Submitted:
02 July 2025
Posted:
03 July 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Molecularly Imprinted Nanoparticles (MIPNPs) Synthesis
2.3. MWCNT Dispersion
2.4. Electrospun layer fabrication
2.5. UV-Crosslinking Process
2.7. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.8. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
2.9. Electrical and Sensing Measurements
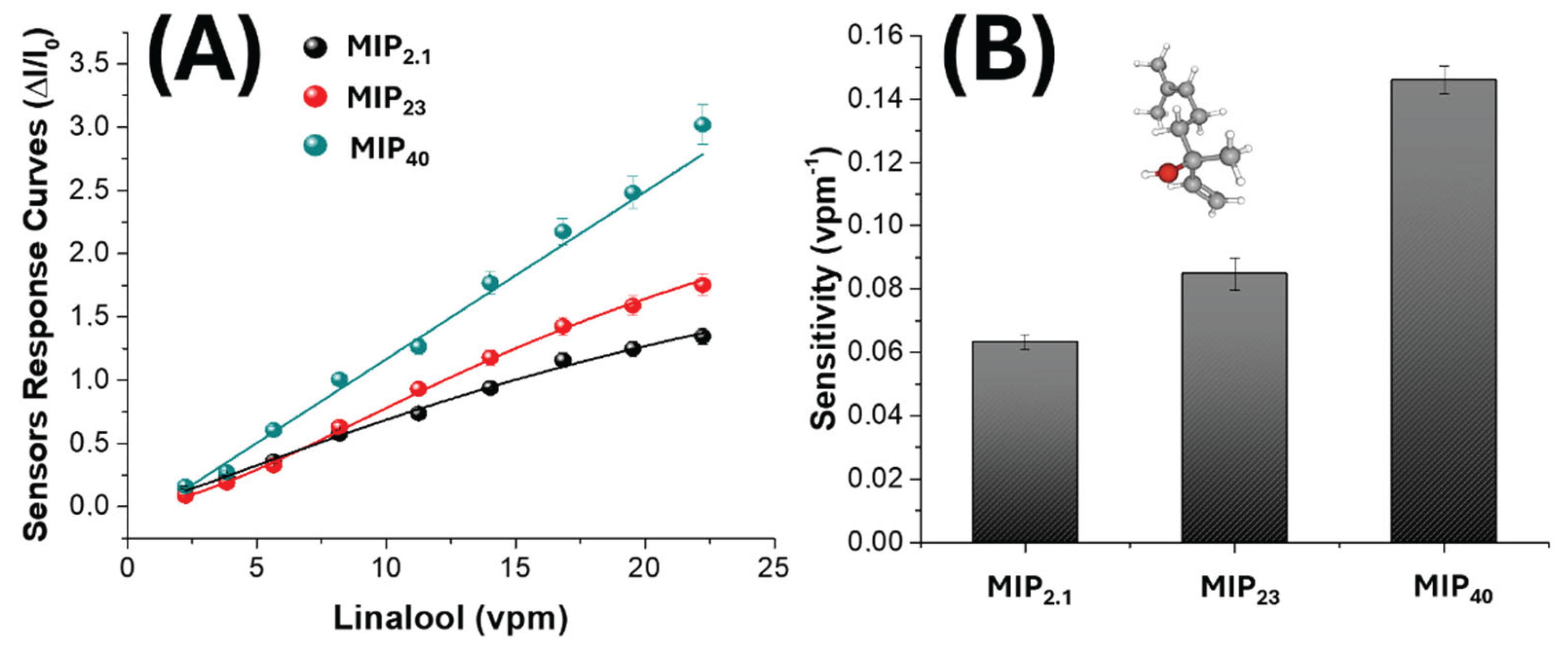
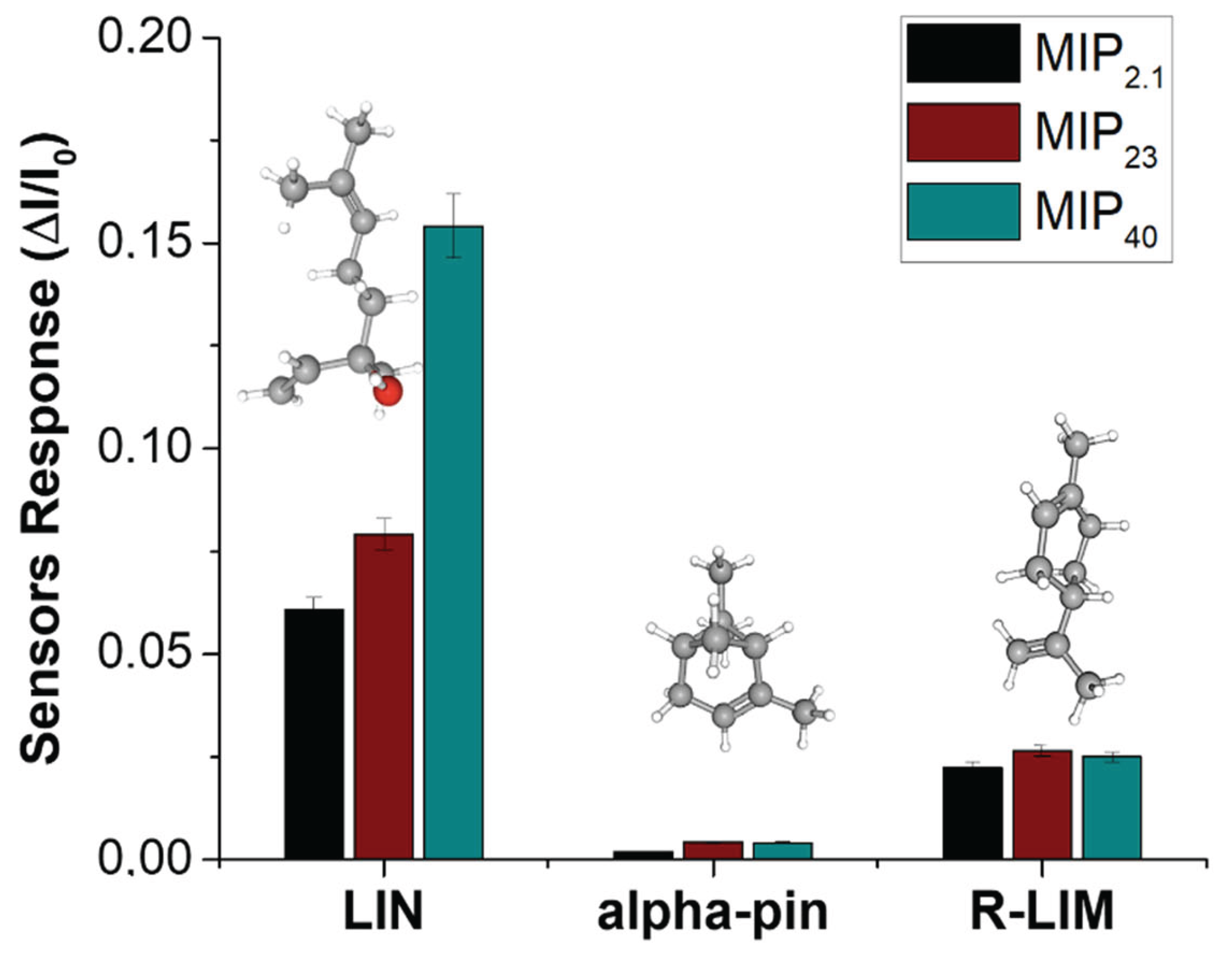
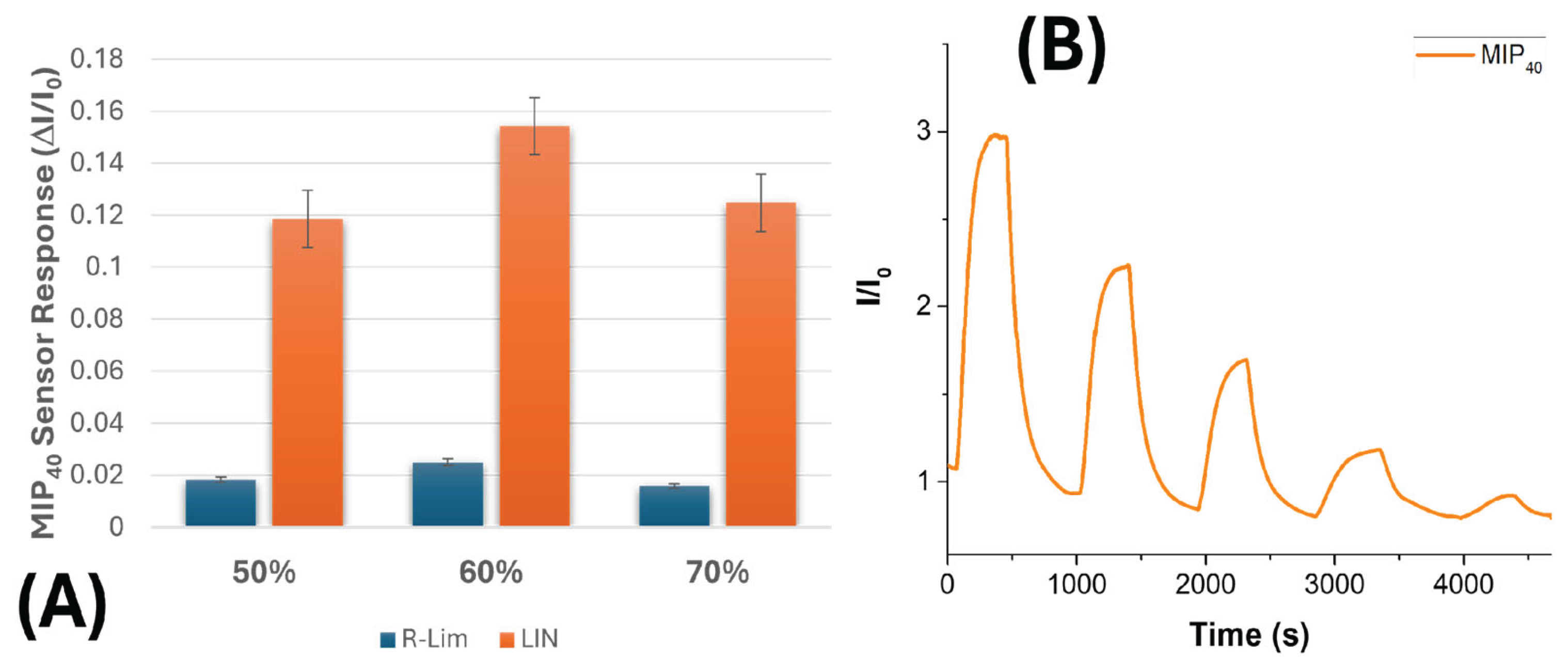
3. Results and Discussion
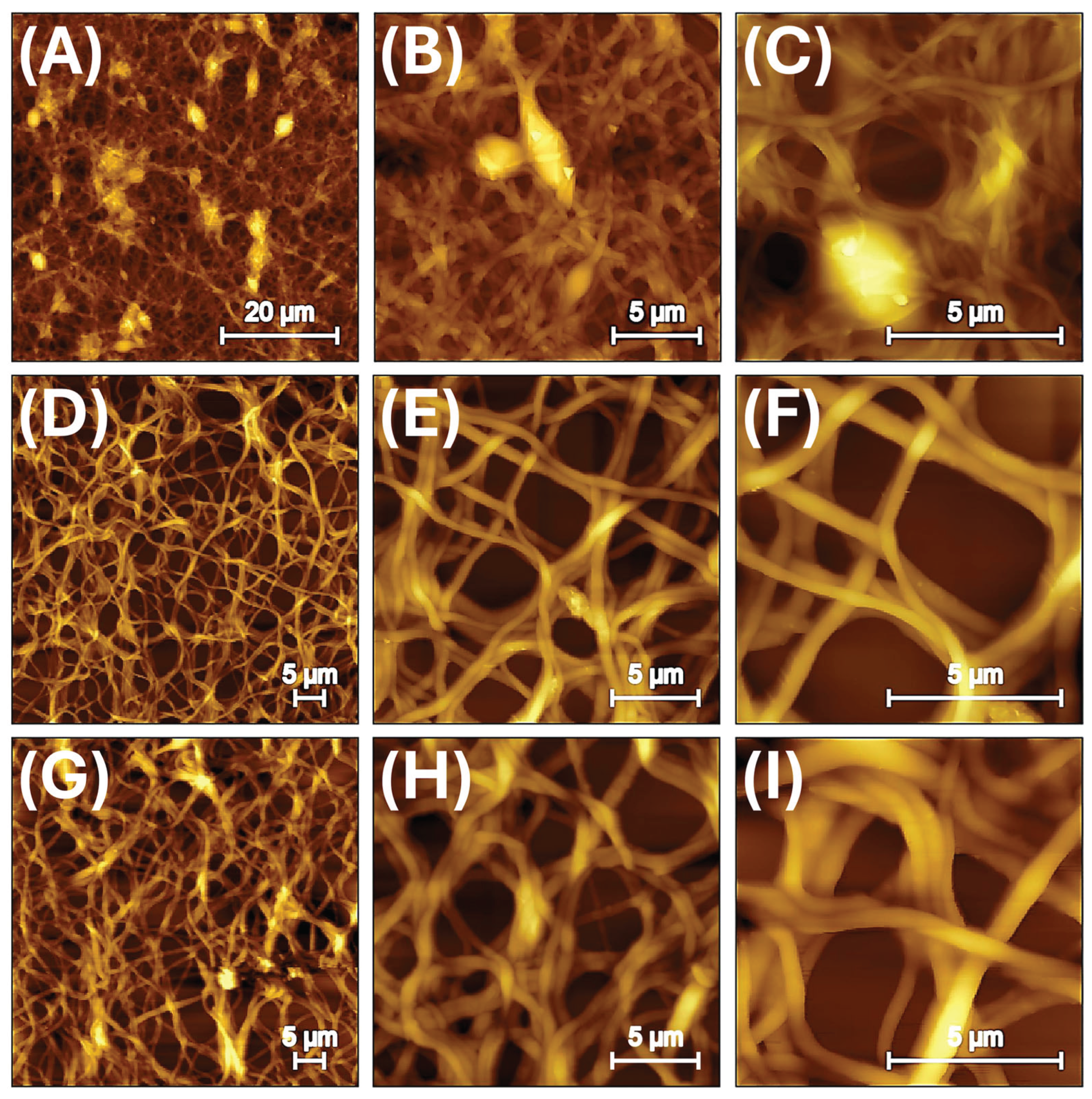
3.1. MIP-NPs Characterization
3.2. Nanofibrous Layers Characterization
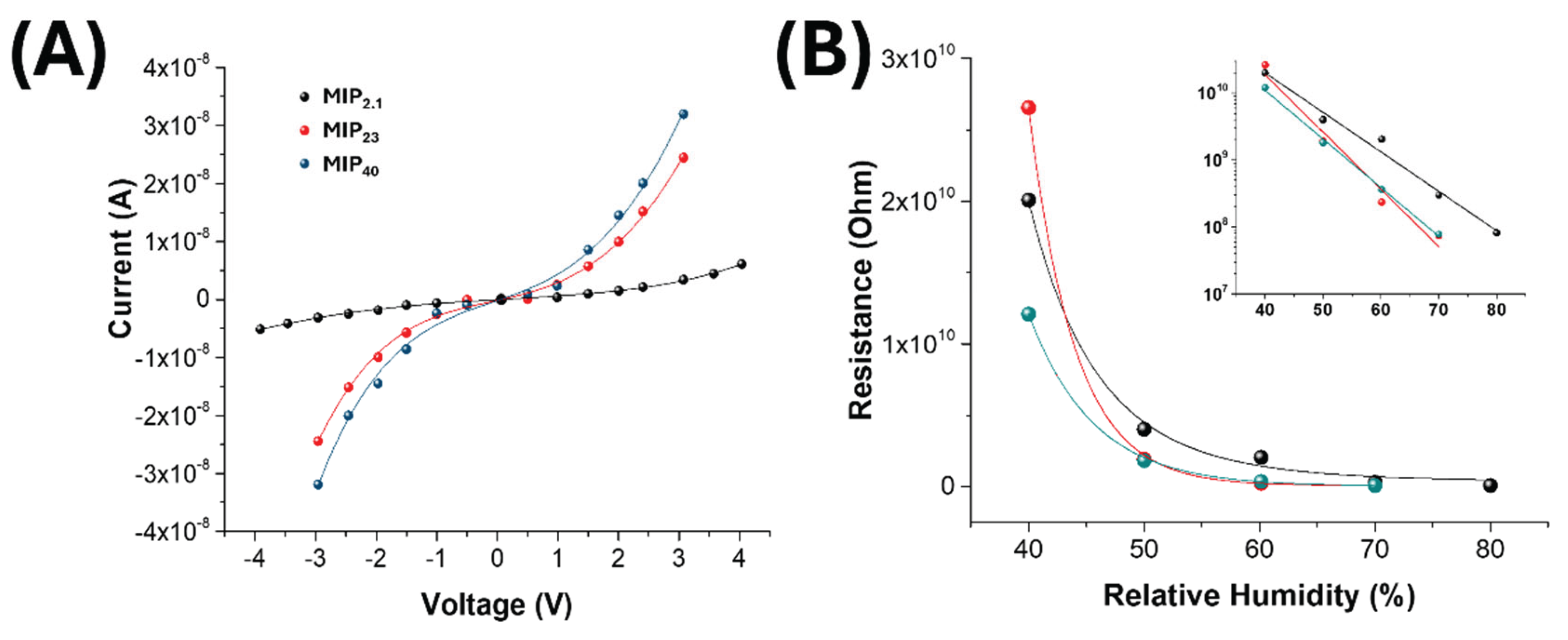
3.3. Electrical and Sensing Characterization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luo, R.; Lun, X.; Gao, R.; Wang, L.; Yang, Y.; Su, X.; Mamun, H.A.; Xu, X.; Li, H.; Li, J. A Review of Biogenic Volatile Organic Compounds from Plants: Research Progress and Future Prospects. Toxics 2025, 13, 364. [CrossRef]
- Maffei, M. Sites of synthesis, biochemistry and functional role of plant volatiles. South Afr. J. Bot. 2010, 76, 612–631. [CrossRef]
- Ramanpong, J.; Tsao, C.; Yin, J.; Wu, C.-D.; Huang, Y.-C.; Yu, C.-P. Effects of forest bathing and the influence of exposure levels on cognitive health in the elderly: Evidence from a suburban forest recreation area. Urban For. Urban Green. 2025, 104. [CrossRef]
- Haluza, D.; Kersten, P.; Lazic, T.; Steinparzer, M.; Godbold, D. Unlocking the Power of Nature: Insights from a 20-Minute Forest Visit on Well-Being. Forests 2025, 16, 792. [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, D.; Vu, T.V.; Tong, S.; Shi, Z.; Harrison, R.M. Formation of secondary organic aerosols from anthropogenic precursors in laboratory studies. npj Clim. Atmospheric Sci. 2022, 5, 1–30. [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Cappellin, L.; Xu, J.; Biasioli, F.; Varotto, C. High-throughput screening for in planta characterization of VOC biosynthetic genes by PTR-ToF-MS. J. Plant Res. 2019, 133, 123–131. [CrossRef]
- Cappellin, L.; Loreto, F.; Aprea, E.; Romano, A.; Del Pulgar, J.S.; Gasperi, F.; Biasioli, F. PTR-MS in Italy: A Multipurpose Sensor with Applications in Environmental, Agri-Food and Health Science. Sensors 2013, 13, 11923–11955. [CrossRef]
- Wasilewski, T.; Orbay, S.; Brito, N.F.; Sikora, K.; Melo, A.C.A.; Melendez, M.E.; Szulczyński, B.; Sanyal, A.; Kamysz, W.; Gębicki, J. Molecularly imprinted polymers for the detection of volatile biomarkers. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2024, 177. [CrossRef]
- Leibl, N.; Haupt, K.; Gonzato, C.; Duma, L. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Chemical Sensing: A Tutorial Review. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 123. [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Ahmadi, Y.; Kim, K.-H. Molecularly imprinted polymers for sensing gaseous volatile organic compounds: opportunities and challenges. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 311, 119931. [CrossRef]
- Macagnano, A.; Molinari, F.N.; Papa, P.; Mancini, T.; Lupi, S.; D’arco, A.; Taddei, A.R.; Serrecchia, S.; De Cesare, F. Nanofibrous Conductive Sensor for Limonene: One-Step Synthesis via Electrospinning and Molecular Imprinting. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1123. [CrossRef]
- Cowen, T.; Cheffena, M. Template Imprinting Versus Porogen Imprinting of Small Molecules: A Review of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers in Gas Sensing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9642. [CrossRef]
- Caldara, M.; van Wissen, G.; Cleij, T.J.; Diliën, H.; van Grinsven, B.; Eersels, K.; Lowdon, J.W. Deposition Methods for the Integration of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers (MIPs) in Sensor Applications. Adv. Sens. Res. 2023, 2. [CrossRef]
- Gavrilă, A.-M.; Stoica, E.-B.; Iordache, T.-V.; Sârbu, A. Modern and Dedicated Methods for Producing Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Layers in Sensing Applications. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3080. [CrossRef]
- Lowdon, J.W.; Diliën, H.; Singla, P.; Peeters, M.; Cleij, T.J.; van Grinsven, B.; Eersels, K. MIPs for commercial application in low-cost sensors and assays – An overview of the current status quo. Sensors Actuators B: Chem. 2020, 325, 128973–128973. [CrossRef]
- Malitesta, C.; Mazzotta, E.; Picca, R.A.; Poma, A.; Chianella, I.; Piletsky, S.A. MIP Sensors—The Electrochemical Approach. Anal Bioanal Chem 2012, 402, 1827–1846.
- González-Vila, A.; Debliquy, M.; Lahem, D.; Zhang, C.; Mégret, P.; Caucheteur, C. Molecularly imprinted electropolymerization on a metal-coated optical fiber for gas sensing applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 244, 1145–1151. [CrossRef]
- Emam, S.; Adedoyin, A.; Geng, X.; Zaeimbashi, M.; Adams, J.; Ekenseair, A.; Podlaha-Murphy, E.; Sun, N.X. A Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Gas Sensor to Sense Butylated Hydroxytoluene in Air. J. Sensors 2018, 2018, 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Debliquy, M.; Dony, N.; Lahem, D.; Tang, X.; Zhang, C.; Raskin, J.-P.; Olivier, M.-G. Acetaldehyde Chemical Sensor based on Molecularly Imprinted Polypyrrole. Procedia Eng. 2016, 168, 569–573. [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Ge, L.; Jiang, T.; Guo, H.; Chen, B.; Liu, C.; Hayashi, K. Fully Inkjet-Printed Chemiresistive Sensor Array Based on Molecularly Imprinted Sol–Gel Active Materials. ACS Sensors 2022, 7, 1819–1828. [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Shi, P.; Sun, Z.; Zhao, N.; Shi, M.; Wu, M.; Ye, C.; Lin, C.-T.; Fu, L. Advancements in Polymer-Assisted Layer-by-Layer Fabrication of Wearable Sensors for Health Monitoring. Sensors 2024, 24, 2903. [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Shi, H.; Han, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, R.; Men, J. Molecularly imprinted polymers by the surface imprinting technique. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 145. [CrossRef]
- Azhdary, P.; Janfaza, S.; Fardindoost, S.; Tasnim, N.; Hoorfar, M. Highly selective molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles (MIP NPs)-based microfluidic gas sensor for tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2023, 1278, 341749. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Guo, L.; Man, C.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X. Emerging biosensors integrated with microfluidic devices: a promising analytical tool for on-site detection of mycotoxins. npj Sci. Food 2025, 9, 1–18. [CrossRef]
- Kamyab, H.; Chelliapan, S.; Tavakkoli, O.; Mesbah, M.; Bhutto, J.K.; Khademi, T.; Kirpichnikova, I.; Ahmad, A.; Aljohani, A.A. A review on carbon-based molecularly-imprinted polymers (CBMIP) for detection of hazardous pollutants in aqueous solutions. Chemosphere 2022, 308, 136471. [CrossRef]
- Electrospinning for High Performance Sensors; Macagnano, A., Zampetti, E., Kny, E., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2015; ISBN 978-3-319-14405-4.
- Molinari, F.N.; Marelli, M.; Berretti, E.; Serrecchia, S.; Coppola, R.E.; De Cesare, F.; Macagnano, A. Cutting-Edge Sensor Design: MIP Nanoparticle-Functionalized Nanofibers for Gas-Phase Detection of Limonene in Predictive Agriculture. Polymers 2025, 17, 326. [CrossRef]
- Wackerlig, J.; Lieberzeit, P.A. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticles in Chemical Sensing—Synthesis, Characterisation and Application. Sens Actuators B Chem 2015, 207, 144–157.
- Nagalingam, S.; Seco, R.; Kim, S.; Guenther, A. Heat stress strongly induces monoterpene emissions in some plants with specialized terpenoid storage structures. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2023, 333. [CrossRef]
- Kask, K.; Kännaste, A.; Talts, E.; Copolovici, L.; Niinemets, Ü. How specialized volatiles respond to chronic and short-term physiological and shock heat stress in Brassica nigra. Plant, Cell Environ. 2016, 39, 2027–2042. [CrossRef]
- Fürstenberg-Hägg, J.; Zagrobelny, M.; Bak, S. Plant Defense against Insect Herbivores. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 10242–10297. [CrossRef]
- Chacón-Fuentes, M.; Bardehle, L.; Seguel, I.; Espinoza, J.; Lizama, M.; Quiroz, A. Herbivory Damage Increased VOCs in Wild Relatives of Murtilla Plants Compared to Their First Offspring. Metabolites 2023, 13, 616. [CrossRef]
- Stringari, G.; Villanueva, J.; Appolloni, E.; Orsini, F.; Villalba, G.; Durany, X.G. Measuring BVOC emissions released by tomato plants grown in a soilless integrated rooftop greenhouse. Heliyon 2023, 10, e23854. [CrossRef]
- Boachon, B.; Junker, R.R.; Miesch, L.; Bassard, J.-E.; Höfer, R.; Caillieaudeaux, R.; Seidel, D.E.; Lesot, A.; Heinrich, C.; Ginglinger, J.-F.; et al. CYP76C1 (Cytochrome P450)-Mediated Linalool Metabolism and the Formation of Volatile and Soluble Linalool Oxides in Arabidopsis Flowers: A Strategy for Defense against Floral Antagonists. Plant Cell 2015, 27, 2972–2990. [CrossRef]
- Avesani, S.; Lazazzara, V.; Robatscher, P.; Oberhuber, M.; Perazzolli, M. Volatile linalool activates grapevine resistance against downy mildew with changes in the leaf metabolome. Curr. Plant Biol. 2023, 35-36. [CrossRef]
- McCallum, E.J.; Cunningham, J.P.; Lücker, J.; Zalucki, M.P.; De Voss, J.J.; Botella, J.R. Increased plant volatile production affects oviposition, but not larval development, in the moth Helicoverpa armigera. J. Exp. Biol. 2011, 214, 3672–3677. [CrossRef]
- Molinari, F.; Medrano, A.V.; Bacigalupe, A.; Escobar, M.M.; Monsalve, L.N. Different dispersion states of MWCNT in aligned conductive electrospun PCL/MWCNT composites. Full- Nanotub. Carbon Nanostructures 2018, 26, 667–674. [CrossRef]
- Macagnano, A.; Molinari, F.N.; Papa, P.; Mancini, T.; Lupi, S.; D’arco, A.; Taddei, A.R.; Serrecchia, S.; De Cesare, F. Nanofibrous Conductive Sensor for Limonene: One-Step Synthesis via Electrospinning and Molecular Imprinting. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1123. [CrossRef]
- Maciejewska, B.M.; Wychowaniec, J.K.; Woźniak-Budych, M.; Popenda, Ł.; Warowicka, A.; Golba, K.; Litowczenko, J.; Fojud, Z.; Wereszczyńska, B.; Jurga, S. UV cross-linked polyvinylpyrrolidone electrospun fibres as antibacterial surfaces. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2019, 20, 979–991. [CrossRef]
- Djunaidi, M.C.; Putri, V.R.; Maharani, N.D.; Lusiana, R.A.; Siahaan, P.; Sunarno, S. Precipitation Polymerization-Based Molecularly Imprinted Polymers: A Novel Approach for Transdermal Curcumin Delivery. Polymers 2024, 16, 3456. [CrossRef]
- Holdsworth, C.I.; Lim, K.F.; Muang-Non, P. Molecularly Imprinted Polymeric Nanoparticles by Precipitation Polymerization and Characterization by Quantitative NMR Spectroscopy. In Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. Methods in Molecular Biology; Martín-Esteban, A., Ed.; Humana: New York, NY, 2021; Vol. 2359, pp. 9–18.
- Suzaei, F.M.; Daryanavard, S.M.; Abdel-Rehim, A.; Bassyouni, F.; Abdel-Rehim, M. Recent molecularly imprinted polymers applications in bioanalysis. Chem. Pap. 2022, 77, 619–655. [CrossRef]
- Karnka, R.; Chaiyasat, P.; Chaiyasat, A. Synthesis of Uniform and Stable Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Particles by Precipitation Polymerization. Orient. J. Chem. 2017, 33, 2370–2376. [CrossRef]
- Hasanah, A.N.; Safitri, N.; Zulfa, A.; Neli, N.; Rahayu, D. Factors Affecting Preparation of Molecularly Imprinted Polymer and Methods on Finding Template-Monomer Interaction as the Key of Selective Properties of the Materials. Molecules 2021, 26, 5612. [CrossRef]
- Aglikov, A.S.; Zhukov, M.V.; Aliev, T.A.; Kozodaev, D.A.; Nosonovsky, M.; Skorb, E.V. New metrics for describing atomic force microscopy data of nanostructured surfaces through topological data analysis. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2024, 670. [CrossRef]
- Langwald, S.V.; Ehrmann, A.; Sabantina, L. Measuring Physical Properties of Electrospun Nanofiber Mats for Different Biomedical Applications. Membranes 2023, 13, 488. [CrossRef]
- Raza, S.; Li, X.; Soyekwo, F.; Liao, D.; Xiang, Y.; Liu, C. A comprehensive overview of common conducting polymer-based nanocomposites; Recent advances in design and applications. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 160. [CrossRef]
- Alam, N.; Abid; Islam, S.S. Advancements in Trace and Low Humidity Sensors Technologies Using Nanomaterials: A Review. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2024, 7, 13836–13864. [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.W.; Bhat, S.I.; Al Qahtani, H.S.; Aamir, M.; Amin, M.N.; Farhan, M.; Aldabal, S.; Khan, M.S.; Jeelani, I.; Nawaz, A.; et al. Recent Progress, Challenges, and Trends in Polymer-Based Sensors: A Review. Polymers 2022, 14, 2164. [CrossRef]
- Hermant, M.C. Manipulating the Percolation Threshold of Carbon Nanotubes in Polymeric Composites, Eindhoven University of Technology: Eindhoven, 2009.
- Sundaray, B.; Subramanian, V.; Natarajan, T.S.; Krishnamurthy, K. Electrical conductivity of a single electrospun fiber of poly(methyl methacrylate) and multiwalled carbon nanotube nanocomposite. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 143114. [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Ding, A.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, W. The Relevant Approaches for Aligning Carbon Nanotubes. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1863. [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi Bonakdar, M.; Rodrigue, D. Electrospinning: Processes, Structures, and Materials. Macromol 2024, 4, 58–103.
- Hossain, M.M.; Islam, A.; Shima, H.; Hasan, M.; Lee, M. Alignment of Carbon Nanotubes in Carbon Nanotube Fibers Through Nanoparticles: A Route for Controlling Mechanical and Electrical Properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 5530–5542. [CrossRef]
- Feldner, A.; Völkle, J.; Lieberzeit, P.; Fruhmann, P. Conductive Molecularly Imprinted Polymers (cMIPs): Rising and Versatile Key Elements in Chemical Sensing. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 299. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H. Water-compatible molecularly imprinted polymers: Promising synthetic substitutes for biological receptors. Polymer 2014, 55, 699–714. [CrossRef]
- Horemans, F.; Weustenraed, A.; Spivak, D.; Cleij, T.J. Towards Water Compatible MIPs for Sensing in Aqueous Media. In Proceedings of the Journal of Molecular Recognition; John Wiley and Sons Ltd., 2012; Vol. 25, pp. 344–351.
- Vial, J.; Jardy, A. Experimental Comparison of the Different Approaches To Estimate LOD and LOQ of an HPLC Method. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 2672–2677. [CrossRef]
- Taleuzzaman, M. Limit of Blank (LOB), Limit of Detection (LOD), and Limit of Quantification (LOQ). Org. Med. Chem. Int. J. 2018, 7, 1–5. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Ghosh, A.; Tudu, B.; Bhuyan, L.P.; Tamuly, P.; Bhattacharyya, N.; Bandyopadhyay, R.; Chatterjee, A. Detection of linalool in black tea using a quartz crystal microbalance sensor. Sensors Actuators B: Chem. 2014, 190, 318–325. [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wu, X.; Chen, S.; Liu, C.; Zhang, W.; Yang, M.; Cheng, J.; Lu, G.; Wang, Z.; Chen, W.; et al. Rapid detection of linalool by QCM gas sensor based on HKUST-1/MWCNT-gel@MIP in early sweetpotato black spot disease. Microchem. J. 2025, 212. [CrossRef]
- Mushannavar, S.; Ghosh, R. Selective Detection of Linalool using WO3–WS2 Composite based Resistive Sensors. Sensors Actuators B: Chem. 2025. [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, S.; Kummara, S.; Gorthala, G.; Ghosh, R. CuO Nanoflake-Based Sensors for Detecting Linalool, Hexanal, and Methyl Salicylate. ACS Agric. Sci. Technol. 2022, 2, 1285–1291. [CrossRef]
- Bhuyan, A.; Tudu, B.; Bandyopadhyay, R.; Gogoi, S.; Department of Chemical Science; Singh, A. Preanodized Screen Printed Carbon Electrode for Detection of Linalool using Three Terminal Network. Int. J. Eng. Adv. Technol. 2019, 9, 477–482. [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Dong, S.; Cao, S.; Cui, Q.; Chen, Q.; Ning, J.; Li, L. A rapid aroma quantification method: Colorimetric sensor-coupled multidimensional spectroscopy applied to black tea aroma. Talanta 2023, 263, 124622. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Fan, J.; Tan, R.; Peng, Q.; Cai, J.; Zhang, W.; Rodriguez-Mendez, M.L. Prediction of Linalool Content in Osmanthus fragrans Using E-Nose Technology. J. Sensors 2022, 2022, 1–11. [CrossRef]

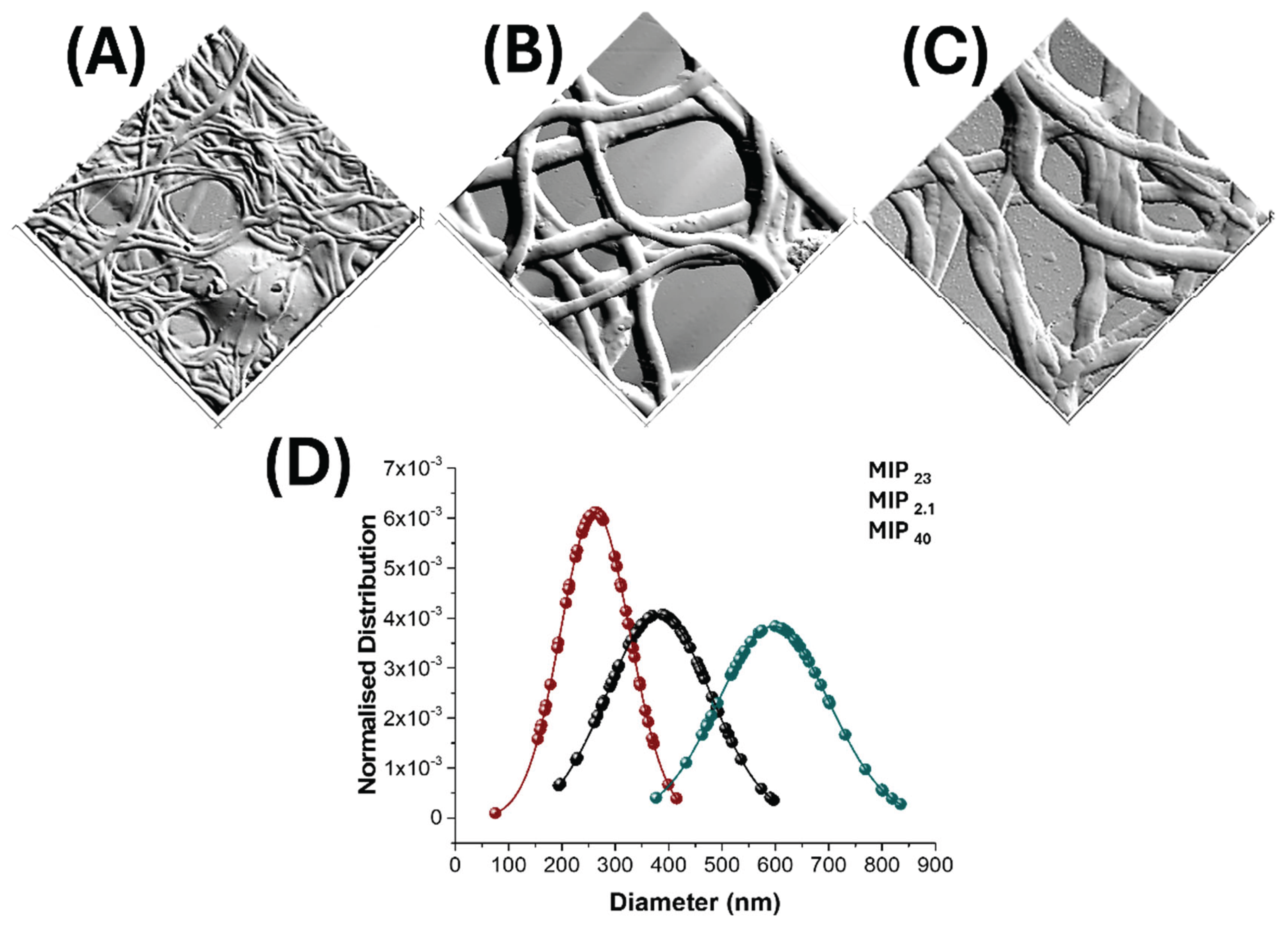
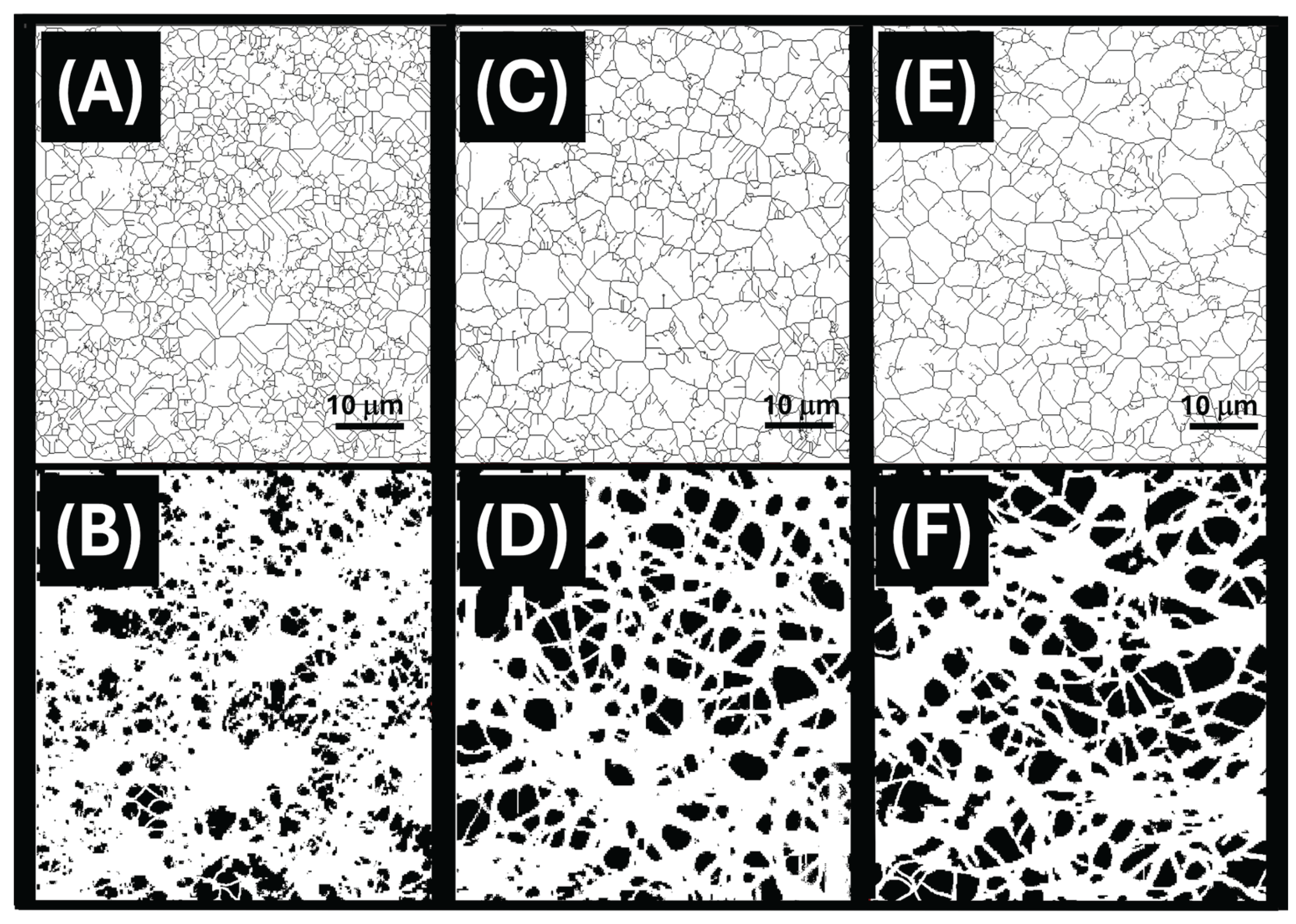
| MIP Loading (%) | Fibre Diameter (nm) | Mean Pore Area (µm²) | Percent Porosity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2.1 | 262 ± 65 | 1.5 ± 3.2 | 22 |
| 23 | 381 ± 98 | 2.9 ± 4.2 | 27 |
| 40 | 596 ± 104 | 4.29± 5.1 | 36 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





