Submitted:
22 December 2025
Posted:
24 December 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Description of the NRDIOS Bucharest Method for Risk Assessment
- Nr - the level of global risk in the workplace;
- ri - risk factor ranking „i”;
- Ri - level of risk for the risk factor „i”;
- n - number of risk factors identified at the workplace.
- Ng = the overall risk level of the power substation;
- rp = workplace rank p, equal to the risk level of the workplace;
- n = number of workplaces;
- Nrp = is the level of overall workplace risk.
3. State of art
- National and European Legislation: In jurisdictions such as Romania (Law 319/2006 harmonized with EU directives), employers are legally required to perform OHS risk assessments covering all work activities, equipment, and environmental conditions;
- Standards for Electrical Safety: Although not specific to substations, standards such as NFPA 70E inform electrical safety practices and safe work protocols (e.g., electrical hazard analysis, arc flash boundary determination).
- NRDIOS (Romanian OHS Institute) Method: Quantitative semi-systemic approach used in recent Romanian academic studies for substations. This method identifies risk factors related to injuries and occupational diseases and calculates a global risk level across work stations. ⸻ It has been applied for 220/110/20 kV substations showing “low – very low risk” when mitigations are implemented;
- Semi-Quantitative & Check-List Methods: Many OHS assessments use predefined checklists to identify hazards, then compute risk as a function of severity and likelihood for each factor. Global risk levels inform prevention strategies;
- ccupational Risk Indices & Compliance Checklists: In some contexts (e.g., South African 132 kV substations), risk assessments integrate compliance scoring with legislative and housekeeping criteria to evaluate facility adherence to safety standards.
- Electrocution & Electrical Shock: Direct contact with live parts or unexpected energization remains the most significant hazard in substations. Safety practices include lockout-tagout procedures and safe distance maintenance;
- Arc Flash & Arc Blast: Arc flash events can cause severe burns, blast pressure injuries, and equipment damage. Modern risk studies (outside OHS domain) highlight the need for modeling and protective equipment specification but inform occupational safety considerations as well.
- Long-Term Exposure: Some epidemiological evidence from 400 kV environments shows no significant chronic health effects from EMF exposure in occupational groups; however, EMF interference with medical implants (e.g., pacemakers) must be considered in risk assessments complying with EU Directive 2013/35/EU;
- Health-Related EMF Studies: Applied research in HV environments links ELF-EMF exposure with potential biological effects, although causation remains debated. Such findings are often integrated into risk assessment narratives when discussing long-term health implications.
- Ground Potential Rise: Fault conditions can create hazardous voltage gradients on substation grounds that risk personnel injury outside the immediate work zone. This phenomenon is a recognized electrical safety concern that must be factored into risk analyses and grounding design.
- Housekeeping & Infrastructure: Poor housekeeping (material storage, oil leakage, obstacles) increases fire risk and trip/fall hazards; fencing and site security also affect occupational safety and community risk profiles;
- Training & Culture: Other research highlights deficits in training, supervision, and enforcement of procedures as key contributors to incidents, underscoring the importance of organizational risk mitigation.
- a)
- Sardanesti (220/110/20 kV): Risk assessment applying the NRDIOS method produced a global risk score classified as low to very low, demonstrating compliance with OSH norms and low likelihood of injury or occupational disease in operational and maintenance staff;
- b)
- Mintia (400/220/110/20 kV): Similar assessments indicate overall low risk levels when protective measures and compliance are in place, illustrating that structured risk assessments can support safety optimization;
- c)
- Portile de Fier (400/220/110/20 kV): Ongoing research focuses on systematic identification of risk factors and proposals for mitigation measures in very high voltage substations using NRDIOS and multidisciplinary knowledge integration.
- a)
- Lack of Unified Global Models: Most research on OHS in substations uses region-specific methods (e.g., NRDIOS), revealing a gap in internationally standardized risk modeling frameworks that integrate electrical engineering hazards with occupational health metrics;
- b)
- Integration of EMF Health Outcomes: Despite some epidemiologic studies, there is limited consensus on chronic EMF exposure effects among HV substation workers, indicating a need for longitudinal studies integrated into risk assessment practice;
- c)
- Dynamic & Real-Time Risk Monitoring: Traditional assessments are static; real-time risk monitoring using sensors and digital safety systems (e.g., predictive analytics or IoT platforms) represents an emerging research frontier not yet widely applied in substations;
- d)
- Multidisciplinary & Holistic Approaches: Integrating organizational, human, electrical, and environmental factors in a unified OHS risk model remains an open research challenge that could improve predictive power and mitigation strategies.
4. Risks Assessment (Accidents and Occupational Illness)
- 400 kV Arad – Sandorfalva OHL (Hungary – ENTSO-E);
- 400 kV Arad – Nadab OHL;
- 400 kV Arad – Mintia OHL (gas power plant – under construction);
- 220 kV Arad – Timisoara OHL;
- 220 kV Arad – Calea Aradului OHL.
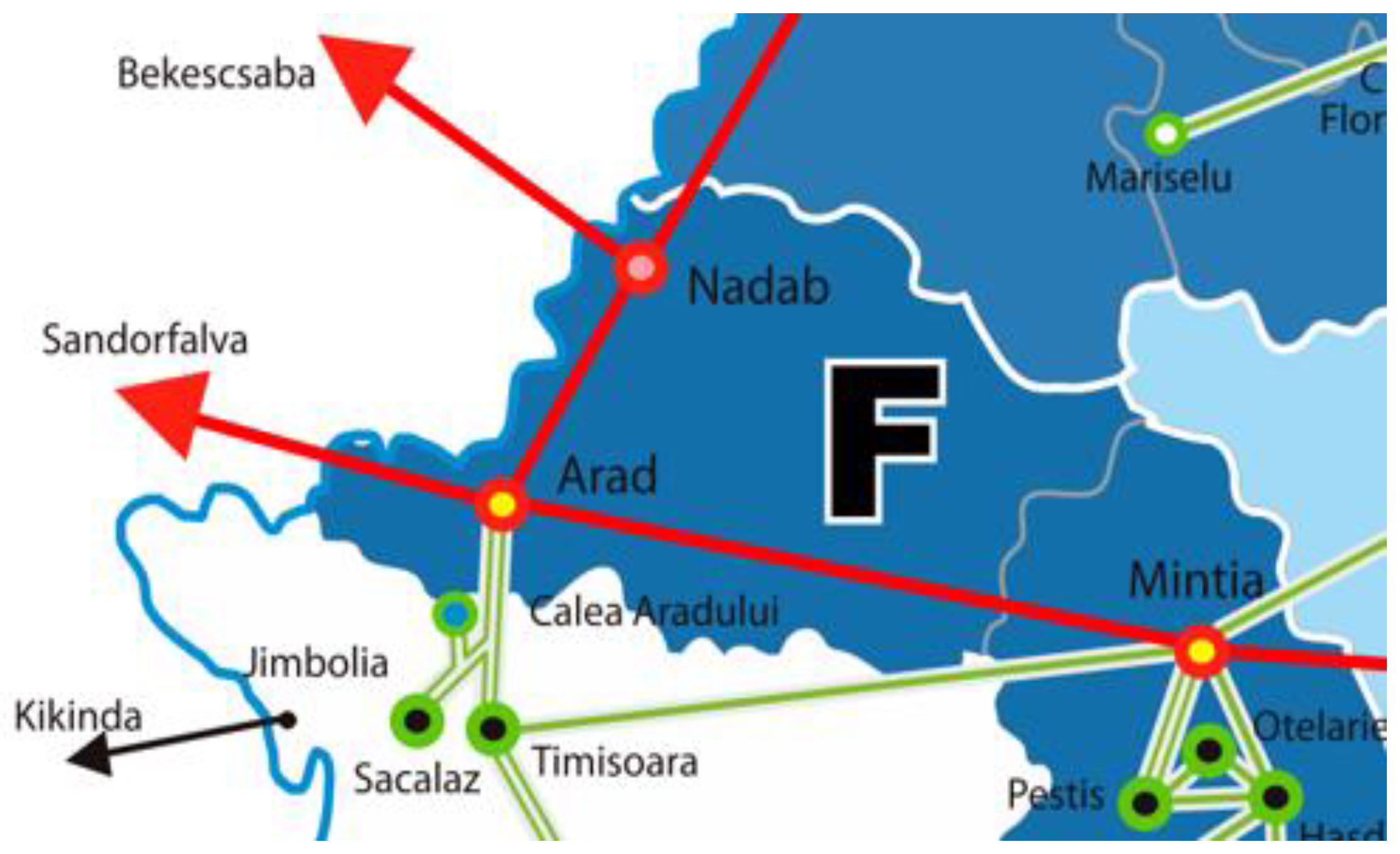
4.1. Assessment of the Global Risk Level
4.1.1. Risk Level Assessment for the Activity: 400 kV and 220 kV Operational Service
- wrong action: incorrect identification of the installation and non-verification of the lack of voltage, when mounting the short circuits; failure to respect the neighbouring distances with risk of electric shock by direct contact; not checking the lack of voltage before mounting the mobile short circuits.
- omissions: omissions of operations during manoeuvres, with risk of burns caused by electric arc, when closing grounding knives or mounting the mobile short circuits without checking the lack of voltage; non-use and/or non-verification of the personal protective equipment provided and/or of the electrical insulating means and devices.
| National Power System |
Assessment Sheet of Workplace |
Number of Exposed Persons: 12 | ||||
| Transelectrica NPG | Exposure Time: 8 Hours/Shift | |||||
| 400 kV and 220 kV Operational Service |
Assessment Team: | |||||
| The composition of the work system | Identified risk factors | CONCRETE FORM OF MANIFESTATION OF RISK FACTORS | Maximum foreseeable consequence | Class of severity |
Class of probability |
Risk level |
| Means of Production | Mechanical risk factors: - falling from the same level |
1. Falling due to distraction when moving through outside power substations | Temporary Work Incapacity 3-45 days |
2 | 1 | 1 |
| Electrical risk factors: - electrical shock hazard |
2. Not using two mobile short circuits in the working area | DEATH | 7 | 2 | 4 | |
| 3. Not using in working area of capacitive load damper (in case of capacitive currents) | DEATH | 7 | 2 | 4 | ||
| Thermal risk factors: - explosion hazard |
4. Explosion of power, voltage, and current transformers, discharge | DEATH | 7 | 1 | 3 | |
| PERFORMER | Wrong actions: - omission of present operations; - not using of means of protections |
5. Not checking the lack of voltage before mounting the mobile short circuits | DEATH | 7 | 2 | 4 |
| 6. Failure to use or verify personal protective equipment, tools and electro-insulating devices provided | DEATH | 7 | 1 | 3 | ||
| WORK ENVIRONMENT | Risk factors: - air temperature |
7. Exposure to adverse weather conditions (high, low temperatures), when operating in outdoor power substations | Temporary Work Incapacity | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| No. | Risk Factor | Risk Level |
Proposed Prevention Measures |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Not using two mobile short circuits in the working area | 4 | Training and unannounced and regular control by the management |
| 2. | Not using in working area of capacitive load damper (in case of capacitive currents) | 4 | |
| 3. | Not checking the lack of voltage before mounting the mobile short circuits | 4 |
4.1.2. Risk Level Assessment for the Activity: 20 kV Operational Service
- wrong action: incorrect identification of the installation and non-verification of the lack of voltage, when mounting the short circuits; failure to respect the neighbouring distances with risk of electric shock by direct contact; not checking the lack of voltage before mounting the mobile short circuits;
- omissions: omissions of operations during maneuvers, with risk of burns caused by electric arc, when closing grounding knives or mounting the mobile short circuits without checking the lack of voltage; non-use and/or non-verification of the personal protective equipment provided and/or of the electrical insulating means and devices.
| National Power System |
Assessment Sheet of Workplace |
Number of Exposed Persons: 12 | |||||
| Transelectrica NPG | Exposure Time: 8 Hours/Shift | ||||||
| 400 kV and 220 kV Operational Service |
Assessment Team: | ||||||
| The composition of the work system | Identified risk factors | CONCRETE FORM OF MANIFESTATION OF RISK FACTORS | Maximum foreseeable consequence | Class of severity |
Class of probability |
Risk level |
|
| Means Of Production | Mechanical risk factors: Hazard movements: - movement under propulsion |
1. Short circuit breaker explosions | DEATH | 7 | 1 | 3 | |
| 2. Discharging explosions during operation | DEATH | 7 | 1 | 3 | |||
| Electrical risk factors: - electric current |
3. Touching of unmarked terminals and installations | DEATH | 7 | 1 | 3 | ||
| 4. Touching live installations when connecting short circuits | DEATH | 7 | 1 | 3 | |||
| 5. Touching the 20 kV busbars during maneuvers | DEATH | 7 | 1 | 3 | |||
| Thermal risk factors: - flames, flame |
6. Burns due to short circuits caused by insulation breaks and explosions | DEATH | 7 | 1 | 3 | ||
| Work Load | Inadequate work load content relative to requirements security | 7. Mounting short circuits by hand | DEATH | 7 | 1 | 3 | |
| Performer | Wrong actions | 8. Failure to respect the neighbouring distances with risk of electric shock by direct contact. | DEATH | 7 | 1 | 3 | |
| 9. Failure to verify the position and/or condition of the components to be operated when maneuvering | DEATH | 7 | 1 | 3 | |||
| Omissions: - omission of operations present in the Maneuver Sheet |
10. Not checking the lack of voltage before installing mobile short circuiting or closing the grounding knives | DEATH | 7 | 1 | 3 | ||
| - not using of means of protection | 11. Failure to use or check personal protective equipment, tools and electro-insulating devices | DEATH | 7 | 1 | 3 | ||
| No. | Risk Factor | Risk Level |
Proposed Prevention Measures |
|---|---|---|---|
| - | No risk factor | - | No proposal measures |
4.1.3. Risk Level Assessment for Activity: 400 kV and 220 kV Primary Circuit Maintenance
- wrong action: misidentification of the installations in which work is being carried out; wrong maneuvers when performing operational tests; exceeding proximity distances when transporting materials to the work area and during work; displacement, stationing in hazardous areas outside the working area; falling from the same level by unbalancing, during the transport of materials within the area of the power substation;
| National Power System |
Assessment Sheet of Workplace |
Number of Exposed Persons: 12 | ||||
| Transelectrica NPG | Exposure Time: 8 Hours/Shift | |||||
| 400 kV and 220 kV Operational Service | Assessment Team: | |||||
| The composition of the work system | Identified risk factors | CONCRETE FORM MANIFESTATION OF RISK FACTORS | Maximum foreseeable consequence | Class of severity |
Class of probability |
Risk level |
| MEANS OF PRODUCTION | Mechanical risk factors: - functional movements of technical machinery |
1. Displacement by means of transport to the workplace – road accident; | DEATH | 7 | 1 | 3 |
| 2. Hazardous surfaces | Temporary Work Incapacity | 2 | 2 | 2 | ||
| Thermal risk factors | 3. Injury by the thermal effect of the electric arc for service and repair personnel when traveling on the area of power substations for fulfilling the work load | 1st degree Disability | 6 | 1 | 3 | |
| Electrical risk factors - indirect touch |
4. Touching of metal parts accidentally under voltage, in conditions of: - damage to insulation from the metal housing; - failure of the protective connection |
DEATH | 7 | 2 | 4 | |
| WORK LOAD | Improper content in relation to security requirements | 5. Improper preparation and/or non-compliance with mandatory steps and measures to secure the work area | DEATH | 7 | 1 | 3 |
| Under/oversized workload in relation to the capacity of the performer | 6. Dynamic, static effort, forced working positions at ground and height when handling and replacing subassemblies and components of primary equipment, insulators replacement | Temporary Work Incapacity 45-180 days |
3 | 2 | 2 | |
| WORK ENVIRONMENT |
Physical risk factors |
7. Inhalation of toxic dust and gases in the while performing painting operations | Temporary Work Incapacity 45-180 days |
3 | 2 | 2 |
| PERFORMER | Wrong actions | 8. Incorrect identification of the installations in which they work, wrong maneuvers when performing functional tests | DEATH | 7 | 1 | 3 |
| 9. Entering the work area unprepared in terms of work safety | DEATH | 7 | 1 | 3 | ||
| 10. Incomplete work permit without specifying all working area insurance conditions | DEATH | 7 | 2 | 4 | ||
| 11. Exceeding neighbouring distances of materials to the work area and during the works | DEATH | 7 | 1 | 3 | ||
| 12. Displacement, stationing in hazardous areas outside the working area | DEATH | 7 | 1 | 3 | ||
| 13. Falling from the same level through imbalance during the transport of materials to the power substation | Temporary Work Incapacity 3-45 days |
2 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Omissions | 14. Not using the personal protective equipment provided or use of non-certified personal protective equipment | DEATH | 7 | 1 | 3 | |
| No. | Risk Factor | Risk Level |
Proposed Preventive Measures |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Touching of accidentally live metal parts under the conditions ok: - damage to the insulation from the metal housing; - failure of the protective connection |
4 | Making connections to the earthing of all technical equipment. Measurements of touch voltages. Compliance with the deadlines for technical revisions. |
| 2 | Incomplete work permit without specifying all working area insurance conditions | 4 | Starting of work only on the gasis of a work permit specifying all the conditions for securing the work area |
| National Power System |
Assessment Sheet of Workplace |
Number of Exposed Persons: 12 | ||||||
| Transelectrica NPG | Exposure Time: 8 Hours/Shift | |||||||
| 400 kV and 220 kV Operational Service |
Assessment Team: | |||||||
| The composition of the work system | Identified risk factors | CONCRETE FORM MANIFESTATION OF RISK FACTORS | Maximum foreseeable consequence | Class of severity |
Class of probability |
Risk level |
||
| Means Of Production | Mechanical risk factors: - functional movements of technical machinery - hazardous surfaces |
1. Traveling by means of transport to the workplace – road accident | DEATH | 7 | 2 | 4 | ||
| 2. Accidents caused by the tension of the MR spring during the adjustment operation The MRI actuator of the IO 20 kV circuit breaker | 3st degree Disability | 4 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| 3. Cutting edges, sting when replacing broken insulators, TT, TC and damaged discharge devices | Temporary Work Incapacity 3-45 days |
2 | 4 | 2 | ||||
| 4. Hazard of explosion TIRBO transformers | DEATH | 7 | 2 | 4 | ||||
| Thermal risk factors | 5. Injury by the thermal effect of the electric arc of service and repair personnel when traveling on the territory power substations of the work load | 1st degree Disability | 6 | 4 | 6 | |||
| Electrical risk factors - indirect touch |
6. Touching of accidentally live metal parts under the conditions: - damage to insulation from the metal housing; - failure of the protective connection |
DEATH | 7 | 4 | 6 | |||
| Work Load | Inadequate content in relation to security requirements | 7. Adequate preparation and/or non-compliance with mandatory steps and measures to secure the work area | DEATH | 7 | 3 | 5 | ||
| Under/oversized workload in relation to the capacity of the performer | 8. Dynamic, static effort, forced working positions at ground and height when handling and replacing subassemblies and components of primary equipments, insulating replacement | Temporary Work Incapacity 45-180 days |
3 | 4 | 3 | |||
| Work Environment | Physical risk factors | 9. Inhalation of toxic dust and gases in the execution of the operations of painting | Temporary Work Incapacity 45-180 days |
3 | 2 | 2 | ||
| Performer | Wrong actions | 10. Incorrect identification of the installations in which they work, wrong maneuvers when performing functional tests | DEATH | 7 | 4 | 6 | ||
| 11. Entering the work area unprepared for work safety | DEATH |
7 | 4 | 6 | ||||
| 12. Incomplete work permit without specifying all working area insurance conditions | DEATH | 7 | 4 | 6 | ||||
| 13. Exceeding the distances of materials to the work area and during the works | DEATH | 7 | 3 | 5 | ||||
| 14. Journeys, stationing in hazardous areas outside the working area | DEATH | 7 | 3 | 5 | ||||
| 15. Falling to the same level through imbalance during the transport of materials to the power substation | Temporary Work Incapacity 3-45 days |
2 | 3 | 2 | ||||
| Omission | 16. Not using the personal protective equipment provided or use of personal protective equipments non-certified | DEATH | 7 | 3 | 5 | |||
4.1.4. Risk Level Assessment for Activity: 20 kV Primary Circuit Maintenance
- wrong action: misidentification of the installations in which work is being carried out; wrong maneuvers when performing operational tests; exceeding proximity distances when transporting materials towards the work area and during work; displacements, stationing in hazardous areas outside the working area; falling from the same level by unbalancing, during the transport of materials within the area of the power substation;
- omissions: non-use of personal protective equipment as provided or use of non-certified personal protective equipment.
| No. | Risk Factor | Risk Level |
Proposed Preventive Measures |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Traveling by means of transport to the workplace – road accident | 4 | Preparation of instructions for maneuvering and working instructions for vehicle in the power substation. Compliance with traffic rules. |
| 2 | Hazard of explosion TIRBO transformers | 4 | Wearing personal protective and work equipment |
| 3 | Injury by the thermal effect of the electric arc of service and repair personnel when traveling on the territory power substations of the work load | 6 | Wearing personal protective and work equipment |
| 4 | Touching of accidentally live metal parts under the conditions: - damage to insulation from the metal housing; - failure of the protective connection |
6 | Making connections to the ground of all technical equipment. Measuring touch voltages. Compliance with the deadlines for technical revisions |
| 5 | Adequate preparation and/or non-compliance with mandatory steps and measures to secure the work area | 5 | Preparation of specific working instructions regarding the delimitation of the area work and the execution and observance of the work |
| 6 | Incorrect identification of the installations in which they work, wrong maneuvers when performing functional tests | 6 | The preparation of appropriate working instructions and the training of personnel on operating conditions in the power substation |
| 7 | Entering the work area unprepared for work safety | 6 | Compliance with the work and safety instructions. Respect for discipline in the workplace. |
| 8 | Incomplete work permit without specifying all working area insurance conditions | 6 | Start work only under the work authorization in which all conditions for securing the working area shall be specified |
| 9 | Exceeding the distances of materials to the work area and during the works | 5 | Withdrawal from service of installations which are below the limit of neighbourhood |
| 10 | Journeys, stationing in hazardous areas outside the working area | 5 | Following the internal instructions for power substation travel |
| 11 | Not using the personal protective equipment provided or use of personal protective equipments non-certified | 5 | Instructions on the use of the personal protective equipment and the certified personal protective equipment |
4.1.5. Risk Level Assessment for Activity: 20 kV Secondary Circuit Maintenance
- electrical risk: direct contact (unprotected terminals, unprotected heating elements); indirect contact (housing, metal parts);
- mechanical risk: functional movements of technical equipments; displacements under the effect of propulsion;
- thermal risk: flames, explosion of molten metal particles.
- protection checks: during the revisions, all the verifications provided by the technical books of protection are performed; the monitoring of the protection system parameters is done from the 20 kV control room;
- measurements and verifications performed by the secondary equipments revisions-repair team: at the internal service panels: checking the electrical connections; measurements at internal service cables; measurements at internal service transformers; checking switching devices and current transformers; calibration of fuses on all circuits; checking the ground connections;
- within the prophylaxis program of the primary equipment from the 20 kV power substations, the following verification are performed: measurements and checks performed on voltage measuring transformers are: measuring the insulation resistance of the windings; measuring the tangent of the dielectric loss angle at the main insulation; measuring the ohmic resistance of the windings; raising the idling characteristic; measuring the secondary load; easurements and checks performed on the current measuring transformers are: measuring the insulation resistance of the windings; measuring the tangent of the dielectric loss angle at the main insulation; measuring the ohmic resistance of the windings; raising the idling characteristic; measuring the secondary load; checking the polarity of the windings; measurements and checks performed on the circuit breakers are: measuring the insulation resistance; checking the contact resistance; checking the ohmic resistance of the triggering and triggering coil; low voltage operation of the control and automation installation; checking the dielectric strength of the oil; measurements and checks performed at power cables are: checking the continuity and identifying the phases; measuring the insulation resistance.
- wrong actions: touching the current paths during the high voltage tests; touching a point of the current paths; touching the terminals of devices, strings of clamps, relays; parking, hazardous movements;
- omissions: non short circuiting of the secondary windings at the current transformers for carrying out works related to low voltage circuits; non short circuiting of the secondary terminals of the current transformers when opening the current circuits for mounting or dismounting the measuring devices; omission of the connection to the null busbar of the internal services of a conductor from the protection circuit to the own busbar; non use and/or non verification of personal protective equipments.
| National Power System |
Assessment Sheet of Workplace |
Number of Exposed Persons: 12 | ||||
| Transelectrica NPG | Exposure Time: 8 Hours/Shift | |||||
| 400 kV and 220 kV Operational Service | Assessment Team: | |||||
| The composition of the work system | Identified risk factors | CONCRETE FORM MANIFESTATION OF RISK FACTORS | Maximum foreseeable consequence | Class of severity |
Class of probability |
Risk level |
|
Means Of Production |
Mechanical risk factors: - movement under dynamic effect |
1. Traveling by means of transport to the intervention area – road accident | DEATH | 7 | 1 | 3 |
| 2. Explosions of primary equipment, during the movement on the 20 kV substation territory to perform service attributions | DEATH | 7 | 1 | 3 | ||
| Electrical risk factors - direct touch |
3. Touching unmarked terminals and installations | DEATH | 7 | 1 | 3 | |
| 4. Touching 20 kV busbar during revisions or repairs | DEATH | 7 | 1 | 3 | ||
| - indirect touch | 5. Touching of accidentally energized metal parts under the conditions of: - insulation failure; - damage to the protective circuit by grounding; - failure to operate the protection or within the time period before the protection is activated. |
DEATH | 7 | 1 | 3 | |
| Thermal risk factors: - flame, flame, explosion of molten metal particles when producing an electric arc |
6. The capture of personnel by the thermal effect of the electric arc at failure of insulation of primary equipment | 1st degree Disability | 6 | 1 | 3 | |
| Work Load | Oversize load in relation to performer's capacity: - psychic stress |
7. Psychic stress on decisions in circuit and scheme modification operations in relation to the consequences of mistakes in performing these operations | Territorial Labour Inspectorate 3-45 days |
2 | 2 | 2 |
| - physical stress |
8. Physical strain, forced working positions during check at the clamp strings. | Temporary Work Incapacity 3-45 days |
2 | 2 | 2 | |
| Work Environment | - lighting | 9. Lighting level in the 20 kV power substation | Temporary Work Incapacity 3-45 days |
2 | 3 | 2 |
| Performer | Wrong actions: - defective execution of operations |
10. Confusion when working on the clamp string in the protection system, resulting in loss of the current transformer secondary circuit, clamp and current transformer terminal overvoltage, electrical shock hazard, transformer failure and untimely equipment tripping | DEATH | 7 | 1 | 3 |
| 11. Touching of current paths-conductors, clamps or test machine busbars during high voltage tests, electrical shock hazard | DEATH | 7 | 1 | 3 | ||
| 12. Not short circuit of secondary windings at current transformer for carrying out works related to low voltage circuit – hazard of electric shock | DEATH | 7 | 1 | 3 | ||
| 13. Touching the terminals of devices, clamps, relays, during voltage checking of secondary circuits under the use of damages personal protective equipment | DEATH | 7 | 1 | 3 | ||
| 14. Not short circuit of the secondary terminals of current transformer when opening current circuits for mounting / dismounting measuring devices | DEATH | 7 | 1 | 3 | ||
| Parking, hazard movings | 15. Parking or moving outside the work area or outside normal routes | DEATH | 7 | 1 | 3 | |
| Omission | 16. Non use and/or non verification of personal protective equipments. | DEATH | 7 | 1 | 3 | |
| No. | Risk Factor | Risk Level |
Proposed Preventive Measures |
|---|---|---|---|
| - | No risk factor | - | No Proposed Preventive Measures |
4.1.6. Global Risk Level Assessment of the 400/220 kV Power Substation
| No. | Workplace |
Level Risk (Nrp) |
| 1 | 400 kV and 220 kV OPERATIONAL SERVICE | 3,4 |
| 2 | 20 kV OPERATIONAL SERVICE | 3 |
| 3 | 400 kV and 220 kV PRIMARY CIRCUIT MAINTENANCE | 2,58 |
| 4 | 20 kV PRIMARY CIRCUIT MAINTENANCE | 4,8 |
| 5 | 20 kV SECONDARY CIRCUIT MAINTENANCE | 2,87 |
5. Interpretation of Results
| 400 kV and 220 kV Operational Service | 20 kV Operational Service |
400 kV and 220 kV Primary Circuit Maintenance | 20 kV Primary Circuit Maintenance |
20 kV Secondary Circuit Maintenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| number risk factor → risk level | number risk factor → risk level | number risk factor → risk level | number risk factor → risk level |
number risk factor → risk level |
| 1 → 1 | 1 → 3 | 1 → 3 | 1 → 4 | 1 → 3 |
| 2 → 4 | 2 → 3 | 2 → 2 | 2 → 3 | 2 → 3 |
| 3 → 4 | 3 → 3 | 3 → 3 | 3 → 2 | 3 → 3 |
| 4 → 3 | 4 → 3 | 4 → 4 | 4 → 4 | 4 → 3 |
| 5 → 4 | 5 → 3 | 5 → 3 | 5 → 6 | 5 → 3 |
| 6 → 3 | 6 → 3 | 6 → 2 | 6 → 6 | 6 → 3 |
| 7 → 1 | 7 → 3 | 7 → 2 | 7 → 5 | 7 → 2 |
| 8 → 3 | 8 → 3 | 8 → 3 | 8 → 2 | |
| 9 → 3 | 9 → 3 | 9 → 2 | 9 → 2 | |
| 10 → 3 | 10 → 4 | 10 → 6 | 10 → 3 | |
| 11 → 3 | 11 → 3 | 11 → 6 | 11 → 3 | |
| 12 → 3 | 12 → 6 | 12 → 3 | ||
| 13 → 1 | 13 → 5 | 13 → 3 | ||
| 14 → 3 | 14 → 5 | 14 → 3 | ||
| 15 → 2 | 15 → 3 | |||
| 16 → 5 | 16 → 3 | |||
| Work environment 14% |
Work environment 9% |
Work environment 7% |
Work environment 6% |
Work environment 6% |
| Performer 29% |
Performer 36% |
Performer 50% |
Performer 43% |
Performer 43% |
| Mean of Production 57% |
Mean of Production 55% |
Mean of Production 29% |
Mean of Production 38% |
Mean of Production 8% |
| Work load 14% |
Work load 13% |
Work load 13% |
||
| Risk level 3,4 Unacceptable |
Risk level 3 Low |
Risk level 2,58 Very Low |
Nivel risk 4,8 Unacceptable |
Nivel risk 2,87 Very low |
| GLOBAL LEVEL RISK 2,97 → RISC LEVEL LOW – VERY LOW | ||||
- the age of the devices in the primary circuits of the 400 kV substation;
- the age of the devices in the primary circuits of the 220 kV substation;
- the age of the devices in the primary circuits of the 20 kV substation;
- the age of the devices in the secundary circuits of the 400 kV substation;
- the age of the devices in the secundary circuits of the 220 kV substation;
- the age of the devices in the secundary circuits of the 20 kV substation.
6. Development of The Prevention and Protection Plan
| Work place | Activity | Assesed risks | Technical and organizational prevention measures | Action in order to echieve the measure | Deadline for completion | Responsible for carrying out the measure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The power substation 400 kV, 220 kV |
Operational Service |
Not using two moving short circuits in the work area | Regular and unannounced management training and control | Compliance with OSH rules | permanent | Responsible for OSH |
| Non-use in the working area of the capacitive load attenuator (in case of capacitive currents) | Regular and unannounced management training and control | |||||
| Not to be verified the lack of voltage before mounting the moving short circuits | Regular training and control of the upper organs | |||||
| Primary Circuit Maintenance | Touching metal parts accidentally under tension under conditions: - failure of insulation against the metal housing; - failure of the protective link. |
Making connections to the grounding belt of all technical equipment |
||||
| Incomplete work permit without specifying all the conditions for working area insurance | Starting work only on the basis of work permit specifying all the conditions for securing the working area | |||||
| The power substation 20 kV |
Primary Circuit Maintenance | Driving by means of transport to work points – road accident | Preparation of instructions for handling and working of vehicles in the station. Compliance with traffic rules. |
|||
| TIRBO transformers explosion hazard | Wearing personal protective and working equipment | |||||
| Injury by the thermal effect of the electric arc of the repair-overhaul personnel while traveling on the territory of the stations for the performance of the work task | Wearing personal protective and working equipment | |||||
| Touching metal parts accidentally under tension under conditions: - failure of insulation against the metal housing; - failure of the protective link. |
Making connections to the grounding belt of all technical equipment. Measurement of touch voltages. Compliance with the deadlines for carrying out technical reviews. |
|||||
| Failure to prepare properly and/or failure to comply with the mandatory steps and measures to ensure the working area | Drawing up specific working instructions on the delimitation of the working area and the performance of the works and their compliance | |||||
| Misidentification of the installations in which they are working, mishandling when performing functional samples | Drawing up appropriate working instructions and training of staff on the working conditions at the substation | |||||
| Entry into the work area unprepared in terms of safety | Compliance with work and work protection instructions. Respect for discipline in the workplace |
|||||
| Incomplete work permit without specifying all the conditions for working area insurance | Starting work only on the basis of work permit specifying all the conditions for securing the working area | |||||
| Exceeding the proximity distances of material transport to the working area and during work | Withdrawal from operation of installations that are below the neighborhood limit | |||||
| Movements, stationary in hazardous areas, outside the working area | Observing the internal instructions for moving to the substation | |||||
| Non-use of personal protectice equipment fitted or use of non-certified PPE | Instructions for the use of certified personal protectice equipment |
7. Conclusion
- 400 kV and 220 kV Operational Service – Risk level 3,4 – Unacceptable;
- 20 kV Operational Service – Risk level 3 – Low;
- 400 kV and 220 kV Primary Circuit Maintenance – Risk level 2,58 – Very Low;
- 20 kV Primary Circuit Maintenance – Nivel risk 4,8 – Unacceptable;
- 20 kV Secondary Circuit Maintenance – Nivel risk 2,87 – Very low.
References
- Petrilean, Dan Codruț; Fîță, Nicolae Daniel; Vasilescu, Gabriel Dragoș; Ilieva-Obretenova, Mila; Tataru, Dorin; Cruceru, Emanuel Alin; Mateiu, Ciprian Ionuț; Nicola, Aurelian; Darabont, Doru-Costin; Cazac, Alin-Marian. Sustainability Management Through the Assessment of Instability and Insecurity Risk Scenarios in Romania’s Energy Critical Infrastructures, MDPI. In Sustainability; Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute, 2025; Volume 17, no. 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, Fîță Nicolae; Dragoș, Păsculescu; Ilieva, Obretenova Mila; Gabriel, Popescu Florin; Teodora, Lazăr; Alin, Cruceru Emanuel; Cristian, Lazăr Dan; Gabriela, Slușariuc; Eugen, Safta Gheorghe; Mihai, Șchiopu Adrian. Vulnerability and Risk Management to Ensure the Occupational Safety of Underground Mines . In Eng; Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute, 2025; Volume 6, no. 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Research and Development Institute of Occupational Safety “Alexandru Darabont” (NRDIOS Bucharest); Romania. Method for Risk Assessment in Terms of OHS; 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Law no. 319/2006 on Occupational Safety and Health (Romania), with subsequent amendments — Provides the legal framework for OHS in Romanian industry, including hazard identification and employer duties for risk management; (cited in multiple Romanian substation studies).
- Transelectrica – Romanian Power Grid – www.transelectrica.ro.
- Ilieva-Obretenova, Mila. Devices and Methods for Microclimate Research in Closed Areas – Underground Mining. Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 2021, 6(4), 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraru, R.; Băbuţ, G. Risk management. In Global approach – Concepts, principles and structure; UNIVERSITAS Publishing House: Petrosani, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Basuc, M.; Năpar, G.; Baltă, M.; Zamfirache, E.; Toaje, E.M.; Vînturache, M.; Stoicescu, D. Occupational Health and Safety – legal requirements and good practices Center for training and professional improvement of the Labor Inspection; Botoșani, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Moraru, R.; Băbuţ, G. Risk analysis; Universitas Publishing House: Petrosani, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Băbuţ, G.; Moraru, R.; Matei, I.; Băncilă, N. Occupational Health and Safety systems. Guiding principles; Focus Publishing House: Petrosani, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Matei, I.; Moraru, R.; Băbuţ, G. Allocation of a level of security – a new concept in risk, risk and safety analysis at work. In ICSPM magazine; Bucharest; Volume no. 3 – 4/1996, pp. 47–52.
- Moraru, R.; Băbuţ, G.; Matei, I. Guide for Professional risk assessment; Focus Publishing House: Petrosani, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Barb, C.M.; Fita, D.N. A comparative analysis of risk assessment techniques from the risk management perspective. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Manufacturing Science and Education—MSE 2019: Trends in New Industrial Revolution, Sibiu, Romania, 5–7 June 2019; Volume 290. [Google Scholar]
- Vasilescu, G.D.; Petrilean, C.D.; Kovacs, A.; Vasilescu, G.V.; Pasculescu, D.; Ilcea, G.I.; Burduhos-Nergis, D.P.; Bejinariu, C. Methodology for Assessing the Degree of Occupational Safety Specific to Hydrotechnical Construction Activities, in order to Increase Their Sustainability. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mixafenti, S.; Moutzouri, A.; Karagkouni, A.; Sartzetaki, M.; Dimitriou, D. Assessment of Occupational Health and Safety Management: Implications for Corporate Performance in the Secondary Sector . Safety 2025, 11(2), 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzoglou, P. D.; Kotzakolios, A. E.; Marhavilas, P. K. Health and Safety Management System (HSMS) and Its Impact on Employee Satisfaction and Performance—A New HSMS Model . Safety 2025, 11(2), 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabiesz, P.; Płaza, G.; Jamil, T. Modern Technologies in Occupational Health and Safety Training: An Analysis of Education, Innovation, and Sustainable Work Practices in Industry . Sustainability 2025, 17(16), 7305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, O.O.; Eteng, M.J.; Anochiwa, L.I.; Njemanze, V.; Agbanike, T.F.; Eyisi, E.; Agha, E.; Chukwu, J.; Igu, N.C.N. Organizational Health/Safety and Employees’ Performance for Sustainable Development . Webology 2021, 18, 1011–1017. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z.; Chupradit, S.; Ku, K.Y.; Nassani, A.A.; Haffar, M. Impact of Employees’ Workplace Environment on Employees’ Performance: A Multi-Mediation Model. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 890400. [Google Scholar]
- Wijesinghe, D.; Jayakumar, V.; Gunarathne, N.; Samudrage, D. Implementing Health and Safety Strategies for Business Sustainability: The Use of Management Controls Systems . Saf. Sci. 2023, 164, 106183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alli, B.O. Fundamental Principles of Occupational Health and Safety, 2nd ed.; International Labour Office: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Šolc, M.; Blaško, P.; Girmanová, L.; Kliment, J. The Development Trend of the Occupational Health and Safety in the Context of ISO 45001:2018 . Standards 2022, 2, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asbury, S. Health and Safety, Environment and Quality Audits: A Risk-based Approach, 4th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Flor-Unda, O.; Fuentes, M.; Dávila, D.; Rivera, M.; Llano, G.; Izurieta, C.; Acosta-Vargas, P. Innovative Technologies for Occupational Health and Safety: A Scoping Review . Safety 2023, 9, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabiesz, P.; Płaza, G.; Jamil, T. Modern Technologies in Occupational Health and Safety Training: An Analysis of Education, Innovation, and Sustainable Work Practices in Industry . Sustainability 2025, 17, 7305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bęś, P.; Strzałkowski, P.; Górniak-Zimroz, J.; Szóstak, M.; Janiszewski, M. Innovative Technologies to Improve Occupational Safety in Mining and Construction Industries—Part I . Sensors 2025, 25, 5201. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reason, J. Managing the Risks of Organizational Accidents, 1st ed.; Routledge: London, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Kirsten, W. The Evolution from Occupational Health to Healthy Workplaces . Am. J. Lifestyle Med. 2022, 18, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, P.; Walters, D. Health & safety at work: Time for change . Inst. Employ. Rights J. 2019, 2, 58–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Florio, F. Chapter 9—Continued Airworthiness and Operation. In Airworthiness, 2nd ed.; De Florio, F., Ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2011; pp. 243–319. [Google Scholar]
- Ispas, L.; Mironeasa, C.; Silvestri, A. A Study on the Emergence and Resilience of Integrated Management Systems in Organizations with an Industrial Profile in Romania. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowski, A.S.; Krasławski, A.; Vairo, T.; Fabiano, B. Process Safety Management Quality in Industrial Corporation for Sustainable Development . Sustainability 2021, 13, 9001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Hoque, A.S.M.; Karmaker, C.L.; Ahmed, S. Integrated approach for occupational health and safety (OHS) risk assessment: An empirical (case) study in small enterprises . Saf. Sci. 2023, 164, 106143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, C.U.; Kirkegaard, M.L.; Dyreborg, J.; Hasle, P. Making occupational health and safety management systems ‘work’: A realist review of the OHSAS 18001 standard . Saf. Sci. 2020, 129, 104843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, C.; Obasi, I.C.; Akinwande, D.V.; Ile, C. The impact of interventions on health, safety and environment in the process industry . Heliyon 2024, 10, e23604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karanikas, N.; Weber, D.; Bruschi, K.; Brown, S. Identification of systems thinking aspects in ISO 45001:2018 on occupational health & safety management . Saf. Sci. 2022, 148, 105671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltelli, A.; Tarantola, S.; Campolongo, F.; Ratto, M. Sensitivity Analysis in Practice: A Guide to Assessing Scientific Models; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Fîță, N.D.; Radu, M.S.; Păsculescu, D.; Popescu, F.G.; Rada, C.; Grigorie, E.; Handra, A.D. Occupational Health and Safety Management–An important pillar of national security from Romania. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Electrical, Computer and Energy Technologies-ICECET; Cape Town, South Africa, 9-10 December 2021; ISBN 978-1-6654-4231-2. [Google Scholar]
- Chatzoglou, P.D.; Kotzakolios, A.E.; Marhavilas, P.K. Health and Safety Management System (HSMS) and Its Impact on Employee Satisfaction and Performance—A New HSMS Model . Safety 2025, 11, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bęś, P.; Strzałkowski, P. Analysis of the Effectiveness of Safety Training Methods. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.X.M.; Arifin, K.; Abas, A.; Ahmad, M.A.; Khairil, M.; Cyio, M.B.; Samad, M.A.; Lampe, I.; Mahfudz, M.; Ali, M.N. Systematic Literature Review on Indicators Use in Safety Management Practices among Utility Industries . Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaşlı, F.; Bolat, B. Evaluation of Occupational Safety Risk in Underground Mining Using Fuzzy Bayesian Network . In Intelligent and Fuzzy Techniques: Smart and Innovative Solutions; Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 1363–1372. [Google Scholar]
- Robson, L.S.; Clarke, J.A.; Cullen, K.; Bielecky, A.; Severin, C.; Bigelow, P.L.; Irvin, E.; Culyer, A.; Mahood, Q. The effectiveness of occupational health and safety management system interventions: A systematic review . Saf. Sci. 2007, 45, 329–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.-C.; Liu, L.; Liu, N. Risk evaluation approaches in failure mode and effects analysis: A literature review . Expert Syst. Appl. 2013, 40, 828–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| No. | Workplaces | Level of risk (nrp) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 400, 220 kV, 110 kV Operating Service | X |
| 2 | 20 kV Operating Service | X |
| 3 | 400, 220 kV, 110 kV Primary Circuit Maintenance | X |
| 4 | 20 kV Primary Circuit Maintenance | X |
| 5 | Secondary Circuit Maintenance | X |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





