Submitted:
28 July 2025
Posted:
29 July 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
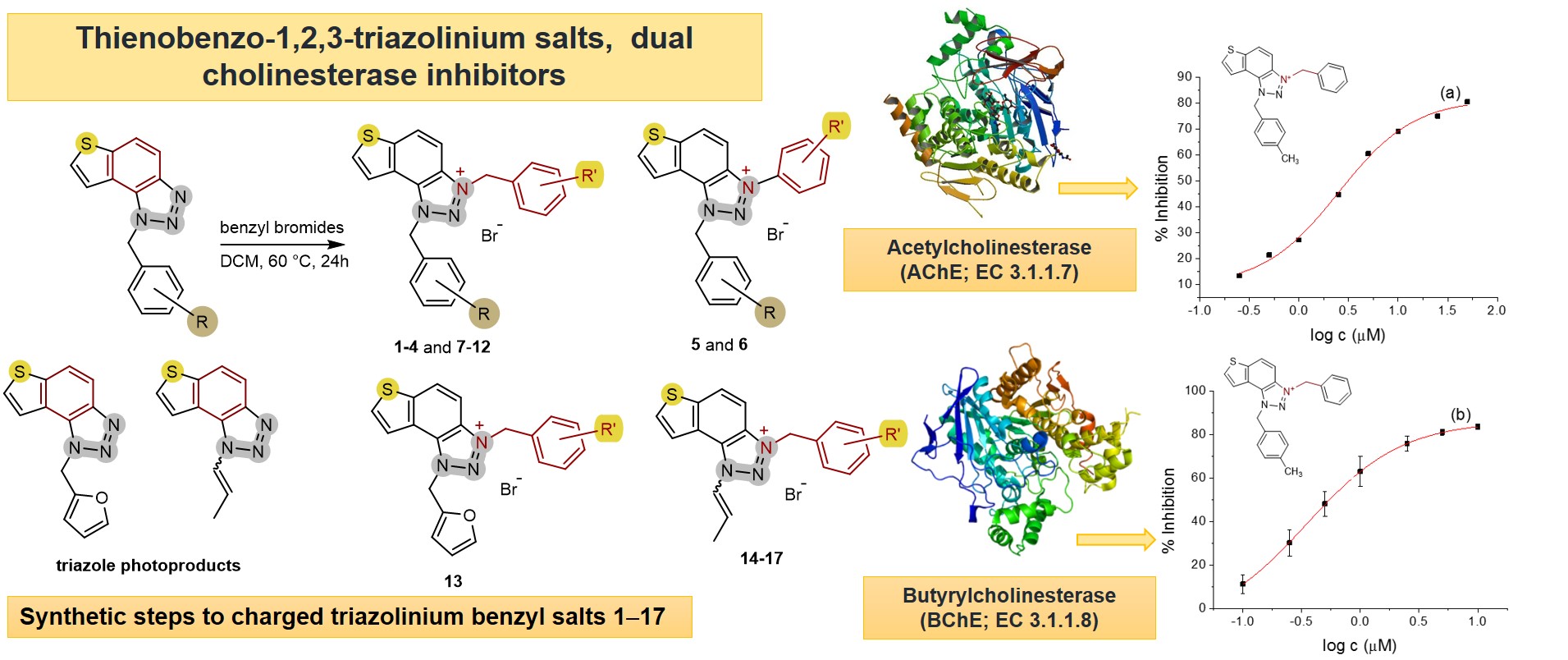
2. Results and Discussion
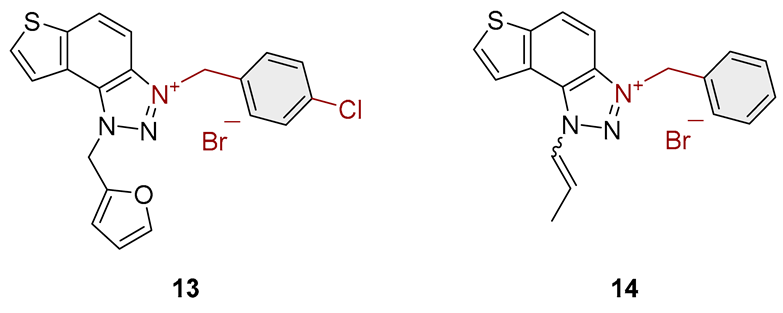
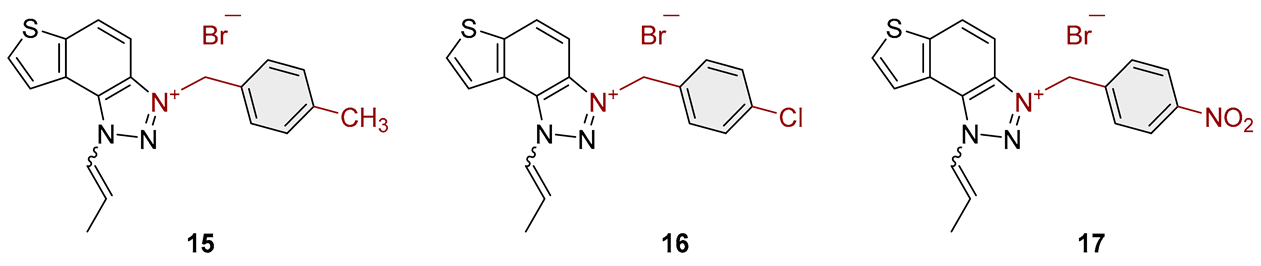
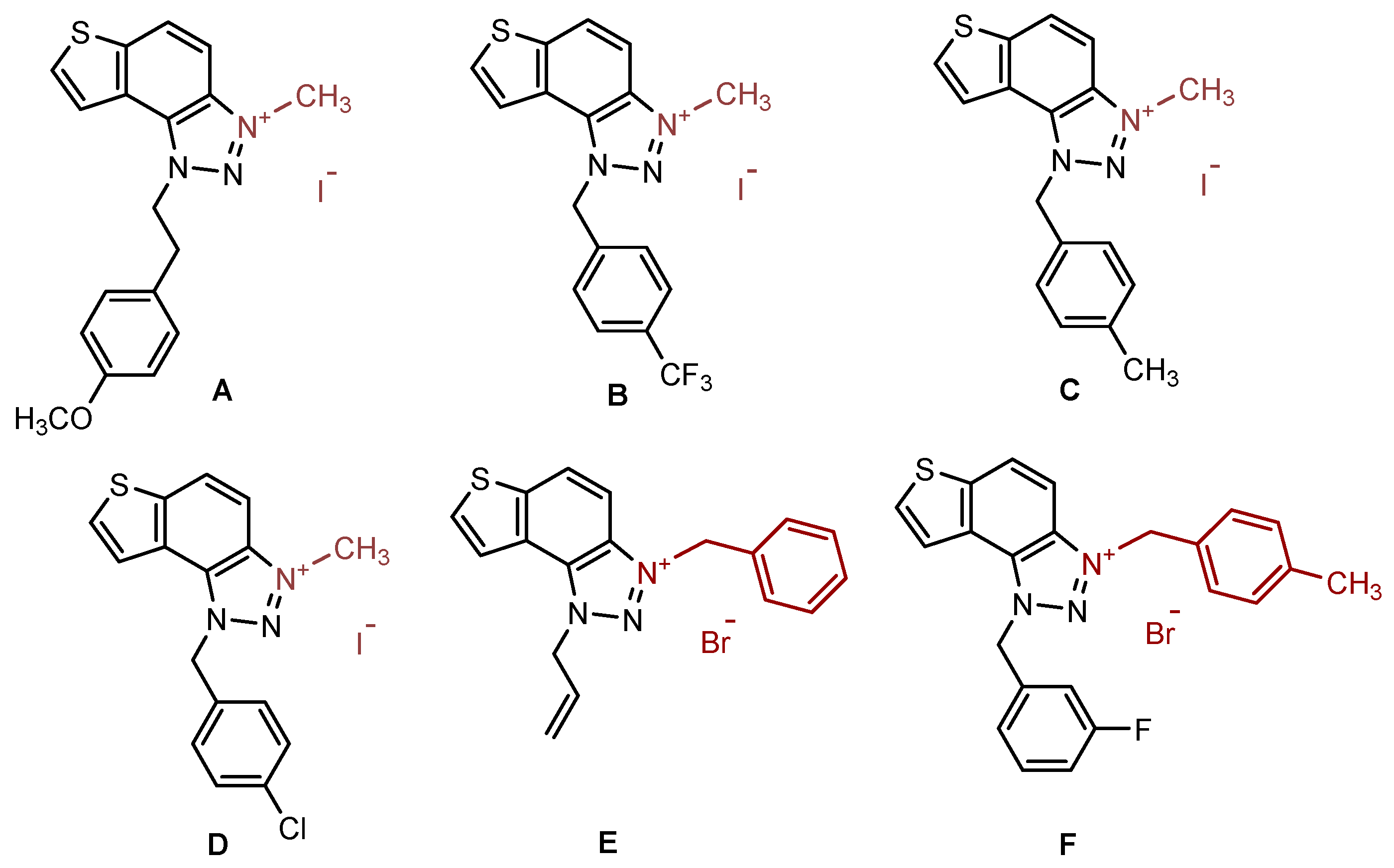
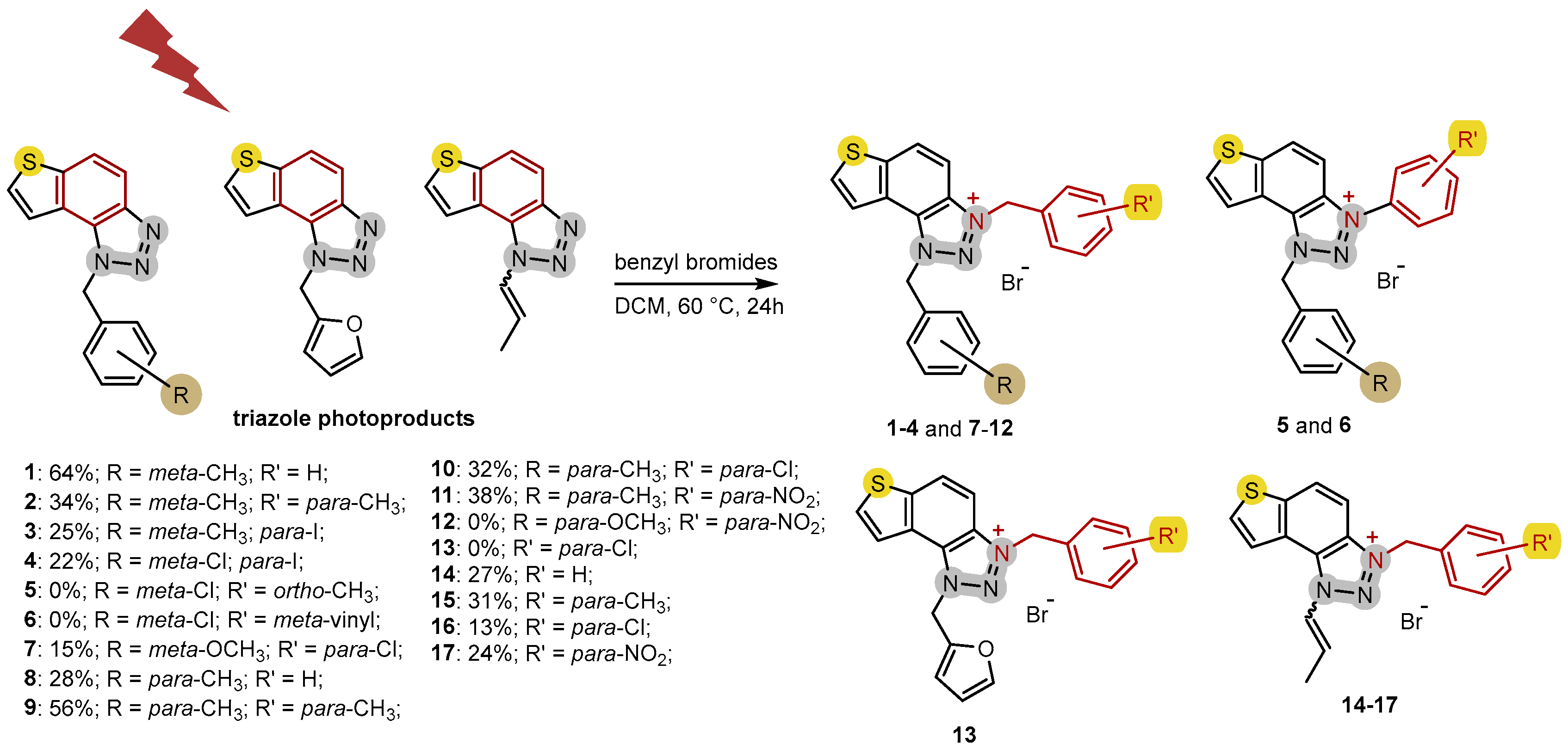
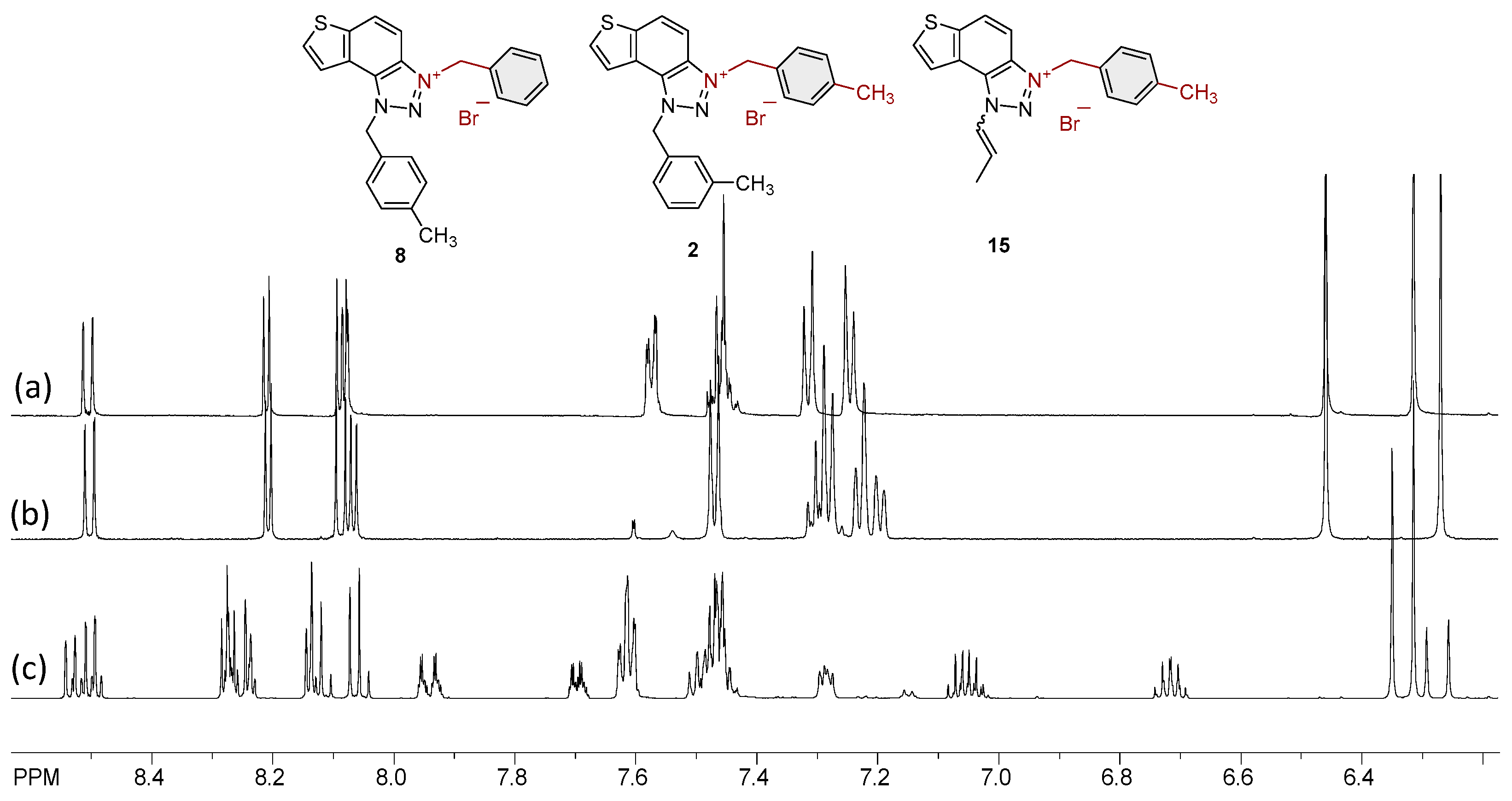
2.1. Photochemically-Assisted Synthesis of Charged Thienobenzo-1,2,3-Triazoles 1–17
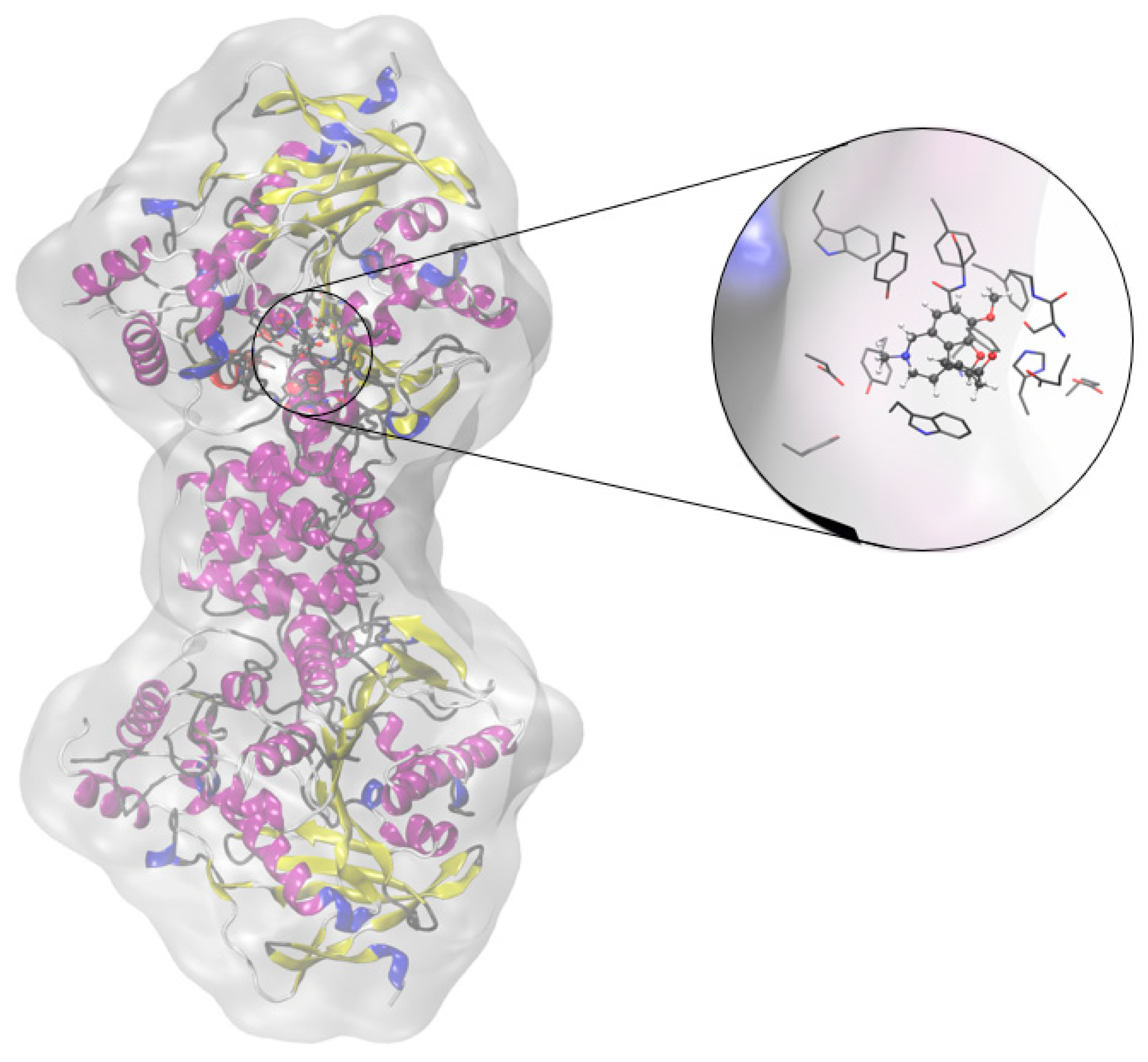
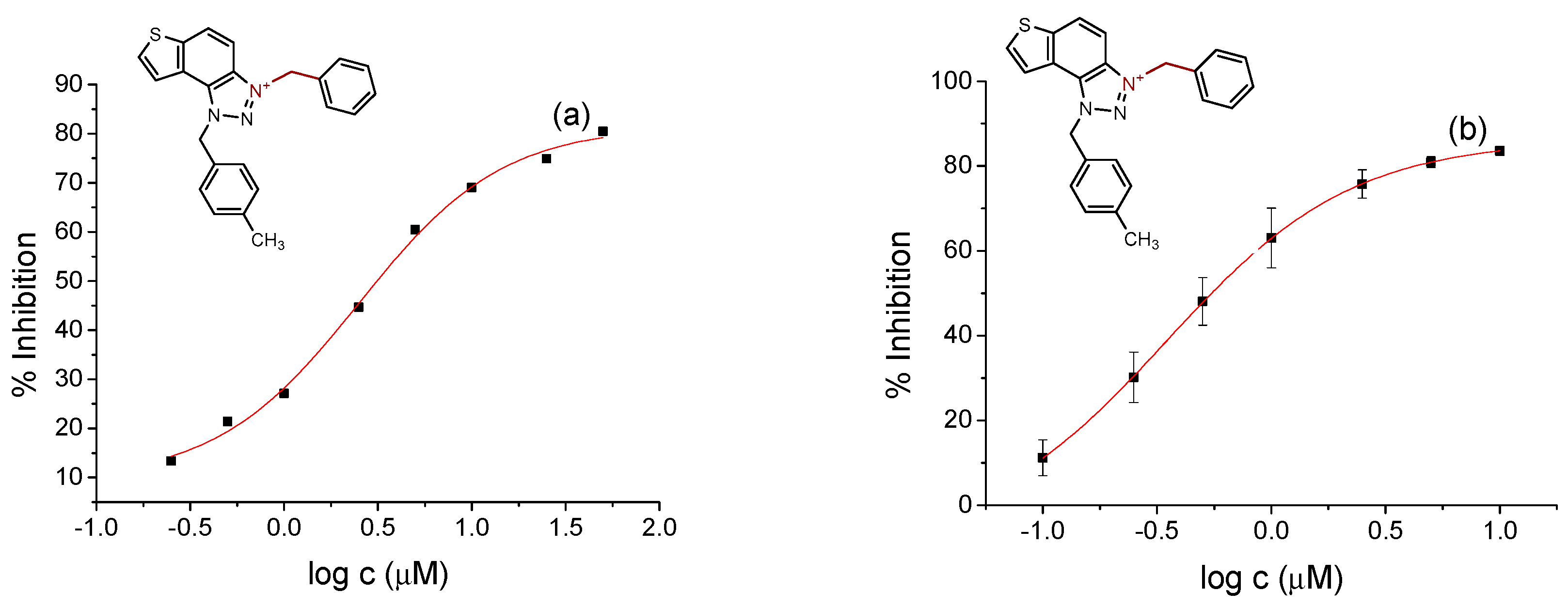
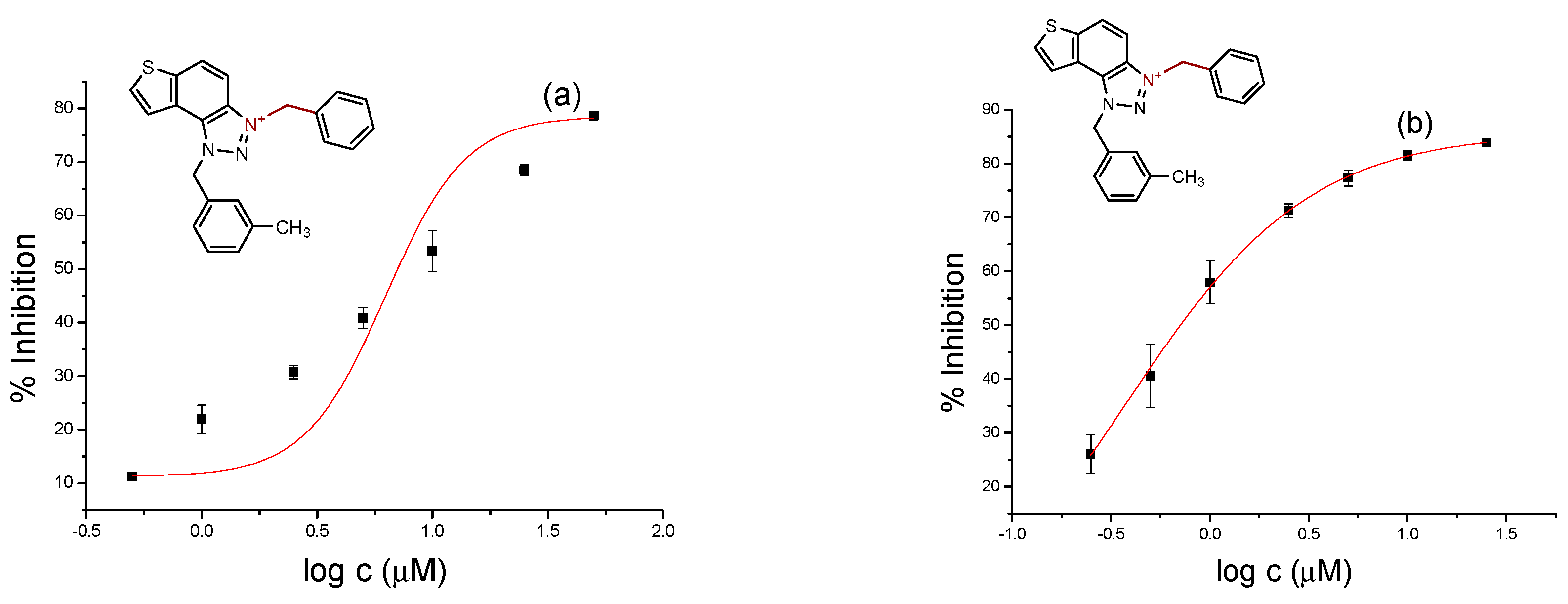
2.2. Cholinesterase Inhibition Activity of Triazolinium Salts 1–17
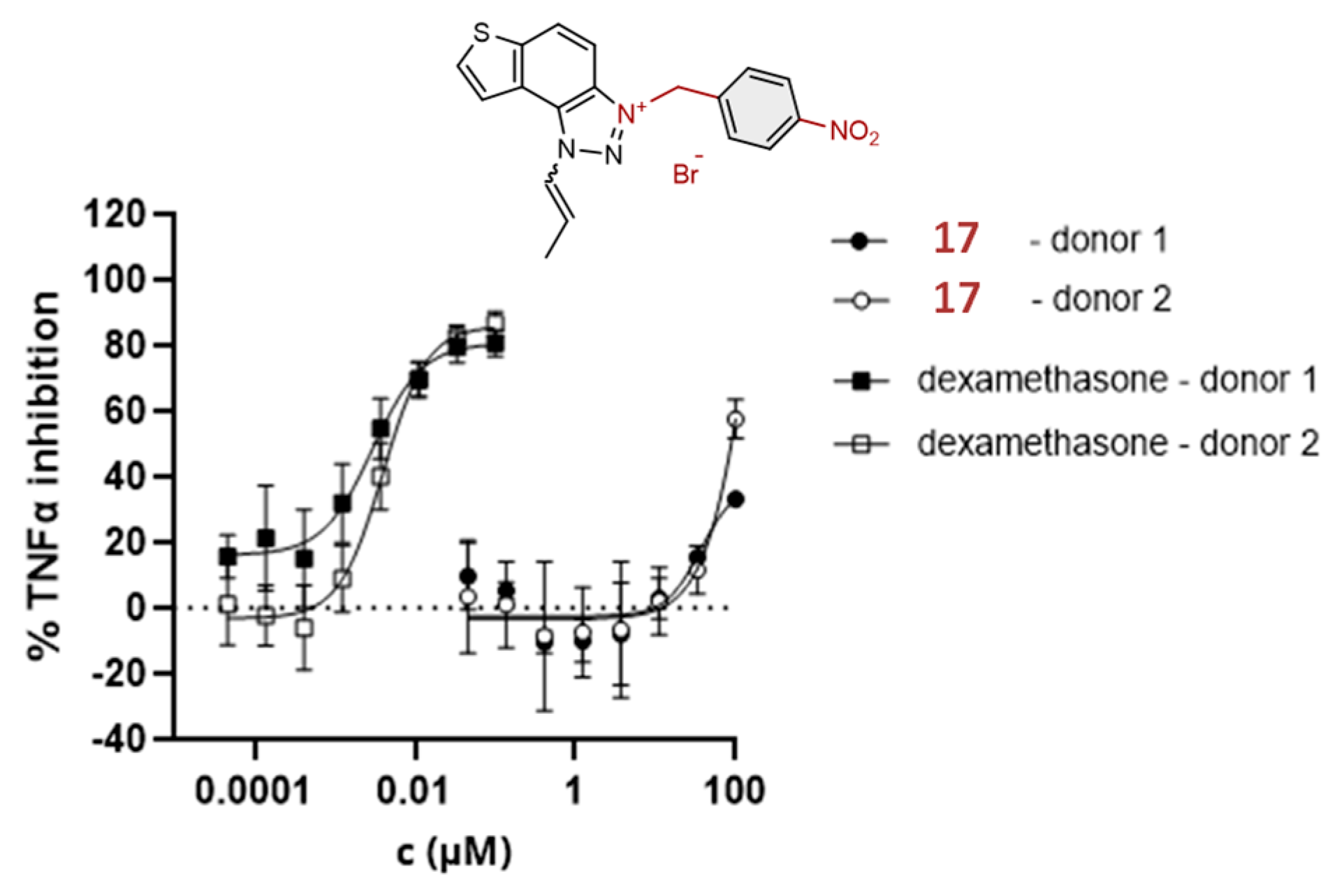
2.3. Anti-Inflammatoty Activity of Triazolinium Salts 1–17
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Remarks
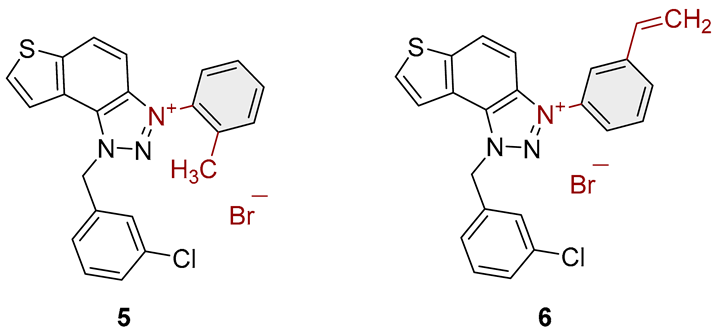
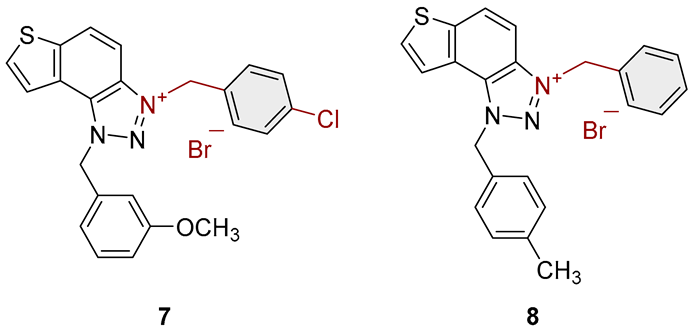
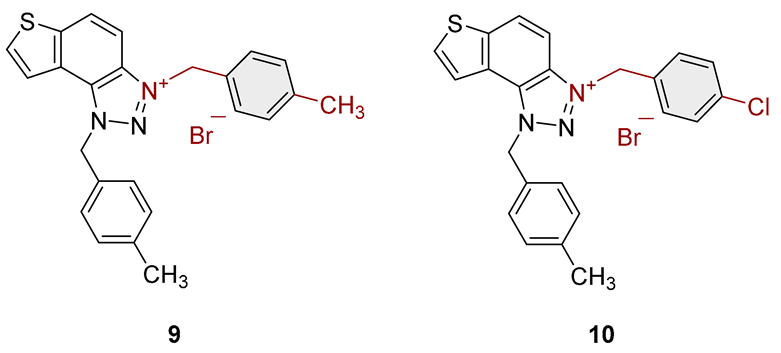
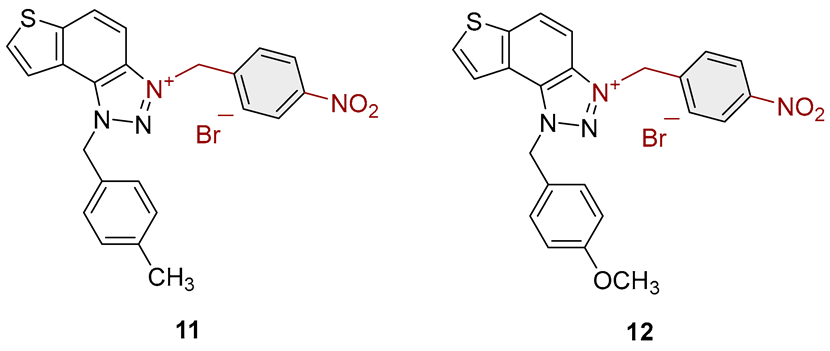
3.2. Synthesis of Bromide Salts 1–17
3.3. In Vitro Cholinesterase Inhibition Activity Measurements of Bromide Salts 1–17
3.4. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of 1–17
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pohanka, M. Inhibitors of Acetylcholinesterase and Butyrylcholinesterase Meet Immunity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 9809–9825. [CrossRef]
- Bajda, M.; Więckowska, A.; Hebda, M.; Guzior, N.; Sotriffer, C.A.; Malawska, B. Structure-Based Search for New Inhibitors of Cholinesterases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 5608–5632. [CrossRef]
- Trang, A.; Khandhar, P.B. Physiology, Acetylcholinesterase. In: StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island (FL), 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539735/ (accessed on 11 June, 2025).
- Masson, P.; Shaihutdinova, Z.; Lockridge, O. Drug and Pro-Drug Substrates and Pseudo-Substrates of Human Butyrylcholinesterase. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2023, 218, 115910. [CrossRef]
- Mesulam, M.M.; Guillozet, A.; Shaw, P.; Levey, A.; Duysen, E.G.; Lockridge, O. Acetylcholinesterase Knockouts establish Central Cholinergic Pathways and can use Butyrylcholinesterase to Hydrolyze Acetylcholine. Neuroscience 2002, 110, 627–639. [CrossRef]
- Guillozet, A.L.; Smiley, J.F.; Mash, D.C. Butyrylcholinesterase in the Life Cvcle of Amyloid Plaques. Ann. Neurol. 1997, 42, 909–918. [CrossRef]
- Mesulam, M.M.; Geula, C. Butyrylcholinesterase Reactivity Dfierentiates the Amyloid Plaques of Aging from Those of Dementia. Ann. Neurol. 1994, 36, 722–727. [CrossRef]
- Darvesh, S.; Walsh, R.; Kumar, R.; Caines, A.; Roberts, S.; Magee, D.; Rockwood, K.; Martin, E. Inhibition of Human Cholinesterases by Drugs Used to Treat Alzheimer Disease. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 2003, 17, 117–126. [CrossRef]
- Cacabelos, R.; Martínez-Iglesias, O.; Cacabelos, N.; Carrera, I.; Corzo, L.; Naidoo, V. Therapeutic Options in Alzheimer’s Disease: From Classic Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors to Multi-Target Drugs with Pleiotropic Activity. Life 2024, 14, 1555. [CrossRef]
- Anand, P.; Singh, B. A Review on Cholinesterase Inhibitors for Alzheimer’s Disease. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2013, 36, 375–399. [CrossRef]
- Talesa, V.N. Acetylcholinesterase in Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Drug Targets 2001, 2, 363–373.
- Greig, N.H.; Utsuki, T.; Yu, Q.S.; Holloway, H.W. A New Therapeutic Target in Alzheimer’s Disease Treatment: Selective Butyrylcholinesterase Inhibition. Curr. Med. Chem. 2005, 12, 237–243.
- Mesulam, M.M.; Guillozet, A.; Shaw, P.; Levey, A. Acetylcholinesterase knockouts establish centrality of cholinergic networks. Ann. Neurol. 2002, 52, 253–256.
- Lane, R.M.; Potkin, S.G.; Enz, A. Targeting Acetylcholinesterase and Butyrylcholinesterase in Dementia. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2006, 1, 101-24. https://doi: 10.1017/S1461145705005833.
- Singh, M.; Kaur, M.; Kukreja, H.; Chugh, R.; Silakari, O.; Singh, D. Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors as Alzheimer therapy: From Nerve Toxins to Neuroprotection, Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 70, 165-188. [CrossRef]
- Roth, B.L.; Driscol, J.; Glennon, R.A. Drugs with Anticholinergic Properties: Functional Roles and Side Effects. Pharmacol. Rev. 2002, 54, 364–385.
- Bosak, A.; Ramić, A.; Šmidlehner, T.; Hrenar, T.; Primožič, I.; Kovarik, Z. Design and Evaluation of Selective Butyrylcholinesterase Inhibitors based on Cinchona Alkaloid Scaffold. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0205193. [CrossRef]
- Bosak, A.; Opsenica, D.M.; Šinko, G.; Zlatar, M.; Kovarik, Z. Structural Aspects of 4-Aminoquinolines as Reversible Inhibitors of Human Acetylcholinesterase and Butyrylcholinesterase. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2019, 308, 101–109. [CrossRef]
- Mamedova, G.; Mahmudova, A.; Mamedov, S.; Erden, Y.; Taslimi, P.; Tüzün, B.; Tas, R.; Farzaliyev, V.; Sujayev, A.; Alwasel, S.H.; Gulçin, I. Novel Tribenzylaminobenzolsulphonylimine based on their Pyrazine and Pyridazines: Synthesis, Characterization, Antidiabetic, Anticancer, Anticholinergic, and Molecular Docking Studies. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 93, 103313. [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, N.A.E.; El-Said Farag, A.; Ezzat, M.A.F.; Akincioglu, H.; Gulçin, I.; Abou-Seri, S.M. Design, Synthesis, In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation of Novel Pyrrolizine-based Compounds with Potential Activity as Cholinesterase Inhibitors and Anti-Alzheimer's Agents. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 93, 103312. [CrossRef]
- Taslimi, P.; Türkan, F.; Cetin, A.; Burhan, H.; Karaman, M.; Bildirici, I.; Gulçin, I.; Şen, F. Pyrazole[3,4-d]pyridazine Derivatives: Molecular docking and Explore of Acetylcholinesterase and Carbonic Anhydrase Enzymes Inhibitors as Anticholinergics Potentials. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 92, 103213. [CrossRef]
- Katalinić, M.; Bosak, A.; Kovarik, Z. Flavonoids as Inhibitors of Human Butyrylcholinesterase Variants. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2014, 52, 64–67.
- Mlakić, M.; Odak, I.; Faraho, I.; Talić, S.; Bosnar, M.; Lasić, K.; Barić, D.; Škorić, I. New Naphtho/thienobenzo-triazoles with Interconnected Anti-inflammatory and Cholinesterase Inhibitory Activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 241, 114616. [CrossRef]
- Mlakić, M.; Selec, I.; Ćaleta, I.; Odak, I.; Barić, D.; Ratković, A.; Molčanov, K.; Škorić, I. New Thienobenzo/Naphtho-Triazoles as Butyrylcholinesterase Inhibitors: Design, Synthesis and Computational Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5879. [CrossRef]
- Mlakić, M.; Faraho, I.; Odak, I.; Kovačević, B.; Raspudić, A.; Šagud, I.; Bosnar, M.; Škorić, I.; Barić, D. Cholinesterase Inhibitory and Anti-Inflammatory Activity of the Naphtho- and Thienobenzo-Triazole Photoproducts: Experimental and Computational Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14676. [CrossRef]
- Mlakić, M.; Faraho, I.; Odak, I.; Talić, S.; Vukovinski, A.; Raspudić, A.; Bosnar, M.; Zadravec, R.; Ratković, A.; Lasić, K.; Marinić, M.; Barić, D.; Škorić, I. Synthesis, Photochemistry and Computational Study of novel 1,2,3-Triazole Heterostilbenes: Expressed Biological Activity of their Electrocyclization Photoproducts, Bioorg. Chem. 2022, 121, 105701. [CrossRef]
- Mlakić, M.; Barić, D.; Ratković, A.; Šagud, I.; Čipor, I.; Piantanida, I.; Odak, I.; Škorić, I. New Charged Cholinesterase Inhibitors: Design, Synthesis, and Characterization. Molecules 2024, 29, 1622. [CrossRef]
- Krátký, M.; Vinšová, J.; Buchta, V.; Stolaříková, J. Quaternary Ammonium-based Cholinesterase Inhibitors: Synthesis and Biological Evaluation. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 1125–1130.
- Mlakić, M.; Sviben, M.; Ratković, A.; Raspudić, A.; Barić, D.; Šagud, I.; Lasić, Z.; Odak, I.; Škorić, I. Efficient Access to New Thienobenzo-1,2,3-Triazolium Salts as Preferred Dual Cholinesterase Inhibitors. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 1391. [CrossRef]
- Jelčić, A.; Raspudić, A.; Barić, D.; Ratković, A.; Šagud, I.; Pongrac, P.; Štefok, D.; Bosnar, M.; Roca, S.; Lasić, Z.; et al. Charged Thienobenzo-1,2,3-Triazoles as Especially Potent Non-Selective Cholinesterase Inhibitors: Design, Anti-Inflammatory Activity, and Computational Study. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1032. [CrossRef]
- Ratković, A.; Mlakić, M.; Dehaen, W.; Opsomer, T.; Barić, D.; Škorić, I. Synthesis and Photochemistry of novel 1,2,3-Triazole di-Heterostilbenes. An Experimental and Computational Study. Spectrochim. Acta. Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2021, 261, 120056. [CrossRef]
- Ellman, G.L.; Courtnex, K.D.; Andres, V.; Featherstone, R.M. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1961, 7, 88-95. [CrossRef]
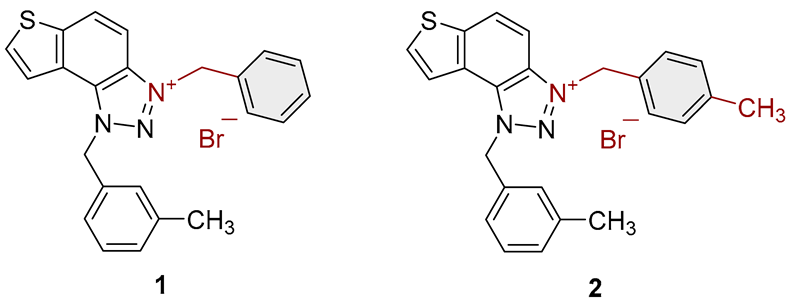
| Compound | Structure | AChE | BChE | ||
| IC50 /μM | Inhibition* (%) | IC50 /μM | Inhibition* (%) | ||
| 1 | 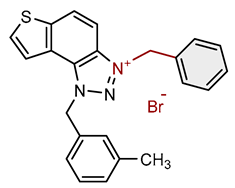 |
6.3 | 78.6 ± 0.5 (50) | 0.4 | 83.9 ± 0.2 (25) |
| 2 | 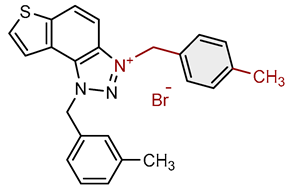 |
4.1 | 82.1 ± 4.2 (50) | 0.3 | 77.6 ± 0.3 (2.5) |
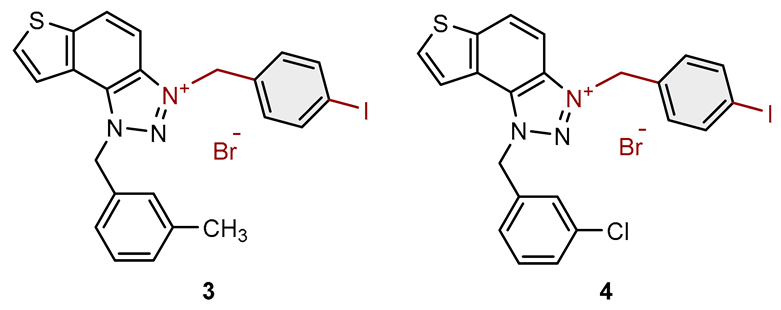
| 3 | 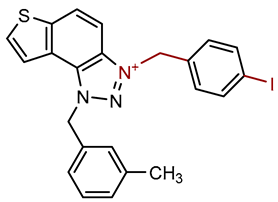 |
5.9 | 76.7 ± 0.5 (50) | 0.7 | 84.9 ± 3.6 (50) |
| 4 | 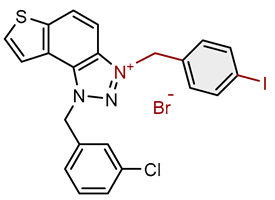 |
14.2 | 74.6 ± 5.0 (50) | 0.8 | 83.2 ± 0.9 (25) |
| 7 | 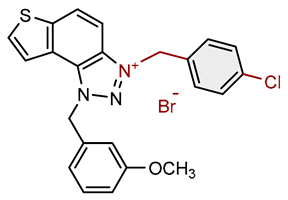 |
11.8 | 79.4 ± 4.9 (100) | 1.0 | 78.2 ± 0.4 (10) |
| 8 | 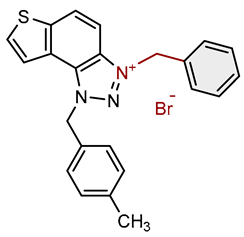 |
2.6 | 80.7 ± 2.3 (50) | 0.4 | 83.6 ± 1.0 (10) |
| 9 | 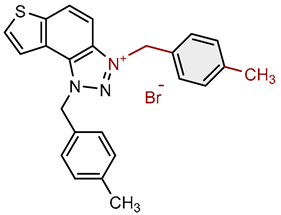 |
5.7 | 78.7 ± 0.6 (50) | 3.5 | 76.6 ± 0.4 (25) |
| 10 | 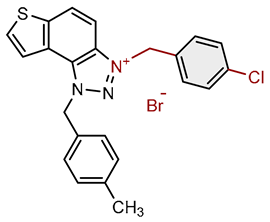 |
6.5 | 81.9 ± 0.6 (100) | 1.5 | 79.9 ± 1.1 (25) |
| 11 | 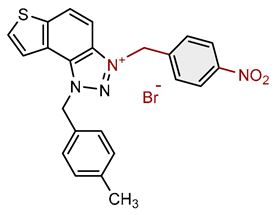 |
3.2 | 83.6 ± 2.1 (50) | 2.7 | 81.1 ± 1.7 (25) |
| 14 | 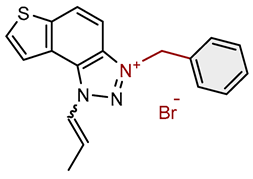 |
4.3 | 84.2 ± 0.5 (100) | 1.0 | 80.4 ± 2.9 (25) |
| 15 | 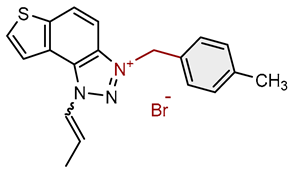 |
14.4 | 82.3 ± 0.8 (250) | 0.9 | 84.0 ± 0.7 (50) |
| 16 | 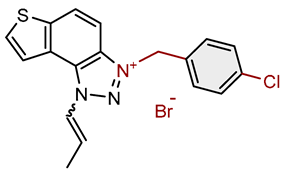 |
5.4 | 82.6 ± 1.1 (250) | 2.3 | 84.8 ± 0.8 (100) |
| 17 | 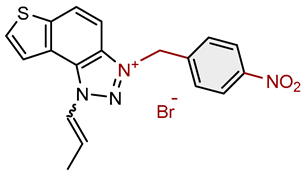 |
63.8 | 62.6 ± 5.3 (100) | 11.4 | 85.5 ± 0.5 (100) |
| Galantamine [29] | 0.15 | - | 7.9 | - | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





