Submitted:
06 August 2025
Posted:
08 August 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Método
Eligibility Criteria of the Studies and Selection Process
Search Strategy
Included Studies
Bias Assessment
Data Análisis
Results
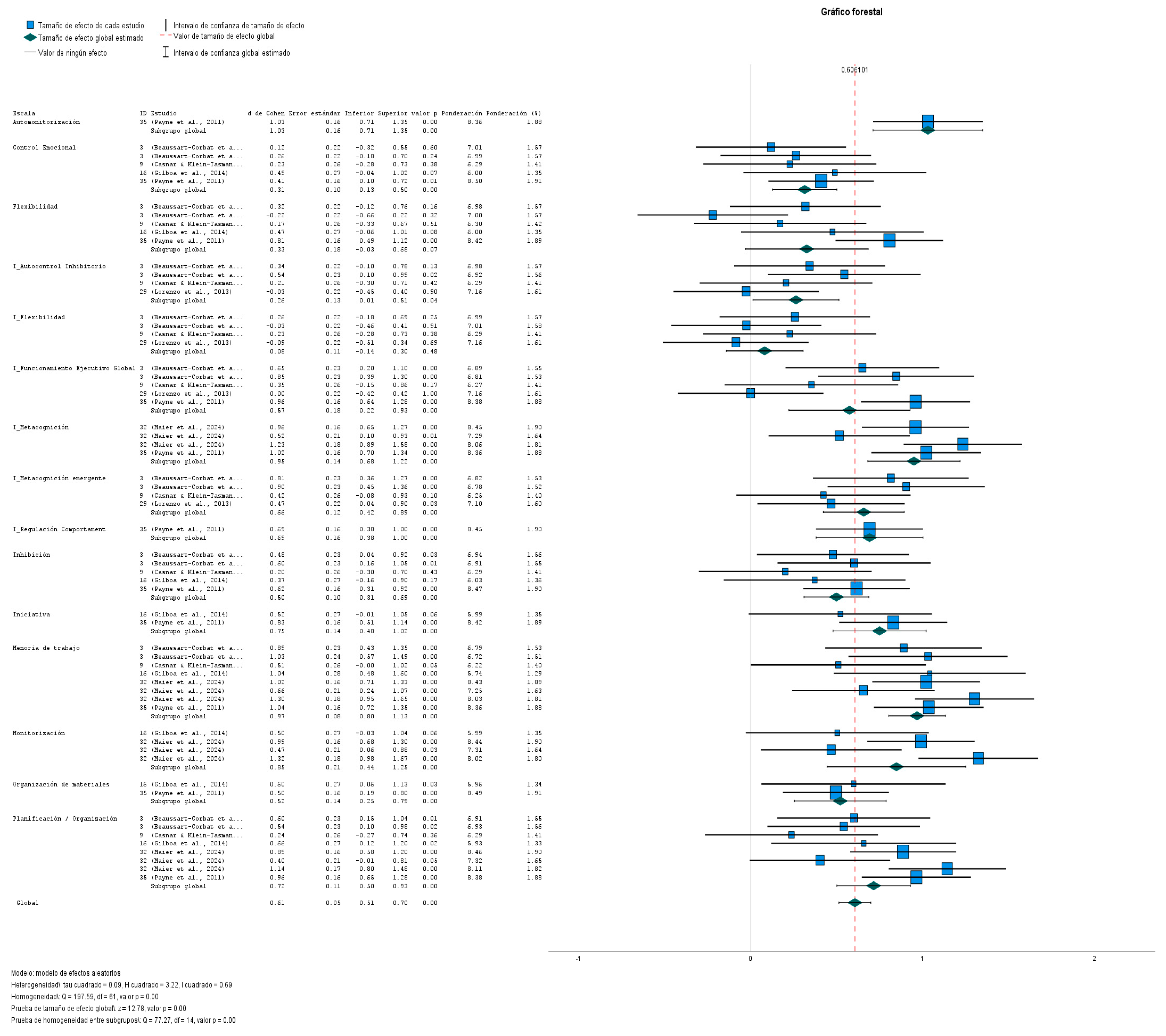
Effect Measures
Homogeneity and Heterogeneity
Forest Plot
Global Effect Size Test
Discussion
Limitations
Conclusions
ANNEX 1: Search Strategy
ANNEX 2: Studies Included in the Meta-Analysis
| Nº | Estudio | Revista/Especifica de oncología | Títle (BRIEF) | País | Sample (n) |
Cancer | Age (diagnosis and/or evaluation) | Sex N(SD) | Methodology | Design | Instrument | Specific results | Meta-analysis |
| 1. | (Beaussart-Corbat et al., 2021) | Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology / NO | NO | France | NF1 Group: (n=33) Control Group: (n=52) Informants: Parents (n=31) Teachers: (n=18) |
Neurofiromatosis Type 1 (NF1) |
3–5 years G. NF1: 56.67 (11.27) months Control Group: 55.75 (10.37) months |
NF1 Group: 17/16 (male/female) Control Group: 27/25 (male/female) |
IV: NF1 Group vs. Control Group DV: BRIEF-P Intellectual Ability (WPPSI-IV) |
Comparative-causal | BRIEF-P (parents and teachers) |
Parents: Flexibility, Inhibition Teachers: Global, Inhibition, and Emotional Control |
YES Informant: parents teachers |
| 2. | (Casnar & Klein-Tasman, 2016) | Journal of Pediatric Psychology / NO | NO | Wisconsin (EE.UU) | NF1 Group: (n=26) Control Group: (n=37) |
Neurofibromatosis Type 1 (NF1) |
NF1 4.53 (0.87) Control Group: l 4.51 (0.89) |
NF1 Men: 17 (65%) Women: 9 (34%) Control Group Men: 23 (62%) Women: 14 (38%) |
IV: NF1 Group vs. Control Group DV: Executive Functioning (BRIEF-P) |
Comparative-causal | BRIEF-P | Executive Functioning of NF1 | YES Informant: parents |
| 3. | (Gilboa et al., 2014) | Neuropsychological Rehabilitation /NO | NO | Israel | NF1 Group: (n= 29) Control Group: (n=27) |
Neurofibromatosis Tipo I (NF1) | NF1 12.3 (2.6) G. Control 12.4 (2.5) |
NF1 Men: 8 Women: 21 Control Group Men: 8 Women: 19 |
IV: NF1 Group vs. Control Group DV: BADS-C BRIEF–Parents ACES–Teacher |
Comparative-causal | BRIEF parents |
Predictor of academic performance | YES Informant: parents |
| 4. | (Lorenzo et al., 2013) | The Journal of Pediatrics / NO | NO | Australia | NF1 Group: (n=43) Control Group: (n=43) |
Neurofibromatosis Tipo 1 (NF1) | NF1 Group 40.23 (0.72) months Control Group 40.16 (0.48) months |
NF1 Group M = 32 (74%) F = 11 (26%) Control Group M = 32 (74%) F = 11 (26%) |
IV: NF1 Group vs. Control Group DV: BASC – II BRIEF-P CADS-P |
Comparativo-causal | BRIEF-P parents |
Preschoolers Cognitive and executive profile |
YES Informant: parents |
| 5. | (Maier et al., 2024) | Child Neuropsychology / NO | NO | Australia | Control Group: (n=55) NF1 Group (n=191): Typical (n=41) NF1 Group: Bordelin (n=30) NF1 Group: Impaired (n=120) |
Neurofribromatosis Tipe 1 (NF1) |
Control 11.81 (2.61) NF1 10.38 (2.36) Typical NF1 11.61 (2.75) Borderline NF1 9.98 (2.29) Impaired NF1 10.06 (2.11) |
Men = Control 22 (40%) NF1 104 (54.45%) Typical NF1 27 (65.85%) Borderline NF1 13 (56.67%) Impaired NF1 64 (53.33%) |
IV: NF1 Group vs. Control Group DV: RCFT, IQ, Visuospatial abilities, BRIEF, Tower of London, The Conners ADHD DSM-IV Scales (CDAS) |
Comparative-causal | BRIEF | FE global | YES Informant: parents |
| 6. | (Payne et al., 2011) | Child Neuropsychology / NO | NO | Australia | NF1 Group: (n=168) Control Group: (n=55) |
Neurofibromatosis Tipe 1 (NF1) |
6–16 NF1 Group = 10.62 (2.28) Control Group = 11.24 |
G. NF1= H=108 M=91 G. Control |
VI; G. NF1 vs. G Control VD: BRIEF, Conners`ADHD DSM-IV Scales (CADS), Wechsler Intelligence Scales for Children-Third Edition or Fourth Edition (WISC-III / WISC-IV) |
Comparative-causal | BRIEF (parents and teachers) |
Attention | YES |
References
- Benzing, V.; Siegwart, V.; Anzeneder, S.; Spitzhüttl, J.; Grotzer, M.; Roebers, C.M.; Steinlin, M.; Leibundgut, K.; Everts, R.; Schmidt, M. The mediational role of executive functions for the relationship between motor ability and academic performance in pediatric cancer survivors. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 2022, 60. [CrossRef]
- Vega, J.N.; Dumas, J.; Newhouse, P.A. Cognitive Effects of Chemotherapy and Cancer-Related Treatments in Older Adults. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2017, 25, 1415–1426. [CrossRef]
- Lehtonen, A.; Howie, E.; Trump, D.; Huson, S.M. Behaviour in children with neurofibromatosis type 1: cognition, executive function, attention, emotion, and social competence. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2012, 55, 111–125. [CrossRef]
- Hendrickson, N.; McCrimmon, A. Test Review: Behavior Rating Inventory of Executive Function®, Second Edition (BRIEF®2) by Gioia, G.A., Isquith, P.K., Guy, S.C., & Kenworthy, L. Can. J. Sch. Psychol. 2019, 34, 73–78.
- Roth, R.M.; Isquith, P.K.; Gioia, G.A. Behavioral Rating Inventory of Executive Function—Adult version. Psychological Assessment Resources; 2005.
- Isquith, P.K.; Crawford, J.S.; Espy, K.A.; Gioia, G.A. Assessment of executive function in preschool-aged children. Ment. Retard. Dev. Disabil. Res. Rev. 2005, 11, 209–215. [CrossRef]
- Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. PLoS Med. 29 de marzo de 2021;18(3):e1003583.
- Santos, C.M.d.C.; Pimenta, C.A.d.M.; Nobre, M.R.C. The PICO strategy for the research question construction and evidence search. Rev. Latino-Americana de Enferm. 2007, 15, 508–511. [CrossRef]
- Wells GA, Wells G, Shea B, Shea B, O’Connell D, Peterson J, et al. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for Assessing the Quality of Nonrandomised Studies in Meta-Analyses. En 2014. Disponible en: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:79550924.
- Beaussart-Corbat, M.-L.; Barbarot, S.; Farges, D.; Martin, L.; Roy, A. Executive functions in preschool-aged children with neurofibromatosis type 1: Value for early assessment. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 2021, 43, 163–175. [CrossRef]
- Casnar, C.L.; Klein-Tasman, B.P. Parent and Teacher Perspectives on Emerging Executive Functioning in Preschoolers With Neurofibromatosis Type 1: Comparison to Unaffected Children and Lab-Based Measures. J. Pediatr. Psychol. 2016. [CrossRef]
- Gilboa, Y.; Rosenblum, S.; Fattal-Valevski, A.; Toledano-Alhadef, H.; Rizzo, A.(.; Josman, N. Using a Virtual Classroom environment to describe the attention deficits profile of children with Neurofibromatosis type 1. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2011, 32, 2608–2613. [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, J.; Barton, B.; Arnold, S.S.; North, K.N. Cognitive Features that Distinguish Preschool-Age Children with Neurofibromatosis Type 1 from Their Peers: A Matched Case-Control Study. J. Pediatr. 2013, 163, 1479–1483.e1. [CrossRef]
- Maier, S.; van Elst, L.T.; Philipsen, A.; Lange, T.; Feige, B.; Glauche, V.; Nickel, K.; Matthies, S.; Alm, B.; Sobanski, E.; et al. Effects of 12-Week Methylphenidate Treatment on Neurometabolism in Adult Patients with ADHD: The First Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled MR Spectroscopy Study. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2601. [CrossRef]
- Payne, J.M.; Hyman, S.L.; Shores, E.A.; North, K.N. Assessment of executive function and attention in children with neurofibromatosis type 1: Relationships between cognitive measures and real-world behavior. Child Neuropsychol. 2011, 17, 313–329. [CrossRef]
- Higgins JPT, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Statistics in Medicine. 15 de junio de 2002;21(11):1539-58.
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [CrossRef]
- Roy S, Mandal N, Ray A, Roy PK, Bhattacharyya A, Saha PK. Effectiveness of neurofeedback training, behaviour management including attention enhancement training and medication in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder – A comparative follow up study. Asian Journal of Psychiatry. 2022;76:103133.
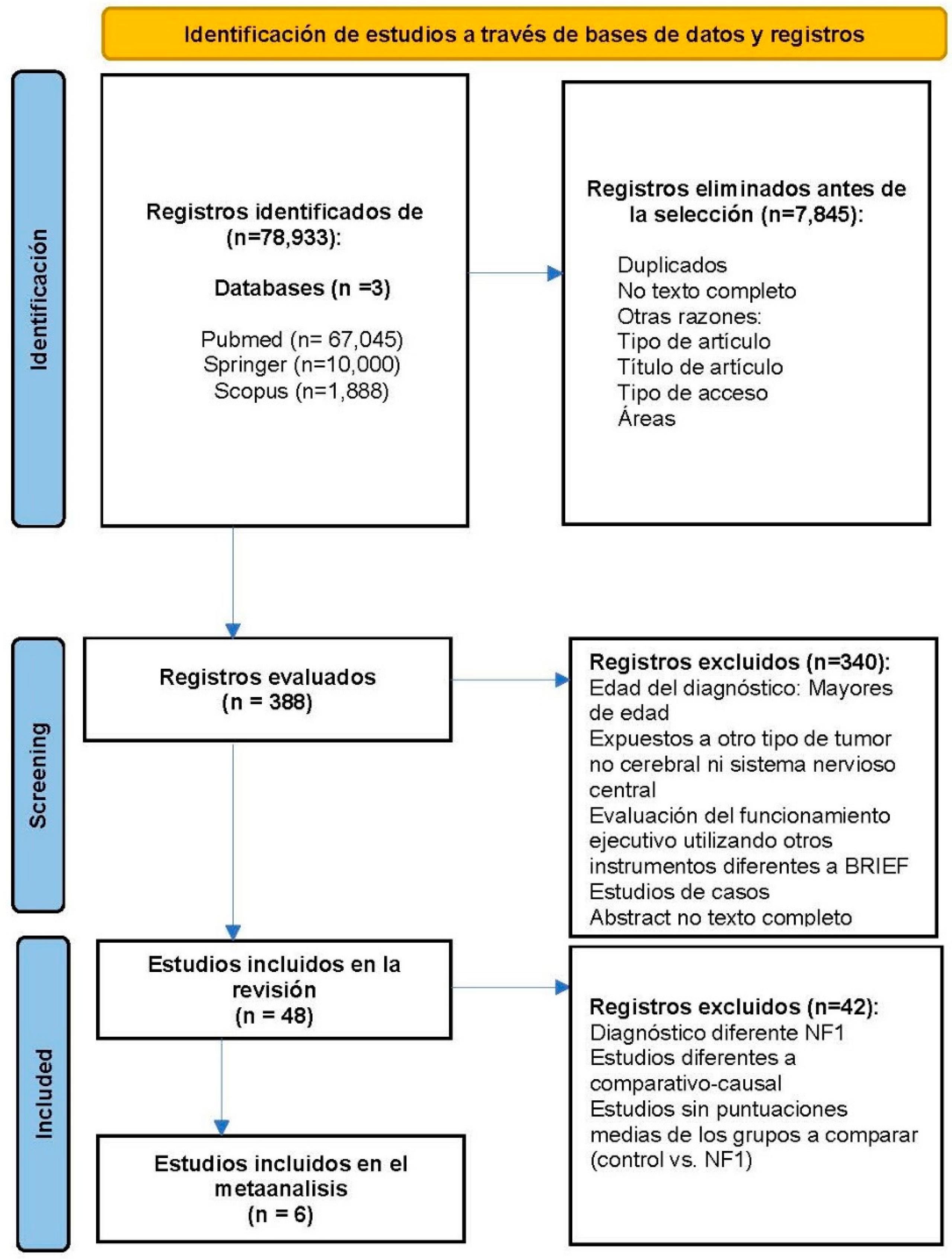
| Inclusion | Exclusion |
| Age at diagnosis: Individuals under 18 years of both sexes | Age at diagnosis: Adults |
| Exposed to a brain tumor in pediatric age and/or exposed to oncological treatments during the fetal period | Exposed to other types of tumors not related to the brain or central nervous system |
| Evaluation of executive functioning using the BRIEF scales in their different versions and translations | Evaluation of executive functioning using other instruments |
| Ex post facto studies (descriptive, comparative-causal) | Case studies |
| Study | Type of study | Dimensions | Total | Risk | |||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | ||||
| 3 | Comparative-causal | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8 | Low |
| 9 | Comparative-causal | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8 | Low |
| 16 | Comparative-causal | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8 | Low |
| 29 | Comparative-causal | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 9 | Low |
| 32 | Comparative-causal | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 9 | Low |
| 35 | Comparative-causal | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 9 | Low |
| Clinical scales / Indixes / Informants | Effect size | Standard error | Z | Sig. (two-tailed) | 95% Confidence interval | 95% Prediction interval | ||||
| Lower | Upper | Lower | Upper | |||||||
| Clinical scales / Indixes | Automonitorizacióna | 1.031 | .1628 | 6.329 | <.001 | .712 | 1.350 | . | . | |
| Control Emocional | .314 | .0955 | 3.290 | .001 | .127 | .501 | .010 | .618 | ||
| Flexibilidad | .325 | .1825 | 1.783 | .075 | -.032 | .683 | -.901 | 1.552 | ||
| I_Autocontrol Inhibitorio | .264 | .1275 | 2.066 | .039 | .014 | .514 | -.464 | .992 | ||
| I_Flexibilidad | .081 | .1141 | .710 | .478 | -.143 | .305 | -.410 | .572 | ||
| I_Funcionamiento Ejecutivo Global | .575 | .1799 | 3.195 | .001 | .222 | .927 | -.642 | 1.792 | ||
| I_Metacognición | .949 | .1368 | 6.938 | <.001 | .681 | 1.218 | -.127 | 2.026 | ||
| I_Metacognición emergente | .658 | .1201 | 5.474 | <.001 | .422 | .893 | .092 | 1.223 | ||
| I_Regulación Comportamenta | .691 | .1588 | 4.353 | <.001 | .380 | 1.002 | . | . | ||
| Inhibición | .498 | .0962 | 5.180 | <.001 | .310 | .687 | .192 | .805 | ||
| Iniciativa | .750 | .1380 | 5.430 | <.001 | .479 | 1.020 | . | . | ||
| Memoria de trabajo | .968 | .0841 | 11.501 | .000 | .803 | 1.132 | .614 | 1.321 | ||
| Monitorización | .848 | .2057 | 4.121 | <.001 | .444 | 1.251 | -.925 | 2.621 | ||
| Organización de materiales | .521 | .1362 | 3.823 | <.001 | .254 | .788 | . | . | ||
| Planificación / Organización | .715 | .1092 | 6.548 | <.001 | .501 | .929 | .095 | 1.335 | ||
| Informants | Padres | .625 | .0501 | 12.484 | .000 | .527 | .724 | .022 | 1.229 | |
| Profesores | .494 | .1410 | 3.503 | <.001 | .218 | .771 | -.412 | 1.401 | ||
| Versions | BRIEF | .815 | .0511 | 15.959 | .000 | .715 | .915 | .375 | 1.255 | |
| BRIEF-P | .381 | .0577 | 6.595 | <.001 | .268 | .494 | -.085 | .847 | ||
| Global | .606 | .0474 | 12.783 | .000 | .513 | .699 | -.012 | 1.224 | ||
| a. It is based on the t-distribution | ||||||||||
| Test of homogeneity | Test of heterogeneity | |||||
| Chi-squared (Q statistic) | gl | Sig. | Tau square | H square | I square (%) | |
| Self-monitoring a | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| Emotional control | 1.731 | 4 | .785 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.0 |
| Flexibility | 15.193 | 4 | .004 | 0.115 | 3.378 | 70.4 |
| Index Inhibitory self-control | 3.526 | 3 | .317 | 0.012 | 1.234 | 19.0 |
| Index Flexibility | 1.770 | 3 | .621 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.0 |
| Index Global executive functioning | 14.681 | 4 | .005 | 0.114 | 3.481 | 71.3 |
| Index Metacognition | 7.067 | 3 | .070 | 0.044 | 2.436 | 58.9 |
| Index Emergent metacognition | 3.160 | 3 | .368 | 0.003 | 1.052 | 5.0 |
| Index Behavioral regulation a | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| Inhibition | 2.322 | 4 | .677 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.0 |
| Initiative | .949 | 1 | .330 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.0 |
| Working memory | 9.341 | 7 | .229 | 0.014 | 1.328 | 24.7 |
| Monitoring | 12.385 | 3 | .006 | 0.128 | 4.280 | 76.6 |
| Materials organization | .107 | 1 | .744 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.0 |
| Planning / Organization | 15.706 | 7 | .028 | 0.052 | 2.287 | 56.3 |
| Parents | 163.862 | 52 | <.001 | 0.088 | 3.163 | 68.4 |
| Teachers | 27.631 | 8 | <.001 | 0.127 | 3.451 | 71.0 |
| BRIEF | 67.367 | 30 | <.001 | 0.044 | 2.281 | 56.2 |
| BRIEF-P | 56.560 | 30 | .002 | 0.049 | 1.893 | 47.2 |
| Global | 197.594 | 61 | <.001 | 0.093 | 3.223 | 69.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




