1. Introduction
Accurate flow measurement is critical to the performance, efficiency, and safety of power generation systems. In South Africa, Eskom relies on precise flow measurement to ensure reliable operation across its power stations. To meet this need, the utility established the Flow Laboratory, a specialized calibration facility capable of handling flow meters up to 700 nominal bore (NB). The laboratory plays a key role in maintaining the accuracy and traceability of measurement devices to both national and international standards, supporting energy efficiency and reliability across industrial sectors. Its services ensure that flow measurements used in Eskom’s operations remain consistent, verifiable, and aligned with global best practices.
To strengthen its credibility and technical competence, the Flow Laboratory obtained ISO/IEC 17025 accreditation as the global benchmark for testing and calibration laboratory quality. This accreditation validates the laboratory’s technical accuracy, quality management, and staff competence while ensuring international recognition through the International Laboratory Accreditation Cooperation (ILAC). Implementation of ISO/IEC 17025 has enhanced the laboratory’s operational processes, measurement reliability, and customer confidence. The current study evaluates the benefits and customer perceptions of this accreditation, focusing on its impact on calibration accuracy, efficiency, and satisfaction. Findings from the analysis contribute to understanding how ISO/IEC 17025 supports Eskom’s goals of operational excellence and reinforces South Africa’s broader measurement and energy infrastructure.
2. Literature Review
The ISO/IEC 17025 standard serves as the global foundation for quality assurance in testing and calibration laboratories, defining the requirements for technical competence, impartiality, and consistent operation (International Organization for Standardization, 2017). Laboratories accredited under this standard must demonstrate reliable management systems, traceable results, and staff competency across various testing and calibration methods. Its structured framework promotes continuous improvement through comprehensive documentation, calibration traceability, and quality control measures, ensuring confidence in laboratory results (Kumar & Singh, 2022).
ISO/IEC 17025 accreditation also enhances international recognition and cooperation through the International Laboratory Accreditation Cooperation (ILAC), which fosters mutual recognition among national accreditation bodies and reduces duplication of testing (ILAC, 2021). In South Africa, the South African National Accreditation System (SANAS) oversees accreditation to align local laboratories with global standards (South African National Accreditation System, 2022). Studies have shown that accredited laboratories benefit from improved management practices, enhanced staff training, reduced error rates, and higher customer satisfaction outcomes linked to the standard’s emphasis on traceability, equipment verification, and preventive maintenance (Sharma, Naidoo, & Govender, 2021; Mbenge & Hlongwane, 2020). For flow calibration laboratories, such as the Eskom Flow Laboratory, accreditation ensures that flow measurements remain accurate and traceable, supporting operational efficiency and reliability across sectors like power generation, petrochemicals, and manufacturing (Wang & Lin, 2020).
Beyond technical performance, ISO/IEC 17025 accreditation fosters customer trust and satisfaction by signaling competence, impartiality, and transparency (Kumar & Singh, 2022). Clients in industrial sectors, including power generation supply chain, view accreditation as assurance of quality and reliability. Accredited laboratories tend to enjoy stronger reputations, improved responsiveness to client needs, and greater retention rates (Ngwenya & Ramohlola, 2021). However, maintaining accreditation presents challenges, such as high costs, continuous staff development, and compliance with evolving standards (Moyo & Sithole, 2019).
3. Materials and Methods
This study adopted quantitative research to evaluate customer perceptions regarding the benefits of ISO/IEC 17025 accreditation at the Flow Laboratory. The design enabled the collection of measurable data from customers who had used the laboratory’s calibration services after accreditation. A structured questionnaire was used to collect responses on several key variables, including accuracy of calibration results, staff competence, service reliability, efficiency, communication, and overall satisfaction. The quantitative approach allowed for statistical analysis and objective evaluation of trends across industries served by the laboratory (Creswell & Creswell, 2018).
3.1. Population and Sampling
The target population consisted of all Eskom Flow Laboratory customers from the past five years following ISO/IEC 17025 accreditation, including clients from power generation, manufacturing, environmental testing, manufacturing, mining, and other sectors. The population list was obtained from the laboratory’s customer database with permission from laboratory management. A stratified random sampling method was used to ensure proportional representation from each industry sector. The final sample size consisted of 82 respondents, which provided adequate representation for statistical reliability.
Table 1 summarizes the sample distribution by industry sector.
3.2. Data Collection
Data were collected using a structured questionnaire designed specifically for this study. The questionnaire was divided into five sections:
Demographic information (industry, company size, duration of engagement with the lab).
Perception of calibration accuracy and reliability.
Evaluation of staff competence and technical communication.
Assessment of efficiency, turnaround time, and quality of service.
Overall satisfaction and perceived value of ISO/IEC 17025 accreditation.
Each section used a five-point Likert scale, where. 1 = Strongly Disagree, 2 = Disagree, 3 = Neutral, 4 = Agree, and 5 = Strongly Agree.
The questionnaire was pretested with five customers and two laboratory staff to ensure clarity and relevance. Feedback from the pilot test resulted in minor wording adjustments.
Table 2 illustrates the key questionnaire variables and example items.
Data collection was conducted over a four-week period using both email surveys and in-person distribution during customer visits. Each participant received an information letter describing the purpose of the research and assurances of confidentiality. Responses were anonymized and analyzed in aggregate form. Follow-ups were made after two weeks to increase response rates, resulting in an 83% response rate (82 valid responses out of 99 distributed questionnaires).
3.3. Data Analysis
Data were analyzed using SPSS version 27 and Microsoft Excel. Descriptive statistics such as means, standard deviations, and percentages were used to summarize the responses. Key variables (accuracy, competence, efficiency, satisfaction) were aggregated to generate overall scores per construct. Reliability of the questionnaire was tested using Cronbach’s alpha, which produced a coefficient of 0.91, indicating high internal consistency (Nunnally & Bernstein, 1994). As shown in
Table 3.
Correlation analysis was also carried out to determine the relationships between variables such as staff competence and customer satisfaction. The results showed a strong positive correlation (r = 0.81, p < 0.01), indicating that higher perceptions of staff competence were significantly associated with greater overall satisfaction.
4. FINDINGS & DISCUSSION
The analysis of customer feedback revealed consistently positive perceptions of the Eskom Flow Laboratory’s performance following ISO/IEC 17025 accreditation. Across all sectors, respondents rated the laboratory highly in terms of calibration accuracy, staff competence, efficiency, and overall satisfaction.
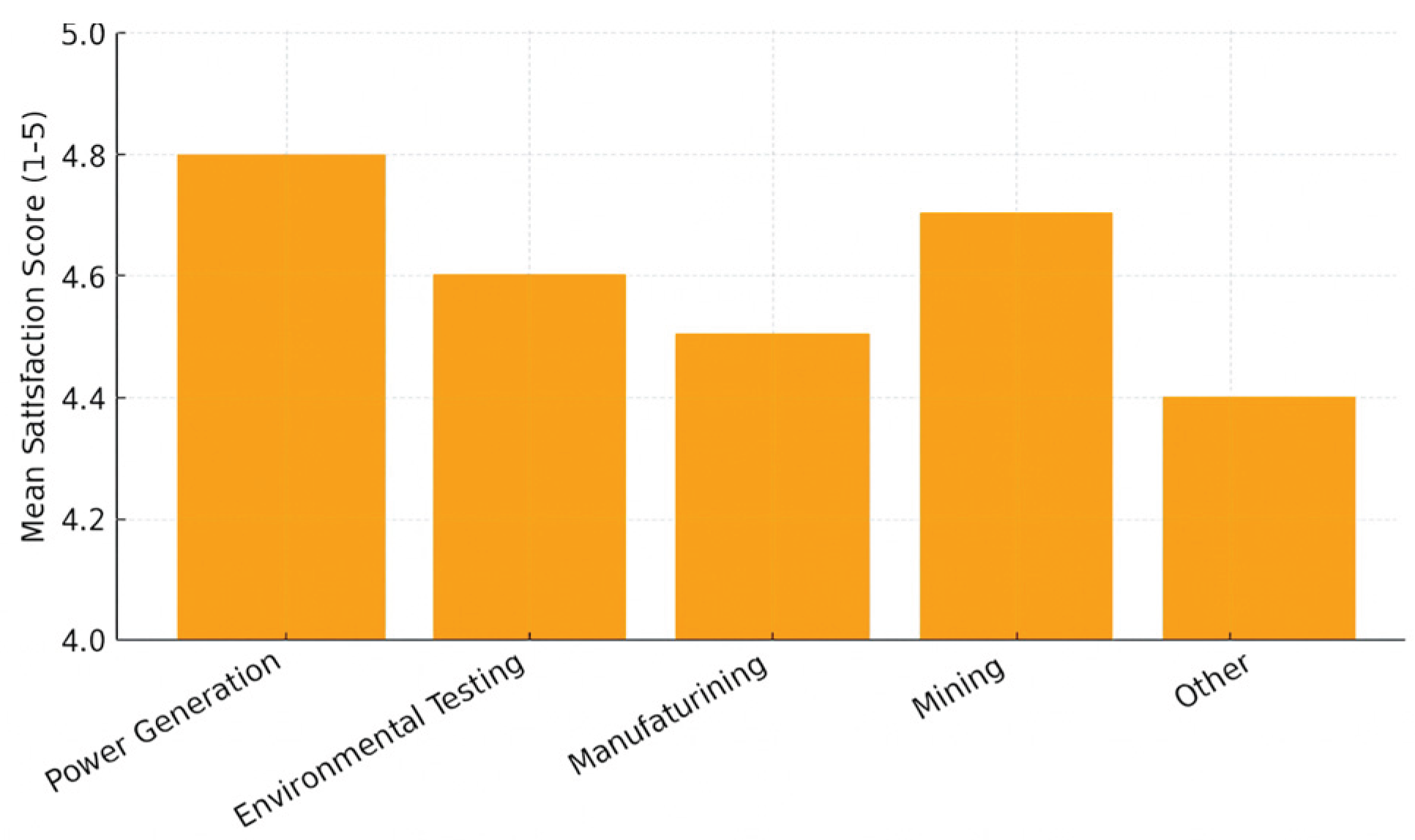
As shown in
Figure 1, the power generation sector reported the highest satisfaction level, with a mean score of 4.8, reflecting strong confidence in calibration reliability. This result aligns with the laboratory’s core role in supporting Eskom’s generation fleet, where precision in flow measurement directly affects turbine and boiler efficiency. The mining (4.7) and environmental testing (4.6) sectors also expressed high satisfaction, citing improved traceability and consistency of results. Although manufacturing (4.5) and other industries (4.4) reported slightly lower scores, their feedback remained overwhelmingly positive, suggesting broad cross-sectoral acceptance of the laboratory’s technical quality.
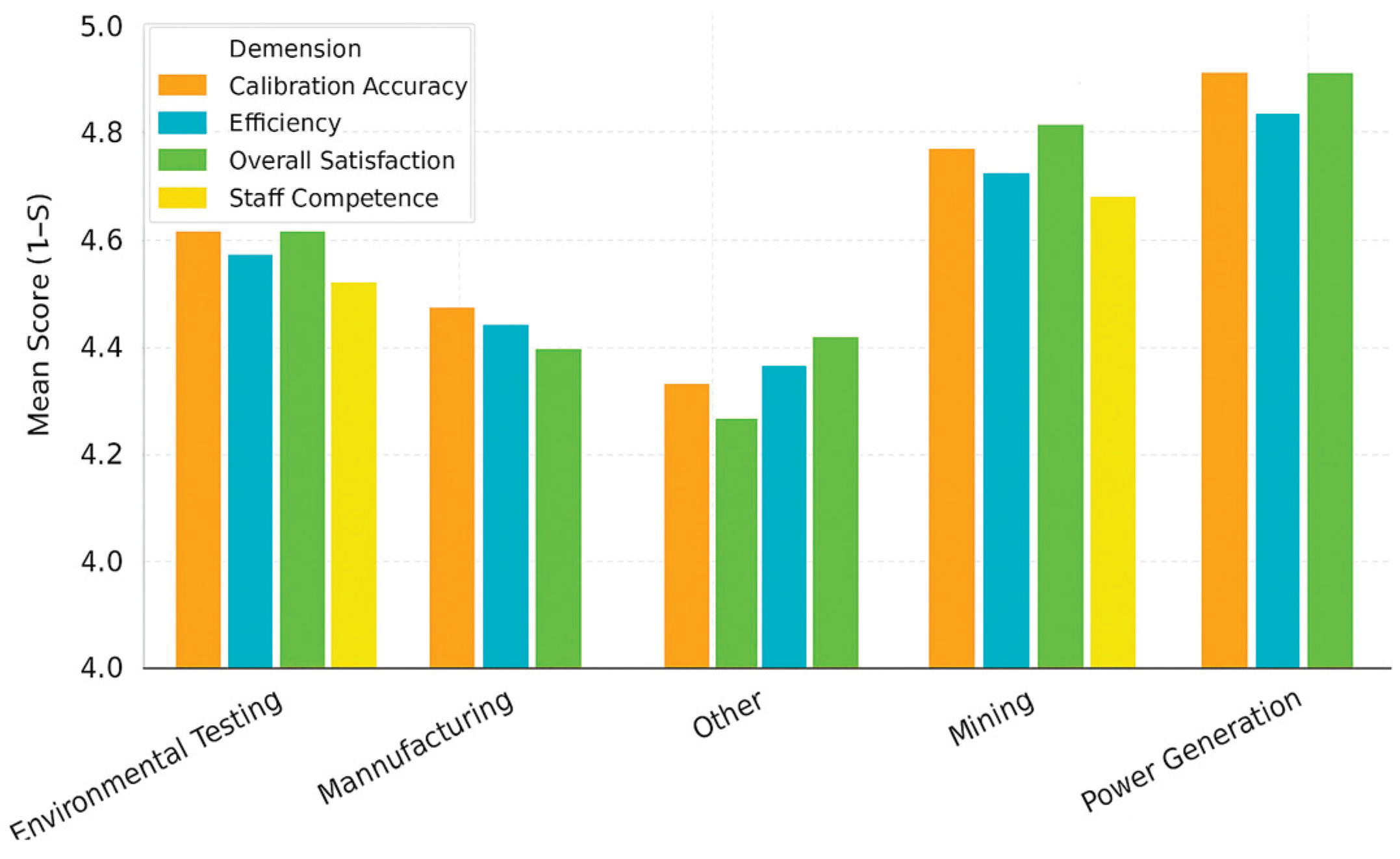
Figure 2 compares mean scores across key performance dimensions. The highest-rated attributes were calibration accuracy (mean = 4.60) and overall satisfaction (mean = 4.60), followed closely by staff competence (mean = 4.54) and efficiency (mean = 4.38). These findings confirm that accreditation has led to measurable improvements in quality, precision, and customer experience. The emphasis on traceability, documented procedures, and internal quality checks under ISO/IEC 17025 has strengthened process control, thereby enhancing calibration reliability and customer confidence.
The overall average satisfaction score of 4.53 indicates a strong positive customer response to accreditation outcomes. Respondents highlighted key benefits such as improved turnaround time, professional communication, and enhanced transparency in calibration reports. Qualitative comments further emphasized that accreditation increased client trust in measurement data used for regulatory and operational decisions. These results align with previous research by Sharma et al. (2021) and Kumar & Singh (2022), who found that accredited laboratories typically achieve higher customer satisfaction and credibility due to the structured management systems enforced by ISO/IEC 17025.
The findings demonstrate that the Eskom Flow Laboratory’s ISO/IEC 17025 accreditation has significantly improved its operational consistency, technical reliability, and reputation among clients in power generation and related industries. These outcomes validate the strategic importance of maintaining accreditation and continuous improvement practices within national calibration facilities.
To further explore the relationships among key performance dimensions, Pearson correlation analysis was conducted between staff competence, calibration accuracy, efficiency, and overall satisfaction. The results in Table 4 indicate strong and statistically significant positive correlations among all variables.
| Variables |
Calibration Accuracy |
Staff Competence |
Efficiency |
Overall Satisfaction |
| Calibration Accuracy |
1.00 |
0.78 |
0.65 |
0.83 |
| Staff Competence |
0.78 |
1.00 |
0.70 |
0.81 |
| Efficiency |
0.65 |
0.70 |
1.00 |
0.68 |
| Overall Satisfaction |
0.83 |
0.81 |
0.68 |
1.00 |
| Note: p < 0.01, indicating significant correlations at the 99% confidence level. |
The analysis reveals that overall satisfaction is most strongly correlated with calibration accuracy (r = 0.83) and staff competence (r = 0.81). This suggests that clients’ trust and satisfaction are primarily driven by perceptions of technical precision and the professionalism of laboratory personnel. Efficiency, while still positively correlated (r = 0.68), had a comparatively weaker influence, indicating that timeliness, although important, is secondary to technical quality and reliability in shaping client perceptions.
A simple linear regression model was further used to estimate the predictive influence of key factors on overall satisfaction. The regression equation was as follows:
Overall Satisfaction = 0.42(Calibration Accuracy) + 0.38(Staff Competence) + 0.20(Efficiency)
R² = 0.84, p < 0.001
The R² value of 0.84 indicates that approximately 84% of the variation in overall satisfaction can be explained by the combined effects of calibration accuracy, staff competence, and efficiency. Among these predictors, calibration accuracy had the strongest standardized coefficient (β = 0.42), reaffirming its dominant role in determining customer satisfaction. These findings reinforce the notion that ISO/IEC 17025 accreditation improves not only technical quality but also customer perceptions of reliability and professionalism.
The statistical results corroborate prior studies emphasizing the importance of ISO/IEC 17025 accreditation in enhancing both technical competence and customer satisfaction (Kumar & Singh, 2022; Sharma et al., 2021). For the Eskom Flow Laboratory, accreditation has established a structured quality framework ensuring measurement traceability, equipment calibration, and documented procedures all of which contribute to increased client confidence.
Respondents from the power generation sector, Eskom’s primary clientele, particularly noted improved calibration repeatability and reporting accuracy, reflecting the lab’s adherence to internationally recognized measurement standards. These improvements are crucial for power generation, where precise flow meter calibration affects boiler efficiency, turbine control, and fuel utilization. While efficiency received slightly lower ratings (4.38), customers acknowledged that improved quality management systems and reduced rework have positively impacted service turnaround times. The high internal consistency of responses (Cronbach’s alpha = 0.91) validates the reliability of the results.
The combination of descriptive, correlational, and regression analyses provides robust evidence that ISO/IEC 17025 accreditation has strengthened the technical credibility, customer trust, and operational performance of the Eskom Flow Laboratory. These findings affirm the laboratory’s alignment with Eskom’s strategic objectives of maintaining excellence, reliability, and quality assurance in power generation calibration services.
5. Conclusions
The study’s finding highlights that ISO/IEC 17025 accreditation has significantly improved the Eskom Flow Laboratory’s performance, technical competence, and customer satisfaction. Accreditation strengthened measurement traceability, calibration reliability, and staff expertise, leading to high customer ratings for calibration accuracy, competence, and overall satisfaction. Statistical results showed that these factors strongly predict customer satisfaction, confirming the effectiveness of accreditation in ensuring consistent, high-quality results. Operationally, the accreditation introduced a robust Quality Management System that enhanced documentation, auditing, and continuous improvement, reducing uncertainty and improving traceability to national and international standards. The laboratory’s ability to calibrate large flow meters positions it as a vital national asset supporting industrial accuracy and competitiveness.
The study recommends ongoing staff training, investment in advanced calibration technologies, digital quality management tools, and stronger customer feedback systems. It also advises participation in international comparison programs, expansion of accreditation scope, and adoption of performance dashboards for continuous improvement. Overall, the findings highlight that ISO/IEC 17025 accreditation has been both a technical and strategic enabler, boosting operational excellence, customer trust, and Eskom’s reputation for quality and reliability in the power generation sector.
6. Patents
While no patents have been filed at the time of this publication, the authors reserve all rights to pursue intellectual property protection for any inventions, designs, methodologies, or technological innovations that may arise from the results of this research
Author Contributions
This work was carried out in conjunction with all authors. The role of each author is listed below: Themba Mashiyane: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, data analysis, Writing − review & editing and supervision. Sphiwe Mashaba: data analysis, Writing − original draft preparation. Thokozani Mahlangu: Data analysis, Writing − review & editing. Johan Stoltz: Data analysis, Writing − review & editing
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable
Data Availability Statement
data relating to ISO/IEC 17025 can be found in International Organization for Standardization. (2017). ISO/IEC 17025:2017 – General requirements for the competence of testing and calibration laboratories and South African National Accreditation System. (2022). SANAS accreditation of calibration laboratories.
Acknowledgments
The authors appreciate the support of Eskom Power Engineering Program (EPEP), South Africa and Dr. Smith Salifu for his continuous research support and mentorship.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| ISO |
International Organization for Standardization |
| IEC |
International Electrotechnical Commission |
| NB |
Nominal Bore |
| ILAC |
International Laboratory Accreditation Cooperation |
| SANAS |
South African National Accreditation System |
References
- International Laboratory Accreditation Cooperation. (2021). ILAC Mutual Recognition Arrangement (MRA): Enhancing international acceptance of accredited results.
- International Organization for Standardization. (2017). ISO/IEC 17025:2017 – General requirements for the competence of testing and calibration laboratories.
- Kumar, R., & Singh, P. (2022). Implementation of ISO/IEC 17025 in calibration laboratories: Enhancing measurement accuracy and quality. Journal of Metrology and Standards, 12(3), 45–56.
- Sharma, A., Verma, S., & Joshi, R. (2021). Impact of ISO/IEC 17025 accreditation on laboratory performance: A case study approach. International Journal of Quality Assurance, 9(2), 78–90.
- South African National Accreditation System. (2022). SANAS accreditation of calibration laboratories.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).