Submitted:
19 October 2025
Posted:
21 October 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. General Considerations for Native Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Protein Species
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Instrument Conditions for Data Acquisition
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Offline Strategies for Isolation, Separation, and Enrichment of Intact Protein Species for nMS Analysis
3.1. Immunoprecipitation (IP)
3.2. Gel Electrophoresis (GE)
3.3. Free-Flow Electrophoresis (FFE)
4. Online Strategies for Isolation, Separation, and Enrichment of Intact Protein Species for nMS Analysis
4.1. Liquid Chromatography (LC)
4.1.1. Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC)
4.1.2. Ion Exchange Chromatography (IEC)
4.1.3. Hydrophobic Interaction Chromatography (HIC)
4.1.4. Affinity Liquid Chromatography (ALC)
4.2. Capillary Electrophoresis (CE)
4.2.1. Capillary Zone Electrophoresis (CZE)
4.2.2. Mobility Capillary Electrophoresis (MoCE)
4.2.3. Affinity Capillary Electrophoresis (ACE)
4.2.4. Capillary Isoelectric Focusing (cIEF)
5. New Frontiers of Native Mass Spectrometry and Proteomics
5.1. Automated Purification, Buffer Exchange, and Individual Ion Mass Spectrometry
5.2. Ion Mobility Spectrometry (IMS)
5.3. Ambient Surface Mass Spectrometry (ASMS)
6. Assessment of nMS Sample Resemblance to the Native Biological State
7. Importance and Challenges of nMS Analysis
8. Conclusion
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ward, J.J.; Sodhi, J.S.; McGuffin, L.J.; Buxton, B.F.; Jones, D.T. Prediction and Functional Analysis of Native Disorder in Proteins from the Three Kingdoms of Life. Journal of Molecular Biology 2004, 337, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tak, I.-u.-R.; Ali, F.; Dar, J.S.; Magray, A.R.; Ganai, B.A.; Chishti, M.Z. Chapter 1 - Posttranslational Modifications of Proteins and Their Role in Biological Processes and Associated Diseases. In Protein Modificomics, Dar, T.A., Singh, L.R., Eds.; Academic Press: 2019; pp. 1-35.
- Ross, C.A.; Poirier, M.A. Protein aggregation and neurodegenerative disease. Nature Medicine 2004, 10, S10–S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Ji, B. Protein conformational transitions coupling with ligand interactions: Simulations from molecules to medicine. Medicine in Novel Technology and Devices 2019, 3, 100026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramazi, S.; Dadzadi, M.; Darvazi, M.; Seddigh, N.; Allahverdi, A. Protein modification in neurodegenerative diseases. MedComm 2024, 5, e674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, D.; Lee, D.; Li, L.; Zhao, Q.; Yu, H. Implications of disease-related mutations at protein-protein interfaces. Current opinion in structural biology 2022, 72, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagassé, H.A.; Alexaki, A.; Simhadri, V.L.; Katagiri, N.H.; Jankowski, W.; Sauna, Z.E.; Kimchi-Sarfaty, C. Recent advances in (therapeutic protein) drug development. F1000Research 2017, 6, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, N. Modifications of therapeutic proteins: challenges and prospects. Cytotechnology 2007, 53, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, C.; Robinson, C.V. Dynamic protein ligand interactions--insights from MS. The FEBS journal 2014, 281, 1950–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, N.F.C.; Lingeman, H.; Irth, H. Sample preparation for peptides and proteins in biological matrices prior to liquid chromatography and capillary zone electrophoresis. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry 2005, 382, 535–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipe, V.; Hawe, A.; Carpenter, J.F.; Jiskoot, W. Analytical approaches to assess the degradation of therapeutic proteins. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry 2013, 49, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaulich, P.T.; Jeong, K.; Kohlbacher, O.; Tholey, A. Influence of different sample preparation approaches on proteoform identification by top-down proteomics. Nature Methods 2024, 21, 2397–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorber, B.; Fischer, F.; Bailly, M.; Roy, H.; Kern, D. Protein analysis by dynamic light scattering: Methods and techniques for students. 2012, 40, 372-382. [CrossRef]
- Greenfield, N.J. Using circular dichroism spectra to estimate protein secondary structure. Nature Protocols 2006, 1, 2876–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, M.M.; Raman, C.S.; Nall, B.T. Isothermal Titration Calorimetry of Protein–Protein Interactions. Methods 1999, 19, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, A.C.; Poudel, N.; Mattsson, J. Protein Structure Analysis and Validation with X-Ray Crystallography. Methods in molecular biology (Clifton, N.J.) 2021, 2178, 377–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Cheng, K.; He, L.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, B.; Jiang, L.; Li, C.; Wang, G.; Yang, Y.; Liu, M. NMR-Based Methods for Protein Analysis. Analytical chemistry 2021, 93, 1866–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parois, P.; Cooper, R.I.; Thompson, A.L. Crystal structures of increasingly large molecules: meeting the challenges with CRYSTALS software. Chemistry Central journal 2015, 9, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Eliezer, D. Sharpening the lens of NMR spectroscopy to study large proteins. Nature Chemistry 2025, 17, 786–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artigues, A.; Nadeau, O.W.; Rimmer, M.A.; Villar, M.T.; Du, X.; Fenton, A.W.; Carlson, G.M. Protein Structural Analysis via Mass Spectrometry-Based Proteomics. In Modern Proteomics – Sample Preparation, Analysis and Practical Applications; Mirzaei, H., Carrasco, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2016; pp. 397–431. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, A.N.; Hsu, K.-L. Emerging opportunities for intact and native protein analysis using chemical proteomics. Analytica Chimica Acta 2025, 1338, 343551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yin, S.; Loo, J.A. Top-Down ESI-ECD-FT-ICR Mass Spectrometry Localizes Noncovalent Protein-Ligand Binding Sites. Journal of the American Chemical Society 2006, 128, 14432–14433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, S.; Loo, J.A. Top-down mass spectrometry of supercharged native protein–ligand complexes. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry 2011, 300, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Cui, W.; Wen, J.; Blankenship, R.E.; Gross, M.L. Native electrospray and electron-capture dissociation in FTICR mass spectrometry provide top-down sequencing of a protein component in an intact protein assembly. Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry 2010, 21, 1966–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Cui, W.; Wen, J.; Blankenship, R.E.; Gross, M.L. Native Electrospray and Electron-Capture Dissociation FTICR Mass Spectrometry for Top-Down Studies of Protein Assemblies. Analytical chemistry 2011, 83, 5598–5606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, R.J.; Damoc, E.; Denisov, E.; Makarov, A.; Heck, A.J.R. High-sensitivity Orbitrap mass analysis of intact macromolecular assemblies. Nature Methods 2012, 9, 1084–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalski, W.P.; Shiell, B.J. Strategies for analysis of electrophoretically separated proteins and peptides. Analytica Chimica Acta 1999, 383, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, H.; Robinson, C.V. Determining the stoichiometry and interactions of macromolecular assemblies from mass spectrometry. Nature Protocols 2007, 2, 715–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobott, F.; Hernández, H.; McCammon, M.G.; Tito, M.A.; Robinson, C.V. A tandem mass spectrometer for improved transmission and analysis of large macromolecular assemblies. Analytical chemistry 2002, 74, 1402–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Sun, L. Mass spectrometry-intensive top-down proteomics: an update on technology advancements and biomedical applications. Analytical Methods 2024, 16, 4664–4682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, C.V. Protein complexes take flight. Nature Structural Biology 2002, 9, 505–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pukala, T.L.; Ruotolo, B.T.; Zhou, M.; Politis, A.; Stefanescu, R.; Leary, J.A.; Robinson, C.V. Subunit architecture of multiprotein assemblies determined using restraints from gas-phase measurements. Structure 2009, 17, 1235–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Lantz, C.; Brown, K.A.; Ge, Y.; Paša-Tolić, L.; Loo, J.A.; Lermyte, F. Higher-order structural characterisation of native proteins and complexes by top-down mass spectrometry. Chemical Science 2020, 11, 12918–12936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackwell, A.E.; Dodds, E.D.; Bandarian, V.; Wysocki, V.H. Revealing the Quaternary Structure of a Heterogeneous Noncovalent Protein Complex through Surface-Induced Dissociation. Analytical chemistry 2011, 83, 2862–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romano, C.A.; Zhou, M.; Song, Y.; Wysocki, V.H.; Dohnalkova, A.C.; Kovarik, L.; Paša-Tolić, L.; Tebo, B.M. Biogenic manganese oxide nanoparticle formation by a multimeric multicopper oxidase Mnx. Nature Communications 2017, 8, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayon, N.J. Features, roles and chiral analyses of proteinogenic amino acids. Aims Molecular Science 2020, 7, 229–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vemula, H.; Ayon, N.J.; Gutheil, W.G. Cytoplasmic peptidoglycan intermediate levels in Staphylococcus aureus. Biochimie 2016, 121, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vemula, H.; Ayon, N.J.; Burton, A.; Gutheil, W.G. Antibiotic Effects on Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Cytoplasmic Peptidoglycan Intermediate Levels and Evidence for Potential Metabolite Level Regulatory Loops. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 2017, 61, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayon, N.J.; Sharma, A.D.; Gutheil, W.G. LC-MS/MS-Based Separation and Quantification of Marfey's Reagent Derivatized Proteinogenic Amino Acid dl-Stereoisomers. Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry 2019, 30, 448–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, A.; Aquino, R.M.; Vidal, H.A.; Wong, C.V.; Luo, R.Y. A liquid chromatography-high-resolution mass spectrometry method for separation and identification of hemoglobin variant subunits with mass shifts less than 1 Da. Journal of mass spectrometry and advances in the clinical lab 2025, 35, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Kennani, S.; Crespo, M.; Govin, J.; Pflieger, D. Proteomic Analysis of Histone Variants and Their PTMs: Strategies and Pitfalls. Proteomes 2018, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bults, P.; Spanov, B.; Olaleye, O.; van de Merbel, N.C.; Bischoff, R. Intact protein bioanalysis by liquid chromatography – High-resolution mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography B 2019, 1110-1111, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajba, L.; Jeong, S.; Chung, D.S.; Guttman, A. Capillary Gel Electrophoresis of Proteins: Historical overview and recent advances. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry 2023, 162, 117024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, M.; Schmidt, C. Native mass spectrometry—A valuable tool in structural biology. 2020, 55, e4578. [CrossRef]
- Masson, G.R.; Burke, J.E.; Ahn, N.G.; Anand, G.S.; Borchers, C.; Brier, S.; Bou-Assaf, G.M.; Engen, J.R.; Englander, S.W.; Faber, J.; et al. Recommendations for performing, interpreting and reporting hydrogen deuterium exchange mass spectrometry (HDX-MS) experiments. Nature Methods 2019, 16, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitner, A.; Walzthoeni, T.; Kahraman, A.; Herzog, F.; Rinner, O.; Beck, M.; Aebersold, R. Probing native protein structures by chemical cross-linking, mass spectrometry, and bioinformatics. Molecular & cellular proteomics : MCP 2010, 9, 1634–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozohanics, O.; Ambrus, A. Hydrogen-Deuterium Exchange Mass Spectrometry: A Novel Structural Biology Approach to Structure, Dynamics and Interactions of Proteins and Their Complexes. Life (Basel, Switzerland) 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitner, A.; Faini, M.; Stengel, F.; Aebersold, R. Crosslinking and Mass Spectrometry: An Integrated Technology to Understand the Structure and Function of Molecular Machines. Trends in Biochemical Sciences 2016, 41, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Li, Z.; Yu, B.; Wang, S.; Shen, Y.; Cong, H. Recent advances on protein separation and purification methods. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science 2020, 284, 102254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, S.L.; Thacker, J.B.; Schug, K.A.; Maráková, K. Sample preparation and fractionation techniques for intact proteins for mass spectrometric analysis. 2021, 44, 211-246. [CrossRef]
- Masse, F.; Parat, M.; Matte, A.; Thauvette, L.; Hélie, G.; Durocher, Y.; Vercauteren, F. Parallelized protein purification: Opportunities and challenges in earlystage biotherapeutics research & development. American Pharmaceutical Review 2017, 20. [Google Scholar]
- Matte, A. Chapter 9 - High-throughput, parallelized and automated protein purification for therapeutic antibody development. In Approaches to the Purification, Analysis and Characterization of Antibody-Based Therapeutics, Matte, A., Ed.; Elsevier: 2020; pp. 181-198.
- Donnelly, D.P.; Rawlins, C.M.; DeHart, C.J.; Fornelli, L.; Schachner, L.F.; Lin, Z.; Lippens, J.L.; Aluri, K.C.; Sarin, R.; Chen, B.; et al. Best practices and benchmarks for intact protein analysis for top-down mass spectrometry. Nature Methods 2019, 16, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heck, A.J.R. Native mass spectrometry: a bridge between interactomics and structural biology. Nature Methods 2008, 5, 927–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafader, J.O.; Melani, R.D.; Schachner, L.F.; Ives, A.N.; Patrie, S.M.; Kelleher, N.L.; Compton, P.D. Native vs Denatured: An in Depth Investigation of Charge State and Isotope Distributions. Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry 2020, 31, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyung, S.-J.; Ruotolo, B.T. Integrating mass spectrometry of intact protein complexes into structural proteomics. PROTEOMICS 2012, 12, 1547–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campuzano, I.D.G.; Loo, J.A. Evolution of Mass Spectrometers for High m/z Biological Ion Formation, Transmission, Analysis and Detection: A Personal Perspective. Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry 2025, 36, 632–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirshenbaum, N.; Michaelevski, I.; Sharon, M. Analyzing large protein complexes by structural mass spectrometry. Journal of visualized experiments : JoVE 2010. [CrossRef]
- Tamara, S.; den Boer, M.A.; Heck, A.J.R. High-Resolution Native Mass Spectrometry. Chemical Reviews 2022, 122, 7269–7326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susa, A.C.; Xia, Z.; Williams, E.R. Native Mass Spectrometry from Common Buffers with Salts That Mimic the Extracellular Environment. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2017, 56, 7912–7915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konermann, L.; Liu, Z.; Haidar, Y.; Willans, M.J.; Bainbridge, N.A. On the Chemistry of Aqueous Ammonium Acetate Droplets during Native Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry. Analytical chemistry 2023, 95, 13957–13966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventouri, I.K.; Malheiro, D.B.A.; Voeten, R.L.C.; Kok, S.; Honing, M.; Somsen, G.W.; Haselberg, R. Probing Protein Denaturation during Size-Exclusion Chromatography Using Native Mass Spectrometry. Analytical chemistry 2020, 92, 4292–4300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konermann, L. Addressing a Common Misconception: Ammonium Acetate as Neutral pH “Buffer” for Native Electrospray Mass Spectrometry. Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry 2017, 28, 1827–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacholarz, K.J.; Barran, P.E. Use of a charge reducing agent to enable intact mass analysis of cysteine-linked antibody-drug-conjugates by native mass spectrometry. EuPA Open Proteomics 2016, 11, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, X.; Gavriilidou, A.F.M.; Zenobi, R. Influence of Alkylammonium Acetate Buffers on Protein–Ligand Noncovalent Interactions Using Native Mass Spectrometry. Journal of The American Society for Mass Spectrometry 2017, 28, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.H.; Wagner, N.D.; Yan, J.; Li, J.; Huang, R.Y.C.; Balog, A.J.; Newitt, J.A.; Chen, G.; Gross, M.L. Native mass spectrometry and gas-phase fragmentation provide rapid and in-depth topological characterization of a PROTAC ternary complex. Cell Chemical Biology 2021, 28, 1528–1538.e1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchand, A.; Gabelica, V. Native Electrospray Mass Spectrometry of DNA G-Quadruplexes in Potassium Solution. Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry 2014, 25, 1146–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemaire, D.; Marie, G.; Serani, L.; Laprévote, O. Stabilization of Gas-Phase Noncovalent Macromolecular Complexes in Electrospray Mass Spectrometry Using Aqueous Triethylammonium Bicarbonate Buffer. Analytical chemistry 2001, 73, 1699–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadavi, D.; Ng, C.Y.; Zhao, Y.; Mathew, A.; Anthony, Ian G.M.; Cillero-Pastor, B.; Cuypers, E.; Siegel, Tiffany P.; Honing, M. Buffer 4-Ethylmorpholinium/Acetate: Exploring a New Alternative Buffer for Native Mass Spectrometry. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry 2025, 39, e10048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, K.A.; Melby, J.A.; Roberts, D.S.; Ge, Y. Top-down proteomics: challenges, innovations, and applications in basic and clinical research. Expert review of proteomics 2020, 17, 719–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vimer, S.; Ben-Nissan, G.; Sharon, M. Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Intact Proteins from Crude Samples. Analytical chemistry 2020, 92, 12741–12749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benesch, J.L.P.; Ruotolo, B.T.; Simmons, D.A.; Robinson, C.V. Protein Complexes in the Gas Phase: Technology for Structural Genomics and Proteomics. Chemical Reviews 2007, 107, 3544–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breuker, K.; McLafferty, F.W. Stepwise evolution of protein native structure with electrospray into the gas phase, 10-12 to 102. 2008, 105, 18145-18152. [CrossRef]
- Stiving, A.Q.; VanAernum, Z.L.; Busch, F.; Harvey, S.R.; Sarni, S.H.; Wysocki, V.H. Surface-Induced Dissociation: An Effective Method for Characterization of Protein Quaternary Structure. Analytical chemistry 2019, 91, 190–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laganowsky, A.; Reading, E.; Hopper, J.T.S.; Robinson, C.V. Mass spectrometry of intact membrane protein complexes. Nature Protocols 2013, 8, 639–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquilina, J.A.; Benesch, J.L.P.; Bateman, O.A.; Slingsby, C.; Robinson, C.V. Polydispersity of a mammalian chaperone: Mass spectrometry reveals the population of oligomers in αB-crystallin. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2003, 100, 10611–10616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostom, A.A.; Sunde, M.; Richardson, S.J.; Schreiber, G.; Jarvis, S.; Bateman, R.; Dobson, C.M.; Robinson, C.V. Dissection of multi-protein complexes using mass spectrometry: Subunit interactions in transthyretin and retinol-binding protein complexes. Proteins: Structure, Function, and Bioinformatics 1998, 33, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, B.L.; Bruce, J.E.; Anderson, G.A.; Hofstadler, S.A.; Rockwood, A.L.; Smith, R.D.; Chilkoti, A.; Stayton, P.S. Dissociation of tetrameric ions of noncovalent streptavidin complexes formed by electrospray ionization. Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry 1995, 6, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fändrich, M.; Tito, M.A.; Leroux, M.R.; Rostom, A.A.; Hartl, F.U.; Dobson, C.M.; Robinson, C.V. Observation of the noncovalent assembly and disassembly pathways of the chaperone complex MtGimC by mass spectrometry. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2000, 97, 14151–14155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilag, L.L.; Videler, H.; McKay, A.R.; Sobott, F.; Fucini, P.; Nierhaus, K.H.; Robinson, C.V. Heptameric (L12)6/L10 rather than canonical pentameric complexes are found by tandem MS of intact ribosomes from thermophilic bacteria. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2005, 102, 8192–8197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lantz, C.; Wei, B.; Zhao, B.; Jung, W.; Goring, A.K.; Le, J.; Miller, J.; Loo, R.R.O.; Loo, J.A. Native Top-Down Mass Spectrometry with Collisionally Activated Dissociation Yields Higher-Order Structure Information for Protein Complexes. J Am Chem Soc 2022, 144, 21826–21830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busch, F.; VanAernum, Z.L.; Ju, Y.; Yan, J.; Gilbert, J.D.; Quintyn, R.S.; Bern, M.; Wysocki, V.H. Localization of Protein Complex Bound Ligands by Surface-Induced Dissociation High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Analytical chemistry 2018, 90, 12796–12801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintyn, R.S.; Zhou, M.; Yan, J.; Wysocki, V.H. Surface-Induced Dissociation Mass Spectra as a Tool for Distinguishing Different Structural Forms of Gas-Phase Multimeric Protein Complexes. Analytical chemistry 2015, 87, 11879–11886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubarev, R.A.; Kelleher, N.L.; McLafferty, F.W. Electron Capture Dissociation of Multiply Charged Protein Cations. A Nonergodic Process. Journal of the American Chemical Society 1998, 120, 3265–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syka, J.E.P.; Coon, J.J.; Schroeder, M.J.; Shabanowitz, J.; Hunt, D.F. Peptide and protein sequence analysis by electron transfer dissociation mass spectrometry. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2004, 101, 9528–9533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Searfoss, R.M.; Zahn, E.; Lin, Z.; Garcia, B.A. Establishing a Top-Down Proteomics Platform on a Time-of-Flight Instrument with Electron-Activated Dissociation. J Proteome Res 2025, 24, 1230–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, J.B.; Li, W.; Holden, D.D.; Zhang, Y.; Griep-Raming, J.; Fellers, R.T.; Early, B.P.; Thomas, P.M.; Kelleher, N.L.; Brodbelt, J.S. Complete Protein Characterization Using Top-Down Mass Spectrometry and Ultraviolet Photodissociation. Journal of the American Chemical Society 2013, 135, 12646–12651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, A.M.; Lössl, P.; Liu, F.; Huguet, R.; Mullen, C.; Yamashita, M.; Zabrouskov, V.; Makarov, A.; Altelaar, A.F.M.; Heck, A.J.R. Benchmarking Multiple Fragmentation Methods on an Orbitrap Fusion for Top-down Phospho-Proteoform Characterization. Analytical chemistry 2015, 87, 4152–4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, J.P.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Brodbelt, J.S. Characterization of Native Protein Complexes Using Ultraviolet Photodissociation Mass Spectrometry. Journal of the American Chemical Society 2014, 136, 12920–12928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, G.E.; McLuckey, S.A. ‘Top down’ protein characterization via tandem mass spectrometry. Journal of Mass Spectrometry 2002, 37, 663–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Volmer, D.A. Electron-based fragmentation methods in mass spectrometry: An overview. Mass spectrometry reviews 2017, 36, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornelli, L.; Srzentić, K.; Toby, T.K.; Doubleday, P.F.; Huguet, R.; Mullen, C.; Melani, R.D.; dos Santos Seckler, H.; DeHart, C.J.; Weisbrod, C.R.; et al. Thorough Performance Evaluation of 213 nm Ultraviolet Photodissociation for Top-down Proteomics*. Molecular & Cellular Proteomics 2020, 19, 405–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzillotti, M.; Brodbelt, J.S. Comparison of Top-Down Protein Fragmentation Induced by 213 and 193 nm UVPD. Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry 2023, 34, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Dagan, S.; Wysocki, V.H. Impact of charge state on gas-phase behaviors of noncovalent protein complexes in collision induced dissociation and surface induced dissociation. Analyst 2013, 138, 1353–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippens, J.L.; Nshanian, M.; Spahr, C.; Egea, P.F.; Loo, J.A.; Campuzano, I.D.G. Fourier Transform-Ion Cyclotron Resonance Mass Spectrometry as a Platform for Characterizing Multimeric Membrane Protein Complexes. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 2018, 29, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Z. Native mass spectrometry analysis of biotherapeutics and aggregates with enhanced sensitivity; 2025.
- Wong, D.L. Sensitive Native Mass Spectrometry of Macromolecules Using Standard Flow LC/MS; 2020.
- Compton, P.D.; Zamdborg, L.; Thomas, P.M.; Kelleher, N.L. On the Scalability and Requirements of Whole Protein Mass Spectrometry. Analytical chemistry 2011, 83, 6868–6874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, D.S.; Loo, J.A.; Tsybin, Y.O.; Liu, X.; Wu, S.; Chamot-Rooke, J.; Agar, J.N.; Paša-Tolić, L.; Smith, L.M.; Ge, Y. Top-down proteomics. Nature Reviews Methods Primers 2024, 4, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaltashov, I.A.; Bobst, C.E.; Pawlowski, J.; Wang, G. Mass spectrometry-based methods in characterization of the higher order structure of protein therapeutics. J Pharm Biomed Anal 2020, 184, 113169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaltashov, I.A.; Bobst, C.E.; Abzalimov, R.R. Mass spectrometry-based methods to study protein architecture and dynamics. Protein science : a publication of the Protein Society 2013, 22, 530–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durbin, K.R.; Robey, M.T.; Voong, L.N.; Fellers, R.T.; Lutomski, C.A.; El-Baba, T.J.; Robinson, C.V.; Kelleher, N.L. ProSight Native: Defining Protein Complex Composition from Native Top-Down Mass Spectrometry Data. Journal of Proteome Research 2023, 22, 2660–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeDuc, R.D.; Taylor, G.K.; Kim, Y.-B.; Januszyk, T.E.; Bynum, L.H.; Sola, J.V.; Garavelli, J.S.; Kelleher, N.L. ProSight PTM: an integrated environment for protein identification and characterization by top-down mass spectrometry. Nucleic Acids Research 2004, 32, W340–W345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellers, R.T.; Greer, J.B.; Early, B.P.; Yu, X.; LeDuc, R.D.; Kelleher, N.L.; Thomas, P.M. ProSight Lite: Graphical software to analyze top-down mass spectrometry data. PROTEOMICS 2015, 15, 1235–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankar, V.; Tibshirani, R.; Zare, R.N. MassExplorer: a computational tool for analyzing desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry data. Bioinformatics 2021, 37, 3688–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Piehowski, P.D.; Wilkins, C.; Zhou, M.; Mendoza, J.; Fujimoto, G.M.; Gibbons, B.C.; Shaw, J.B.; Shen, Y.; Shukla, A.K.; et al. Informed-Proteomics: open-source software package for top-down proteomics. Nature Methods 2017, 14, 909–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, Q.; Xun, L.; Liu, X. TopPIC: a software tool for top-down mass spectrometry-based proteoform identification and characterization. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 3495–3497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Sirotkin, Y.; Shen, Y.; Anderson, G.; Tsai, Y.S.; Ting, Y.S.; Goodlett, D.R.; Smith, R.D.; Bafna, V.; Pevzner, P.A. Protein Identification Using Top-Down Spectra. Molecular & Cellular Proteomics 2012, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urh, M.; Simpson, D.; Zhao, K. Affinity chromatography: general methods. Methods in enzymology 2009, 463, 417–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tchikov, V.; Fritsch, J.; Kabelitz, D.; Schütze, S. 2 - Immunomagnetic Isolation of Subcellular Compartments. In Methods in Microbiology, Kabelitz, D., Kaufmann, S.H.E., Eds.; Academic Press: 2010; Volume 37, pp. 21-33.
- Husain, A.; Begum, N.A.; Kobayashi, M.; Honjo, T. Native Co-immunoprecipitation Assay to Identify Interacting Partners of Chromatin-associated Proteins in Mammalian Cells. Bio-protocol 2020, 10, e3837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosseau, C.; Grunau, C. Native Chromatin Immunoprecipitation. In Epigenetics Protocols; Tollefsbol, T.O., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, 2011; pp. 195–212. [Google Scholar]
- Thorne, A.W.; Myers, F.A.; Hebbes, T.R. Native Chromatin Immunoprecipitation. In Epigenetics Protocols, Tollefsbol, T.O., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, 2004; pp. 21–44. [Google Scholar]
- Solier, C.; Langen, H. Antibody-based proteomics and biomarker research—Current status and limitations. 2014, 14, 774-783. [CrossRef]
- Guo, A.; Gu, H.; Zhou, J.; Mulhern, D.; Wang, Y.; Lee, K.A.; Yang, V.; Aguiar, M.; Kornhauser, J.; Jia, X.; et al. Immunoaffinity enrichment and mass spectrometry analysis of protein methylation. Molecular & cellular proteomics : MCP 2014, 13, 372–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebollela, A.; Campos, R.; Carraro, M.; Pinheiro, N.; Bitencour, A.; Spagnol, V.; Cline, E.; Ayon, N.; Mcgee, J.; Viola, K. Antibody assisted biochemical isolation and conformational analysis of native Alzheimer's relevant Abeta oligomers. In Proceedings of the Journal of Neurochemistry, 2023; pp. 104-104.
- Chang, I.-F. Mass spectrometry-based proteomic analysis of the epitope-tag affinity purified protein complexes in eukaryotes. 2006, 6, 6158-6166. [CrossRef]
- Tomomori-Sato, C.; Sato, S.; Conaway, R.C.; Conaway, J.W. Immunoaffinity Purification of Protein Complexes from Mammalian Cells. In Gene Regulation: Methods and Protocols; Bina, M., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, 2013; pp. 273–287. [Google Scholar]
- Huttlin, E.L.; Ting, L.; Bruckner, R.J.; Gebreab, F.; Gygi, M.P.; Szpyt, J.; Tam, S.; Zarraga, G.; Colby, G.; Baltier, K.; et al. The BioPlex Network: A Systematic Exploration of the Human Interactome. Cell 2015, 162, 425–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huttlin, E.L.; Bruckner, R.J.; Paulo, J.A.; Cannon, J.R.; Ting, L.; Baltier, K.; Colby, G.; Gebreab, F.; Gygi, M.P.; Parzen, H.; et al. Architecture of the human interactome defines protein communities and disease networks. Nature 2017, 545, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olinares, P.D.B.; Dunn, A.D.; Padovan, J.C.; Fernandez-Martinez, J.; Rout, M.P.; Chait, B.T. A Robust Workflow for Native Mass Spectrometric Analysis of Affinity-Isolated Endogenous Protein Assemblies. Analytical chemistry 2016, 88, 2799–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, O.S.; Deindl, S.; Comolli, L.R.; Hoelz, A.; Downing, K.H.; Nairn, A.C.; Kuriyan, J. Oligomerization states of the association domain and the holoenyzme of Ca2+/CaM kinase II. 2006, 273, 682-694. [CrossRef]
- Antrobus, R.; Borner, G.H.H. Improved Elution Conditions for Native Co-Immunoprecipitation. PLOS ONE 2011, 6, e18218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Abad, L.; Chatterjee, L.; Cristea, I.M.; Varjosalo, M. Mapping protein–protein interactions by mass spectrometry. Mass spectrometry reviews 2024, n/a. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, X.; Tian, M.; Yin, J.; Duan, H.; Tian, Y.; Wang, H.; Xia, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Biofunctionalized dissolvable hydrogel microbeads enable efficient characterization of native protein complexes. Nature Communications 2024, 15, 8633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smisek, D.L.; Hoagland, D.A. Agarose gel electrophoresis of high molecular weight, synthetic polyelectrolytes. Macromolecules 1989, 22, 2270–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schägger, H. Tricine–SDS-PAGE. Nature Protocols 2006, 1, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoji, M.; Kato, M.; Hashizume, S. Electrophoretic recovery of proteins from polyacrylamide gel. Journal of Chromatography A 1995, 698, 145–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurien, B.T.; Scofield, R.H. Extraction of Proteins from Gels: A Brief Review. In Protein Electrophoresis: Methods and Protocols; Kurien, B.T., Scofield, R.H., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, 2012; pp. 403–405. [Google Scholar]
- Ruggiero-Lopez, D.; Louisot, P.; Martin, A. A nondenaturing preparative gel electrophoresis system for the recovery of functional proteins. Application to the identification of an endogenous protein inhibitor of fucosyl-transferase activities. Anal Biochem 1993, 212, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seelert, H.; Krause, F. Preparative isolation of protein complexes and other bioparticles by elution from polyacrylamide gels. 2008, 29, 2617-2636. [CrossRef]
- Vallejos, R.H.; Ceccarelli, E.; Chan, R. Evidence for the existence of a thylakoid intrinsic protein that binds ferredoxin-NADP+ oxidoreductase. Journal of Biological Chemistry 1984, 259, 8048–8051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivoal, J.; Smith, C.R.; Moraes, T.F.; Turpin, D.H.; Plaxton, W.C. A Method for Activity Staining after Native Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis Using a Coupled Enzyme Assay and Fluorescence Detection: Application to the Analysis of Several Glycolytic Enzymes. Analytical Biochemistry 2002, 300, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowakowski, A.B.; Wobig, W.J.; Petering, D.H. Native SDS-PAGE: high resolution electrophoretic separation of proteins with retention of native properties including bound metal ions. Metallomics 2014, 6, 1068–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittig, I.; Braun, H.-P.; Schägger, H. Blue native PAGE. Nature Protocols 2006, 1, 418–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittig, I.; Schägger, H. Features and applications of blue-native and clear-native electrophoresis. 2008, 8, 3974-3990. [CrossRef]
- SchÄGger, H. 5 - Blue Native Electrophoresis. In Membrane Protein Purification and Crystallization (Second Edition); Hunte, C., Von Jagow, G., SchÄGger, H., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, 2003; pp. 105–130. [Google Scholar]
- Pupo, E.; López, C.M.; Alonso, M.; Hardy, E. High-efficiency passive elution of bacterial lipopolysaccharides from polyacrylamide gels. Electrophoresis 2000, 21, 526–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittig, I.; Karas, M.; Schägger, H. High Resolution Clear Native Electrophoresis for In-gel Functional Assays and Fluorescence Studies of Membrane Protein Complexes *. Molecular & Cellular Proteomics 2007, 6, 1215–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittig, I.; Schägger, H. Advantages and limitations of clear-native PAGE. Proteomics 2005, 5, 4338–4346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkozy, D.; Guttman, A. Analysis of Peptides and Proteins by Native and SDS Capillary Gel Electrophoresis Coupled to Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry via a Closed-Circuit Coaxial Sheath Flow Reactor Interface. Analytical chemistry 2023, 95, 7082–7086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timón-Gómez, A.; Pérez-Pérez, R.; Nyvltova, E.; Ugalde, C.; Fontanesi, F.; Barrientos, A. Protocol for the Analysis of Yeast and Human Mitochondrial Respiratory Chain Complexes and Supercomplexes by Blue Native Electrophoresis. STAR protocols 2020, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, V.; Orenday-Tapia, L.; Ieva, R. Analysis of Transmembrane β-Barrel Proteins by Native and Semi-native Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis. In Transmembrane β-Barrel Proteins: Methods and Protocols; Ieva, R., Ed.; Springer US: New York, NY, 2024; pp. 133–145. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, E.P.; Partridge, M.A.; Padula, M.P.; Gauci, V.J.; Malladi, C.S.; Coorssen, J.R. Top-down proteomics: Enhancing 2D gel electrophoresis from tissue processing to high-sensitivity protein detection. 2014, 14, 872-889. [CrossRef]
- Drews, O.; Zong, C.; Ping, P. Exploring proteasome complexes by proteomic approaches. 2007, 7, 1047-1058. [CrossRef]
- Pieper, R.; Gatlin, C.L.; Makusky, A.J.; Russo, P.S.; Schatz, C.R.; Miller, S.S.; Su, Q.; McGrath, A.M.; Estock, M.A.; Parmar, P.P.; et al. The human serum proteome: Display of nearly 3700 chromatographically separated protein spots on two-dimensional electrophoresis gels and identification of 325 distinct proteins. 2003, 3, 1345-1364. [CrossRef]
- Munawar, N.; Olivero, G.; Jerman, E.; Doyle, B.; Streubel, G.; Wynne, K.; Bracken, A.; Cagney, G. Native gel analysis of macromolecular protein complexes in cultured mammalian cells. 2015, 15, 3603-3612. [CrossRef]
- Ezsias, B.; Goessweiner-Mohr, N.; Siligan, C.; Horner, A.; Vargas, C.; Keller, S.; Pohl, P. Clear Native Gel Electrophoresis for the Purification of Fluorescently Labeled Membrane Proteins in Native Nanodiscs. 2025, 2025.2003.2021.644524. [CrossRef]
- Bonaventura, C.; Bonaventura, J.; Stevens, R.; Millington, D. Acrylamide in Polyacrylamide Gels Can Modify Proteins during Electrophoresis. Analytical Biochemistry 1994, 222, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besse, S.; Bulteau, A.L.; Boucher, F.; Riou, B.; Swynghedauw, B.; de Leiris, J. Antioxidant treatment prevents cardiac protein oxidation after ischemia-reperfusion and improves myocardial function and coronary perfusion in senescent hearts. Journal of physiology and pharmacology : an official journal of the Polish Physiological Society 2006, 57, 541–552. [Google Scholar]
- Ernst, A.; Stolzing, A.; Sandig, G.; Grune, T. Antioxidants effectively prevent oxidation-induced protein damage in OLN 93 cells. Archives of biochemistry and biophysics 2004, 421, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, E.; Clad, A. Electroelution of fixed and stained membrane proteins from preparative sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels into a membrane trap. Anal Biochem 1986, 154, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Öfverstedt, L.-G.; Sundelin, J.; Johansson, G. Recovery of proteins on a milligram scale from polyacrylamide electrophoresis gels, exemplified by purification of a retinol-binding protein. Analytical Biochemistry 1983, 134, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernabeu, C.; Conde, F.P.; Vazouez, D. Extraction of pure ribosomal protein and removal of Coomassie blue from acrylamide gels. Analytical Biochemistry 1978, 84, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulle, H.; Schoel, B.; Kaufmann, S.H. Direct blotting with viable cells of protein mixtures separated by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Journal of immunological methods 1990, 133, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persidis, A.; Harcombe, A.A. Simultaneous electroelution of proteins from denaturing or native gels into a well matrix. Anal Biochem 1992, 201, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, P.; Heron, I. Simultaneous electroelution of whole SDS-polyacrylamide gels for the direct cellular analysis of complex protein mixtures. Journal of immunological methods 1993, 161, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, J.C.; Doucette, A.A. Gel-Eluted Liquid Fraction Entrapment Electrophoresis: An Electrophoretic Method for Broad Molecular Weight Range Proteome Separation. Analytical chemistry 2008, 80, 1568–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skinner, O.S.; Do Vale, L.H.; Catherman, A.D.; Havugimana, P.C.; de Sousa, M.V.; Compton, P.D.; Kelleher, N.L. Native GELFrEE: a new separation technique for biomolecular assemblies. Analytical chemistry 2015, 87, 3032–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, O.S.; Haverland, N.A.; Fornelli, L.; Melani, R.D.; Do Vale, L.H.F.; Seckler, H.S.; Doubleday, P.F.; Schachner, L.F.; Srzentić, K.; Kelleher, N.L.; et al. Top-down characterization of endogenous protein complexes with native proteomics. Nature Chemical Biology 2018, 14, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durbin, K.R.; Fornelli, L.; Fellers, R.T.; Doubleday, P.F.; Narita, M.; Kelleher, N.L. Quantitation and Identification of Thousands of Human Proteoforms below 30 kDa. Journal of Proteome Research 2016, 15, 976–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catherman, A.D.; Durbin, K.R.; Ahlf, D.R.; Early, B.P.; Fellers, R.T.; Tran, J.C.; Thomas, P.M.; Kelleher, N.L. Large-scale top-down proteomics of the human proteome: membrane proteins, mitochondria, and senescence. Molecular and Cellular Proteomics 2013, 12, 3465–3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Rijkers, D.T.S.; Post, H.; Heck, A.J.R. Proteome-wide profiling of protein assemblies by cross-linking mass spectrometry. Nature Methods 2015, 12, 1179–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bier, M. New Principle of Preparative Electrophoresis. 1957, 125, 1084-1085. [CrossRef]
- Turgeon, R.T.; Bowser, M.T. Micro free-flow electrophoresis: theory and applications. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry 2009, 394, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islinger, M.; Wildgruber, R.; Völkl, A. Preparative free-flow electrophoresis, a versatile technology complementing gradient centrifugation in the isolation of highly purified cell organelles. Electrophoresis 2018, 39, 2288–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raymond, D.E.; Manz, A.; Widmer, H.M. Continuous Separation of High Molecular Weight Compounds Using a Microliter Volume Free-Flow Electrophoresis Microstructure. Analytical chemistry 1996, 68, 2515–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islinger, M.; Eckerskorn, C.; Völkl, A. Free-flow electrophoresis in the proteomic era: A technique in flux. Electrophoresis 2010, 31, 1754–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Kwon, J.-S. Microfluidic free-flow electrophoresis: A promising tool for protein purification and analysis in proteomics. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry 2022, 109, 79–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohlheyer, D.; Eijkel, J.C.T.; van den Berg, A.; Schasfoort, R.B.M. Miniaturizing free-flow electrophoresis – a critical review. Electrophoresis 2008, 29, 977–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohlheyer, D.; Eijkel, J.C.T.; Schlautmann, S.; van den Berg, A.; Schasfoort, R.B.M. Bubble-Free Operation of a Microfluidic Free-Flow Electrophoresis Chip with Integrated Pt Electrodes. Analytical chemistry 2008, 80, 4111–4118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, H.; Kim, Y.; Lim, G. Continuous particle separation using pressure-driven flow-induced miniaturizing free-flow electrophoresis (PDF-induced μ-FFE). Scientific Reports 2016, 6, 19911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayan, K.; Ganar, K.; Deshpande, S.; Boom, R.M.; Nikiforidis, C.V. Continuous counter-current electrophoretic separation of oleosomes and proteins from oilseeds. Food Hydrocolloids 2023, 144, 109053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouvry-Patat, S.A.; Torres, M.P.; Quek, H.-H.; Gelfand, C.A.; O'Mullan, P.; Nissum, M.; Schroeder, G.K.; Han, J.; Elliott, M.; Dryhurst, D.; et al. Free-flow electrophoresis for top-down proteomics by Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry. 2008, 8, 2798-2808. [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Wilker, E.W.; Yaffe, M.B.; Jensen, K.F. Microfluidic Preparative Free-Flow Isoelectric Focusing: System Optimization for Protein Complex Separation. Analytical chemistry 2010, 82, 1253–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, G.; Islinger, M.; Weber, P.; Eckerskorn, C.; Völkl, A. Efficient separation and analysis of peroxisomal membrane proteins using free-flow isoelectric focusing. Electrophoresis 2004, 25, 1735–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouvry-Patat, S.A.; Torres, M.P.; Quek, H.-H.; Gelfand, C.A.; O'Mullan, P.; Nissum, M.; Schroeder, G.K.; Han, J.; Elliott, M.; Dryhurst, D.; et al. Free-flow electrophoresis for top-down proteomics by Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry. Proteomics 2008, 8, 2798–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D'Atri, V.; Murisier, A.; Fekete, S.; Veuthey, J.-L.; Guillarme, D. Current and future trends in reversed-phase liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry of therapeutic proteins. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry 2020, 130, 115962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaltashov, I.A.; Pawlowski, J.W.; Yang, W.; Muneeruddin, K.; Yao, H.; Bobst, C.E.; Lipatnikov, A.N. LC/MS at the whole protein level: Studies of biomolecular structure and interactions using native LC/MS and cross-path reactive chromatography (XP-RC) MS. Methods 2018, 144, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muneeruddin, K.; Thomas, J.J.; Salinas, P.A.; Kaltashov, I.A. Characterization of small protein aggregates and oligomers using size exclusion chromatography with online detection by native electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Analytical chemistry 2014, 86, 10692–10699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, C.L.; Snyder, W.K.; Swietlicka, M.A.; VanSchoiack, A.D.; Austin, C.R.; McFarland, B.J. Size-exclusion chromatography can identify faster-associating protein complexes and evaluate design strategies. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakawa, T.; Ejima, D.; Li, T.; Philo, J.S. The critical role of mobile phase composition in size exclusion chromatography of protein pharmaceuticals. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2010, 99, 1674–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehkirch, A.; Hernandez-Alba, O.; Colas, O.; Beck, A.; Guillarme, D.; Cianférani, S.J.J.o.C.B. Hyphenation of size exclusion chromatography to native ion mobility mass spectrometry for the analytical characterization of therapeutic antibodies and related products. 2018, 1086, 176-183. [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Xing, T.; Wang, S.; Daly, T.J.; Li, N.J.A.C. Coupling mixed-mode size exclusion chromatography with native mass spectrometry for sensitive detection and quantitation of homodimer impurities in bispecific IgG. 2019, 91, 11417-11424. [CrossRef]
- van Schaick, G.; Haselberg, R.; Somsen, G.W.; Wuhrer, M.; Domínguez-Vega, E. Studying protein structure and function by native separation–mass spectrometry. Nature Reviews Chemistry 2022, 6, 215–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyon, A.; Beck, A.; Colas, O.; Sandra, K.; Guillarme, D.; Fekete, S.J.J.o.C.A. Evaluation of size exclusion chromatography columns packed with sub-3 μm particles for the analysis of biopharmaceutical proteins. 2017, 1498, 80-89. [CrossRef]
- Fekete, S.; Ganzler, K.; Guillarme, D.J.J.o.p.; analysis, b. Critical evaluation of fast size exclusion chromatographic separations of protein aggregates, applying sub-2 μm particles. 2013, 78, 141-149. [CrossRef]
- Ventouri, I.K.; Veelders, S.; Passamonti, M.; Endres, P.; Roemling, R.; Schoenmakers, P.J.; Somsen, G.W.; Haselberg, R.; Gargano, A.F.G. Micro-flow size-exclusion chromatography for enhanced native mass spectrometry of proteins and protein complexes. Analytica Chimica Acta 2023, 1266, 341324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Kou, Q.; Guo, R.; Yang, Z.; Chen, D.; Liu, X.; Hong, H.; Sun, L. Native Proteomics in Discovery Mode Using Size-Exclusion Chromatography–Capillary Zone Electrophoresis–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Analytical chemistry 2018, 90, 10095–10099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehkirch, A.; Hernandez-Alba, O.; Colas, O.; Beck, A.; Guillarme, D.; Cianférani, S. Hyphenation of size exclusion chromatography to native ion mobility mass spectrometry for the analytical characterization of therapeutic antibodies and related products. Journal of Chromatography B 2018, 1086, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deslignière, E.; Ehkirch, A.; Botzanowski, T.; Beck, A.; Hernandez-Alba, O.; Cianférani, S. Toward Automation of Collision-Induced Unfolding Experiments through Online Size Exclusion Chromatography Coupled to Native Mass Spectrometry. Analytical chemistry 2020, 92, 12900–12908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Z.; Holmark, T.; van der Zon, A.A.M.; Tseliou, V.; Mutti, F.G.; Astefanei, A.; Gargano, A.F.G. Nanoflow Size Exclusion Chromatography–Native Mass Spectrometry of Intact Proteoforms and Protein Complexes. Analytical chemistry 2025, 97, 12241–12250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekete, S.; Beck, A.; Veuthey, J.-L.; Guillarme, D.J.J.o.p.; analysis, b. Ion-exchange chromatography for the characterization of biopharmaceuticals. 2015, 113, 43-55. [CrossRef]
- Füssl, F.; Cook, K.; Scheffler, K.; Farrell, A.; Mittermayr, S.; Bones, J. Charge Variant Analysis of Monoclonal Antibodies Using Direct Coupled pH Gradient Cation Exchange Chromatography to High-Resolution Native Mass Spectrometry. Analytical chemistry 2018, 90, 4669–4676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Füssl, F.; Trappe, A.; Cook, K.; Scheffler, K.; Fitzgerald, O.; Bones, J. Comprehensive characterisation of the heterogeneity of adalimumab via charge variant analysis hyphenated on-line to native high resolution Orbitrap mass spectrometry. mAbs 2019, 11, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Füssl, F.; Criscuolo, A.; Cook, K.; Scheffler, K.; Bones, J. Cracking Proteoform Complexity of Ovalbumin with Anion-Exchange Chromatography–High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry under Native Conditions. Journal of Proteome Research 2019, 18, 3689–3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Raoufi, F.; Bailly, M.A.; Fayadat-Dilman, L.; Tomazela, D. Hyphenation of strong cation exchange chromatography to native mass spectrometry for high throughput online characterization of charge heterogeneity of therapeutic monoclonal antibodies. mAbs 2020, 12, 1763762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Xing, T.; Wang, S.; Daly, T.J.; Li, N. Coupling Mixed-Mode Size Exclusion Chromatography with Native Mass Spectrometry for Sensitive Detection and Quantitation of Homodimer Impurities in Bispecific IgG. Analytical chemistry 2019, 91, 11417–11424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, M.S.; Rogers, H.T.; Chapman, E.A.; Chan, H.-J.; Krichel, B.; Gao, Z.; Larson, E.J.; Ge, Y. Online Mixed-Bed Ion Exchange Chromatography for Native Top-Down Proteomics of Complex Mixtures. Journal of Proteome Research 2024, 23, 2315–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shire, S.J. 2 - Analytical tools used in the formulation and assessment of stability of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs). In Monoclonal Antibodies, Shire, S.J., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: 2015; pp. 17-44.
- Queiroz, J.A.; Tomaz, C.T.; Cabral, J.M.S. Hydrophobic interaction chromatography of proteins. Journal of Biotechnology 2001, 87, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fekete, S.; Veuthey, J.-L.; Beck, A.; Guillarme, D.J.J.o.p.; analysis, b. Hydrophobic interaction chromatography for the characterization of monoclonal antibodies and related products. 2016, 130, 3-18. [CrossRef]
- Xiu, L.; Valeja, S.G.; Alpert, A.J.; Jin, S.; Ge, Y.J.A.c. Effective protein separation by coupling hydrophobic interaction and reverse phase chromatography for top-down proteomics. 2014, 86, 7899-7906. [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Peng, Y.; Valeja, S.G.; Xiu, L.; Alpert, A.J.; Ge, Y.J.A.c. Online hydrophobic interaction chromatography–mass spectrometry for top-down proteomics. 2016, 88, 1885-1891. [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Lin, Z.; Alpert, A.J.; Fu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Pritts, W.A.; Ge, Y.J.A.c. Online hydrophobic interaction chromatography–mass spectrometry for the analysis of intact monoclonal antibodies. 2018, 90, 7135-7138. [CrossRef]
- Gilroy, J.J.; Eakin, C.M.J.J.o.C.B. Characterization of drug load variants in a thiol linked antibody-drug conjugate using multidimensional chromatography. 2017, 1060, 182-189. [CrossRef]
- Kempen, T.; Cadang, L.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, K.; Chen, T.; Wei, B. Online native hydrophobic interaction chromatography-mass spectrometry of antibody-drug conjugates. mAbs 2025, 17, 2446304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, B.; Han, G.; Tang, J.; Sandoval, W.; Zhang, Y.T. Native Hydrophobic Interaction Chromatography Hyphenated to Mass Spectrometry for Characterization of Monoclonal Antibody Minor Variants. Analytical chemistry 2019, 91, 15360–15364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, E.L.; Poddar, S.; Iftekhar, S.; Suh, K.; Woolfork, A.G.; Ovbude, S.; Pekarek, A.; Walters, M.; Lott, S.; Hage, D.S. Affinity chromatography: A review of trends and developments over the past 50 years. Journal of Chromatography B 2020, 1157, 122332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliver, C.; Jamur, M.C. Immunocytochemical methods and protocols. Methods in Molecular Biology 2010, 588, iv–v. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, C.A.S.; Kong, S.E.; Washburn, M.P. Affinity purification of protein complexes for analysis by multidimensional protein identification technology. Protein Expression and Purification 2012, 86, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaCava, J.; Molloy, K.R.; Taylor, M.S.; Domanski, M.; Chait, B.T.; Rout, M.P. Affinity Proteomics to Study Endogenous Protein Complexes: Pointers, Pitfalls, Preferences and Perspectives. BioTechniques 2015, 58, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlothauer, T.; Rueger, P.; Stracke, J.O.; Hertenberger, H.; Fingas, F.; Kling, L.; Emrich, T.; Drabner, G.; Seeber, S.; Auer, J. Analytical FcRn affinity chromatography for functional characterization of monoclonal antibodies. In Proceedings of the MAbs, 2013; pp. 576-586.
- Lippold, S.; Nicolardi, S.; Domínguez-Vega, E.; Heidenreich, A.-K.; Vidarsson, G.; Reusch, D.; Haberger, M.; Wuhrer, M.; Falck, D. Glycoform-resolved FcɣRIIIa affinity chromatography–mass spectrometry. In Proceedings of the MAbs, 2019; pp. 1191-1196.
- Prinston, J.E.; Peng, W.; Provoncha, K.; Moon, Y.; Koufos, E.; Sandu, C.; Fu, Y.; Yan, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, N.; et al. A target affinity enrichment workflow to characterize critical post-translational modifications within therapeutic antibodies. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2025, 114, 103710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotham, V.C.; Liu, A.P.; Wang, S.; Li, N. A generic platform to couple affinity chromatography with native mass spectrometry for the analysis of therapeutic monoclonal antibodies. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis 2023, 228, 115337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwenzer, A.-K.; Kruse, L.; Jooß, K.; Neusüß, C. Capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry for protein analyses under native conditions: Current progress and perspectives. Proteomics 2024, 24, 2300135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Yang, Z.; McCool, E.N.; Lubeckyj, R.A.; Chen, D.; Sun, L. Capillary zone electrophoresis-mass spectrometry for top-down proteomics. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry 2019, 120, 115644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haselberg, R.; de Jong, G.J.; Somsen, G.W.J.J.o.C.a. Capillary electrophoresis–mass spectrometry for the analysis of intact proteins. 2007, 1159, 81-109. [CrossRef]
- Haselberg, R.; Ratnayake, C.K.; de Jong, G.J.; Somsen, G.W.J.J.o.C.A. Performance of a sheathless porous tip sprayer for capillary electrophoresis–electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry of intact proteins. 2010, 1217, 7605-7611. [CrossRef]
- Hajba, L.; Guttman, A.J.T.T.i.A.C. Recent advances in column coatings for capillary electrophoresis of proteins. 2017, 90, 38-44. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xiang, Y.; Xu, W. Probing protein higher-order structures by native capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry 2022, 157, 116739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Liang, Z.; Xu, T.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Chen, D.; Pham, L.; Du, W.; Sun, L. Investigating native capillary zone electrophoresis-mass spectrometry on a high-end quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometer for the characterization of monoclonal antibodies. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry 2021, 462, 116541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belov, A.M.; Viner, R.; Santos, M.R.; Horn, D.M.; Bern, M.; Karger, B.L.; Ivanov, A.R. Analysis of Proteins, Protein Complexes, and Organellar Proteomes Using Sheathless Capillary Zone Electrophoresis - Native Mass Spectrometry. Journal of The American Society for Mass Spectrometry 2017, 28, 2614–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jooß, K.; McGee, J.P.; Melani, R.D.; Kelleher, N.L. Standard procedures for native CZE-MS of proteins and protein complexes up to 800 kDa. Electrophoresis 2021, 42, 1050–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Qi, Z.; Moeller, W.; Wysocki, V.H.; Sun, L. Native Proteomics by Capillary Zone Electrophoresis-Mass Spectrometry. 2024, 63, e202408370. [CrossRef]
- Jooß, K.; Schachner, L.F.; Watson, R.; Gillespie, Z.B.; Howard, S.A.; Cheek, M.A.; Meiners, M.J.; Sobh, A.; Licht, J.D.; Keogh, M.-C.; et al. Separation and Characterization of Endogenous Nucleosomes by Native Capillary Zone Electrophoresis–Top-Down Mass Spectrometry. Analytical chemistry 2021, 93, 5151–5160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drouin, N.; Boccard, J.; Rudaz, S.; González-Ruiz, V. Data Analysis Strategies in CE–MS for Metabolomics. In Capillary Electrophoresis-Mass Spectrometry for Proteomics and Metabolomics; 2022; pp. 35-63. [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, S.A.; Chen, W.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Fang, F.; Liu, X.; Sun, L. Pilot Evaluation of the Long-Term Reproducibility of Capillary Zone Electrophoresis–Tandem Mass Spectrometry for Top-Down Proteomics of a Complex Proteome Sample. Journal of Proteome Research 2024, 23, 1399–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, W.; Hong, J.; Xiang, Y.; Xu, W.J.C.s. Rapid 3-dimensional shape determination of globular proteins by mobility capillary electrophoresis and native mass spectrometry. 2020, 11, 4758-4765. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wu, H.; Zhang, R.; Fang, X.; Xu, W. Structure and effective charge characterization of proteins by a mobility capillary electrophoresis based method. Chemical Science 2019, 10, 7779–7787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubský, P.; Dvořák, M.; Ansorge, M. Affinity capillary electrophoresis: the theory of electromigration. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry 2016, 408, 8623–8641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Vega, E.; Haselberg, R.; Somsen, G.W.; de Jong, G.J. Simultaneous Assessment of Protein Heterogeneity and Affinity by Capillary Electrophoresis–Mass Spectrometry. Analytical chemistry 2015, 87, 8781–8788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.; Wu, H.; Zhang, R.; He, M.; Xu, W. The Coupling of Taylor Dispersion Analysis and Mass Spectrometry to Differentiate Protein Conformations. Analytical chemistry 2020, 92, 5200–5206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Weber, S.G. Determination of binding constants by affinity capillary electrophoresis, electrospray ionization mass spectrometry and phase-distribution methods. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry 2008, 27, 738–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domínguez-Vega, E.; Haselberg, R.; Somsen, G.W.; de Jong, G.J. Simultaneous assessment of protein heterogeneity and affinity by capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry. Analytical chemistry 2015, 87, 8781–8788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuignier, K.; Veuthey, J.L.; Carrupt, P.A.; Schappler, J. Characterization of drug-protein interactions by capillary electrophoresis hyphenated to mass spectrometry. Electrophoresis 2012, 33, 3306–3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Dou, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Man, S.; Wolfs, K.; Adams, E.; Van Schepdael, A. On-line screening of matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors by capillary electrophoresis coupled to ESI mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography B 2013, 930, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mironov, G.G.; Clouthier, C.M.; Akbar, A.; Keillor, J.W.; Berezovski, M.V. Simultaneous analysis of enzyme structure and activity by kinetic capillary electrophoresis-MS. Nature Chemical Biology 2016, 12, 918–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fermas, S.; Gonnet, F.; Sutton, A.; Charnaux, N.; Mulloy, B.; Du, Y.; Baleux, F.; Daniel, R. Sulfated oligosaccharides (heparin and fucoidan) binding and dimerization of stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1/CXCL 12) are coupled as evidenced by affinity CE-MS analysis. Glycobiology 2008, 18, 1054–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langmajerová, M.; Řemínek, R.; Pelcová, M.; Foret, F.; Glatz, Z. Combination of on-line CE assay with MS detection for the study of drug metabolism by cytochromes P450. Electrophoresis 2015, 36, 1365–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davoine, C.; Fillet, M. Hyphenation of Affinity Capillary Electrophoresis with Mass Spectrometry for the Study of Ligand–Protein Interactions: n-Methylmorpholine Acetate Buffer and Polydopamine-Based Coating as Key Assets. Analytical chemistry 2025, 97, 3988–3995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanigliulo, A.; Bortolotti, F.; Pascali, J.; Tagliaro, F. Chapter 15 Forensic toxicological screening with capillary electrophoresis and related techniques. In Handbook of Analytical Separations, Bogusz, M.J., Ed.; Elsevier Science B.V.: 2008; Volume 6, pp. 513-534. [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Sun, L. A Mini Review on Capillary Isoelectric Focusing-Mass Spectrometry for Top-Down Proteomics. 2021, 9. [CrossRef]
- Kristl, T.; Stutz, H.; Wenz, C.; Rozing, G. Principles and Applications of Capillary Isoelectric Focusing. 2014, 1-50.
- Lopez-Soto-Yarritu, P.; Díez-Masa, J.C.; Cifuentes, A.; de Frutos, M. Improved capillary isoelectric focusing method for recombinant erythropoietin analysis. Journal of Chromatography A 2002, 968, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonslow, B.R.; Kang, S.A.; Gestaut, D.R.; Graczyk, B.; Davis, T.N.; Sabatini, D.M.; Yates, J.R., 3rd. Native capillary isoelectric focusing for the separation of protein complex isoforms and subcomplexes. Analytical chemistry 2010, 82, 6643–6651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybylski, C.; Mokaddem, M.; Prull-Janssen, M.; Saesen, E.; Lortat-Jacob, H.; Gonnet, F.; Varenne, A.; Daniel, R. On-line capillary isoelectric focusing hyphenated to native electrospray ionization mass spectrometry for the characterization of interferon-γ and variants. Analyst 2015, 140, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Han, L.; Sun, L. Automated Capillary Isoelectric Focusing-Mass Spectrometry with Ultrahigh Resolution for Characterizing Microheterogeneity and Isoelectric Points of Intact Protein Complexes. Analytical chemistry 2022, 94, 9674–9682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Lamp, J.; Xia, Q.; Zhang, Y. Capillary Isoelectric Focusing-Mass Spectrometry Method for the Separation and Online Characterization of Intact Monoclonal Antibody Charge Variants. Analytical chemistry 2018, 90, 2246–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naghdi, E.; Reinau, M.E.; Krogh, T.N.; Neusüß, C. Chemical Mobilization-Based Capillary Isoelectric Focusing–Mass Spectrometry Using the nanoCEasy Interface for Pharmaceutical Protein Analysis. Analytical chemistry 2024, 96, 12827–12837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Diaz, R.; Wehr, T.; Zhu, M. Capillary isoelectric focusing. 1997, 18, 2134-2144. [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Diaz, R.; Zhu, M.; Wehr, T. Strategies to improve performance of capillary isoelectric focusing. Journal of Chromatography A 1997, 772, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Pawliszyn, J. Universal detection for capillary isoelectric focusing without mobilization using concentration gradient imaging system. Analytical chemistry 1992, 64, 224–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Pawliszyn, J. Capillary isoelectric focusing with a universal concentration gradient imaging system using a charge-coupled photodiode array. Analytical chemistry 1992, 64, 2934–2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Pawliszyn, J. Dual Detection for Capillary Isoelectric Focusing with Refractive Index Gradient and Absorption Imaging Detectors. Analytical chemistry 1994, 66, 867–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas-Solano, O.; Babu, K.; Park, S.S.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Sosic, Z.; Boumajny, B.; Zeng, M.; Cheng, K.-C.; Reed-Bogan, A.; et al. Intercompany Study to Evaluate the Robustness of Capillary Isoelectric Focusing Technology for the Analysis of Monoclonal Antibodies. Chromatographia 2011, 73, 1137–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.Z.; Que, A.H.; Mo, J.J. Analysis of charge heterogeneities in mAbs using imaged CE. 2009, 30, 714-722. [CrossRef]
- Kwok, T.; Chan, S.L.; Courtney, M.; Zhou, M.; Huang, T.; Bo, T.; Li, V.; Chen, T. Imaged capillary isoelectric focusing tandem high-resolution mass spectrometry using nano electrospray ionization (ESI) for protein heterogeneity characterization. Analytical Biochemistry 2023, 680, 115312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, G.; Du, M.; Bo, T.; Chen, T.; Huang, T. Imaged Capillary Isoelectric Focusing Coupled to High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry (icIEF-MS) for Cysteine-Linked Antibody-Drug Conjugate (ADC) Heterogeneity Characterization Under Native Condition. Electrophoresis 2024, 45, 1915–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rustandi, R.R.; Peklansky, B.; Anderson, C.L. Use of imaged capillary isoelectric focusing technique in development of diphtheria toxin mutant CRM197. 2014, 35, 1065-1071. [CrossRef]
- Loughney, J.W.; Minsker, K.; Ha, S.; Rustandi, R.R. Development of an imaged capillary isoelectric focusing method for characterizing the surface charge of mRNA lipid nanoparticle vaccines. Electrophoresis 2019, 40, 2602–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, T.; Yang, F.; Yan, B.; Michels, D.A.; Huang, T.; Pawliszyn, J. Recent developments of imaged capillary isoelectric focusing technology for in-depth biopharmaceutical characterization. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry 2025, 187, 118212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghizzani, V.; Ascione, A.; Gonnella, F.; Massolini, G.; Luciani, F. Exploring imaged capillary isoelectric focusing parameters for enhanced charge variants quality control. Frontiers in chemistry 2025, 13, 1536222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; McElroy, W.; Pawliszyn, J.; Heger, C.D. Imaged capillary isoelectric focusing: Applications in the pharmaceutical industry and recent innovations of the technology. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry 2022, 150, 116567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, F.; Hendrickson, C.L.; Marshall, A.G. High Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Analytical chemistry 2012, 84, 708–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makarov, A.; Denisov, E.; Lange, O.; Horning, S. Dynamic range of mass accuracy in LTQ orbitrap hybrid mass spectrometer. Journal of The American Society for Mass Spectrometry 2006, 17, 977–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafader, J.O.; Melani, R.D.; Senko, M.W.; Makarov, A.A.; Kelleher, N.L.; Compton, P.D. Measurement of Individual Ions Sharply Increases the Resolution of Orbitrap Mass Spectra of Proteins. Analytical chemistry 2019, 91, 2776–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafader, J.O.; Melani, R.D.; Durbin, K.R.; Ikwuagwu, B.; Early, B.P.; Fellers, R.T.; Beu, S.C.; Zabrouskov, V.; Makarov, A.A.; Maze, J.T.; et al. Multiplexed mass spectrometry of individual ions improves measurement of proteoforms and their complexes. Nature Methods 2020, 17, 391–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, R.V.; Zydney, A.L. Protein Ultrafiltration. In Encyclopedia of Industrial Biotechnology; 2010; pp. 1-25.
- Majors, R.E. Sample Preparation for Large-Scale Protein Purification. LCGC Europe pp. 82-92.
- Park, H.-M.; Winton, V.J.; Drader, J.J.; Manalili Wheeler, S.; Lazar, G.A.; Kelleher, N.L.; Liu, Y.; Tran, J.C.; Compton, P.D. Novel Interface for High-Throughput Analysis of Biotherapeutics by Electrospray Mass Spectrometry. Analytical chemistry 2020, 92, 2186–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGee, J.P.; Senko, M.W.; Jooß, K.; Des Soye, B.J.; Compton, P.D.; Kelleher, N.L.; Kafader, J.O. Automated Control of Injection Times for Unattended Acquisition of Multiplexed Individual Ion Mass Spectra. Analytical chemistry 2022, 94, 16543–16548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Des Soye, B.J.; McGee, J.P.; Hollas, M.A.R.; Forte, E.; Fellers, R.T.; Melani, R.D.; Wilkins, J.T.; Compton, P.D.; Kafader, J.O.; Kelleher, N.L. Automated Immunoprecipitation, Sample Preparation, and Individual Ion Mass Spectrometry Platform for Proteoforms. Analytical chemistry 2024, 96, 13879–13887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horlebein, J.; Moon, E.; Szekeres, G.P.; von Helden, G.; Österlund, N.; Pagel, K. Gas-phase purification enables structural studies of amyloid intermediates. Trends in Chemistry 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, S.L.; Wyttenbach, T.; Baumketner, A.; Shea, J.-E.; Bitan, G.; Teplow, D.B.; Bowers, M.T. Amyloid β-Protein: Monomer Structure and Early Aggregation States of Aβ42 and Its Pro19 Alloform. Journal of the American Chemical Society 2005, 127, 2075–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, S.L.; Dupuis, N.F.; Lazo, N.D.; Wyttenbach, T.; Condron, M.M.; Bitan, G.; Teplow, D.B.; Shea, J.-E.; Ruotolo, B.T.; Robinson, C.V.; et al. Amyloid-β protein oligomerization and the importance of tetramers and dodecamers in the aetiology of Alzheimer's disease. Nature Chemistry 2009, 1, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupuis, N.F.; Wu, C.; Shea, J.-E.; Bowers, M.T. The Amyloid Formation Mechanism in Human IAPP: Dimers Have β-Strand Monomer−Monomer Interfaces. Journal of the American Chemical Society 2011, 133, 7240–7243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.P.; Radford, S.E.; Ashcroft, A.E. Elongated oligomers in β2-microglobulin amyloid assembly revealed by ion mobility spectrometry-mass spectrometry. 2010, 107, 6794-6798. [CrossRef]
- Loo, J.A.; Berhane, B.; Kaddis, C.S.; Wooding, K.M.; Xie, Y.; Kaufman, S.L.; Chernushevich, I.V. Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry and ion mobility analysis of the 20S proteasome complex. Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry 2005, 16, 998–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruotolo, B.T.; Giles, K.; Campuzano, I.; Sandercock, A.M.; Bateman, R.H.; Robinson, C.V. Evidence for Macromolecular Protein Rings in the Absence of Bulk Water. 2005, 310, 1658-1661. [CrossRef]
- Politis, A.; Park, A.Y.; Hyung, S.-J.; Barsky, D.; Ruotolo, B.T.; Robinson, C.V. Integrating Ion Mobility Mass Spectrometry with Molecular Modelling to Determine the Architecture of Multiprotein Complexes. PLOS ONE 2010, 5, e12080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Sandercock, A.M.; Fraser, C.S.; Ridlova, G.; Stephens, E.; Schenauer, M.R.; Yokoi-Fong, T.; Barsky, D.; Leary, J.A.; Hershey, J.W.; et al. Mass spectrometry reveals modularity and a complete subunit interaction map of the eukaryotic translation factor eIF3. 2008, 105, 18139-18144. [CrossRef]
- Lane, L.A.; Fernández-Tornero, C.; Zhou, M.; Morgner, N.; Ptchelkine, D.; Steuerwald, U.; Politis, A.; Lindner, D.; Gvozdenovic, J.; Gavin, A.-C.; et al. Mass Spectrometry Reveals Stable Modules in holo and apo RNA Polymerases I and III. Structure 2011, 19, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uetrecht, C.; Barbu, I.M.; Shoemaker, G.K.; van Duijn, E.; Heck, A.J.R. Interrogating viral capsid assembly with ion mobility–mass spectrometry. Nature Chemistry 2011, 3, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christofi, E.; Barran, P. Ion Mobility Mass Spectrometry (IM-MS) for Structural Biology: Insights Gained by Measuring Mass, Charge, and Collision Cross Section. Chemical Reviews 2023, 123, 2902–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horlebein, J.; Moon, E.; Szekeres, G.P.; von Helden, G.; Österlund, N.; Pagel, K. Gas-phase purification enables structural studies of amyloid intermediates. Trends in Chemistry 2025, 7, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liénard, R.; Duez, Q.; Grayson, S.M.; Gerbaux, P.; Coulembier, O.; De Winter, J. Limitations of ion mobility spectrometry-mass spectrometry for the relative quantification of architectural isomeric polymers: A case study. 2020, 34, e8660. [CrossRef]
- Vickers, S.; Aldobiyan, I.; Lowen, S.M.; Irving, J.A.; Lomas, D.A.; Thalassinos, K. Top-Down Ion Mobility Mass Spectrometry Reveals a Disease Associated Conformational Ensemble of Alpha-1-antitrypsin. Journal of the American Chemical Society 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocurek, K.I.; Griffiths, R.L.; Cooper, H.J. Ambient ionisation mass spectrometry for in situ analysis of intact proteins. 2018, 53, 565-578. [CrossRef]
- Clendinen, C.S.; Monge, M.E.; Fernández, F.M. Ambient mass spectrometry in metabolomics. Analyst 2017, 142, 3101–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, N.J.; Griffiths, R.L.; Edwards, R.L.; Cooper, H.J. Native Liquid Extraction Surface Analysis Mass Spectrometry: Analysis of Noncovalent Protein Complexes Directly from Dried Substrates. Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry 2015, 26, 1320–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, R.L.; Cooper, H.J. Direct Tissue Profiling of Protein Complexes: Toward Native Mass Spectrometry Imaging. Analytical chemistry 2016, 88, 606–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, R.L.; Konijnenberg, A.; Viner, R.; Cooper, H.J. Direct Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Protein Complexes and Intact Proteins up to >70 kDa from Tissue. Analytical chemistry 2019, 91, 6962–6966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hale, O.J.; Cooper, H.J. Native Mass Spectrometry Imaging and In Situ Top-Down Identification of Intact Proteins Directly from Tissue. Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry 2020, 31, 2531–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglass, K.A.; Venter, A.R. Protein analysis by desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry and related methods. 2013, 48, 553-560. [CrossRef]
- Ambrose, S.; Housden, N.G.; Gupta, K.; Fan, J.; White, P.; Yen, H.-Y.; Marcoux, J.; Kleanthous, C.; Hopper, J.T.S.; Robinson, C.V. Native Desorption Electrospray Ionization Liberates Soluble and Membrane Protein Complexes from Surfaces. 2017, 56, 14463-14468. [CrossRef]
- Ambrose, S.; Housden, N.G.; Gupta, K.; Fan, J.; White, P.; Yen, H.Y.; Marcoux, J.; Kleanthous, C.; Hopper, J.T.S.; Robinson, C.V. Native Desorption Electrospray Ionization Liberates Soluble and Membrane Protein Complexes from Surfaces. Angewandte Chemie (International ed. in English) 2017, 56, 14463–14468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hale, O.J.; Cooper, H.J. Native Mass Spectrometry Imaging of Proteins and Protein Complexes by Nano-DESI. Analytical chemistry 2021, 93, 4619–4627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saibil, H.R. Cryo-EM in molecular and cellular biology. Molecular cell 2022, 82, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterling, H.J.; Batchelor, J.D.; Wemmer, D.E.; Williams, E.R. Effects of Buffer Loading for Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry of a Noncovalent Protein Complex that Requires High Concentrations of Essential Salts. Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry 2010, 21, 1045–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.J.; Jordan, J.S.; Williams, E.R. Is Native Mass Spectrometry in Ammonium Acetate Really Native? Protein Stability Differences in Biochemically Relevant Salt Solutions. Analytical chemistry 2024, 96, 17586–17593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnke, J.-S.; Urner, L.H. Emergence of mass spectrometry detergents for membrane proteomics. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry 2023, 415, 3897–3909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomioka, Y.; Arakawa, T.; Akuta, T.; Nakagawa, M.; Ishibashi, M. Analysis of proteins by agarose native gel electrophoresis in the presence of solvent additives. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2022, 198, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Arakawa, T. Application of native polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for protein analysis: Bovine serum albumin as a model protein. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2019, 125, 566–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breuker, K.; McLafferty, F.W. Stepwise evolution of protein native structure with electrospray into the gas phase, 10−12 to 102 s. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2008, 105, 18145–18152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breuker, K.; Oh, H.; Horn, D.M.; Cerda, B.A.; McLafferty, F.W. Detailed Unfolding and Folding of Gaseous Ubiquitin Ions Characterized by Electron Capture Dissociation. Journal of the American Chemical Society 2002, 124, 6407–6420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schennach, M.; Breuker, K. Proteins with highly similar native folds can show vastly dissimilar folding behavior when desolvated. Angewandte Chemie (International ed. in English) 2014, 53, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyttenbach, T.; Bowers, M.T. Structural Stability from Solution to the Gas Phase: Native Solution Structure of Ubiquitin Survives Analysis in a Solvent-Free Ion Mobility–Mass Spectrometry Environment. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B 2011, 115, 12266–12275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, I.K. Revealing the fates of proteins in the gas phase. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry 2024, 504, 117312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanucara, F.; Holman, S.W.; Gray, C.J.; Eyers, C.E. The power of ion mobility-mass spectrometry for structural characterization and the study of conformational dynamics. Nature Chemistry 2014, 6, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailov, V.A.; Mize, T.H.; Benesch, J.L.P.; Robinson, C.V. Mass-Selective Soft-Landing of Protein Assemblies with Controlled Landing Energies. Analytical chemistry 2014, 86, 8321–8328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longchamp, J.-N.; Rauschenbach, S.; Abb, S.; Escher, C.; Latychevskaia, T.; Kern, K.; Fink, H.-W. Imaging proteins at the single-molecule level. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2017, 114, 1474–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.; Hoffmann, W.; Warnke, S.; Bowers, M.T.; Pagel, K.; von Helden, G. Retention of Native Protein Structures in the Absence of Solvent: A Coupled Ion Mobility and Spectroscopic Study. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2016, 55, 14173–14176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Browne, S.J.; Vachet, R.W. Exploring Salt Bridge Structures of Gas-Phase Protein Ions using Multiple Stages of Electron Transfer and Collision Induced Dissociation. Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry 2014, 25, 604–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Happonen, L.J.; Varjosalo, M. State-of-the-Art and Future Directions in Structural Proteomics. Molecular & Cellular Proteomics 2025, 24, 101065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, G.B.; Muthurajan, U.M.; Bowerman, S.; Luger, K. Analytical Ultracentrifugation (AUC): An Overview of the Application of Fluorescence and Absorbance AUC to the Study of Biological Macromolecules. Current Protocols in Molecular Biology 2020, 133, e131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabilloud, T.; Lelong, C. Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis in proteomics: A tutorial. Journal of Proteomics 2011, 74, 1829–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Some, D.; Amartely, H.; Tsadok, A.; Lebendiker, M. Characterization of Proteins by Size-Exclusion Chromatography Coupled to Multi-Angle Light Scattering (SEC-MALS). Journal of visualized experiments : JoVE 2019. [CrossRef]
- Housmans, J.A.J.; Wu, G.; Schymkowitz, J.; Rousseau, F. A guide to studying protein aggregation. The FEBS journal 2023, 290, 554–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woldeyes, M.A.; Calero-Rubio, C.; Furst, E.M.; Roberts, C.J. Light Scattering to Quantify Protein-Protein Interactions at High Protein Concentrations. Methods in molecular biology (Clifton, N.J.) 2019, 2039, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haass, C.; Selkoe, D.J. Soluble protein oligomers in neurodegeneration: lessons from the Alzheimer's amyloid β-peptide. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology 2007, 8, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goure, W.F.; Krafft, G.A.; Jerecic, J.; Hefti, F. Targeting the proper amyloid-beta neuronal toxins: a path forward for Alzheimer’s disease immunotherapeutics. Alzheimer's Research & Therapy 2014, 6, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cline, E.N.; Bicca, M.A.; Viola, K.L.; Klein, W.L. The Amyloid-β Oligomer Hypothesis: Beginning of the Third Decade. Journal of Alzheimer's Disease 2018, 64, S567–s610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neale, C.V.T.; Harvey, S.R.; Chetyrkin, S.; Wysocki, V.H.; Schey, K.L. Endogenous Aquaporin-0 Lipid Binding in Ocular Lens Tissue via Native Mass Spectrometry. Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, J.S.; Harper, C.C.; Zhang, F.; Kofman, E.; Sam, M.; Zaragoza, J.P.; Bhagwat, B.; Fayadat-Dilman, L.; Williams, E.R. Characterizing Monoclonal Antibody Aggregation Using Charge Detection Mass Spectrometry and Industry Standard Methods. Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, S.; Chaturvedi, M.; Fatima, S.; Priya, S. Environmental factors modulating protein conformations and their role in protein aggregation diseases. Toxicology 2022, 465, 153049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A. Understanding protein subcellular compartmentalization signals. Nature Methods 2025, 22, 651–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benfey, P.N.; Mitchell-Olds, T. From Genotype to Phenotype: Systems Biology Meets Natural Variation. 2008, 320, 495-497. [CrossRef]
- Morris, R.; Black, K.A.; Stollar, E.J. Uncovering protein function: from classification to complexes. Essays Biochem 2022, 66, 255–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zinovyeva, A.Y. Protein Extract Preparation and Co-immunoprecipitation from Caenorhabditis elegans. Journal of visualized experiments : JoVE 2020. [CrossRef]
- Tokmakov, A.A.; Kurotani, A.; Sato, K.I. Protein pI and Intracellular Localization. Frontiers in molecular biosciences 2021, 8, 775736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locke, D.K., Irina V.; Harris, Andrew L. Isoelectric points and post-translational modifications of connexin26 and connexin32. The FASEB Journal 2006, 20, 1221–1223. [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Z.; Mavridou, D.; Damian, M.; Mutti, F.G.; Schoenmakers, P.J.; Gargano, A.F.G. Characterization of Complex Proteoform Mixtures by Online Nanoflow Ion-Exchange Chromatography-Native Mass Spectrometry. Analytical chemistry 2024, 96, 8880–8885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, C.M.; Schneider, O.L.; Tichy, S.; Huge, B.J.; Champion, M.M. Capillary Isoelectric Focusing of Proteins and Peptides Using an In-Line cIEF-ESI Interface with Improved MS Characteristics. Analytical chemistry 2025, 97, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landreh, M.; Sahin, C.; Gault, J.; Sadeghi, S.; Drum, C.L.; Uzdavinys, P.; Drew, D.; Allison, T.M.; Degiacomi, M.T.; Marklund, E.G. Predicting the Shapes of Protein Complexes through Collision Cross Section Measurements and Database Searches. Analytical chemistry 2020, 92, 12297–12303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruotolo, B.T. Collision Cross Sections for Native Proteomics: Challenges and Opportunities. Journal of Proteome Research 2022, 21, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batra, J.; Hultquist, J.F.; Liu, D.; Shtanko, O.; Von Dollen, J.; Satkamp, L.; Jang, G.M.; Luthra, P.; Schwarz, T.M.; Small, G.I.; et al. Protein Interaction Mapping Identifies RBBP6 as a Negative Regulator of Ebola Virus Replication. Cell 2018, 175, 1917–1930.e1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, N.; Krammer, E.-M.; Stengel, F.; Adams, Q.; Van Liefferinge, F.; Hubin, E.; Chaves, R.; Efremov, R.; Aebersold, R.; Vandenbussche, G.; et al. Lipidated apolipoprotein E4 structure and its receptor binding mechanism determined by a combined cross-linking coupled to mass spectrometry and molecular dynamics approach. PLOS Computational Biology 2018, 14, e1006165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Robinson, C.V. When proteomics meets structural biology. Trends in Biochemical Sciences 2010, 35, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
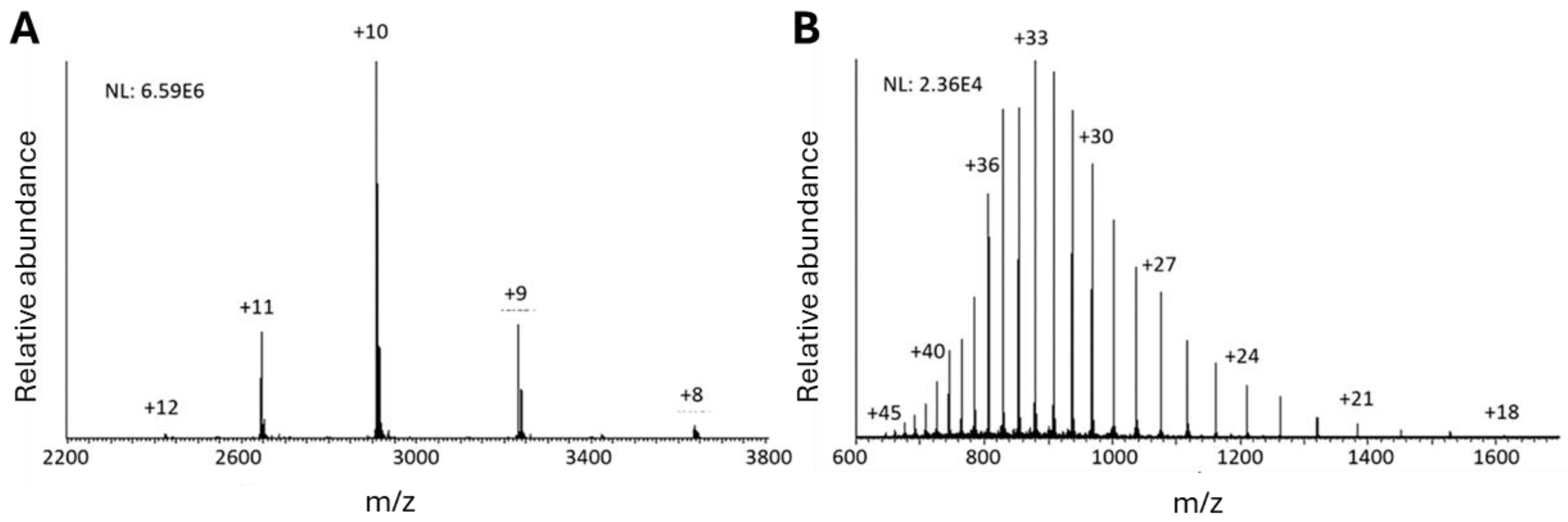
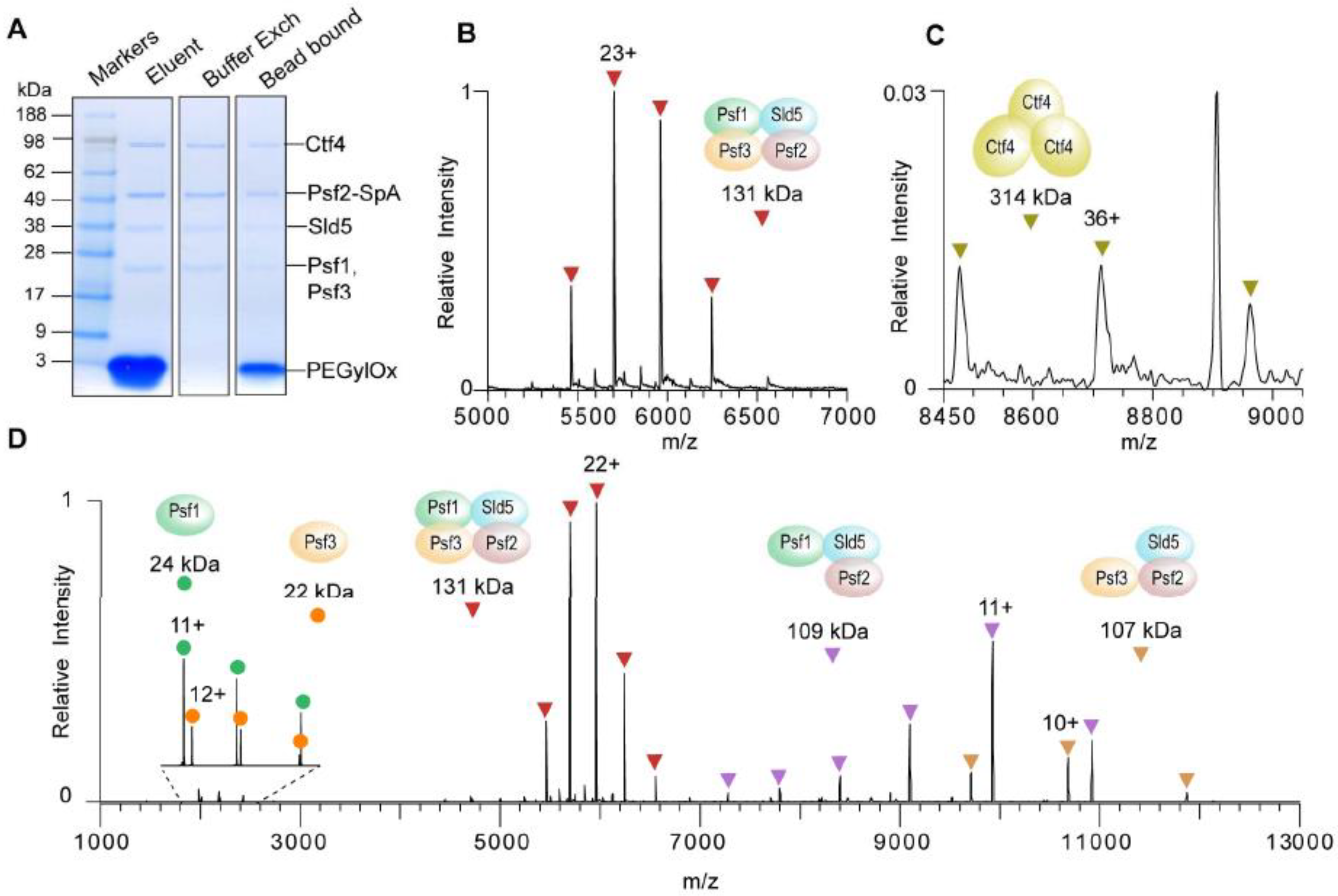
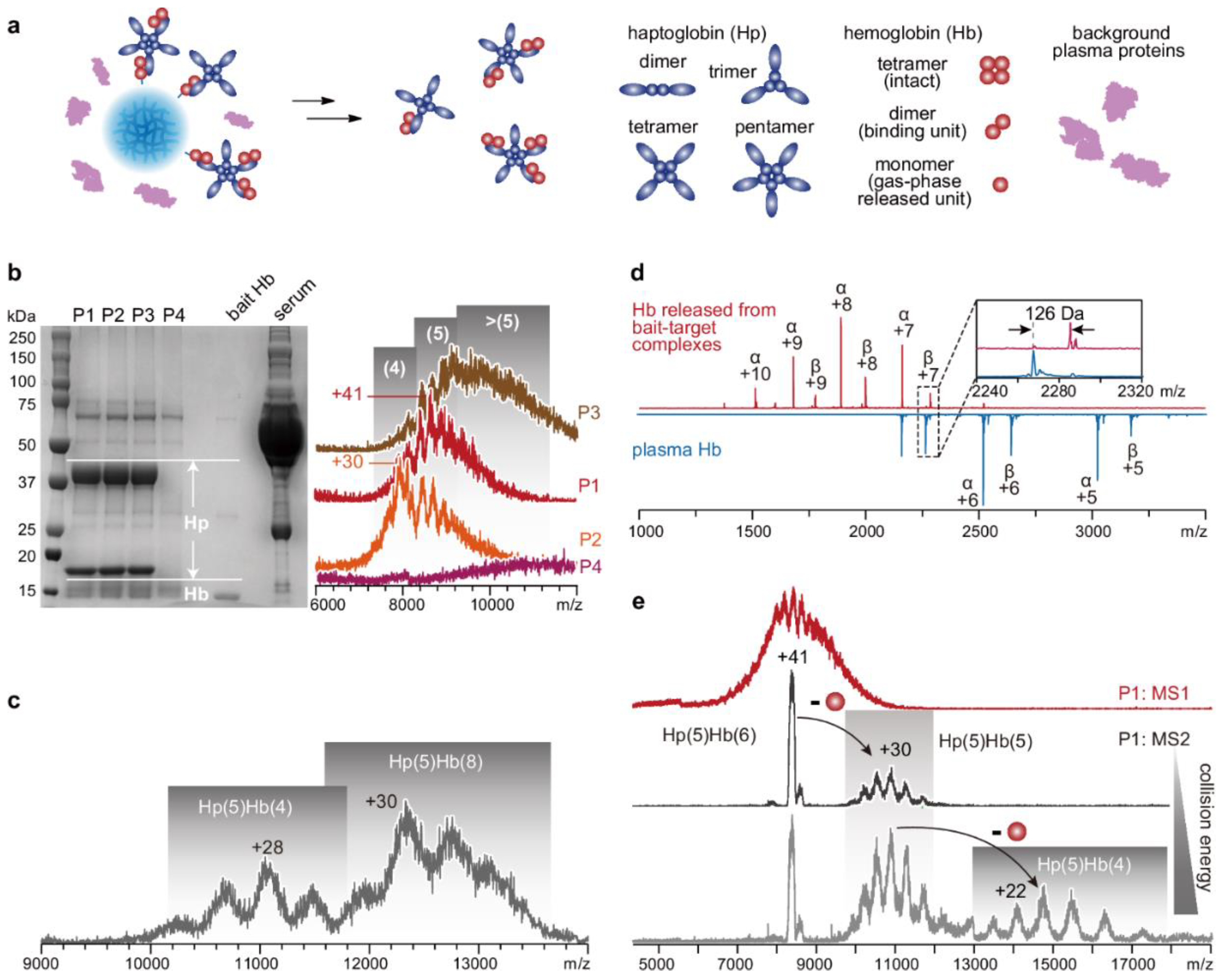
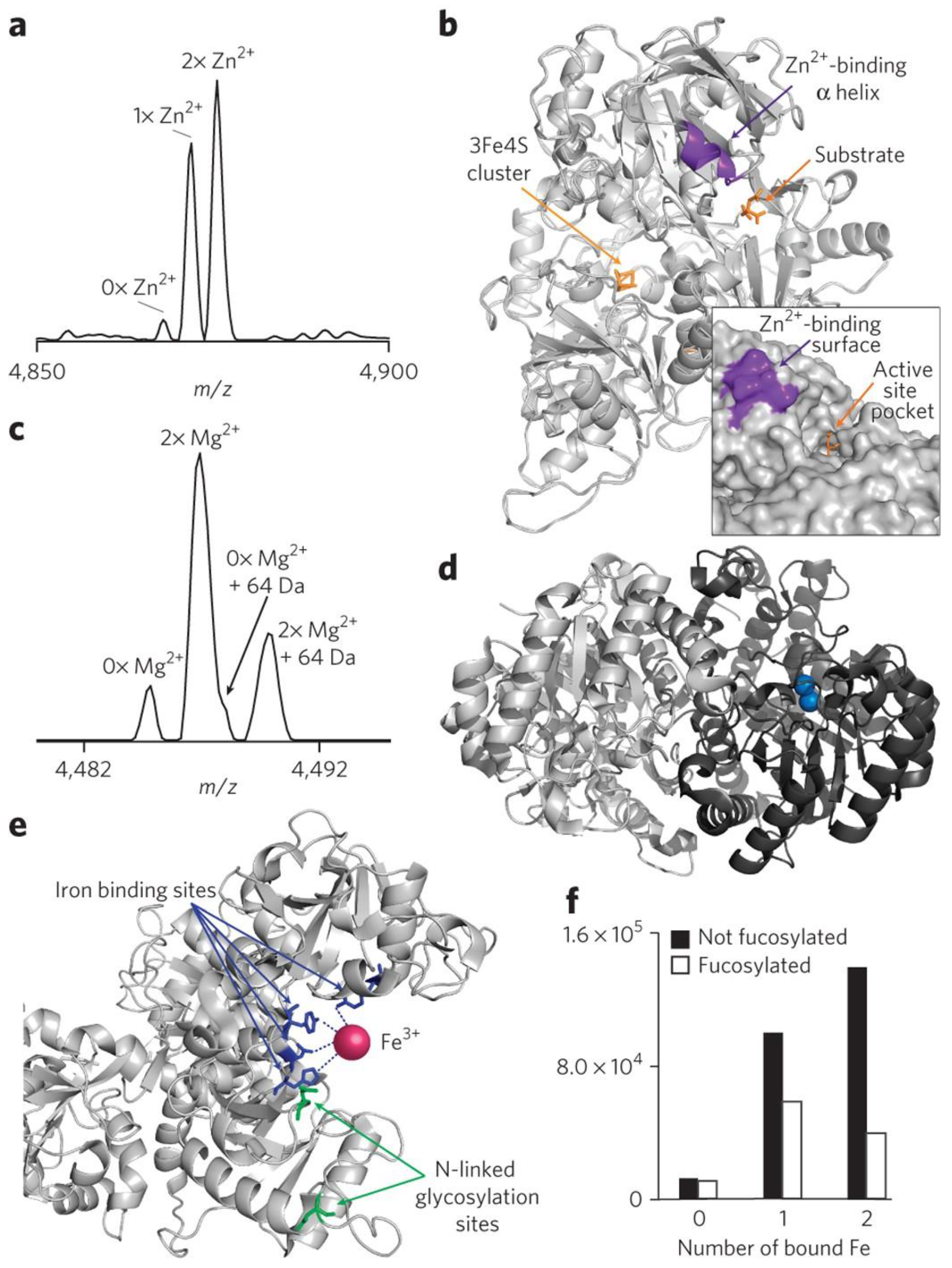
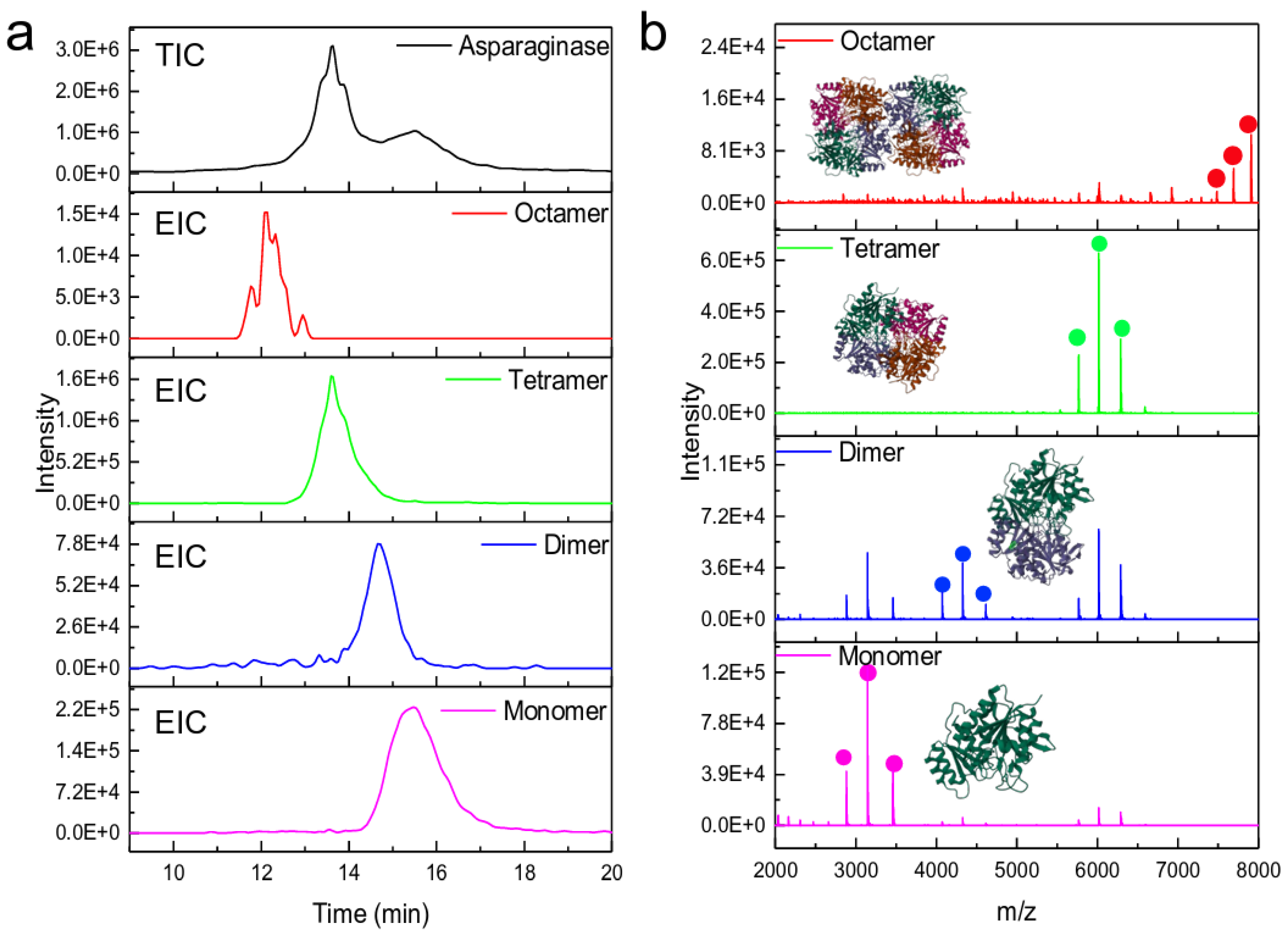
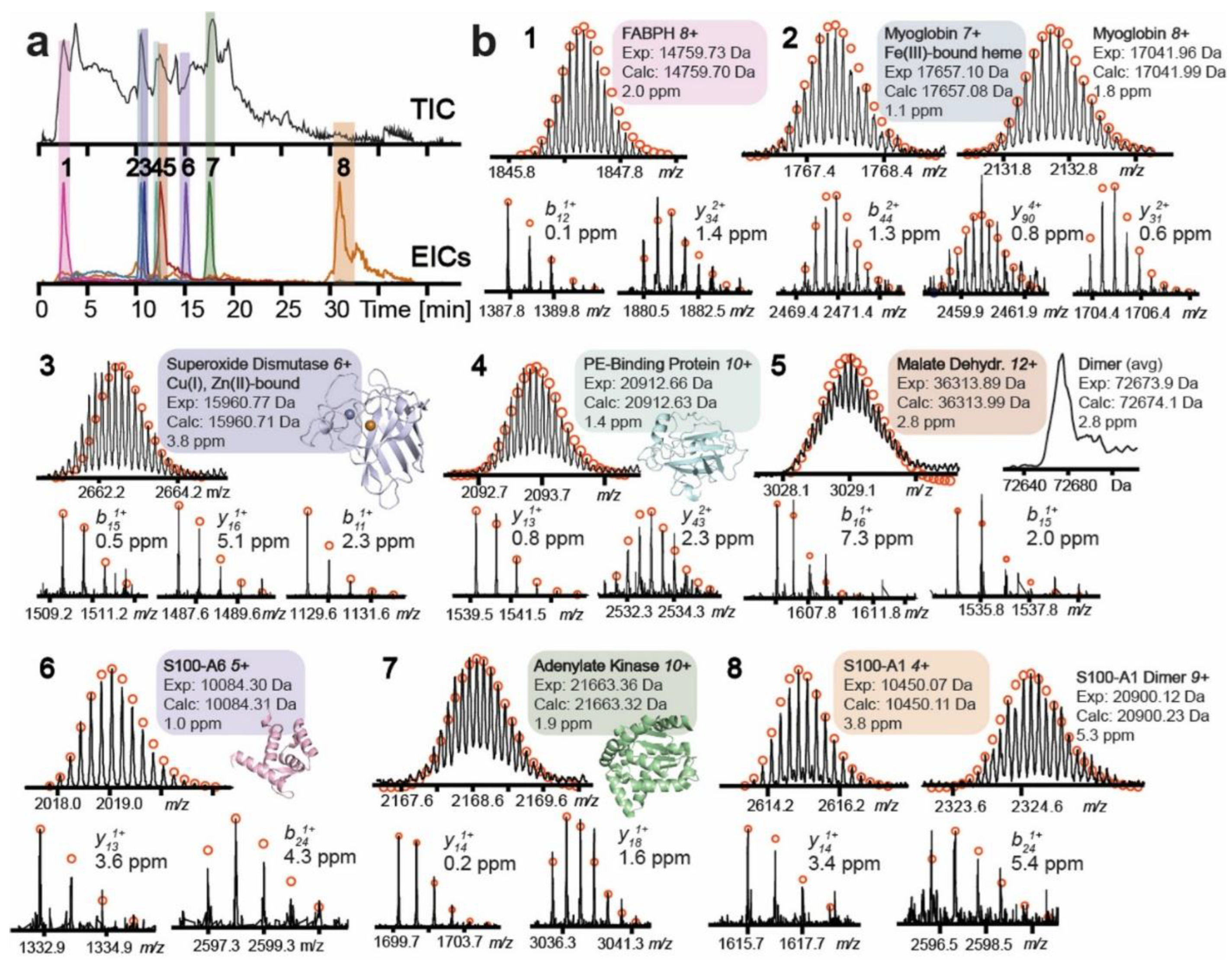
 : fucose;
: fucose;  N-acetyl-glucosamine (GlcNAc);
N-acetyl-glucosamine (GlcNAc);  : mannose. c. FcRn-MS analysis of a mixture of a wild-type mAb and its YTE-format. The insets show the deconvoluted mass spectra for the two TIC peaks. © Elsevier, reprinted with permission [216].
: mannose. c. FcRn-MS analysis of a mixture of a wild-type mAb and its YTE-format. The insets show the deconvoluted mass spectra for the two TIC peaks. © Elsevier, reprinted with permission [216].
 : fucose;
: fucose;  N-acetyl-glucosamine (GlcNAc);
N-acetyl-glucosamine (GlcNAc);  : mannose. c. FcRn-MS analysis of a mixture of a wild-type mAb and its YTE-format. The insets show the deconvoluted mass spectra for the two TIC peaks. © Elsevier, reprinted with permission [216].
: mannose. c. FcRn-MS analysis of a mixture of a wild-type mAb and its YTE-format. The insets show the deconvoluted mass spectra for the two TIC peaks. © Elsevier, reprinted with permission [216].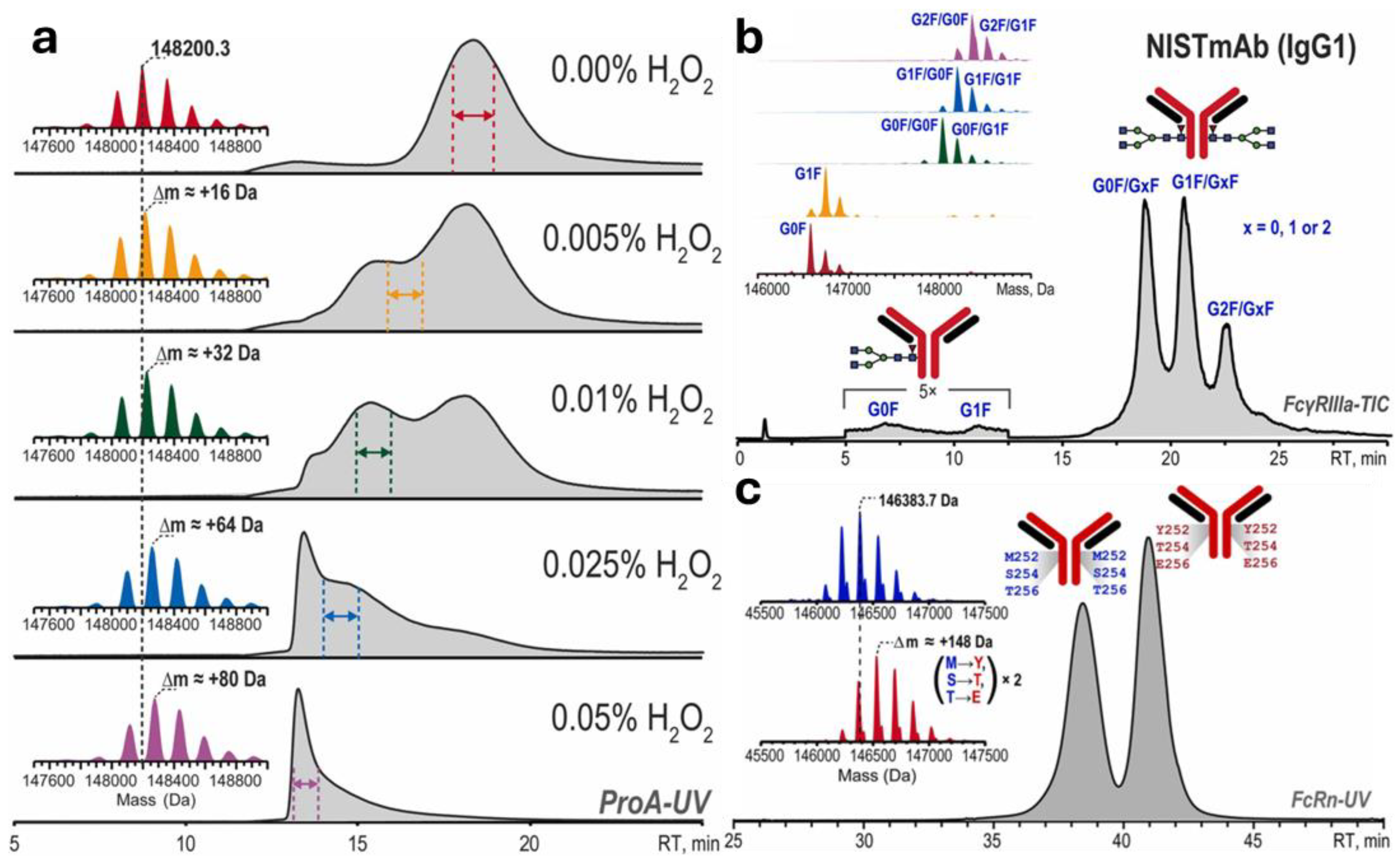
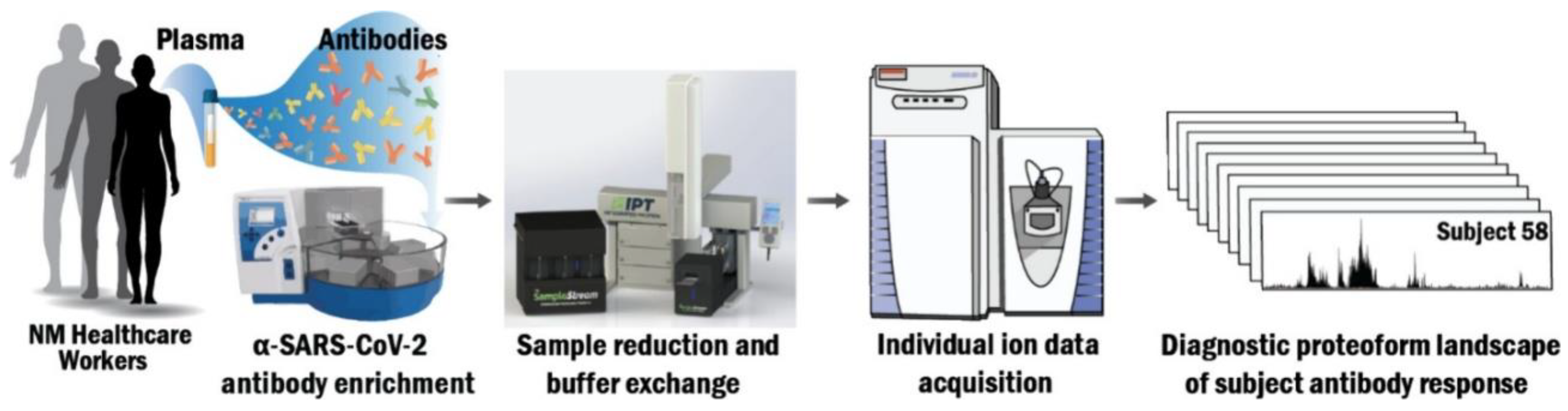
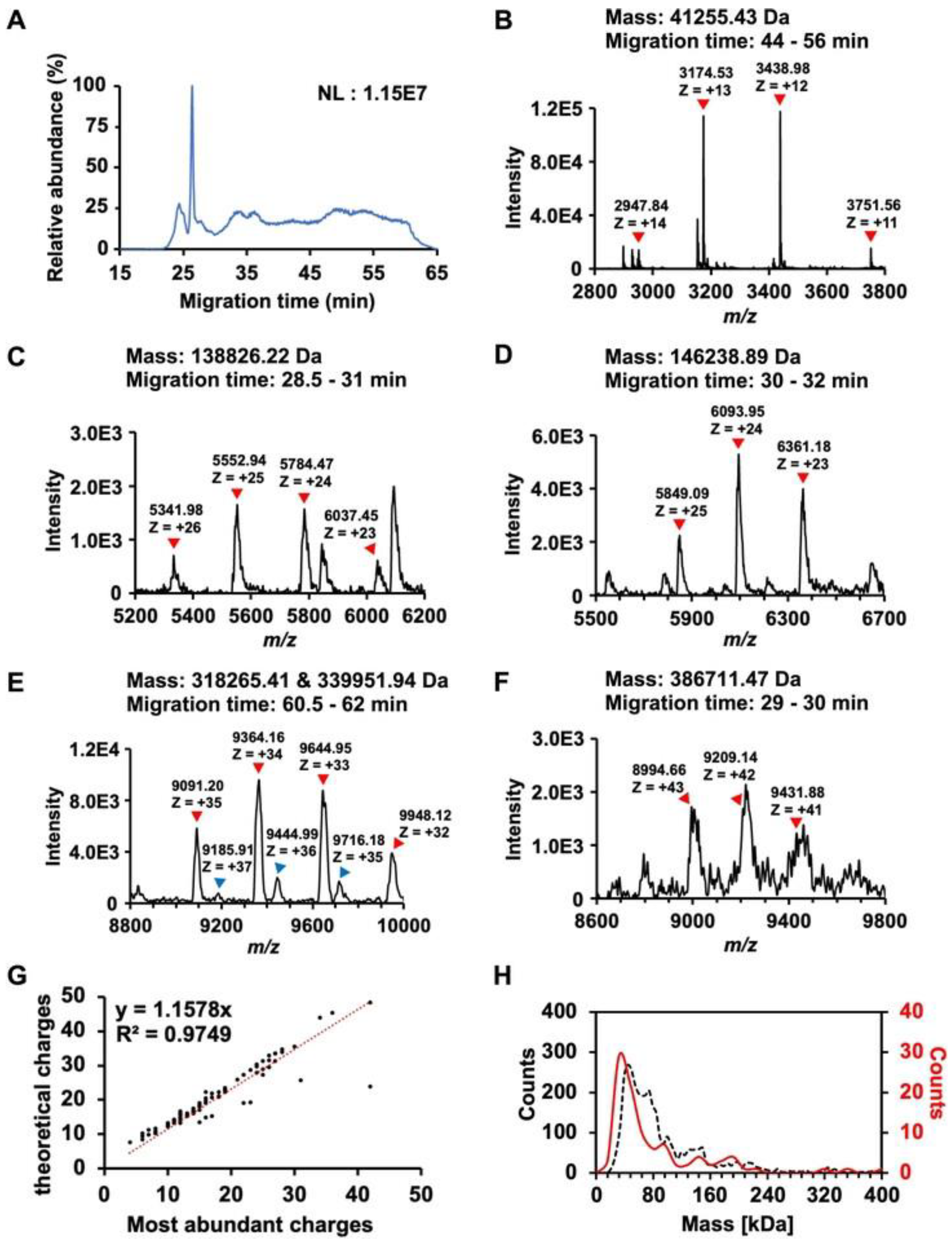
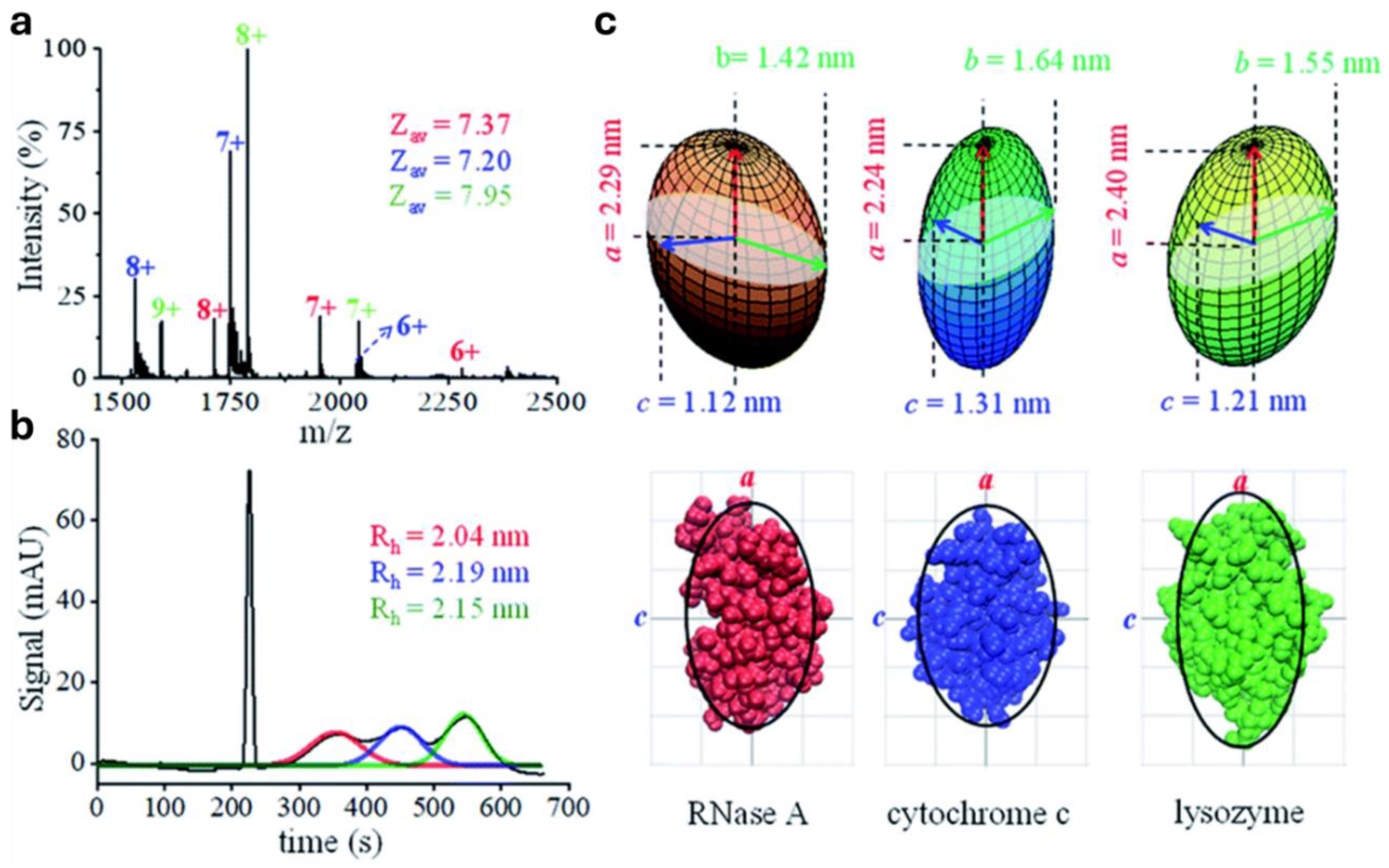
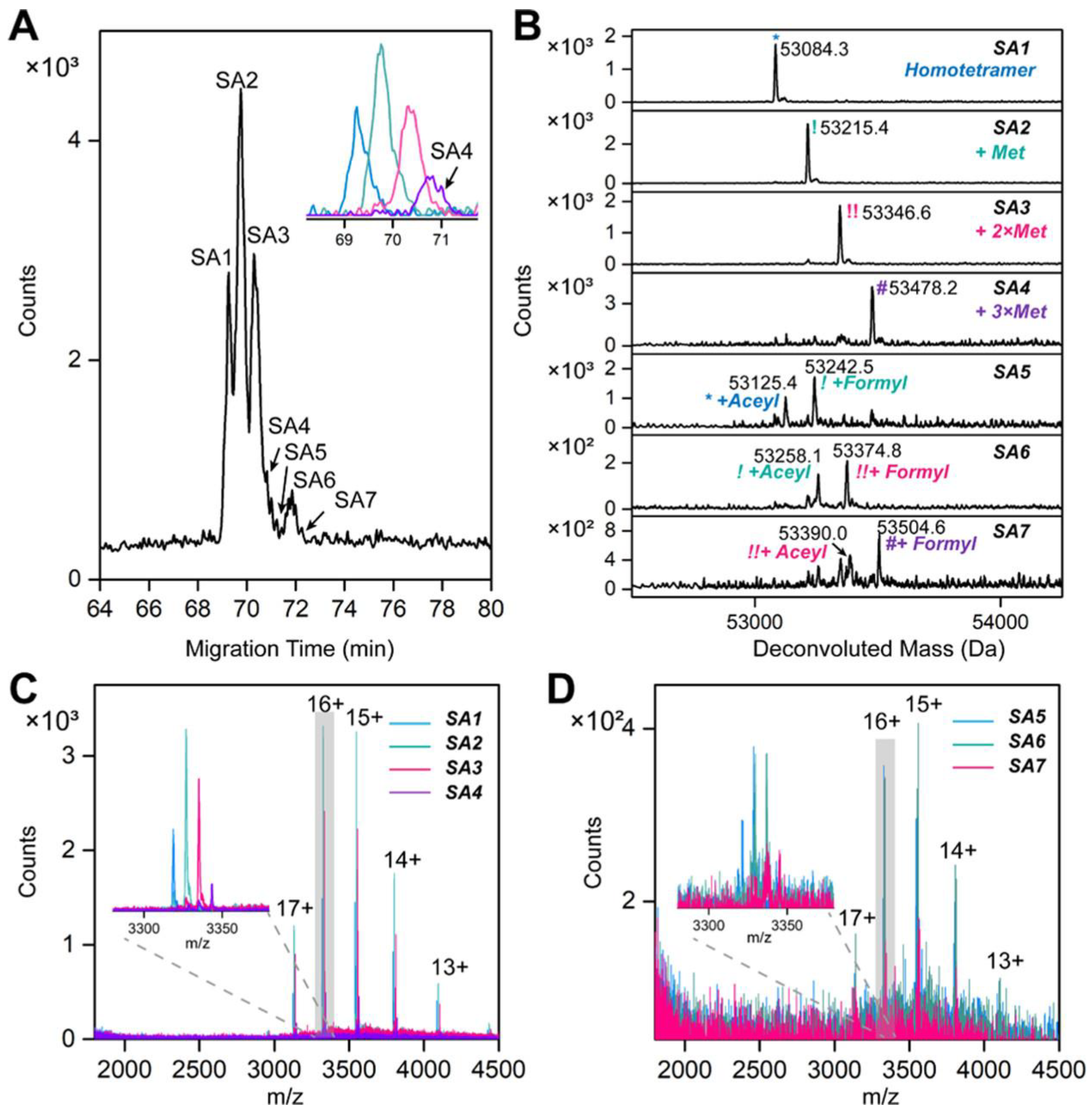
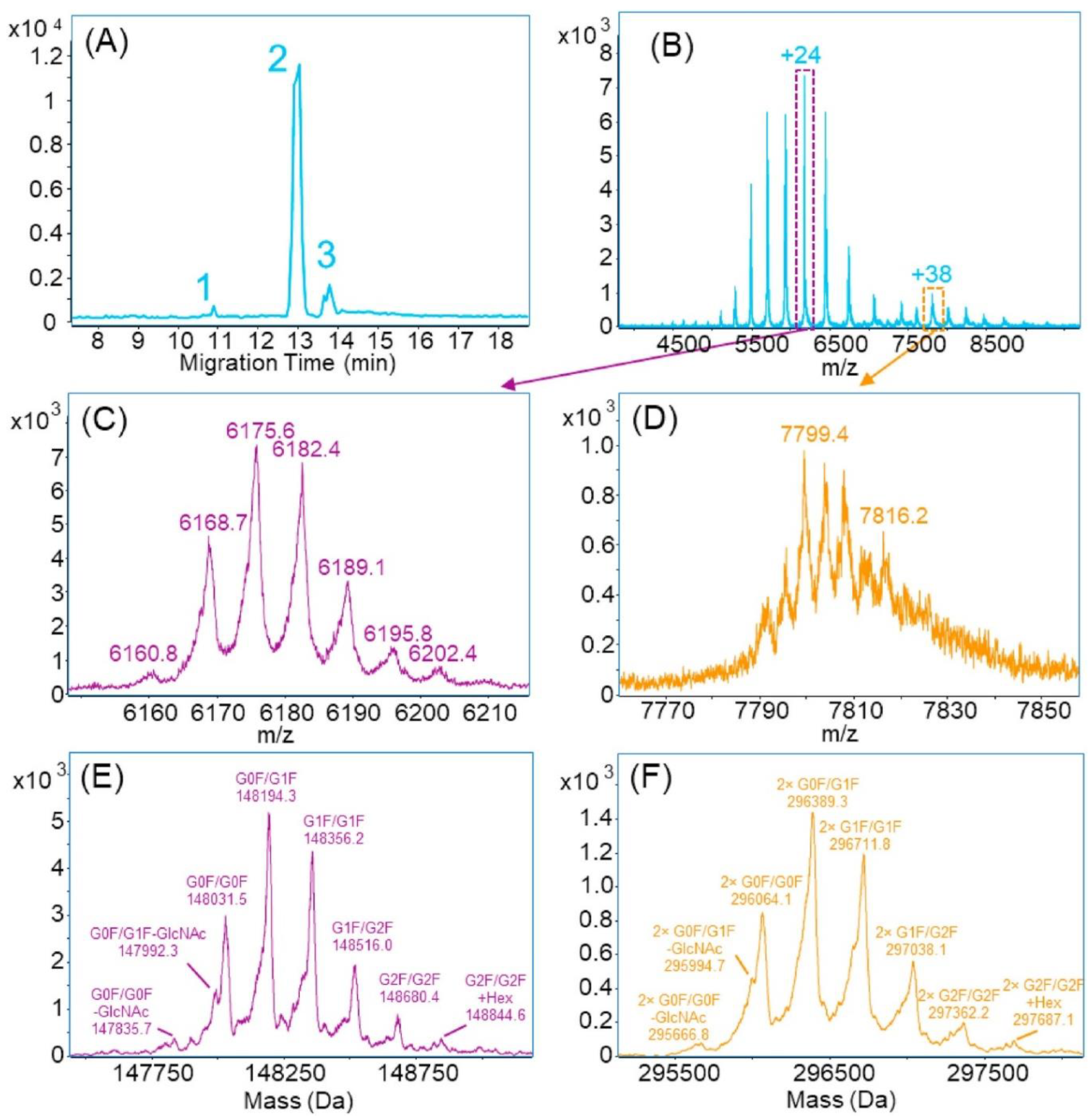

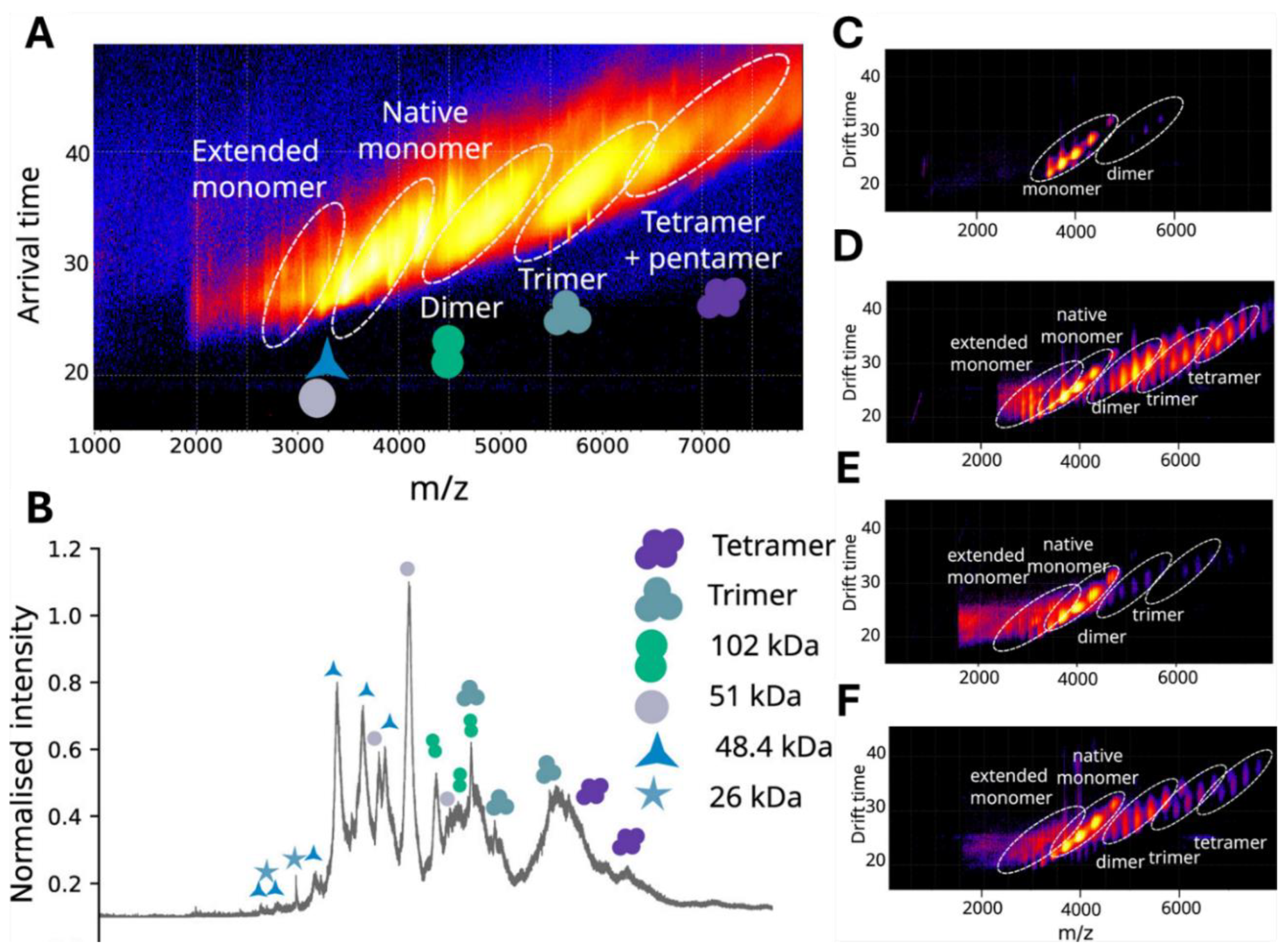
| Instrument | Parameter Settings | Analyzed Protein Species, their Concentration, and Sample Introduction Approach | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bruker 15-Tesla SolarisX FT-ICR MS | Capillary voltage: 0.7-0.95 kV Dry gas temperature: 100 °C Dry gas flow rate: 3.0 L/min Ion Funnel RF amplitude: 300 Vapp Ion Funnel 1 voltage: 150 V Ion Funnel 2 volage: 6 V Skimmer 1: 50-125 V Skimmer 2: 5 V Multipole 1 RF Frequency: 2 MHz Quadrupole RF frequency: 1.4 MHz Transfer Hexapole RF Frequency: 1 MHz Ion accumulation time: 500 ms |
Membrane protein complex, E. coli AquaporinZ homotetramer (97 kDa) (15-30 µM), acquired via direct nanospray-ESI | [95] |
| Waters Synapt G2-HDMS Q-TOF MS | Capillary voltage: 0.5-1 kV1, 0.8-1.2 kV2 Sample cone: 40 V Source temperature: 30 °C Trap CE: 4-110 V1 (High trap CE used for unfolding), 4-102 Transfer CE: 3V1, 2V2 Trap pressure: 3 × 10-3 mbar1, 7 × 10-3 mbar2 Transfer pressure: 3 × 10-3 mbar1, 6.7 × 10-3 mbar2 Trap direct current (DC) bias: -2V1, 3V2 |
1Membrane protein complex, E. coli AquaporinZ homotetramer (97 kDa) (15-30 µM), acquired via direct nanospray-ESI 2Noncovalent protein-ligand complex: Lysozyme and tri-N-acetylchitotriose (NAG3), Trypsin/Pefabloc, Carbonic Anhydrase II/Chlorothiazide, β-Lactoglobulin A/Lauric Acid (5 µM concentration for each protein with 5-25 µM of ligand), acquired via direct nano-ESI |
1[95] 2[65] |
| Thermo Fisher Scientific Q Exactive HF Plus Orbitrap EMR MS | Source voltage: 1.5 kV Capillary temperature: 100 °C and 50 °C FT resolution: 140,000 (at 200 m/z) In-source CID voltage: 10 V HCD CE: 10 V Automatic gain control (AGC) target: 5 × 106 |
Proteolysis-targeting chimeras (PROTACs)-ternary complex (5 µM), acquired via direct nanospray-ESI | [66] |
| SCIEX ZenoTOF 7600 | Spray voltage: 3500 V Curtain gas: 40 psi CAD gas: 9 Ion source gas 1: 60 psi Ion source gas 2: 60 psi Source temperature: 250-300 °C Declustering potential (DP): 120 V CE: 12 V Accumulation time: 0.25 s Time bins to sum: 120 |
NIST mAb (0.7-7 µM, converted from published concentration), ADC (Enhertu) (0.6-6 µM, converted from published concentration), acquired via microflow SEC-ESI-MS | [96] |
| Agilent 6545XT AdvanceBio LC/Q-TOF | Dry gas temperature: 365 °C3, 150 °C4 Dry gas flow: 12 L/min3, 10 L/min4 Nebulizer: 35 psig3, 30 psig4 Sheath gas temperature: 300 °C3, 150 °C4 Sheath gas flow: 12 L/min3, 10 L/min4 Capillary voltage: 5500 V3, 5000 V4 Nozzle voltage: 2000 V Fragmentor: 300 V3, 250 V4 Skimmer: 220 V3, 100 V4 Acquisition rate: 1 spectrum/s |
3Intact protein complex: Pyruvate kinase tetramer (232 kDa), glutamate dehydrogenase hexamer (335 kDa) and β-galactosidase tetramer (466 kDa) (2-20 µM), acquired via microflow SEC-ESI-MS 4Intact protein: Myoglobin (Concentration/amount injected not reported), acquired via microflow SEC-ESI-MS |
[97] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





