Submitted:
03 October 2025
Posted:
03 October 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Study Area, Dataset and Methods
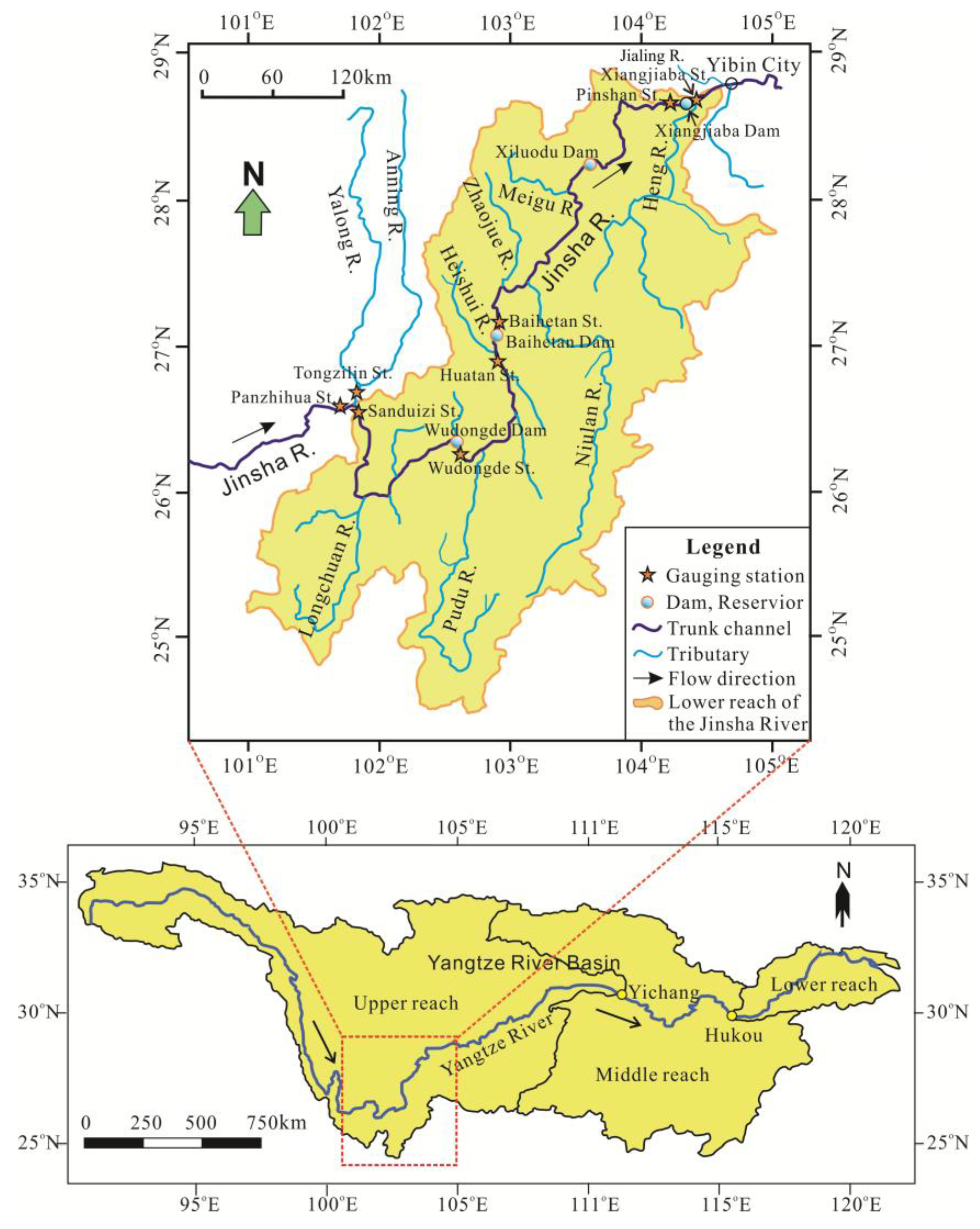
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Dataset
2.3. Methods
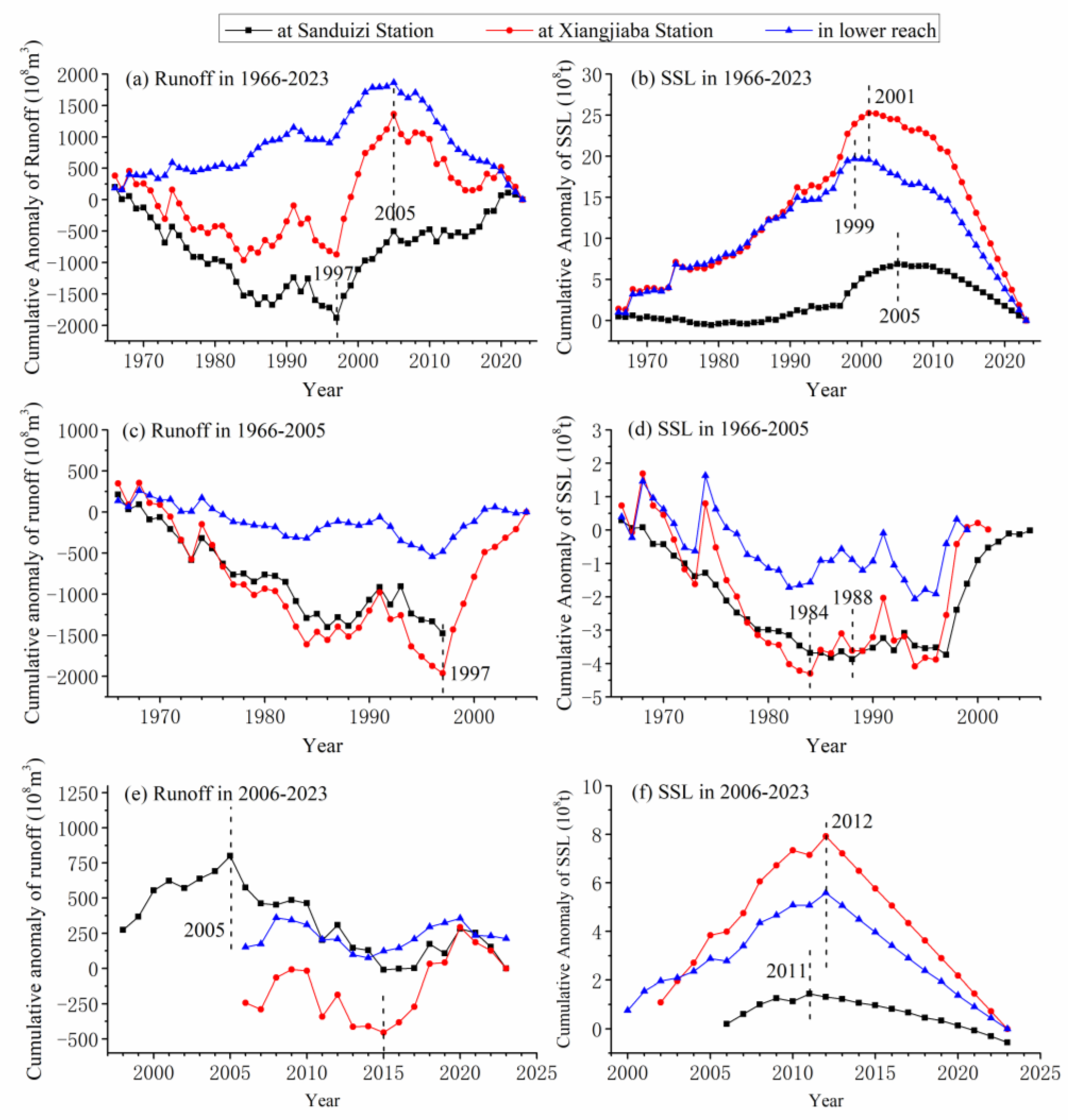
2.3.1. Cumulative Anomaly Method
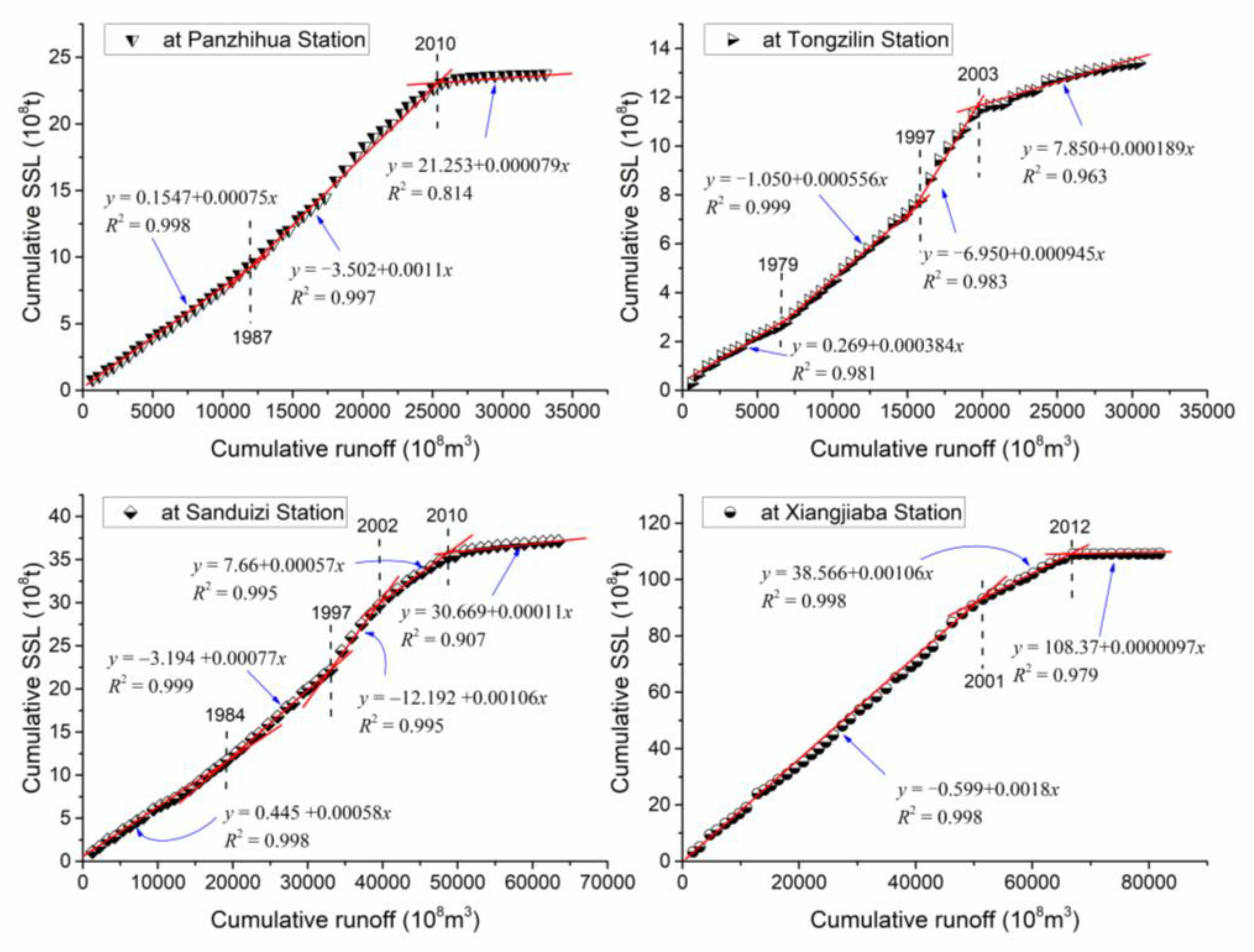
2.3.2. Double Mass Curve Method
2.3.3. Mann-Kendall Method
2.3.4. Regression Analysis Method
3. Results
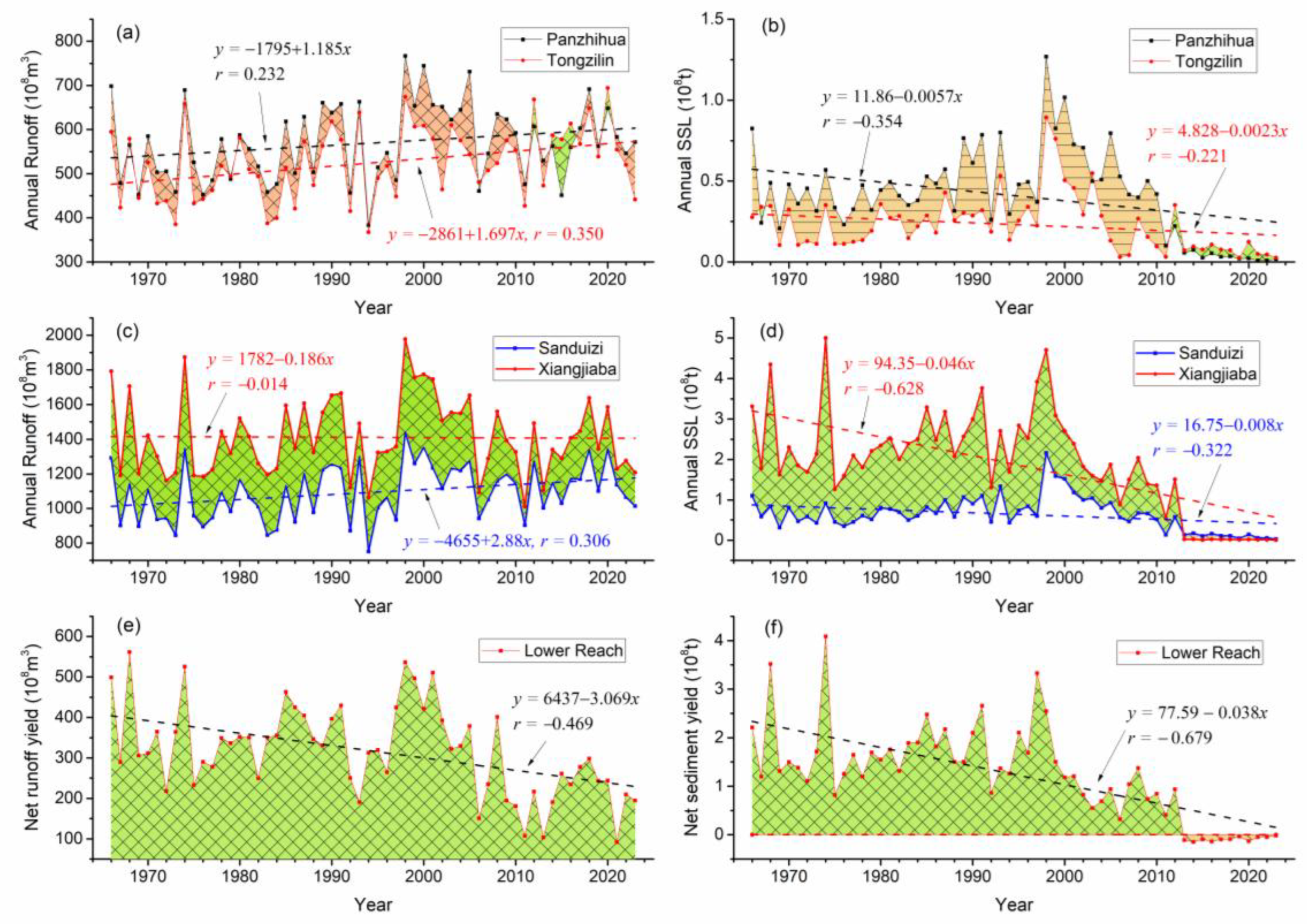
3.1. The Variation Trend of Long-Series Water and Suspended-Sediment
3.1.1. Average Rate of Change
3.1.2. Variation Trend and Significance
3.1.3. Abrupt Change Time and Its Characteristics
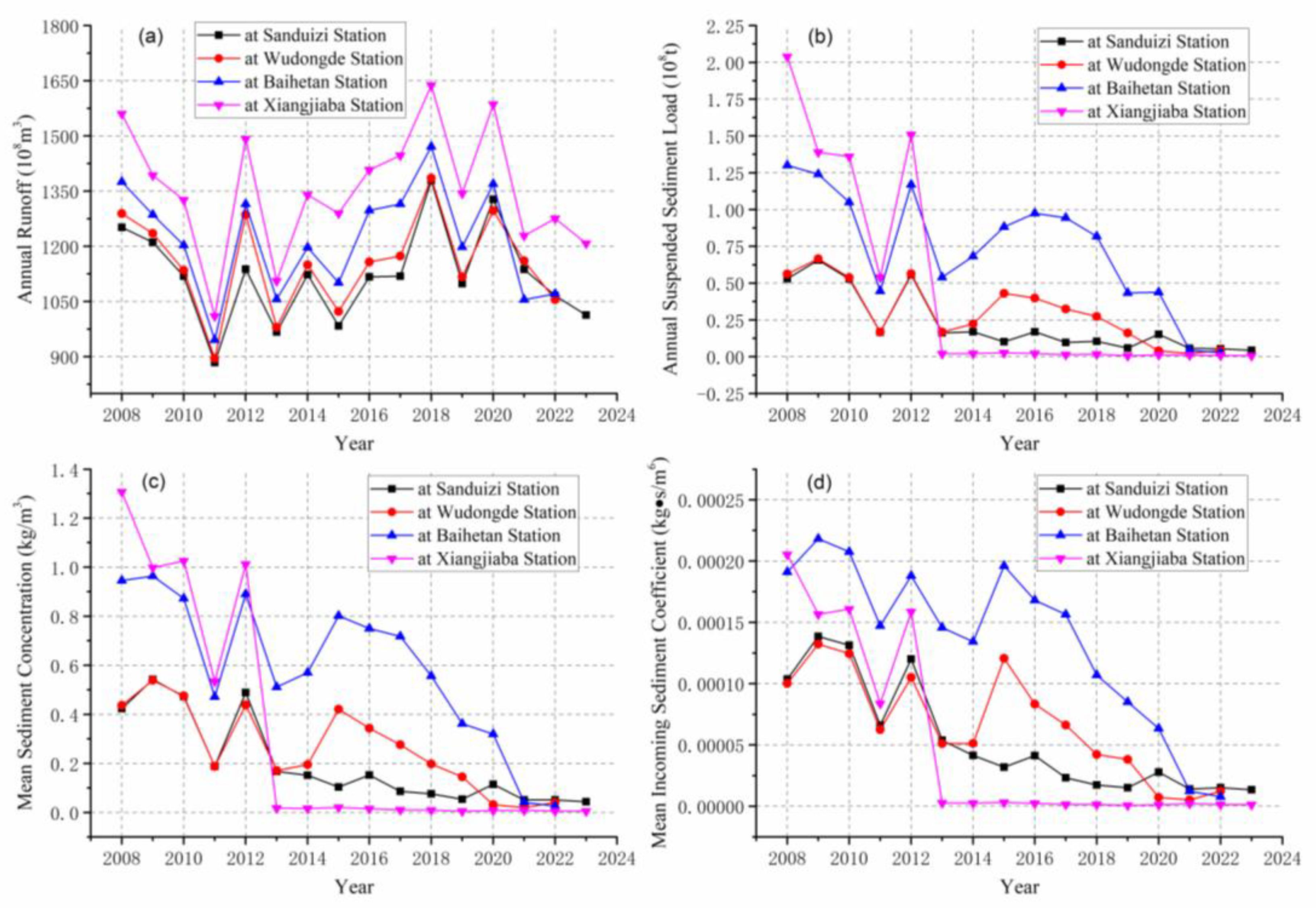
3.2. Comparison of Water-Sediment Processes Before and After Dam Construction
3.2.1. The Trend of Interannual Changes
3.2.2. The Trend of Monthly Variation
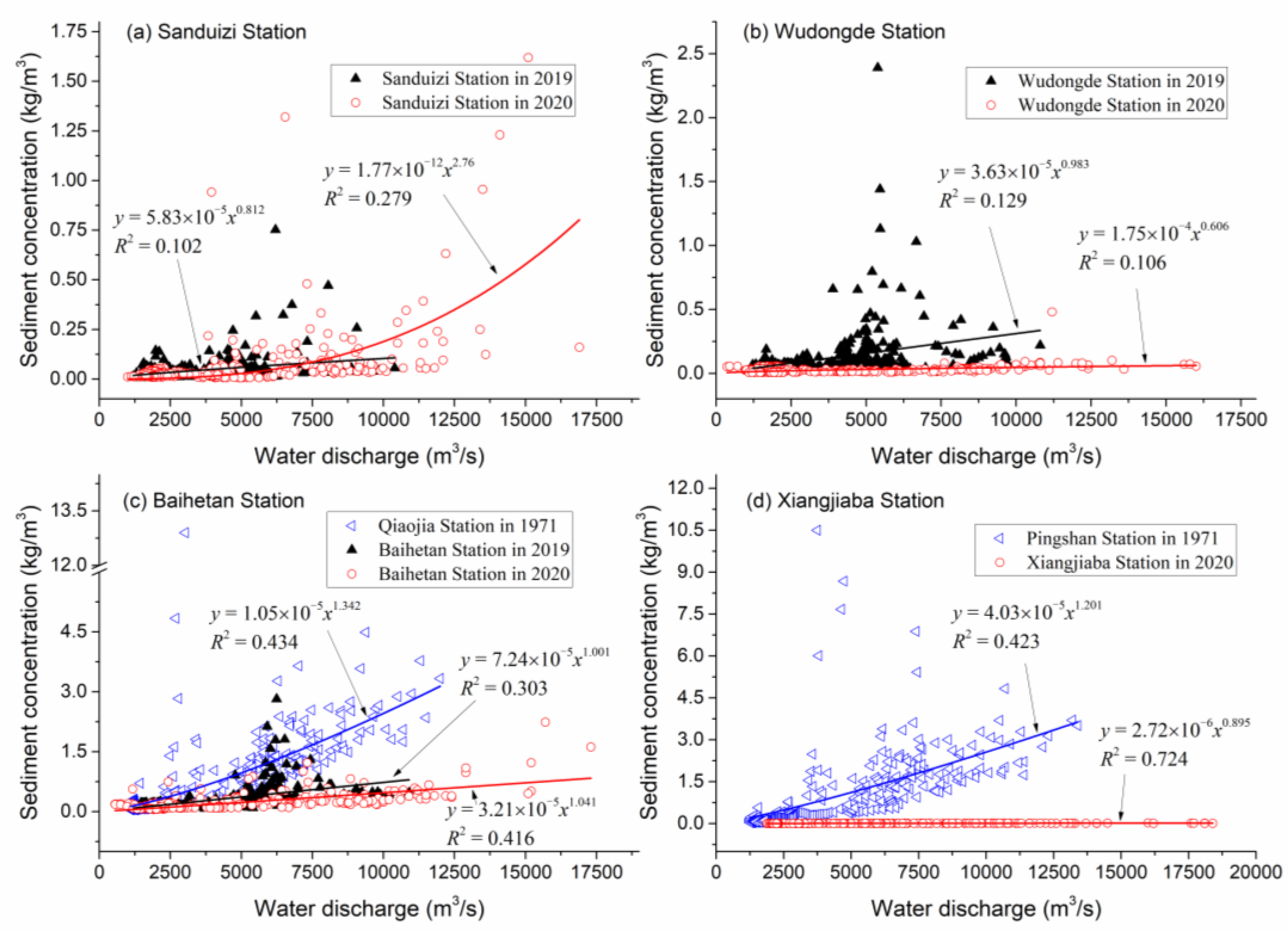
3.2.3. Water-Sediment Relationships Before and After Dam Construction
4. Discussion
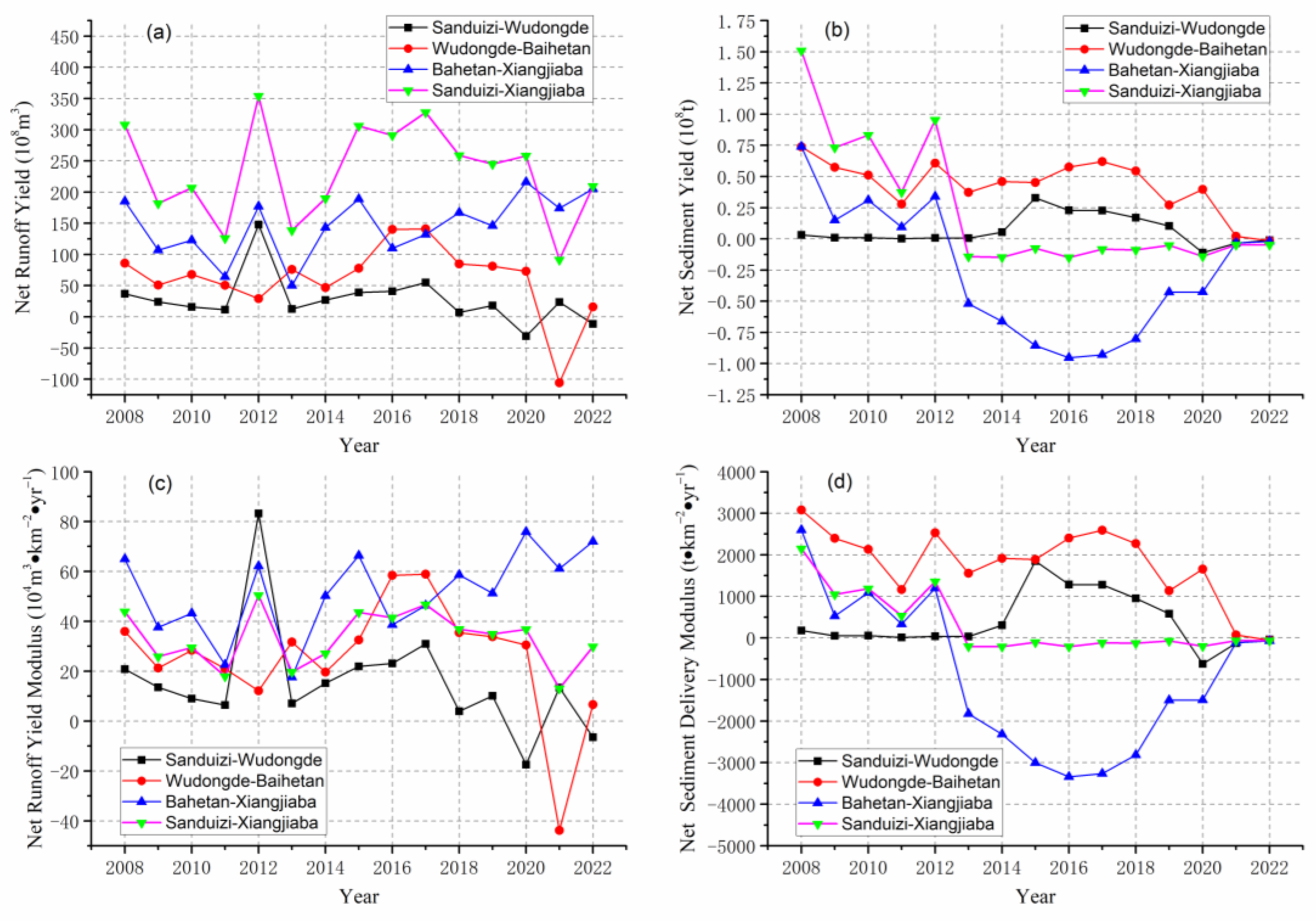
4.1. Sediment Trapping Effect of Cascade Dams Causes Abrupt Changes in SSL
4.2. Cascade Dams Alter Hydrological and Sediment Connectivity in a Differential Manner
4.3. The Impacts of Climate and Other Human Activities
5. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bell, J.L.; Sloan, L.C.; Snyder, M.A. Regional Changes in Extreme Climatic Events: A Future Climate Scenario. J Climate 2004, 17, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brönnimann, S.; Luterbacher, J.; Staehelin, J.; Svendby, T.M.; Hansen, G.; Svene, T. Extreme climate of the global troposphere and stratosphere in 1940–42 related to Elniño. Nature 2004, 431, 971–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, B.; Li, S.; Xu, C.; Li, C. Influence of climate variability and reservoir operation on streamflow in the Yangtze River. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, X. Changes of water and sediment processes in the Yellow River and their responses to ecological protection during the last six decades. Water 2023, 15, 2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.G.; Hu, C.H.; Liu, X.; Shi, H.L. Study on variations of runoff and sediment load in the Upper Yangtze River and main influence factors. J. Sediment. Res. 2016, 41, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.L.; Xu, K.H.; Milliman, J.D.; Yang, H.F.; Wu, C.S. Decline of Yangtze River water and sediment discharge: Impact from natural and anthropogenic changes. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.J.; et al. Rate and distribution of sedimentation in the Tree Gorges Reservoir, upper Yangtze River. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2018, 144, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, H.; Kao, S.J.; Dai, M. The role of mega dams in reducing sediment fluxes: A case study of large Asian rivers. J. Hydrol. 2012, 464, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Li, D.; Wang, X. Analysis of the sediment trapping by reservoirs in the upper Yangtze River. Adv. Eng. Sci. 2015, 47, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.J.; Liu, J.T. Impacts of large dams on downstream fluvial sedimentation: an example of the Three Gorges Dam (TGD) on the Changjiang (Yangtze River). J. Hydrol. 2013, 480, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, H.; Zhu, L. Main flow migration in the middle Yangtze River influenced by cascade reservoirs: Characteristics, controlling factors, trends, and ecological impact. Land 2023, 12, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.P.; Zhou, L.P.; Zhu, L.L.; Liu, W.L.; Wang, J.J. Impact of upstream reservoirs on geomorphic evolution in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River. Earth Surf. Proc. Landf. 2023, 48, 582–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.J.; Du, J.Z.; Zhang, X.L.; Su, N.; Li, J.F. Variation of riverine material loads and environmental consequences on the Changjiang (Yangtze) estuary in recent decades (1955−2008). Environ. Sci. Technol 2011, 45, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.L.; Dong, X.Y.; Chen, Z.F. Sediment deposition of cascade reservoirs in the Lower Jinsha River and its impact on Three Gorges Reservoir. J. Yangtze River Sci. Res. Inst. 2016, 34, 1–7. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, J.; Xu, Q.X. Sediment trapping effect by reservoirs in the Jinsha River basin. Adv. Water Sci. 2018, 29, 482–491. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yan, H.C.; Zhang, X.F.; Xu, Q.X. Unprecedented sedimentation in response to emerging cascade reservoirs in the upper Yangtze River Basin. Catena 2022, 209, 105833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.L.; Chen, D.; Yang, C.G.; Chen, K.B.; LI, S.X. Sediment deposition of cascade reservoirs in the lower Jinsha River and scouring of river channel under dam. J. Lake Sci. 2023, 35, 1097–1110. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Feng, S.H.; Deng, A.J.; Wang, D.W.; Yin, Ye. Characteristics analysis of sediment deposition in the Xiluodu Reservoir. J. Sediment. Res. 2021, 46, 16–22. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Z.D.; Dong, X.Y.; Zhang, F.; Qin, L.L. Study on runoff and sediment characteristics and reservoir deposition in Xiluodu Reservoir of the Jinsha River. J. Sediment. Res. 2022, 47, 22–25. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Gao, Y.; Cao, L.; Dong, X.; Ma,, Y.; Zheng, Y. Sediment deposition within cascade reservoirs: a case study of Baihetan Reservoir in the lower Jinshajiang River, China. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 20706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ping, Y.R.; Du, T. Sedimentation characteristics in the initial period of Baihetan Hydropower Station. “Ecol. Environ. Monit. Three Gorges 2025, 10, 45–51. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S. Variations in sedimentation rate and corresponding adjustments of longitudinal gradient in the cascade reservoirs of the lower Jinsha River. Water 2025, 17, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S. Adjustment of thalweg longitudinal profile in response to sediment silting in cascade reservoirs: A case study of the lower Jinsha River. J. Geog. Sci. 2025, 35, 1497–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.M.; Zhang, X.Q.; Gao, P.; Wang, F. Theory of double mass curves and its applications in hydrology and meteorology. J. China Hydrol. 2010, 30, 47–51. 33. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ran, L.; Wang, S.; Fan, X. Channel change at Toudaoguai Station and its responses to the operation of upstream reservoirs in the upper Yellow River. J. Geogr. Sci. 2010, 20, 231–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merriam, C.F. A comprehensive study of the rainfall on the Susquehanna Valley. Eos Trans. Amer. Geophys. Union 1937, 18, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric tests against trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G. Rank Correlation Methods; Charles Griffin and Company Ltd.: London, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, X.G. Analysis of sedimentation formation area in Yalong River Basin and influences of human activities. Adv. Eng. Sci. 1998, 2, 103–118. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y. Q.; Deng, A.; Dong, X.; Qin, L.; Zhang, B. Study on the spatial-temporal variations of runoff and sediment in the lower reach of Jinsha River. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2023, 54, 1309–1322. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Z.X.; Feng, J.W.; Zhang, l.; Song, K.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, Z.C.; Liang, X.L. The impact of precipitation on the water-sediment relationship in the Yalong River Basin. In Proceedings of the China Water Resources Academic Conference; 2022; pp. 347–359. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Gao, H.; Li, Z.; Su, H. Terraces development and their implications for valley evolution of the Jinsha River from Qiaojia to Menggu. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2020, 75, 1095–1105. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.C.; Zhang, H.L.; Xia, S. Q.; Pang, J.Z. Runoff and sediment discharge variations and corresponding driving mechanism in Jinsha River Basin. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2023, 30, 107–115. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Xia, J.Q.; Deng, S.S.; Lu, J.Y.; Xu, Q.X.; Zong, Q.L.; Tan, G.M. Dynamic channel adjustments in the Jingjiang reach of the middle Yangtze River. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.C.; Zhang, X.F.; Xu, Q.X. Variation of runoff and sediment inflows to the Tree Gorges Reservoir: Impact of upstream cascade reservoirs. J. Hydrol 2021, 603, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, T.M.; Xie, Yy. X.; Zeng, H. Analysis of precipitation change characteristics in the Jinsha River Basin. J. China West Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2025. (in Chinese). https://link.cnki.net/urlid/51.1699.N.20250107. 1157.002.
- Ju, Y.; Zhang, K.; Li, B. f.; Tao, R.; Zhang, J.; Wu, X.Y. Spatiotemporal distribution of actual evapotranspiration and its influencing factors in the Jinsha River Basin. Water Resour. Prot. 2022, 38, 104–110. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaner, N.; Voisin, N.; Nijssen, B.; Lettenmaier, D.P. The contribution of glacier melt to streamfow. Environ Res Lett. 2012, 7, 34029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radić, V.; Hock, R. Glaciers in the earth’s hydrological cycle: assessments of glacier mass and runoff changes on global and regional scales. Surv Geophys. 2013, 35, 813–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farinotti, D.; Pistocchi, A.; Huss, M. From dwindling ice to headwater lakes: could dams replace glaciers in the European Alps? Environ Res Lett. 2016, 11, 054022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Q.; Wang, T.T.; Feng, Y.; Wang, H.; Sun, F.B.; Liu, W.B. Projection of the impact of climate change and reservoir on the flow regime in the Yangtze River basin. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2025, 80, 41–60. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]

| Reservoirs | Initial storage |
Controlled basin area (105 km2) |
Storage Capacity (109 m3) |
Regulating capacity (109 m3) |
Installed capacity (GW) |
Global ranking |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wudongde | Jan. 2020 | 4.068 | 7.408 | 3.0 | 10.2 | 7 |
| Baihetan | Apr. 2021 | 4.303 | 20.627 | 10.4 | 16.0 | 2 |
| Xiluodu | May 2013 | 4.544 | 12.670 | 6.46 | 13.9 | 4 |
| Xiangjiaba | Oct. 2012 | 4.588 | 5.163 | 0.903 | 6.4 | 11 |
| Sum | 45.868 | 20.763 | 46.5 |
| Station name |
Location | Start year |
Controlled drainage area | Data sequence |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Size (km2) | Rate (%) | ||||
| Luning | Lower Yanlong River | 1959 | 108277 | 23.59 | 1966−2008 |
| Tongzilin | Above the outlet of the Yalong River | 1998 | 128363 | 27.98 | 2009−2023 |
| Panzhihua | Above the confluence of Yangtze and Yalong Rivers | 1965 | 259177 | 56.49 | 1966−2023 |
| Sanduizi | Inlet of the study river reach | 2006 | 388571 | 84.69 | 2009−2023 |
| Wudongde | Upper part of the study river reach | 1998 | 406347 | 88.57 | 2008−2023 |
| Baihetan | Middle part of the study river reach | 2014 | 430308 | 93.79 | 2015−2023 |
| Pingshan | Above the outlet of the study river reach | 1954 | 458592 | 99.95 | 1966−2008 |
| Xiangjiaba | Outlet of the study river reach | 2008 | 458800 | 100.00 | 2009−2023 |
| Gauging station | Runoff | Suspended sediment load | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time span | S | Z | Time span | S | Z | |
| Tongzilin | 1966–2023 | 378 | 2.53** | 1966-2023 | −370 | −2.48** |
| Panzhihua | 1966–2023 | 232 | 1.55 | 1966-2023 | −381 | −2.55** |
| Sanduizi | 1966–2023 | 340 | 2.27* | 1966-2023 | −418 | −2.79*** |
| Xiangjiaba | 1966–2023 | 52 | 0.34 | 1966-2023 | −701 | −4.70*** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





