Submitted:
14 July 2025
Posted:
16 July 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Luzhou-Flavour Liquor Manufacturing Process and Sample Collection
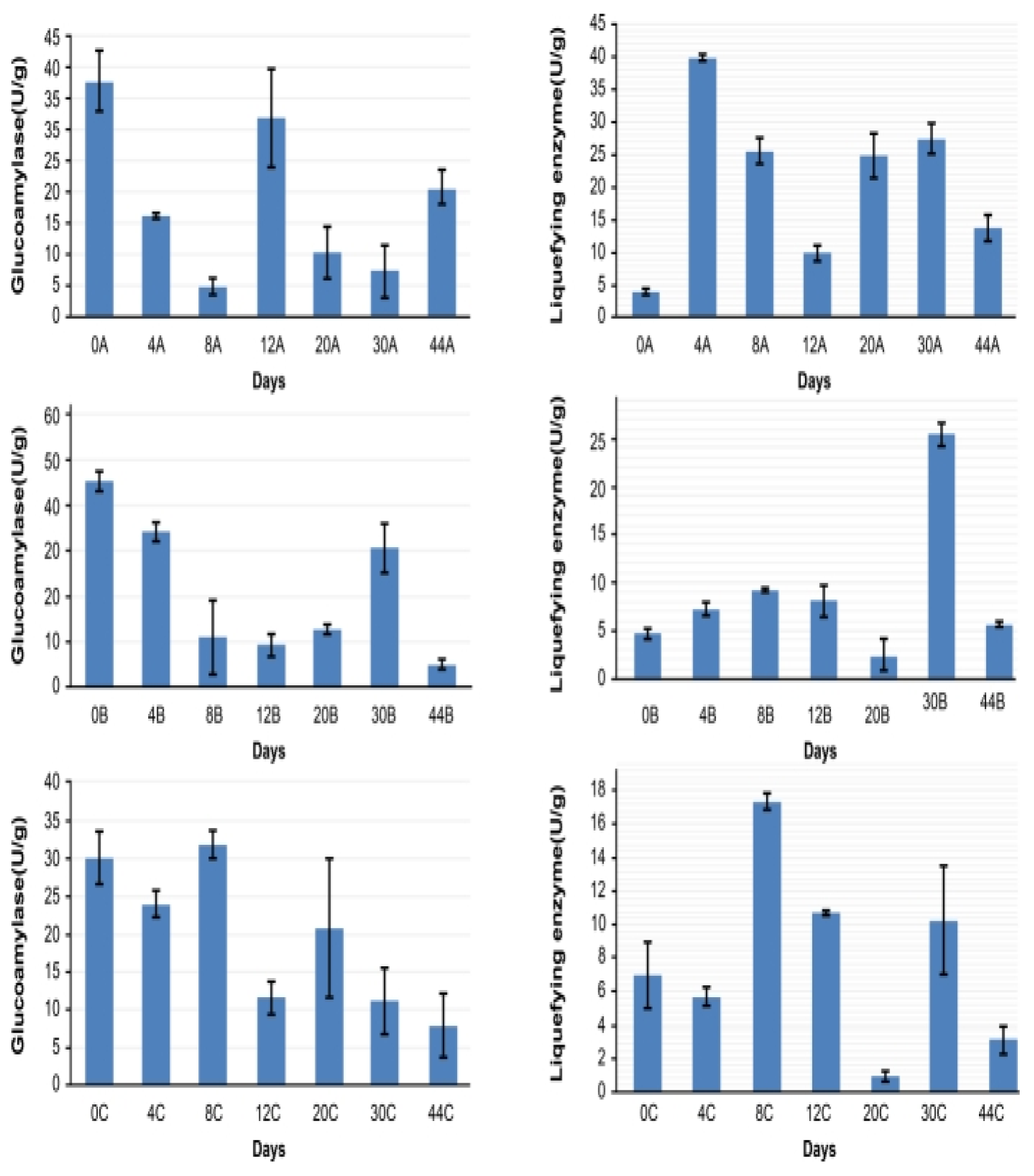
2.3. Analysis of Glucoamylase and Liquefying Enzyme Activity and Volatile Compound Content in Fermented Grains During Fermentation
2.4. High-Throughput Sequencing (HTS) Analysis
2.4.1. Extraction of Total DNA from Samples for HTS
2.4.2. Bioinformatics Analysis
Data Quality Control
Read Merging and Optimization
3. Results
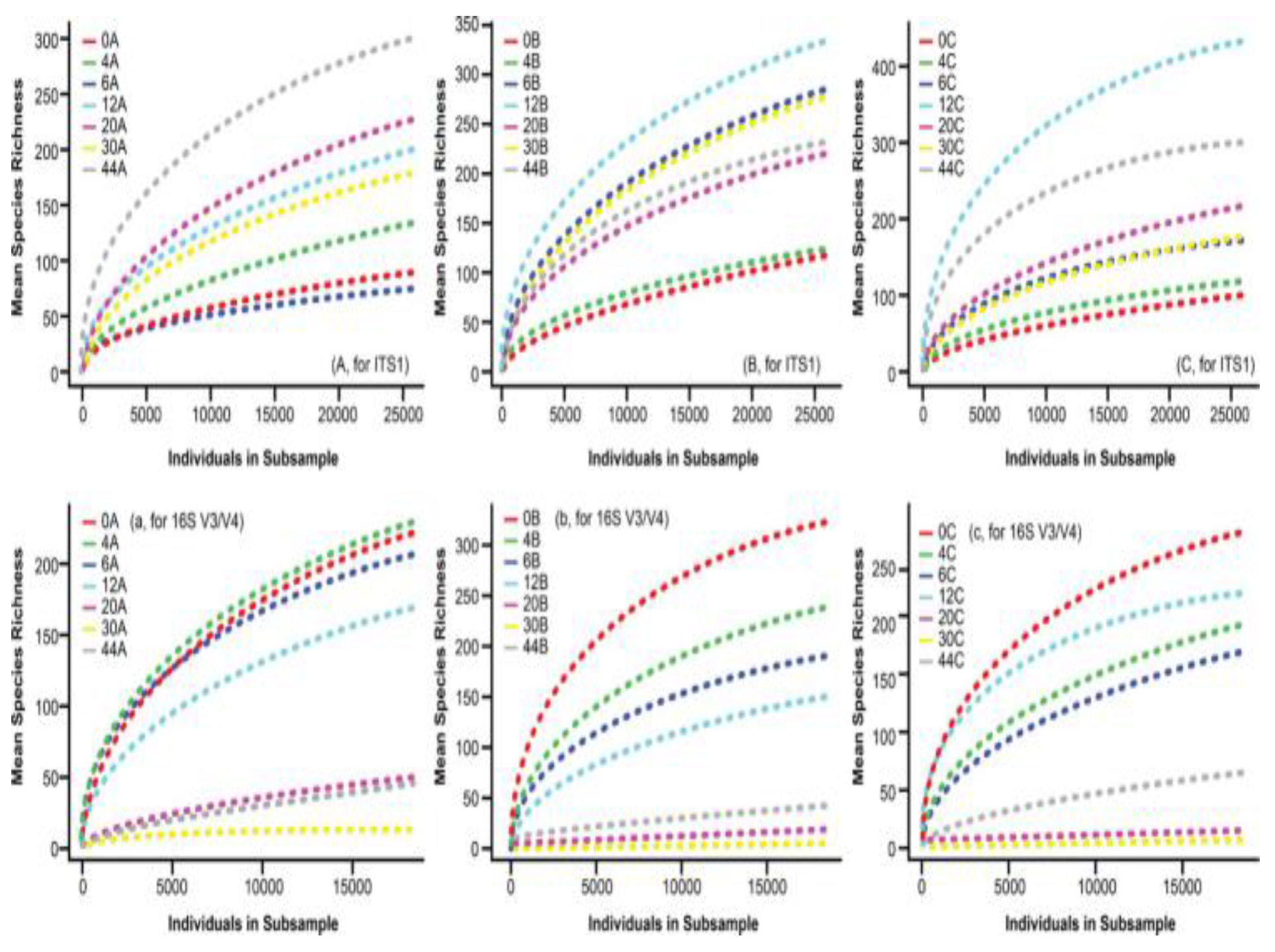
3.1. HTS Rarefaction Curves
3.2. HTS Shannon–Wiener Curve
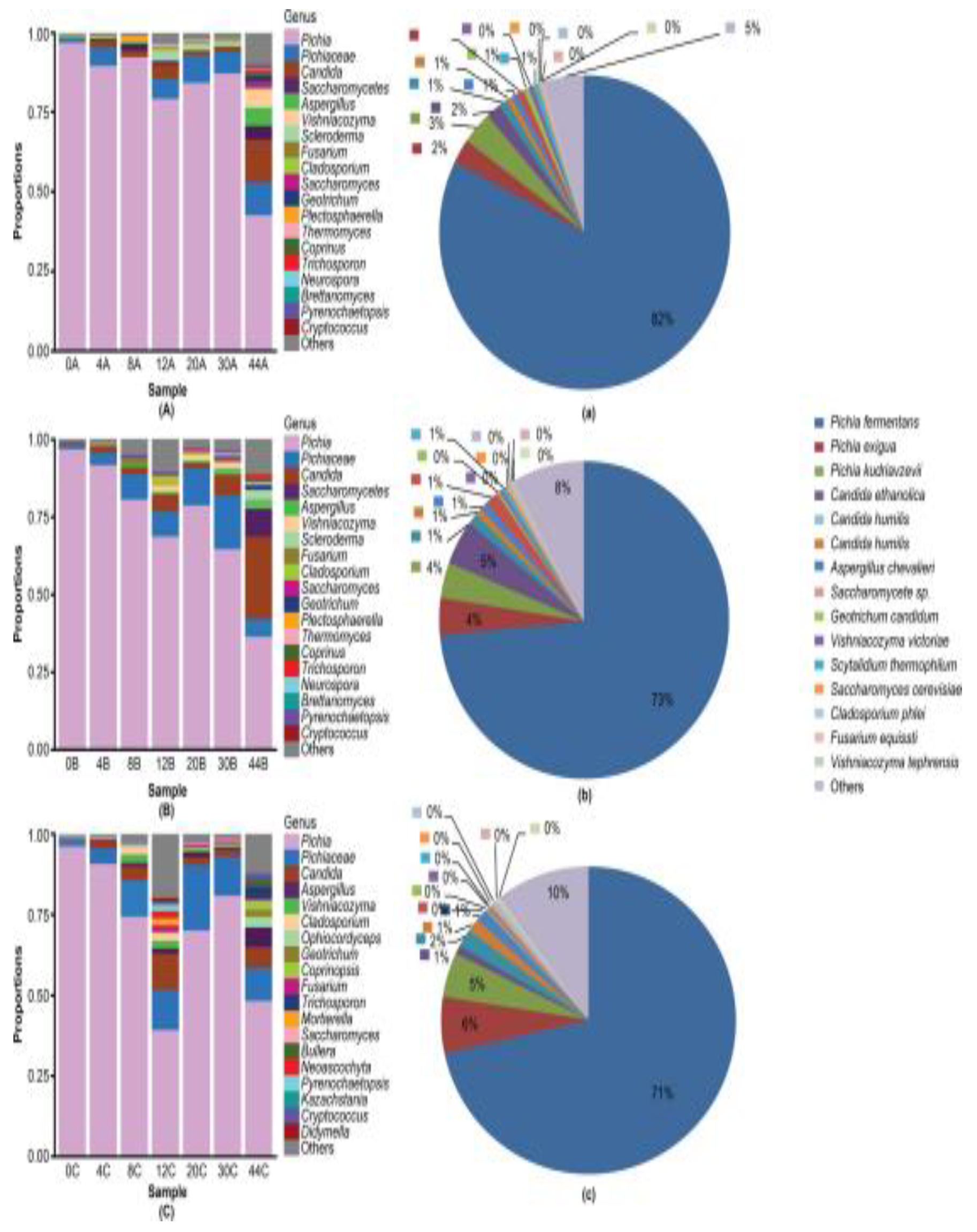
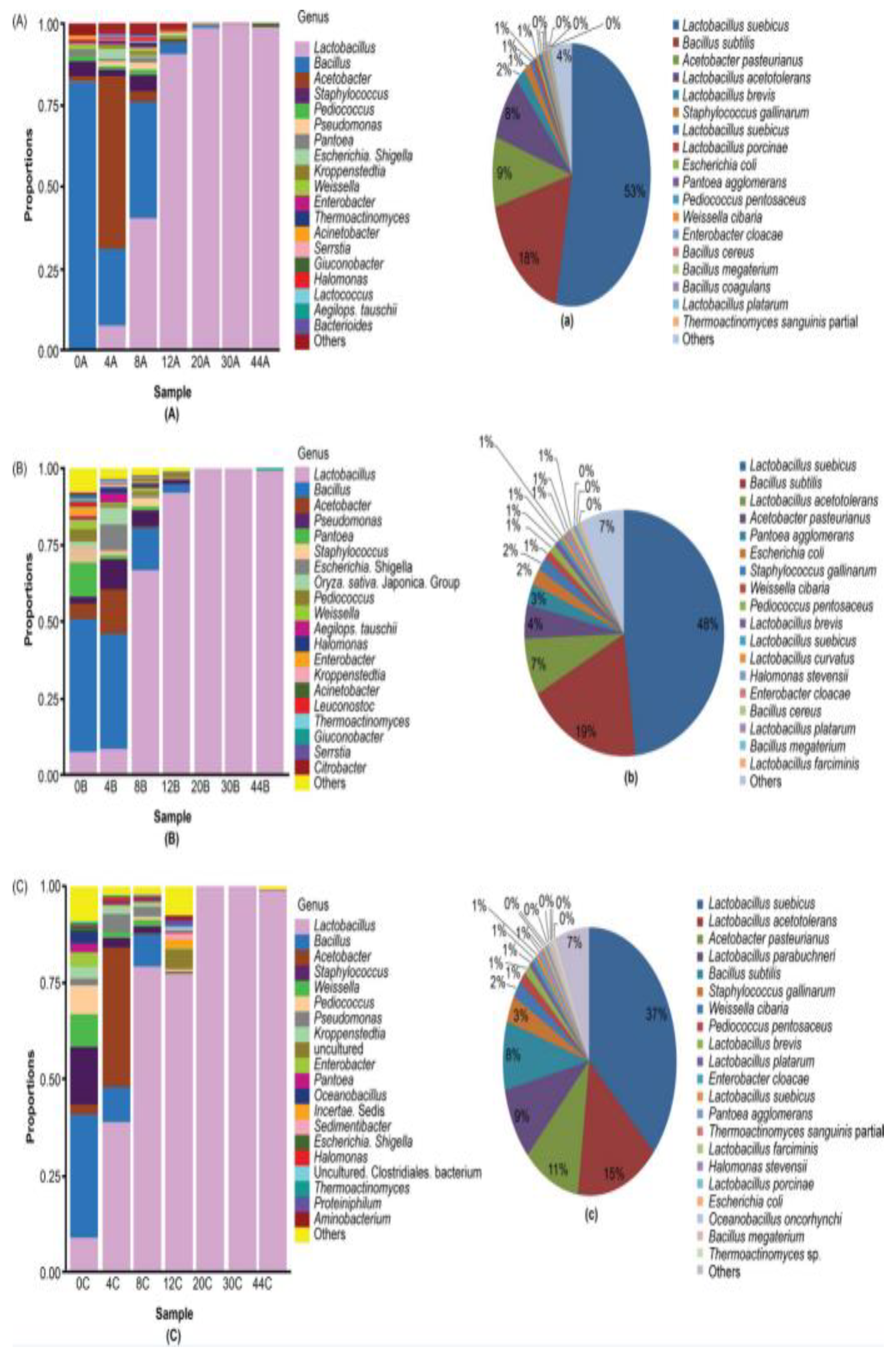
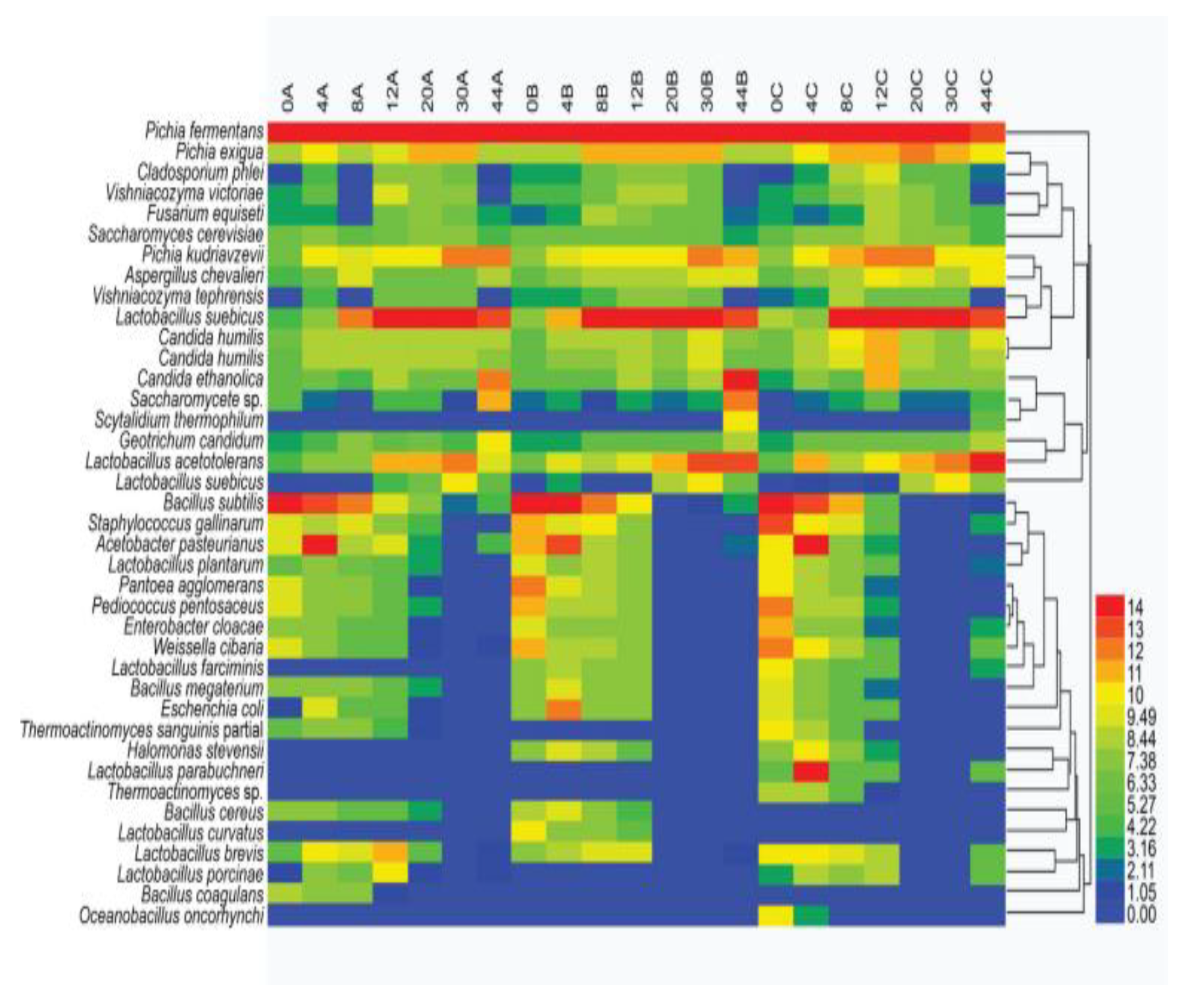
3.3. Dominant Microbes in the Fermented Grain Layers Based on HTS
3.4. Tree-Structure Analysis of Multiple Sample Similarity Based on UniFrac of HTS
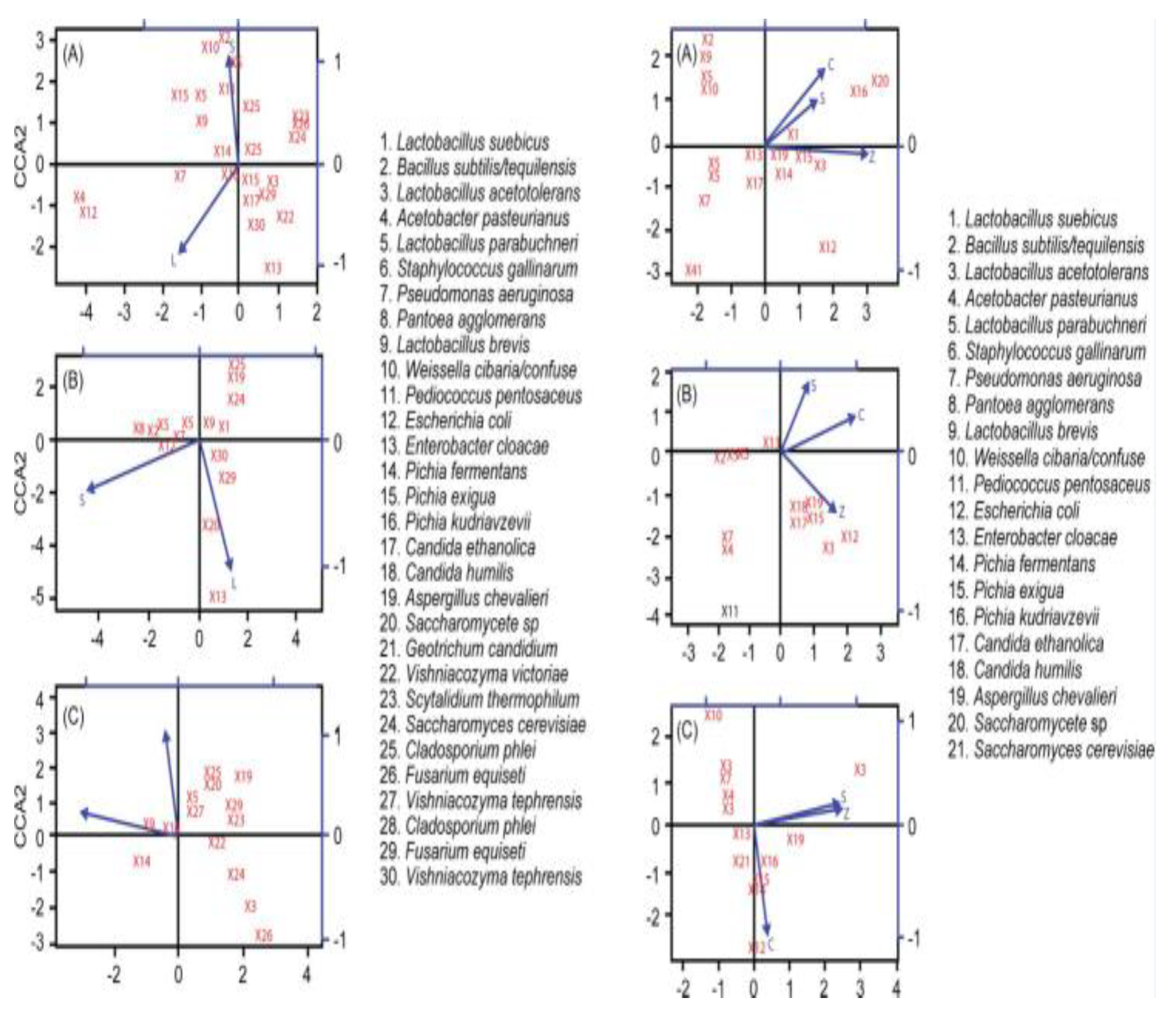
3.5. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
3.6. Population Succession of Dominant Microorganisms During Liquor Fermentation Based on HTS
3.7. Correlation Between Dominant Strains, Enzyme Activity, and Volatile Component Content
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Q.; Lin, B.; Tang, J.; An, L.; Jiang, W.; Li, R.; Zhang, G.; Yang, Q.; Yang, S.; Chen, S. Studying on genetic diversity and metabolic differences of Saccharomyces cerevisiae in baijiu. Eur Food Res Technol 2024, 250, 1619–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Han, M.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Lang, Y.; Hu, S.; Li, X.; Sun, B. Exploring the differences in sauce-flavour Daqu from different regions and its contribution to baijiu brewing based on microbial communities and flavours. Int J Food Sci Technol 2024, 59, 7357–7371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Luo, H.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, W. Microbial diversity in jiuqu and its fermentation features: saccharification, alcohol fermentation and flavors generation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 2023, 107, 25–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Zou, W.; Shen, C.H.; Yang, J.G. Basic flavor types and component characteristics of Chinese traditional liquors: a review. J Food Sci 2020, 85, 4096–4107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Sun, B.; Fan, G.; Teng, C.; Xiong, K.; Zhu, Y.; Li, J.; Li, X. The brewing process and microbial diversity of strong flavour Chinese spirits: a review. J Inst Brew 2017, 123, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Liu, G.; Li, A.; Liang, C.; Ren, C.; Xu, Y. Domination of pit mud microbes in the formation of diverse flavour compounds during Chinese strong aroma-type baijiu fermentation. LWT 2021, 137, 110442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, W.; Li, K.; Liu, S.; Xing, Y.; Li, M.; Che, Z. Microbial succession in the traditional Chinese Luzhou-flavor liquor fermentation process as evaluated by SSU rRNA profiles. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 2013, 29, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Zhang, Q.; Zhong, X.T.; Jia, B.H.; Yuan, C.H.; Liu, S.; Che, Z.M.; Xiang, W.L. Microbial diversity and succession in the Chinese Luzhou-flavor liquor fermenting cover lees as evaluated by SSU rRNA profiles. Indian J Microbiol 2013, 53, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, H.; Luo, Q.; Zhang, A.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, W. Comparison of bacterial community in matured and degenerated pit mud from Chinese Luzhou-flavour liquor distillery in different regions. J Inst Brew 2016, 122, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Chen, L.; Yang, S.; Li, Y.; Jin, L.; He, X.; He, L.; Ao, X.; Liu, S.; Liu, A.; et al. Metagenome and analysis of metabolic potential of the microbial community in pit mud used for Chinese strong-flavor liquor production. Food Res Int 2021, 143, 110294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.Y.; Wang, Q.; Chen, Z.; Mao, D.M.; Liang, Z.W. Correlation analysis between amino acids and bacterial communities of Wuliangye-flavour liquor fermentation in aged fermentation pit. Int Food Res J 2022, 29, 892–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Pan, D.; Xia, Q.; Sun, Y.; Geng, F.; Cao, J.; Zhou, C. The combination of high-throughput sequencing and LC-MS/MS reveals the mechanism of Staphylococcus inoculation on bacterial community succession and taste development during the processing of dry-cured bacon. J Sci Food Agric 2023, 103, 7187–7198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metin, B.; Pehlivanoğlu, H.; Yildirim Servi, E.Y.; Arıcı, M. Bacterial dynamics of Hardaliye, a fermented grape beverage, determined by highthroughput sequencing. J Agr Sci-Tarim Bili 2023, 29, 756–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, X.; Han, P.J.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Y.H.; He, J.M.; Zhou, X.X.; Wu, Y.Y.; Bai, F.Y.; Yang, J.G. Study on isolation and identification and population succession law of bacterial in fermented grains during the brewing of Luzhou-flavour Liquor. Sci Technol Food Ind 2017, 30, 169–174. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.G.; Su, C.; Dou, X.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, S.; Ao, Z.; Shen, C. Analysis of yeast succession during the fermentation of Luzhou-flavor liquor and its effect on the formation of selected flavor components. Food Sci. [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.G.; Dou, X.; Ma, Y.Y. Diversity and dynamic succession of microorganisms during Daqu preparation for Luzhou-flavour liquor using second-generation sequencing technology. J Inst Brew 2018, 124, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Xiao, H.; Peng, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X.; Han, Y. Analysis of bacterial diversity of Chinese Luzhou-flavor liquor brewed in different seasons by Illumina MiSeq sequencing. Ann Microbiol 2016, 66, 1293–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.G.; Dou, X.; Han, P.J.; Bai, F.Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, S.Y.; Qin, H.; Ma, Y.Y. Microbial diversity in Daqu during production of Luzhou flavored liquor. J Am Soc Brew Chem 2017, 75, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.B.; Wang, S.C.; Wei, G.G.; Zhang, K.G. Investigation of the main parameters during the fermentation of Chinese Luzhou-flavour liquor. J Inst Brew 2015, 121, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; McGlinn, D.; Minchin, P.R. Vegan: community ecology package. Rpackage Version 1.17-3, 2010. Available online:.
- Narayan, A.; Jain, K.; Shah, A.R.; Madamwar, D. An efficient and cost-effective method for DNA extraction from athalassohaline soil using a newly formulated cell extraction buffer. 3 Biotech 2016, 6, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J.; et al. Introducing Mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community -supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. Uchime improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amato, K.R.; Yeoman, C.J.; Kent, A.; Righini, N.; Carbonero, F.; Estrada, A.; Gaskins, H.R.; Stumpf, R.M.; Yildirim, S.; Torralba, M.; et al. Habitat degradation impacts black howler monkey (Alouatta pigra) gastrointestinal microbiomes. ISME J 2013, 7, 1344–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Sheng, H.F.; He, Y.; Wu, J.Y.; Jiang, Y.X.; Tam, N.F.Y.; Zhou, H.W. Comparison of the levels of bacterial diversity in fresh water, intertidal wetland, and marine sediments by using millions of Illumina tags. Appl Environ Microbiol 2012, 78, 8264–8271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noval Rivas, M.; Burton, O.T.; Wise, P.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Hobson, S.A.; Garcia Lloret, M.; Chehoud, C.; Kuczynski, J.; DeSantis, T.; Warrington, J.; et al. A microbiota signature associated with experimental food allergy promotes allergic sensitization and anaphylaxis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2013, 131, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.F.; Wu, C.D.; Zhang, L.Q.; Zheng, J.; Zhou, R.Q. Characterization of eubacterial and archaeal community diversity in the pit mud of Chinese Luzhou-flavor liquor by nested PCR–DGGE. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 2014, 30, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, M.; Diao, Q.Y.; Jiang, C.G.; Yan, G.L.; Tu, Y.; Zhang, N.F. Review for effect of Lactobacillus buchneri on the silage in the journal listing of OriProbe. Acta Prataculturae Sin 2011, 5, 266–271. [Google Scholar]
- Yumoto, I.; Hirota, K.; Nodasaka, Y.; Nakajima, K. Oceanobacillus oncorhynchi sp. nov., a halotolerant obligate alkaliphile isolated from the skin of a rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss), and emended description of the genus Oceanobacillus. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2005, 55, 1521–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Lin, W.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Gan, X.; Luo, L.; Lin, W.T. Effect of bioaugmented inoculation on microbiota dynamics during solid-state fermentation of Daqu starter using autochthonous of Bacillus, Pediococcus, Wickerhamomyces and Saccharomycopsis. Food Microbiol 2017, 61, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Sun, B. Effect of fermentation processing on the flavor of baijiu. J Agric Food Chem 2018, 66, 5425–5432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao,C., Lu, Z., Zhang X., Wang, S., Li,D., Shen, C., Shi,J.; Xu, Z. Bacterial community succession in fermented grains of Luzhou-flavor baijiu. Acta Microbiologica Sinica 2019. 59(1), 195-204. [CrossRef]
- Xiao,C.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S.; Ao, L.; Sen C.; Shi, J.; Xu, Z. Succession of the fungal community on fermented grains of Luzhou-flavor baijiu through fermentation. Chin J Appl Environ Biol 2018,24 ( 5 ): 1081-1086. [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Huang, J.; Zhou, R.; Wu, C.; Jin, Y. Effect of fortified Daqu on the microbial community and flavor in Chinese strong-flavor liquor brewing process. Front Microbiol 2019, 10, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Qiao, Z.; Shigematsu, T.; Tang, Y.; Hu, C.; Morimura, S.; Kida, K. Analysis of the bacterial community in Zaopei during production of Chinese Luzhou-flavor liquor, J. Inst. Brew. 2005, 111, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C. , Pruesse, E., Yilmaz, P., Gerken, J., Schweer, T., Yarza, P., Peplies, J.; Glockner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Research. [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y. , Zhang, X. J., Zhao, L.P., and Xu, Y. Analysis and comparison of the bacterial community in fermented grains during the fermentation for two different styles of Chinese liquor. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 35, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Huang, J.; Qin, H.; He, G.; Zhou, R.; Yang, Y.; Qiu, C.; Zhang, S. Evolving the core microbial community in pit mud based on bioturbation of fortified Daqu. Can J Microbiol 2021, 67, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang,W.; Zhao,D.; Tian,S.; You,L.; Wang,S.; Feng,R.; Feng,F.; Zhang, Z.; Cui,X. Phylogenetic diversity of cultivable bacteria during the brewing process of the Luzhou-flavor liquor in Yibin,Sichuan province,China. Acta Microbiologica Sinica 2011, 51( 10), 1351 - 1357. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




