Submitted:
04 November 2025
Posted:
05 November 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methods of the Current Study
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Selection Process
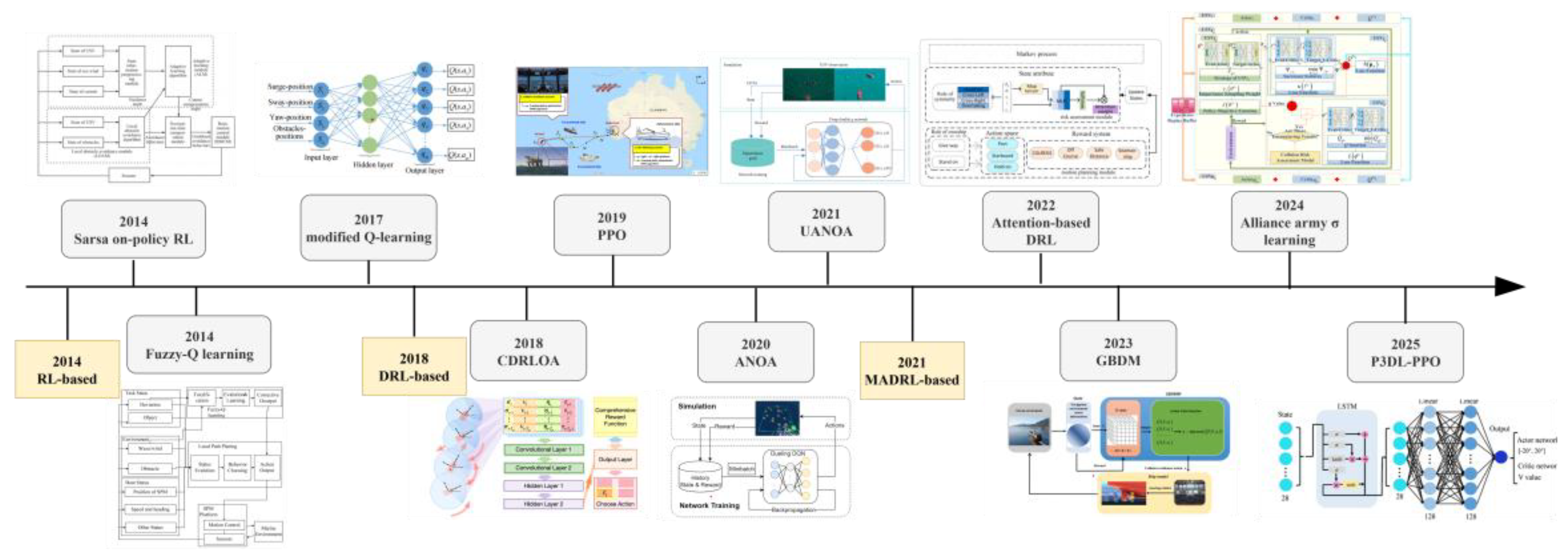
3. Single-Agent Collision Avoidance
3.1. Collision Avoidance in Static Environment
3.2. Collision Avoidance in Dynamic Environment
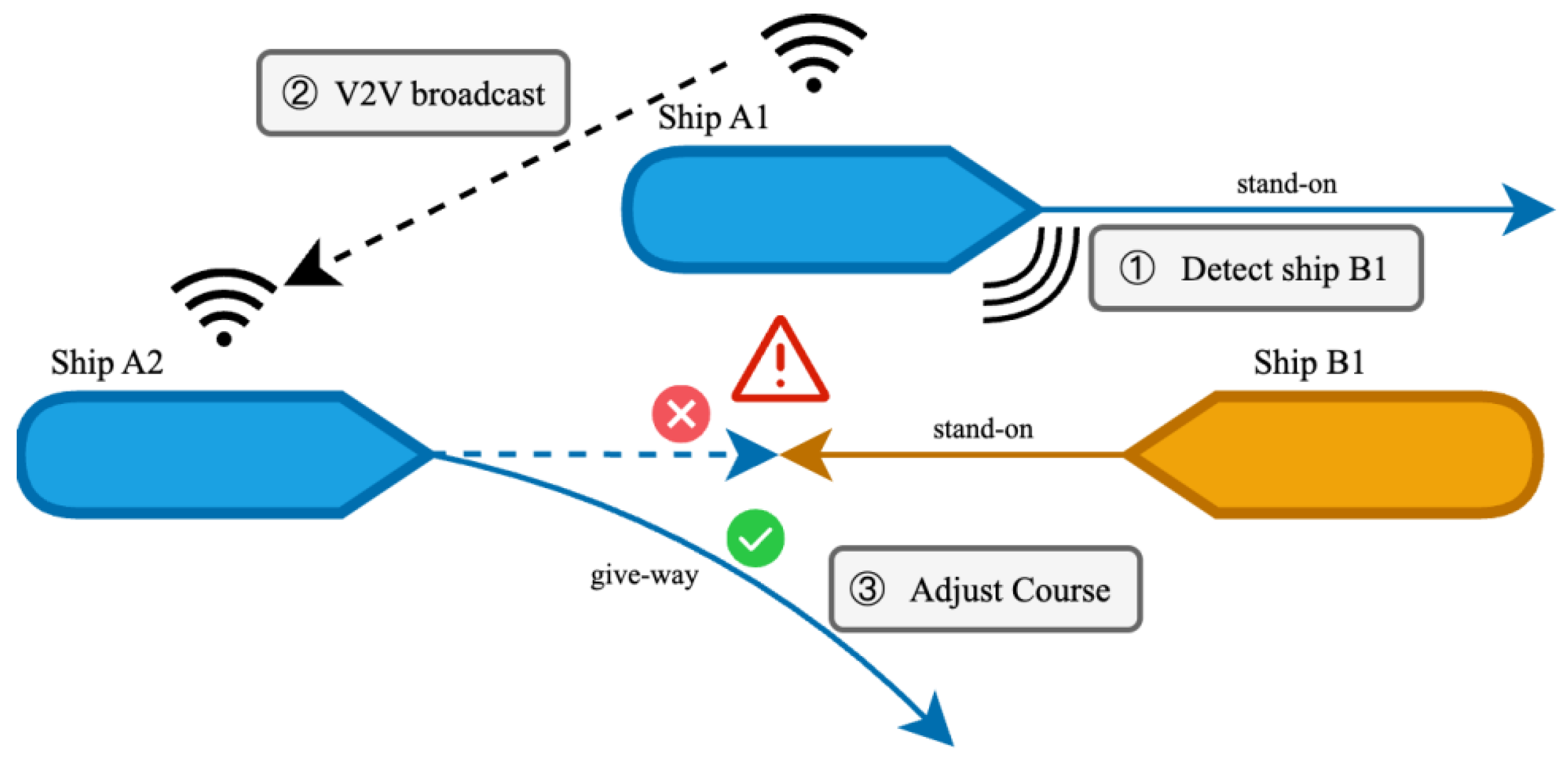
4. Multi-Agent Collision Avoidance
4.1. Collision Avoidance in Collaborative Environment
4.2. Collision Avoidance in Non-Collaborative Environment
5. Challenges and Future Directions
5.1. Limitations and Open Challenges of Present RL Solutions
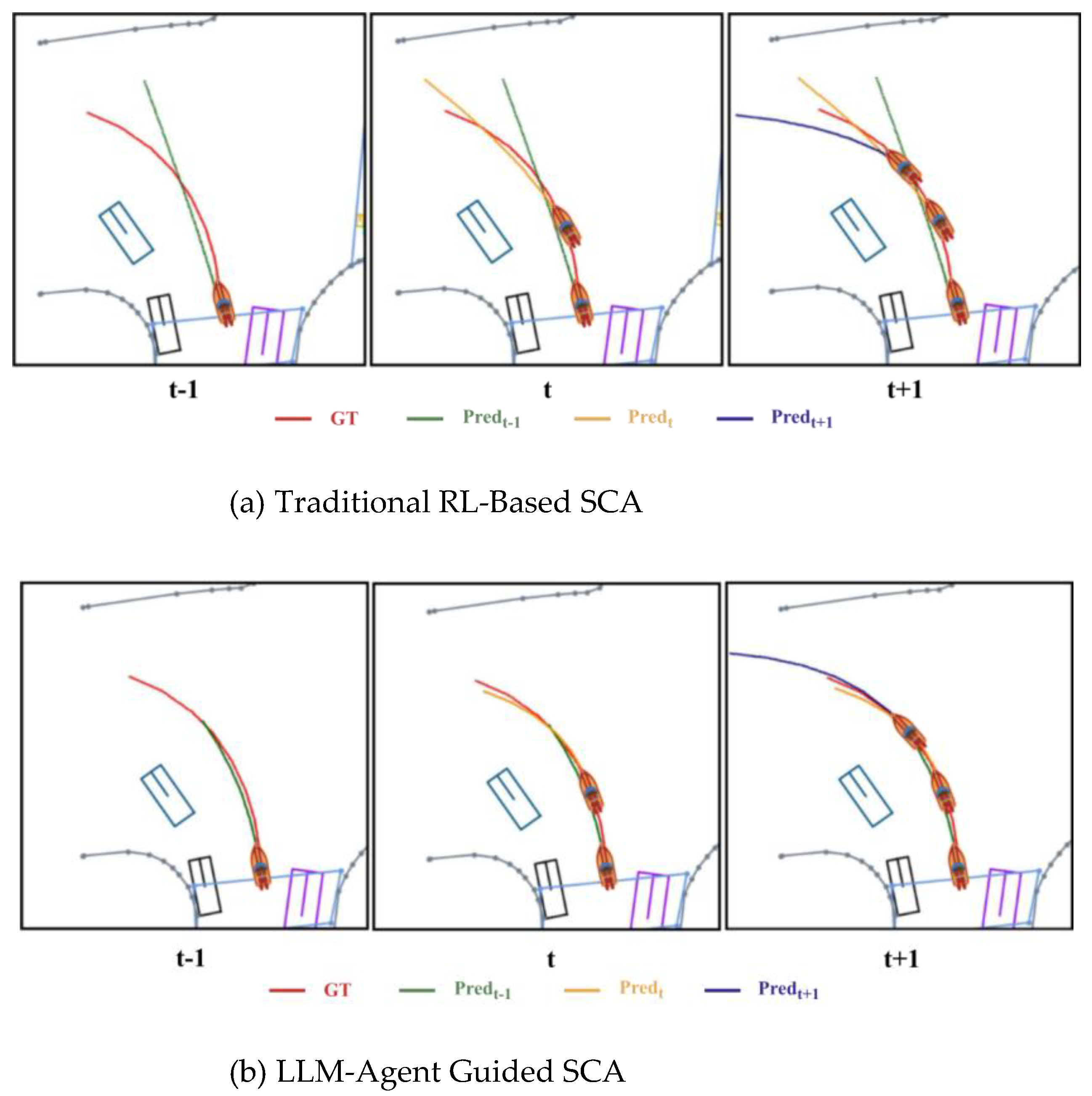
5.2. LLM Enhanced Decision for SCA

Abbreviations
| AABSRL | Avoidance Algorithm Based on Sarsa on-policy Reinforcement Learning |
| ADRL | Attention-Based Deep Reinforcement Learning |
| ANOA | Autonomous Navigation and Obstacle Avoidance |
| CDRLOA | Concise DRL Obstacle Avoidance |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Networks |
| COLREGs | Convention on The International Regulations for Preventing Collisions At Sea |
| CPA | Closest Point of Approach |
| DDPG | Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient |
| DE | Differential Evolution |
| DEDRL | Differential Evolution Deep Reinforcement Learning |
| Dec-POMDP | Decentralized Partially Observable Markov Decision Process |
| DQN | Deep Q-Network |
| DRL | Deep Reinforcement Learning |
| DRQN | Deep Recurrent Q-network |
| GBDM | Generalized Behavior Decision-Making |
| HRVO | Hybrid Reciprocal Velocity Obstacle |
| ITDRL3 | Three-layer Hierarchical Deep Reinforcement Learning |
| LLM | Large Language Model |
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
| MARL | Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning |
| MDP | Markov Decision Process |
| MLLM | Multi-Modal LLM |
| MPC | Model Predictive Control |
| OZT | Obstacle Zone by Target |
| PER | Prioritized Experience Replay |
| POMDP | Partially Observable Markov Decision Process |
| PPO | Proximal Policy Optimization |
| RL | Reinforcement Learning |
| RVO | Reciprocal Velocity Obstacle |
| SCA | Ship Collision Avoidance |
| SMDP | Semi-Markov Decision Process |
| ToT | Tree-of-Thought |
| UANOA | Autonomous Navigation and Obstacle Avoidance in USVs |
| UMVs | Underactuated Unmanned Vessels |
| USVs | Unmanned Surface Vehicles |
| V2V | Vessel-to-Vessel |
| VO | Velocity Obstacle |
| WOS | Web of Science |
References
- Uflaz, E.; Akyuz, E.; Arslan, O.; et al. Analysing human error contribution to ship collision risk in congested waters under the evidential reasoning SPAR-H extended fault tree analysis. Ocean Engineering, 2023, 287, 115758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Ma, X.; Wang, T.; et al. A data-driven approach to determine the distinct contribution of human factors to different types of maritime accidents. Ocean Engineering, 2024, 295, 116874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X. ; qian, Zheng, Q. ; Guo, Y. Maritime accident causation: A spatiotemporal and HFACS-Based approach. Ocean Engineering, 2025, 340, 122329. [Google Scholar]
- Fiorini, P.; Shiller, Z. Motion planning in dynamic environments using velocity obstacles. The international journal of robotics research, 1998, 17, 760–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van, den, Berg, J.; Lin, M.; Manocha, D. Reciprocal velocity obstacles for real-time multi-agent navigation. In Proceedings of 2008 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation, Pasadena, CA, USA, 19-23 May 2008; pp. 1928–1935.
- Snape, J. ; Van, Den, Berg, J. ; Guy, S. J. et al. The hybrid reciprocal velocity obstacle. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2011, 27, 696–706. [Google Scholar]
- Kao, S. L.; Lee, K. T.; Chang, K. Y.; et al. A fuzzy logic method for collision avoidance in vessel traffic service. The journal of navigation, 2007, 60, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldwell, C. V.; Dunlap, D. D.; Collins, E. G. Motion planning for an autonomous underwater vehicle via sampling based model predictive control. Proceedings of OCEANS 2010 MTS/IEEE SEATTLE, Seattle, WA, USA, 20-23 September 2010; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Kaelbling, L. P.; Littman, M. L.; Moore, A. W. Reinforcement learning: A survey. Journal of artificial intelligence research, 1996, 4, 237–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puterman, M. L. Markov decision processes. Handbooks in operations research and management science, 1990, 2, 331–434. [Google Scholar]
- Watkins C J C H, Dayan P. Q-learning. Machine learning, 1992, 8, 279–292.
- Mnih, V.; Kavukcuoglu, K.; Silver, D.; et al. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning. nature, 2015, 518, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillicrap, T. P.; Hunt, J. J.; Pritzel, A.; et al. Continuous control with deep reinforcement learning. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1509.02971. [Google Scholar]
- Schulman, J.; Wolski, F.; Dhariwal, P.; et al. Proximal policy optimization algorithms. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1707.06347. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, J.; Kim, N. Collision avoidance for an unmanned surface vehicle using deep reinforcement learning. Ocean Engineering, 2020, 199, 107001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, E.; Heiberg, A.; Rasheed, A.; et al. COLREG-compliant collision avoidance for unmanned surface vehicle using deep reinforcement learning. Ieee Access, 2020, 8, 165344–165364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Hashimoto, H.; Matsuda, A.; et al. Automatic collision avoidance of multiple ships based on deep Q-learning. Applied Ocean Research, 2019, 86, 268–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busoniu, L.; Babuska, R. ; De, Schutter. B. Multi-agent reinforcement learning: A survey. In Proceedings of 2006 9th international conference on control, automation, robotics and vision, Singapore, 05-08 December 2006; pp. 1–6.
- Chen, C.; Ma, F.; Xu, X.; et al. A novel ship collision avoidance awareness approach for cooperating ships using multi-agent deep reinforcement learning. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2021, 9, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshioka, H.; Hashimoto, H.; Matsuda, A. Artificial Intelligence for Cooperative Collision Avoidance of Ships Developed by Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning. Proceedings of International Conference on Offshore Mechanics and Arctic Engineering, Singapore, 09-14 June, 2024; pp. 125392–125400.
- Zheng, S.; Luo, L. Multi-Agent Cooperative Navigation with Interlaced Deep Reinforcement Learning. Proceedings of 2024 IEEE 6th International Conference on Civil Aviation Safety and Information Technology (ICCASIT), Hangzhou, China, 23-25 October, 2024; pp. 409–414.
- Wang, Z.; Chen, P.; Chen, L.; et al. Collaborative Collision Avoidance Approach for USVs Based on Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2025, 26, 4780–4794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Tang, P.; Su, Y.; et al. An adaptive obstacle avoidance algorithm for unmanned surface vehicle in complicated marine environments. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2014, 1, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Pang, Y.; Li, H.; et al. Local path planning method of the self-propelled model based on reinforcement learning in complex conditions. Journal of Marine Science and Application, 2014, 13, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhopale, P.; Kazi, F.; Singh, N. Reinforcement learning based obstacle avoidance for autonomous underwater vehicle. Journal of Marine Science and Application, 2019, 18, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Chen, H.; Chen, C.; et al. The autonomous navigation and obstacle avoidance for USVs with ANOA deep reinforcement learning method. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2020, 196, 105201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, N.; Huang, S.; Kong, C. Reinforcement Learning-Based Autonomous Navigation and Obstacle Avoidance for USVs under Partially Observable Conditions. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2021, 2021, 5519033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhang, W. Concise deep reinforcement learning obstacle avoidance for underactuated unmanned marine vessels. Neurocomputing, 2018, 272, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Hashimoto, H.; Matsuda, A.; et al. Automatic collision avoidance of multiple ships based on deep Q-learning. Applied Ocean Research, 2019, 86, 268–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Roh, M. I. COLREGs-compliant multiship collision avoidance based on deep reinforcement learning. Ocean Engineering, 2019, 191, 106436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, P.; Zhang, Y.; Shaobo, W. Intelligent ship collision avoidance algorithm based on DDQN with prioritized experience replay under COLREGs. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2022, 10, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alayrac, J. B.; Donahue, J.; Luc, P.; et al. Flamingo: a visual language model for few-shot learning. Advances in neural information processing systems, 2022, 35, 23716–23736. [Google Scholar]
- Sawada, R.; Sato, K.; Majima, T. Automatic ship collision avoidance using deep reinforcement learning with LSTM in continuous action spaces. Journal of Marine Science and Technology, 2021, 26, 509–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Ma, F.; Xu, X.; et al. A novel ship collision avoidance awareness approach for cooperating ships using multi-agent deep reinforcement learning. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2021, 9, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Liu, S.; Lin, Y. Dynamic navigation and area assignment of multiple USVs based on multi-agent deep reinforcement learning. Sensors, 2022, 22, 6942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nantogma, S.; Zhang, S.; Yu, X.; et al. Multi-USV dynamic navigation and target capture: A guided multi-agent reinforcement learning approach. Electronics, 2023, 12, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Wang, X.; Cao, X.; et al. Multi-USV Formation Control and Obstacle Avoidance Under Virtual Leader. Proceedings of 2023 China Automation Congress (CAC), Chongqing, China, 17-19 November 2023; pp. 3411–3416.
- Glorennec, P. Y.; Jouffe, L. ; Fuzzy Q-learning. Proceedings of 6th international fuzzy systems conference, Barcelona, Spain, 05-05 July, 1997; pp. 659–662.
- Zhang, J.; Ren, J.; Cui, Y.; et al. Multi-USV task planning method based on improved deep reinforcement learning. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024, 11, 18549–18567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockman, G.; Cheung, V.; Pettersson, L.; et al. Openai gym. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1606.01540. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Xiao, Y. Intelligent ships collision avoidance and navigation method based on deep reinforcement learning. Proceedings of 2021 International Conference on Computer Information Science and Artificial Intelligence (CISAI), Kunming, China, 17-19 September, 2021; pp. 573–578.
- Jiang, L.; An, L.; Zhang, X.; et al. A human-like collision avoidance method for autonomous ship with attention-based deep reinforcement learning. Ocean Engineering, 2022, 264, 112378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, W.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, C.; et al. Generalized behavior decision-making model for ship collision avoidance via reinforcement learning method. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2023, 11, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Weng, J.; Zhou, Y. Ship collision avoidance method in starboard-to-starboard head-on situations. Proceedings of 2023 7th International Conference on Transportation Information and Safety (ICTIS), Xi’an, China, 04-06 August, 2023; pp. 609–614.
- Niu, Y.; Zhu, F.; Zhai, P. An autonomous decision-making algorithm for ship collision avoidance based on DDQN with prioritized experience replay. Proceedings of 2023 7th International Conference on Transportation Information and Safety (ICTIS), Xi’an, China, 04-06 August, 2023; pp. 1174–1180.
- Zheng, K.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C.; et al. A partially observable multi-ship collision avoidance decision-making model based on deep reinforcement learning. Ocean & Coastal Management, 2023, 242, 106689. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.; Liao, Z.; Chen, D. Differential Evolution Deep Reinforcement Learning Algorithm for Dynamic Multiship Collision Avoidance with COLREGs Compliance. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2025, 13, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S. P. ; Sutton, R, S. Reinforcement learning with replacing eligibility traces. Machine learning, 1996, 22, 123–158. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, S.; Yu, D.; Zhao, J.; et al. Tree of thoughts: Deliberate problem solving with large language models. Advances in neural information processing systems, 2023, 36, 11809–11822. [Google Scholar]

| Scene type | Triggering condition | Reward value | Key parameter |
|---|---|---|---|
| Successful SCA | no collision risk | +10,) | Sub-reward weights: |
| Collision penalty | distance to the target vessel | -10 | Critical distance threshold: 0.3 NM |
| Potential risk penalty | Predicting danger | -1 | Observation vector dimension: 35 danger sectors |
| Neutral state | No significant events | 0 | N/A |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





