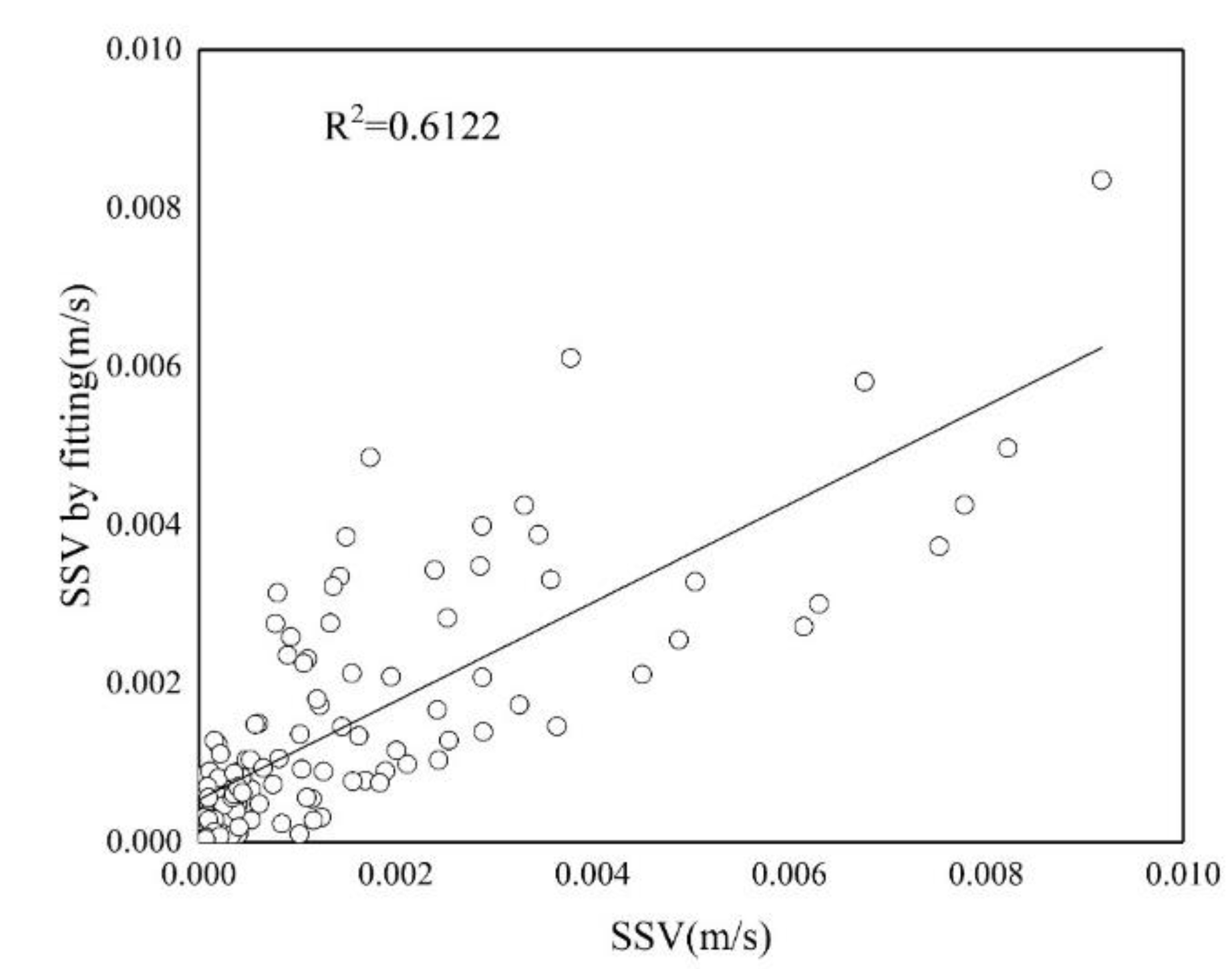
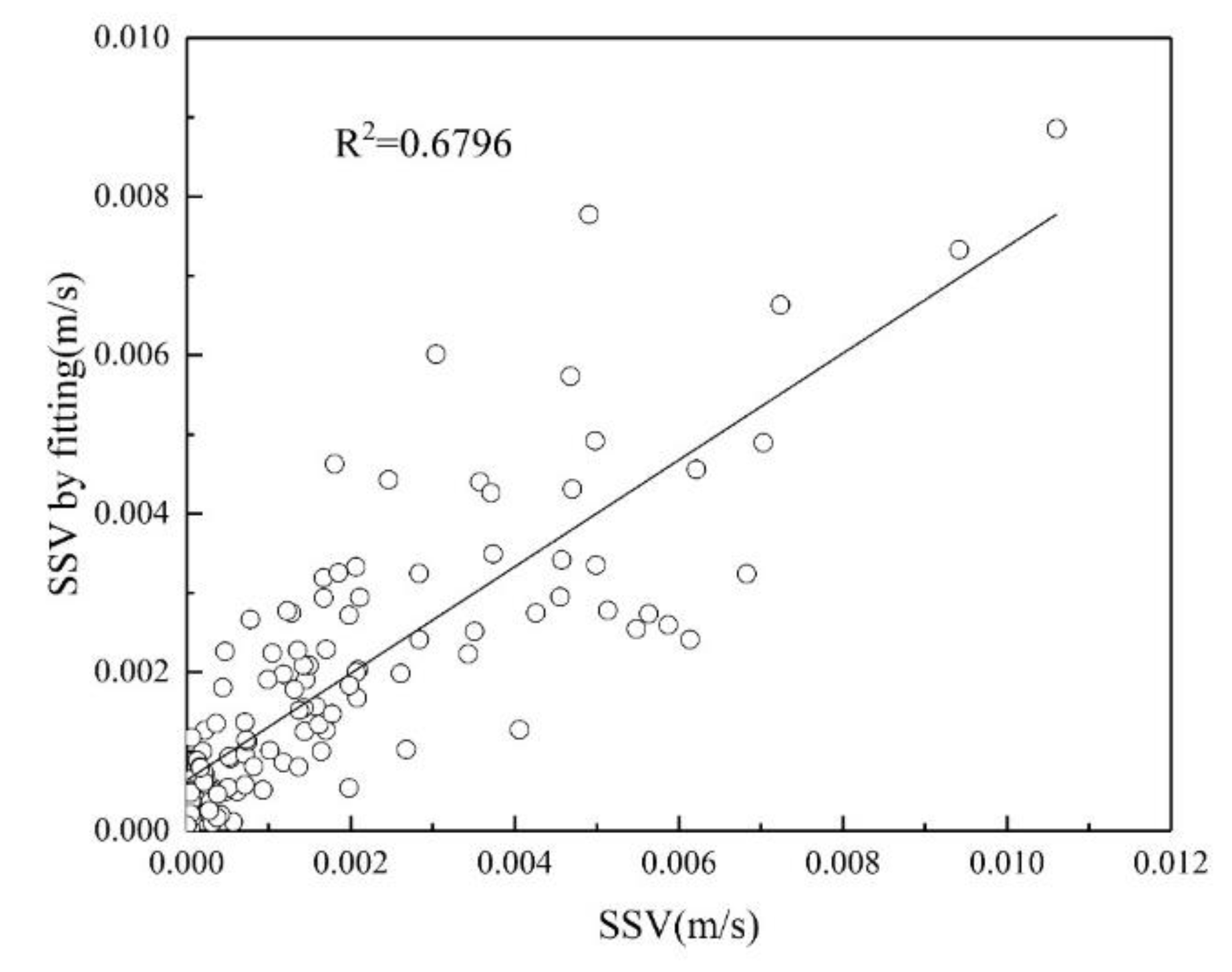
Han Xue et al. [
13] improved the Rouse equation, considering three physical quantities related to relative water depth, reference point concentration and flow velocity as independent variables, and the surface sediment concentration as a "random variable". A regression analysis was conducted on the vertical concentration distribution of sediment at the measurement point in Haian Bay, Qiongzhou Strait, and three dimensionless physical quantities
,
and
were introduced to improve the calculation accuracy. The improved formula is as follows:
The settling velocity of sediment is an important part of studying the concentration distribution of suspended sediment. The settling velocity of viscous sediments is influenced by the concentration of suspended sediment, turbulence and the composition of the concentration of suspended sediment. It is more scientific and reasonable to represent the physical quantities related to flow velocity with turbulence. Among them, turbulence shear is usually quantified by the root mean square velocity gradient G, which was first proposed by Camp and Stein [
14].
The root mean square velocity gradient G is defined as the turbulent energy dissipation ε divided by the square root of the fluid's kinematic viscosity ν. The relationship formula of turbulent shear G is as follows
For stable, uniform conditions where the diffusion of turbulent kinetic energy is ignored, it is assumed that the turbulent energy dissipation ε is equal to the turbulent energy generation P:
Suppose a logarithmic velocity profile:
Furthermore, it is assumed that the maximum shear τ at the bed layer linearly decreases to zero on the surface:
Among them: is the shear velocity that determines the uniformity of suspension, h is the water depth, z is the relative water depth, v is the kinematic viscosity of the fluid, which is at 25 degrees, and k is the Karman constant of non-stratified flow, with a value of 0.408.
Replace "
" in formula (2) with "
lnG" to obtain the following new formula:
In the formula: c represents the sediment concentration of each layer; h represents water depth; z represents the relative water depth; represents the concentration of surface sediment. G is the root mean square velocity gradient that turbulence is usually quantified.
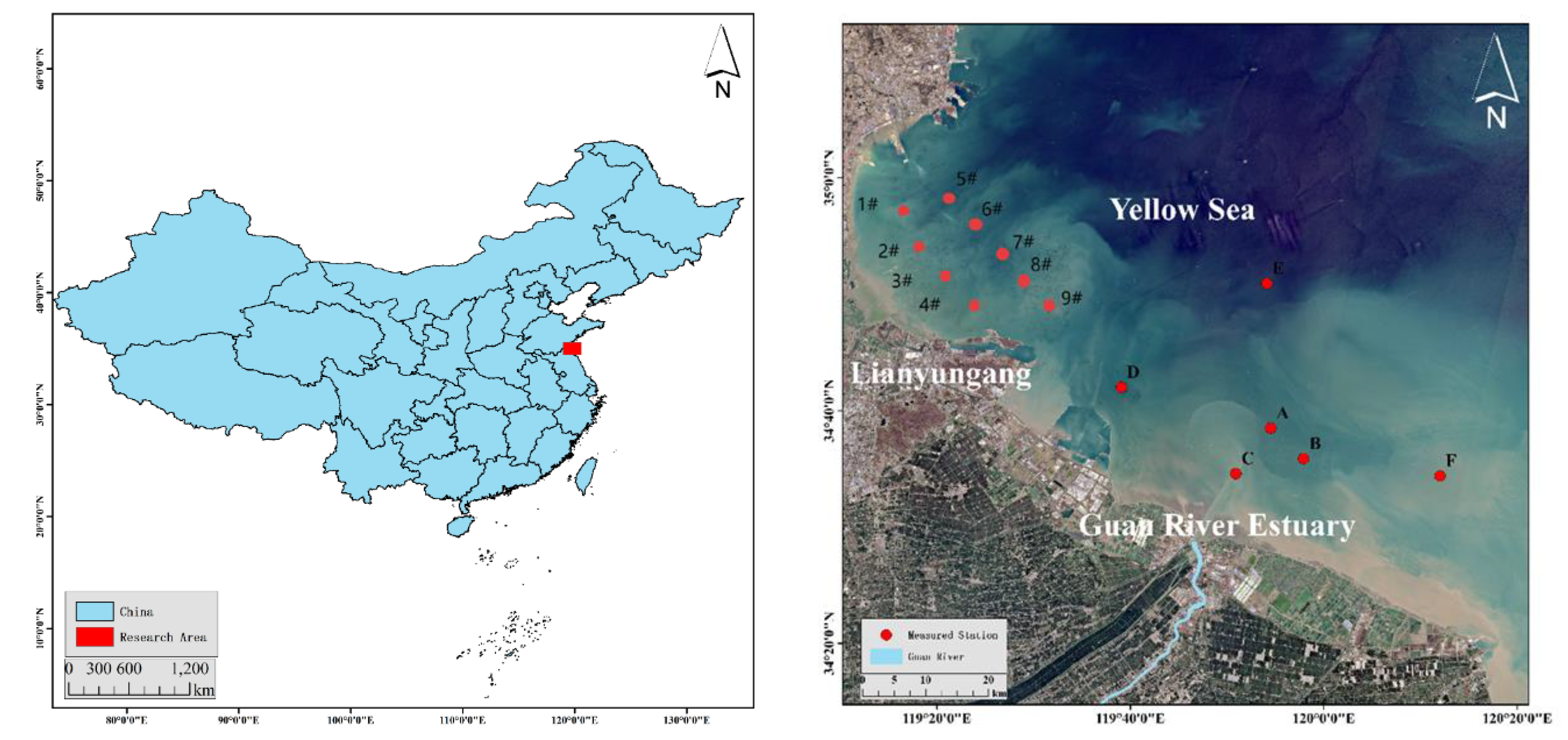
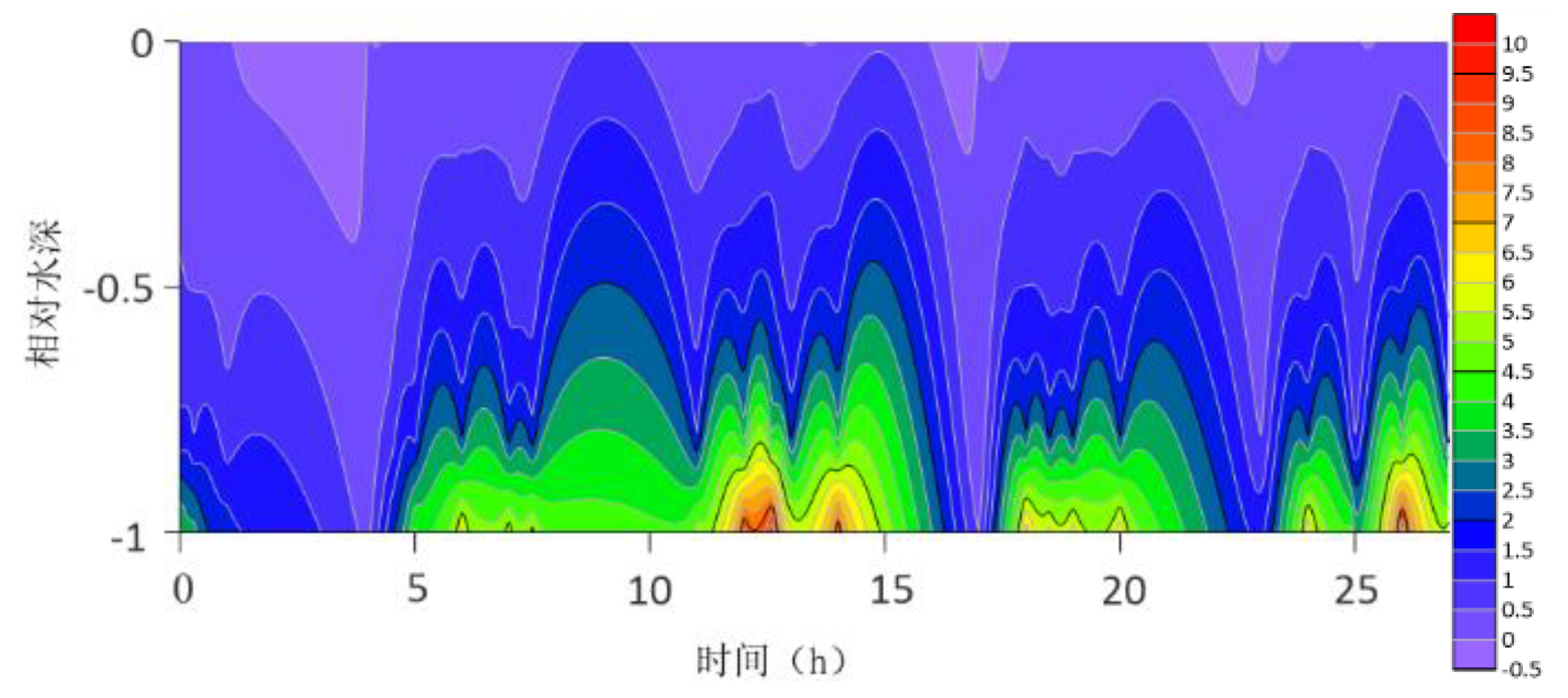
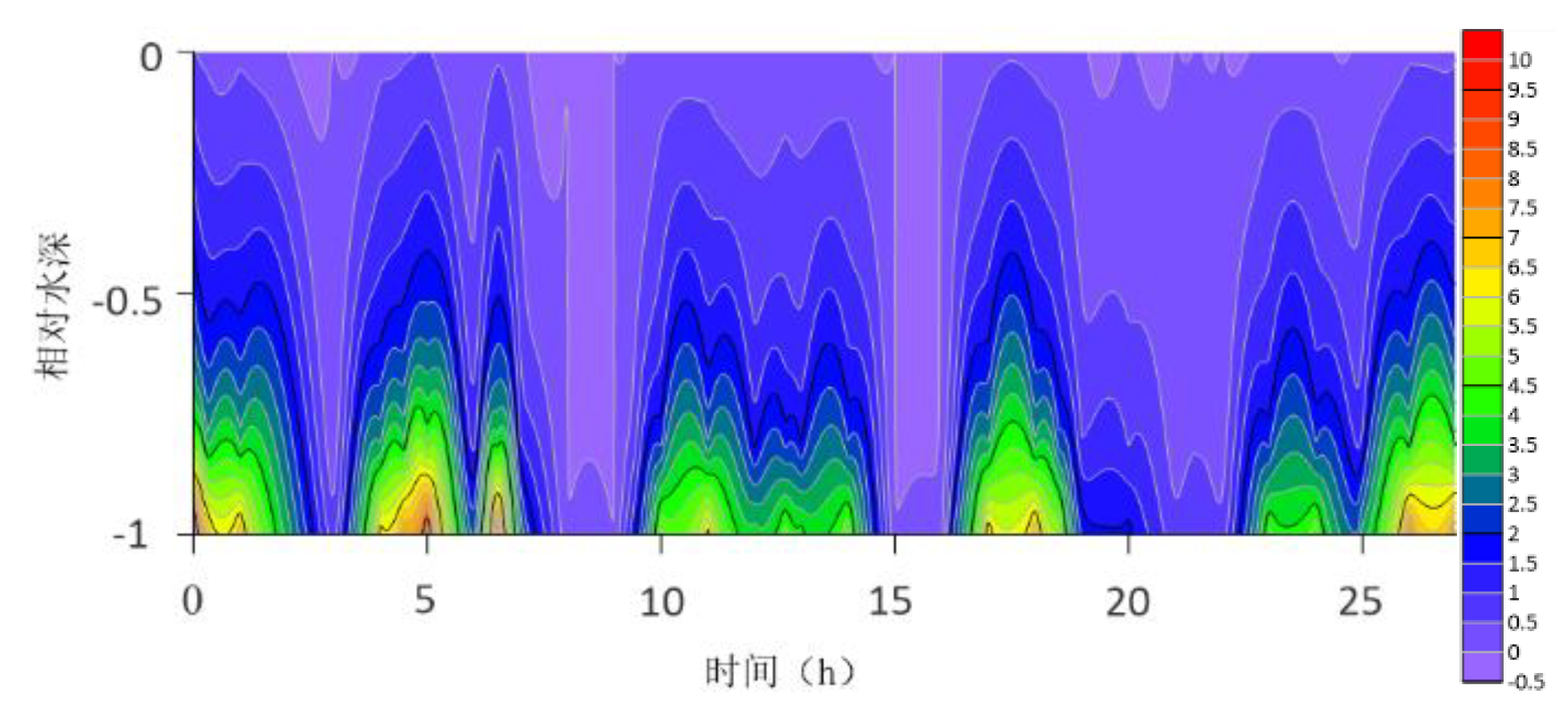
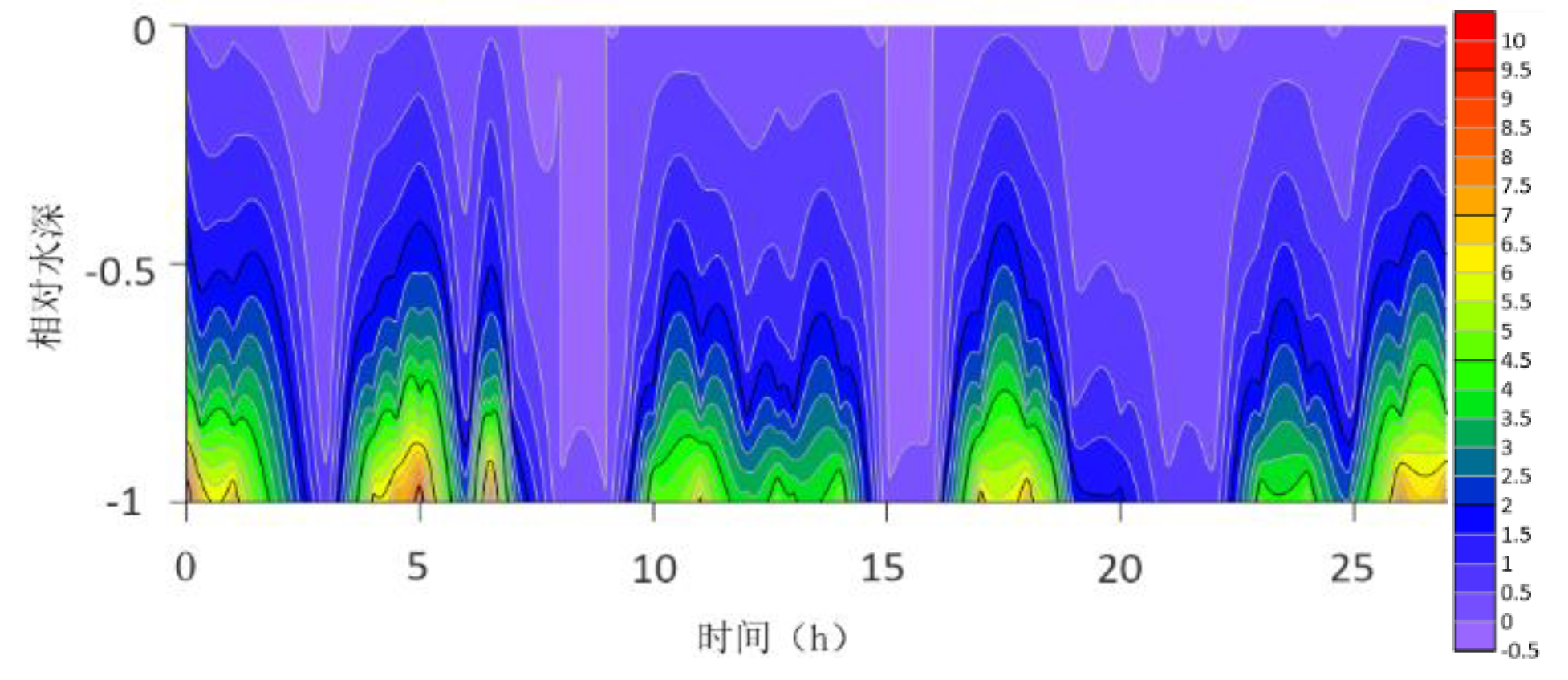
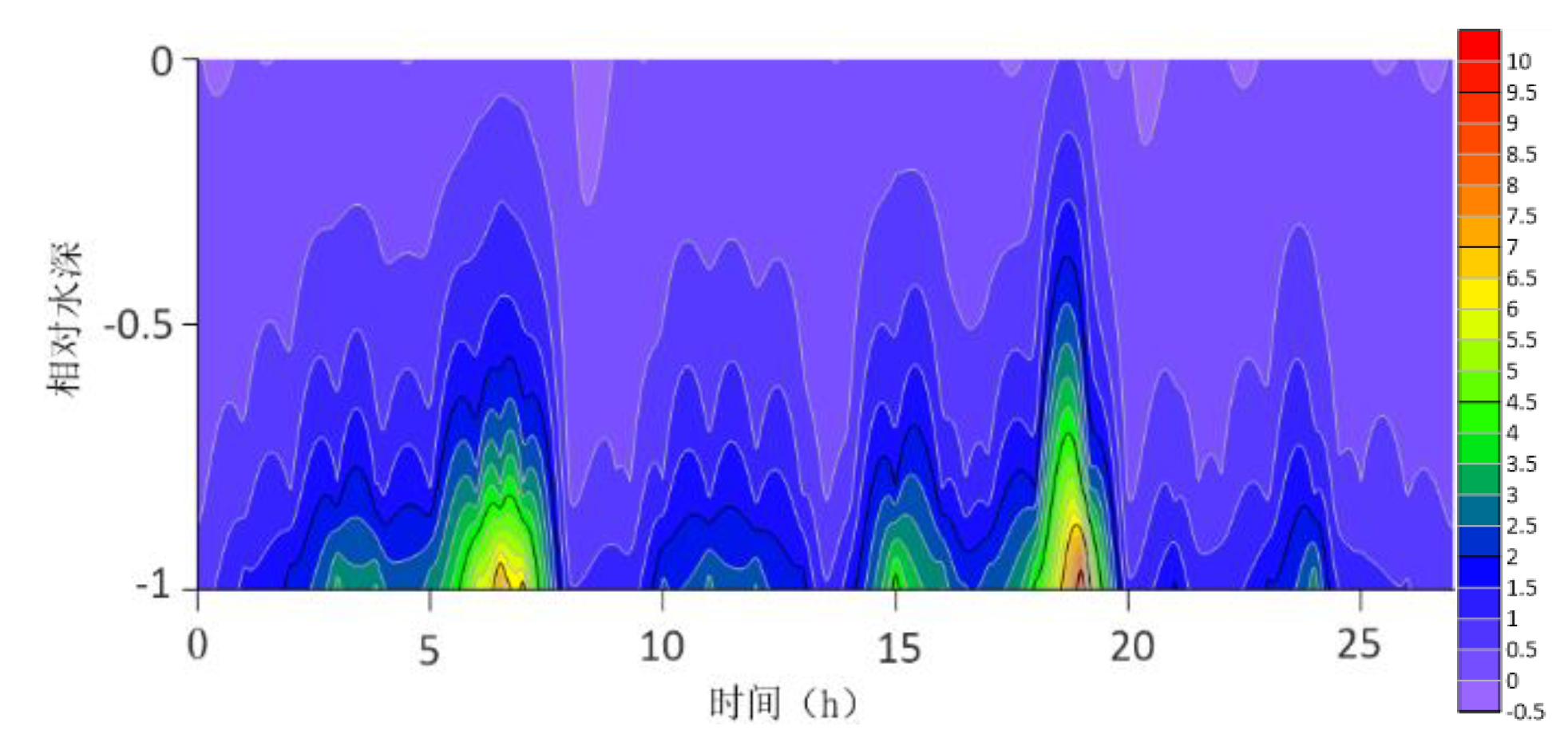
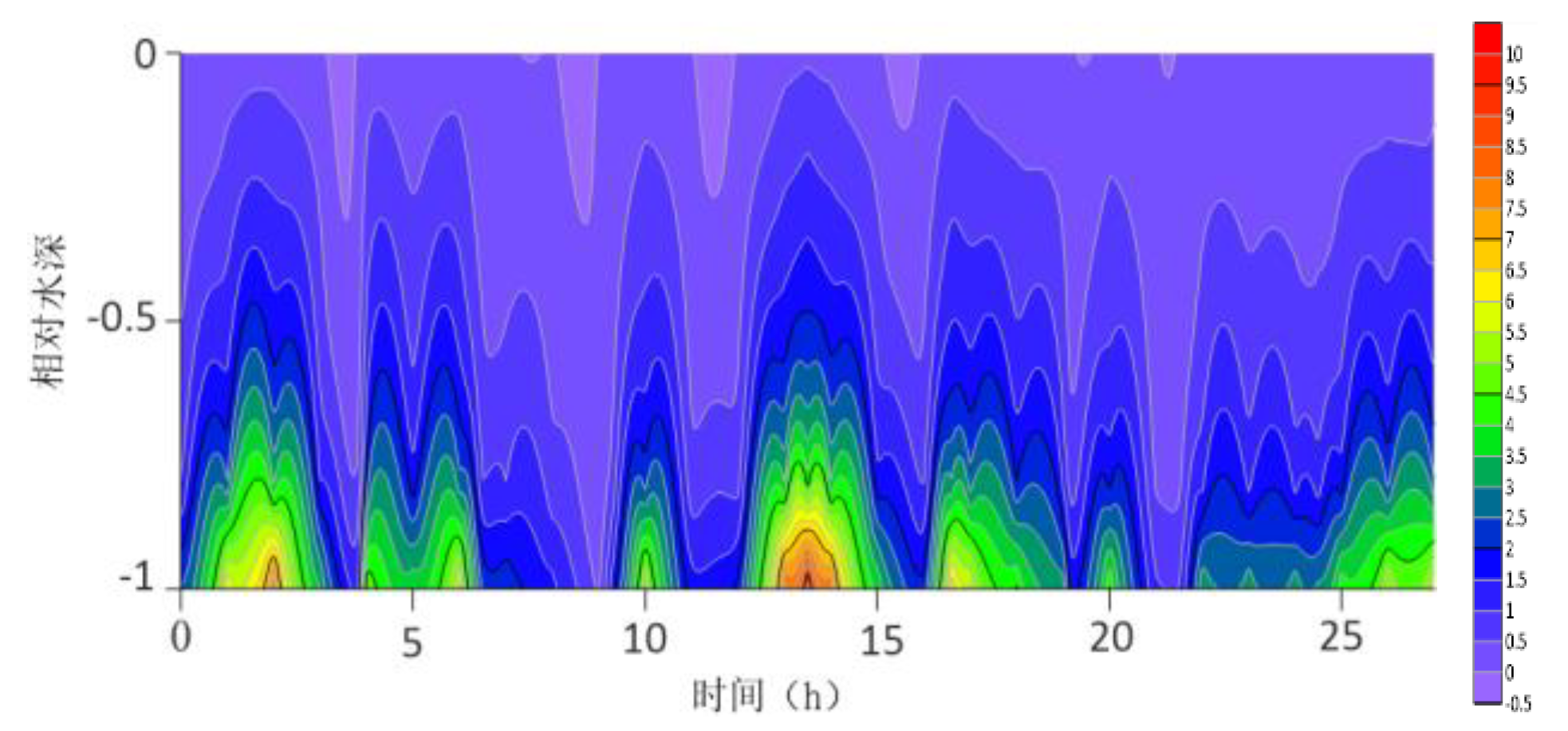
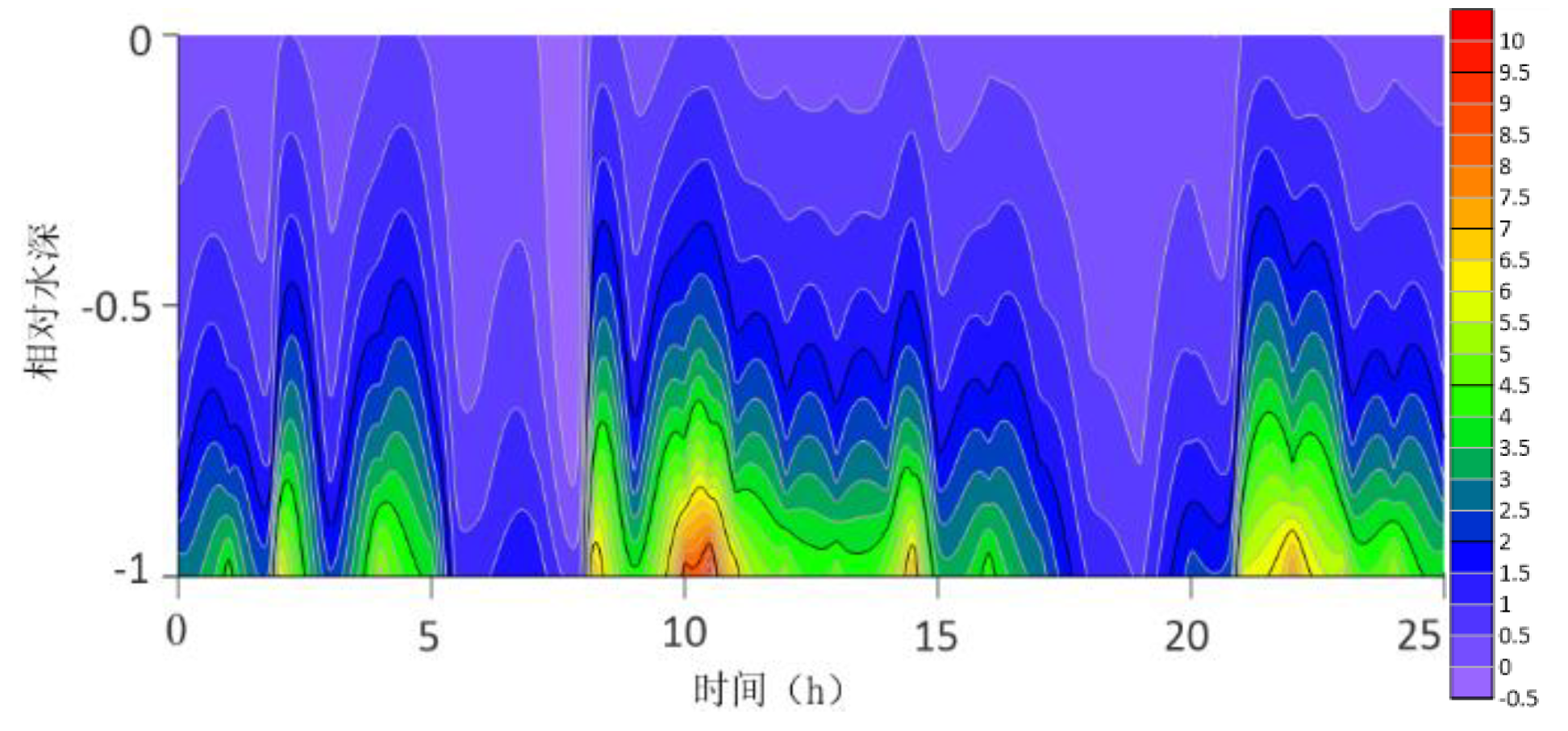
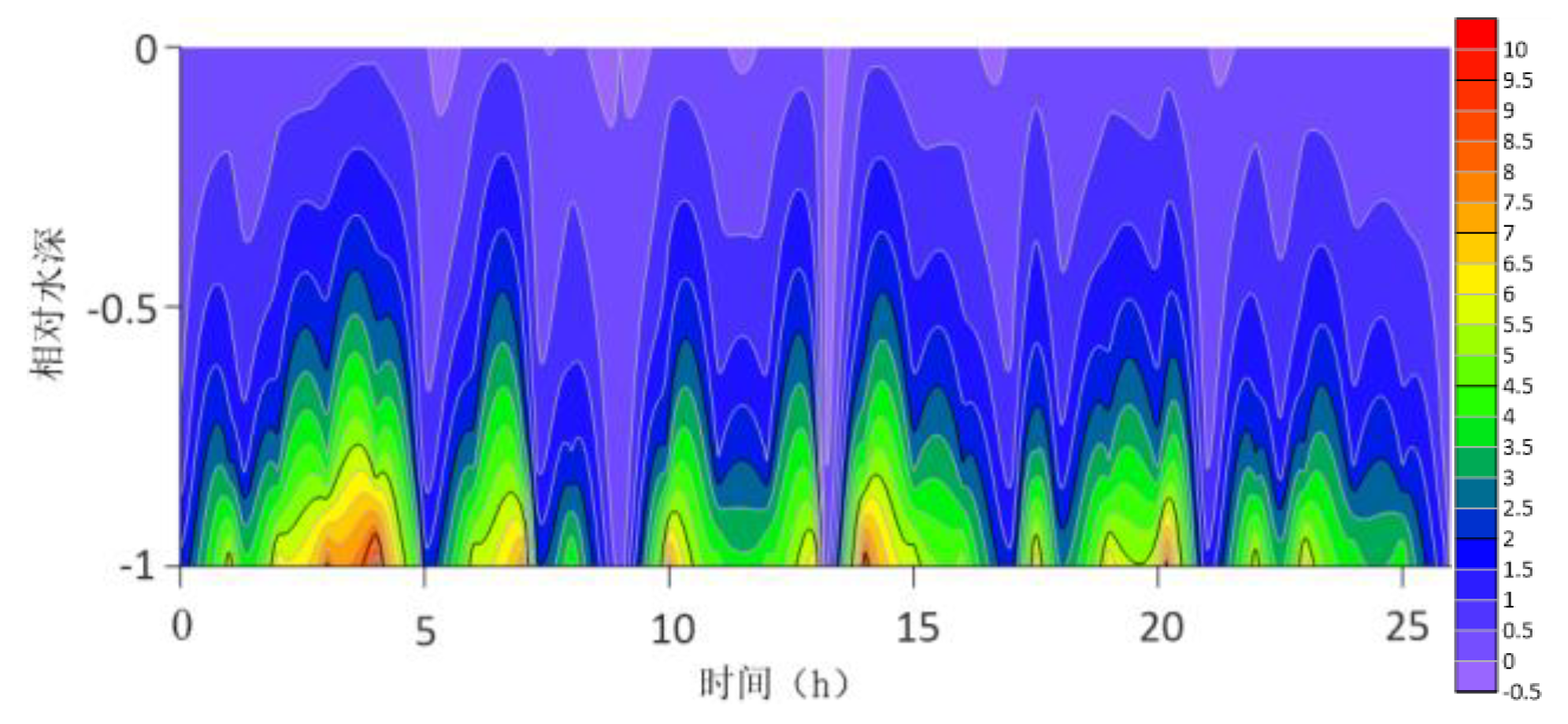
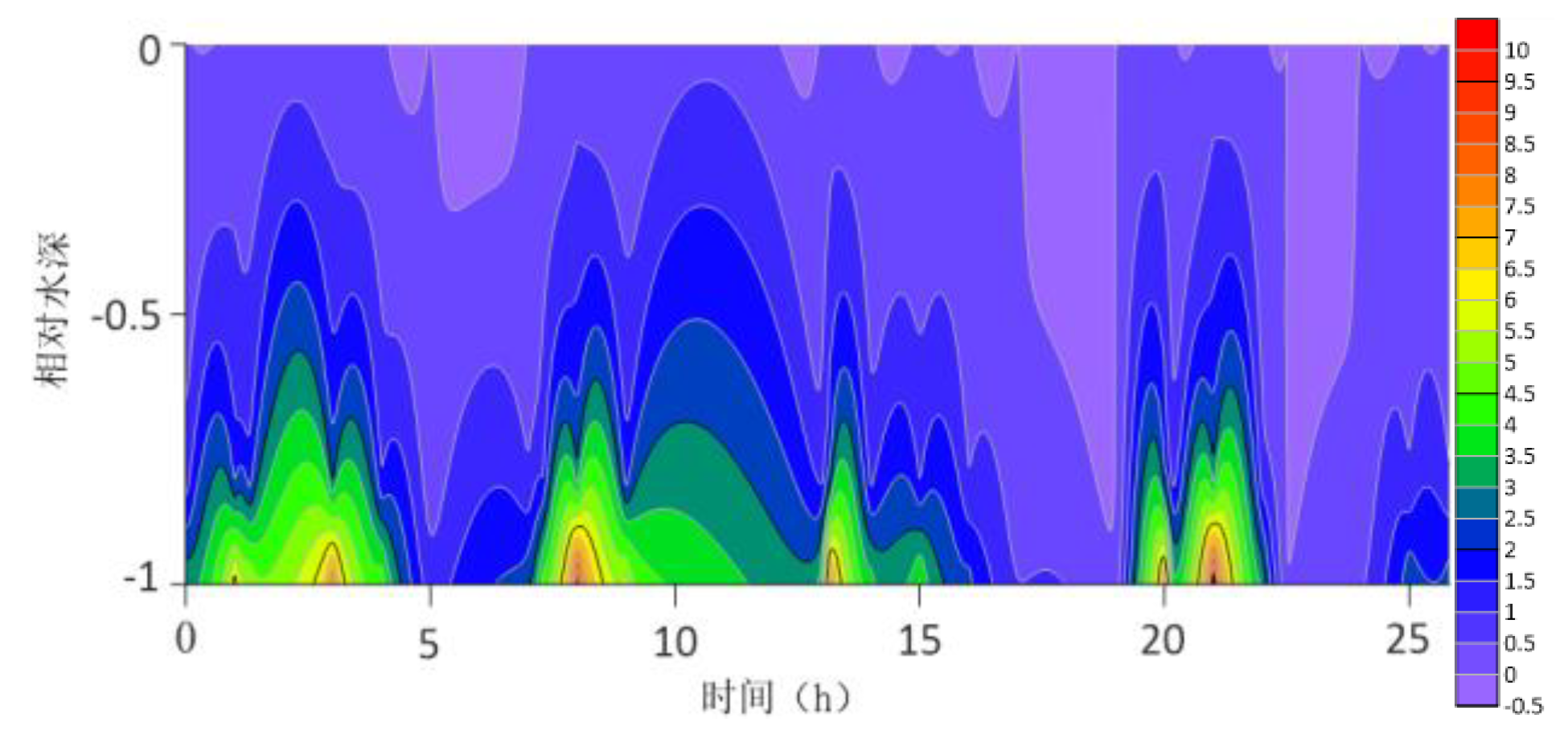
The location maps of each research station (
Figure 2) and the variations of turbulent shear at different times at each station are shown in the following figures (
Figure 2,
Figure 3,
Figure 4,
Figure 5,
Figure 6,
Figure 7,
Figure 8,
Figure 9,
Figure 10,
Figure 11,
Figure 12 and
Figure 13) :
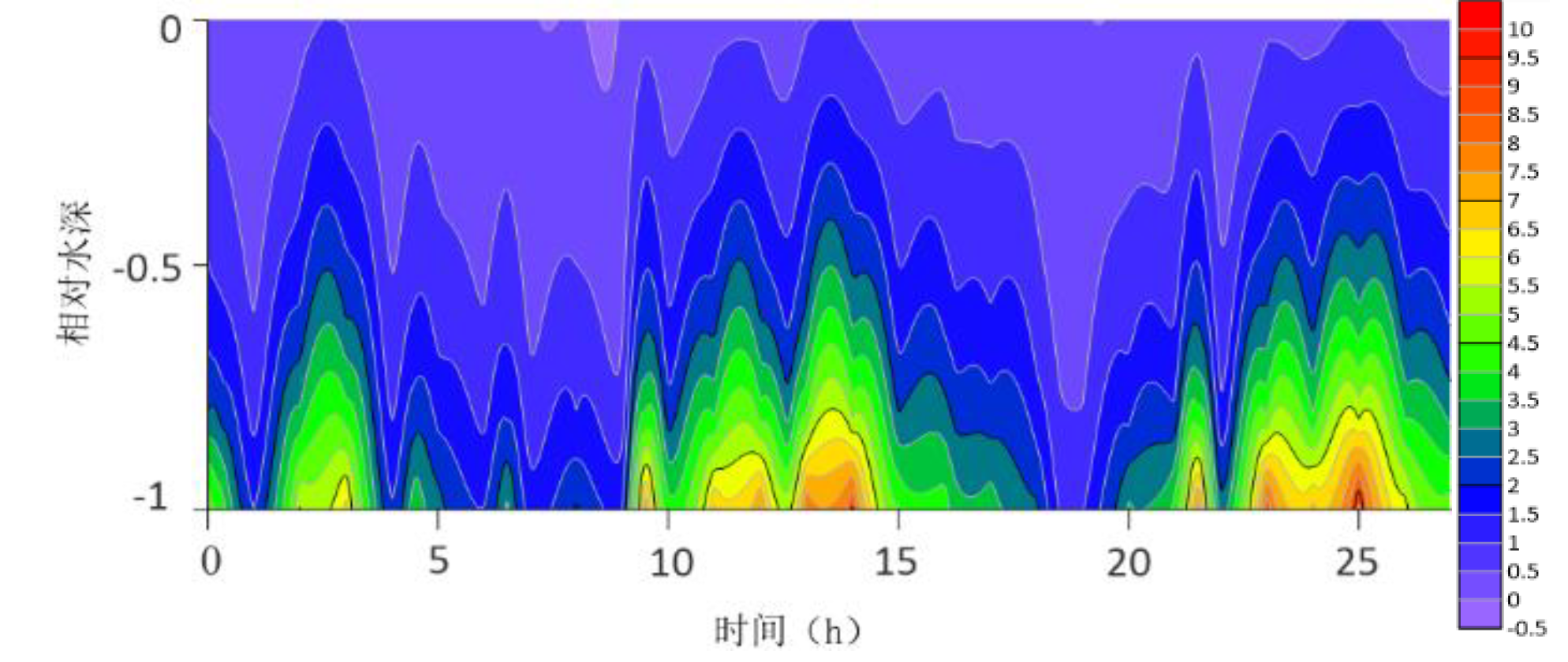
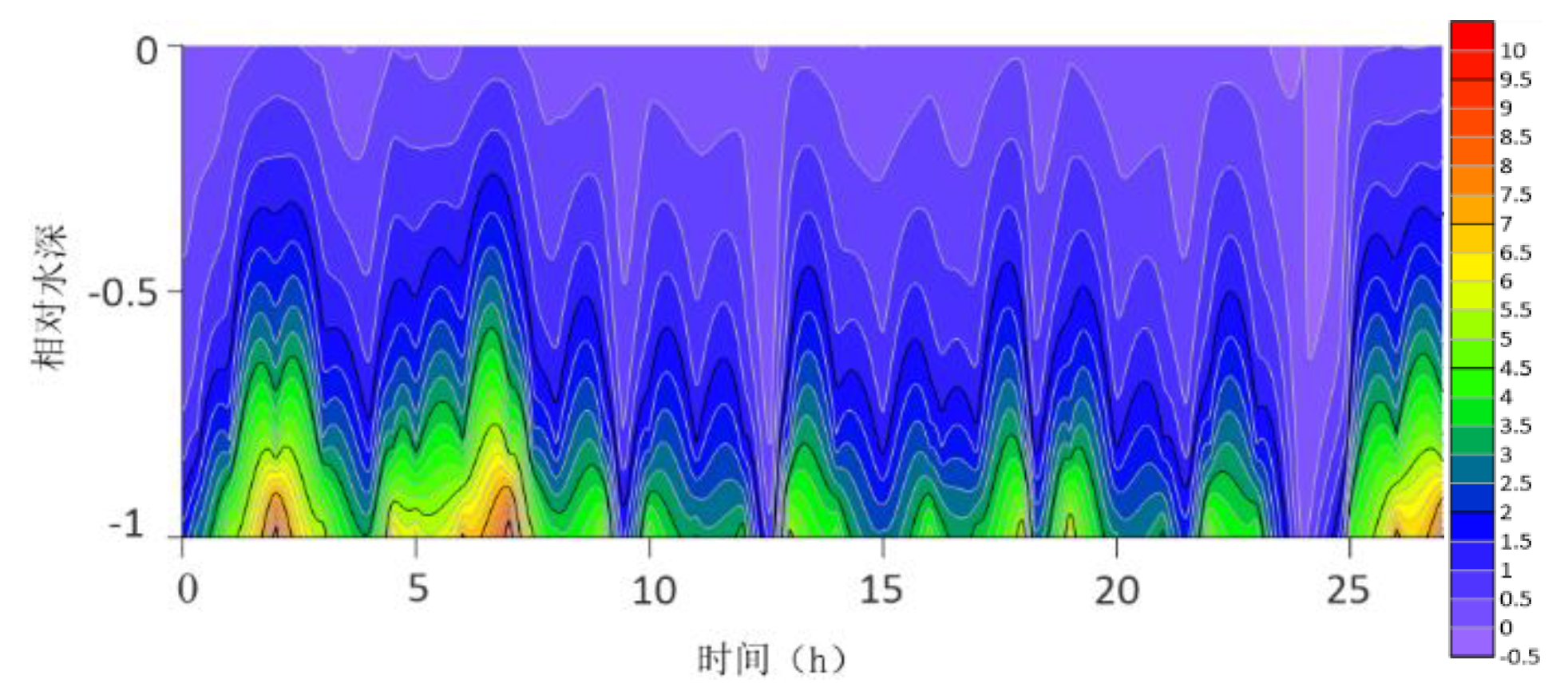
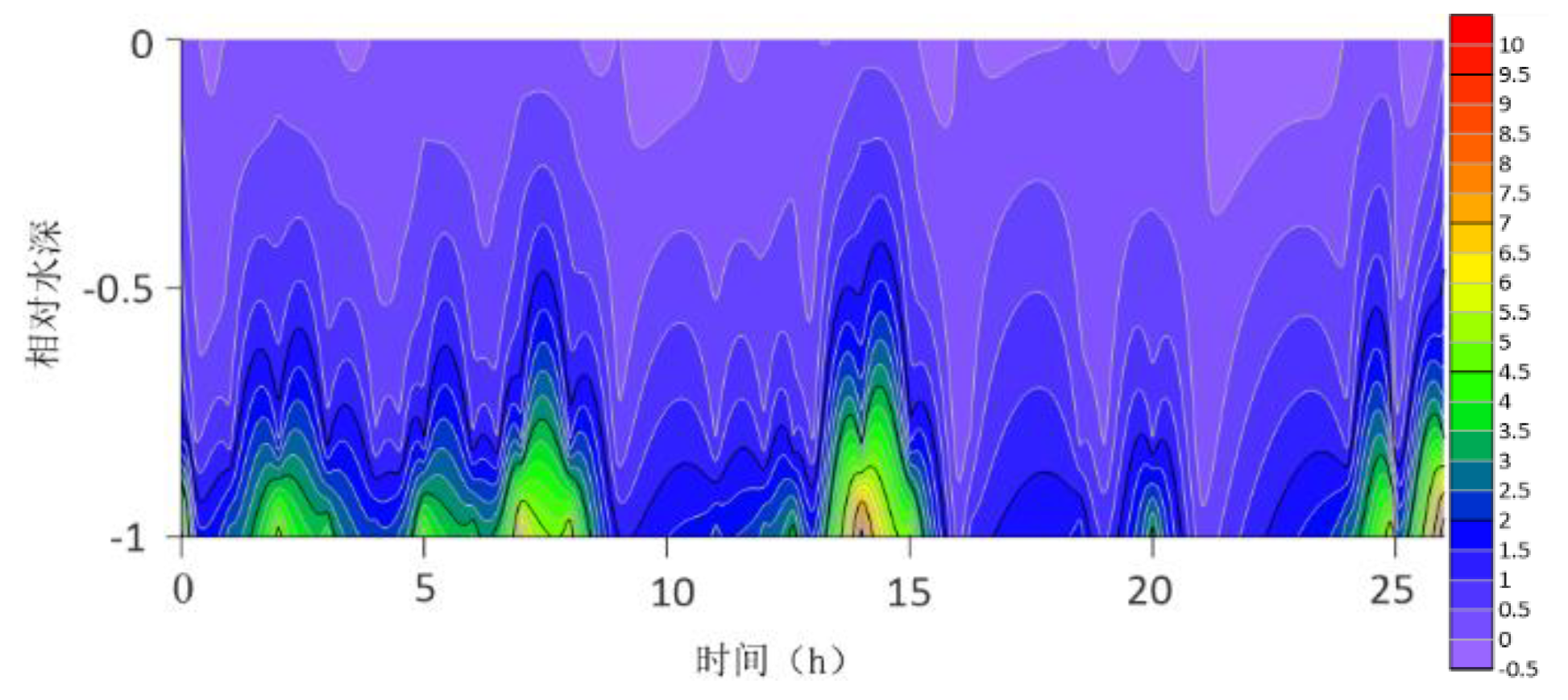
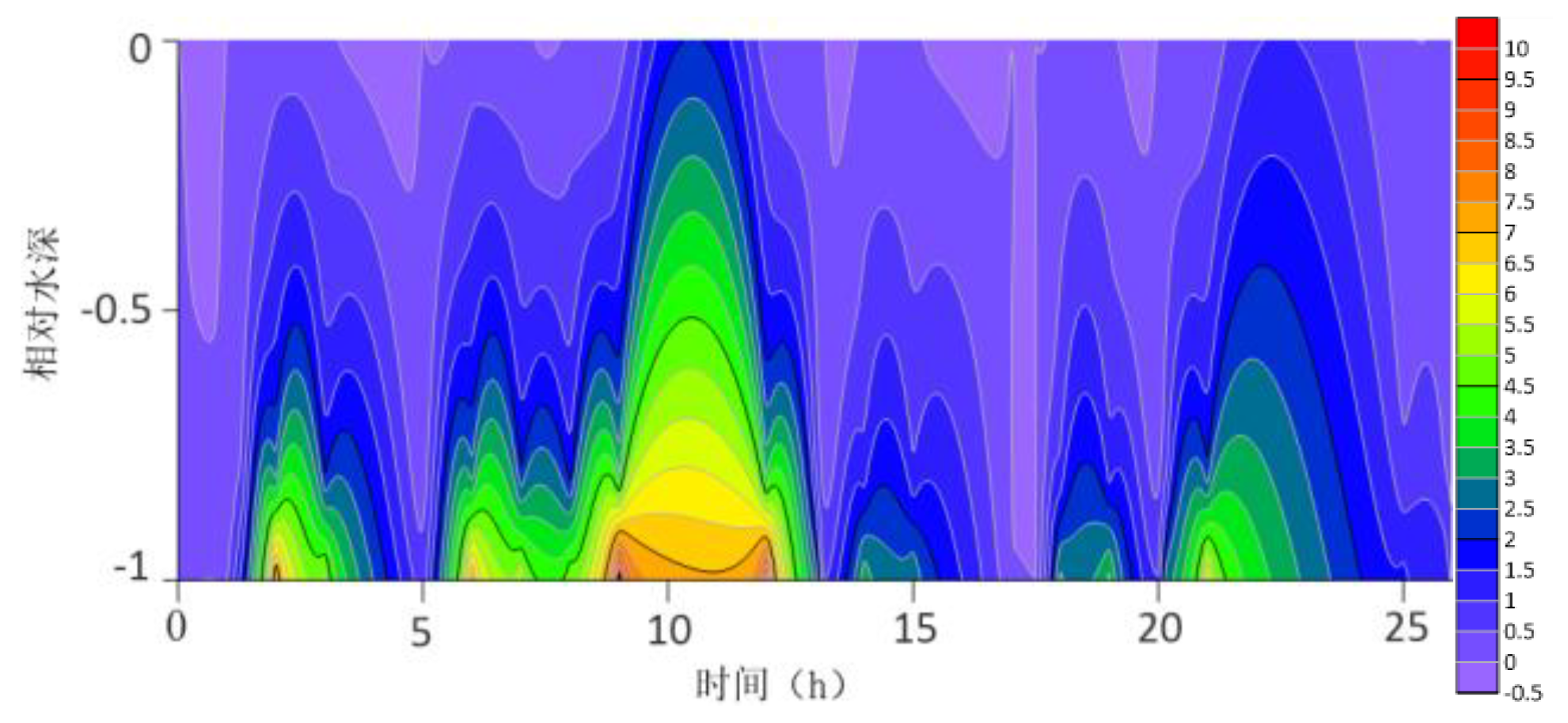
The contour lines of the turbulent shear G obtained from the velocity profile are shown in
Figure 2,
Figure 3,
Figure 4,
Figure 5,
Figure 6,
Figure 7,
Figure 8,
Figure 9,
Figure 10,
Figure 11,
Figure 12 and
Figure 13. The variation range of G throughout the water column is -0.5S
−1 to 10 S
−1. G is higher at the bottom than at the surface because the turbulence near the bottom is greater. For most time periods, G varies between 0S
−1 and 7S
−1. During the research period, the mid-tide peak of the G value was another distinct feature. The peak value of G coincides with the peak value of the current speed because G is a function of speed.