Submitted:
25 December 2025
Posted:
26 December 2025
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
- 2.1. Experimental Sites
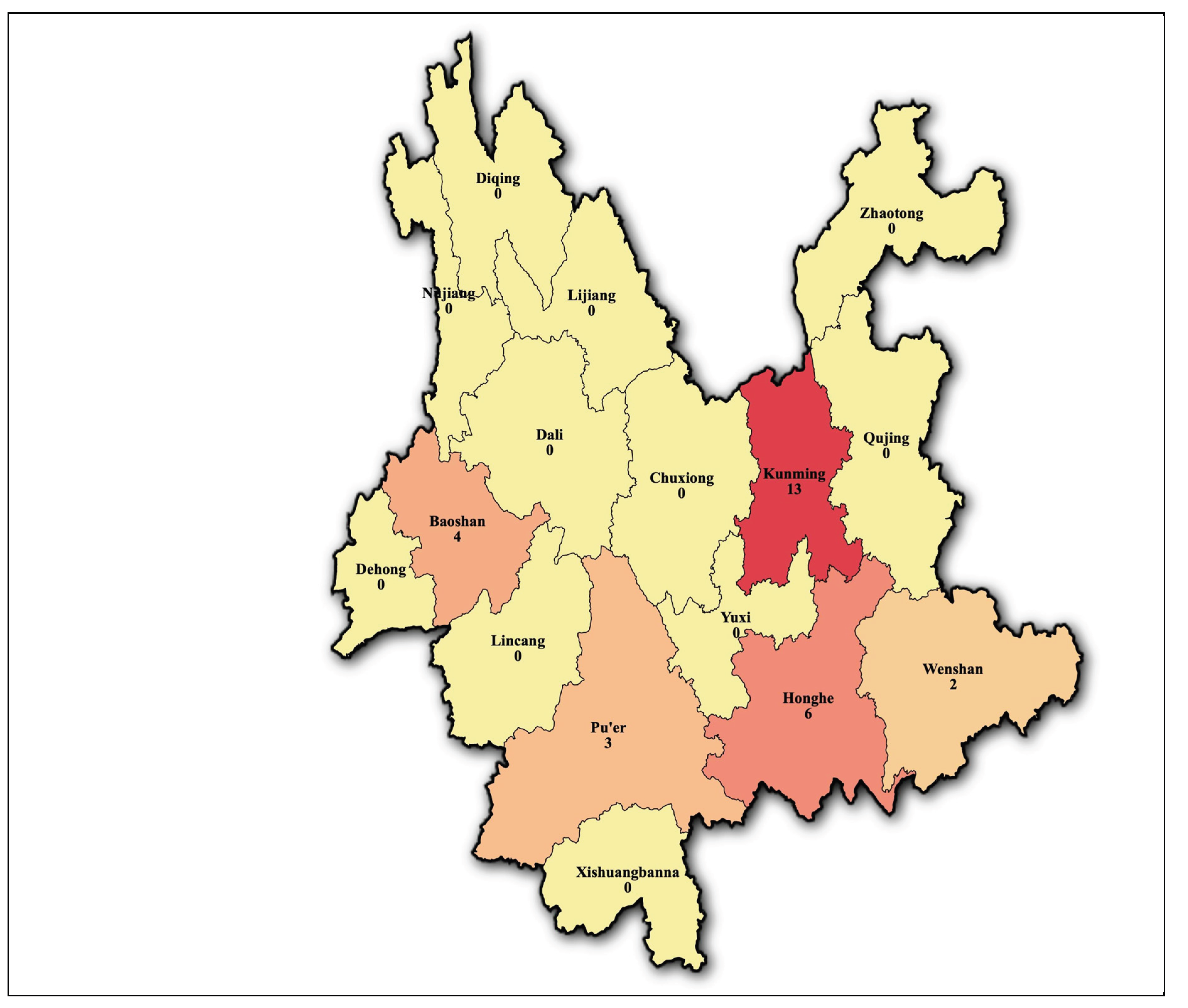
2.2. Experimental Materials
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Determination of Indices and Methods
2.4.1. Sensory Quality Evaluation
| Sensory indicators | Scoring Criteria | Score | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| odor | It has a strong butyric or ammonia odor, or almost no sour taste. It has a strong butyric acid taste, or a pungent, burnt, or musty smell. It has a weak butyric acid taste, or a strong sour taste and a weak aromatic taste. It has a strong or distinct aroma of bread, without any butyric acid odor. |
2 4 10 14 |
||
| Structure | Stem and leaf rot or severe pollution The stem and leaf structure is visibly damaged, or there is mild contamination. Slight damage to stem and leaf structure The stem and leaf structure is intact and clearly visible. |
0 1 2 4 |
||
| Color | Severe discoloration, turning dark green or brown. Slight discoloration, turning light yellow or yellowish-green. It closely resembles the color of the raw material, turning light brown after drying. |
0 1 2 |
||
| Total Score | 16-20 | 10-15 | 5-9 | 0-4 |
| grade | Level 1 Excellent | Level 2 is acceptable | Level 3 Intermediate | Level 4 corruption |
2.4.2. Determination of Nutrient Content
2.4.3. Determination of Fermentation Quality
2.4.4. Gray Relational Analysis Method for Evaluating Nutritional Value
2.4.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Analysis
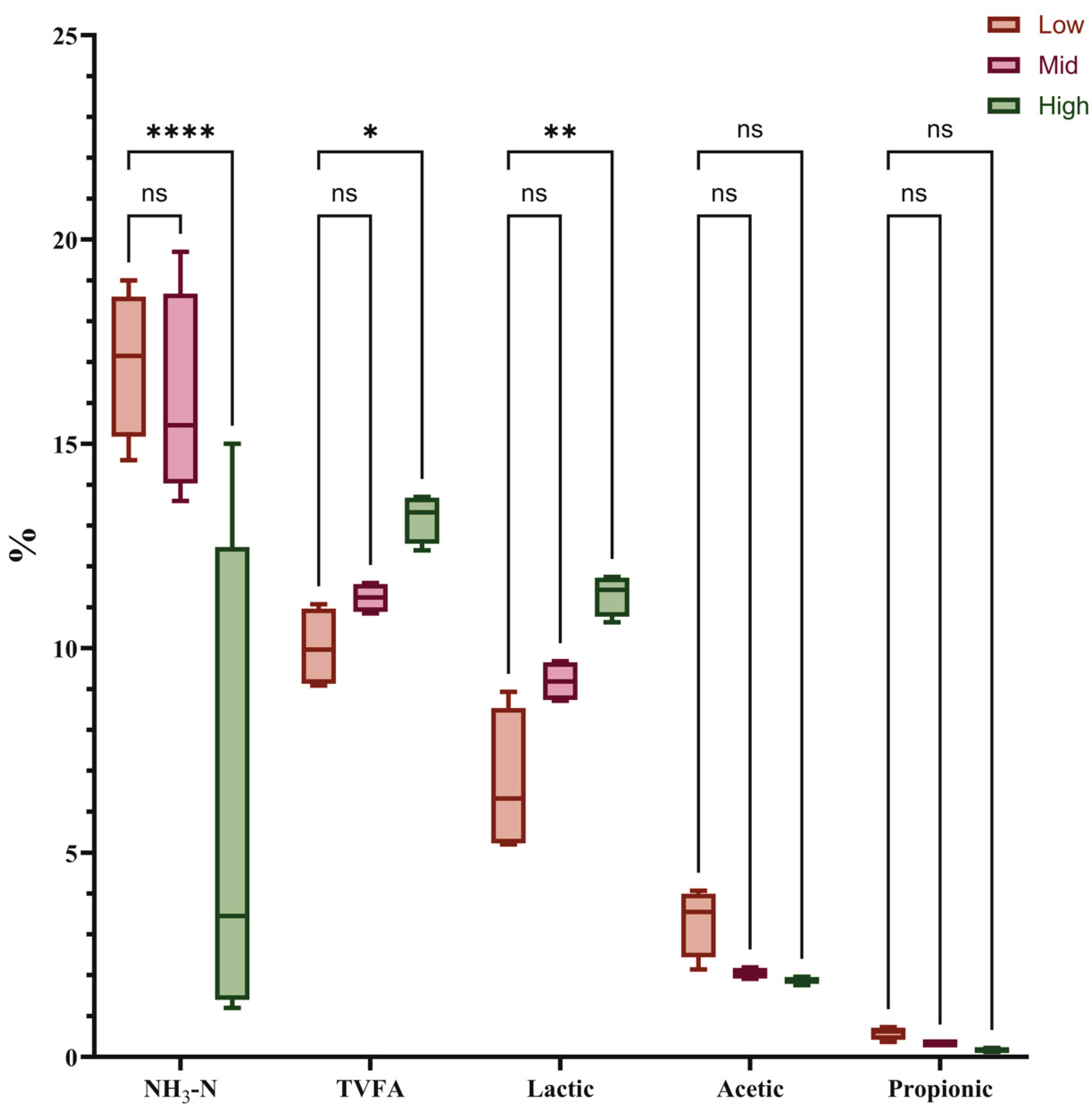
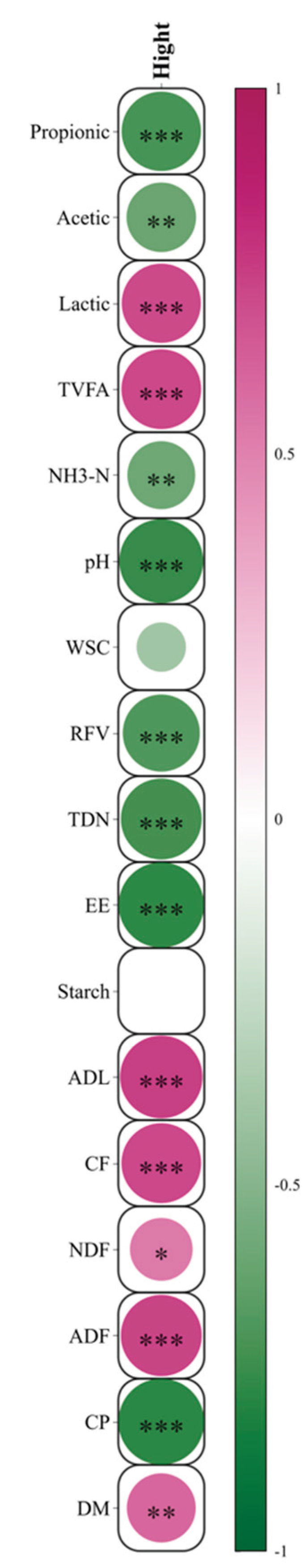
3.1. Effects of Growth Height on Ensiling Quality and Cellulose Degradation of Juncao
| Item | Group | SEM | p-Vaule | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low | Mid | High | |||
| DM | 12.90Aa | 12.65Aa | 14.98Bb | 0.34 | <0.01 |
| CP | 13.93Cc | 10.18Bb | 7.85Aa | 0.76 | <0.01 |
| ADF | 40.76Aa | 43.40Bb | 45.40Cc | 0.64 | <0.01 |
| NDF | 62.98 | 64.33 | 65.25 | 0.42 | 0.67 |
| CF | 36.75Aa | 39.40Bb | 40.83Cc | 0.56 | <0.01 |
| ADL | 3.50Aa | 3.95Bb | 5.01Cc | 0.20 | <0.01 |
| Starch | 0.40Aa | 0.90Bb | 0.40Aa | 0.09 | 0.02 |
| EE | 3.89Cc | 2.83Bb | 2.22Aa | 0.21 | <0.01 |
| TDN | 59.58Cc | 57.58Bb | 55.88Aa | 0.50 | <0.01 |
| RFV | 84.50Bb | 79.75Aa | 76.00Aa | 1.21 | <0.01 |
| WSC | 1.64 | 1.50 | 1.23 | 0.10 | 0.27 |
| pH | 4.41Cc | 4.00Bb | 3.32Aa | 0.14 | <0.01 |
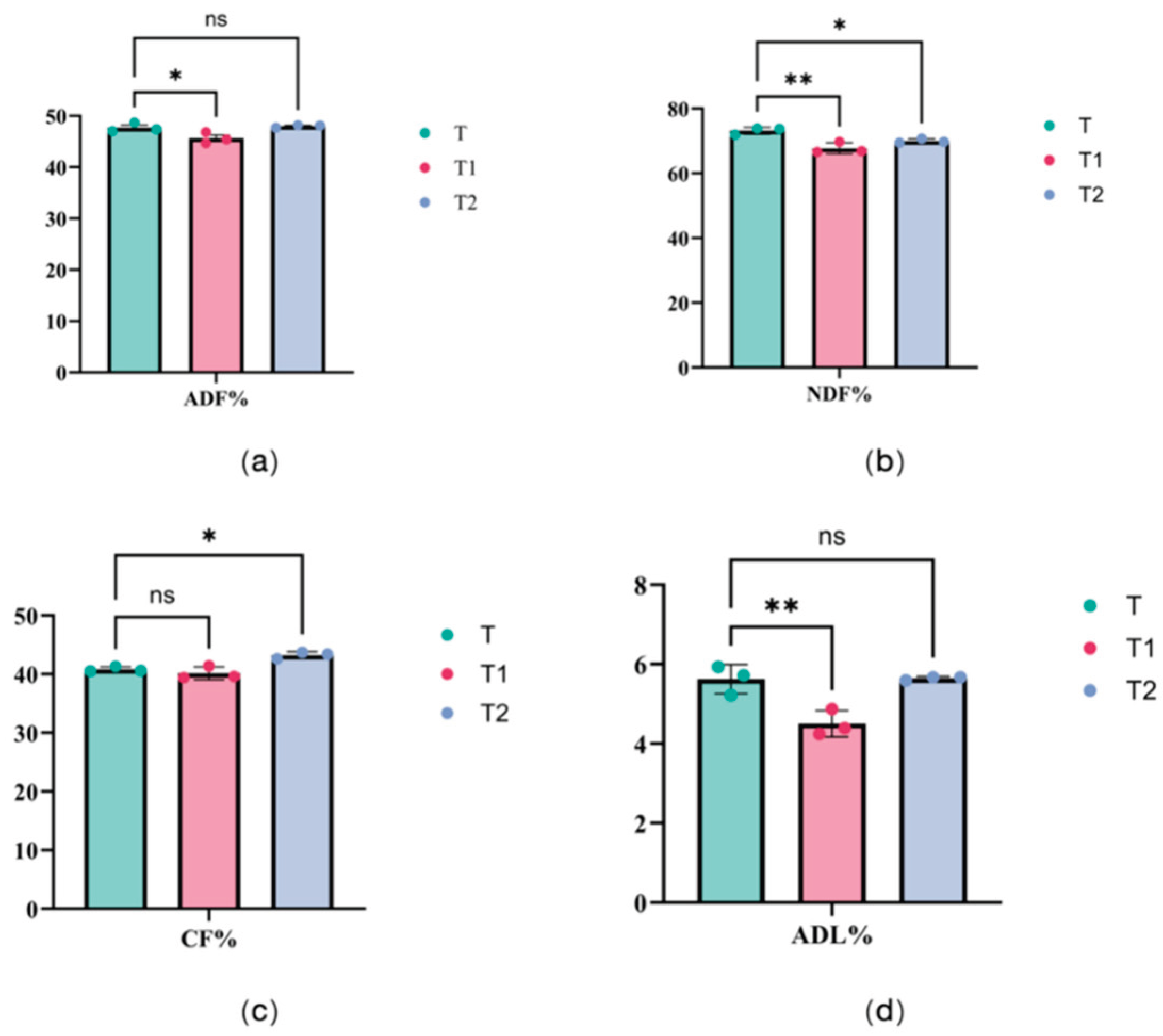
3.2. Effects of Silage Additives on Silage Quality and Cellulose Degradation of Juncao
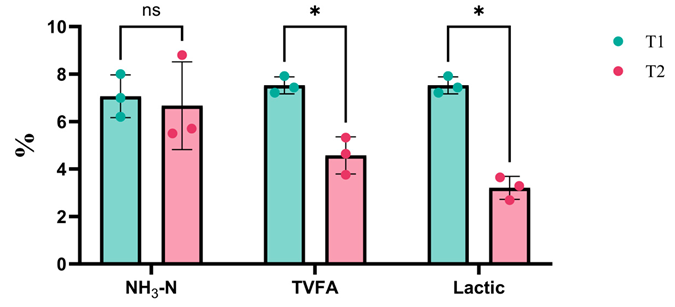
3.3. Impact of Microbial Inoculants on Silage Quality and Cellulose Degradation of Juncao
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ineichen, S.M.; Zumwald, J.; Reidy, B.; Nemecek, T. Feed-food and land use competition of lowland and mountain dairy cow farms. animal 2023, 17(12), 101028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triveni, B.; Rao, K.; Teja, A.; RaviKumar, M.; Singh, T. Hybrid napier grass a potential asset for livestock production. 2022, 11, 4081–4083. [Google Scholar]
- Dong-sheng, Y.; Yu-chi, N.I.U.; Yu-fei, Y.; Xin-lei, J.; Shui-yuan Ha, O. Effect of nutrient quality in different parts, height treatments, and silage time of Cenchrus fungigraminus in Hetao area. Feed Res. 2024, 47(17), 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coblentz, W.K.; Akins, M.S. Silage review: Recent advances and future technologies for baled silages. J Dairy Sci. 2018, 101(5), 4075–4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muck, R.E.; Kung, L., Jr.; Collins, M. Silage Production. In Forages; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 2020; pp. 767–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, F.F.; Kemp, S.E.; Schmidt, R.J.; Cardoso, F.C. Effects of cut height and inoculant application on yield, nutrient composition, fermentative profile, and in vitro degradability of brown midrib whole-plant corn silage. Appl Anim Sci. 2023, 39(3), 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarekegn, A.; Nurfeta, A.; Bayssa, M. Height at harvest and additives influence desho grass (Pennisetum glaucifolium) silage fermentation quality, animal preference and nutritional value.
- Kim, D.; Lee, K.; Choi, K. Role of LAB in Silage Fermentation: Effect on Nutritional Quality and Organic Acid Production—An Overview. In Cent Res Environ Dis Fac Publ; 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonda, H.; Nikodinoska, I.; Le Cocq, K.; Moran, C.A. Efficacy of six lactic acid bacteria strains as silage inoculants in forages with different dry matter and water-soluble carbohydrate content. Grass Forage Sci. 2023, 78(4), 636–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoye, C.O.; Wang, Y.; Gao, L.; et al. The performance of lactic acid bacteria in silage production: A review of modern biotechnology for silage improvement. Microbiol Res. 2023, 266, 127212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qingfeng, Zhao; Zeren, Wang; Yong, Li; Fuli, Hu; Lu, Han; Pingjun, Zhu. Effects of compound probiotics on the quality of fermented giant reed feed. Feed Res. 2022, 45(22), 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeren, Wang; Yong, Li; Qingfeng, Zhao; Pingjun, Zhu; Fuli, Hu. Effects of fermented giant reed feed on growth performance, slaughter performance, meat quality and serum biochemical indicators in sheep. Feed Res. 2022, 45(24), 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauly, T.; Wyss, U. Efficacy testing of silage additives—Methodology and existing schemes. Grass Forage Sci. 2019, 74(2), 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, L.; Shaver, R.D.; Grant, R.J.; Schmidt, R.J. Silage review: Interpretation of chemical, microbial, and organoleptic components of silages. J Dairy Sci. 2018, 101(5), 4020–4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muck: Effects of silage additives on ensiling - Google. Available online: https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?title=Effect%20of%20silage%20additives%20on%20ensiling&publication_year=1997&author=R.E.%20Muck&author=L.%20Kung%20Jr (accessed on 12 December 2025).
- Pinho, R.M.A.; Santos, E.M.; Carvalho GGPde et, a.l. Microbial and fermentation profiles, losses and chemical composition of silages of buffel grass harvested at different cutting heights. Rev Bras Zootec. 2013, 42, 850–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- REM Inoculation of silage and its effects on silage quality. Informational Conference with Dairy and Forage Industries; US Dairy Forage Res Center, 1996; pp. 43–51. Available online: https://cir.nii.ac.jp/crid/1572824500598991488 (accessed on 12 December 2025).
- Santos, E.M.; Pereira, O.G.; Garcia, R.; et al. Microbial populations, fermentative profile and chemical composition of signalgrass silages at different regrowth ages. Rev Bras Zootec. 2011, 40, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, E.; Mao, N.; Liu, S.; et al. Effects of different wet distillers’ grains ratios on fermentation quality, nitrogen fractions and bacterial communities of total mixed ration silage. BMC Microbiol. 2025, 25(1), 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouwehand, A.C. Silage Fermentation. In Lactic Acid Bacteria, 6th ed.; CRC Press, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Franco, M.; Rinne, M. Dry Matter Content and Additives with Different Modes of Action Modify the Preservation Characteristics of Grass Silage. Fermentation 2023, 9(7), 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Liu, H.; Gao, Z.; et al. Whole-plant corn silage improves rumen fermentation and growth performance of beef cattle by altering rumen microbiota. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022, 106(11), 4187–4198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, G.M.; Santos, E.M.; de Oliveira, J.S.; et al. Isolation of Acetic Acid-Producing Bacterial Strains and Utilization as Microbial Inoculants in Sorghum Silages. Agriculture 2025, 15(3), 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Wittouck, S.; Salvetti, E.; et al. A taxonomic note on the genus Lactobacillus: Description of 23 novel genera, emended description of the genus Lactobacillus Beijerinck 1901, and union of Lactobacillaceae and Leuconostocaceae. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2020, 70(4), 2782–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oskoueian, E.; Jahromi, M.F.; Jafari, S.; Shakeri, M.; Le, H.H.; Ebrahimi, M. Manipulation of Rice Straw Silage Fermentation with Different Types of Lactic Acid Bacteria Inoculant Affects Rumen Microbial Fermentation Characteristics and Methane Production. Vet Sci. 2021, 8(6), 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, J.; Dong, Z.; Li, J.; Shao, T. Synergistic Effects of Exogenous Lactobacillus plantarum and Fibrolytic Enzymes on Fermentation Quality, Fiber Degradation, and In Vitro Digestibility of Napiergrass (Pennisetum purpureum) Silage. Agronomy 2025, 15(2), 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemos, M.F.; Andrade, A.P.; Silva PHFda et, a.l. Nutritional value, fermentation losses and aerobic stability of elephant grass (Pennisetum purpureum Schum.) silage treated with exogenous fibrolytic enzymes. Acta Sci Anim Sci. 2020, 42, e48272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, S.A.; Abdullahi, S.; Tinat, P.I.; Taha, M. Chemical composition, fermentation characteristics and anti-nutritional content of ensiled maize cob - sweet potato vine mixture. Sci World J. 2025, 20(3), 1236–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, F.; et al. Effects of Sugar Cane Molasses Addition on the Fermentation Quality, Microbial Community, and Tastes of Alfalfa Silage. Animals 2021, 11(2), 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Application of condensed molasses fermentation solubles and lactic acid bacteria in corn silage production - Chen - 2020 - Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture - Wiley Online Library. Available online: https://scijournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/jsfa.10304 (accessed on 12 December 2025). [CrossRef]
| Number | Region | Silage time (month/day) | cuts | Silage Method | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J1 | Jianshui County | 5/25 | 1 | Bag storage | |
| J2 | 5/25 | 1 | Bag storage | Add 4% cornmeal | |
| J3 | 6/27 | 1 | Barrel storage | ||
| J4 | 7/25 | 1 | Barrel storage | ||
| J5 | 7/25 | 1 | Barrel storage | Add 10% rice bran | |
| J6 | 7/25 | 1 | Barrel storage | Add 10% rice bran and 0.1% brown sugar | |
| Y1 | Yanshan County | 6/21 | 1 | Bag storage | |
| Y2 | 11/1 | 2 | Bag storage | 48 hours after mowing | |
| S1 | Simao District | 7/30 | 1 | Bag storage | |
| S2 | 7/30 | 1 | Lower layer of cellar | ||
| S3 | 7/30 | 1 | Upper layer of cellar | ||
| C1 | Changning County | 7/10 | 1 | Bag storage | |
| C2 | 7/24 | 1 | Bag storage | Withering after cutting | |
| C3 | 9/10 | 2 | Bag storage | ||
| C4 | 10/19 | 2 | Bag storage | 24 hours after cutting and wilting | |
| X1 | Xundian County | 7/15 | 1 | Barrel storage | |
| X2 | 7/15 | 1 | Barrel storage | After chopping, let it wilt for 24 hours. | |
| X3 | 7/15 | 1 | Barrel storage | After chopping, let it wilt for 48 hours. | |
| X4 | 7/15 | 1 | Barrel storage | Add hay to adjust the moisture content to 70%. | |
| X5 | 7/15 | 1 | Barrel storage | Add hay to adjust the moisture content to 78%. | |
| X6 | 11/12 | 2 | Barrel storage | ||
| X7 | 11/12 | 1 | Barrel storage | ||
| X8 | 11/12 | 2 | Barrel storage | Add local hay to adjust moisture content to 75%. | |
| X9 | 11/12 | 2 | Barrel storage | Add hay to adjust the moisture content to 75%. | |
| X10 | 11/12 | 2 | Barrel storage | Add hay to adjust the moisture content to 80%. |
| Item | Height | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100~150cm | 150~200cm | 200~250cm | 250~300cm | |
| DM/% | 11.85 | 11.65 | 14.30 | 15.27 |
| CP/% | 14.20 | 10.50 | 9.70 | 11.30 |
| ADF/% | 40.35 | 43.40 | 45.15 | 47.70 |
| NDF/% | 66.25 | 70.90 | 70.60 | 73.13 |
| CF | 34.75 | 39.30 | 39.10 | 40.80 |
| ADL | 4.23 | 5.10 | 5.61 | 5.62 |
| Starch /% | 0.20 | 0.55 | 0.45 | 0.33 |
| EE | 2.60 | 2.10 | 1.60 | 1.48 |
| TDN/% | 57.05 | 53.55 | 51.60 | 52.80 |
| RFV | 80.50 | 72.50 | 71.00 | 66.00 |
| WSC/% | 5.35 | 4.20 | 4.41 | 6.10 |
| Item | Group | p-Vaule | |
|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | T2 | ||
| DM | 14.33±0.51 | 14.07±0.49 | 0.55 |
| CP | 13.47±0.57 | 12.20±0.44 | 0.04 |
| ADF | 45.63±1.07 | 48.00±0.26 | 0.05 |
| NDF | 67.70±1.73 | 69.93±0.68 | 0.11 |
| CF | 40.13±1.10 | 43.23±0.57 | 0.02 |
| ADL | 4.50±0.33 | 5.64±0.05 | 0.02 |
| Starch | 0.43±0.06 | 0.47±0.21 | 0.80 |
| EE | 2.52±0.13 | 2.11±0.04 | 0.02 |
| TDN | 58.10±0.79 | 54.57±0.51 | 0.005 |
| RFV | 73.67±3.21 | 68.67±0.58 | 0.11 |
| WSC | 1.57±0.06 | 1.80±0.10 | 0.04 |
| pH | 4.06±0.03 | 4.57±0.78 | 0.001 |
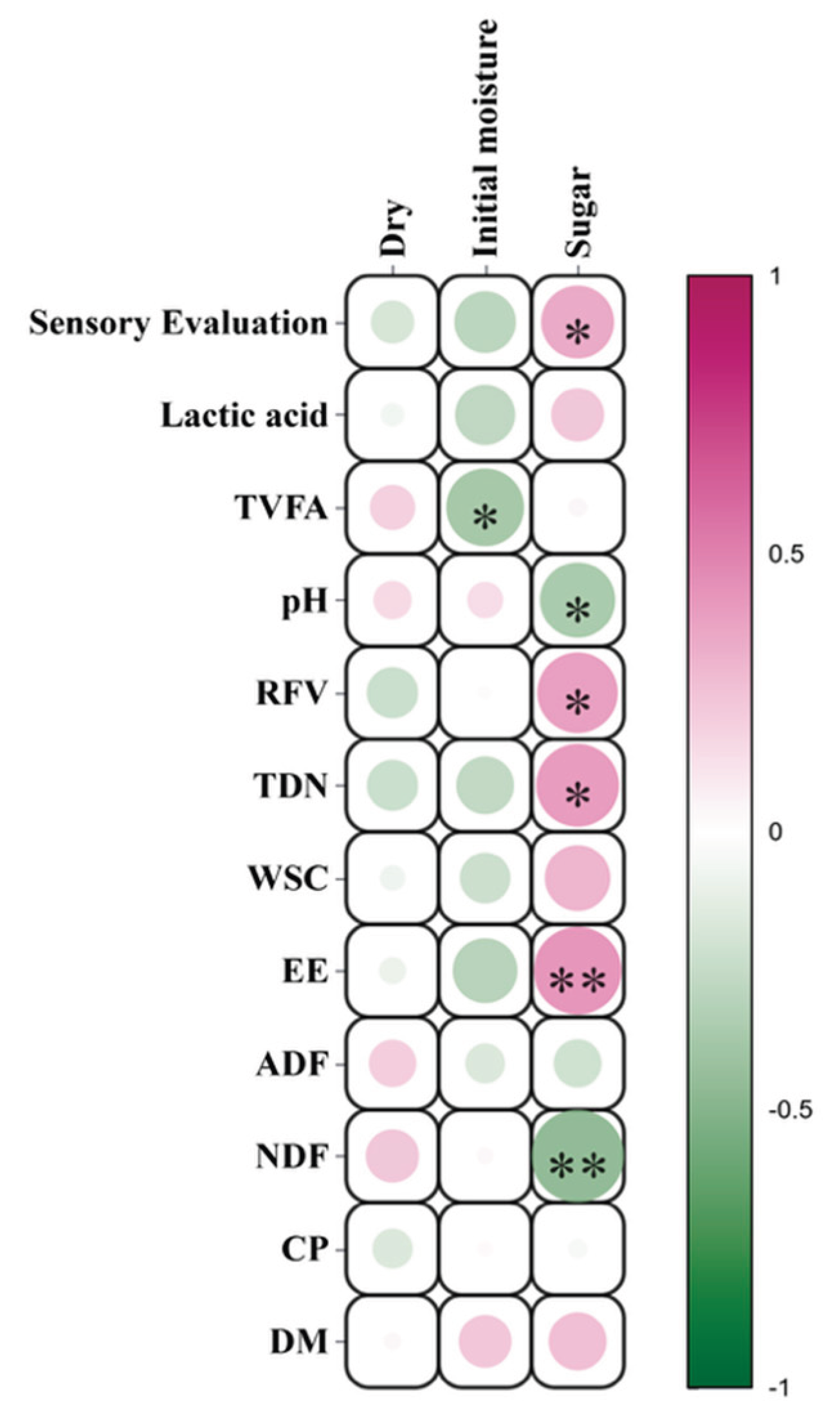
| Number | DM | CP | NDF | ADF | EE | WSC | TDN | RFV | pH | TVFA | Lactic Acid | Sensory Evaluation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J1 | 20.10 | 9.70 | 69.10 | 43.00 | 2.88 | 0.97 | 56.10 | 75 | 4.22 | 7.4 | 5.69 | 17.85 |
| J2 | 25.20 | 8.70 | 50.30 | 31.40 | 3.18 | 1.71 | 61.80 | 119 | 3.7 | 7.14 | 6.21 | 18.10 |
| J3 | 18.80 | 10.40 | 64.90 | 44.00 | 3.33 | 2.83 | 58.40 | 78 | 3.5 | 9.61 | 8.88 | 15.80 |
| J4 | 19.70 | 4.50 | 70.60 | 49.60 | 2.04 | 1.90 | 52.80 | 66 | 3.45 | 10.75 | 8.81 | 17.00 |
| J5 | 27.10 | 6.30 | 64.40 | 48.10 | 3.43 | 1.65 | 56.90 | 74 | 3.35 | 9.18 | 6.68 | 17.56 |
| J6 | 27.40 | 6.10 | 64.00 | 47.10 | 3.39 | 1.85 | 57.80 | 76 | 3.34 | 9.03 | 6.39 | 17.56 |
| Y1 | 19.60 | 7.10 | 71.10 | 45.40 | 2.62 | 2.00 | 53.10 | 70 | 4.47 | 5.68 | 4.21 | 17.57 |
| Y2 | 32.60 | 3.20 | 76.30 | 56.20 | 0.63 | 1.10 | 50.30 | 55 | 3.63 | 8.93 | 4.79 | 17.75 |
| S1 | 23.90 | 7.60 | 73.20 | 54.10 | 1.52 | 1.03 | 51.00 | 59 | 3.42 | 7.53 | 7.15 | 17.46 |
| S2 | 19.90 | 5.90 | 72.40 | 51.50 | 1.68 | 1.80 | 51.70 | 63 | 4.14 | 8.43 | 3.74 | 17.00 |
| S3 | 18.10 | 5.20 | 75.60 | 53.50 | 2.32 | 1.40 | 48.50 | 58 | 4.8 | 10.06 | 0.79 | 13.55 |
| C1 | 16.80 | 8.30 | 71.20 | 49.00 | 2.24 | 0.08 | 47.80 | 66 | 5.08 | 8.11 | 2.37 | 9.78 |
| C2 | 27.60 | 6.00 | 69.40 | 46.50 | 1.66 | 0.38 | 49.40 | 71 | 4.16 | 6.8 | 5.45 | 15.17 |
| C3 | 16.80 | 8.10 | 73.70 | 52.60 | 2.4 | 0.60 | 50.80 | 61 | 4.47 | 5.93 | 2.18 | 17.00 |
| C4 | 22.70 | 5.50 | 71.50 | 49.70 | 1.87 | 1.30 | 53.90 | 65 | 3.58 | 9.78 | 6.9 | 16.81 |
| X1 | 15.50 | 10.9 | 69.90 | 48.50 | 2.99 | 1.60 | 56.20 | 68 | 4.7 | 5.52 | 2.6 | 14.10 |
| X2 | 15.30 | 8.20 | 71.90 | 49.60 | 2.96 | 1.30 | 51.40 | 65 | 5.24 | 8.61 | 1.79 | 8.90 |
| X3 | 17.10 | 10.2 | 71.70 | 47.70 | 3.37 | 1.10 | 48.70 | 67 | 5.23 | 10.25 | 2.3 | 9.00 |
| X4 | 30.10 | 5.80 | 73.20 | 48.40 | 1.61 | 1.00 | 45.80 | 65 | 4.36 | 4.92 | 1.15 | 14.80 |
| X5 | 22.00 | 7.40 | 72.90 | 48.70 | 2.08 | 1.10 | 46.90 | 65 | 4.72 | 7.25 | 1.66 | 16.10 |
| X6 | 18.40 | 10.50 | 66.30 | 44.40 | 2.79 | 0.90 | 58.90 | 76 | 3.48 | 9.79 | 7.71 | 17.79 |
| X7 | 29.00 | 7.90 | 68.60 | 47.40 | 1.73 | 1.00 | 55.30 | 71 | 3.63 | 9.38 | 6.32 | 16.29 |
| X8 | 25.30 | 9.20 | 68.00 | 44.30 | 2.1 | 1.00 | 52.20 | 74 | 3.95 | 7.42 | 4.52 | 14.58 |
| X9 | 26.00 | 7.80 | 70.70 | 46.50 | 1.47 | 1.10 | 51.60 | 69 | 3.96 | 7.4 | 4.81 | 14.25 |
| X10 | 22.60 | 8.20 | 69.10 | 46.60 | 1.80 | 0.90 | 51.70 | 71 | 4.32 | 5.24 | 3.3 | 12.21 |
| Number | EWRD | Rank | WRD | Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| J1 | 0.6750 | 7 | 0.6916 | 7 |
| J2 | 0.8209 | 1 | 0.8314 | 1 |
| J3 | 0.8096 | 2 | 0.8107 | 2 |
| J4 | 0.7038 | 6 | 0.7156 | 6 |
| J5 | 0.7397 | 5 | 0.7578 | 5 |
| J6 | 0.7424 | 3 | 0.7600 | 4 |
| Y1 | 0.6307 | 15 | 0.6424 | 14 |
| Y2 | 0.6340 | 12 | 0.6529 | 11 |
| S1 | 0.6459 | 10 | 0.6634 | 10 |
| S2 | 0.6089 | 17 | 0.6230 | 16 |
| S3 | 0.5759 | 23 | 0.5875 | 22 |
| C1 | 0.5544 | 25 | 0.5636 | 25 |
| C2 | 0.6003 | 18 | 0.6122 | 18 |
| C3 | 0.5829 | 19 | 0.6000 | 19 |
| C4 | 0.6566 | 9 | 0.6729 | 9 |
| X1 | 0.6340 | 11 | 0.6447 | 13 |
| X2 | 0.5825 | 20 | 0.5897 | 21 |
| X3 | 0.6333 | 14 | 0.6407 | 15 |
| X4 | 0.5726 | 24 | 0.5835 | 24 |
| X5 | 0.5818 | 21 | 0.5946 | 20 |
| X6 | 0.7412 | 4 | 0.7609 | 3 |
| X7 | 0.6741 | 8 | 0.6902 | 8 |
| X8 | 0.6337 | 13 | 0.6457 | 12 |
| X9 | 0.6103 | 16 | 0.6217 | 17 |
| X10 | 0.5778 | 22 | 0.5874 | 23 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.





